



生物多样性 ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (5): 431-439. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09087 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2009.09087
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康; 昆虫多样性与生态功能
• 论文 • 下一篇
刘满强1,*( ), 黄菁华1, 陈小云1, 王峰1, 葛成2, 苏昱1, 邵波3, 汤英1, 李辉信1, 胡锋1
), 黄菁华1, 陈小云1, 王峰1, 葛成2, 苏昱1, 邵波3, 汤英1, 李辉信1, 胡锋1
收稿日期:2009-04-09
接受日期:2009-06-26
出版日期:2009-09-20
发布日期:2009-09-20
通讯作者:
刘满强
作者简介:*E-mail: liumq@njau.edu.cn基金资助:
Manqiang Liu1,*( ), Jinghua Huang1, Xiaoyun Chen1, Feng Wang1, Cheng Ge2, Yu Su1, Bo Shao3, Ying Tang1, Huixin Li1, Feng Hu1
), Jinghua Huang1, Xiaoyun Chen1, Feng Wang1, Cheng Ge2, Yu Su1, Bo Shao3, Ying Tang1, Huixin Li1, Feng Hu1
Received:2009-04-09
Accepted:2009-06-26
Online:2009-09-20
Published:2009-09-20
Contact:
Manqiang Liu
摘要:
地上和地下部生物群落的交互作用对于调控陆地生态过程具有重要作用。在盆栽条件下利用2×2析因设计研究了褐飞虱(Nilaparvata lugens)取食不同水稻品种后对土壤线虫群落的影响。结果表明, 褐飞虱侵害水稻9 d后, 感虫品种(广四和汕优63)的土壤线虫总数、属数及自生线虫(食细菌线虫、食真菌线虫和捕食性线虫)数量增加, 并且一般达到显著水平(P<0.05); 而上述指标在抗虫品种(汕优559和IR36)土壤中则呈现相反的趋势。植食性线虫数量在强感虫品种广四上显著增加(P<0.05), 而在强抗虫品种IR36上显著减少(P<0.05)。褐飞虱和水稻品种对土壤线虫的生态指数(线虫通道指数、Shannon-Wiener指数、成熟度指数、富集指数和结构指数)没有明显影响, 可能与供试土壤线虫群落组成单一及褐飞虱作用时间较短有关。总之, 褐飞虱强烈影响土壤线虫数量、群落组成和营养结构, 并且作用的方向(促进或抑制)和程度依赖于水稻的品种特性, 揭示出地上部植食者的短期侵害将对稻田土壤生态系统的结构和功能产生深远影响。
刘满强, 黄菁华, 陈小云, 王峰, 葛成, 苏昱, 邵波, 汤英, 李辉信, 胡锋 (2009) 地上部植食者褐飞虱对不同水稻品种土壤线虫群落的影响. 生物多样性, 17, 431-439. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09087.
Manqiang Liu, Jinghua Huang, Xiaoyun Chen, Feng Wang, Cheng Ge, Yu Su, Bo Shao, Ying Tang, Huixin Li, Feng Hu (2009) Aboveground herbivory by the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) affects soil nematode communities under different rice varieties. Biodiversity Science, 17, 431-439. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09087.
| 变量 Variable | 褐飞虱 (BP)1) | 水稻品种(V)2) | 交互作用 (BP ×V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 线虫总数 Nematode abundance | 14.2** | 6.1** | 40.1** |
| 线虫属 Nematode genera | 2.8NS | 1.9NS | 3.5* |
| 食细菌线虫数 Bacterivores | 8.1** | 4.2* | 28.0** |
| 食真菌线虫数 Fungivores | 2.5NS | 4.1* | 4.6* |
| 植食性线虫数 Herbivores | 1.0NS | 1.9NS | 1.8NS |
| 捕食性线虫数 Predators | 7.6* | 3.0* | 5.1** |
| 线虫通道指数 NCR Nematode channel ratio | 0.5NS | 2.3NS | 1.7NS |
| 多样性指数 (H') Shannon-Wiener index | 1.8NS | 1.4NS | 1.1NS |
| 成熟度指数 (MI) Maturity index | 0.4NS | 0.5NS | 1.3NS |
| 富集指数 (EI) Enrichment index | 1.9NS | 1.8NS | 1.7NS |
| 结构指数 (SI) Structure index | 5.6* | 1.1NS | 2.4NS |
表1 褐飞虱(自由度d.f.=1)、水稻品种(d.f.=3)及其交互作用(d.f.=3)对土壤线虫群落的影响(方差分析F值和显著性水平)
Table 1 Summary of ANOVA F-values for the effects of brown planthopper (d.f. = 1; with or without Nilaparvata lugens), rice variety (d.f. = 3; four varieties), and their interactions (d.f. = 3) on soil nematode community
| 变量 Variable | 褐飞虱 (BP)1) | 水稻品种(V)2) | 交互作用 (BP ×V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 线虫总数 Nematode abundance | 14.2** | 6.1** | 40.1** |
| 线虫属 Nematode genera | 2.8NS | 1.9NS | 3.5* |
| 食细菌线虫数 Bacterivores | 8.1** | 4.2* | 28.0** |
| 食真菌线虫数 Fungivores | 2.5NS | 4.1* | 4.6* |
| 植食性线虫数 Herbivores | 1.0NS | 1.9NS | 1.8NS |
| 捕食性线虫数 Predators | 7.6* | 3.0* | 5.1** |
| 线虫通道指数 NCR Nematode channel ratio | 0.5NS | 2.3NS | 1.7NS |
| 多样性指数 (H') Shannon-Wiener index | 1.8NS | 1.4NS | 1.1NS |
| 成熟度指数 (MI) Maturity index | 0.4NS | 0.5NS | 1.3NS |
| 富集指数 (EI) Enrichment index | 1.9NS | 1.8NS | 1.7NS |
| 结构指数 (SI) Structure index | 5.6* | 1.1NS | 2.4NS |
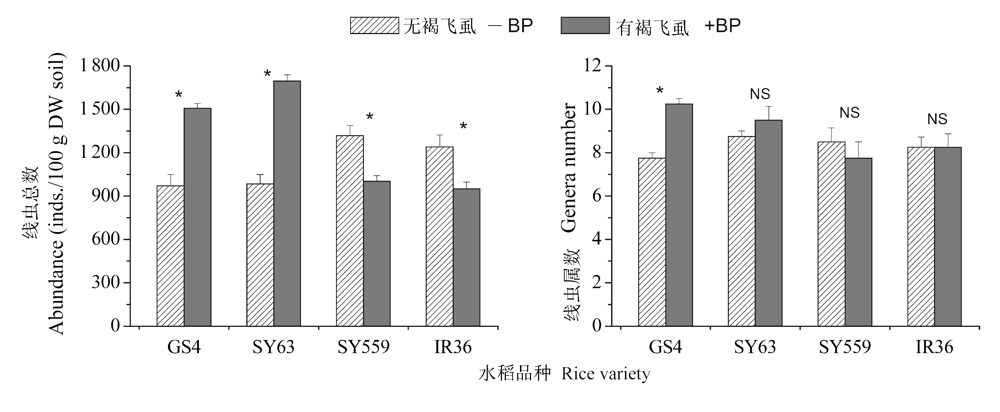
图1 不同水稻品种在褐飞虱作用下对土壤线虫总数和类群属数的影响(平均值±标准误)。同一水稻品种内柱形图上的星号*代表接种褐飞虱的影响达到显著水平(P < 0.05), NS表示未达到显著水平, t-检验。
Fig. 1 Abundance and genera number (Mean ± SE) of soil nematode community as affected by rice varieties and brown planthopper (-BP, brown planthopper absent, +BP, brown planthopper present). The asterisk * above histograms under each rice variety represent significant effects of brown planthopper at P = 0.05 level, t-test.
| 类群(属) Taxa (Genus) | 缩写Abbr. | c-p | 广四 GS4 | 汕优63 SY63 | 汕优559 SY559 | IR36 IR36 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -BP | +BP | -BP | +BP | -BP | +BP | -BP | +BP | |||||||||||
| 食细菌线虫 Bacterivores | ||||||||||||||||||
| 原杆属 Protorhabditis | Pro. | 1 | 371.3 | 702.4 | 530.6 | 860.2 | 697.5 | 576.4 | 631.2 | 458.8 | ||||||||
| 中杆属 Mesorhabditis | Mes. | 1 | 363.2 | 549.5 | 202.0 | 425.4 | 262.1 | 163.3 | 253.2 | 297.6 | ||||||||
| 钩唇属 Diploscapter | Dip. | 1 | 105.7 | 26.4 | 13.1 | 95.0 | 88.7 | 4.7 | 63.8 | 49.0 | ||||||||
| 板唇属 Chiloplacus | Chi. | 2 | 50.3 | 59.5 | 104.5 | 96.1 | 116.0 | 88.6 | 134.1 | 32.6 | ||||||||
| 头叶属 Cephalobus | Cep. | 2 | 2.1 | 11.9 | 6.3 | 16.1 | 7.2 | 4.4 | 2.3 | 18.0 | ||||||||
| 真头叶属 Eucephalobus | Euc. | 2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.2 | 0 | 6.2 | 2.3 | 15.1 | 0 | ||||||||
| 连胃属 Chronogaster | Chr. | 2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.6 | 2.1 | 8.9 | 0.0 | 2.7 | ||||||||
| 地单宫属 Geomonhyster | Geo. | 2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.1 | 12.3 | 3.0 | 2.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||
| 食真菌线虫 Fungivores | ||||||||||||||||||
| 滑刃属 Aphelenchoides | Aes. | 2 | 5.8 | 28.1 | 6.2 | 8.0 | 8.2 | 4.4 | 14.3 | 6.4 | ||||||||
| 真滑刃属 Aphelenchus | Aus. | 2 | 4.3 | 5.1 | 0.0 | 7.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||
| 植食性线虫 Herbivores | ||||||||||||||||||
| 盾线属 Scutellonema | Scu. | 3 | 65.0 | 95.6 | 99.4 | 138.0 | 114.0 | 134.3 | 119.6 | 77.9 | ||||||||
| 野外垫刃属 Aglenchus | Agl. | 2 | 0.0 | 4.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||
| 丝尾垫刃属 Filenchus | Fil. | 2 | 0.0 | 10.6 | 9.6 | 0.0 | 3.4 | 7.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||
| 捕食性线虫 Predators | ||||||||||||||||||
| 无咽属 Alaimus | Ala. | 4 | 3.7 | 7.9 | 2.0 | 4.6 | 0.0 | 5.2 | 6.2 | 3.6 | ||||||||
| 克拉克属 Clarkus | Cla. | 4 | 0.0 | 6.0 | 1.7 | 28.9 | 8.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.8 | ||||||||
表2 不同水稻品种在褐飞虱作用(-BP: 无褐飞虱, +BP, 有褐飞虱)下土壤各类群线虫的数量(个/100 g干土)
Table 2 Soil nematode number (ind./100 g DW soil) of different individual taxa as affected by rice varieties and brown planthopper (-BP, brown planthopper absent, +BP, brown planthopper present)
| 类群(属) Taxa (Genus) | 缩写Abbr. | c-p | 广四 GS4 | 汕优63 SY63 | 汕优559 SY559 | IR36 IR36 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -BP | +BP | -BP | +BP | -BP | +BP | -BP | +BP | |||||||||||
| 食细菌线虫 Bacterivores | ||||||||||||||||||
| 原杆属 Protorhabditis | Pro. | 1 | 371.3 | 702.4 | 530.6 | 860.2 | 697.5 | 576.4 | 631.2 | 458.8 | ||||||||
| 中杆属 Mesorhabditis | Mes. | 1 | 363.2 | 549.5 | 202.0 | 425.4 | 262.1 | 163.3 | 253.2 | 297.6 | ||||||||
| 钩唇属 Diploscapter | Dip. | 1 | 105.7 | 26.4 | 13.1 | 95.0 | 88.7 | 4.7 | 63.8 | 49.0 | ||||||||
| 板唇属 Chiloplacus | Chi. | 2 | 50.3 | 59.5 | 104.5 | 96.1 | 116.0 | 88.6 | 134.1 | 32.6 | ||||||||
| 头叶属 Cephalobus | Cep. | 2 | 2.1 | 11.9 | 6.3 | 16.1 | 7.2 | 4.4 | 2.3 | 18.0 | ||||||||
| 真头叶属 Eucephalobus | Euc. | 2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.2 | 0 | 6.2 | 2.3 | 15.1 | 0 | ||||||||
| 连胃属 Chronogaster | Chr. | 2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.6 | 2.1 | 8.9 | 0.0 | 2.7 | ||||||||
| 地单宫属 Geomonhyster | Geo. | 2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.1 | 12.3 | 3.0 | 2.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||
| 食真菌线虫 Fungivores | ||||||||||||||||||
| 滑刃属 Aphelenchoides | Aes. | 2 | 5.8 | 28.1 | 6.2 | 8.0 | 8.2 | 4.4 | 14.3 | 6.4 | ||||||||
| 真滑刃属 Aphelenchus | Aus. | 2 | 4.3 | 5.1 | 0.0 | 7.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||
| 植食性线虫 Herbivores | ||||||||||||||||||
| 盾线属 Scutellonema | Scu. | 3 | 65.0 | 95.6 | 99.4 | 138.0 | 114.0 | 134.3 | 119.6 | 77.9 | ||||||||
| 野外垫刃属 Aglenchus | Agl. | 2 | 0.0 | 4.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||
| 丝尾垫刃属 Filenchus | Fil. | 2 | 0.0 | 10.6 | 9.6 | 0.0 | 3.4 | 7.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||
| 捕食性线虫 Predators | ||||||||||||||||||
| 无咽属 Alaimus | Ala. | 4 | 3.7 | 7.9 | 2.0 | 4.6 | 0.0 | 5.2 | 6.2 | 3.6 | ||||||||
| 克拉克属 Clarkus | Cla. | 4 | 0.0 | 6.0 | 1.7 | 28.9 | 8.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.8 | ||||||||
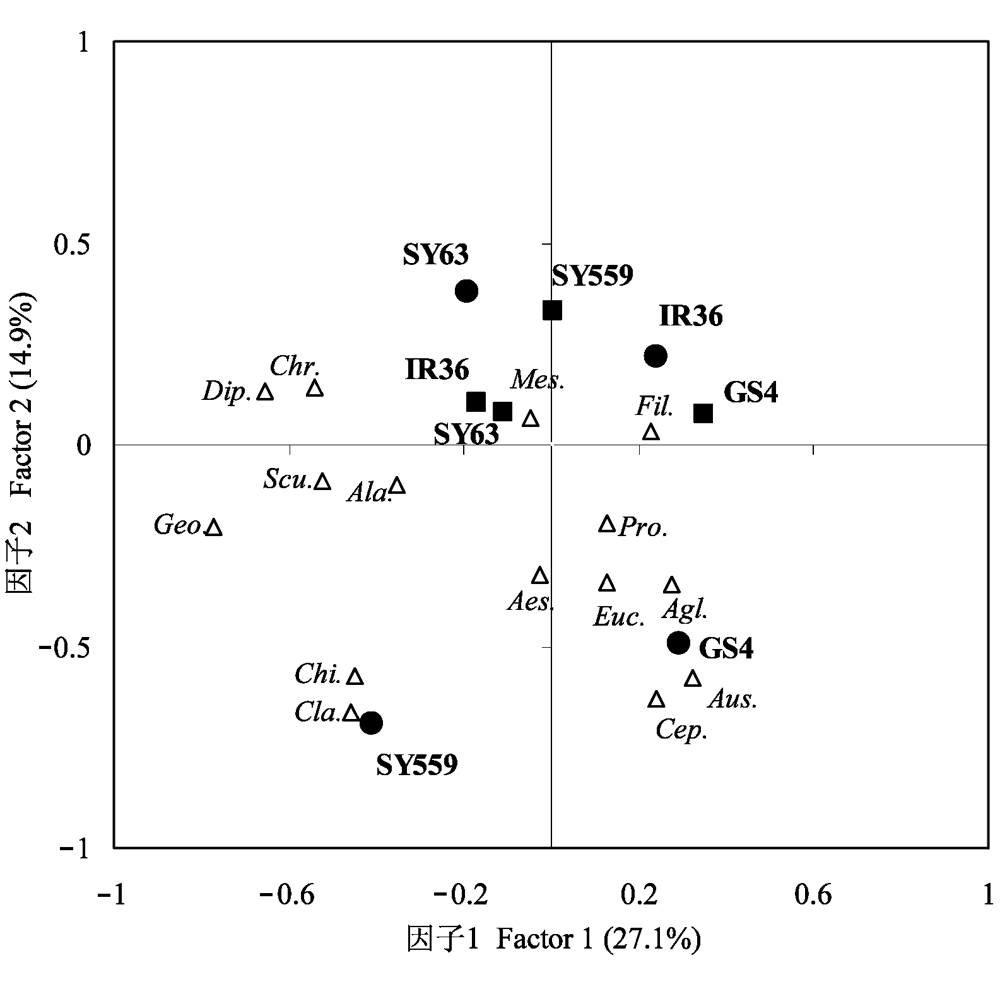
图2 土壤线虫群落组成在褐飞虱和水稻品种影响下的主成分分析。△代表线虫属名, 斜体字母含义见表2, GS4, SY63, SY559和IR36代表不同水稻品种, ■无褐飞虱, ●有褐飞虱。
Fig. 2 Principle component analysis (PCA) of soil nematode community composition influenced by rice varieties and brown planthopper. Variables of nematode genera (△) are represented by italic lowercases with full names in Table 2. GS4, SY63, SY559 and IR36 represent different rice varieties, respectively. (■) Brown planthopper absent, (●) Brown planthopper present.
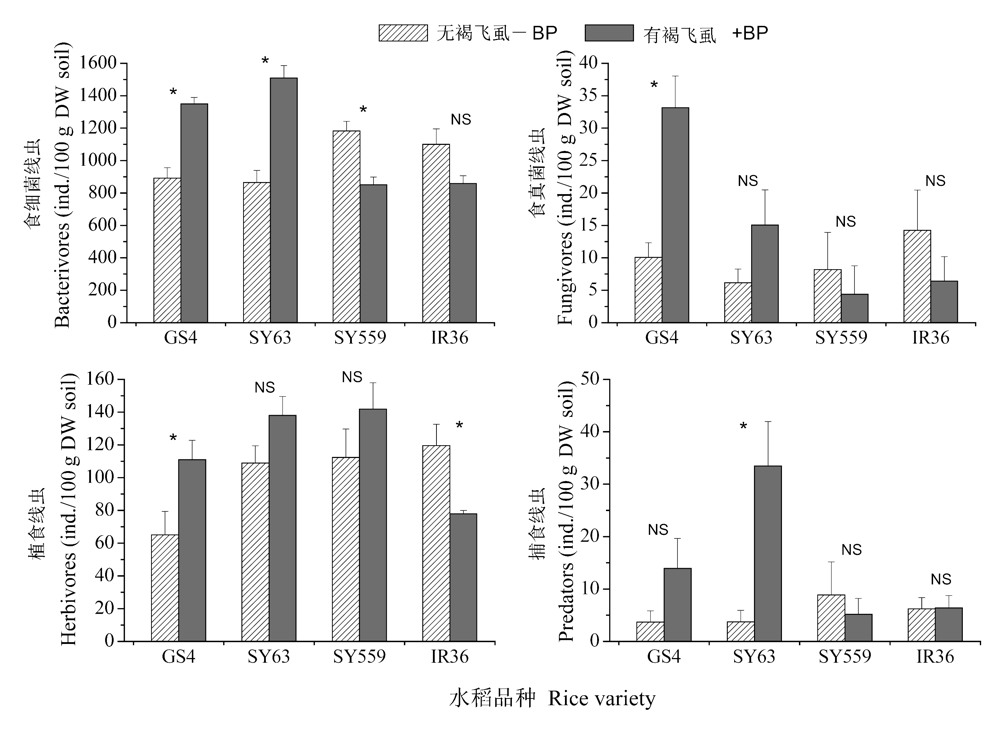
图3 不同水稻品种在褐飞虱作用下对土壤线虫营养类群的影响(平均值±标准误)。同一水稻品种内柱形图上的星号代表接种褐飞虱的影响达到显著水平(P < 0.05), NS表示未达到显著水平, t-检验。
Fig. 3 Trophic groups (Mean ± SE) of soil nematode community as affected by rice varieties and brown planthopper (-BP, brown planthopper absent, +BP, brown planthopper present), The asterisk * above histograms under each rice variety represent significant effects of brown planthopper at P = 0.05 level, t-test.
| 生态指数 Ecological indices | 广四 GS4 | 汕优63 SY63 | 汕优559 SY559 | IR36 IR36 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -BP | +BP | -BP | +BP | -BP | +BP | -BP | +BP | ||||||||
| 线虫通道指数 (NCR) Nematode channel ratio | 0.989±0.004 | 0.976±0.008* | 0.993±0.005 | 0.990±0.008NS | 0.993±0.009 | 0.994±0.012NS | 0.986±0.014 | 0.993±0.008NS | |||||||
| 多样性指数 (H') Shannon-Wiener index | 1.58±0.004 | 1.45±0.067* | 1.42±0.078 | 1.52±0.106NS | 1.43±0.121 | 1.31±0.270NS | 1.52±0.204 | 1.39±0.170NS | |||||||
| 成熟度指数 (MI) Maturity index | 1.01±0.034 | 1.02±0.044NS | 1.02±0.048 | 1.06±0.105NS | 1.04±0.042 | 0.99±0.068NS | 1.05±0.014 | 1.00±0.038NS | |||||||
| 富集指数 (EI) Enrichment index | 98.14±0.75 | 97.98±0.73NS | 95.94±0. 57 | 97.38±1.58NS | 96.69±0.48 | 96.00±3.36NS | 95.57±1.72 | 98.04±1.31* | |||||||
| 结构指数 (SI) Structure index | 20.20±23.56 | 28.43±20.03NS | 8.97±10.67 | 47.76±11.63* | 16.37±26.18 | 10.37±12.92NS | 13.33±9.67 | 30.19±21.61* | |||||||
表3 不同水稻品种在褐飞虱作用(-BP: 无褐飞虱, +BP, 有褐飞虱)下土壤线虫群落的生态指数(Mean±SD)
Table 3 Ecological indices of soil nematode community as affected by rice varieties and brown planthopper (-BP, brown planthopper absent, +BP, brown planthopper present)
| 生态指数 Ecological indices | 广四 GS4 | 汕优63 SY63 | 汕优559 SY559 | IR36 IR36 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -BP | +BP | -BP | +BP | -BP | +BP | -BP | +BP | ||||||||
| 线虫通道指数 (NCR) Nematode channel ratio | 0.989±0.004 | 0.976±0.008* | 0.993±0.005 | 0.990±0.008NS | 0.993±0.009 | 0.994±0.012NS | 0.986±0.014 | 0.993±0.008NS | |||||||
| 多样性指数 (H') Shannon-Wiener index | 1.58±0.004 | 1.45±0.067* | 1.42±0.078 | 1.52±0.106NS | 1.43±0.121 | 1.31±0.270NS | 1.52±0.204 | 1.39±0.170NS | |||||||
| 成熟度指数 (MI) Maturity index | 1.01±0.034 | 1.02±0.044NS | 1.02±0.048 | 1.06±0.105NS | 1.04±0.042 | 0.99±0.068NS | 1.05±0.014 | 1.00±0.038NS | |||||||
| 富集指数 (EI) Enrichment index | 98.14±0.75 | 97.98±0.73NS | 95.94±0. 57 | 97.38±1.58NS | 96.69±0.48 | 96.00±3.36NS | 95.57±1.72 | 98.04±1.31* | |||||||
| 结构指数 (SI) Structure index | 20.20±23.56 | 28.43±20.03NS | 8.97±10.67 | 47.76±11.63* | 16.37±26.18 | 10.37±12.92NS | 13.33±9.67 | 30.19±21.61* | |||||||
| [1] | Bazot S, Mikola J, Nguyen C, Robin C (2005) Defoliation-induced changes in carbon allocation and root soluble carbon concentration in field-grown Lolium perenne plants: do they affect carbon availability, microbes and animal trophic groups in soil? Functional Ecology, 19,886-896. |
| [2] | Bardgett RD, Wardle DA (2003) Herbivore-mediated linkages between aboveground and belowground communities. Ecology, 84,2258-2268. |
| [3] | Butenschoen O, Marhan S, Scheu S (2008) Response of soil microorganisms and endogeic earthworms to cutting of grassland plants in a laboratory experiment. Applied Soil Ecology, 38,152-160. |
| [4] |
Bongers T (1990) The maturity index: an ecological measure of environmental disturbance based on nematode species composition. Oecologia, 83,14-19.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
Bongers T, Ferris H (1999) Nematode community structure as a bioindicator in environmental monitoring. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 14,224-228.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] | Chen JM (陈建明), Yu XP (俞晓平), Cheng JA (程家安), Lü ZX (吕仲贤), Zheng XS (郑许松), Xu HX (徐红星) (2003) Evaluation for tolerance and compensation of rice varieties to infesting of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Chinese Journal of Rice Science (中国水稻科学), 17,265-269. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Chen W (陈威), Zhou Q (周强), Li X (李欣), He GF (何国锋) (2006) Physiological responses of different rice cultivars under herbivore stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 26,2161-2166. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Chen XY (陈小云), Liu MQ (刘满强), Hu F (胡锋), Mao XF (毛小芳), Li HX (李辉信) (2007) Contributions of soil micro-fauna (protozoa and nematodes) to rhizosphere ecological functions. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 27,3132-3143. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Christensen S, Bjørnlund L, Vestergård M (2007) Decomposer biomass in the rhizosphere to assess rhizodeposition. Oikos, 116,65-74. |
| [10] | Cohen MB, Alam SN, Medina EB, Bernal CC (1997) Brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, resistance in rice cultivar IR64: mechanism and role in successful N. lugens management in central Luzon, Philippines. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 85,221-229. |
| [11] | de Deyn GB, Raaijamakers CE, van Ruijven J, Berendse F, van der Putten WH (2004) Plant species identity and diversity effects on different trophic levels of nematodes in the soil food web. Oikos, 106,576-586. |
| [12] | de Deyn GB, van Ruijven J, Raaijmakers CE, de Ruiter PC, van der Putten WH (2007) Above- and belowground insect herbivores differentially affect soil nematode communities in species-rich plant communities. Oikos, 116,923-930. |
| [13] | Ferris H, Bongers T, de Goede RGM (2001) A framework for soil food web diagnostics: extension of the nematode faunal analysis concept. Applied Soil Ecology, 18,13-29. |
| [14] | Fu S, Kisselle KW, Coleman DC, Hendrix PF, Crossley DA Jr (2001) Short-term impacts of aboveground herbivory (grasshopper) on the abundance and 14C activity of soil nematodes in conventional tillage and no-till agroecosystems. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33,1253-1258. |
| [15] | Griffiths BS, Caul S (1993) Migration of bacterial-feeding nematodes, but not protozoa, to decomposing grass residues. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 15,201-207. |
| [16] | Harrison KA, Bardgett RD (2008) Impacts of grazing and browsing by large herbivores on soils and soil biological properties. In:The Ecology of Browsing and Grazing (eds Gordon IJ, Prins HH), pp.201-216. Springer-Verlag, New York. |
| [17] |
Karban R, Chen Y (2007) Induced resistance in rice against insects. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 97,327-335.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] | Li HX (李辉信), Liu MQ (刘满强), Hu F (胡锋), Chen XY (陈小云), He YQ (何圆球) (2002) Nematode abundance under different vegetations restored on degraded red soil. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 22,1882-1889. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Li Q (李琪), Liang WJ (梁文举), Jiang Y (姜勇) (2007) Present situation and prospect of soil nematode diversity in farmland ecosystems. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 15,134-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | Li YJ (李玉娟), Wu JH (吴纪华), Chen HL (陈慧丽), Chen JK (陈家宽) (2005) Nematodes as bioindicator of soil health: methods and applications. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 16,1541-1546. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Liao CH (廖崇惠), Li JX (李健雄) (2009) Re-evaluating the character and application of density-group index (DG). Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 17,127-134. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [22] |
Mulder C, Den Hollander HA, Hendriks AJ (2008) Aboveground herbivory shapes the biomass distribution and flux of soil invertebrates. PLoS ONE, 3,e3573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003573.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] | Neher DA, Weicht TR, Moorhead DL, Sinsabaugh RL (2004) Elevated CO2 alter functional attributes of nematode communities in forest soils. Functional Ecology, 18,584-591. |
| [24] | Patra AK, Abbadie L, Clays-Josserand A, Degrange V, Grayston SJ, Loiseau P, Louault F, Mahmood S, Nazaret S, Philippot L, Poly F, Prosser JI, Richaume A, Le Roux X (2005) Effects of grazing on microbial functional groups involved in soil N dynamics. Ecological Monographs, 75,65-80. |
| [25] | Porazinska DL, Bardgett RD, Blaauw MB, Hunt HW, Parsons AN, Seastedt TR, Wall DH (2003) Relationships at the aboveground-belowground interface: plants, soil biota, and soil processes. Ecological Monographs, 73,377-395. |
| [26] | Poveda K, Steffan-Dewenter I, Scheu S, Tscharntke T (2007) Plant-mediated interactions between below- and aboveground processes:decomposition, herbivory,parasitism and pollination. In: Indirect Interaction Webs: Non-trophic Linkages Through Induced Plant Traits (eds Ohgushi T, Craig T, Price P), pp.147-163. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [27] | Schweitzer JA, Bailey JK, Hart SC, Wimp GM, Chapman SK, Whitham TG (2005) The interaction of plant genotype and herbivory decelerate leaf litter decomposition and alter nutrient dynamics. Oikos, 110,133-145. |
| [28] | Tang Y (汤英), Liu MQ (刘满强), Wang F (王峰), Chen FJ (陈法军), Shao B (邵波), Su Y (苏昱), Ge C (葛成), Huang JH (黄菁华), Li HX (李辉信), Hu F (胡锋) (2009) Herbivory of brown planthopper ( Nilaparvata lugens) affects rice plant growth and belowground soil labile organic carbon and nitrogen fractions. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), accepted. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] |
Vestergård M, Bjørnlund L, Christensen S (2004) Aphid effects on rhizosphere microorganisms and microfauna depend more on barley growth phase than on soil fertilization. Oecologia, 141,84-93.
URL PMID |
| [30] | Wang SJ (王邵军), Cai QJ (蔡秋锦), Ruan HH (阮宏华) (2007) Soil nematode community response to vegetation restoration in northern Fujian. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 15,356-364. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Wang SJ (王邵军), Ruan HH (阮宏华) (2008) Feedback mechanisms of soil biota to aboveground biology in terrestrial ecosystems. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 16,407-416. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] |
Wardle DA (2006) The influence of biotic interactions on soil biodiversity. Ecology Letters, 9,870-886.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] | Wardle DA, Williamson WM, Yeates GW, Bonner KI (2005) Trickle-down effects of aboveground trophic cascades on the soil food web. Oikos, 111,348-358. |
| [34] | Wardle DA, Yeates GW, Williamson WM, Bonner KI, Barker GM (2004) Linking aboveground and belowground communities: the indirect influence of aphid species identity and diversity on a three trophic level soil food web. Oikos, 107,283-294. |
| [35] | Wu JH (吴纪华), Song CY (宋慈玉), Chen JK (陈家宽) (2007) Effect of microbivorous nematodes on plant growth and soil nutrient cycling: a review. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 15,124-133. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [36] |
Yeates GW, Bongers T, de Goede RGM, Freckman DW, Georgieva S (1993) Feeding habits in soil nematode families and genera—an outline for soil ecologists. Journal of Nematology, 25,315-331.
URL PMID |
| [1] | 姚祝, 魏雪, 马金豪, 任晓, 王玉英, 胡雷, 吴鹏飞. 气候暖湿化对高寒草甸土壤线虫群落的短期影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23483-. |
| [2] | 刘笑彤, 田艺佳, 刘汉文, 梁翠影, 姜思维, 梁文举, 张晓珂. 下辽河平原农田土壤线虫群落组成的季节变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22222-. |
| [3] | 蒋林惠, 罗琌, 肖正高, 李大明, 陈小云, 刘满强, 胡锋. 长期施肥对水稻生长和抗虫性的影响: 解析土壤生物的贡献[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(8): 907-915. |
| [4] | 华萃, 吴鹏飞, 何先进, 朱波. 紫色土区不同秸秆还田量对土壤线虫群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(3): 392-400. |
| [5] | 刘雨迪, 陈小云, 刘满强, 秦江涛, 李辉信, 胡锋. 不同稻作年限下土壤微生物学性质和线虫群落特征的变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(3): 334-342. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn