



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 22478. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022478 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022478
收稿日期:2022-08-21
接受日期:2022-09-27
出版日期:2023-03-20
发布日期:2023-01-18
通讯作者:
赵晶晶,李添明
作者简介:zhaojj37@mail2.sysu.edu.cn基金资助:
Jingjing Zhao1,*( ), Haibin Jia2, Tien Ming Lee1,3,*(
), Haibin Jia2, Tien Ming Lee1,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-08-21
Accepted:2022-09-27
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-01-18
Contact:
Jingjing Zhao,Tien Ming Lee
摘要:
蚯蚓(地龙)是一种常见的动物类中药资源, 在心脑血管等疾病的治疗中具有较高的药用价值。近年来, 为大量获取野生蚯蚓, 高效获取蚯蚓的方式“电击”法应运而生, 但过度攫取可能会威胁蚯蚓的野外生存。为了解“电击”蚯蚓存在的潜在威胁和影响, 本文利用1998年2月至2022年7月的地龙市场价格数据及2004‒2021年的市场供应量和需求量数据, 分析了地龙市场价格的波动规律及其与供应、需求间的关系, 并通过贝叶斯结构时间序列模型探究了“电击”蚯蚓对供应量和价格的影响。结果表明: (1)自1998年以来, 地龙价格整体呈上升态势, 具有一定的季节性波动规律, 截至2022年产新季地龙干重价格涨至175元/kg; (2)地龙市场价值逐年增加, 目前价格偏离价值, 市场处于不稳定状态; (3) 2013年“电击”法推广后, 与未进行“电击法”推广的预测结果相比较, 在控制需求的情况下, 地龙供应量显著增加, 市场价格显著下降。相较于未进行“电击法”推广的预测结果, 供应量的平均值相对增加40%, 价格相对下降44%。为加强我国野生动物资源的保护与可持续利用, 强烈建议加快建立野生药用动物资源的市场监测预警机制, 强化野生药用动物资源市场秩序整顿和规范, 并通过市场与政策相互协调将可持续性融入野生药用动物资源利用的全过程。
赵晶晶, 贾海彬, 李添明 (2023) 野生药用动物资源蚯蚓(地龙)的市场现状及可持续利用对策. 生物多样性, 31, 22478. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022478.
Jingjing Zhao, Haibin Jia, Tien Ming Lee (2023) Market status and the sustainable utilization strategy of wild earthworm (earth dragon) for medicinal use. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22478. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022478.
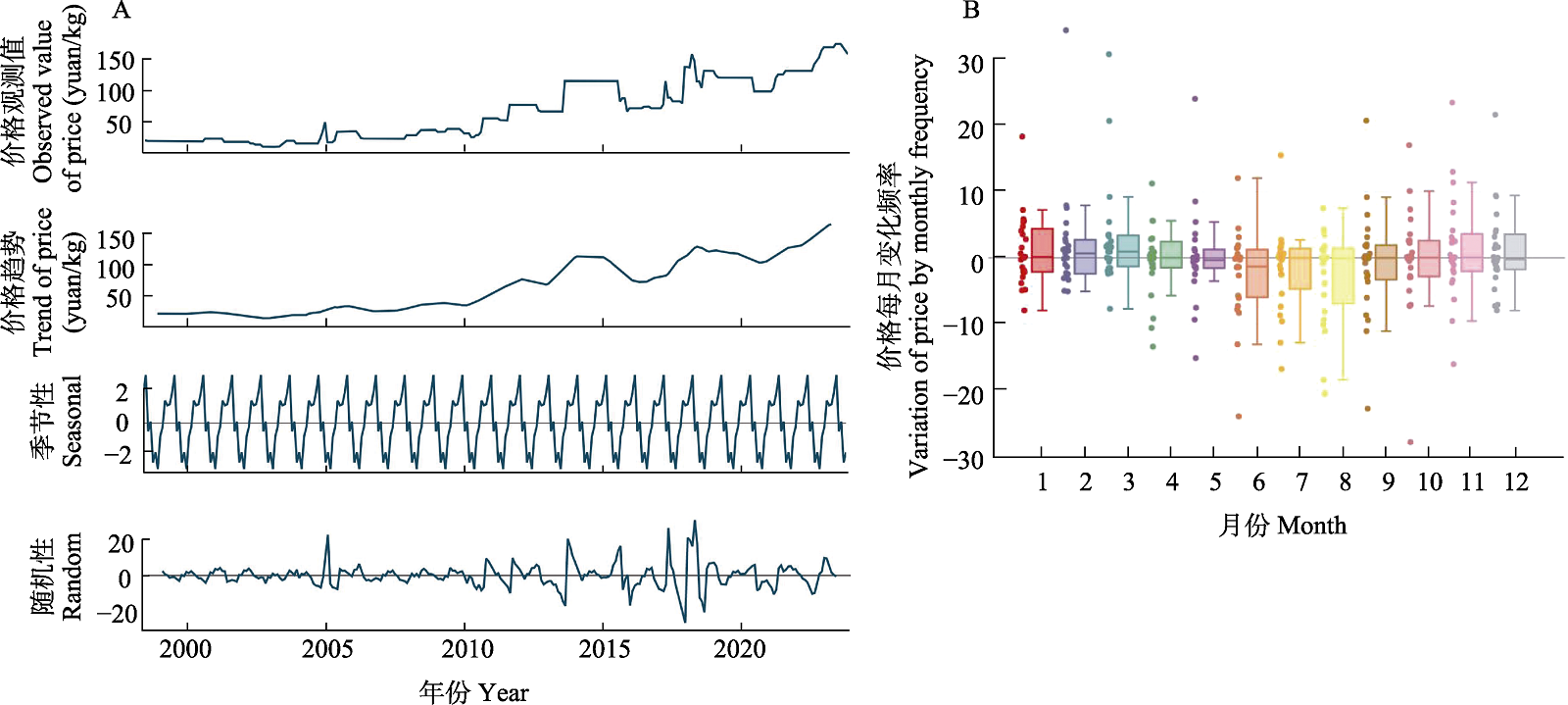
图1 1998?2022年地龙市场价格时间序列分析。A: 地龙市场价格时间序列分解; B: 去趋势后地龙价格季节性波动规律。
Fig. 1 Time series analysis of earth dragons (earthworms) market price between 1998 and 2022. (A) Decomposition of the market price time series of earth dragons (earthworms); (B) The seasonal fluctuation of earth dragons price after detrending analysis.
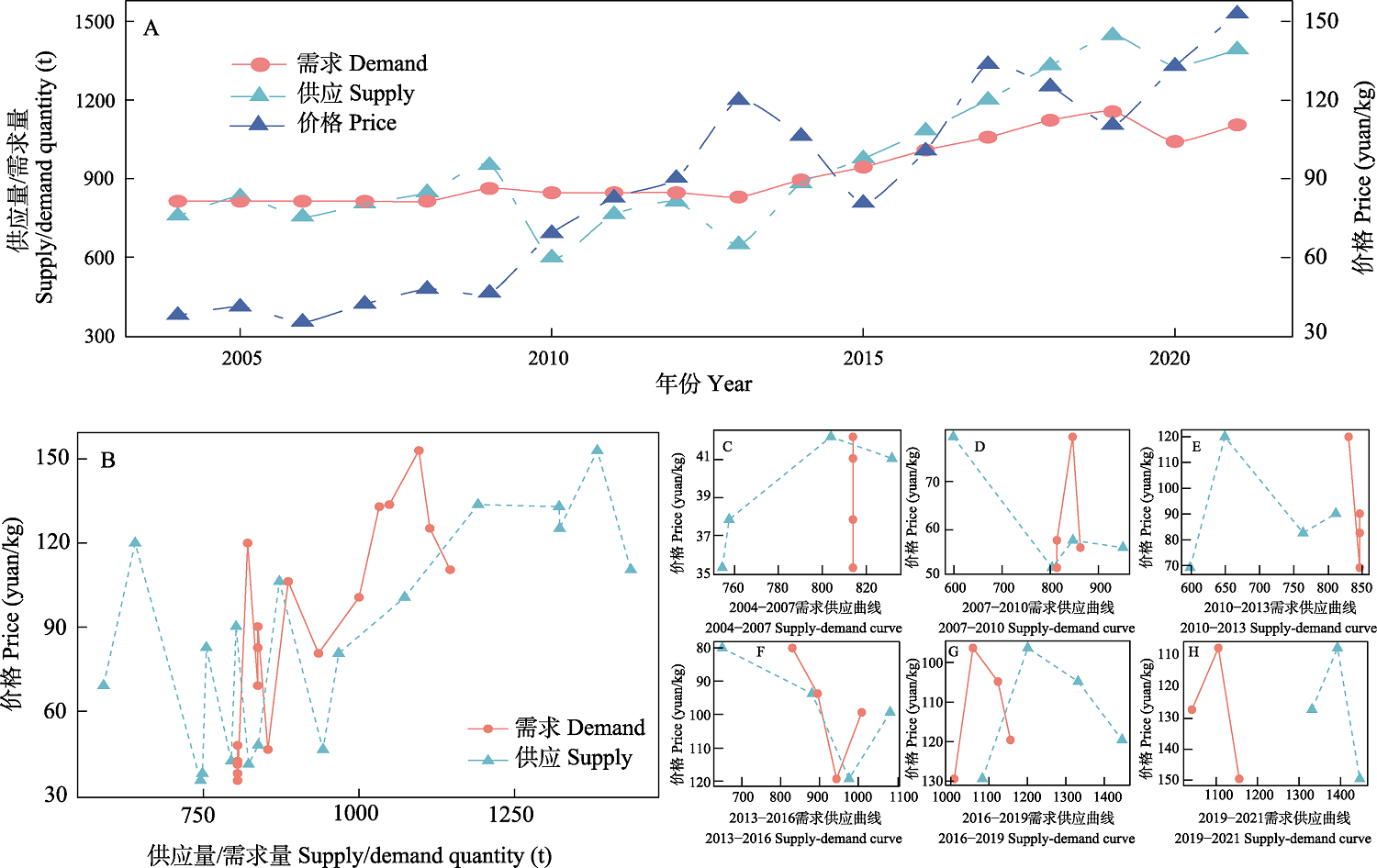
图2 2004?2021年间地龙市场供需变化特征和供需曲线分析。A: 2004?2021年间地龙市场价格、供需变化特征; B?H: 不同年份的供需曲线。图B?H中, 供应曲线与需求曲线交汇的点为均衡价格。
Fig. 2 The characteristics of earth dragons (earthworms) price, supply and demand changes and analysis of supply and demand curves from 2004 to 2021. (A) The characteristics of earth dragons (earthworms) supply and demand changes during 2004?2021; (B?H) Supply-demand curves during different year duration. In Figures B?H, the points are the equilibrium price, which is the intersection of the supply curve and the demand curve.
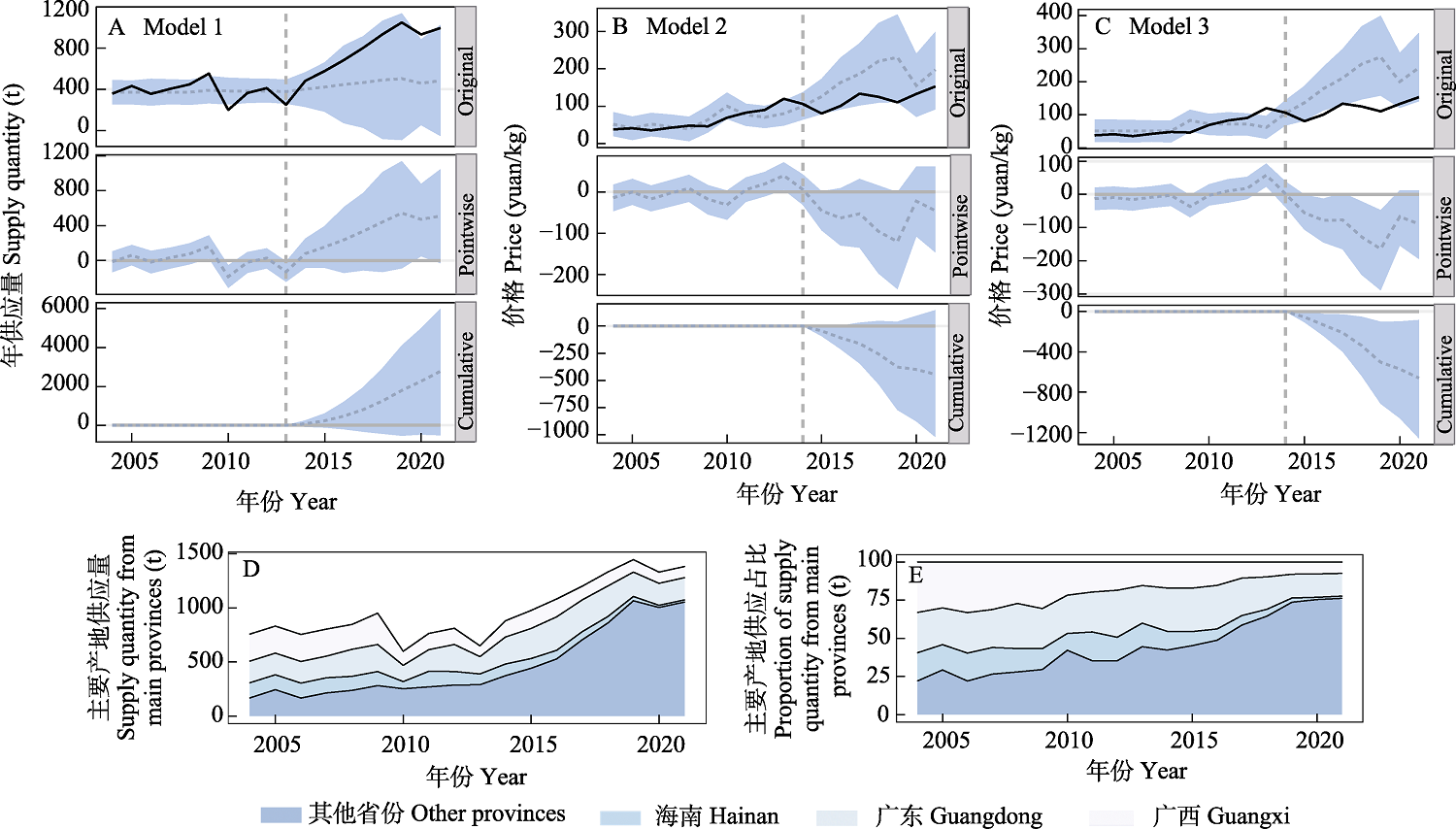
图3 “电击”法获取地龙对供应量和市场价格的影响。A: 在控制需求的情况下对供应量的影响; B: 在控制需求和供应的情况下对价格的影响; C: 在控制需求的情况下对价格的影响; D: 2004?2021年地龙各产区供应量变化; E: 2004?2021年地龙各产区间供应量占比变化。A, B和C: 第一张图(Original)中实线为“电击”法推广前后的实际结果, 虚线是根据实际结果进行反事实推断“电击”法未推广的模型预测值, 阴影区域为95%的置信区间; 第二张图(Pointwise)虚线为第一张图中的实际观测值与预测值(假如未实施“电击”法的模型预测)之间的差值; 第三张图(Cumulative)虚线为第二张图中差值的累积值, 反映“电击”法推广后的累计影响。
Fig. 3 The effect of using “electric shocking” methods to harvest earthworm on supply quantity and market price. (A) The effect of harvest on supply (A) after controlling the demand variable; The effect of harvest on market price (B) after controlling for demand and supply and (C) after controlling for demand; (D) The supply changes of earth dragons across various main provinces from 2004 to 2021; (E) The proportion changes of supply of earth dragons across various main provinces from 2004 to 2021. For Figures A, B, and C: In the top panel row, the solid line represents the original value, while the dotted line represents the predicted value based on the original results for the counterfactual prediction (i.e., if the “electric shocking” methods was not popularized), and the shaded area represents the 95% confidence interval. The middle panel row is the difference value between the original value and predicted value in the upper panel. The bottom panel row is the sum of the values of the middle panel, reflecting a plot of the cumulative effect of the “electric shocking” methods.
| 模型名称 Model name | 模型1 Model 1 | 模型2 Model 2 | 模型3 Model 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 响应变量 Response variable | 供应 Supply quantity (t) | 价格 Price (yuan/kg) | 价格 Price (yuan/kg) | |||
| 控制变量 Control variable | 需求量 Demand quantity | 供应量与需求量 Supply & demand quantity | 需求量 Demand quantity | |||
| 平均 Average | 累计 Cumulative | 平均 Average | 累计Cumulative | 平均 Average | 累计Cumulative | |
| 平均实际值 Actual | 1,205 | 9,643 | 119 | 836 | 119 | 836 |
| 平均预测值(标准差) Prediction (SD) | 858 (203) | 6,866 (1,621) | 183 (42) | 1,281 (294) | 214 (42) | 1,496 (292) |
| 95%置信区间 CI | [458, 1,270] | [3,662, 10,158] | [99, 265] | [691, 1,856] | [132, 299] | [921, 2,091] |
| 绝对效应(标准差) Absolute effect (SD) | 347 (203) | 2,778 (1,621) | ?63 (42) | ?444 (294) | ?94 (42) | ?659 (292) |
| 95%置信区间 CI | [?64, 748] | [?515, 5,981] | [?146, 21] | [?1,019, 145] | [?179, ?12] | [?1,255, ?85] |
| 相对效应(标准差) Relative effect (SD) | 40% (24%) | 40% (24%) | ?35% (23%) | ?35% (23%) | ?44% (20%) | ?44% (20%) |
| 95%置信区间 CI | [?7.5%, 87%] | [?7.5%, 87%] | [?80%, 11%] | [?80%, 11%] | [?84%, ?5.7%] | [?84%, ?5.7%] |
| 后验尾区概率 P Posterior tail-area probability P | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.01 | |||
| 因果影响的后验概率 Posterior probability of a causal effect | 95.6% | 93.0% | 99.7% | |||
表1 “电击”法获取地龙对供应量和市场价格影响的后验推论
Table 1 Posterior inference of impacts on supply quantity and market price
| 模型名称 Model name | 模型1 Model 1 | 模型2 Model 2 | 模型3 Model 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 响应变量 Response variable | 供应 Supply quantity (t) | 价格 Price (yuan/kg) | 价格 Price (yuan/kg) | |||
| 控制变量 Control variable | 需求量 Demand quantity | 供应量与需求量 Supply & demand quantity | 需求量 Demand quantity | |||
| 平均 Average | 累计 Cumulative | 平均 Average | 累计Cumulative | 平均 Average | 累计Cumulative | |
| 平均实际值 Actual | 1,205 | 9,643 | 119 | 836 | 119 | 836 |
| 平均预测值(标准差) Prediction (SD) | 858 (203) | 6,866 (1,621) | 183 (42) | 1,281 (294) | 214 (42) | 1,496 (292) |
| 95%置信区间 CI | [458, 1,270] | [3,662, 10,158] | [99, 265] | [691, 1,856] | [132, 299] | [921, 2,091] |
| 绝对效应(标准差) Absolute effect (SD) | 347 (203) | 2,778 (1,621) | ?63 (42) | ?444 (294) | ?94 (42) | ?659 (292) |
| 95%置信区间 CI | [?64, 748] | [?515, 5,981] | [?146, 21] | [?1,019, 145] | [?179, ?12] | [?1,255, ?85] |
| 相对效应(标准差) Relative effect (SD) | 40% (24%) | 40% (24%) | ?35% (23%) | ?35% (23%) | ?44% (20%) | ?44% (20%) |
| 95%置信区间 CI | [?7.5%, 87%] | [?7.5%, 87%] | [?80%, 11%] | [?80%, 11%] | [?84%, ?5.7%] | [?84%, ?5.7%] |
| 后验尾区概率 P Posterior tail-area probability P | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.01 | |||
| 因果影响的后验概率 Posterior probability of a causal effect | 95.6% | 93.0% | 99.7% | |||
| [1] | Bai FZ (2022) Soil warning behind an environmental lawsuit. Farmer’s Daily, July 8, 2022. (in Chinese) |
| [白锋哲 (2022) 一起环境讼案背后的土壤警示. 农民日报, 2022年7月8日.] | |
| [2] |
Bi YJ, Sun ZJ (2018) Mechanisms of earthworms to alleviate continuous cropping obstacles through regulating soil microecology. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1103-1115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[毕艳孟, 孙振钧 (2018) 蚯蚓调控土壤微生态缓解连作障碍的作用机制. 生物多样性, 26, 1103-1115.]
DOI |
|
| [3] | Brodersen KH, Gallusser F, Koehler J, Remy N, Scott SL (2015) Inferring causal impact using Bayesian structural time-series models. Annals of Applied Statistics, 9, 247-274. |
| [4] | Chen D, Wang HW (2013) Thoughts on the regulation policy of Chinese herbal medicine price. China Price Supervision and Check, (1), 42-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈达, 王火旺 (2013) 对中药材价格调控监管政策的思考. 中国价格监督检查, (1), 42-44.] | |
| [5] | Cheng M, Yang G, Huang LQ (2021) Summary of the Development Report of Chinese Traditional Medicine Resources in 2019—Development of Chinese traditional medicine resources in the last 70 years and future prospect. China Food & Drag Administration Magazine, (3), 17-27. |
| [程蒙, 杨光, 黄璐琦 (2021) 《中国中药资源发展报告(2019)》综述——中药资源发展七十年历程与展望. 中国食品药品监管, (3), 17-27.] | |
| [6] | Chen S, Wang Y, Zhao Z, Leon CJ, Henry RJ (2015) Sustainable utilization of TCM resources. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/613836. |
| [7] |
Cheung H, Doughty H, Hinsley A, Hsu E, Lee TM, Milner-Gulland EJ, Possingham H, Biggs D (2021) Understanding traditional Chinese medicine to strengthen conservation outcomes. People and Nature, 3, 115-128.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Cui XS, Xie JB, Zhang YQ, Jin PB, Gao XQ, Dong XH (2019) Analysis of market price influence of Chinese herbal medicine based on supply and demand curve. Northern Horticulture, 23, 152-156. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [崔旭盛, 解军波, 张彦青, 靳鹏博, 高秀强, 董学会 (2019) 基于供需曲线的中药材市场价格影响分析. 北方园艺, 23, 152-156.] | |
| [9] | Cunningham AB, Long X (2019) Linking resource supplies and price drivers: Lessons from traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) price volatility and change, 2002-2017. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 229, 205-214. |
| [10] | Dagum EB (2010) Time series modeling and decomposition. Statistica, 70, 433-457. |
| [11] | Dong LL, Shen MX, Shi LL, Shen Y, Wang HH, Lu CY (2022) Biochar combined with earthworm cast application affects rice yield and nutrient uptake. Crops, (5), 67-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [董林林, 沈明星, 施林林, 沈园, 王海候, 陆长婴 (2022) 生物质炭配施蚯蚓粪对水稻产量及养分吸收的影响. 作物杂志, (5), 67-77.] | |
| [12] |
He J (2018) Harvest and trade of caterpillar mushroom (Ophiocordyceps sinensis) and the implications for sustainable use in the Tibet Region of Southwest China. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 221, 86-90.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Hu SF, Cheng Y, Pan R, Zou FS, Lee TM (2022) Understanding the social impacts of enforcement activities on illegal wildlife trade in China. Ambio, 51, 1643-1657.
DOI |
| [14] | Li Q (2022) A benefit chain of wild earthworms. China Youth Daily, July 20, 2022. (in Chinese) |
| [李强 (2022) 一条野生蚯蚓的利益链. 中国青年报, 2022年7月20日.] | |
| [15] | Lin YP, Tian B, Qu XL, Song Y (2019) Analysis and countermeasures on the School of Pharmaly, sustainable development of traditional Chinese medicine resources. Pharmacy and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica, 10(5/6), 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [林义平, 田斌, 瞿孝兰, 宋英 (2019) 中药资源可持续发展现状分析及对策. 中药与临床, 10(5/6), 1-7.] | |
| [16] | Long XC, Guo BL (2017) Electronic Trading Specification Grade Standard for 200 Kinds of Chinese Herbal Medicine Commodity. China Medical Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [龙兴超, 郭宝林 (2017) 200种中药材商品电子交易规格等级标准. 中国医药科技出版社, 北京.] | |
| [17] | Mathieu J (2018) EGrowth: A global database on intraspecific body growth variability in earthworm. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 122, 71-80. |
| [18] |
Milupi I, Somers M, Ferguson W (2017) Local ecological knowledge and community-based management of wildlife resources: A study of the Mumbwa and Lupande Game Management areas of Zambia. Southern African Journal of Environmental Education, 33, 25-38.
DOI URL |
| [19] | National Pharmacopoeia Committee (2020) Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (2020 Edition). China Medical Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [[国家药典委员会 (2020) 中华人民共和国药典 (2020年版). 中国医药科技出版社, 北京.] | |
| [20] |
Sun MM, Chao HZ, Zheng XX, Deng SP, Ye M, Hu F (2020) Ecological role of earthworm intestinal bacteria in terrestrial environments: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 740, 140008.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Sun ZJ (2015) Earthworm as a biopharmaceutical: From traditional to precise. European Journal of BioMedical Research, 1, 28-35. |
| [22] | Wu HY, Xu ZL (2022) Provenance traceability of earthworm based on the principal component analysis and discriminant analysis. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 42, 387-393. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴海燕, 徐芝亮 (2022) 基于主成分分析和判别分析的广地龙产地溯源研究. 药物分析杂志, 42, 387-393.] | |
| [23] | Yang XY (2012) Estimation of China’s demand and supply curve of corns and the market forecasting. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 30, 134-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨晓芸 (2012) 我国玉米供需曲线估测与市场预测. 陕西科技大学学报(自然科学版), 30, 134-139.] | |
| [24] | Yuan P, Shen JL (2014) Causes and optimized strategies of price fluctuations for genuine traditional Chinese medicinal materials. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 45, 3503-3508. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [袁盼, 申俊龙 (2014) 道地中药材价格波动的成因与优化策略. 中草药, 45, 3503-3508.] | |
| [25] |
Zhang C, Zhou B, Wu JL, Lü MR, Chen XF, Yuan ZY, Xiao L, Dai J (2018) Application of earthworms on soil remediation in Southern China. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1091-1102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张池, 周波, 吴家龙, 吕美蓉, 陈旭飞, 袁中友, 肖玲, 戴军 (2018) 蚯蚓在我国南方土壤修复中的应用. 生物多样性, 26, 1091-1102.]
DOI |
|
| [26] | Zhang HY (2022) Behind the “earth dragon instrument” is the thought of the black production. Prosecutorial View, (12), 72-73. (in Chinese) |
| [张宏羽 (2022) “地龙仪”背后的黑产. 检察风云, (12), 72-73.] | |
| [27] |
Zhang WX, Chen DM, Zhao CC (2007) Functions of earthworm in ecosystem. Biodiversity Science, 15, 142-153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张卫信, 陈迪马, 赵灿灿 (2007) 蚯蚓在生态系统中的作用. 生物多样性, 15, 142-153.]
DOI |
|
| [28] |
Zhang Y, Xiao ZG, Jiang LH, Qian L, Chen XY, Chen FJ, Hu F, Liu MQ (2018) Nitrogen levels modify earthworm- mediated tomato growth and resistance to pests. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1296-1307. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张宇, 肖正高, 蒋林惠, 钱蕾, 陈小云, 陈法军, 胡锋, 刘满强 (2018) 施氮水平影响蚯蚓介导的番茄生长及抗虫性. 生物多样性, 26, 1296-1307.]
DOI |
|
| [29] | Zhao RH, Jia HB, Zhou YH, Zhu Y, Liu R, Guo S, Duan JA (2020) Combination of protection and development is the way to solve the dilemma of sustainable utilization of animal medicine. Modern Chinese Medicine, 22, 835-839. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵润怀, 贾海彬, 周永红, 朱悦, 刘睿, 郭盛, 段金廒 (2020) 我国动物药资源供给现状及可持续发展的思考. 中国现代中药, 22, 835-839.] | |
| [30] | Zhu WL (2015) Price Impact Factors and Realization Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine—Case Study of Pseudo-Ginseng. PhD dissertation, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱婉丽 (2015) 中药资源价格影响因素与实现机制研究: 三七药材为例. 博士学位论文, 南京中医药大学, 南京.] |
| [1] | 黄婧, 孙美, 余文峰, 武建勇, 田怀珍. 我国网络平台本土兰科植物贸易状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21233-. |
| [2] | 张丛林, 褚梦真, 张慧智, 乔海娟, 黄宝荣. 青藏高原国家公园群游憩可持续性管理评估指标体系[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 780-789. |
| [3] | 杨锐,彭钦一,曹越,钟乐,侯姝彧,赵智聪,黄澄. 中国生物多样性保护的变革性转变及路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(9): 1032-1040. |
| [4] | 梦梦, 马建章, 尹峰, 陈文汇, 纪建伟. 我国典型城市外来野生脊椎动物贸易状况及管理对策[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(10): 1137-1143. |
| [5] | 田瑜, 邬建国, 寇晓军, 李钟汶, 王天明, 牟溥, 葛剑平. 东北虎种群的时空动态及其原因分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(3): 211-225. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()