



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (5): 630-643. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020134 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020134
史湘莹2,3,张晓川1,肖凌云1,李彬彬4,刘金梅5,杨方义6,赵翔3,程琛3,吕植1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-04-01
接受日期:2020-06-08
出版日期:2020-05-20
发布日期:2020-06-19
通讯作者:
吕植
Xiangying Shi2,3,Xiaochuan Zhang1,Lingyun Xiao1,Binbin V Li4,Jinmei Liu5,Fangyi Yang6,Xiang Zhao3,Chen Cheng3,Zhi Lü1,3,*( )
)
Received:2020-04-01
Accepted:2020-06-08
Online:2020-05-20
Published:2020-06-19
Contact:
Zhi Lü
摘要:
新冠肺炎疫情的暴发, 使得对野生动物的消费与贸易中的公共健康安全问题引起广泛关注。为了给相关的立法和政策制定提供参考, 我们通过网络对于全国及部分海外华人发放问卷进行了调查, 共收回74,040份有效问卷。根据问卷调查结果, 本文对普通公众对于野生动物消费和贸易立法意愿及影响因素进行了分析。研究结果包括: (1)公众对全面取缔野味餐馆和集市、禁止消费野味、禁止野生动物及其制品的买卖以及禁止野生动物商业性活体展演的立法动议持赞成态度的比例均超过90%; (2)现有野生动物消费群体经历新冠肺炎疫情后倾向于停止消费行为; (3)曾经消费野生动物或周围有人从事野生动物相关产业的群体相比其他人群更有可能不支持全面禁止对野生动物的消费和贸易。结果表明, 全国人民代表大会常务委员会禁食野生动物的决定和修改野生动物保护法的动议在受高等教育者和城镇居民中有良好的公众基础。
史湘莹, 张晓川, 肖凌云, 李彬彬, 刘金梅, 杨方义, 赵翔, 程琛, 吕植 (2020) 新冠肺炎时期公众对野生动物消费和贸易意愿的调查. 生物多样性, 28, 630-643. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020134.
Xiangying Shi, Xiaochuan Zhang, Lingyun Xiao, Binbin V Li, Jinmei Liu, Fangyi Yang, Xiang Zhao, Chen Cheng, Zhi Lü (2020) Public perception of wildlife consumption and trade during the COVID-19 outbreak. Biodiversity Science, 28, 630-643. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020134.
| 变量 Variables | 类型 Type | 定义 Definition |
|---|---|---|
| 背景特征 Background | ||
| 性别 Gender (GND) | 分类 Categorical | 女: 1; 男: 0 Female, 1; Male, 0 |
| 省份 Province (PRV) | 分类 Categorical | 每个省生成一个虚拟变量 Provincial dummies |
| 城乡 Urbanization (URB) | 分类 Categorical | 城镇: 1; 农村: 0 Urban, 1; rural, 0 |
| 年龄 Age (AGE) | 分类 Categorical | 虚拟变量(1, 0): AGE1: 0-18岁; AGE2: 19-30岁; AGE3: 31-55岁; AGE4, 56岁以上 Dummies (1, 0): AGE1, 0-18 years old; AGE2, 19-30 years old; AGE3, 31-55 years old; AGE4, above 56 years old |
| 教育程度 Education level (EDU) | 分类 Categorical | 虚拟变量(1, 0): EDU1: 小学及以下; EDU2: 初高中; EDU3: 大学; EDU4: 研究生及以上 Dummies (1, 0): EDU1, Below primary school; EDU2, Middle or high school; EDU3, Graduate; EDU4, Post graduate |
| 月收入 Monthly income level (CNY) (INC) | 分类 Categorical | 虚拟变量(1, 0): INC1: 0-1,000元; INC2: 1,000-5,000元; INC3: 5,000-10,000元; INC4: 10,000- 30,000元; INC5: 大于30,000元 Dummies (1, 0): INC1, 0-1,000 CNY; INC2, 1,000-5,000 CNY; INC3, 5,000-10,000 CNY; INC4, 10,000- 30,000 CNY; INC5, above 30,000 CNY |
| 看到周围有人吃野味次数 See surrounding people eat wildlife (times) (EAT) | 分类 Categorical | 虚拟变量(1, 0): EAT1: 无; EAT2: 1-3次; EAT3: 3-10次; EAT4: 10次以上 Dummies (1, 0): EAT1, None; EAT2, 1-3 times; EAT3, 3-10 times; EAT4, above 10 times |
| 工作/兴趣是否自然保护相关 Engaged or interested in nature conservation (CSV) | 分类 Categorical | 是: 1; 否: 0 Yes, 1; No, 0 |
| 周围有人从事野生动物利用相关产业 Engaged either directly or indirectly in wildlife-related industries (IND) | 分类 Categorical | 有任意类型: 1; 无: 0 Any type, 1; None, 0 |
| 过去有消费野生动物行为 Consumed wildlife in the past (CSM) | 分类 Categorical | 有: 1; 无: 0 Yes, 1; No, 0 |
| 过去消费野生动物, 现在停止 Consumed wildlife in the past but tend to stop now (STOPCSM) | 分类 Categorical | 有: 1; 无: 0 Yes, 1; No, 0 |
| 过去有自然观察野生动物行为 Observed wildlife in the past (WAT) | 分类 Categorical | 有: 1; 无: 0 Yes, 1; No, 0 |
| 过去有自然观察, 现在停止 Observed wildlife in the past but stop now (STOPWAT) | 分类 Categorical | 有: 1; 无: 0 Yes, 1; No, 0 |
| 过去无自然观察, 现在开始 Never observe wildlife before but will start to observe wildlife now (MOREWAT) | 分类 Categorical | 有: 1; 无: 0 Yes, 1; No, 0 |
| 对相关法规了解情况 Knowledge about related laws (LAW) | 有序 Ordinal | 否: 1; 听说过一些: 2; 是: 3 No, 1; Some, 2; Yes, 3 |
| 对相关许可证了解情况 Knowledge about related certificates (CER) | 有序 Ordinal | 不了解: 1; 听过但不了解: 2; 了解: 3 No, 1; Have heard but don’t know much, 2; Know very well, 3 |
| 对立法动议的态度 Attitude towards legislation motion | ||
| 取缔野味集市和餐馆 Ban on wildlife markets and restaurants (BMKT) | 有序 Ordinal | 强烈不赞成: 1; 不倾向赞成: 2; 中立: 3; 倾向赞成: 4; 强烈赞成: 5 Strongly disagree, 1; Disagree, 2; Neutral, 3; Agree, 4; Strongly agree, 5 |
| 禁止消费者食用野味 Ban on wildlife eating (BEAT) | 有序 Ordinal | 强烈不赞成: 1; 不倾向赞成: 2; 中立: 3; 倾向赞成: 4; 强烈赞成: 5 Strongly disagree, 1; Disagree, 2; Neutral, 3; Agree, 4; Strongly agree, 5 |
| 禁止野生动物及制品买卖 Ban on wildlife and wildlife product trade (BPDT) | 有序 Ordinal | 强烈不赞成: 1; 不倾向赞成: 2; 中立: 3; 倾向赞成: 4; 强烈赞成: 5 Strongly disagree, 1; Disagree, 2; Neutral, 3; Agree, 4; Strongly agree, 5 |
| 禁止在动物园之外展示野生动物活体展演 Ban commercial exhibition of wild animals outside zoos (BSHW) | 有序 Ordinal | 强烈不赞成: 1; 不倾向赞成: 2; 中立: 3; 倾向赞成: 4; 强烈赞成: 5 Strongly disagree, 1; Disagree, 2; Neutral, 3; Agree, 4; Strongly agree, 5 |
表1 调查问卷变量名称及定义
Table 1 Questionnaire variables and definations
| 变量 Variables | 类型 Type | 定义 Definition |
|---|---|---|
| 背景特征 Background | ||
| 性别 Gender (GND) | 分类 Categorical | 女: 1; 男: 0 Female, 1; Male, 0 |
| 省份 Province (PRV) | 分类 Categorical | 每个省生成一个虚拟变量 Provincial dummies |
| 城乡 Urbanization (URB) | 分类 Categorical | 城镇: 1; 农村: 0 Urban, 1; rural, 0 |
| 年龄 Age (AGE) | 分类 Categorical | 虚拟变量(1, 0): AGE1: 0-18岁; AGE2: 19-30岁; AGE3: 31-55岁; AGE4, 56岁以上 Dummies (1, 0): AGE1, 0-18 years old; AGE2, 19-30 years old; AGE3, 31-55 years old; AGE4, above 56 years old |
| 教育程度 Education level (EDU) | 分类 Categorical | 虚拟变量(1, 0): EDU1: 小学及以下; EDU2: 初高中; EDU3: 大学; EDU4: 研究生及以上 Dummies (1, 0): EDU1, Below primary school; EDU2, Middle or high school; EDU3, Graduate; EDU4, Post graduate |
| 月收入 Monthly income level (CNY) (INC) | 分类 Categorical | 虚拟变量(1, 0): INC1: 0-1,000元; INC2: 1,000-5,000元; INC3: 5,000-10,000元; INC4: 10,000- 30,000元; INC5: 大于30,000元 Dummies (1, 0): INC1, 0-1,000 CNY; INC2, 1,000-5,000 CNY; INC3, 5,000-10,000 CNY; INC4, 10,000- 30,000 CNY; INC5, above 30,000 CNY |
| 看到周围有人吃野味次数 See surrounding people eat wildlife (times) (EAT) | 分类 Categorical | 虚拟变量(1, 0): EAT1: 无; EAT2: 1-3次; EAT3: 3-10次; EAT4: 10次以上 Dummies (1, 0): EAT1, None; EAT2, 1-3 times; EAT3, 3-10 times; EAT4, above 10 times |
| 工作/兴趣是否自然保护相关 Engaged or interested in nature conservation (CSV) | 分类 Categorical | 是: 1; 否: 0 Yes, 1; No, 0 |
| 周围有人从事野生动物利用相关产业 Engaged either directly or indirectly in wildlife-related industries (IND) | 分类 Categorical | 有任意类型: 1; 无: 0 Any type, 1; None, 0 |
| 过去有消费野生动物行为 Consumed wildlife in the past (CSM) | 分类 Categorical | 有: 1; 无: 0 Yes, 1; No, 0 |
| 过去消费野生动物, 现在停止 Consumed wildlife in the past but tend to stop now (STOPCSM) | 分类 Categorical | 有: 1; 无: 0 Yes, 1; No, 0 |
| 过去有自然观察野生动物行为 Observed wildlife in the past (WAT) | 分类 Categorical | 有: 1; 无: 0 Yes, 1; No, 0 |
| 过去有自然观察, 现在停止 Observed wildlife in the past but stop now (STOPWAT) | 分类 Categorical | 有: 1; 无: 0 Yes, 1; No, 0 |
| 过去无自然观察, 现在开始 Never observe wildlife before but will start to observe wildlife now (MOREWAT) | 分类 Categorical | 有: 1; 无: 0 Yes, 1; No, 0 |
| 对相关法规了解情况 Knowledge about related laws (LAW) | 有序 Ordinal | 否: 1; 听说过一些: 2; 是: 3 No, 1; Some, 2; Yes, 3 |
| 对相关许可证了解情况 Knowledge about related certificates (CER) | 有序 Ordinal | 不了解: 1; 听过但不了解: 2; 了解: 3 No, 1; Have heard but don’t know much, 2; Know very well, 3 |
| 对立法动议的态度 Attitude towards legislation motion | ||
| 取缔野味集市和餐馆 Ban on wildlife markets and restaurants (BMKT) | 有序 Ordinal | 强烈不赞成: 1; 不倾向赞成: 2; 中立: 3; 倾向赞成: 4; 强烈赞成: 5 Strongly disagree, 1; Disagree, 2; Neutral, 3; Agree, 4; Strongly agree, 5 |
| 禁止消费者食用野味 Ban on wildlife eating (BEAT) | 有序 Ordinal | 强烈不赞成: 1; 不倾向赞成: 2; 中立: 3; 倾向赞成: 4; 强烈赞成: 5 Strongly disagree, 1; Disagree, 2; Neutral, 3; Agree, 4; Strongly agree, 5 |
| 禁止野生动物及制品买卖 Ban on wildlife and wildlife product trade (BPDT) | 有序 Ordinal | 强烈不赞成: 1; 不倾向赞成: 2; 中立: 3; 倾向赞成: 4; 强烈赞成: 5 Strongly disagree, 1; Disagree, 2; Neutral, 3; Agree, 4; Strongly agree, 5 |
| 禁止在动物园之外展示野生动物活体展演 Ban commercial exhibition of wild animals outside zoos (BSHW) | 有序 Ordinal | 强烈不赞成: 1; 不倾向赞成: 2; 中立: 3; 倾向赞成: 4; 强烈赞成: 5 Strongly disagree, 1; Disagree, 2; Neutral, 3; Agree, 4; Strongly agree, 5 |
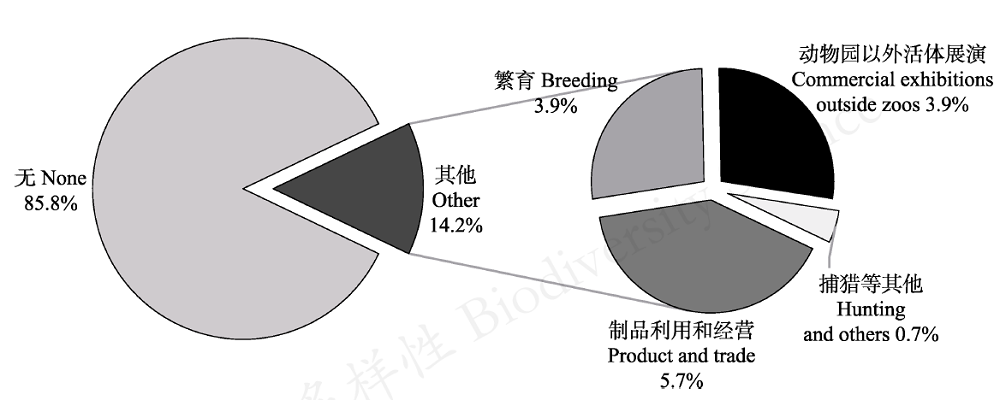
图3 调查样本中周围是否有人从事野生动物繁育利用相关产业的分布情况
Fig. 3 The percentage distribution of the people with other people around or themselves engaged in wildlife related industry in the survey sample
| 变量 Variables | 停止消费 Stop consumption | 停止观察 Stop observation | 增加观察 More observation | 变量 Variables | 停止消费 Stop consumption | 停止观察 Stop observation | 增加观察 More observation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IND | -1.175*** | (-9.54) | -0.100* | (-1.67) | 0.094* | (1.75) | EDU2 | 0.608** | (2.34) | 0.109 | (0.82) | 0.249** | (2.18) |
| CSV | -0.485*** | (-2.92) | -2.089*** | (-46.58) | 1.872*** | (46.85) | EDU3 | 1.078*** | (4.02) | -0.393*** | (-2.95) | 0.031 | (0.27) |
| WAT | -0.423*** | (-2.69) | - | - | EDU4 | 0.972*** | (3.31) | -0.629*** | (-4.43) | -0.217* | (-1.78) | ||
| CSM | - | 0.104* | (1.76) | 0.271*** | (4.83) | INC2 | 0.264 | (1.29) | 0.156** | (2.16) | 0.151** | (2.56) | |
| URB | 0.487*** | (2.83) | -0.641*** | (-10.45) | -0.274*** | (-5.31) | INC3 | 0.026 | (0.12) | -0.017 | (-0.21) | 0.097 | (1.54) |
| GND | 1.329*** | (7.98) | 0.355*** | (7.74) | -0.039 | (-1.00) | INC4 | -0.196 | (-0.82) | -0.208** | (-2.32) | -0.001 | (-0.01) |
| EAT2 | 0.408*** | (2.67) | -0.198*** | (-3.80) | 0.147*** | (3.30) | INC5 | -0.291 | (-1.06) | -0.111 | (-0.90) | 0.197* | (1.76) |
| EAT3 | 0.245 | (1.29) | -0.075 | (-0.94) | 0.101 | (1.34) | PRV | YES | YES | YES | |||
| EAT4 | -0.575*** | (-3.23) | 0.191* | (1.87) | 0.592*** | (6.21) | 截距 Constant | 1.573*** | (3.42) | 0.187 | (0.97) | -2.963*** | (-17.53) |
| AGE2 | -0.433 | (-1.39) | -0.086 | (-0.69) | 0.352*** | (3.16) | 样本量 Observations | 6,166 | 20,234 | 34,220 | |||
| AGE3 | 0.365 | (1.16) | 0.174 | (1.40) | 0.522*** | (4.69) | 准R2 Pseudo R2 | 0.182 | 0.217 | 0.151 | |||
| AGE4 | 1.103*** | (2.72) | 0.129 | (0.92) | 0.508*** | (4.15) | 似然比 Loglikelihood | -1,106 | -7,612 | -11,525 | |||
表2 对新冠肺炎后野生动物消费和观察行为变化的Logit模型估计结果
Table 2 The Logit model on the factors affecting wildlife consumption and observation behavior change after COVID-19
| 变量 Variables | 停止消费 Stop consumption | 停止观察 Stop observation | 增加观察 More observation | 变量 Variables | 停止消费 Stop consumption | 停止观察 Stop observation | 增加观察 More observation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IND | -1.175*** | (-9.54) | -0.100* | (-1.67) | 0.094* | (1.75) | EDU2 | 0.608** | (2.34) | 0.109 | (0.82) | 0.249** | (2.18) |
| CSV | -0.485*** | (-2.92) | -2.089*** | (-46.58) | 1.872*** | (46.85) | EDU3 | 1.078*** | (4.02) | -0.393*** | (-2.95) | 0.031 | (0.27) |
| WAT | -0.423*** | (-2.69) | - | - | EDU4 | 0.972*** | (3.31) | -0.629*** | (-4.43) | -0.217* | (-1.78) | ||
| CSM | - | 0.104* | (1.76) | 0.271*** | (4.83) | INC2 | 0.264 | (1.29) | 0.156** | (2.16) | 0.151** | (2.56) | |
| URB | 0.487*** | (2.83) | -0.641*** | (-10.45) | -0.274*** | (-5.31) | INC3 | 0.026 | (0.12) | -0.017 | (-0.21) | 0.097 | (1.54) |
| GND | 1.329*** | (7.98) | 0.355*** | (7.74) | -0.039 | (-1.00) | INC4 | -0.196 | (-0.82) | -0.208** | (-2.32) | -0.001 | (-0.01) |
| EAT2 | 0.408*** | (2.67) | -0.198*** | (-3.80) | 0.147*** | (3.30) | INC5 | -0.291 | (-1.06) | -0.111 | (-0.90) | 0.197* | (1.76) |
| EAT3 | 0.245 | (1.29) | -0.075 | (-0.94) | 0.101 | (1.34) | PRV | YES | YES | YES | |||
| EAT4 | -0.575*** | (-3.23) | 0.191* | (1.87) | 0.592*** | (6.21) | 截距 Constant | 1.573*** | (3.42) | 0.187 | (0.97) | -2.963*** | (-17.53) |
| AGE2 | -0.433 | (-1.39) | -0.086 | (-0.69) | 0.352*** | (3.16) | 样本量 Observations | 6,166 | 20,234 | 34,220 | |||
| AGE3 | 0.365 | (1.16) | 0.174 | (1.40) | 0.522*** | (4.69) | 准R2 Pseudo R2 | 0.182 | 0.217 | 0.151 | |||
| AGE4 | 1.103*** | (2.72) | 0.129 | (0.92) | 0.508*** | (4.15) | 似然比 Loglikelihood | -1,106 | -7,612 | -11,525 | |||
| 变量 Variables | 对相关法规了解情况 Knowledge about related laws | 对相关许可证了解情况 Knowledge about related certificates | 变量 Variables | 对相关法规了解情况 Knowledge about related laws | 对相关许可证了解情况 Knowledge about related certificates | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IND | 0.458*** | (10.11) | 0.642*** | (14.39) | EDU3 | 0.143* | (1.65) | 0.400*** | (4.85) |
| CSV | 0.416*** | (11.69) | 0.398*** | (11.33) | EDU4 | 0.033 | (0.36) | 0.487*** | (5.52) |
| WAT | 0.251*** | (6.91) | 0.366*** | (10.32) | INC2 | 0.169*** | (3.87) | 0.121*** | (2.76) |
| CSM | -0.058 | (-1.26) | 0.070 | (1.57) | INC3 | 0.171*** | (3.56) | 0.135*** | (2.85) |
| EAT2 | 0.193*** | (5.73) | 0.270*** | (8.13) | INC4 | 0.132** | (2.41) | 0.116** | (2.16) |
| EAT3 | 0.264*** | (4.32) | 0.430*** | (7.82) | INC5 | 0.064 | (0.78) | 0.167** | (2.15) |
| EAT4 | 0.507*** | (5.95) | 0.626*** | (7.87) | PRV | YES | YES | ||
| URB | 0.104*** | (3.42) | 0.209*** | (6.81) | 截距项1 Constant cut1 | -0.016 | (-0.13) | 0.223* | (1.95) |
| GND | -0.161*** | (-5.95) | -0.350*** | (-12.95) | 截距项2 Constant cut2 | 2.766*** | (22.19) | 2.973*** | (25.67) |
| AGE2 | -0.329*** | (-3.71) | -0.610*** | (-7.54) | 样本量 Observations | 54,315 | 54,310 | ||
| AGE3 | 0.058 | (0.66) | -0.545*** | (-6.73) | 准R2 Pseudo R2 | 0.0376 | 0.0518 | ||
| AGE4 | 0.483*** | (5.05) | -0.298*** | (-3.33) | 似然比 Loglikelihood | -52,011 | -49,248 | ||
| EDU2 | 0.206** | (2.36) | 0.246*** | (2.96) | |||||
表3 对野生动物利用相关法规和证照了解情况的排序Logit模型估计结果
Table 3 The ordered Logit model on the factors affecting knowledge about wildlife related laws and certificates
| 变量 Variables | 对相关法规了解情况 Knowledge about related laws | 对相关许可证了解情况 Knowledge about related certificates | 变量 Variables | 对相关法规了解情况 Knowledge about related laws | 对相关许可证了解情况 Knowledge about related certificates | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IND | 0.458*** | (10.11) | 0.642*** | (14.39) | EDU3 | 0.143* | (1.65) | 0.400*** | (4.85) |
| CSV | 0.416*** | (11.69) | 0.398*** | (11.33) | EDU4 | 0.033 | (0.36) | 0.487*** | (5.52) |
| WAT | 0.251*** | (6.91) | 0.366*** | (10.32) | INC2 | 0.169*** | (3.87) | 0.121*** | (2.76) |
| CSM | -0.058 | (-1.26) | 0.070 | (1.57) | INC3 | 0.171*** | (3.56) | 0.135*** | (2.85) |
| EAT2 | 0.193*** | (5.73) | 0.270*** | (8.13) | INC4 | 0.132** | (2.41) | 0.116** | (2.16) |
| EAT3 | 0.264*** | (4.32) | 0.430*** | (7.82) | INC5 | 0.064 | (0.78) | 0.167** | (2.15) |
| EAT4 | 0.507*** | (5.95) | 0.626*** | (7.87) | PRV | YES | YES | ||
| URB | 0.104*** | (3.42) | 0.209*** | (6.81) | 截距项1 Constant cut1 | -0.016 | (-0.13) | 0.223* | (1.95) |
| GND | -0.161*** | (-5.95) | -0.350*** | (-12.95) | 截距项2 Constant cut2 | 2.766*** | (22.19) | 2.973*** | (25.67) |
| AGE2 | -0.329*** | (-3.71) | -0.610*** | (-7.54) | 样本量 Observations | 54,315 | 54,310 | ||
| AGE3 | 0.058 | (0.66) | -0.545*** | (-6.73) | 准R2 Pseudo R2 | 0.0376 | 0.0518 | ||
| AGE4 | 0.483*** | (5.05) | -0.298*** | (-3.33) | 似然比 Loglikelihood | -52,011 | -49,248 | ||
| EDU2 | 0.206** | (2.36) | 0.246*** | (2.96) | |||||
| 变量 Variables | 取缔野味集市和餐馆 Ban on wildlife meat markets and restaurants | 禁止消费者食用野味 Ban on wildlife eating on consumers | 禁止野生动物及制品买卖 Ban on wildlife and wildlife product trade | 禁止动物园之外展示野生动物活体 Ban commercial exhibition of wild animals outside zoos | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IND | -0.239*** | (-4.20) | -0.338*** | (-5.74) | -0.464*** | (-8.41) | -0.379*** | (-7.67) |
| CSV | -0.123** | (-2.25) | -0.130** | (-2.19) | -0.139** | (-2.55) | -0.079* | (-1.65) |
| WAT | 0.072 | (1.37) | -0.038 | (-0.66) | -0.131** | (-2.52) | -0.121*** | (-2.63) |
| CSM | -0.598*** | (-11.03) | -0.653*** | (-11.62) | -0.631*** | (-11.83) | -0.389*** | (-7.89) |
| EAT2 | 0.099** | (1.96) | 0.078 | (1.51) | 0.040 | (0.83) | 0.048 | (1.11) |
| EAT3 | 0.231*** | (2.98) | 0.130* | (1.65) | 0.154** | (2.08) | 0.164** | (2.44) |
| EAT4 | 0.339*** | (3.38) | 0.331*** | (3.08) | 0.514*** | (4.67) | 0.263*** | (2.86) |
| URB | 0.417*** | (9.95) | 0.240*** | (5.20) | 0.014 | (0.31) | 0.192*** | (4.95) |
| GND | 0.393*** | (8.49) | 0.762*** | (15.76) | 0.724*** | (16.47) | 0.592*** | (15.55) |
| AGE2 | 0.394*** | (4.05) | 0.169 | (1.58) | 0.260*** | (2.63) | 0.292*** | (3.33) |
| AGE3 | 0.680*** | (6.85) | 0.533*** | (4.88) | 0.729*** | (7.18) | 0.552*** | (6.20) |
| AGE4 | 0.799*** | (6.46) | 0.608*** | (4.55) | 0.855*** | (6.84) | 0.359*** | (3.44) |
| EDU2 | 0.110 | (1.04) | 0.206* | (1.77) | 0.070 | (0.58) | 0.023 | (0.24) |
| EDU3 | 0.439*** | (4.15) | 0.415*** | (3.58) | 0.284** | (2.37) | 0.343*** | (3.47) |
| EDU4 | 0.541*** | (4.70) | 0.416*** | (3.39) | 0.244* | (1.96) | 0.381*** | (3.61) |
| INC2 | 0.017 | (0.28) | 0.154** | (2.33) | 0.147** | (2.30) | 0.032 | (0.57) |
| INC3 | 0.245*** | (3.54) | 0.299*** | (4.12) | 0.214*** | (3.13) | 0.083 | (1.37) |
| INC4 | 0.111 | (1.39) | 0.123 | (1.50) | 0.083 | (1.08) | -0.034 | (-0.50) |
| INC5 | 0.078 | (0.67) | 0.050 | (0.43) | 0.040 | (0.38) | -0.125 | (-1.27) |
| PRV | YES | YES | YES | YES | ||||
| 截距1 Constant cut1 | -2.198*** | (-13.92) | -3.121*** | (-17.94) | -3.111*** | (-19.01) | -2.541*** | (-18.04) |
| 截距2 Constant cut2 | -1.827*** | (-11.59) | -2.658*** | (-15.54) | -2.599*** | (-16.09) | -2.056*** | (-14.71) |
| 截距3 Constant cut3 | -1.451*** | (-9.22) | -2.002*** | (-11.90) | -1.896*** | (-11.95) | -1.397*** | (-10.04) |
| 截距4 Constant cut4 | -0.741*** | (-4.73) | -1.061*** | (-6.38) | -0.914*** | (-5.83) | -0.706*** | (-5.10) |
| 样本量 Observations | 54,454 | 54,454 | 54,449 | 54,453 | ||||
| 准R2 Pseudo R2 | 0.0365 | 0.0413 | 0.0399 | 0.0267 | ||||
| 似然比 Loglikelihood | -33,619 | -29,045 | -31,312 | -40,879 | ||||
表4 对立法动议态度影响因素的排序Logit模型估计结果
Table 4 The ordered Logit model on the factors affect perception on 4 legislation motions
| 变量 Variables | 取缔野味集市和餐馆 Ban on wildlife meat markets and restaurants | 禁止消费者食用野味 Ban on wildlife eating on consumers | 禁止野生动物及制品买卖 Ban on wildlife and wildlife product trade | 禁止动物园之外展示野生动物活体 Ban commercial exhibition of wild animals outside zoos | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IND | -0.239*** | (-4.20) | -0.338*** | (-5.74) | -0.464*** | (-8.41) | -0.379*** | (-7.67) |
| CSV | -0.123** | (-2.25) | -0.130** | (-2.19) | -0.139** | (-2.55) | -0.079* | (-1.65) |
| WAT | 0.072 | (1.37) | -0.038 | (-0.66) | -0.131** | (-2.52) | -0.121*** | (-2.63) |
| CSM | -0.598*** | (-11.03) | -0.653*** | (-11.62) | -0.631*** | (-11.83) | -0.389*** | (-7.89) |
| EAT2 | 0.099** | (1.96) | 0.078 | (1.51) | 0.040 | (0.83) | 0.048 | (1.11) |
| EAT3 | 0.231*** | (2.98) | 0.130* | (1.65) | 0.154** | (2.08) | 0.164** | (2.44) |
| EAT4 | 0.339*** | (3.38) | 0.331*** | (3.08) | 0.514*** | (4.67) | 0.263*** | (2.86) |
| URB | 0.417*** | (9.95) | 0.240*** | (5.20) | 0.014 | (0.31) | 0.192*** | (4.95) |
| GND | 0.393*** | (8.49) | 0.762*** | (15.76) | 0.724*** | (16.47) | 0.592*** | (15.55) |
| AGE2 | 0.394*** | (4.05) | 0.169 | (1.58) | 0.260*** | (2.63) | 0.292*** | (3.33) |
| AGE3 | 0.680*** | (6.85) | 0.533*** | (4.88) | 0.729*** | (7.18) | 0.552*** | (6.20) |
| AGE4 | 0.799*** | (6.46) | 0.608*** | (4.55) | 0.855*** | (6.84) | 0.359*** | (3.44) |
| EDU2 | 0.110 | (1.04) | 0.206* | (1.77) | 0.070 | (0.58) | 0.023 | (0.24) |
| EDU3 | 0.439*** | (4.15) | 0.415*** | (3.58) | 0.284** | (2.37) | 0.343*** | (3.47) |
| EDU4 | 0.541*** | (4.70) | 0.416*** | (3.39) | 0.244* | (1.96) | 0.381*** | (3.61) |
| INC2 | 0.017 | (0.28) | 0.154** | (2.33) | 0.147** | (2.30) | 0.032 | (0.57) |
| INC3 | 0.245*** | (3.54) | 0.299*** | (4.12) | 0.214*** | (3.13) | 0.083 | (1.37) |
| INC4 | 0.111 | (1.39) | 0.123 | (1.50) | 0.083 | (1.08) | -0.034 | (-0.50) |
| INC5 | 0.078 | (0.67) | 0.050 | (0.43) | 0.040 | (0.38) | -0.125 | (-1.27) |
| PRV | YES | YES | YES | YES | ||||
| 截距1 Constant cut1 | -2.198*** | (-13.92) | -3.121*** | (-17.94) | -3.111*** | (-19.01) | -2.541*** | (-18.04) |
| 截距2 Constant cut2 | -1.827*** | (-11.59) | -2.658*** | (-15.54) | -2.599*** | (-16.09) | -2.056*** | (-14.71) |
| 截距3 Constant cut3 | -1.451*** | (-9.22) | -2.002*** | (-11.90) | -1.896*** | (-11.95) | -1.397*** | (-10.04) |
| 截距4 Constant cut4 | -0.741*** | (-4.73) | -1.061*** | (-6.38) | -0.914*** | (-5.83) | -0.706*** | (-5.10) |
| 样本量 Observations | 54,454 | 54,454 | 54,449 | 54,453 | ||||
| 准R2 Pseudo R2 | 0.0365 | 0.0413 | 0.0399 | 0.0267 | ||||
| 似然比 Loglikelihood | -33,619 | -29,045 | -31,312 | -40,879 | ||||
| [1] | Cronbach LJ (1951) Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika, 16, 297-334. |
| [2] |
Cronbach LJ, Shavelson RJ (2004) My current thoughts on coefficient alpha and successor procedures. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 64, 391-418.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Hufnagel L, Brockmann D, Geisel T (2004) Forecast and control of epidemics in a globalized world. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 101, 15124-15129. |
| [4] |
Ji W, Wang W, Zhao X, Zai J, Li X (2020) Cross‐species transmission of the newly identified coronavirus 2019‐nCoV. Journal of Medical Virology, 92, 433-440.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
Jones KE, Patel NG, Levy MA, Storeygard A, Balk D, Gittleman JL, Daszak P (2008) Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature, 451, 990-993.
URL PMID |
| [6] |
Karesh WB, Cook RA, Bennett EL, Newcomb J (2005) Wildlife trade and global disease emergence. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 11, 1000.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] | Karesh WB, Cook RA, Gilbert M, Newcomb J (2007) Implications of wildlife trade on the movement of avian influenza and other infectious diseases. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 43(Suppl. 3), S55. |
| [8] |
Lam TT, Shum MH, Zhu HC, Tong YG, Ni XB, Liao YS, Wei W, Cheung WY, Li WJ, Li LF, Leung GM (2020) Identifying SARS-CoV-2 related coronaviruses in Malayan pangolins. Nature, 583, 282-285.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] |
Liu Z, Xiao X, Wei X, Li J, Yang J, Tan H, Zhu J, Zhang Q, Wu J, Liu L (2020) Composition and divergence of coronavirus spike proteins and host ACE2 receptors predict potential intermediate hosts of SARS‐CoV‐2. Journal of Medical Virology, 92, 595-601.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] |
Marta-Pedroso C, Freitas H, Domingos T (2007) Testing for the survey mode effect on contingent valuation data quality: A case study of web based versus in-person interviews. Ecological Economics, 62, 388-398.
DOI URL |
| [11] | National Statistic Administration (2011) 2010 China’s Sixth National Population Census data report (No.1). China Journal of Family Planning, 19(8), 65-66. (in Chinese ) |
| [ 中华人民共和国国家统计局 (2011) 2010年第六次全国人口普查主要数据公报(第1号). 中国计划生育学杂志, 19(8), 65-66.] | |
| [12] | Qin C (2008) The animals and emerging infectious diseases. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 28(3), 133-137. (in Chinese with English abstract ) |
| [ 秦川 (2008) 动物与新发传染病. 实验动物与比较医学, 28(3), 133-137.] | |
| [13] |
Swift L, Hunter PR, Lees AC, Bell DJ (2007) Wildlife trade and the emergence of infectious diseases. EcoHealth, 4, 25.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Wang LS, Wang YR, Ye DW, Liu QQ (2020) A review of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) based on current evidence. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 55, 105948.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] |
White PC, Jennings NV, Renwick AR, Barker NH (2005) Questionnaires in ecology: A review of past use and recommendations for best practice. Journal of Applied Ecology, 42, 421-430.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Zeng Y, Ping XG, Wei FW (2020) A conceptual framework and definitions for the term “wild animal”. Biodiversity Science, 28, 541-549. (in Chinese with English abstract ) |
| [ 曾岩, 平晓鸽, 魏辅文 (2020) “野生动物”的概念框架和术语定义. 生物多样性, 28, 541-549.] | |
| [17] | Zeng Y, Vaupel JW, Xiao Z, Zhang C, Liu Y (2001) The healthy longevity survey and the active life expectancy of the oldest old in China. Population: An English Selection, 13(1), 95-116. |
| [18] | Zhang JS, Liang B, Zhang SY (2003) Zoonosis based on wildlife and human: Elementary introduction. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 38(4), 123-127. (in Chinese with English abstract ) |
| [ 张劲硕, 梁冰, 张树义 (2003) 浅议野生动物与人类共患疾病. 动物学杂志, 38(4), 123-127.] | |
| [19] | Zhang T, Wu Q, Zhang Z (2020) Probable pangolin origin of SARS-CoV-2 associated with the COVID-19 outbreak. Current Biology, 30, 1078. |
| [20] |
Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, Si HR, Zhu Y, Li B, Huang CL, Chen HD (2020) A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature, 579, 270-273.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] | Zhou ZH, Jiang ZG (2004) Definition and extension of the concepts “wildlife”, “wild fauna and flora” and “wild origin”. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 302-307. (in Chinese with English abstract ) |
| [ 周志华, 蒋志刚 (2004) 野生生物, 野生动植物和野生来源的定义及范畴. 生态学报, 24, 302-307.] |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 周志华, 金效华. 中国野生植物保护管理的政策、法律制度分析和建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1583-1590. |
| [3] | 吕植, 顾垒, 闻丞, 王昊, 钟嘉. 中国自然观察2014: 一份关于中国生物多样性保护的独立报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(5): 570-574. |
| [4] | 樊祥国, 周宇晶, 刘宝祥, 冯庚菲, 樊恩源. 《濒危野生动植物种国际贸易公约》中有关水生生物物种的提案和对策研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2008, 16(5): 516-524. |
| [5] | 李义明. 野生动物狩猎、贸易和狩猎持续性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2001, 09(4): 414-421. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()