



Biodiv Sci ›› 2014, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (4): 449-457. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.14101 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2014.14101
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ting Wang1, Siyuan Ren1, Zhiliang Yuan2, Yan Zhu3, Na Pan1, Luxin Li1, Yongzhong Ye2,*( )
)
Received:2014-05-26
Accepted:2014-07-16
Online:2014-07-20
Published:2014-07-24
Contact:
Ye Yongzhong
Ting Wang, Siyuan Ren, Zhiliang Yuan, Yan Zhu, Na Pan, Luxin Li, Yongzhong Ye. Effects of density dependence on the spatial patterns of Quercus aliena var. acuteserrata trees in deciduous broad-leaved forest in the Baotianman Nature Reserve, central China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(4): 449-457.
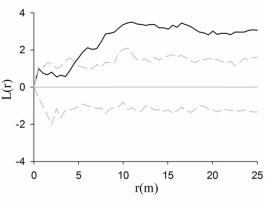
Fig. 1 Spatial patterns of Quercus aliena var. acuteserrata deadwoods in the 1-ha plot in the Baotianman National Nature Reserve. The solid black line represents the point pattern of the dead trees, the confidence interval is showed by the region between the two dashed gray lines.
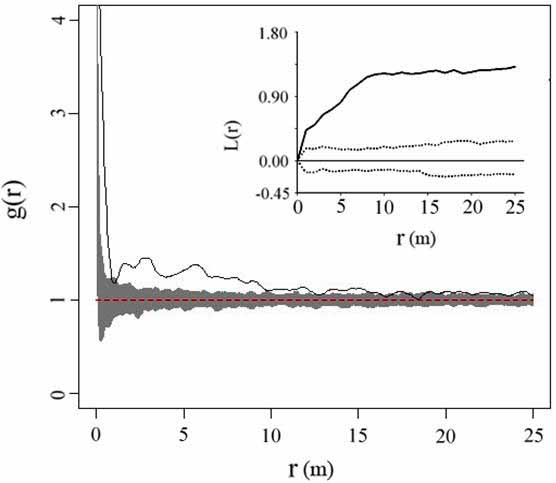
Fig. 2 Spatial patterns of living Q. aliena var. acuteserrata trees in the 1-ha plot in Baotianman Nature Reserve. It presents the double correlation functions g(r) and L(r) functions pattern analysis with complete spatial randomness model. The solid black line represents the point pattern of the living trees, the confidence interval is shown by the gray part and the region between the two dashed lines.
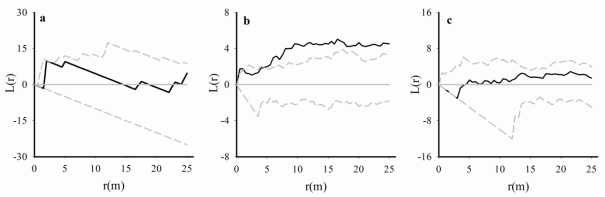
Fig. 3 Point pattern analysis of Q. aliena var. acuteserrata deadwoods at different growth stages in the 1-ha plot in the Baotianman National Nature Reserve. The solid black line represents the point pattern of the dead trees, the confidence interval is shown by the region between the dotted lines. A, Saplings (1 cm ≤ DBH < 10 cm); B, Juveniles (10 cm ≤ DBH <20 cm); C, Adult trees (DBH ≥20 cm).
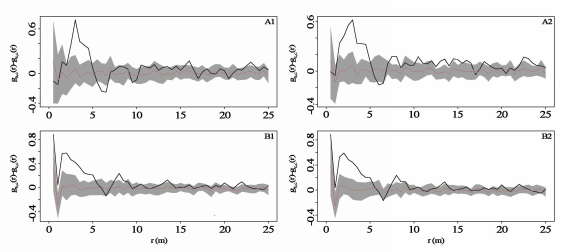
Fig. 4 Examples for density dependent effect within a case-control design in the 1-ha plot in the Baotianman National Nature Reserve. The pattern of adult trees serves as “control”, which corrects for possible heterogeneity in habitat quality, the pattern of smaller size classes serves as “cases”. A, Saplings (1 cm ≤ DBH <10 cm); B, Juveniles (10 cm ≤ DBH < 20 cm); C, Adult trees (DBH ≥ 20 cm). A1 and B1 represent the negative density dependence analysis of pre-mortality saplings and juveniles; A2 and B2 show the negative density dependence analysis of post-mortality saplings and juveniles, respectively.
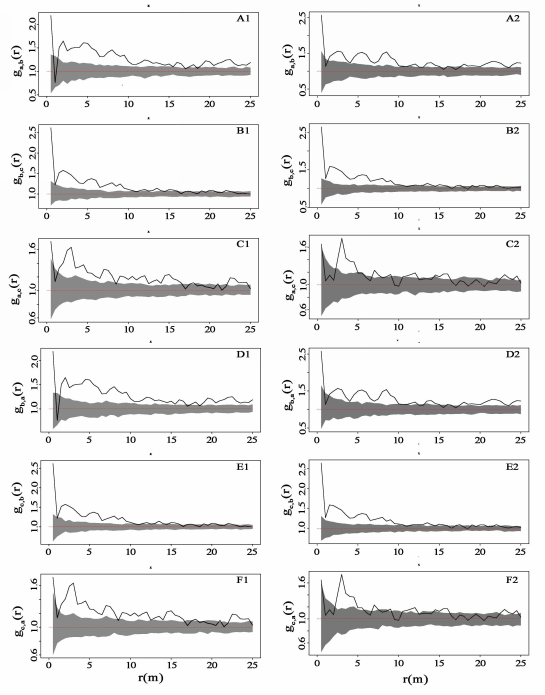
Fig. 5 Comparative analysis of the correlation of pre-mortality and post-mortality of Quercus aliena var. acuteserrata trees at different growth stages by using double correlation functions g12 (r) and random labeling null model. A1to F1 for pre-mortality trees, A2 to F2 for post-mortality trees. a, Saplings (1 cm ≤ DBH <10 cm); b, Juveniles (10 cm ≤ DBH <20 cm); c, Adult trees (DBH ≥20 cm). It shows the 99% confidence interval (grey section) after 999 times circles with Monte Carlo simulation.
| [1] | Franklin JF, Shugart HH, Harmon ME (1987) Tree death as an ecological process.BioScience, 37, 550-556. |
| [2] | Barot S, Gignoux J, Menaut JC (1999) Demography of a savanna palm tree: predictions from comprehensive spatial pattern analyses.Ecology, 80, 1987-2005. |
| [3] | Besag J (1977) Contribution to the discussion of Dr. Ripley’s paper.Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, B39,193-195. |
| [4] | Bravo-Oviedo A, Sterba H, del Río M, Bravo F (2006) Competition-induced mortality for mediterranean Pinus pinaster Ait and P. sylvestris L.Forest Ecology and Management, 222, 88-98. |
| [5] | Bugmann H (2001) A review of forest gap models.Climatic Change, 51, 259-305. |
| [6] | Comita LS, Hubbell SP (2009) Local neighborhood and species’ shade tolerance influence survival in a diverse seedling bank. Ecology, 90, 328-334. |
| [7] | Condit R, Ashton PS, Baker P, Bunyavejchewin S, Gunatilleke S, Gunatilleke N, Hubbell SP, Foster RB, Itoh A, LaFrankie J V, Lee HS, Losos E, Manokaran N, Sukumar R, Yamakura T (2000) Spatial patterns in the distribution of tropical tree species.Science, 288, 1414-1418. |
| [8] | Condit R (1995) Research in large long-term tropical forest plots.Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 18-22. |
| [9] | Das A, Battles J, van Mantgem PJ, Stephenson NL (2008) Spatial elements of mortality risk in old-growth forests. Ecology, 89, 1744-1756. |
| [10] | Diggle PJ, Chetwynd AG (1991) Second order analysis of spatial clustering for inhomogeneous populations.Biometrics, 47, 1155-1163. |
| [11] | Gatrell AC, Bailey TC, Diggle PJ (1996) Spatial point pattern analysis and its application in geographical epidemiology.Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers, 21, 256-274. |
| [12] | Getzin S, Dean C, He FL, Trofymow J, Wiegand K, Wiegand T (2006) Spatial patterns and competition of tree species in a Douglas fir chronosequence on Vancouver Island.Ecography, 29, 671-682. |
| [13] | Greig-Smith P (1983) Quantitative Plant Ecology, 3rd edn. Blackwell, Oxford. |
| [14] | Hardy OJ, Sonké B (2004) Spatial pattern analysis of tree species distribution in a tropical rain forest of Cameroon: assessing the role of limited dispersal and niche differentiation.Forest Ecology and Management, 197, 191-202. |
| [15] | He FL, Duncan RP (2000) Density dependent effects on tree survival in an old growth Douglas fir forest. Journal of Ecology, 88, 676-688. |
| [16] | HilleRisLambers J, Clark JS, Beckage B (2002) Density dependent mortality and the latitudinal gradient in species diversity. Nature, 417, 732-735. |
| [17] | Howe HF, Schupp EW, Westley LC (1985) Early consequences of seed dispersal for a neotropical tree (Virola surinamensis).Ecology, 66, 781-791. |
| [18] | Hubbell SP, Ahumada JA, Condit R, Foster RB (2001) Local neighborhood effects on long-term survival of individual trees in a Neotropical forest.Ecological Research, 16, 859-875. |
| [19] | Hubbell SP (2004) Two decades of research on the BCI forest dynamics plot. In: Tropical Forest Diversity and Dynamism: Findings from a Large-Scale Plot Network, pp. 8-30. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [20] | Hyatt LA, Rosenberg MS, Howard TG, Bole G, Fang W, Anastasia J, Gurevitch J (2003) The distance dependence prediction of the Janzen-Connell hypothesis: a meta-analysis.Oikos, 103, 590-602. |
| [21] | Illian J, Penttinen A, Stoyan H, Stoyan D (2008) Statistical Analysis and Modelling of Spatial Point Patterns. Scitech Book News. |
| [22] | Monserud RA, Thomas L, Hubert S (2004) Are self-thinning constraints needed in a tree-specific mortality model? Forest Science, 50, 848-858. |
| [23] | Moravie MA, Robert A (2003) A model to assess relationships between forest dynamics and spatial structure.Journal of Vegetation Science, 14, 823-834. |
| [24] | Murrell D, Purves D, Law R (2002) Intraspecific aggregation and species coexistence.Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 17, 211-212. |
| [25] | Oliver CD, Larson BC (1990) Forest Stand Dynamics. McGrawHill, New York. |
| [26] | Pacala SW, Canham CD, Saponara J, Silander JA, Kobe RK, Ribbens E (1996) Forest models defined by field measurements: estimation, error analysis and dynamics.Ecological Monographs, 66, 1-43. |
| [27] | Packer A, Clay K (2000) Soil pathogens and spatial patterns of seedling mortality in a temperate tree.Nature, 404, 278-281. |
| [28] | Ratikainen II, Gill JA, Gunnarsson TG, Sutherland WJ, Kokko H (2008) When density dependence is not instantaneous: theoretical developments and management implications.Ecology Letters, 11, 184-198. |
| [29] | Ripley BD (1976) The second-order analysis of stationary point processes.Journal of Applied Probability, 13, 255-266. |
| [30] | Song CS (宋朝枢) (1999) Scientific Investigation in the Baotianman Nature Reserve (宝天曼自然保护区科学考察集). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [31] | Sterner RW, Ribic CA, Schatz GE (1986) Testing for life historical changes in spatial patterns of four tropical tree species.Journal of Ecology, 74, 621-633. |
| [32] | Temesgen H, Mitchell SJ (2005) An individual-tree mortality model for complex stands of southeastern British Columbia.Western Journal of Applied Forestry, 20, 101-109. |
| [33] | Waring RH (1987) Characteristics of trees predisposed to die. BioScience, 37, 569-574. |
| [34] | Wiegand TA, Moloney K (2004) Rings circles and null models for point pattern analysis in ecology.Oikos, 104, 209-229. |
| [35] | Wright SJ (2002) Plant diversity in tropical forests: a review of mechanisms of species coexistence.Oecologia, 130, 1-14. |
| [36] | Yoda K, Kira T, Ogawa H, Hozumi K (1963) Self-thinning in overcrowded pure stands under cultivated and natural conditions.Journal of Biology, Osaka City University, 14, 107-129. |
| [37] | Lu XL (卢训令), Hu N (胡楠), Ding SY (丁圣彦), Liao BH (廖秉华), Fang HP (房会普) (2010) Study on photosynthetic ecophysiological characteristics of Quercus aliena var. acuteserrata in the Funiu Mountain Nature Reserve. Journal of Henan University (Natural Science) (河南大学学报(自然科学版)), 40, 617-621. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [38] | Zhang JY (张俊艳), Cheng KW (成克武), Zang RG (臧润国) (2014) The spatial distribution patterns and associations of the principal trees and shrubs in a natural tropical coniferous forest on Hainan Island, China.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 22,129-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [39] | Zhu Y (祝燕) (2009) The Prevalence of Density Dependence in Gutianshan Subtropical Evergreen Broadleaved Forest, China (古田山亚热带常绿阔叶林密度制约普遍性研究). PhD dissertation, Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | Li Yanpeng, Chen Jie, Lu Chunyang, Xu Han. Community characteristics of a 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [2] | Xuemeng Li, Jibao Jiang, Zenglu Zhang, Xiaojing Liu, Yali Wang, Yizhao Wu, Yinsheng Li, Jiangping Qiu, Qi Zhao. Earthworm biodiversity and its influencing factors in Baotianman National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23352-. |
| [3] | Di Lin, Shuanglin Chen, Que Du, Wenlong Song, Gu Rao, Shuzhen Yan. Investigation of species diversity of myxomycetes in Dabie Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23242-. |
| [4] | Jingci Meng, Guodong Wang, Guanglan Cao, Nanlin Hu, Meiling Zhao, Yantong Zhao, Zhenshan Xue, Bo Liu, Wenhua Piao, Ming Jiang. Patterns and drivers of plant species richness in Phragmites australis marshes in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23194-. |
| [5] | Zhichao Xu, Meihui Zhu, Zikun Mao, Xugao Wang. Effects of nitrogen addition on seedling dynamics in a broad-leaved Korean pine forest in Northeast China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24255-. |
| [6] | Liyuan Wang, Huijian Hu, Jie Jiang, Yiming Hu. Species richness patterns of mammals and birds and their drivers in the Nanling Mountain Range [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23026-. |
| [7] | Zhifa Liu, Xincai Wang, Yuening Gong, Daojian Chen, Qiang Zhang. Diversity and elevational distribution of birds and mammals based on infrared camera monitoring in Guangdong Nanling National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 22689-. |
| [8] | Junyi Yang, Xiao Guan, Junsheng Li, Jingjing Liu, Haojing Hao, Huairui Wang. Spatial patterns and interrelationships between biodiversity and ecosystem services in the Wujiang River Basin [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 23061-. |
| [9] | Shengxian Yang, Qing Yang, Xiaodong Li, Xin Chao, Huiqiu Liu, Lanruoxue Wei, Sang Ba. Deterministic processes dominate the geographic distribution pattern and community assembly of phytoplankton in typical plateau rivers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 23092-. |
| [10] | Bingyang Ding, Xiaofeng Jin, Yonghua Zhang, Genyou Li, Zhenghai Chen, Fanggang Zhang. Distribution pattern and floristic regionalization of wild seed plants in Zhejiang Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22515-. |
| [11] | Xiang Liu, Mu Liu, Yao Xiao. The effect of foliar fungal pathogens on plant species coexistence: Progress and challenges [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22525-. |
| [12] | Honghu Meng, Yigang Song. Biogeographic patterns in Southeast Asia: Retrospectives and perspectives [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23261-. |
| [13] | Ruihe Gao, Shiming Fan, Jianghai Dong, Rongjiao Li, Zhiwei Zhang. Characteristics and vertical distribution of insect functional groups along an altitude gradient in Guandi Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(10): 23152-. |
| [14] | Gaohui Liu, Jianguo Cui, Yue Wang, Hongliang Wang, Bao Xiang, Nengwen Xiao. Amphibian diversity and its spatio-temporal distribution patterns in Kangding City, Sichuan Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(6): 21494-. |
| [15] | Yating Wang, Dinghai Zhang, Zhishan Zhang. Spatial distribution and interspecific correlation of Haloxylon persicum and H. ammodendron on fixed dunes of the Gurbantunggut Desert, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(3): 21280-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()