



Biodiv Sci ›› 2014, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (4): 458-466. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13232 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2014.13232
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2013-10-28
Accepted:2014-02-26
Online:2014-07-20
Published:2014-07-24
Contact:
Zhuang Ping
Ping Zhuang. Analysis of the flowering-leafing phenorhythm of 42 Rhododendron species conserved ex situ in Dujiangyan, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(4): 458-466.
| 地理区系 Geographic flora | 观察种数 No. of species | F→L | F+L | L∈F | L+F | L→F | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||||||
| 中国-日本亚区 Sino-Japan subregion | 18 | 10 | 55.6 | 2 | 11.1 | 3 | 16.7 | 3 | 16.7 | - | - | ||||
| 常绿杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Hymenanthes | 11 | 7 | 63.6 | 2 | 18.2 | 2 | 18.2 | 1 | 9.1 | - | - | ||||
| 杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Rhododendron | 5 | 3 | 60.0 | - | - | 1 | 20.0 | 1 | 20.0 | - | - | ||||
| 中国-喜玛拉雅亚区 Sino-Himalaya subregion | 12 | 1 | 8.3 | 4 | 33.3 | 2 | 16.7 | 3 | 25.0 | 2 | 16.7 | ||||
| 常绿杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Hymenanthes | 4 | - | - | 2 | 50.0 | 1 | 25.0 | - | - | 1 | 25.0 | ||||
| 杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Rhododendron | 8 | 1 | 12.5 | 2 | 25.0 | 1 | 12.5 | 3 | 37.5 | 1 | 12.5 | ||||
| 两亚区共有 Common species between the two subregions | 12 | 4 | 33.3 | 1 | 8.3 | 3 | 25.0 | 2 | 16.7 | 2 | 16.7 | ||||
| 常绿杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Hymenanthes | 5 | 2 | 40.0 | - | - | 2 | 40.0 | 1 | 20.0 | - | - | ||||
| 杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Rhododendron | 6 | 2 | 33.3 | 1 | 16.7 | 1 | 16.7 | 1 | 16.7 | 1 | 16.7 | ||||
Table 1 Relationship between flowering-leafing phenorhythm type and the area-type of 42 Rhododendron species
| 地理区系 Geographic flora | 观察种数 No. of species | F→L | F+L | L∈F | L+F | L→F | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||||||
| 中国-日本亚区 Sino-Japan subregion | 18 | 10 | 55.6 | 2 | 11.1 | 3 | 16.7 | 3 | 16.7 | - | - | ||||
| 常绿杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Hymenanthes | 11 | 7 | 63.6 | 2 | 18.2 | 2 | 18.2 | 1 | 9.1 | - | - | ||||
| 杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Rhododendron | 5 | 3 | 60.0 | - | - | 1 | 20.0 | 1 | 20.0 | - | - | ||||
| 中国-喜玛拉雅亚区 Sino-Himalaya subregion | 12 | 1 | 8.3 | 4 | 33.3 | 2 | 16.7 | 3 | 25.0 | 2 | 16.7 | ||||
| 常绿杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Hymenanthes | 4 | - | - | 2 | 50.0 | 1 | 25.0 | - | - | 1 | 25.0 | ||||
| 杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Rhododendron | 8 | 1 | 12.5 | 2 | 25.0 | 1 | 12.5 | 3 | 37.5 | 1 | 12.5 | ||||
| 两亚区共有 Common species between the two subregions | 12 | 4 | 33.3 | 1 | 8.3 | 3 | 25.0 | 2 | 16.7 | 2 | 16.7 | ||||
| 常绿杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Hymenanthes | 5 | 2 | 40.0 | - | - | 2 | 40.0 | 1 | 20.0 | - | - | ||||
| 杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Rhododendron | 6 | 2 | 33.3 | 1 | 16.7 | 1 | 16.7 | 1 | 16.7 | 1 | 16.7 | ||||
| 矫正海拔区间(m) Rectified elevation range | 观察种数 No. of species | F→L | F+L | L∈F | L+F | L→F | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||||||
| <1,500 | 5 | 2 | 40.0 | - | - | 1 | 20.0 | 1 | 20.0 | 1 | 20.0 | ||||
| 1,500-2,000 | 8 | 4 | 50.0 | 1 | 12.5 | 2 | 25.0 | 1 | 12.5 | - | - | ||||
| 2,000-2,500 | 12 | 6 | 50.0 | 2 | 16.7 | 1 | 8.3 | 2 | 16.7 | 1 | 8.3 | ||||
| 2,500-3,000 | 12 | 3 | 25.0 | 3 | 25.0 | 2 | 16.7 | 3 | 25.0 | 1 | 8.3 | ||||
| >3,000 | 5 | - | - | 1 | 20.0 | 2 | 40.0 | 1 | 20.0 | 1 | 20.0 | ||||
Table 2 Relationship between the flowering-leafing phenorhythm type and the elevation range of 42 Rhododendron species
| 矫正海拔区间(m) Rectified elevation range | 观察种数 No. of species | F→L | F+L | L∈F | L+F | L→F | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||||||
| <1,500 | 5 | 2 | 40.0 | - | - | 1 | 20.0 | 1 | 20.0 | 1 | 20.0 | ||||
| 1,500-2,000 | 8 | 4 | 50.0 | 1 | 12.5 | 2 | 25.0 | 1 | 12.5 | - | - | ||||
| 2,000-2,500 | 12 | 6 | 50.0 | 2 | 16.7 | 1 | 8.3 | 2 | 16.7 | 1 | 8.3 | ||||
| 2,500-3,000 | 12 | 3 | 25.0 | 3 | 25.0 | 2 | 16.7 | 3 | 25.0 | 1 | 8.3 | ||||
| >3,000 | 5 | - | - | 1 | 20.0 | 2 | 40.0 | 1 | 20.0 | 1 | 20.0 | ||||
| 类群 Group | 观察种数 No. of species | F→L | F+L | L∈F | L+F | L→F | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||||||
| 常绿杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Hymenanthes | 21 | 9 | 42.9 | 4 | 19.1 | 5 | 23.8 | 2 | 9.5 | 1 | 4.8 | ||||
| 云锦杜鹃亚组 Subsect. Fortunea | 6 | 4 | 66.7 | - | - | 1 | 17.5 | 1 | 17.5 | - | - | ||||
| 银叶杜鹃亚组 Subsect. Argyrophylla | 5 | 3 | 60.0 | 2 | 40.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
| 麻花杜鹃亚组 Subsect. Maculifera | 3 | 1 | 33.3 | - | - | 1 | 33.3 | 1 | 33.3 | ||||||
| 杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Rhododendron | 18 | 6 | 33.3 | 3 | 16.7 | 3 | 16.7 | 5 | 27.8 | 1 | 5.6 | ||||
| 三花杜鹃亚组 Subsect. Triflora | 13 | 2 | 15.4 | 3 | 23.1 | 2 | 15.4 | 5 | 38.6 | 1 | 7.7 | ||||
| 映山红亚属 Subgen. Tsutsusi | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 50.0 | 1 | 50.0 | ||||
| 羊踯躅亚属 Subgen. Pentanthera | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 100.0 | ||||
| 合计 Total | 42 | 15 | 35.7 | 7 | 21.4 | 8 | 19.1 | 8 | 19.1 | 4 | 9.5 | ||||
Table 3 Relationship between the flowering-leafing phenorhythm type and phylogeny of 42 Rhododendron species
| 类群 Group | 观察种数 No. of species | F→L | F+L | L∈F | L+F | L→F | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||||||
| 常绿杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Hymenanthes | 21 | 9 | 42.9 | 4 | 19.1 | 5 | 23.8 | 2 | 9.5 | 1 | 4.8 | ||||
| 云锦杜鹃亚组 Subsect. Fortunea | 6 | 4 | 66.7 | - | - | 1 | 17.5 | 1 | 17.5 | - | - | ||||
| 银叶杜鹃亚组 Subsect. Argyrophylla | 5 | 3 | 60.0 | 2 | 40.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
| 麻花杜鹃亚组 Subsect. Maculifera | 3 | 1 | 33.3 | - | - | 1 | 33.3 | 1 | 33.3 | ||||||
| 杜鹃亚属 Subgen. Rhododendron | 18 | 6 | 33.3 | 3 | 16.7 | 3 | 16.7 | 5 | 27.8 | 1 | 5.6 | ||||
| 三花杜鹃亚组 Subsect. Triflora | 13 | 2 | 15.4 | 3 | 23.1 | 2 | 15.4 | 5 | 38.6 | 1 | 7.7 | ||||
| 映山红亚属 Subgen. Tsutsusi | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 50.0 | 1 | 50.0 | ||||
| 羊踯躅亚属 Subgen. Pentanthera | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 100.0 | ||||
| 合计 Total | 42 | 15 | 35.7 | 7 | 21.4 | 8 | 19.1 | 8 | 19.1 | 4 | 9.5 | ||||
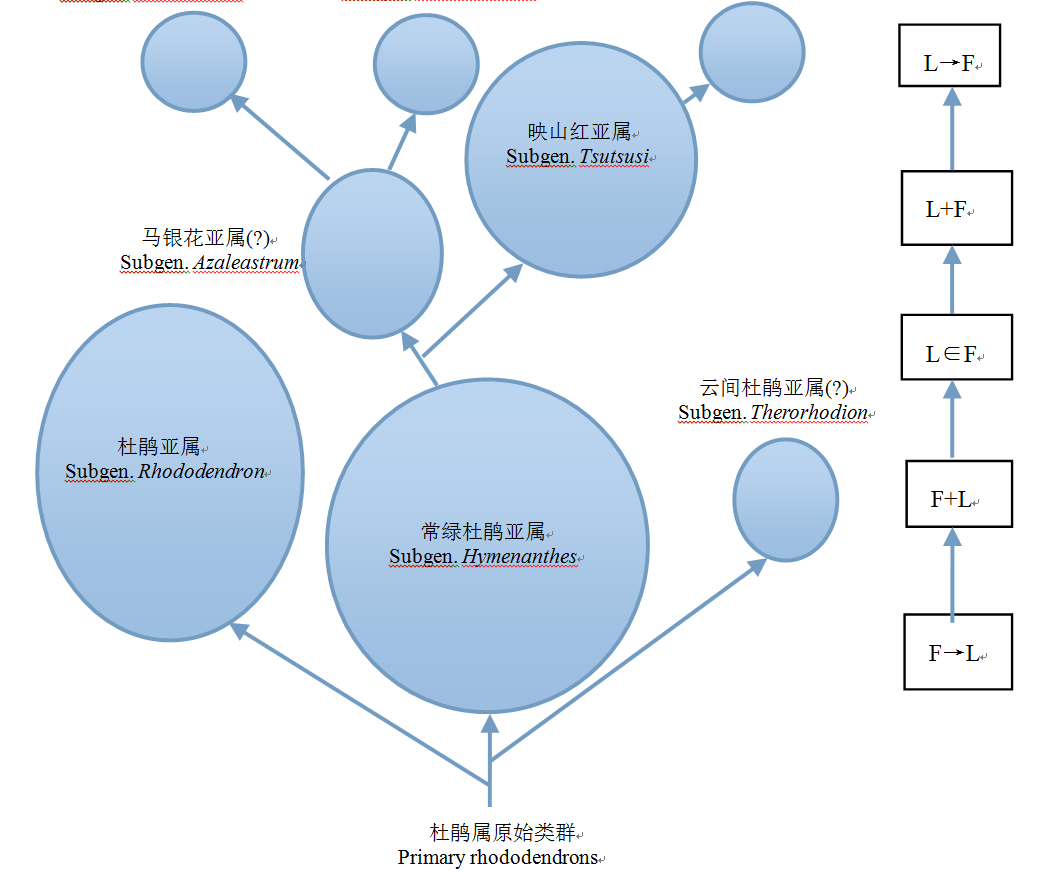
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic relationship of Rhododendron subgenera and evolutional sequence of their flowering-leafing phenorhythm type. The meaning of each phenorhythm type shows in Table 1. “?” shows the flowering-leafing phenorhythm type is not clear in the subgenera.
| 花叶节律模式 Phenorhythmotype | 种类 Species | 来源 Source | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 开花展叶物候时间 Phenologic timing of flowering and leafing① | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3月 March | 4月Apr. | 5月May | 6月June | 7月July | ||||
| F→L: 先花后叶型Flowering before leafing | 美容杜鹃 R. calophytum | 龙池 Longchi | 2,000 | ○○○○ △△△△△△ | ||||
| 腺果杜鹃 R. davidii | 龙池 Longchi | 1,800 | ○○○○△△△△ | |||||
| 山光杜鹃 R. oreodoxa | 龙池 Longchi | 2,500 | ○○○○○ △△△ | |||||
| 团叶杜鹃 R. orbiculare | 汶川 Wenchuan | 2,500 | ○○○ △△△△△ | |||||
| 大王杜鹃 R. rex | 椅子丫口 Yiziyakou | 2,500 | ○○○○ △△△△△ | |||||
| 紫斑杜鹃 R. strigillosum var. monosematum | 峨眉山 Emeishan | 2,500 | ○○○○△△△△△ | |||||
| 岷江杜鹃 R. hunnewellianum | 龙池 Longchi | 1,400 | ○○○○○○△△△ | |||||
| 海绵杜鹃 R. pingianum | 峨眉山 Emeishan | 2,400 | ○○○△△△ | |||||
| 繁花杜鹃 R. floribundum | 龙肘山 Longzhoushan | 2,900 | ○○○ △△△△△△△△ | |||||
| 百合花杜鹃 R .liliiflorum | 庐山 Lushan | 1,300 | ○○○○△△△△△ | |||||
| 多鳞杜鹃 R. polylepis | 龙池 Longchi | 1,700 | ○○○○△△△△△ | |||||
| 黄花杜鹃 R. lutescensx | 龙池 Longchi | 1,700 | ○○○△△△ | |||||
| 红棕杜鹃 R. rubiginosum | 木里 Muli | 3,200 | ○○○△△△△ | |||||
| 柔毛碎米花 R. mollicomum | 战河 Zhanhe | 3,200 | ○○○△△△△ | |||||
| 腋花杜鹃 R. racemosum | 战河 Zhanhe | 2,700 | ○○○△△△△ | |||||
| F+L: 先花后叶、部分重叠型 Flowering ahead and covering part time of leafing | 窄叶杜鹃 R. araiophyllum | 新主 Xinzhu | 2,600 | ○◎◎△ | ||||
| 银叶杜鹃 R. argyrophyllum | 峨眉山 Emeishan | 2,200 | ○○◎◎△ | |||||
| 峨嵋银叶杜鹃 R. argyrophylum subsp. omeiense | 龙池 Longchi | 1,800 | ○○◎◎△△ | |||||
| 巴郎杜鹃 R. balangense | 卧龙 Wolong | 2,700 | ○◎◎△ | |||||
| 基毛杜鹃 R. rigidum | 木里 Muli | 3,200 | ○◎◎△△ | |||||
| 紫花杜鹃 R. amesiae | 海螺沟 Hailuogou | 3,500 | ○◎◎△ | |||||
| 张口杜鹃 R. augustinii subsp. chasmanthum | 片马 Pianma | 3,100 | ○◎◎◎△△ | |||||
| L∈F: 叶期包花期型 Leafing covers flowering , | 喇叭杜鹃 R. discolor | 龙池 Longchi | 1,600 | △◎◎◎△ | ||||
| 绒毛杜鹃 R. pachytrichum | 海螺沟 Hailuogou | 3,200 | △◎◎◎△ | |||||
| 马缨杜鹃 R. delavayi | 大方 Dafang | 1,700 | △△△◎◎◎△ | |||||
| 皱皮杜鹃 R. wiltonii | 峨眉山 Emeishan | 2,400 | △◎◎◎△ | |||||
| 毛肋杜鹃 R. augustinii | 龙池 Longchi | 2,000 | △△◎◎◎△ | |||||
| 云南杜鹃 R. yunnanense | 玉龙雪山 Yulongxueshan | 3,600 | △◎◎◎△ | |||||
| 硬毛杜鹃 R. hirtipes | 多雄拉 Duoxiongla | 3,500 | △◎◎◎△△△△△△△△△△△△△△ | |||||
| 亮鳞杜鹃 R. heliolepis | 泸定 Luding | 3,100 | △△△◎◎◎△ | |||||
| L+F: 先叶后花、部分重叠型 Leafing ahead and covering part time of flowering | 大白杜鹃 R. decorum | 泸定 Luding | 1,800 | △◎◎○○ | ||||
| 硬叶杜鹃 R. tatsienense | 片马 Pianma | 3,200 | △△◎◎○ | |||||
| 长毛杜鹃 R. trichanthum | 川西 Chuanxi | 2,200 | △△◎○○ | |||||
| 问客杜鹃 R. ambiguum | 龙池 Longchi | 2,400 | △◎◎◎○ | |||||
| 山育杜鹃 R. oreotrephes | 泸定 Luding | 3,000 | △△◎◎○○ | |||||
| 三花杜鹃 R. triflorum | 多雄拉 Duoxiongla | 3,000 | △△△◎○○ | |||||
| 映山红 R. simsii | 大方 Dafang | 1,700 | △△△◎◎○ | |||||
| 长鳞杜鹃 R. longesquamatum | 龙池 Longchi | 2,700 | △△◎○○ | |||||
| L→F: 先叶后花型Leafing before flowering | 云雾杜鹃 R. chamaethomsonii | 多雄拉 Duoxiongla | 4,000 | △△△ ○○○ | ||||
| 白面杜鹃 R. zaleucum | 玉龙雪山 Yulongxueshan | 3,400 | △△△○○○ | |||||
| 亮毛杜鹃 R. microphyton | 无量山 Wuliangshan | 2,700 | △△△△○○○ | |||||
| 羊踯躅 R. moll | 庐山 Lushan | 1,300 | △△△△○○○○ | |||||
Table S1 Flowering-leafing phenorhythm type of 42 Rhododendron species conserved ex situ in Dujiangyan, Sichuan Province
| 花叶节律模式 Phenorhythmotype | 种类 Species | 来源 Source | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 开花展叶物候时间 Phenologic timing of flowering and leafing① | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3月 March | 4月Apr. | 5月May | 6月June | 7月July | ||||
| F→L: 先花后叶型Flowering before leafing | 美容杜鹃 R. calophytum | 龙池 Longchi | 2,000 | ○○○○ △△△△△△ | ||||
| 腺果杜鹃 R. davidii | 龙池 Longchi | 1,800 | ○○○○△△△△ | |||||
| 山光杜鹃 R. oreodoxa | 龙池 Longchi | 2,500 | ○○○○○ △△△ | |||||
| 团叶杜鹃 R. orbiculare | 汶川 Wenchuan | 2,500 | ○○○ △△△△△ | |||||
| 大王杜鹃 R. rex | 椅子丫口 Yiziyakou | 2,500 | ○○○○ △△△△△ | |||||
| 紫斑杜鹃 R. strigillosum var. monosematum | 峨眉山 Emeishan | 2,500 | ○○○○△△△△△ | |||||
| 岷江杜鹃 R. hunnewellianum | 龙池 Longchi | 1,400 | ○○○○○○△△△ | |||||
| 海绵杜鹃 R. pingianum | 峨眉山 Emeishan | 2,400 | ○○○△△△ | |||||
| 繁花杜鹃 R. floribundum | 龙肘山 Longzhoushan | 2,900 | ○○○ △△△△△△△△ | |||||
| 百合花杜鹃 R .liliiflorum | 庐山 Lushan | 1,300 | ○○○○△△△△△ | |||||
| 多鳞杜鹃 R. polylepis | 龙池 Longchi | 1,700 | ○○○○△△△△△ | |||||
| 黄花杜鹃 R. lutescensx | 龙池 Longchi | 1,700 | ○○○△△△ | |||||
| 红棕杜鹃 R. rubiginosum | 木里 Muli | 3,200 | ○○○△△△△ | |||||
| 柔毛碎米花 R. mollicomum | 战河 Zhanhe | 3,200 | ○○○△△△△ | |||||
| 腋花杜鹃 R. racemosum | 战河 Zhanhe | 2,700 | ○○○△△△△ | |||||
| F+L: 先花后叶、部分重叠型 Flowering ahead and covering part time of leafing | 窄叶杜鹃 R. araiophyllum | 新主 Xinzhu | 2,600 | ○◎◎△ | ||||
| 银叶杜鹃 R. argyrophyllum | 峨眉山 Emeishan | 2,200 | ○○◎◎△ | |||||
| 峨嵋银叶杜鹃 R. argyrophylum subsp. omeiense | 龙池 Longchi | 1,800 | ○○◎◎△△ | |||||
| 巴郎杜鹃 R. balangense | 卧龙 Wolong | 2,700 | ○◎◎△ | |||||
| 基毛杜鹃 R. rigidum | 木里 Muli | 3,200 | ○◎◎△△ | |||||
| 紫花杜鹃 R. amesiae | 海螺沟 Hailuogou | 3,500 | ○◎◎△ | |||||
| 张口杜鹃 R. augustinii subsp. chasmanthum | 片马 Pianma | 3,100 | ○◎◎◎△△ | |||||
| L∈F: 叶期包花期型 Leafing covers flowering , | 喇叭杜鹃 R. discolor | 龙池 Longchi | 1,600 | △◎◎◎△ | ||||
| 绒毛杜鹃 R. pachytrichum | 海螺沟 Hailuogou | 3,200 | △◎◎◎△ | |||||
| 马缨杜鹃 R. delavayi | 大方 Dafang | 1,700 | △△△◎◎◎△ | |||||
| 皱皮杜鹃 R. wiltonii | 峨眉山 Emeishan | 2,400 | △◎◎◎△ | |||||
| 毛肋杜鹃 R. augustinii | 龙池 Longchi | 2,000 | △△◎◎◎△ | |||||
| 云南杜鹃 R. yunnanense | 玉龙雪山 Yulongxueshan | 3,600 | △◎◎◎△ | |||||
| 硬毛杜鹃 R. hirtipes | 多雄拉 Duoxiongla | 3,500 | △◎◎◎△△△△△△△△△△△△△△ | |||||
| 亮鳞杜鹃 R. heliolepis | 泸定 Luding | 3,100 | △△△◎◎◎△ | |||||
| L+F: 先叶后花、部分重叠型 Leafing ahead and covering part time of flowering | 大白杜鹃 R. decorum | 泸定 Luding | 1,800 | △◎◎○○ | ||||
| 硬叶杜鹃 R. tatsienense | 片马 Pianma | 3,200 | △△◎◎○ | |||||
| 长毛杜鹃 R. trichanthum | 川西 Chuanxi | 2,200 | △△◎○○ | |||||
| 问客杜鹃 R. ambiguum | 龙池 Longchi | 2,400 | △◎◎◎○ | |||||
| 山育杜鹃 R. oreotrephes | 泸定 Luding | 3,000 | △△◎◎○○ | |||||
| 三花杜鹃 R. triflorum | 多雄拉 Duoxiongla | 3,000 | △△△◎○○ | |||||
| 映山红 R. simsii | 大方 Dafang | 1,700 | △△△◎◎○ | |||||
| 长鳞杜鹃 R. longesquamatum | 龙池 Longchi | 2,700 | △△◎○○ | |||||
| L→F: 先叶后花型Leafing before flowering | 云雾杜鹃 R. chamaethomsonii | 多雄拉 Duoxiongla | 4,000 | △△△ ○○○ | ||||
| 白面杜鹃 R. zaleucum | 玉龙雪山 Yulongxueshan | 3,400 | △△△○○○ | |||||
| 亮毛杜鹃 R. microphyton | 无量山 Wuliangshan | 2,700 | △△△△○○○ | |||||
| 羊踯躅 R. moll | 庐山 Lushan | 1,300 | △△△△○○○○ | |||||
| [1] | Billings WD (1974) Adaptations and origins of alpine plants.Arctic and Alpine Research, 6, 129-142. |
| [2] | Billings WD, Mooney HA (1968) The ecology of arctic and alpine plant.Biological Reviews, 43, 481-529. |
| [3] | Brody AK (1997) Effects of pollinators, herbivores, and seed predators on flowering phenology.Ecology, 78, 1624-1631. |
| [4] | Chamberlain DF, Hyam R, Argent G (1996) The Genus Rhododendron: Its Classification and Synonymy. Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh, Edinburgh. |
| [5] | Chen CD (陈昌笃), Zhuang P (庄平), Hu JC (胡锦矗) (2000) Biodiversity Research and Conservation in Dujiangyan,China (都江堰生物多样性研究与保护), pp. 11-27. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [6] | Christian K (translated by Wu N (吴宁), Luo P (罗朋)) (2009) Alpine Plant Life: Functional Plant Ecology of High Mountain Ecosystems (高山植物功能生态学), pp. 7-36, 87-96, 190-194, 223-236. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [7] | Cullen J, Chamberlain DF (1978) A preliminary synopsis of the genus Rhododendron.Notes from the Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh, 36, 105-126. |
| [8] | Dahl E (1986) Zonation in arctic and alpine tundra and fell-field ecobiomes. In: Ecosystem Theory Application (ed. Polunin N), pp. 35-62. Wiley, London. |
| [9] | Ding BY (丁炳扬), Jin XF (金孝锋) (2009) Taxonomic Study on Rhododendron Subgen. Tsutsusi Sleumer (Ericaceae) (杜鹃花属映山红亚属的分类研究), pp. 246-256. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [10] | Escaravage N, Wagner J (2004) Pollination effectiveness and pollen dispersal in a Rhododendron ferrugineum (Ericaceae) population.Plant Biology, 6, 606-615. |
| [11] | Fang MY, Fang RZ (2005) Flora of China, Vol. 14. pp. 255-455. Science Press, Beijing. |
| [12] | Fang RZ (方瑞征), Min TL (闵天禄) (1981) The influence of uplift of Himalayas on the floristic formation of genus Rhododendron.Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 3, 147-157. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Fang RZ (方瑞征), Min TL (闵天禄) (1995) The floristic study on the genus Rhododendron.Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 17, 359-379. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Fennera M (1998) The phenology of growth and reproduction in plants. Perspectives in Plant Ecology,Evolution and Systematics, 1, 78-91. |
| [15] | Forrest J, Abraham JM (2010) Toward a synthetic understanding of the role of phenology in ecology and evolution.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 365, 3101-3112. |
| [16] | Gaku K (1993) Relationships between flowering time and fruit set of the entomophilous alpine shrub, Rhododendron aureum (Ericaceae), inhabiting snow patches.American Journal of Botany, 80, 1300-1304. |
| [17] | Gaku K, Akira SH, Yuka K (2011) Pollination efficiency of bumblebee queens and workers in the alpine shrub Rhododendron aureum.International Journal of Plant Sciences, 172, 70-77. |
| [18] | Ge QS (葛全胜), Dai JH (戴君虎), Zheng JY (郑景云) (2010) The progress of phenology studies and challenges to modern phenology research in China.Disciplinary Development(科学发展), 25, 310-316. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Gibbs D, Chamberlain D, Argent G (2011) The Red List of Rhododendrons, pp. 6-8Botanic Gardens Conservation International, Richmond, UK. |
| [20] | Hideyuki D, Mayumi T, Izumi K (2010) Genetic diversity increases regional variation in phenological dates in response to climate change.Global Change Biology, 16, 373-379. |
| [21] | Hirao AS, Kameyama Y, Ohara M, Isagi Y, Kudo G (2006) Seasonal changes in pollinator activities influence pollen dispersal and seed production of the alpine shrub Rhododendron aureum (Ericaceae).Molecular Ecology, 15, 1165-1173. |
| [22] | Hu WG (胡文光) (1990) A study on the genus Rhododendron L. Subsection Fortunea Sleumer in China.Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 12, 367-374. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Kudo G, Ida TY, Tani T (2008) Linkages between phenology, pollination, photosynthesis, and reproduction in deciduous forest understory plants.Ecology, 89, 321-331. |
| [24] | Li YN (李亚男), Yang DM (杨冬梅), Sun SC (孙书存), Gao XM (高贤明) (2008) Effects of twig size on biomass allocation within twigs and on Lamina area supporting efficiency in Rhododendron: allometric scaling analyses.Journal of Plant Ecology(植物生态学报), 32, 1175-1183. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Makrodimos N, Blionis GJ, Krigas N, Vokou D (2007) Flower morphology, phenology and visitor patterns in an alpine community on Mt. Olympos, Greece. Flora, 203, 449-468. |
| [26] | Malciūtė A, Naujalis JR, Šaulienė I (2010) The seasonal development characteristic of different rhododendrons taxa and cultivars in Northern Lithuania. 1. Leafing peculiarities.Agriculture, 97, 107-114. |
| [27] | Miller-Rushing AJ, Inouye DW (2009) Variation in the impact of climate change on flowering phenology and abundance: an examination of two pairs of closely related wildflower species.American Journal of Botany, 96, 1821-1829. |
| [28] | Min TL (闵天禄), Fang RZ (方瑞征) (1979) On the origin and geographic distribution of genus Rhododendron L.Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 1, 121-127. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Min TL (闵天禄), Fang RZ (方瑞征) (1990) The phylogeny and evolution of genus Rhododendron.Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 12, 353-365. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Molau U (1993) Relationships between flowering phenology and life history strategies in tundra plants.Arctic and Alpine Research, 25, 391-402. |
| [31] | Nilsen ET (2003) Unique anatomical traits in leaves of Rhododendron section Vireya: a discussion of functional significance. In: Rhododendrons in Horticulture and Science (eds Argent G, McFarlane M), pp. 20-36. Edinburg, Scotland. |
| [32] | Sailesh R, Eike L, Krishna KS, Kaiyun G, Xu JC (2013) Flowering phenology of tree rhododendron along an elevation gradient in two sites in the Eastern Himalayas.International Journal of Biometeorology, 57, 225-240. |
| [33] | Sun H (孙航) (2002) Tethys retreat and Himalayas- Hengduanshan Mountains uplift and their significance on the origin and development of the Sino-Himalayan elements and alpine flora.Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 24, 273-288. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] | Wan WM (宛渭敏), Liu XZ (刘秀珍) (1979) Observation Method for China’s Phenology (中国物候观测方法), pp. 1-40. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [35] | Wu ZY (吴征镒) (1991) The areal-types of Chinese genera of seed plant.Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 13(Suppl. IV), 1-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [36] | Wu ZY (吴征镒), Sun H (孙航), Zhou ZK (周浙昆), Li DZ (李德铢), Peng H (彭华) (2011) Floristics of Seed Plants of China (中国种子植物区系地理), pp. 52-120. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [37] | Xiong ZX (熊子仙), Du Q (杜青), Wang QD (王启德) (2000) Taxon and anatomy leaves in Rhododendron from China.Guihaia(广西植物), 20, 335-338. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [38] | Ying TS (应俊生), Chen ML (陈梦玲) (2011) Plant Geography of China (中国植物地理), pp. 68-79. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [39] | Zhuang P (庄平) (2012) Discussion on the Rhododendron geographical distribution types and their cause of formation in China.Guihaia(广西植物), 32, 150-156. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [40] | Zhuang P (庄平), Gao XM (高贤明) (2002) The concept of “The West China Rainy Zone” and its significance to the biodiversity conservation in China.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 10, 339-344. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [41] | Zhuang P (庄平), Zheng YR (郑元润), Shao HM (邵慧敏), Wang F (王飞) (2012) An assessment on the adaptability of Rhododendron plants under ex situ conservation.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 20, 665-675. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [42] | Zhuang P (庄平), Wang F (王飞), Shao HM (邵慧敏) (2013) Comparative study on Rhododendron and its distribution in W-Sichuan and SE-Tibet.Guihaia(广西植物), 33, 791-797. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | Renxiu Yao, Yan Chen, Xiaoqin Lü, Jianghu Wang, Fujun Yang, Xiaoyue Wang. Altitude-related environmental factors shape the phenotypic characteristics and chemical profile of Rhododendron [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22259-. |
| [2] | Jiejie Cheng, Meijun Li, Taohua Yuan, Hong Huang, Guili Yang, Xinxiang Bai. A dataset on wild Rhododendron and geographical distribution information in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(9): 1175-1180. |
| [3] | Yuhan Shi, Zongxin Ren, Yanhui Zhao, Hong Wang. Effect of climate change on the distribution and phenology of plants, insect pollinators, and their interactions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(4): 495-506. |
| [4] | Manru Li, Ling Zhang. Overview of the reproductive phenology of mistletoes [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(7): 833-841. |
| [5] | Zhuang Ping. Progress on the fertility of Rhododendron [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(3): 327-338. |
| [6] | Zhihuan Huang, Qifeng Lu, Yingzhuo Chen. Comparative study on reproductive success of Corydalis sheareri (Papaveraceae) between alkaline limestone soil and red soil habitats in a karst area [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(9): 972-980. |
| [7] | Shuoli Zheng, Xiaoling Tian, Chengling Huang, Lingjun Wang, Yuan Feng, Jingli Zhang. Molecular and morphological evidence for natural hybridization between Rhododendron decorum and R. delavayi (Ericaceae) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(6): 627-637. |
| [8] | Jun Sun, Bing Xue. Marine phytoplankton diversity and the impact of global climate change [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(7): 739-747. |
| [9] | Shaoshuai Yu, Qicong Xu, Caili Lin, Shengjie Wang, Guozhong Tian. Genetic diversity of phytoplasmas: research status and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(2): 205-215. |
| [10] | Xiaoli Hu, Chia-Hao Chang-Yang, Xiangcheng Mi, Yanjun Du, Zhaoyang Chang. Influence of climate, phylogeny, and functional traits on flowering phenology in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, East China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(5): 601-609. |
| [11] | Xiaoting Xu, Zhiheng Wang, Dimitar Dimitrov, Carsten Rahbek. Using NCBIminer to search and download nucleotide sequences from GenBank [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(4): 550-555. |
| [12] | Lei Li, Jiakuan Chen. Influence of climate change on wild plants and the conservation strategies [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(5): 549-563. |
| [13] | Hong Wu,Xuemei Yang,Huimin Shao,Fei Wang. Germplasm resource base for rhododendron horticulture: status, probl- ems and countermeasures [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(5): 628-634. |
| [14] | Juan Li,Cong Guo,Zhishu Xiao. Fruit composition and seed dispersal strategies of woody plants in a Dujiangyan subtropical forest, Southwest China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(5): 572-581. |
| [15] | Caroline A. Polgar, Richard B. Primack. Leaf out phenology in temperate forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(1): 111-116. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()
