



Biodiv Sci ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 24286. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024286 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024286
• Technology and Methodologies • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lei Chen1, Zhiyong Xu1,*( )(
)( ), Pukun Su1, Xiaotian Lai1, Zhao Zhao1,2(
), Pukun Su1, Xiaotian Lai1, Zhao Zhao1,2( )
)
Received:2024-07-01
Accepted:2024-09-07
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-12-05
Contact:
*E-mail: ezyxu@njust.edu.cn
Supported by:Lei Chen, Zhiyong Xu, Pukun Su, Xiaotian Lai, Zhao Zhao. Exploring the application of frequency-dependent acoustic diversity index in human-dominated areas[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24286.
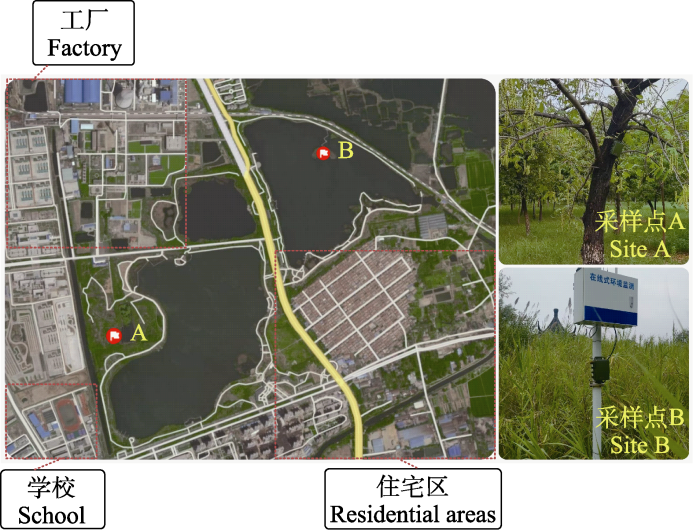
Fig. 1 Locations of two passive acoustic recorders in Jiangsu Jiuli Lake National Wetland Park. Site A represents a terrestrial sampling point, and site B is surrounded by a lake.
| 物种 Species | 鸟鸣声时频分布结构 Sound unit shape | 频率范围 Frequency range (kHz) | 鸟鸣声片段数量 Number of segments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 长尾山雀 Aegithalos glaucogularis | 受频率调制类型 Frequency modulated whistles (FM) | 5-7 | 303 |
| 灰喜鹊 Cyanopica cyanus | 可变频率分量宽带类型 Broadband with varying frequency components (BVF) | 1-8 | 273 |
| 田鹀 Emberiza rustica | 宽带脉冲类型 Broadband pulses (BP) | 5.5-8 | 280 |
| 游隼 Falco peregrinus | 强谐波类型 Strong harmonics (SH) | 0.5-8 | 282 |
| 棕头鸦雀 Paradoxornis webbianus | 恒定频率类型 Constant frequency (CF) | 2-5 | 275 |
Table 1 Details of bird species and vocalization segments used in this work
| 物种 Species | 鸟鸣声时频分布结构 Sound unit shape | 频率范围 Frequency range (kHz) | 鸟鸣声片段数量 Number of segments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 长尾山雀 Aegithalos glaucogularis | 受频率调制类型 Frequency modulated whistles (FM) | 5-7 | 303 |
| 灰喜鹊 Cyanopica cyanus | 可变频率分量宽带类型 Broadband with varying frequency components (BVF) | 1-8 | 273 |
| 田鹀 Emberiza rustica | 宽带脉冲类型 Broadband pulses (BP) | 5.5-8 | 280 |
| 游隼 Falco peregrinus | 强谐波类型 Strong harmonics (SH) | 0.5-8 | 282 |
| 棕头鸦雀 Paradoxornis webbianus | 恒定频率类型 Constant frequency (CF) | 2-5 | 275 |
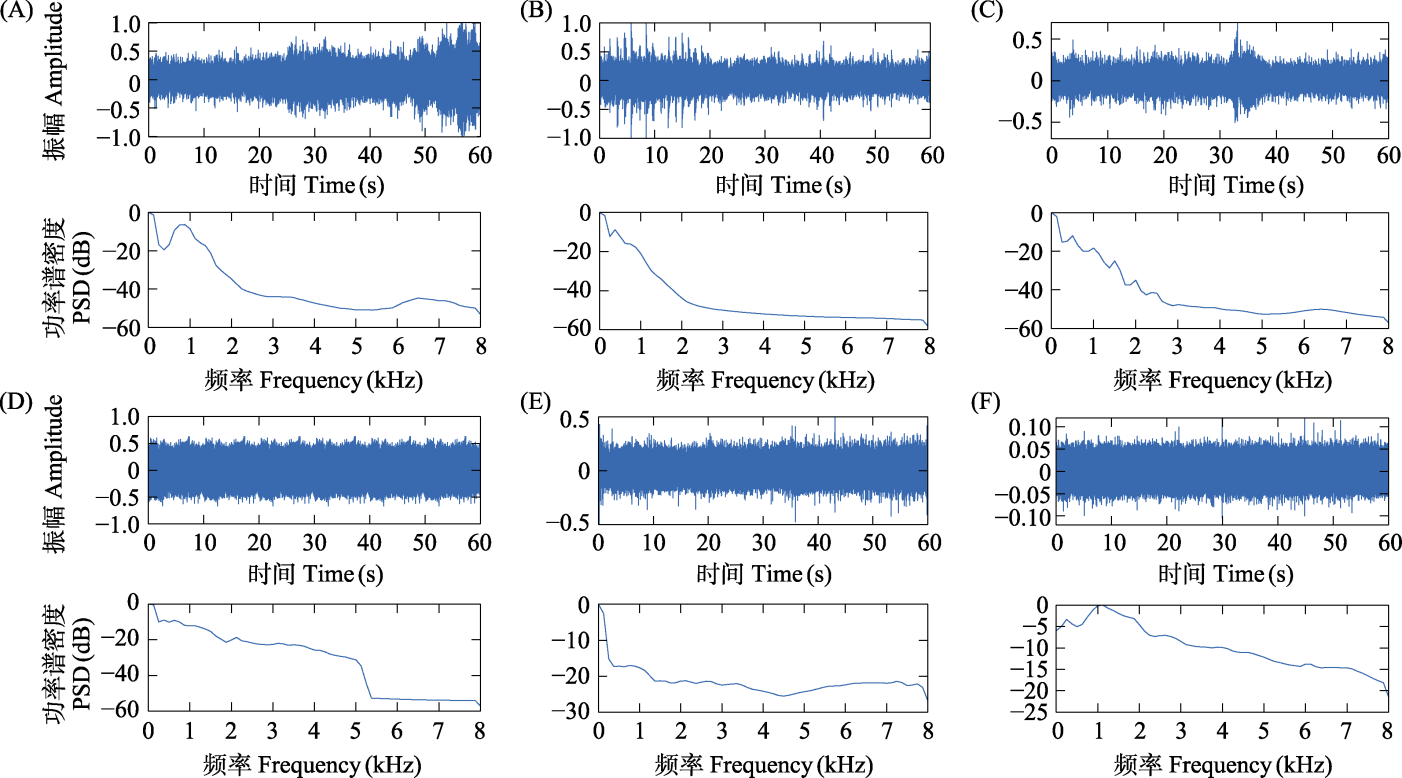
Fig. 3 Temporal waveforms and normalized power spectra density (PSD) of six interference sound signals. (A) Ambulance siren; (B) Pile-driving noise; (C) Car horn; (D) Lawn mower sound; (E) Rain sound; (F) Flowing water sound.
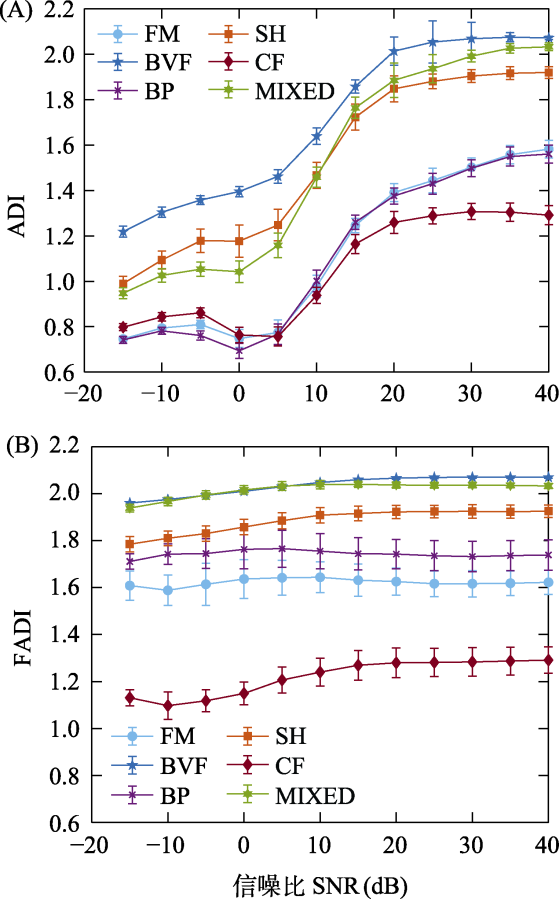
Fig. 5 Comparison of ADI (A) and FADI (B) with SNR under different sound unit shapes. ADI, Acoustic diversity index; FADI, Frequency-dependent acoustic diversity index; FM, Frequency modulated whistles; BVF, Broadband with varying frequency components; BP, Broadband pulse; SH, Strong harmonics; CF, Constant frequency; MIXED, Mixed sound unit shapes.
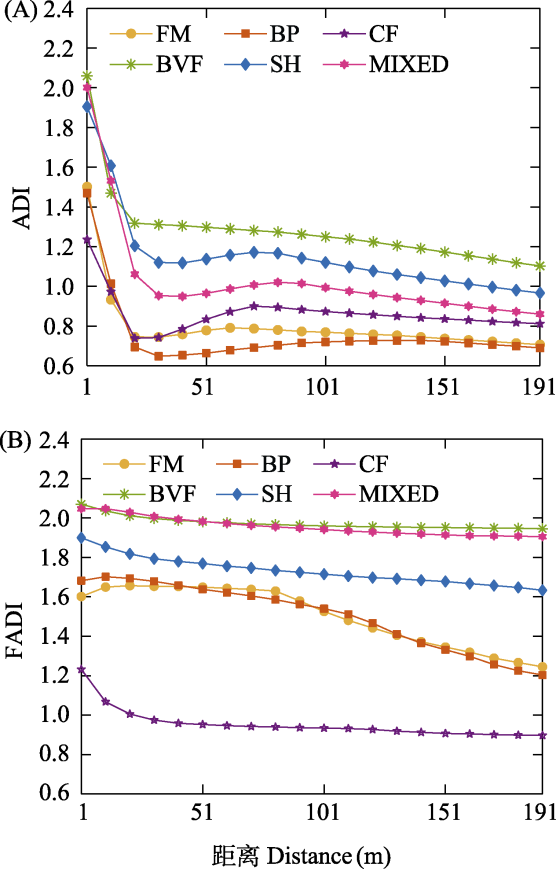
Fig. 6 Comparison of ADI (A) and FADI (B) with distance under different sound unit shapes. ADI, Acoustic diversity index; FADI, Frequency-dependent acoustic diversity index; FM, Frequency modulated whistles; BVF, Broadband with varying frequency components; BP, Broadband pulse; SH, Strong harmonics; CF, Constant frequency; MIXED, Mixed sound unit shapes.
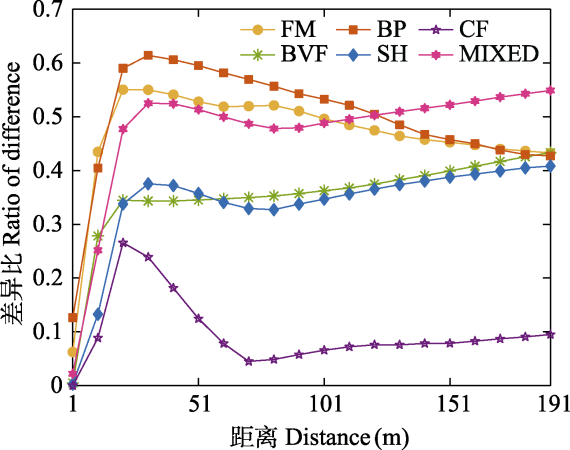
Fig. 7 The ratio of difference with distance under different sound unit shapes. FM, Frequency modulated whistles; BVF, Broadband with varying frequency components; BP, Broadband pulse; SH, Strong harmonics; CF, Constant frequency; MIXED, Mixed sound unit shapes.
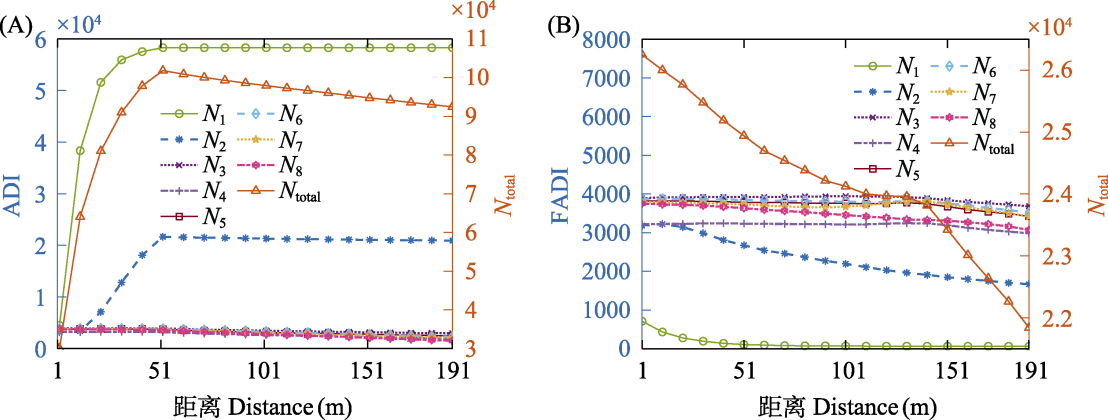
Fig. 9 The number of time-frequency bins with a value of 1 in each frequency band (Ni) and their sum (Ntotal) with distance in the calculation of ADI (A) and FADI (B)
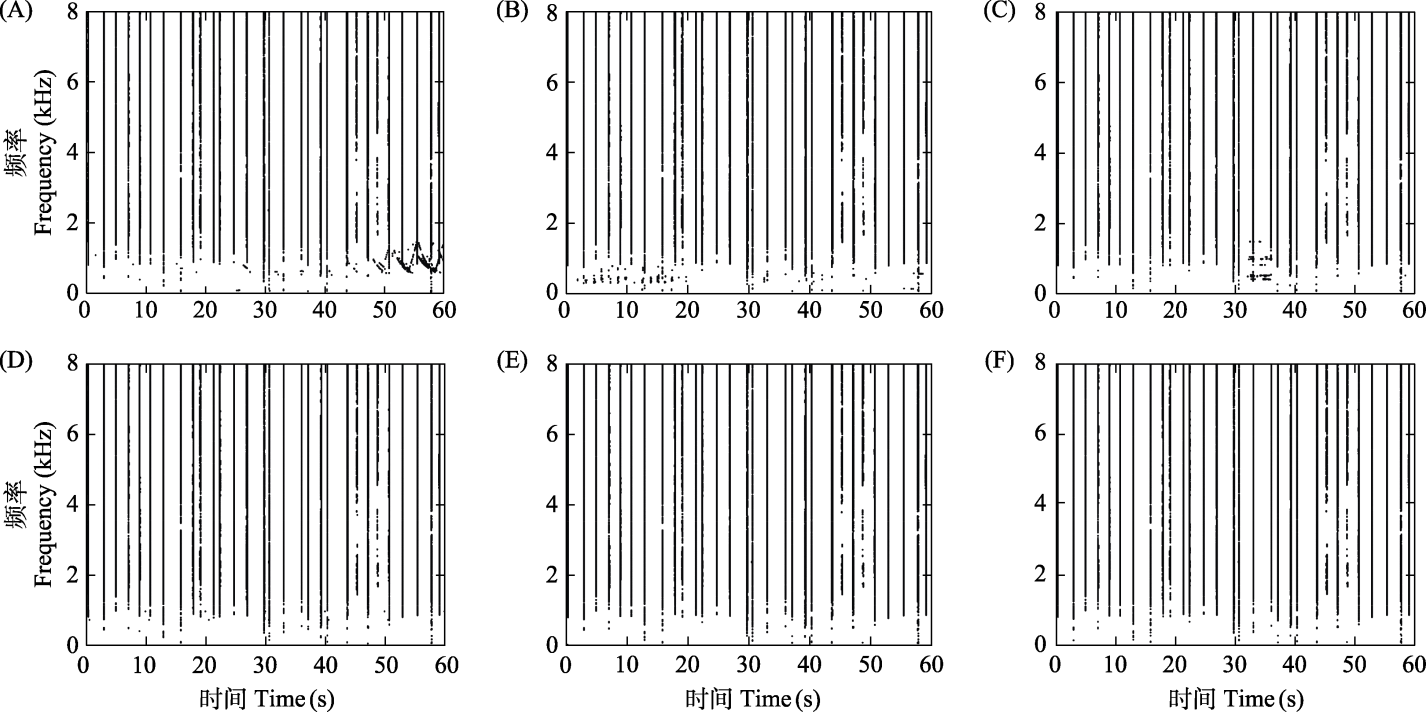
Fig. 10 The binary spectrogram of FADI at a high SINR condition (SINR = 30 dB) with different interference backgrounds: (A) Ambulance siren; (B) Pile-driving noise; (C) Car horn; (D) Lawn mower sound; (E) Rain sound; (F) Flowing water sound.
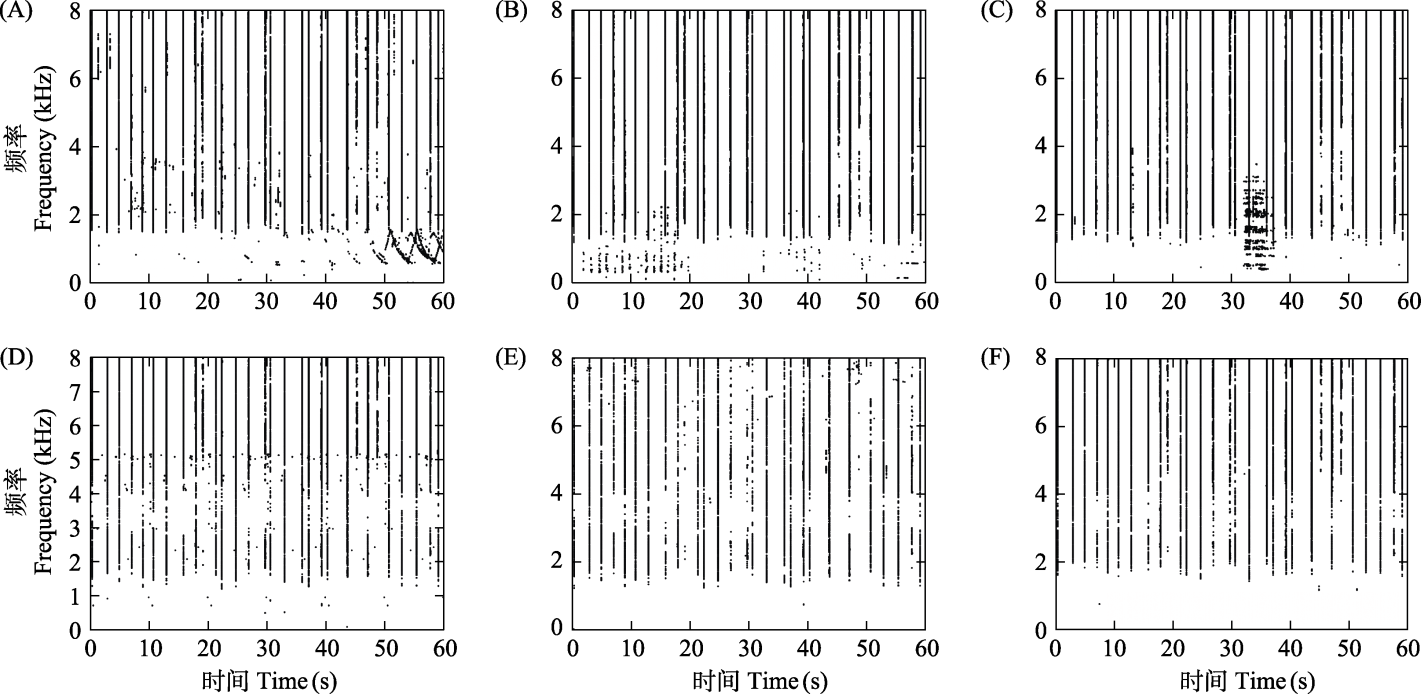
Fig. 11 The binary spectrogram of FADI at a low SINR condition (SINR = -5 dB) with different interference backgrounds: (A) Ambulance siren; (B) Pile-driving noise; (C) Car horn; (D) Lawn mower sound; (E) Rain sound; (F) Flowing water sound.
| [1] | Beason RD, Riesch R, Koricheva J (2023) Investigating the effects of tree species diversity and relative density on bird species richness with acoustic indices. Ecological Indicators, 154, 110652. |
| [2] | Bradfer-Lawrence T, Bunnefeld N, Gardner N, Willis SG, Dent DH (2020) Rapid assessment of avian species richness and abundance using acoustic indices. Ecological Indicators, 115, 106400. |
| [3] |
Bradfer-Lawrence T, Gardner N, Bunnefeld L, Bunnefeld N, Willis SG, Dent DH (2019) Guidelines for the use of acoustic indices in environmental research. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 1796-1807.
DOI |
| [4] | Brandes TS (2008) Automated sound recording and analysis techniques for bird surveys and conservation. Bird Conservation International, 18, S163-S173. |
| [5] | Buxton RT, Agnihotri S, Robin VV, Goel A, Balakrishnan R (2018) Acoustic indices as rapid indicators of avian diversity in different land-use types in an Indian biodiversity hotspot. Journal of Ecoacoustics, 2, 8. |
| [6] | Buxton RT, Pearson AL, Allou C, Fristrup K, Wittemyer G (2021) A synthesis of health benefits of natural sounds and their distribution in national parks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 118, e2013097118. |
| [7] | Cappe O (1994) Elimination of the musical noise phenomenon with the Ephraim and Malah noise suppressor. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 2, 345-349. |
| [8] | Cohen I (2004) Speech enhancement using a noncausal Apriori SNR estimator. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 11, 725-728. |
| [9] | Depraetere M, Pavoine S, Jiguet F, Gasc A, Duvail S, Sueur J (2012) Monitoring animal diversity using acoustic indices: Implementation in a temperate woodland. Ecological Indicators, 13, 46-54. |
| [10] | Diaz SDU, Gan JL, Tapang GA (2023) Acoustic indices as proxies for bird species richness in an urban green space in Metro Manila. PLoS ONE, 18, e0289001. |
| [11] |
Dooley JM, Brown MT (2020) The quantitative relation between ambient soundscapes and landscape development intensity in North Central Florida. Landscape Ecology, 35, 113-127.
DOI |
| [12] | Doser JW, Finley AO, Kasten EP, Gage SH (2020) Assessing soundscape disturbance through hierarchical models and acoustic indices: A case study on a shelterwood logged northern Michigan forest. Ecological Indicators, 113, 106244. |
| [13] | Elise S, Urbina-Barreto I, Pinel R, Mahamadaly V, Bureau S, Penin L, Adjeroud M, Kulbicki M, Bruggemann JH (2019) Assessing key ecosystem functions through soundscapes: A new perspective from coral reefs. Ecological Indicators, 107, 105623. |
| [14] | Fairbrass AJ, Rennert P, Williams C, Titheridge H, Jones KE (2017) Biases of acoustic indices measuring biodiversity in urban areas. Ecological Indicators, 83, 169-177. |
| [15] | Fuller S, Axel AC, Tucker D, Gage SH (2015) Connecting soundscape to landscape: Which acoustic index best describes landscape configuration? Ecological Indicators, 58, 207-215. |
| [16] | Gage SH, Axel AC (2014) Visualization of temporal change in soundscape power of a Michigan lake habitat over a 4-year period. Ecological Informatics, 21, 100-109. |
| [17] | Gagne E, Perez-Ortega B, Hendry AP, Melo-Santos G, Walmsley SF, Rege-Colt M, Austin M, May-Collado LJ (2022) Dolphin communication during widespread systematic noise reduction—A natural experiment amid COVID-19 lockdowns. Frontiers in Remote Sensing, 3, 934608. |
| [18] | Gasc A, Sueur J, Jiguet F, Devictor V, Grandcolas P, Burrow C, Depraetere M, Pavoine S (2013) Assessing biodiversity with sound: Do acoustic diversity indices reflect phylogenetic and functional diversities of bird communities? Ecological Indicators, 25, 279-287. |
| [19] | Hendriks RC, Heusdens R, Jensen J (2010) MMSE based noise PSD tracking with low complexity. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 4266-4269. Dallas, TX, USA. |
| [20] | Hyland EB, Schulz A, Quinn JE (2023) Quantifying the Soundscape: How filters change acoustic indices. Ecological Indicators, 148, 110061. |
| [21] | Lellouch L, Pavoine S, Jiguet F, Glotin H, Sueur J (2014) Monitoring temporal change of bird communities with dissimilarity acoustic indices. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 5, 495-505. |
| [22] | Marler PR, Slabbekoorn H (2004) Nature’s Music:The Science of Birdsong. Academic Press, San Diego. |
| [23] | Martin R (2001) Noise power spectral density estimation based on optimal smoothing and minimum statistics. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 9, 504-512. |
| [24] | McWilliam JN, Hawkins AD (2013) A comparison of inshore marine soundscapes. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 446, 166-176. |
| [25] | Metcalf OC, Baccaro F, Barlow J, Berenguer E, Bradfer- Lawrence T, Chesini Rossi L, do Vale ÉM, Lees AC (2024) Listening to tropical forest soils. Ecological Indicators, 158, 111566. |
| [26] |
Moreno-Gómez FN, Bartheld J, Silva-Escobar AA, Briones R, Márquez R, Penna M (2019) Evaluating acoustic indices in the Valdivian rainforest, a biodiversity hotspot in South America. Ecological Indicators, 103, 1-8.
DOI |
| [27] | Parker TA (1991) On the use of tape recorders in avifaunal surveys. The Auk, 108, 443-444. |
| [28] | Pieretti N, Duarte MHL, Sousa-Lima RS, Rodrigues M, Young RJ, Farina A (2015) Determining temporal sampling schemes for passive acoustic studies in different tropical ecosystems. Tropical Conservation Science, 8, 215-234. |
| [29] | Rodriguez A, Gasc A, Pavoine S, Grandcolas P, Gaucher P, Sueur J (2014) Temporal and spatial variability of animal sound within a neotropical forest. Ecological Informatics, 21, 133-143. |
| [30] | Rohling H (1983) Radar CFAR thresholding in clutter and multiple target situations. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, (4), 608-621. |
| [31] | Rosenstock SS, Anderson DR, Giesen KM, Leukering T, Carter MF (2002) Landbird counting techniques: Current practices and an alternative. The Auk, 119, 46-53. |
| [32] | Ross SRPJ, Friedman NR, Dudley KL, Yoshimura M, Yoshida T, Economo EP (2018) Listening to ecosystems: Data-rich acoustic monitoring through landscape-scale sensor networks. Ecological Research, 33, 135-147. |
| [33] |
Rumelt RB, Basto A, Mere Roncal C (2021) Automated audio recording as a means of surveying tinamous (Tinamidae) in the Peruvian Amazon. Ecology and Evolution, 11, 13518-13531.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | Shamon H, Paraskevopoulou Z, Kitzes J, Card E, Deichmann JL, Boyce AJ, McShea WJ (2021) Using ecoacoustics metrices to track grassland bird richness across landscape gradients. Ecological Indicators, 120, 106928. |
| [35] | Sohn J, Kim NS, Sung W (1999) A statistical model-based voice activity detection. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 6, 1-3. |
| [36] | Sueur J, Farina A, Gasc A, Pieretti N, Pavoine S (2014) Acoustic indices for biodiversity assessment and landscape investigation. Acta Acustica United with Acustica, 100, 772-781. |
| [37] | Sueur J, Krause B, Farina A (2019) Climate change is breaking earth’s beat. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 34, 971-973. |
| [38] | Sugai LSM, Llusia D (2019) Bioacoustic time capsules: Using acoustic monitoring to document biodiversity. Ecological Indicators, 99, 149-152. |
| [39] | Towsey M, Zhang L, Cottman-Fields M, Wimmer J, Zhang JL, Roe P (2014) Visualization of long-duration acoustic recordings of the environment. Procedia Computer Science, 29, 703-712. |
| [40] | van der Lee GH, Desjonquères C, Sueur J, Kraak MHS, Verdonschot PFM (2020) Freshwater ecoacoustics: Listening to the ecological status of multi-stressed lowland waters. Ecological Indicators, 113, 106252. |
| [41] | Weir LA, Mossman MJ (2005) North American amphibian monitoring program (NAAMP). In: Amphibian Declines (ed. Lannoo M), pp.307-313. University of California Press, Berkeley. |
| [42] | Xia BY, Bao CC (2014) Wiener filtering based speech enhancement with Weighted Denoising Auto-encoder and noise classification. Speech Communication, 60, 13-29. |
| [43] | Xu ZY, Chen L, Pijanowski BC, Zhao Z (2023) A frequency-dependent acoustic diversity index: A revision to a classic acoustic index for soundscape ecological research. Ecological Indicators, 155, 110940. |
| [44] | Zhang CY, Zhang Y, Zheng XJ, Gao XH, Hao ZZ (2024) Influence of recording devices and environmental noise on acoustic index scores: Implications for bird sound-based assessments. Ecological Indicators, 159, 111759. |
| [45] | Zhao Z, Xu ZY, Bellisario K, Zeng RW, Li N, Zhou WY, Pijanowski BC (2019) How well do acoustic indices measure biodiversity? Computational experiments to determine effect of sound unit shape, vocalization intensity, and frequency of vocalization occurrence on performance of acoustic indices. Ecological Indicators, 107, 105588. |
| [46] | Znidersic E, Towsey M, Roy WK, Darling SE, Truskinger A, Roe P, Watson DM (2020) Using visualization and machine learning methods to monitor low detectability species—The least bittern as a case study. Ecological Informatics, 55, 101014. |
| [1] | Haotian Bai, Shang Yu, Xinyuan Pan, Jiale Ling, Juan Wu, Kaiqi Xie, Yang Liu, Xueye Chen. AI-assisted recognition for passive acoustic monitoring of birds in urban wetland parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24188-. |
| [2] | Jiangjian Xie, Chen Shen, Feiyu Zhang, Zhishu Xiao. Cross-regional bird species recognition method integrating audio and ecological niche information [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24259-. |
| [3] | Qianrong Guo, Shufei Duan, Jie Xie, Xueyan Dong, Zhishu Xiao. Advances in bird sound annotation methods for passive acoustic monitoring [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24313-. |
| [4] | Yingying Liu, Lixin Gong, Hao Zeng, Jiang Feng, Yongjun Dong, Lei Wang, Tinglei Jiang. Application of passive acoustic monitoring in Chiropteran research [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24233-. |
| [5] | Wantao Huang, Zezhou Hao, Zixin Zhang, Zhishu Xiao, Chengyun Zhang. A comparison of bird sound recognition performance among acoustic recorders [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24273-. |
| [6] | Le Li, Chengyun Zhang, Nancai Pei, Bingtao Gao, Na Wang, Jiarui Li, Ruichen Wu, Zezhou Hao. Correlation analysis of urban green landscape patterns and bird diversity based on passive acoustic monitoring technology [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24296-. |
| [7] | Zezhou Hao, Chengyun Zhang, Le Li, Bingtao Gao, Wei Zeng, Chun Wang, Zixuan Wang, Wantao Huang, Yue Zhang, Nancai Pei, Zhishu Xiao. Applications of passive acoustic monitoring and evaluation in urban bird research [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24123-. |
| [8] | Wanjun Hu, Zezhou Hao, Canwei Xia, Jiangjian Xie. Wetland soundscape recording scheme and feature selection for soundscape classification [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24121-. |
| [9] | Zhishu Xiao, Jianguo Cui, Daiping Wang, Zhitao Wang, Jinhong Luo, Jie Xie. Interdisciplinary development trends of contemporary bioacoustics and the opportunities for China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22423-. |
| [10] | Yifei Sun, Shizheng Wang, Jiawei Feng, Tianming Wang. Diel and seasonal variability of the forest soundscape in the Northeast China Tiger and Leopard National Park [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22523-. |
| [11] | Shizheng Wang, Yifei Sun, Zhenzhen Li, Yue Shu, Jiawei Feng, Tianming Wang. Effects of bird migration on the temporal patterns of the wetland soundscape in the downstream region of the Tumen River Basin of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22337-. |
| [12] | Haigang Ma, Penglai Fan. Application, progress, and future perspective of passive acoustic monitoring in terrestrial mammal research [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22374-. |
| [13] | Keyi Wu, Wenda Ruan, Difeng Zhou, Qingchen Chen, Chengyun Zhang, Xinyuan Pan, Shang Yu, Yang Liu, Rongbo Xiao. Syllable clustering analysis-based passive acoustic monitoring technology and its application in bird monitoring [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22370-. |
| [14] | Qi Bian, Cheng Wang, He Cheng, Dan Han, Yilin Zhao, Luqin Yin. Exploring the application of acoustic indices in the assessment of bird diversity in urban forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22080-. |
| [15] | Enzhu Zhong, Zhenhua Guan, Xingce Zhou, Youjie Zhao, Han Li, Shaobin Tan, Kunrong Hu. Application of passive acoustic monitoring technology in the monitoring of western black crested gibbons [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(1): 109-117. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()