



Biodiv Sci ›› 2018, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (7): 738-748. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018017 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018017
• Original Papers: Microbial Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Shaoshuai Yu, Caili Lin, Shengjie Wang, Wenxin Zhang, Guozhong Tian*( )
)
Received:2018-01-16
Accepted:2018-03-26
Online:2018-07-20
Published:2018-09-11
Contact:
Tian Guozhong
About author:# Co-first authors
Shaoshuai Yu, Caili Lin, Shengjie Wang, Wenxin Zhang, Guozhong Tian. Structures of the tuf gene and its upstream part genes and characteristic analysis of conserved regions and activity from related gene promoters of a phytoplasma[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(7): 738-748.
| 引物 Primer | 序列 Sequence (5’-3’) | 长度 Length (nt) | Tm (℃) | G+C (%) | 扩增长度 Length amplified (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| op1 | 5'-GATTGACATGGCTAAGTTAACG-3' | 22 | 54.9 | 40.9 | 3,676 |
| op2 | 5'-TACACCTTTGTTTCCGTGGC-3' | 20 | 58.4 | 50.0 | |
| op3 | 5'-AGGTAGCGGTCAAGAAGAAAT-3' | 21 | 55.4 | 42.9 | 6,965 |
| op4 | 5'-GAACCGCAAAGAACTGGG-3' | 18 | 56.0 | 55.6 | |
| op5 | 5'-AATATTATTGACACTCCCGGAC-3' | 22 | 55.5 | 40.9 | 2,661 |
| op6 | 5'-ACTCTACCAGTAACAACAGTTCCTC-3' | 25 | 56.1 | 44.0 | |
| op7 | 5'-CACATTTTATTAGCGCGCC-3' | 19 | 57.2 | 47.4 | 1,519 |
| op8 | 5'-AAAACCTAACGCAATCATGG-3' | 20 | 55.5 | 40.0 |
Table 1 Information of the primers used to amplify the large DNA fragments
| 引物 Primer | 序列 Sequence (5’-3’) | 长度 Length (nt) | Tm (℃) | G+C (%) | 扩增长度 Length amplified (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| op1 | 5'-GATTGACATGGCTAAGTTAACG-3' | 22 | 54.9 | 40.9 | 3,676 |
| op2 | 5'-TACACCTTTGTTTCCGTGGC-3' | 20 | 58.4 | 50.0 | |
| op3 | 5'-AGGTAGCGGTCAAGAAGAAAT-3' | 21 | 55.4 | 42.9 | 6,965 |
| op4 | 5'-GAACCGCAAAGAACTGGG-3' | 18 | 56.0 | 55.6 | |
| op5 | 5'-AATATTATTGACACTCCCGGAC-3' | 22 | 55.5 | 40.9 | 2,661 |
| op6 | 5'-ACTCTACCAGTAACAACAGTTCCTC-3' | 25 | 56.1 | 44.0 | |
| op7 | 5'-CACATTTTATTAGCGCGCC-3' | 19 | 57.2 | 47.4 | 1,519 |
| op8 | 5'-AAAACCTAACGCAATCATGG-3' | 20 | 55.5 | 40.0 |
| 引物 Primer | 引物序列 Primer sequences (5’-3’) | 引物大小 Primer size (bp) | Tm (℃) | 引入酶切位点 Restriction site added |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPf | cccaagcttACAACCTTACACTAAAAAAC | 29 | 45 | Hind III |
| TP4f | cccaagcttACAACCTTAAACTAAAAAAC | 29 | 45 | Hind III |
| TPr | cgcggatcCATTTTTCAAAGGCCTC | 25 | 45 | BamH I |
Table 2 Primers used to amplify tuf gene promoters
| 引物 Primer | 引物序列 Primer sequences (5’-3’) | 引物大小 Primer size (bp) | Tm (℃) | 引入酶切位点 Restriction site added |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPf | cccaagcttACAACCTTACACTAAAAAAC | 29 | 45 | Hind III |
| TP4f | cccaagcttACAACCTTAAACTAAAAAAC | 29 | 45 | Hind III |
| TPr | cgcggatcCATTTTTCAAAGGCCTC | 25 | 45 | BamH I |
| 株系 Strain | 级别 Group | 扩增序列长度 Sequence amplified length (bp) | 编码区长度 Coding region length (bp) | 非编码区长度 Non-coding region length (bp) | 氨基酸长度/个 Amino acid sequence length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PaWB-sdyz | 16SrI-D | 12,746 | 12,307 | 439 | 4,096 |
| PaWB-fjfz | 16SrI-D | 12,745 | 12,307 | 438 | 4,096 |
| LY-fjya1 | 16SrI-B | 12,748 | 12,307 | 441 | 4,096 |
| OY-M | 16SrI-B | 12,745 | 12,307 | 438 | 4,096 |
| AYWB | 16SrI-A | 12,735 | 12,343 | 392 | 4,107 |
| PAa | 16SrXII | 12,611 | 12,211 | 400 | 4,063 |
| SLY | 16SrXII | 12,611 | 12,211 | 400 | 4,063 |
| AT | 16SrX | 12,835 | 12,301 | 534 | 4,093 |
| PG-8A | 4,587 | 4,158 | 429 | 1,382 |
Table 3 Length of sequence amplified, coding region, non-coding region and amino acid sequence of phytoplasmas as well as reference strains
| 株系 Strain | 级别 Group | 扩增序列长度 Sequence amplified length (bp) | 编码区长度 Coding region length (bp) | 非编码区长度 Non-coding region length (bp) | 氨基酸长度/个 Amino acid sequence length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PaWB-sdyz | 16SrI-D | 12,746 | 12,307 | 439 | 4,096 |
| PaWB-fjfz | 16SrI-D | 12,745 | 12,307 | 438 | 4,096 |
| LY-fjya1 | 16SrI-B | 12,748 | 12,307 | 441 | 4,096 |
| OY-M | 16SrI-B | 12,745 | 12,307 | 438 | 4,096 |
| AYWB | 16SrI-A | 12,735 | 12,343 | 392 | 4,107 |
| PAa | 16SrXII | 12,611 | 12,211 | 400 | 4,063 |
| SLY | 16SrXII | 12,611 | 12,211 | 400 | 4,063 |
| AT | 16SrX | 12,835 | 12,301 | 534 | 4,093 |
| PG-8A | 4,587 | 4,158 | 429 | 1,382 |
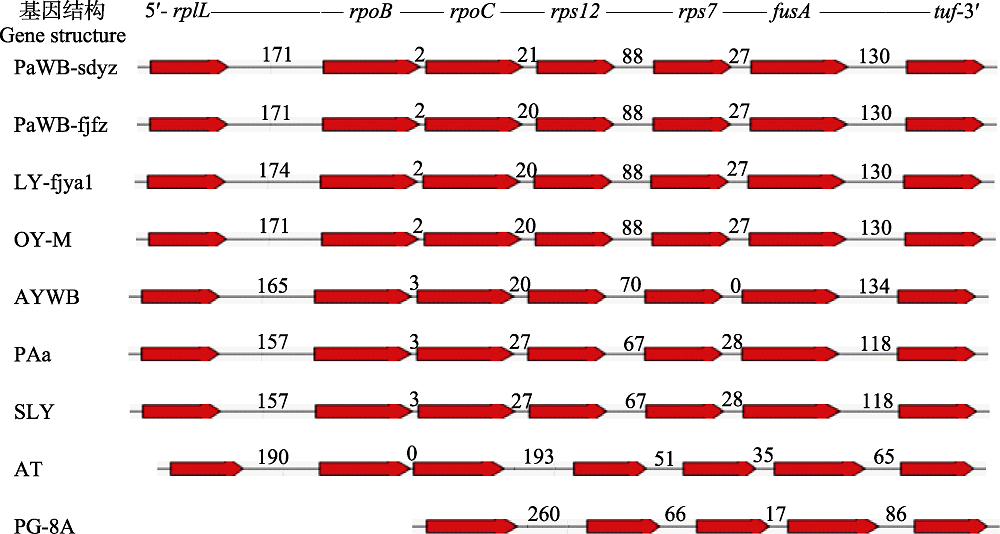
Fig. 1 Gene structure diagram of tuf gene and its upstream genes from different phytoplasmas. The codes of samples in the figure were shown in “1.1” and “1.2.3”. Numbers represented the length of intergenic sequences (bp).
| 株系 Strains | rplL-rpoB | rpoC-rps12 | rps12-rps7 | fusA-tuf | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -35 | -10 | -35 | -10 | -35 | -10 | -35 | -10 | |
| PaWB-sdyz | TTGCAT | TATACC | - | - | ATAAAA | AAAAAT | TTGTGA | TATATT |
| PaWB-fjfz | TTGCAT | TATACC | - | - | ATAAAA | AAAAAT | TTGTGA | TATATT |
| LY-fjya1 | TTGCAT | TATACC | - | - | ATAAAA | AAAAAT | TTGTAA | TATATT |
| OY-M | TTGAAT | TATAAC | - | - | ATAAAA | AAAAAT | TTGTGA | TATATT |
| AYWB | TTGCAT | TATACC | - | - | - | - | TTGTGA | TATTAT |
| PAa | TTGTAT | TTTAAT | - | - | - | - | TTGATA | TATATT |
| SLY | TTGTAT | TTTAAT | - | - | - | - | TTGATA | TATATT |
| AT | ATGATA | AATAAT | TTGACT | TATAAT | - | - | - | - |
| PG-8A | - | - | TTGACA | TATAAT | - | - | ATGATA | TATTGT |
Table 4 Characteristics of conserved region of relevant gene promoter of phytoplasma rplL-tuf intergenic sequences
| 株系 Strains | rplL-rpoB | rpoC-rps12 | rps12-rps7 | fusA-tuf | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -35 | -10 | -35 | -10 | -35 | -10 | -35 | -10 | |
| PaWB-sdyz | TTGCAT | TATACC | - | - | ATAAAA | AAAAAT | TTGTGA | TATATT |
| PaWB-fjfz | TTGCAT | TATACC | - | - | ATAAAA | AAAAAT | TTGTGA | TATATT |
| LY-fjya1 | TTGCAT | TATACC | - | - | ATAAAA | AAAAAT | TTGTAA | TATATT |
| OY-M | TTGAAT | TATAAC | - | - | ATAAAA | AAAAAT | TTGTGA | TATATT |
| AYWB | TTGCAT | TATACC | - | - | - | - | TTGTGA | TATTAT |
| PAa | TTGTAT | TTTAAT | - | - | - | - | TTGATA | TATATT |
| SLY | TTGTAT | TTTAAT | - | - | - | - | TTGATA | TATATT |
| AT | ATGATA | AATAAT | TTGACT | TATAAT | - | - | - | - |
| PG-8A | - | - | TTGACA | TATAAT | - | - | ATGATA | TATTGT |
| 保守区域 Conserved region | -35区 -35 region | -10区 -10 region | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 序列特征 Sequence characteristic | A(10) | A(0) | A(8) | A(17) | A(25) | A(85) | A(10) | A(96) | A(8) | A(98) | A(19) | A(0) |
| T(90) | T(100) | T(0) | T(75) | T(6) | T(15) | T(90) | T(4) | T(92) | T(2) | T(73) | T(90) | |
| G(0) | G(0) | G(92) | G(0) | G(67) | G(0) | G(0) | G(0) | G(0) | G(0) | G(0) | G(0) | |
| C(0) | C(0) | C(0) | C(8) | C(2) | C(0) | C(0) | C(0) | C(0) | C(0) | C(8) | C(10) | |
Table 5 Nucleotide and its frequency in different sites of conserved regions of some phytoplasma gene promoters
| 保守区域 Conserved region | -35区 -35 region | -10区 -10 region | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 序列特征 Sequence characteristic | A(10) | A(0) | A(8) | A(17) | A(25) | A(85) | A(10) | A(96) | A(8) | A(98) | A(19) | A(0) |
| T(90) | T(100) | T(0) | T(75) | T(6) | T(15) | T(90) | T(4) | T(92) | T(2) | T(73) | T(90) | |
| G(0) | G(0) | G(92) | G(0) | G(67) | G(0) | G(0) | G(0) | G(0) | G(0) | G(0) | G(0) | |
| C(0) | C(0) | C(0) | C(8) | C(2) | C(0) | C(0) | C(0) | C(0) | C(0) | C(8) | C(10) | |
| 株系 Strain | PaWB-sdyz | PaWB-fjfz | LY-fjya1 | OY-M | AYWB | PAa | SLY | AT | PG-8A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PaWB-sdyz | 100 | ||||||||
| PaWB-fjfz | 99.7 | 100 | |||||||
| LY-fjya1 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 100 | ||||||
| OY-M | 99.6 | 99.6 | 99.4 | 100 | |||||
| AYWB | 95.9 | 95.9 | 95.9 | 96.0 | 100 | ||||
| PAa | 81.1 | 81.1 | 81.2 | 81.1 | 81.1 | 100 | |||
| SLY | 81.1 | 81.1 | 81.2 | 81.1 | 81.1 | 99.9 | 100 | ||
| AT | 72.7 | 72.8 | 72.9 | 72.8 | 73.3 | 73.6 | 73.6 | 100 | |
| PG-8A | 71.2 | 71.3 | 71.4 | 71.3 | 71.4 | 71.3 | 71.3 | 70.9 | 100 |
Table 6 Homology matrix of rplL-tuf nucleotide sequence coding region in MLSA analysis
| 株系 Strain | PaWB-sdyz | PaWB-fjfz | LY-fjya1 | OY-M | AYWB | PAa | SLY | AT | PG-8A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PaWB-sdyz | 100 | ||||||||
| PaWB-fjfz | 99.7 | 100 | |||||||
| LY-fjya1 | 99.3 | 99.3 | 100 | ||||||
| OY-M | 99.6 | 99.6 | 99.4 | 100 | |||||
| AYWB | 95.9 | 95.9 | 95.9 | 96.0 | 100 | ||||
| PAa | 81.1 | 81.1 | 81.2 | 81.1 | 81.1 | 100 | |||
| SLY | 81.1 | 81.1 | 81.2 | 81.1 | 81.1 | 99.9 | 100 | ||
| AT | 72.7 | 72.8 | 72.9 | 72.8 | 73.3 | 73.6 | 73.6 | 100 | |
| PG-8A | 71.2 | 71.3 | 71.4 | 71.3 | 71.4 | 71.3 | 71.3 | 70.9 | 100 |
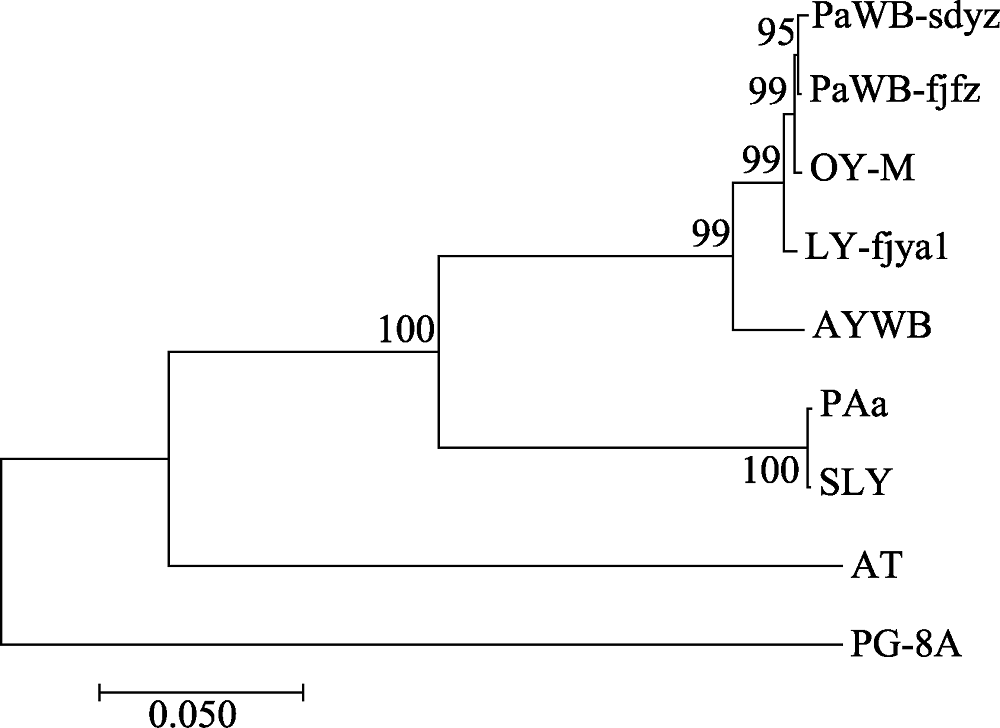
Fig. 2 Phylogenetic tree of the phytoplasma strains reconstructed based on the concatenated gene sequences data set of rplL-tuf nucleotide sequence coding region. The codes in the figure were shown in “1.1” and “1.2.3”.
| 株系 Strain | PaWB-sdyz | PaWB-fjfz | LY-fjya1 | OY-M | AYWB | PAa | SLY | AT | PG-8A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PaWB-sdyz | 100 | ||||||||
| PaWB-fjfz | 99.3 | 100 | |||||||
| LY-fjya1 | 99.3 | 98.6 | 100 | ||||||
| OY-M | 99.3 | 98.6 | 98.6 | 100 | |||||
| AYWB | 94.6 | 94.3 | 94.1 | 94.1 | 100 | ||||
| PAa | 71.9 | 71.8 | 71.3 | 72.3 | 73.2 | 100 | |||
| SLY | 71.9 | 71.8 | 71.3 | 72.3 | 73.2 | 100 | 100 | ||
| AT | 50.7 | 51.3 | 51.4 | 51.3 | 51.1 | 51.4 | 51.4 | 100 | |
| PG-8A | 41.8 | 41.3 | 41.5 | 41.8 | 41.3 | 40.2 | 40.2 | 44.8 | 100 |
Table 7 Homology matrix of rplL-tuf nucleotide sequence non-coding region in MLSA analysis
| 株系 Strain | PaWB-sdyz | PaWB-fjfz | LY-fjya1 | OY-M | AYWB | PAa | SLY | AT | PG-8A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PaWB-sdyz | 100 | ||||||||
| PaWB-fjfz | 99.3 | 100 | |||||||
| LY-fjya1 | 99.3 | 98.6 | 100 | ||||||
| OY-M | 99.3 | 98.6 | 98.6 | 100 | |||||
| AYWB | 94.6 | 94.3 | 94.1 | 94.1 | 100 | ||||
| PAa | 71.9 | 71.8 | 71.3 | 72.3 | 73.2 | 100 | |||
| SLY | 71.9 | 71.8 | 71.3 | 72.3 | 73.2 | 100 | 100 | ||
| AT | 50.7 | 51.3 | 51.4 | 51.3 | 51.1 | 51.4 | 51.4 | 100 | |
| PG-8A | 41.8 | 41.3 | 41.5 | 41.8 | 41.3 | 40.2 | 40.2 | 44.8 | 100 |
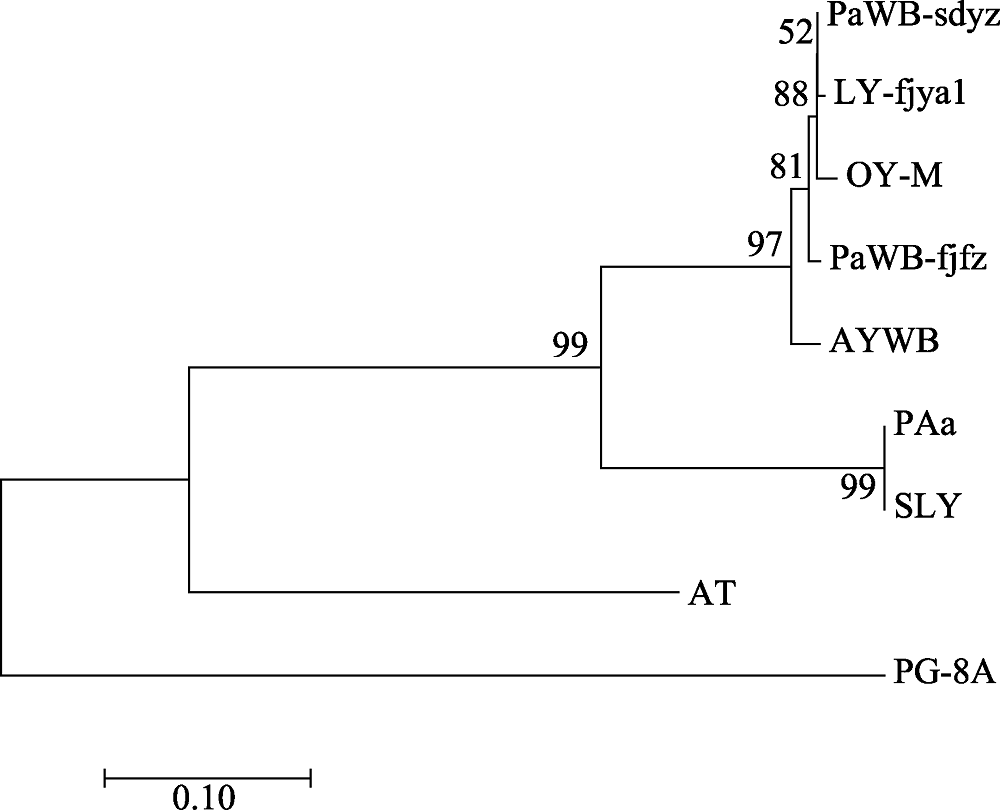
Fig. 3 Phylogenetic tree of the phytoplasma strains reconstructed based on the concatenated gene sequences data set of rplL-tuf nucleotide sequence non-coding region. The codes in the figure are shown in “1.1” and “1.2.3”.
| 株系 Strain | PaWB-sdyz | PaWB-fjfz | LY-fjya1 | OY-M | AYWB | PAa | SLY | AT | PG-8A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PaWB-sdyz | 100 | ||||||||
| PaWB-fjfz | 99.6 | 100 | |||||||
| LY-fjya1 | 98.9 | 99.0 | 100 | ||||||
| OY-M | 99.4 | 99.5 | 99.2 | 100 | |||||
| AYWB | 97.8 | 97.9 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 100 | ||||
| PAa | 83.8 | 83.9 | 84.1 | 83.9 | 83.7 | 100 | |||
| SLY | 83.8 | 83.9 | 84.1 | 83.9 | 83.7 | 99.8 | 100 | ||
| AT | 69.8 | 69.9 | 70.0 | 69.9 | 69.8 | 69.0 | 69.0 | 100 | |
| PG-8A | 74.9 | 75.1 | 74.9 | 75.0 | 74.8 | 74.1 | 73.9 | 70.4 | 100 |
Table 8 Homology matrix of RplL-TUF amino acid sequence in MLSA analysis
| 株系 Strain | PaWB-sdyz | PaWB-fjfz | LY-fjya1 | OY-M | AYWB | PAa | SLY | AT | PG-8A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PaWB-sdyz | 100 | ||||||||
| PaWB-fjfz | 99.6 | 100 | |||||||
| LY-fjya1 | 98.9 | 99.0 | 100 | ||||||
| OY-M | 99.4 | 99.5 | 99.2 | 100 | |||||
| AYWB | 97.8 | 97.9 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 100 | ||||
| PAa | 83.8 | 83.9 | 84.1 | 83.9 | 83.7 | 100 | |||
| SLY | 83.8 | 83.9 | 84.1 | 83.9 | 83.7 | 99.8 | 100 | ||
| AT | 69.8 | 69.9 | 70.0 | 69.9 | 69.8 | 69.0 | 69.0 | 100 | |
| PG-8A | 74.9 | 75.1 | 74.9 | 75.0 | 74.8 | 74.1 | 73.9 | 70.4 | 100 |
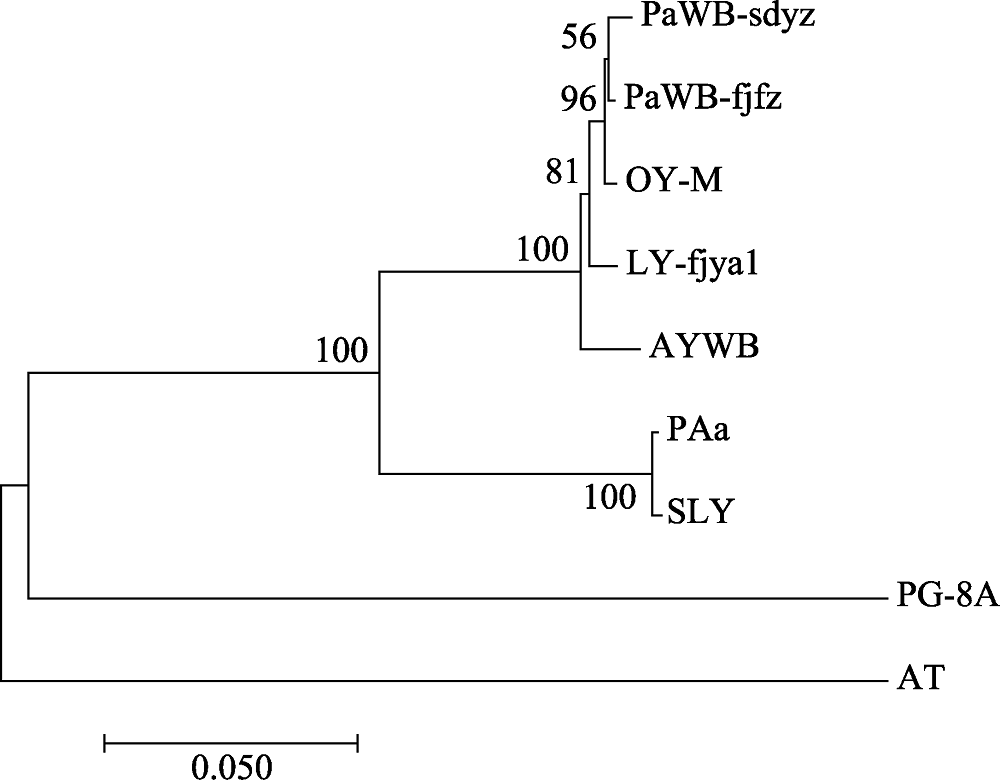
Fig. 4 Phylogenetic tree of the phytoplasma strains reconstructed based on the concatenated sequences data set of RplL-TUF amino acid sequence. The codes in the figure are shown in “1.1” and “1.2.3”.
| [1] | Andersen MT, Liefting LW, Havukkala I, Beever RE (2013) Comparison of the complete genome sequence of two closely related isolates of ‘Candidatus phytoplasma australiense’ reveals genome plasticity. BMC Genomics, 14, 529. |
| [2] | Bai XD, Zhang JH, Ewing A, Miller SA, Radek AJ, Shevchenko DV, Tsukerman K, Walunas T, Lapidus A, Campbell JW, Hogenhout SA (2006) Living with genome instability: The adaptation of phytoplasma to diverse environments of their insect and plant hosts. Journal of Bacteriology, 188, 3682-3696. |
| [3] | Du HT, Zhu HY, Wang JM, Zhao W, Tao XL, Ba CF, Tian YM, Su YH (2014) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms and activity analysis of the promoter and enhancer of the pig lactase gene. Gene, 545, 56-60. |
| [4] | Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution, 39, 783-791. |
| [5] | Ishii Y, Kakizawa S, Hoshi A, Maejima K, Kagiwada S, Yamaji Y, Oshima K, Namba S (2009) In the non-insect- transmissible line of onion yellows phytoplasma (OY-NIM), the plasmid-encoded transmembrane protein ORF3 lacks the major promoter region. Microbiology, 155, 2058-2067. |
| [6] | Kube M, Schneider B, Kuhl H, Dandekar T, Heitmann K, Migdoll AM, Reinhardt R, Seemüller E (2008) The linear chromosome of the plant-pathogenic mycoplasma ‘Candidatus phytoplasma mali’. BMC Genomics, 9, 306. |
| [7] | Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33, 1870-1874. |
| [8] | Lee IM, Hammond RW, Davis RE, Gundersen DE (1993) Universal amplification and analysis of pathogen 16S rDNA for classification and identification of mycoplasma like organisms. Phytopathology, 83, 834-842. |
| [9] | Li MG (2004) Advanced Molecular Genetics. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李明刚 (2004) 高级分子遗传学. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [10] | Liu Z, Zhang L, Xue C, Fang H, Zhao J, Liu M (2017) Genome-wide identification and analysis of MAPK and MAPKK gene family in Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.). BMC Genomics, 18, 855. |
| [11] | Miyata S, Furuki K, Oshima K, Sawayanagi T, Nishigawa H, Jung HY, Ugaki M, Namba S (2002a) Complete nucleotide sequence of the S10-spc operon of phytoplasma: Gene organization and genetic code resemble those of Bacillus subtilis. DNA and Cell Biology, 21, 527-534. |
| [12] | Miyata S, Furuki K, Sawayanagi T, Oshima K, Kuboyama T, Tsuchizaki T, Ugaki M, Namba S (2002b) Gene arrangement and sequence of str operon of phytoplasma resemble those of Bacillus more than those of Mycoplasma. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 68, 62-67. |
| [13] | Oshima K, Kakizawa S, Nishigawa H, Jung HY, Wei W, Suzuki S, Arashida R, Nakata D, Miyata S, Ugaki M, Namba S (2004) Reductive evolution suggested from the complete genome sequence of a plant-pathogenic phytoplasma. Nature Genetics, 36, 27-29. |
| [14] | Post LE, Nomura M (1980) DNA sequences from the str operon of Escherichia coli. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 255, 4660-4666. |
| [15] | Ren ZG (2014) The Qualitative and Quantitative Detection and Identification of Several Important Phytoplasmas in China. Postdoctoral Research Report, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [任争光 (2014) 我国几种重要植原体定性和定量检测鉴定研究.博士后研究报告, 中国林业科学研究院, 北京.] | |
| [16] | Salehi M, Hosseini SAE, Salehi E, Bertaccini A (2017) Genetic diversity and vector transmission of phytoplasmas associated with sesame phyllody in Iran. Folia Microbiologica, 62, 99-109. |
| [17] | Sanangelantoni AM, Tiboni O (1993) The chromosomal location of genes for elongation factor Tu and ribosomal protein S10 in the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis provides clues to the ancestral organization of the str and S10 operons in prokaryotes. Journal of General Microbiology, 139, 2579-2584. |
| [18] | Tran-Nguyen LTT, Kube M, Schneider B, Reinhardt R, Gibb KS (2008) Comparative genome analysis of ‘Candidatus phytoplasma australiense’ (subgroup tuf-Australia I; rp-A) and ‘Ca. phytoplasma asteris’ strains OY-M and AY-WB. Journal of Bacteriology, 190, 3979-3991. |
| [19] | Turner PC (translated by Liu JY, Liu WY) (2010) Molecular Biology, 3rd edn. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [特纳(著), 刘进元, 刘文颖 (译) (2010) 分子生物学, 第3版. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [20] | Wang SJ (2017) Establishment of Molecular Detection Technology and Genetic Diversity Analysis of Plant Phytoplasma in China. PhD dissertation, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王圣洁 (2017) 重要林木植原体分子检测技术的研发和遗传多样性研究. 博士学位论文, 中国林业科学研究院, 北京.] | |
| [21] | Yang YH (2008) Molecular Biology of the Gene. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [杨业华 (2008) 基因的分子生物学. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [22] | Yu SS, Xu QC, Lin CL, Wang SJ, Tian GZ (2016a) Genetic diversity of phytoplasmas: Research status and prospects. Biodiversity Science, 24, 205-215. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于少帅, 徐启聪, 林彩丽, 王圣洁, 田国忠 (2016a) 植原体遗传多样性研究现状与展望. 生物多样性, 24, 205-215.] | |
| [23] | Yu SS, Lin CL, Pan J, Ren ZG, Piao CG, Wang LF, Guo MW, Tian GZ (2016b) Comparative analysis of structure, function and genetic variation of upstream sequences adjoining tuf gene in paulownia and jujube witches’-broom phytoplasmas. Microbiology China, 43, 1060-1069. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于少帅, 林彩丽, 潘皎, 任争光, 朴春根, 汪来发, 郭民伟, 田国忠 (2016b) 泡桐丛枝和枣疯病植原体tuf基因上游序列结构、功能和遗传变异比较分析. 微生物学通报, 43, 1060-1069.] | |
| [24] | Zhang Y, Han Q, Li C, Li W, Fan H, Xing Q, Yan B (2014) Genetic analysis of the TBX1 gene promoter in indirect inguinal hernia. Gene, 535, 290-293. |
| [25] | Zhu YX, Li Y (2002)Modern Molecular Biology, 2nd edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [朱玉贤, 李毅 (2002)现代分子生物学, 第2版. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [26] | Zurawski G, Zurawski SM (1985) Structure of the Escherichia coli S10 ribosomal protein operon. Nucleic Acids Research, 13, 4521-4526. |
| [1] | Jiachen Wang, Tangjun Xu, Wei Xu, Gaoji Zhang, Yijin You, Honghua Ruan, Hongyi Liu. Impact of urban landscape pattern on the genetic structure of Thereuopoda clunifera population in Nanjing, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | Kexin Cao, Jingwen Wang, Guo Zheng, Pengfeng Wu, Yingbin Li, Shuyan Cui. Effects of precipitation regime change and nitrogen deposition on soil nematode diversity in the grassland of northern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [3] | Shiyi Long, Bobo Zhang, Yuchen Xia, Yangfan Fei, Yani Meng, Bingwei Lü, Yueqing Song, Pu Zheng, Taoran Guo, Jian Zhang, Shaopeng Li. Effects of diversity and temporal stability of native communities on the biomass of invasive species Solidago canadensis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24263-. |
| [4] | Linjun He, Wenjing Yang, Yuhao Shi, Kezhemo Ashuo, Yu Fan, Guoyan Wang, Jingji Li, Songlin Shi, Guihua Yi, Peihao Peng. Effects of plant community phylogeny and functional diversity on Ageratina adenophora invasion under fire disturbance [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24269-. |
| [5] | Qingduo Li, Dongmei Li. Analysis for the prevalence of global bat-borne Bartonella [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [6] | Chen Feng, Jie Zhang, Hongwen Huang. Parallel situ conservation: A new plant conservation strategy to integrate in situ and ex situ conservation of plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [7] | Hailing Qi, Pengzhen Fan, Yuehua Wang, Jie Liu. Genetic diversity and population structure of Juglans regia from six provinces in northern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [8] | Yuanyuan Xiao, Wei Feng, Yangui Qiao, Yuqing Zhang, Shugao Qin. Effects of soil microbial community characteristics on soil multifunctionality in sand-fixation shrublands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22585-. |
| [9] | Fei Xiong, Hongyan Liu, Dongdong Zhai, Xinbin Duan, Huiwu Tian, Daqing Chen. Population genetic structure of Pelteobagrus vachelli in the upper Yangtze River based on genome re-sequencing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [10] | Yiyue He, Yuying Liu, Fubin Zhang, Qiang Qin, Yu Zeng, Zhenyu Lü, Kun Yang. Genetic diversity and population structure of Saurogobio dabryi under cascade water conservancy projects in the Jialing River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [11] | Weiyue Sun, Jiangping Shu, Yufeng Gu, Morigengaowa, Xiajin Du, Baodong Liu, Yuehong Yan. Conservation genomics analysis revealed the endangered mechanism of Adiantum nelumboides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [12] | Xiaoyan Jiang, Shengjie Gao, Yan Jiang, Yun Tian, Xin Jia, Tianshan Zha. Species diversity, functional diversity, and phylogenetic diversity in plant communities at different phases of vegetation restoration in the Mu Us sandy grassland [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21387-. |
| [13] | Togtokh Mongke, Dongyi Bai, Tugeqin Bao, Ruoyang Zhao, Tana An, Aertengqimike Tiemuqier, Baoyindeligeer Mongkejargal, Has Soyoltiin, Manglai Dugarjaviin, Haige Han. Assessment of SNPs-based genomic diversity in different populations of Eastern Asian landrace horses [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [14] | Jing Cui, Mingfang Xu, Qun Zhang, Yao Li, Xiaoshu Zeng, Sha Li. Differences in genetic diversity of Pleuronichthys cornutus in the coastal water of China and Japan based on three mitochondrial markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [15] | Xinyu Cai, Xiaowei Mao, Yiqiang Zhao. Methods and research progress on the origin of animal domestication [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(4): 21457-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()