



Biodiv Sci ›› 2016, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (11): 1279-1287. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016024 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016024
Special Issue: 生物入侵
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lin Liu1, Shuqing An2, Yingbiao Zhi3, Mingxiang Zhang1, Hongli Li1,*( )
)
Received:2016-01-17
Accepted:2016-05-09
Online:2016-11-20
Published:2016-12-14
Contact:
Li Hongli
Lin Liu, Shuqing An, Yingbiao Zhi, Mingxiang Zhang, Hongli Li. Effects of different sediment type and burial depth on growth traits and biomass accumulation of Spartina anglica[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(11): 1279-1287.
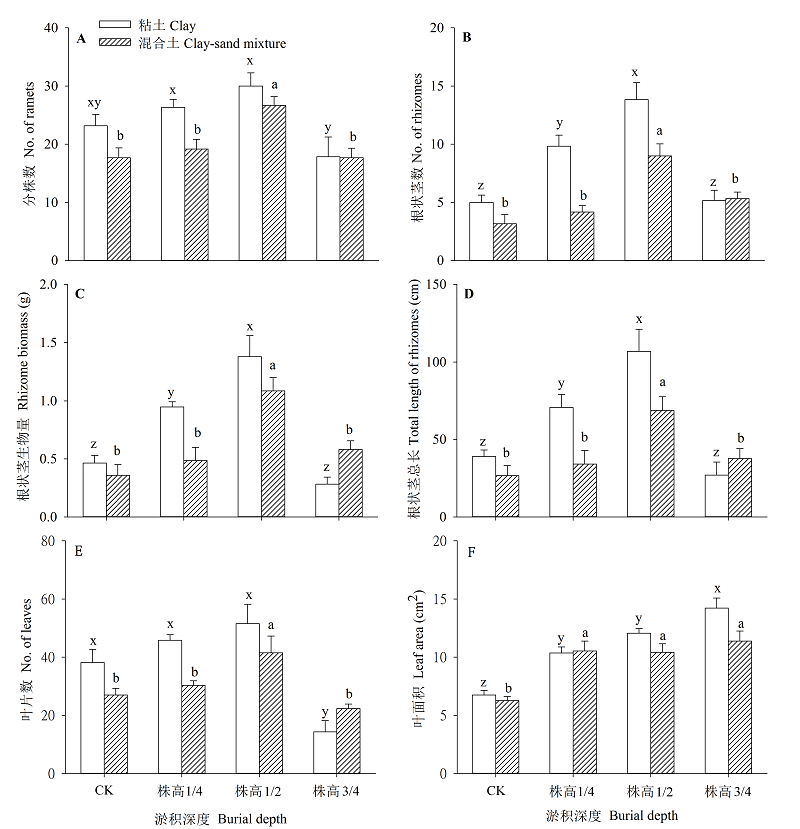
Fig. 1 Clonal and leaf traits of Spartina anglica under different soil types and the four burial depth treatments (Mean + SE). Means sharing the same letter are not different at P = 0.05 within sediment type treatments (Duncan tests). Furthermore, CK, 1/4 plant height, 1/2 height and 3/4 height were established with unburied, 25% buried, 50% buried and 75% buried, respectively.
| 性状指标 Traits | 土壤质地 Sediment type (S) | 淤积深度 Burial depth (B) | 土壤质地×淤积深度 S × B | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1, 40 | P | F3, 40 | P | F3, 40 | P | |||
| (A)克隆繁殖和叶性状指标 Clonal and leaf traits | ||||||||
| 分株数 No. of ramets | 7.9 | 0.008 | 9.8 | <0.001 | 1.1 | 0.359 | ||
| 根状茎数 No. of rhizomes | 6.5 | 0.014 | 25.4 | <0.001 | 4.5 | 0.008 | ||
| 根状茎生物量 Rhizome biomass | 3.9 | 0.057 | 28.5 | <0.001 | 5.2 | 0.004 | ||
| 根状茎总长 Total length of rhizomes | 9.8 | 0.003 | 18.1 | <0.001 | 3.6 | 0.023 | ||
| 叶片数 No. of leaves | 6.4 | 0.015 | 17.5 | <0.001 | 3.4 | 0.028 | ||
| 叶面积 Leaf area | 6.5 | 0.014 | 32.9 | <0.001 | 2.0 | 0.127 | ||
| (B)生物量积累 Biomass accumulation | ||||||||
| 总生物量 Total biomass | 1.0 | 0.328 | 49.4 | <0.001 | 10.8 | <0.001 | ||
| 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass | 0.1 | 0.770 | 48.0 | <0.001 | 12.1 | <0.001 | ||
| 地下生物量 Belowground biomass | 6.6 | 0.014 | 44.1 | <0.001 | 7.3 | <0.001 | ||
| 根生物量 Root biomass | 11.0 | 0.002 | 23.8 | <0.001 | 2.6 | 0.064 | ||
Table 1 Results of ANOVAs testing the effects of sediment type and burial depth on clonal and growth traits, and biomass accumulation of Spartina anglica
| 性状指标 Traits | 土壤质地 Sediment type (S) | 淤积深度 Burial depth (B) | 土壤质地×淤积深度 S × B | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1, 40 | P | F3, 40 | P | F3, 40 | P | |||
| (A)克隆繁殖和叶性状指标 Clonal and leaf traits | ||||||||
| 分株数 No. of ramets | 7.9 | 0.008 | 9.8 | <0.001 | 1.1 | 0.359 | ||
| 根状茎数 No. of rhizomes | 6.5 | 0.014 | 25.4 | <0.001 | 4.5 | 0.008 | ||
| 根状茎生物量 Rhizome biomass | 3.9 | 0.057 | 28.5 | <0.001 | 5.2 | 0.004 | ||
| 根状茎总长 Total length of rhizomes | 9.8 | 0.003 | 18.1 | <0.001 | 3.6 | 0.023 | ||
| 叶片数 No. of leaves | 6.4 | 0.015 | 17.5 | <0.001 | 3.4 | 0.028 | ||
| 叶面积 Leaf area | 6.5 | 0.014 | 32.9 | <0.001 | 2.0 | 0.127 | ||
| (B)生物量积累 Biomass accumulation | ||||||||
| 总生物量 Total biomass | 1.0 | 0.328 | 49.4 | <0.001 | 10.8 | <0.001 | ||
| 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass | 0.1 | 0.770 | 48.0 | <0.001 | 12.1 | <0.001 | ||
| 地下生物量 Belowground biomass | 6.6 | 0.014 | 44.1 | <0.001 | 7.3 | <0.001 | ||
| 根生物量 Root biomass | 11.0 | 0.002 | 23.8 | <0.001 | 2.6 | 0.064 | ||
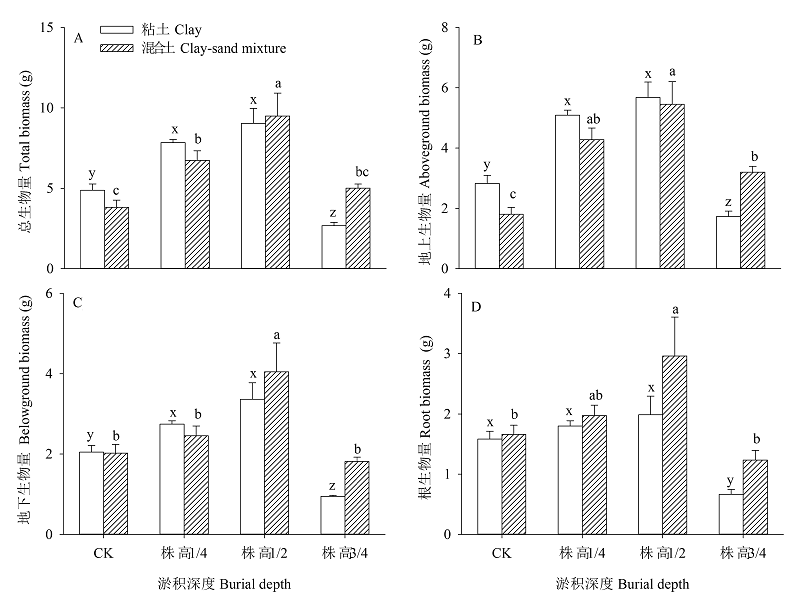
Fig. 2 Biomass of Spartina anglica under differet soil types and the four burial depth treatments (Mean + SE). Means sharing the same letter are not different at P = 0.05 within sediment type treatments (Duncan tests). Furthermore, CK, 1/4 plant height, 1/2 plant height and 3/4 plant height were established with unburied, 25% buried, 50% buried and 75% buried, respectively.
| 1 | An SQ, Gu BH, Zhou CF, Wang ZS, Deng ZF, Zhi YB, Li HL, Chen L, Yu DH, Liu YH (2007) Spartina invasion in China: implications for invasive species management and future research. Weed Research, 47, 183-191. |
| 2 | Balke T, Klaassen PC, Garbutt A, Wal DVD, Herman PMJ, Bouma TJ (2012) Conditional outcome of ecosystem engineering: a case study on tussocks of the salt marsh pioneer Spartina anglica. Geomorphology, 153-154, 232-238. |
| 3 | Brown JF (1997) Effects of experimental burial on survival, growth, and resource allocation of three species of dune plants. Journal of Ecology, 85, 151-158. |
| 4 | Chen JH, Wang L, Li YL, Zhang WQ, Fu XH, Le YQ (2012) Effect of Spartina alterniflora invasion and its controlling technologies on soil microbial respiration of a tidal wetland in Chongming Dongtan, China. Ecological Engineering, 41, 52-59. |
| 5 | Chung CH, Zhuo RZ, Xu GW (2004) Creation of Spartina plantations for reclaiming Dongtai, China, tidal flats and offshore sands. Ecological Engineering, 23, 135-150. |
| 6 | Crawford JT, Stone AG (2015) Relationships between soil composition and Spartina alterniflora die back in an Atlantic salt marsh. Wetlands, 35, 13-20. |
| 7 | Cutajar J, Shimeta J, Nugegoda D (2012) Impacts of the invasive grass Spartina anglica on benthic macrofaunal assemblages in a temperate Australian saltmarsh. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 464, 107-120. |
| 8 | Deng ZF, An SQ, Zhi YB, Zhou CF, Chen L, Zhao CJ, Fang SB, Li HL (2006) Preliminary studies on invasive model and outbreak mechanism of exotic species, Spartina alterniflora Loisel. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26, 2678-2686. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邓自发, 安树青, 智颖飙, 周长芳, 陈琳, 赵聪蛟, 方淑波, 李红丽 (2006) 外来种互花米草入侵模式与爆发机制. 生态学报, 26, 2678-2686.] | |
| 9 | Deng ZF, An SQ, Zhao CJ, Chen L, Zhou CF, Zhi YB, Li HL (2008) Sediment burial stimulates the growth and propagule production of Spartina alterniflora Loisel. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 76, 818-826. |
| 10 | Ewing K (1996) Tolerance of four wetland plant species to flooding and sediment deposition. Environmental & Experimental Botany, 36, 131-146. |
| 11 | Gao XY, Dou XP, Zhu MC (2013) Research of hazard evaluation on sediment deposition downstream of the sluice in estuaries. The Ocean Engineering, 31(5), 55-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高祥宇, 窦希萍, 朱明成 (2013) 入海河口闸下河道泥沙淤积危害评估研究. 海洋工程, 31(5), 55-61.] | |
| 12 | He J, Zhao CJ, Qing H, Gan L, An SQ (2009) Effect of soil-water condition on morphological plasticity of clonal plant Spartina alterniflora. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29, 3518-3524. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [何军, 赵聪蛟, 清华, 甘琳, 安树青 (2009) 土壤水分条件对克隆植物互花米草表型可塑性的影响. 生态学报, 29, 3518-3524.] | |
| 13 | Jarvis JC, Moore KA (2015) Effects of seed source, sediment type, and burial depth on mixed-annual and perennial Zostera marina L. seed germination and seedling establishment. Estuaries and Coasts, 38, 964-978. |
| 14 | Jiang M, Lü XG, Yang Q (2006) Wetland soil and its system of environmental function assessment. Wetland Science, 4, 168-173. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姜明, 吕宪国, 杨青 (2006) 湿地土壤及其环境功能评价体系. 湿地科学, 4, 168-173.] | |
| 15 | Kent M, Owen NW, Dale P, Newnham RM, Giles TM (2001) Studies of vegetation burial: a focus for biogeography and biogeomorphology? Progress in Physical Geography, 25, 455-482. |
| 16 | Kim D, Caims DM, Bartholdy J (2013) Tidal creek morphology and sediment type influence spatial trends in salt marsh vegetation. The Professional Geographer, 65, 544-560. |
| 17 | Koch EW (2001) Beyond light: physical, geological, and geochemical parameters as possible submersed aquatic vegetation habitat requirements. Estuaries, 24, 1-17. |
| 18 | Li HL, Lei GC, Zhi YB, Perter B, Zhao L, Wang Y, Deng ZF, Liu YH, Liu FD, An SQ (2011) Phenotypic responses of Spartina anglica to duration of tidal immersion. Ecological Research, 26, 395-402 |
| 19 | Li HL, Wang YY, An SQ, Zhi YB, Lei GC, Zhang MX (2014a) Sediment type affects competition between a native and an exotic species in coastal China. Scientific Reports, 4, 6748. |
| 20 | Li HL, An SQ, Zhi YB, Chao Y, Zhao L, Zhou CF, Deng ZF, Su W, Liu YH (2008) Protogynous, pollen limitation and low seed production reasoned for the dieback of Spartina anglica in coastal China. Plant Science, 174, 299-309. |
| 21 | Li HL, Zhi YB, An SQ, Zhao L, Zhou CF, Deng ZF, Gu SP (2009) Density-dependent effects on the dieback of exotic species Spartina anglica in coastal China. Ecological Engineering, 35, 544-552. |
| 22 | Li HL, Zhi YB, Lei GC, Zhao L, An SQ, Deng ZF (2010) Physiological responses of clonal plant Spartina anglica to simulated tidal waterlogging time. Wetland Science, 8, 125-131. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李红丽, 智颖飙, 雷光春, 安树青, 赵磊, 邓自发 (2010) 外来克隆植物大米草对模拟潮汐淹水时间的生理响应. 湿地科学, 8, 125-131.] | |
| 23 | Li HL, Zhi YB, Zhao L, An SQ, Deng ZF, Zhou CF, Gu SP (2007) Eco-physiological responses of the declining population Spartina anglica to N and P fertilizer addition. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27, 2725-2732. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李红丽, 智颖飙, 赵磊, 安树青, 邓自发, 周长芳, 顾舒平 (2007) 大米草(Spartina anglica)自然衰退种群对N、P添加的生态响应. 生态学报, 27, 2725-2732.] | |
| 24 | Li QY, Zhao WZ (2006) Seedling emergence and growth responses of five desert species to sand burial depth. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26, 1802-1808. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李秋艳, 赵文智 (2006) 五种荒漠植物幼苗出土及生长对沙埋深度的响应. 生态学报, 26, 1802-1808.] | |
| 25 | Li XP, Tang GG, Wang DS, Xu HQ (1998) Studies on the community characteristics, the distribution and succession patterns of wetland vegetation in Jiangsu Province. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences), 22, 47-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李湘萍, 汤庚国, 王定胜, 徐惠强 (1998) 江苏湿地植物群落学特征及其分布和演替规律. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 22, 47-52.] | |
| 26 | Li ZJ, Wang WQ, Zhang YH (2014b) Recruitment and herbivory affect spread of invasive Spartina alterniflora in China. Ecology, 95, 1972-1980. |
| 27 | Mariska TB, Nicola S, Han O, Wim HP (2009) Plant-soil feedback induces shifts in biomass allocation in the invasive plant Chromolaena odorata. Journal of Ecology, 97, 1281-1290. |
| 28 | Maun MA (2011) Adaptations of plants to burial in coastal sand dunes. Canadian Journal of Botany, 76, 713-738. |
| 29 | Min FY, Wang YP (2008) Study on the sediment siltation downstream tidal barriers in the north of Jiangsu Province. Marine Science, 32(12), 87-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [闵凤阳, 汪亚平 (2008) 江苏淤泥质海岸入海河道闸下淤积研究. 海洋科学, 32(12), 87-91.] | |
| 30 | Nehring S, Hesse K (2008) Invasive alien plants in marine protected areas: the Spartina anglica affair in the European Wadden Sea. Biological Invasions, 10, 937-950. |
| 31 | Nie HL, Wu N, Liang SM, Wang HL, Zhang YM (2006) Effects of different sand burial depths on the growth of fragments of Tortula desertorum. Arid Zone Research, 23(1), 66-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [聂华丽, 吴楠, 梁少民, 王红玲, 张元明 (2006) 不同沙埋深度对刺叶墙藓植株碎片生长的影响. 干旱区研究, 23(1), 66-70.] | |
| 32 | Nielsen LK, Vermaat JE, Wesseling I, Borum J, Hansen O (2002) Sediment properties along gradients of siltation in South-East Asia. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 54, 127-137. |
| 33 | Owen NW, Martin K, Pamela DM (2004) Plant species and community responses to sand burial on the machair of the Outer Hebrides, Scotland. Journal of Vegetation Science, 15, 669-678. |
| 34 | Perumal VJ, Maun MA (2006) Ecophysiological response of dune species to experimental burial under field and controlled conditions. Vegetatio, 184, 89-104. |
| 35 | Pezeshki SR, Delaune RD, Pardue JH (1992) Sediment addition enhances transpiration and growth of Spartina alterniflora in deteriorating Louisiana Gulf Coast salt marshes. Wetlands Ecology & Management, 1, 185-189. |
| 36 | Pye K (1995) Controls on long-term saltmarsh accretion and erosion in the Wash, eastern England. Journal of Coastal Research, 11, 337-356. |
| 37 | Ren ME (1986)The integrative investigation reports of coastal line and tideland resources in Jiangsu Province, China. Marine Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [任美锷 (1986)江苏海岸带与海涂资源综合调查报告. 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| 38 | Sánchez JM, Sanleon DG, Izco J (2001) Primary colonisation of mudflat estuaries by Spartina maritima (Curtis) Fernald in Northwest Spain: vegetation structure and sediment accretion. Aquatic Botany, 69, 15-25. |
| 39 | Sciegienka JK, Keren EN, Menalled FD (2011) Impact of root fragment dimension, weight, burial depth, and water regime on Cirsium arvense emergence and growth. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 91, 1027-1036. |
| 40 | Shen YM, Zeng H, Wang H, Liu YM, Chen ZY (2005) Characteristics of halophyte and associated soil along aggradational muddy coasts in Jiangsu Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25, 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈永明, 曾华, 王辉, 刘咏梅, 陈子玉 (2005) 江苏典型淤长岸段潮滩盐生植被及其土壤肥力特征. 生态学报, 25, 1-6.] | |
| 41 | Sun ZG, Song HL, Sun WG, Sun J (2014) Effects of continual burial by sediment on morphological traits and dry mass allocation of Suaeda salsa seedlings in the Yellow River estuary: an experimental study. Ecological Engineering, 68, 176-183. |
| 42 | Tian YB, Song GY, Ai TC (2002) Wetland soil and its ecological functions. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 21(6), 36-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [田应兵, 宋光煜, 艾天成 (2002) 湿地土壤及其生态功能. 生态学杂志, 21(6), 36-39.] | |
| 43 | Walls RL, Wardrop DH, Brooks RP (2005) The impact of experimental sedimentation and flooding on the growth and germination of floodplain trees. Plant Ecology, 176, 203-213. |
| 44 | Wang Q, An SQ, Ma ZJ, Zhao B, Chen JK, Li B (2006) Invasive Spartina alterniflora: biology, ecology and management. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica, 44, 559-588. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王卿, 安树青, 马志军, 赵斌, 陈家宽, 李博 (2006) 入侵植物互花米草——生物学、生态学及管理. 植物分类学报, 44, 559-588.] | |
| 45 | Willis JM, Hester MW (2004) Interactive effects of salinity, flooding, and soil type on Panicum hemitomon. Wetlands, 24, 43-50. |
| 46 | Yang D, Wan FX (2014) Research progress on invasive alien species Spartina alterniflora. Plant Protection, 40(2), 5-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨东, 万福绪 (2014) 外来入侵种互花米草的研究进展. 植物保护, 40(2), 5-10.] | |
| 47 | Yu GH, Bao SD (1992) Experimental study of erosion prevention and siltation acceleration on Lüsi beach. The Ocean Engineering, 1(1), 65-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [喻国华, 鲍曙东 (1992) 吕泗海滩防蚀促淤的试验研究. 海洋工程, 1(1), 65-74.] | |
| 48 | Zhang XL, Shi SL, Pan GX, Li LQ, Zhang XH, Li ZP (2008) Changes in eco-chemical properties of a mangrove wetland under Spartina invasion from Zhangjiangkou, Fujian, China. Advances in Earth Science, 23, 974-981. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张祥霖, 石盛莉, 潘根兴, 李恋卿, 张旭辉, 李志鹏 (2008) 互花米草入侵下福建漳江口红树林湿地土壤生态化学变化. 地球科学进展, 23, 974-981.] | |
| 49 | Zhang YL, Chen LJ (2010) Evolvement of soil properties during reversal of desertification: research progress. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 29, 1440-1450. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张玉兰, 陈利军 (2010) 沙漠化逆转过程中土壤性状演变综述. 生态学杂志, 29, 1440-1450.] | |
| 50 | Zhi YB, Li HL, An SQ, Zhao L, Zhou CF, Deng ZF (2007) Inter-specific competition: Spartina alterniflora is replacing Spartina anglica in coastal China. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 74, 437-448. |
| 51 | Zhong CX (1985) A brief history and overseas review of Spartina anglica. Journal of Nanjing University-Album of Spartina Research Progress, 1-30. (in Chinese) |
| [仲崇信 (1985) 大米草简史及国外研究概况. 南京大学学报——米草研究的进展专集, 1-30.] |
| [1] | Xiao-Qing Wu Meihui Zhang Suting Ge Manshu Li Kun Song Guochun Shen Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Woody Plant Species Diversity and Aboveground Biomass during Near-Natural Forest Reconstruction in Shanghai: A Case Study from the Eco-Island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn