



Biodiv Sci ›› 2010, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (5): 523-527. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.523 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2010.523
• Research Brief • Previous Articles
Zhigang Li1, Fuwen Wei2, Jiang Zhou1,2,*( )
)
Received:2010-03-02
Accepted:2010-08-22
Online:2010-09-20
Published:2010-09-20
Contact:
Jiang Zhou
Zhigang Li, Fuwen Wei, Jiang Zhou. Mitochondrial DNA D-loop sequence analysis and population rejuvena- tion of Hainan gibbons (Nomascus hainanus)[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(5): 523-527.
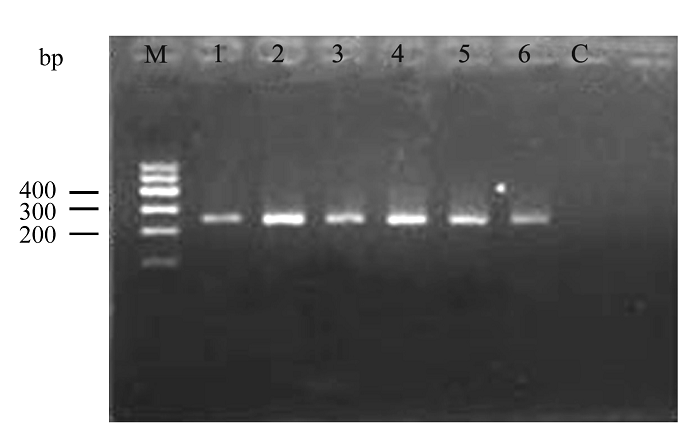
Fig. 1 The amplification result of partial mtDNA control region of six Hainan gibbon individuals in Group B. M indicates the Marker; C indicates control; 1-6 are the sample codes.
| Indiv- idual codes | 变异位点 Variable sites | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-10 | 11-20 | 21-30 | 31-40 | 41-50 | 51-60 | 61-70 | 71-80 | 81-90 | |
| 1 | TAGAACATCC | CCTCCCCATT | TCAACATTCC | AAACCTACCC | AACATGCGTA | TCAACCAACC | AAGATAGTCC | ATCTCGGACA | TGGCACATTA |
| 2 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
| 3 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - A- - - - - - - |
| 4 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - .- - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
| 5 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
| 6 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
Table 1 Variable sites of mitochondrial DNA control region among six individuals
| Indiv- idual codes | 变异位点 Variable sites | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-10 | 11-20 | 21-30 | 31-40 | 41-50 | 51-60 | 61-70 | 71-80 | 81-90 | |
| 1 | TAGAACATCC | CCTCCCCATT | TCAACATTCC | AAACCTACCC | AACATGCGTA | TCAACCAACC | AAGATAGTCC | ATCTCGGACA | TGGCACATTA |
| 2 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
| 3 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - A- - - - - - - |
| 4 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - .- - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
| 5 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
| 6 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
| [1] | Chivers DJ (1974) The siamang in Malaysia: a field study of a primate in a tropical rain forest. Contributions to Primatology, 4, 1-335. |
| [2] | Cowlishaw G, Dunbar R (2000) Primate Conservation Biology. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [3] | Frankham R (1998) Inbreeding and extinction: island populations. Conservation Biology, 12, 665-675. |
| [4] | Frankham R, Ballou JD, Briscoe DA (2002) Introduction to Conservation Genetics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [5] | He L (何丽), Zhang YG (张于光), Li DQ (李迪强), Li DQ (李大全) (2010) Analysis on mitochondrial DNA D-loop sequences genetic polymorphism of Rhinopithecus roxellana. Chinese Journal of Zoology (动物学杂志), 45(1), 70-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Hayaishi SH, Kawamoto YH (2006) Low genetic diversity and biased distribution of mitochondrial DNA haplotypes in the Japanese macaque (Macaca fuscata yakui) on Yakushima Island. Primates, 47, 158-164. |
| [7] | Irwin DW, Kcher TD, Wilson AC (1991) Evolution of cytochrome b gene of mammals. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 32, 128-144. |
| [8] |
Jeanmougin F, Thompson JD, Gouy M, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1998) Multiple sequence alignment with Clustal X. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 23, 403-405.
URL PMID |
| [9] | Kressirer P (1993) Eine Molekulare Phylogenie der Gibbons (Hylobatidae). Diplomarbeit der Fakultat fur Biologie der Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitat, Munchen. |
| [10] |
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobusen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics, 17, 1244-1245.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
Liu ZJ, Ren BP, Wei FW, Long YC, Hao YL, Li M (2007) Phylogeography and population structure of the Yunnan snub-nosed monkey (Rhinopithecus bieti) inferred from mitochondrial control region DNA sequence analysis. Molecular Ecology, 16, 3334-3349.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
Liu ZH, Jiang HS (1989) Population structure of Hylobates concolor in Bawangling Nature Reserve, Hainan, China. American Journal of Primatology, 19, 247-254.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] | Monda K, Simmons RE, Kressirer P, Su B, Woodruff DS (2007) Mitochondrial DNA hypervariable region-1 sequence variation and phylogeny of the concolor gibbons, Nomascus. American Journal of Primatology, 69, 1285-1306. |
| [14] |
Rozas J, Rozas R (1999) DnaSP version 3: an integrated program for molecular population genetics and molecular evolution analysis. Bioinformatics, 15, 174-175.
URL PMID |
| [15] | Soulé ME, Orians GH, Boersma PD (2001) Conservation Biology: Research Priorities for the Next Decade. Society for Conservation Biology, Island Press, Washington. |
| [16] | Young AG, Clarke GM (2000) Genetics Demography and Variability of Fragment Population. Cambridge University Press, London. |
| [17] | Zhou J, Wei FW, Li M, Zhang JF, Wang DL, Pan RL (2005) Hainan black-crested gibbon is headed for extinction. International Journal of Primatology, 26, 453-465. |
| [18] | Zhang BW, Li M, Ma LC, Wei FW (2006) A widely applicable protocol for DNA isolation from fecal samples. Biochemical Genetics, 44, 503-512. |
| [19] | Zhou J, Wei FW, Li M, Pui Lok CB, Wang DL (2008) Reproductive characters and mating behaviour of wild Nomascus hainanus. International Journal of Primatology, 29, 1037-1046. |
| [1] | Jiachen Wang, Tangjun Xu, Wei Xu, Gaoji Zhang, Yijin You, Honghua Ruan, Hongyi Liu. Impact of urban landscape pattern on the genetic structure of Thereuopoda clunifera population in Nanjing, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | Kexin Cao, Jingwen Wang, Guo Zheng, Pengfeng Wu, Yingbin Li, Shuyan Cui. Effects of precipitation regime change and nitrogen deposition on soil nematode diversity in the grassland of northern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [3] | Shiyi Long, Bobo Zhang, Yuchen Xia, Yangfan Fei, Yani Meng, Bingwei Lü, Yueqing Song, Pu Zheng, Taoran Guo, Jian Zhang, Shaopeng Li. Effects of diversity and temporal stability of native communities on the biomass of invasive species Solidago canadensis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24263-. |
| [4] | Linjun He, Wenjing Yang, Yuhao Shi, Kezhemo Ashuo, Yu Fan, Guoyan Wang, Jingji Li, Songlin Shi, Guihua Yi, Peihao Peng. Effects of plant community phylogeny and functional diversity on Ageratina adenophora invasion under fire disturbance [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24269-. |
| [5] | Qingduo Li, Dongmei Li. Analysis for the prevalence of global bat-borne Bartonella [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [6] | Chen Feng, Jie Zhang, Hongwen Huang. Parallel situ conservation: A new plant conservation strategy to integrate in situ and ex situ conservation of plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [7] | Hailing Qi, Pengzhen Fan, Yuehua Wang, Jie Liu. Genetic diversity and population structure of Juglans regia from six provinces in northern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [8] | Yuanyuan Xiao, Wei Feng, Yangui Qiao, Yuqing Zhang, Shugao Qin. Effects of soil microbial community characteristics on soil multifunctionality in sand-fixation shrublands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22585-. |
| [9] | Fei Xiong, Hongyan Liu, Dongdong Zhai, Xinbin Duan, Huiwu Tian, Daqing Chen. Population genetic structure of Pelteobagrus vachelli in the upper Yangtze River based on genome re-sequencing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [10] | Yiyue He, Yuying Liu, Fubin Zhang, Qiang Qin, Yu Zeng, Zhenyu Lü, Kun Yang. Genetic diversity and population structure of Saurogobio dabryi under cascade water conservancy projects in the Jialing River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [11] | Weiyue Sun, Jiangping Shu, Yufeng Gu, Morigengaowa, Xiajin Du, Baodong Liu, Yuehong Yan. Conservation genomics analysis revealed the endangered mechanism of Adiantum nelumboides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [12] | Xiaoyan Jiang, Shengjie Gao, Yan Jiang, Yun Tian, Xin Jia, Tianshan Zha. Species diversity, functional diversity, and phylogenetic diversity in plant communities at different phases of vegetation restoration in the Mu Us sandy grassland [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21387-. |
| [13] | Togtokh Mongke, Dongyi Bai, Tugeqin Bao, Ruoyang Zhao, Tana An, Aertengqimike Tiemuqier, Baoyindeligeer Mongkejargal, Has Soyoltiin, Manglai Dugarjaviin, Haige Han. Assessment of SNPs-based genomic diversity in different populations of Eastern Asian landrace horses [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [14] | Jing Cui, Mingfang Xu, Qun Zhang, Yao Li, Xiaoshu Zeng, Sha Li. Differences in genetic diversity of Pleuronichthys cornutus in the coastal water of China and Japan based on three mitochondrial markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [15] | Xinyu Cai, Xiaowei Mao, Yiqiang Zhao. Methods and research progress on the origin of animal domestication [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(4): 21457-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()