



Biodiv Sci ›› 2010, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (3): 215-226. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.215 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2010.215
Special Issue: 生物安全
• Special Issue • Next Articles
Lei Wang, Chao Yang, Bao-Rong Lu( )
)
Received:2010-01-13
Accepted:2010-04-28
Online:2010-05-20
Published:2012-02-08
Contact:
Bao-Rong Lu
Lei Wang, Chao Yang, Bao-Rong Lu. Establishing diagnostic platform for environmental biosafety assessment of genetically modified plants based on the decision-tree method[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(3): 215-226.
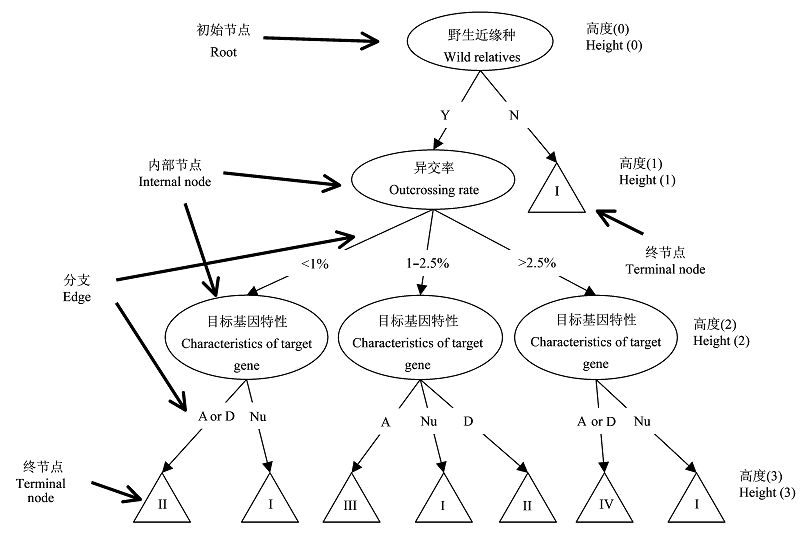
Fig. 1 A sketch map of decision tree assessing the risk of target gene escaping from transgenic crops to wild relatives. Root and internal nodes represent classification attributes such as wild relatives, outcrossing rate and trait of target gene, denoted by ellipse. Edges represent classification strategies such as the existence of wild relatives, denoted by arrows and the classification strategy options above. Terminal nodes represent classes namely classification results, denoted by triangle. The height of the entire decision tree is three, and the indication of the height for all nodes is provided at the right of the figure. Y, Present; N, Absent; A, Benefit; Nu, Neutral; D, Disbenefit.
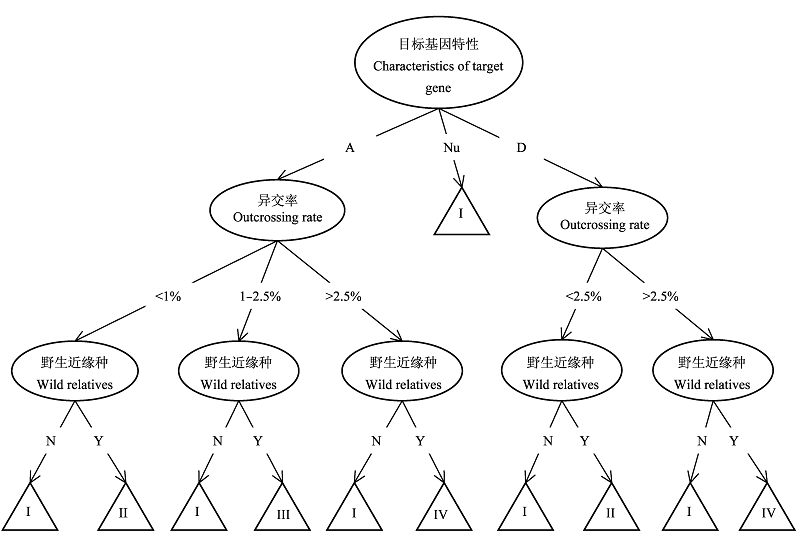
Fig. 2 Another sketch map of decision tree assessing the risk of target gene escaping from transgenic crops to its wild relatives. Compared with , three classification attributes in this decision tree have different locations. Thus although established by the same training set, decision trees in and have distinct frameworks and complexity.
| 转基因受体作物 Transgene recipient crop | 释放环境(省份) Environment (province) | 目标基因 Target gene | 野生近缘种* Wild relatives* | 野生种异交率 Outcrossing rate of wild relatives | 转基因特性** Transgene characteristics** | 风险等级 Rank of risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 栽培稻 Rice | 广西 Guangxi | cry1Ab | Y | <10% | A | IV |
| 栽培稻 Rice | 广西 Guangxi | psy | Y | <10% | Nu | I |
| 栽培稻 Rice | 广西 Guangxi | dam | Y | <10% | D | IV |
| 栽培稻 Rice | 山西 Shanxi | cry1Ab | N | <10% | A | I |
| 栽培稻 Rice | 山西 Shanxi | psy | N | <10% | Nu | I |
| 栽培稻 Rice | 山西 Shanxi | dam | N | <10% | D | I |
| 大豆 Soybean | 吉林 Jilin | cp4 epsps | Y | <2% | A | III |
| 大豆 Soybean | 吉林 Jilin | fad2 | Y | <2% | Nu | I |
| 大豆 Soybean | 吉林 Jilin | barnase | Y | <2% | D | II |
| 大豆 Soybean | 青海 Qinghai | cp4 epsps | N | <2% | A | I |
| 大豆 Soybean | 青海 Qinghai | fad2 | N | <2% | Nu | I |
| 大豆 Soybean | 青海 Qinghai | barnase | N | <2% | D | I |
| 小麦 Wheat | 新疆 Xinjiang | als | Y | <1% | A | II |
| 小麦 Wheat | 新疆 Xinjiang | bla | Y | <1% | Nu | I |
| 小麦 Wheat | 新疆 Xinjiang | TA29-barnase | Y | <1% | D | II |
| 小麦 Wheat | 辽宁 Liaoning | als | N | <1% | A | I |
| 小麦 Wheat | 辽宁 Liaoning | bla | N | <1% | Nu | I |
| 小麦 Wheat | 辽宁 Liaoning | TA29-barnase | N | <1% | D | I |
Table 1 An example of training set used for establishing a decision tree to assess environmental risks caused by transgene flow from genetically modified rice (Oryza sativa), soybean (Glycine max), and wheat (Triticum aestivum) to their wild relatives (O. rufipogon, G. soja,Aegilops tauschii)
| 转基因受体作物 Transgene recipient crop | 释放环境(省份) Environment (province) | 目标基因 Target gene | 野生近缘种* Wild relatives* | 野生种异交率 Outcrossing rate of wild relatives | 转基因特性** Transgene characteristics** | 风险等级 Rank of risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 栽培稻 Rice | 广西 Guangxi | cry1Ab | Y | <10% | A | IV |
| 栽培稻 Rice | 广西 Guangxi | psy | Y | <10% | Nu | I |
| 栽培稻 Rice | 广西 Guangxi | dam | Y | <10% | D | IV |
| 栽培稻 Rice | 山西 Shanxi | cry1Ab | N | <10% | A | I |
| 栽培稻 Rice | 山西 Shanxi | psy | N | <10% | Nu | I |
| 栽培稻 Rice | 山西 Shanxi | dam | N | <10% | D | I |
| 大豆 Soybean | 吉林 Jilin | cp4 epsps | Y | <2% | A | III |
| 大豆 Soybean | 吉林 Jilin | fad2 | Y | <2% | Nu | I |
| 大豆 Soybean | 吉林 Jilin | barnase | Y | <2% | D | II |
| 大豆 Soybean | 青海 Qinghai | cp4 epsps | N | <2% | A | I |
| 大豆 Soybean | 青海 Qinghai | fad2 | N | <2% | Nu | I |
| 大豆 Soybean | 青海 Qinghai | barnase | N | <2% | D | I |
| 小麦 Wheat | 新疆 Xinjiang | als | Y | <1% | A | II |
| 小麦 Wheat | 新疆 Xinjiang | bla | Y | <1% | Nu | I |
| 小麦 Wheat | 新疆 Xinjiang | TA29-barnase | Y | <1% | D | II |
| 小麦 Wheat | 辽宁 Liaoning | als | N | <1% | A | I |
| 小麦 Wheat | 辽宁 Liaoning | bla | N | <1% | Nu | I |
| 小麦 Wheat | 辽宁 Liaoning | TA29-barnase | N | <1% | D | I |
| [1] |
Ammann K (2005) Effects of biotechnology on biodiversity: herbicide-tolerant and insect-resistant GM crops. Trends in Biotechnology, 23, 388-394.
URL PMID |
| [2] |
Bates SL, Zhao JZ, Roush RT, Shelton AM (2005) Insect resistance management in GM crops: past, present and future. Nature Biotechnology, 23, 57-62.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] | Bauer E, Kohavi R (1999) An empirical comparison of voting classification algorithms: bagging, boosting, and variants. Machine Learning, 36, 105-139. |
| [4] | Breiman L, Friedman JH, Olshen RA, Stone CJ (1984) Classification and Regression Trees. Wadsworth Publishing Company, Monterey. |
| [5] | Breslow LA, Aha DW (1997) Simplifying decision trees: a survey. Knowledge Engineering Review, 12, 1-40. |
| [6] | Brodley CE, Utgoff PE (1992) Multivariate versus univariate decision trees. University of Massachusetts COINS Technical Report (No. UM-CS-1992-008). Computer and Information Science Department, University of Massachusetts, Massachusetts. |
| [7] | Brodley CE, Utgoff PE (1995) Multivariate decision trees. Machine Learning, 19, 45-77. |
| [8] | Buntine W (1992) Learning classification trees. Statistics and Computing, 2, 63-73. |
| [9] | Conner AJ, Glare TR, Nap JP (2003) The release of genetically modified crops into the environment. Part II. Overview of ecological risk assessment. Plant Journal, 33, 19-46. |
| [10] | Dalecky A, Bourguet D, Ponsard S (2007) Does the European corn borer disperse enough for a sustainable control of resistance to Bt maize via the High Dose/Refuge strategy. Cahiers Agricultures, 16, 171-176. |
| [11] | Dietterich TG (2000) An experimental comparison of three methods for constructing ensembles of decision trees: bagging, boosting, and randomization. Machine Learning, 40, 139-157. |
| [12] | Ellstrand NC (2003) Current knowledge of gene flow in plants: implications for transgene flow. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, Biological Science, 358, 1163-1170. |
| [13] |
Garcia-Alonso M, Jacobs E, Raybould A, Nickson TE, Sowig P, Willekens H, Van Der Kouwe P, Layton R, Amijee F, Fuentes AM, Tencalla F (2006) A tiered system for assessing the risk of genetically modified plants to non-target organisms. Environmental Biosafety Research, 5, 57-65.
URL PMID |
| [14] | Hunt EB (1962) Concept Learning: An Information Processing Problem. John Wiley, New York. |
| [15] | Hunt EB, Marin J, Stone PJ (1966) Experiments of Induction. Academic Press, New York. |
| [16] | James C (2009) Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2009. ISAAA Brief No. 41. ISAAA: Ithaca, NY, USA. |
| [17] | Janikow CZ (1998) Fuzzy decision trees: issues and methods. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics, 28, 1-14. |
| [18] | Kuiper HA, Kleter GA, Noteborn HPJM, Kok EJ (2001) Assessment of the food safety issues related to genetically modified foods. Plant Journal, 27, 503-528. |
| [19] | Landeweerd G, Timmers T, Gersema E, Bins M, Halic M (1983) Binary tree versus single level tree classification of white blood cells. Pattern Recognition, 16, 571-577. |
| [20] | Li GP, Wu KM, Gould F, Wang JK, Miao J, Gao XW, Guo YY (2007) Increasing tolerance to Cry1Ac cotton to cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera, was firmed in Bt cotton farming area of China. Ecological Entomology, 32, 366-375. |
| [21] | Lim TS, Loh WY, Shin YS (2000) A comparison of prediction accuracy, complexity, and training time of thirty-three old and new classification algorithms. Machine Learning, 40, 203-228. |
| [22] | Lu BR (卢宝荣), Fu Q (傅强), Shen ZC (沈志成) (2008) Commercialization of transgenic rice in China: potential environmental biosafety issues. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 16, 426-436. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Lu BR, Snow AA (2005) Gene flow from genetically modified rice and its environmental consequences. BioScience, 55, 669-678. |
| [24] | Lu BR (卢宝荣), Xia H (夏辉), Yang X (杨箫), Jin X (金鑫), Liu P (刘苹), Wang W (汪魏) (2009) Evolutionary theory of hybridization introgression: its implication in environmental risk assessment and research of transgene escape. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 17, 362-377. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] |
Lu BR, Yang C (2009) Gene flow from genetically modified rice to its wild relatives: assessing potential ecological consequences. Biotechnology Advances, 27, 1083-1091.
URL PMID |
| [26] | Mahesh P, Paul MM (2003) An assessment of the effectiveness of decision tree methods for land cover classification. Remote Sensing of Environment, 86, 554-565. |
| [27] | Meredith C (2005) Allergenic potential of novel foods. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 64, 487-490. |
| [28] | Messeguer J, Marfà V, Català MM, Guiderdoni E, Melé E (2004) A field study of pollen-mediated gene flow from Mediterranean GM rice to conventional rice and the red rice weed. Molecular Breeding, 13, 103-112. |
| [29] | Mingers J (1989a) An empirical comparison of selection measures for decision-tree induction. Machine Learning, 3, 319-342. |
| [30] | Mingers J (1989b) An empirical comparison of pruning methods for decision tree induction. Machine Learning, 4, 227-243. |
| [31] | Niblett T, Bratko I (1986) Learning decision rules in noisy domains. In: Proceedings of Expert Systems 1986, The 6th Annual Technical Conference on Research and Development in Expert Systems III (ed. Bramer MA), pp.25-34. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [32] |
O’Callaghan M, Glare TR, Burgess EPJ, Malone LA (2005) Effects of plants genetically modified for insect resistance on non-target organisms. Annual Review of Entomology, 50, 271-292.
URL PMID |
| [33] | Oates T, Jensen D (1997) The effects of training set sizes on decision tree complexity. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Machine Learning (ed. Fisher DH), pp.254-262. Morgan Kaufman, Nashville. |
| [34] |
Oliveira AR, Castro TR, Capalbo DMF, Delalibera I (2007) Toxicological evaluation of genetically modified cotton (Bollgard ®) and Dipel ® WP on the non-target soil mite Scheloribates praeincisus (Acari: Oribatida). Experimental and Applied Acarology, 41, 191-201.
DOI URL PMID |
| [35] |
Poulsen LK (2004) Allergy assessment of foods or ingredients derived from biotechnology, gene-modified organisms, or novel foods. Molecular Nutrition and Food Research, 48, 413-423.
DOI URL PMID |
| [36] | Quinlan JR (1979) Discovering rules by induction from large collections of examples. In: Expert Systems in the Micro-electronic Age(ed. Michie D). Edinburgh University Press, Edinburgh. |
| [37] | Quinlan JR (1983) Learning efficient classification procedures and their application to chess end games. In: Machine Learning: An Artificial Intelligence Approach (eds. Michalski RS, Carbonell JG, Mitchell TM),pp.463-482. Tioga Press, Palo Alto. |
| [38] | Quinlan JR (1986) Induction of decision trees. Machine Learning, 1, 81-106. |
| [39] | Quinlan JR (1993) C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning. Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo. |
| [40] | Quinlan JR (1996) Improved use of continuous attributes in C4.5. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 4, 77-90. |
| [41] | Quinlan JR, Rivest RL (1989) Inferring decision trees using the minimum description length principle. Information and Computation, 80, 227-248. |
| [42] | Romeis J, Bartsch D, Bigler F, Candolfi MP, Gielkens MMC, Hartley SE, Hellmich RL, Huesing JE, Jepson PC, Layton R, Quemada H, Raybould A, Rose RI, Schiemann J, Sears MK, Shelton AM, Sweet J, Vaituzis Z, Wolt JD (2006) Moving through the tiered and methodological framework for non-target arthropod risk assessment of transgenic insecticidal crops. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on the Biosafety of Genetically Modified Organisms (ed. Roberts A), pp.64-69. Korea ISBR, Jeju Island. |
| [43] | Rounds E (1980) A combined nonparametric approach to feature selection and binary decision tree design. Pattern Recognition, 12, 313-317. |
| [44] | Safavian SR, Landgrebe D (1991) A survey of decision tree classifier methodology. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics, 21, 660-674. |
| [45] | Schuermann J, Doster W (1984) A decision-theoretic approach to hierarchical classifier design. Pattern Recognition, 17, 359-369. |
| [46] | Swain PH, Hauska H (1977) The decision tree classifier: design and potential. IEEE Transaction Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 3, 142-147. |
| [47] | Utgoff PE (1989) Incremental induction of decision trees. Machine Learning, 4, 161-186. |
| [48] | Utgoff PE, Brodley CE (1990) An incremental method for finding multivariate splits for decision trees. In: Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Machine Learning (eds. Porter BW, Mooney RJ),pp.58-65. Morgan Kaufmann, Austin. |
| [49] | Wu C, Landgrebe D, Swain P (1975) The decision tree approach to classification. Technical Report (No. TR-EE-75-17). School of Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette. |
| [50] |
Wu KM (2007) Monitoring and management strategy for Helicoverpa armigera resistance to Bt cotton in China. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 95, 220-223.
URL PMID |
| [51] | You KC, Fu KS (1976) An approach to the design of a linear binary tree classifier. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Symposium on Machine Processing of Remotely Sensed Data (eds. Swain PH, Morrison DB, Parks DE). Purdue University, West Lafayette. |
| [52] | Yuan YF, Shaw MJ (1995) Induction of fuzzy decision trees. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 69, 125-139. |
| [1] | Sanhe Li, Kai Liu, Wenjun Zha, Huashan Xu, Peide Li, Lei Zhou, Aiqing You. Effects of transgenic rice H23 with BPH9 and Bar genes resistant to brown planthopper and herbicide on non-target organisms [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(4): 488-494. |
| [2] | Zhengjun Guan,Shunbao Lu,Yanlin Huo,Haoyong Hao,Jianbin Cao,Wei Wei,Biao Liu. Effects of Bt crops on non-target insect pests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(6): 636-644. |
| [3] | Haining Qin, Lina Zhao, Shengxiang Yu, Huiyuan Liu, Bo Liu, Nianhe Xia, Hua Peng, Zhenyu Li, Zhixiang Zhang, Xingjin He, Linke Yin, Yulin Lin, Quanru Liu, Yuantong Hou, Yan Liu, Qixin Liu, Wei Cao, Jianqiang Li, Shilong Chen, Xiaohua Jin, Tiangang Gao, Wenli Chen, Haiying Ma, Yuying Geng, Xiaofeng Jin, Chaoyang Chang, Hong Jiang, Lei Cai, Chunxin Zang, Jianyong Wu, Jianfei Ye, Yangjun Lai, Bing Liu, Qinwen Lin, Naxin Xue. Evaluating the endangerment status of China’s angiosperms through the red list assessment [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(7): 745-757. |
| [4] | Shan Li, Jiakuan Chen, Xiaoming Wang. Global distribution, entry routes, mechanisms and consequences of invasive freshwater fish [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(6): 672-685. |
| [5] | Minghao Qiu, Yue Huang, Jieqing Zhang, Yi Huang. International negotiations on synthetic biology and China’s implementation strategies within the Convention on Biological Diversity framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(1): 114-120. |
| [6] | Weichang Huang, Xiangyu Zhou, Ziyi Ni, Li Shao. An assessment of the extinction risk of Calanthe from China based on specimens and field observations [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(4): 493-498. |
| [7] | Xi’ao Zhang,Xiaoyun Sui,Zhi Lü,Yifeng Chen. A prediction of the global habitat of two invasive fishes (Pseudorasbora parva and Carassius auratus) from East Asia using Maxent [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(2): 182-188. |
| [8] | Chengxiang Xu,Zizhong Li,Daohong Li. Relationships between the diversity of animal communities and the lighting environment and content of heavy metals in soils in Guizhou Zhijin Cave [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(1): 62-70. |
| [9] | Zhengjun Guan, Lei Pei, Markus Schmidt, Wei Wei. Assessment and management of biosafety in synthetic biology [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(2): 138-150. |
| [10] | Ruiting Ju, Bo Li. A risk analysis system for alien species in urban green spaces and application to the 2010 Expo, Shanghai [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(1): 12-23. |
| [11] | Bao-Rong Lu, Hui Xia, Xiao Yang, Xin Jin, Ping Liu, Wei Wang. [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(4): 362-377. |
| [12] | Bao-Rong Lu, Qiang Fu, Zhicheng Shen. Commercialization of transgenic rice in China: potential environmental biosafety issues [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2008, 16(5): 426-436. |
| [13] | LI Yi-Ming. Population viability analysis in conservation biology: precision and uses [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2003, 11(4): 340-350. |
| [14] | WANG Hong-Xing, CHEN Xin, TANG Jian-Jun, SHIMIZU Katsuyoshi. Influence of released transgenic pest and disease resistant crops on plant associated microorganisms in soil [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2002, 10(2): 232-237. |
| [15] | WAN Fang-Hao, GUO Jian-Ying, WANG De-Hui. Alien invasive species in China: their damages and management strategies [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2002, 10(1): 119-125. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()