



Biodiv Sci ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (3): 280-287. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08293 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2009.08293
• Editorial • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hu Yuan1,2, Yinbo Zhang3, Haining Qin4, Yan Liu1, Mei Yu2,*( )
)
Received:2008-11-17
Accepted:2009-05-04
Online:2009-05-20
Published:2009-05-20
Contact:
Mei Yu
Hu Yuan, Yinbo Zhang, Haining Qin, Yan Liu, Mei Yu. The in situconservation of state key protected wild plants in national nature reserves in China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(3): 280-287.
| 科数 Number of families | 属数 Number of genera | 种数 Number of species | 占保护植物比例 Proportion (%) | I级植物种数 Species under Class I | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蕨类植物 Ferns | 14 | 17 | 36 | 12.16 | 6 |
| 裸子植物 Gymnosperms | 7 | 23 | 66 | 22.30 | 34 |
| 被子植物 Angiosperms | 68 | 151 | 194 | 65.54 | 33 |
| 总计 Total | 89 | 191 | 296 | 100.00 | 73 |
Table 1 The number of state key protected wild plants in China
| 科数 Number of families | 属数 Number of genera | 种数 Number of species | 占保护植物比例 Proportion (%) | I级植物种数 Species under Class I | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蕨类植物 Ferns | 14 | 17 | 36 | 12.16 | 6 |
| 裸子植物 Gymnosperms | 7 | 23 | 66 | 22.30 | 34 |
| 被子植物 Angiosperms | 68 | 151 | 194 | 65.54 | 33 |
| 总计 Total | 89 | 191 | 296 | 100.00 | 73 |
| 科数 Number of families (%) | 属数 Number of genera (%) | 种数 Number of species (%) | I级保护种数 Species under Class I | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蕨类植物 Ferns | 11 (78.57) | 14 (82.35) | 26 (72.22) | 3 (50.00) |
| 裸子植物 Gymnosperms | 7 (100.00) | 22 (95.65) | 56 (84.85) | 27 (79.41) |
| 被子植物 Angiosperms | 61 (89.71) | 124 (82.12) | 155 (79.90) | 26 (78.79) |
| 保护植物总数 Total | 79 (88.76) | 160 (83.77) | 237 (80.07) | 56 (76.71) |
Table 2 The number of state key protected wild plants in the national nature reserves and the percentage accounting for the total protected wild plants
| 科数 Number of families (%) | 属数 Number of genera (%) | 种数 Number of species (%) | I级保护种数 Species under Class I | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蕨类植物 Ferns | 11 (78.57) | 14 (82.35) | 26 (72.22) | 3 (50.00) |
| 裸子植物 Gymnosperms | 7 (100.00) | 22 (95.65) | 56 (84.85) | 27 (79.41) |
| 被子植物 Angiosperms | 61 (89.71) | 124 (82.12) | 155 (79.90) | 26 (78.79) |
| 保护植物总数 Total | 79 (88.76) | 160 (83.77) | 237 (80.07) | 56 (76.71) |
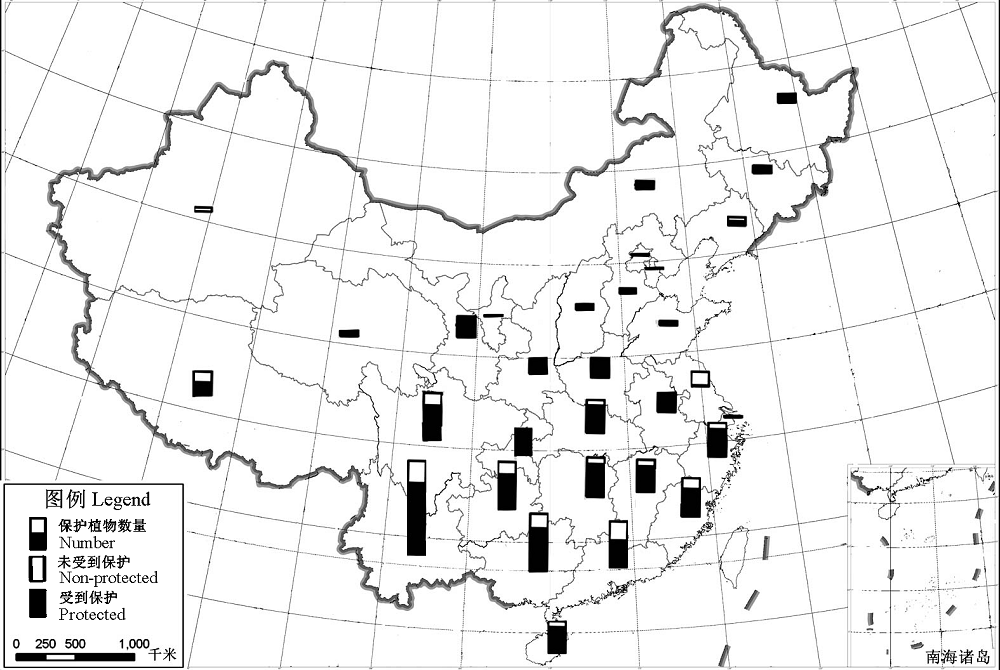
Fig. 2 The distribution of the state key protected wild plants in different provinces and in the national nature reserves in China. Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan are not included.
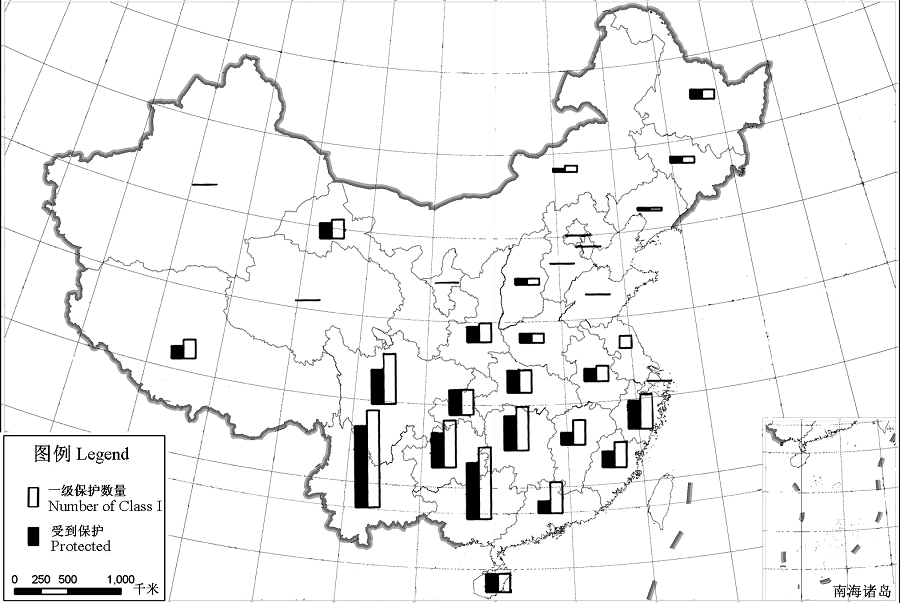
Fig. 3 The distribution of the first class state key protected wild plants in different provinces and in the national nature reserves in China. Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan are not included.
| 类型 Types | 分布地点 Locations |
|---|---|
| 蕨类植物 Ferns | |
| 光叶蕨 Cystoathyrium chinense | 四川省天全县二郎山鸳鸯岩至团牛坪 From Yuanyangyan to Tuanniuping of Erlang Mountains in Tianquan County, Sichuan |
| 台湾水韭 Iso?tes taiwanensis | 台湾省台北县七星山 Qixing Mountain inTai-Pei County, Taiwan |
| 云贵水韭 Iso?tes yunguiensis | 贵州省平坝县、贵阳市; 云南省昆明市北郊黑龙潭、寻甸县 Pingba County and Guiyang City, Guizhou, Heilongtan in the north of Kunming City, and Xundian Country, Yunnan |
| 裸子植物 Gymnosperms | |
| 元宝山冷杉 Abies yuanbaoshanensis | 广西融水县元宝山 Yuanbao Mountain, Rongshui County, Guangxi |
| 台湾穗花杉 Amentotaxus formosana | 台湾省屏东县里龙山、台东县大武山 Li Long Mountain, Pingdong County, and Dawu Mountain, Taidong County, Taiwan |
| 巨柏 Cupressus gigantea | 西藏波密县易贡、朗县雅鲁藏布江流域以东、林芝县尼洋河下游、米林县河谷地区 Yigong of Bomi County, east of Yaluzangbu River of Lang County, lower reaches of Niyang River of Linzhi County, and Valley area in Milin County, Tibet |
| 德保苏铁 Cycas debaoensis | 广西德保县扶平乡扶平村, 那坡县 Fuping Village, Fuping Town, Debao County, and Napo County, Guangxi |
| 锈毛苏铁 Cycas ferruginea | 广西桂林市雁山、田东、田阳 Yanshan, Tiandong and Tianyang, Guilin City, Guangxi |
| 台东苏铁 Cycas taitungensis | 台湾省台东县 Taidong County, Taiwan |
| 密叶红豆杉 Taxus fuana | 西藏吉隆县吉隆镇叶隆村、鲁嘎村 Yelong Village and Luga Village, Jilong Town, Jilong County, Tibet |
| 被子植物 Angiosperms | |
| 峨眉拟单性木兰 Parakmeria omeiensis | 四川省峨眉山市峨眉山红椿坪, 峨嵋山清音阁以上二道桥至茶棚一带 From Erdaoqiao to Chapeng, Qingyinge and Hongchunping, Emei Mountain, Emeishan City, Sichuan |
| 膝柄木 Bhesa robusta | 广西东兴市江平镇、合浦县南康镇 Jiangping Town, Dongxing City and Nankang Town, Hepu County, Guangxi |
| 萼翅藤 Calycopteris floribunda | 云南省盈江县那邦坝至红崩河镇沿羯羊河左岸 Along the left bank of the Xieyang River, from Nabangba to Hongbenghe Town, Yingjiang County, Yunnan |
| 普陀鹅耳枥 Carpinus putoensis | 浙江省舟山市舟山群岛普陀岛佛顶山 Foding Mountain, Putuo Island, Zhoushan Archipelago, Zhoushan City, Zhejiang |
| 报春苣苔 Primulina tabacum | 广东省乐昌市、连州市、乳源县、阳山县; 湖南省宁远县 Lechang City, Lianzhou City, Ruyuan County and Yangshan County, Guangdong and Ningyuan County, Hunan |
| 长喙毛茛泽泻 Ranalisma rostratum | 浙江省丽水市莲都区四明山、湖南省茶陵县尧水乡 Siming Mountain, Liandu district, Lishui City, Zhejiang, and Raoshui Town, Chaling County, Hunan |
| 辐花苣苔 Thamnocharis esquirolii | 贵州省兴仁县、贞丰县 Xingren County and Zhenfeng County, Guizhou |
Table 3 Major distribution areas of the first class state key protected plants currently unprotected by the national nature reserves
| 类型 Types | 分布地点 Locations |
|---|---|
| 蕨类植物 Ferns | |
| 光叶蕨 Cystoathyrium chinense | 四川省天全县二郎山鸳鸯岩至团牛坪 From Yuanyangyan to Tuanniuping of Erlang Mountains in Tianquan County, Sichuan |
| 台湾水韭 Iso?tes taiwanensis | 台湾省台北县七星山 Qixing Mountain inTai-Pei County, Taiwan |
| 云贵水韭 Iso?tes yunguiensis | 贵州省平坝县、贵阳市; 云南省昆明市北郊黑龙潭、寻甸县 Pingba County and Guiyang City, Guizhou, Heilongtan in the north of Kunming City, and Xundian Country, Yunnan |
| 裸子植物 Gymnosperms | |
| 元宝山冷杉 Abies yuanbaoshanensis | 广西融水县元宝山 Yuanbao Mountain, Rongshui County, Guangxi |
| 台湾穗花杉 Amentotaxus formosana | 台湾省屏东县里龙山、台东县大武山 Li Long Mountain, Pingdong County, and Dawu Mountain, Taidong County, Taiwan |
| 巨柏 Cupressus gigantea | 西藏波密县易贡、朗县雅鲁藏布江流域以东、林芝县尼洋河下游、米林县河谷地区 Yigong of Bomi County, east of Yaluzangbu River of Lang County, lower reaches of Niyang River of Linzhi County, and Valley area in Milin County, Tibet |
| 德保苏铁 Cycas debaoensis | 广西德保县扶平乡扶平村, 那坡县 Fuping Village, Fuping Town, Debao County, and Napo County, Guangxi |
| 锈毛苏铁 Cycas ferruginea | 广西桂林市雁山、田东、田阳 Yanshan, Tiandong and Tianyang, Guilin City, Guangxi |
| 台东苏铁 Cycas taitungensis | 台湾省台东县 Taidong County, Taiwan |
| 密叶红豆杉 Taxus fuana | 西藏吉隆县吉隆镇叶隆村、鲁嘎村 Yelong Village and Luga Village, Jilong Town, Jilong County, Tibet |
| 被子植物 Angiosperms | |
| 峨眉拟单性木兰 Parakmeria omeiensis | 四川省峨眉山市峨眉山红椿坪, 峨嵋山清音阁以上二道桥至茶棚一带 From Erdaoqiao to Chapeng, Qingyinge and Hongchunping, Emei Mountain, Emeishan City, Sichuan |
| 膝柄木 Bhesa robusta | 广西东兴市江平镇、合浦县南康镇 Jiangping Town, Dongxing City and Nankang Town, Hepu County, Guangxi |
| 萼翅藤 Calycopteris floribunda | 云南省盈江县那邦坝至红崩河镇沿羯羊河左岸 Along the left bank of the Xieyang River, from Nabangba to Hongbenghe Town, Yingjiang County, Yunnan |
| 普陀鹅耳枥 Carpinus putoensis | 浙江省舟山市舟山群岛普陀岛佛顶山 Foding Mountain, Putuo Island, Zhoushan Archipelago, Zhoushan City, Zhejiang |
| 报春苣苔 Primulina tabacum | 广东省乐昌市、连州市、乳源县、阳山县; 湖南省宁远县 Lechang City, Lianzhou City, Ruyuan County and Yangshan County, Guangdong and Ningyuan County, Hunan |
| 长喙毛茛泽泻 Ranalisma rostratum | 浙江省丽水市莲都区四明山、湖南省茶陵县尧水乡 Siming Mountain, Liandu district, Lishui City, Zhejiang, and Raoshui Town, Chaling County, Hunan |
| 辐花苣苔 Thamnocharis esquirolii | 贵州省兴仁县、贞丰县 Xingren County and Zhenfeng County, Guizhou |
| [1] | Department of Nature and Ecology Conservation, Ministry of Environmental Protection (国家环境保护总局自然生态保护司), Nanjing Institute of Environmental Sciences, Mnistry of Environmental Protection (国家环境保护总局南京环境科学研究所) (2006) National Nature Reserves of China (中国国家级自然保护区). China Environmental Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [2] | Brooks TM, Bakarr MI, Boucher T, Da Fonseca GAB, Hiltontaylor C, Hoekstra JM, Moritz T, Olivieri S, Parrish J, Pressey RL, Rodrigues ASL, Sechrest W, Stettersfield A, Strahm W, Stuart SN (2004) Coverage provided by the global protected-area system: is it enough? BioScience, 54,1081-1091. |
| [3] | Chai Y (柴勇), Meng GT (孟广涛), Wu L (武力) (2007) Structure characteristics and resource protection of national key protected plants in Gaoligongshan National Nature Reserve. Journal of West China Forestry Science (西部林业科学), 36(4),57-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Chen XC (陈西仓), Pei JH (裴俊华) (2006) National level priority wild plant resources in Gansu Province. Forest By-Product and Speciality in China (中国林副特产), (1),44-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Cui GF (崔国发) (2004) Special research fields and hot spots in science of nature reserves. Journal of Beijing Forestry University (北京林业大学学报), 26(6),102-105. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Eken G, Bennun L, Brooks TM, Darwall W, Fishpool LDC, Foster M, Knox D, Langhammer P, Matiku P, Radford E, Salaman P, Sechrest W, Smith ML, Spector S, Tordoff A (2004) Key biodiversity areas as site conservation targets. BioScience, 54,1110-1118. |
| [7] | Gao HS (高海山), Xu WB (许为斌), Liu Y (刘演) (2007) Investigation of the national key protected wild plants in Huaping Nature Reserve Guangxi, China. Chinese Wild Plant Resources (中国野生植物资源), 26(3),28-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Ge JW (葛继稳), Wu JQ (吴金清), Zhu ZQ (朱兆泉), Yang JY (杨敬元), Lei Y (雷耘) (1998) The present status and in-situ conservation of the rare and endangered plants in Hubei Province. Chinese Biodiversity (生物多样性), 6,220-228. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Jiang MK (蒋明康), Wang Z (王智), Qin WH (秦卫华), He ZH (贺昭和) (2006) Effectiveness of national priority wildlife protection in nature reserves. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment (生态与农村环境学报), 22(4),35-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] | Jiang MK (蒋明康), Wang Z (王智), Zhu GQ (朱广庆), Tao SM (陶思明), Zhou HL (周海丽) (2004) Chinese nature reserve classification standard based on IUCN protected area categories. Rural Eco-Environment (农村生态环境), 20(2),1-6, 11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Jiang ZG (蒋志刚) (2005) On the upper limit of the area of the strictly protected nature reserves in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 25,1205-1212. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Jennings MD (2000) Gap analysis: concepts, methods, and recent results. Landscape Ecology, 15,5-20. |
| [13] | Jin SH (金水虎), Yu J (俞建), Ding BY (丁炳扬), Yu MJ (于明坚), Jiang WM (姜维梅) (2002) Current situation of distribution and conservation of national wild plants for protection in Zhejiang Province. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Sciences and Technology (浙江林业科技), 22(2),48-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Li DQ (李迪强), Jiang ZG (蒋志刚), Wang ZW (王祖望) (1999) Biodiversity spatial characteristics and GAP analysis in Qinghai Lake region. Journal of Natural Resources (自然资源学报), 14,47-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Li XX (李潇晓) (2008) The present situation and managing countermeasure of the nature reserves of Guangxi. Journal of Guangxi Academy of Sciences (广西科学院学报), 24,141-143. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Li YY (李玉媛), SiMa YK (司马永康), Fang B (方波), Guo LQ (郭立群), Jiang H (蒋宏), Zhao WS (赵文书) (2003) Current situation and evaluation of natural resources of the priority protection wild plants in Yunnan Province of China. Acta Botanica Yunnanica (云南植物研究), 25,181-191. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Li ZP (李忠平), Tang XP (唐小平) (2006) In situ Conservation of National Key Protected Wild Plants in China (国家重点野生植物的就地保护). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [18] | Luo YP (罗彦平), Liu JC (刘俊昌) (2007) The research on status of the utilization and protection of wild plants and relevant countermeasures. Forest Inventory and Planning (林业调查规划), 32(3),132-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | MacDougall AS, Loo JA, Clayden SR, Goltz JG, Hinds HR (1998) Defining conservation priorities for plant taxa in southeastern New Brunwick, Canada using herbarium records. Biological Conservation, 86,325-338. |
| [20] | Maiorano L, Falcucci A, Boitani L (2006) Gap analysis of terrestrial vertebrates in Italy: priorities for conservation planning in a human dominated landscape. Biological Conservation, 133,455-473. |
| [21] |
Margules CR, Pressey RL (2000) Systematic conservation planning. Nature, 405,243-253.
URL PMID |
| [22] | Miao SY (缪绅裕), Wang HL (王厚鳞), He XT (何晓婷), Lin MS (林慕珊) (2008) Evaluation on the sustainable development potential of forestry nature reserves in Guangdong Province, China. Journal of Guangzhou University (Natural Science Edition) (广州大学学报(自然科学版)), 7(2),10-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] |
Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, Da Fonseca GAB, Kent J (2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature, 403,853-858.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | Pressey RL, Whish GL, Barrett TW, Watts ME (2002) Effectiven of protected areas in north-eastern New South Wales: recent trends in six measures. Biological Conservation, 106,57-69. |
| [25] | Pressey RL, Taffs KH (2001) Sampling of land types by protected areas: three measures of effectiveness applied to western New South Wales. Biological Conservation, 101,105-117. |
| [26] | Pu YH (蒲云海), Li HP (李洪鹏), Zhang YK (张应坤) (2007) Current situation and protective strategies of national key protected wild plants in Hubei Province. Hubei Forestry Science and Technology (湖北林业科技), (3),47-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Rodrigues ASL, Akcakaya HR, Andelman SJ, Bakarr MI, Boitani L, Brooks TM, Chanson JS, Fishpool LDC, Da Fonseca GAB, Gaston KJ, Hoffmann M, Marquet PA, Pilgrim JD, Pressey RL, Schipper J, Sechrest W, Stuart SN, Underhill LG, Waller RW, Watts MEJ, Xie Y (2004) Global gap analysis: priority regions for expanding the global protected-area network. BioScience, 54,1092-1100. |
| [28] |
Rodrigues ASL, Andelman SJ, Bakarr MI, Boitani L, Brooks TM, Cowling RM, Fishpool LDC, Da Fonseca GAB, Gaston KJ, Hoffmann M, Long JS, Marquet PA, Pilgrim JD, Pressey RL, Schipper J, Sechrest W, Stuart SN, Underhill LG, Waller RW, Watts MEJ, Xie Y (2004) Effectiveness of the global protected area network in representing species diversity. Nature, 428,640-643.
URL PMID |
| [29] | Root KV, Akcakaya HR, Ginzburg L (2003) A multispecies approach to ecological valuation and conservation. Conservation Biology, 17,196-206. |
| [30] | Scott JM, Davis F, Custi B, Noss R, Butterfield B, Groves C, Anderson H, Caicco S, D'erchia F, Edwards TC, Ulliman J, Wright RG (1993) GAP analysis: A geographic approach to protection of biological diversity. Wildlife Monographs, 123,1-41. |
| [31] | Scott JM, Davis FW, McGhie RG, Wright RG, Groves C, Estes J (2001) Nature reserves: do they capture the full range of America's biological diversity? Ecological Applications, 11,999-1007. |
| [32] | Stem C, Margoluis R, Salafsky N, Brown M (2005) Monitoring and evaluation in conservation: a review of trends and approaches. Conservation Biology, 19,295-309. |
| [33] | Sun MJ (孙孟军), Chen ZH (陈征海), Weng WS (翁卫松), Ying SD (应顺东), Du Q (杜群) (2001) New records on the distribution of the rare and endangered plants in Zhejiang. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Sciences and Technology (浙江林业科技), 21(4),7-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] |
Turner WR, Wilcove DS, Swain HM (2006) Assessing the effectiveness of reserve acquisition programs in protecting rare and threatened species. Conservation Biology, 20,1657-1669.
DOI URL PMID |
| [35] | Wang CT (王昌腾) (2007) A study on in situ conservation of important national protected wild plants in Zhejiang Province. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology (福建林业科技), 34,235-239. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [36] | Wang YE (王银娥), Zhang J (张军), Yang FY (杨风英), Chen AQ (陈爱青) (2006) Approach on protective countermeasures of rare and endangered wild plants in Shanxi Province. Shanxi Forestry Science and Technology (山西林业科技), (3),4-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [37] | Xie ZH (谢志红), Xu YX (徐永新) (2003) Evaluation of management effectiveness of the nature reserves from Hunan Province. Hunan Forestry Science and Technology (湖南林业科技), 30 (2),7-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [38] | Yu H (喻泓), Zhang XS (张学顺), Yang XH (杨晓晖), Xiao SG (肖曙光), Luo JC (罗菊春), Cui GF (崔国发) (2007) A new category system of China nature reserves based on their attributes. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 18,2289-2294. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [39] | Yu YF (于永福) (1999) The national key protected wild plants in China. Plants (植物杂志), (5),3-11. (in Chinese) |
| [40] | Zang M (臧敏), Huang LF (黄立发), Li DY (李典友), Mao SJ (毛尚俊), Qiu XL (邱筱兰), Ling Y (凌云) (2007) Space-time analysis on the national protected wild plants in Jiangxi Province. Guihaia (广西植物), 27 (1),77-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [41] | Zhang YB (张殷波), Ma KP (马克平) (2008a) Geographic distribution characteristics of the national key protected wild plants in China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 19,1670-1675. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [42] | Zhang YB, Ma KP (2008b) Geographical distribution patterns and status assessment of threatened plants in China. Biodiversity and Conservation, 17,1783-1798. |
| [1] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [2] | Guo Yutong, Li Sucui, Wang Zhi, Xie Yan, Yang Xue, Zhou Guangjin, You Chunhe, Zhu Saning, Gao Jixi. Coverage and distribution of national key protected wild species in China’s nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [3] | Xuemeng Li, Jibao Jiang, Zenglu Zhang, Xiaojing Liu, Yali Wang, Yizhao Wu, Yinsheng Li, Jiangping Qiu, Qi Zhao. Earthworm biodiversity and its influencing factors in Baotianman National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23352-. |
| [4] | Qifan Wang, Xiaohui Liu, Ziwei Zhu, Lei Liu, Xinxue Wang, Xuyang Ji, Shaochun Zhou, Zidong Zhang, Hongyu Dong, Minghai Zhang. Mammal and avian diversity in Beijicun National Nature Reserve, Heilongjiang Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 24024-. |
| [5] | Di Suo, Ruoxi Yu, Yuanhui Li, Jiliang Xu. Problem review and optimization path of local legislation in nature reserves in China based on empirical analysis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23287-. |
| [6] | Xiaolin Liu, Yougui Wu, Minhua Zhang, Xiaorong Chen, Zhicheng Zhu, Dingyun Chen, Shu Dong, Buhang Li, Bingyang Ding, Yu Liu. Community composition and structure of a 25-ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical forest in Baishanzu, Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [7] | Xiaolong Huang, Bingshun Meng, Haibo Li, Wei Ran, Wei Yang, Cheng Wang, Bo Xie, Xu Zhang, Jingcheng Ran, Mingming Zhang. Interspecific associations between Rhinopithecus brelichi and its sympatric species using infrared cameras [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23402-. |
| [8] | Xianglin Yang, Caiyun Zhao, Junsheng Li, Fangfang Chong, Wenjin Li. Invasive plant species lead to a more clustered community phylogenetic structure: An analysis of herbaceous plants in Guangxi’s national nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [9] | Ruirui Mao, Tuo Shen, Hui Li, Linchu Tian, Hairong Tan, Lirong Lu, Xiaogang Wu, Zongji Fan, Guoyi Wu, Jie Li, Yong Wu, Bicheng Zhu, Zhishu Xiao. A dataset of call characteristics of anuran from the Chebaling National Nature Reserve, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24356-. |
| [10] | Chen Feng, Jie Zhang, Hongwen Huang. Parallel situ conservation: A new plant conservation strategy to integrate in situ and ex situ conservation of plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [11] | Guofa Cui. Discussion and suggestions on several key issues in the integration and optimization of protected areas [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 22447-. |
| [12] | Xinyi Zhong, Fan Zhao, Xue Yao, Yuru Wu, Yin Xu, Shunyao Yu, Jingyun Lin, Jianfeng Hao. Relationship between herbaceous plant diversity and soil anti-scourability under different maintenance measures at Sanxingdui City Wall [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23169-. |
| [13] | Chao Xing, Yi Lin, Zhiqiang Zhou, Lianjun Zhao, Shiwei Jiang, Zhenzhen Lin, Jiliang Xu, Xiangjiang Zhan. The establishment of terrestrial vertebrate genetic resource bank and species identification based on DNA barcoding in Wanglang National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [14] | Xinjing Wu, Jinfeng Chen, Guofa Cui. Proposals for updating the List of National Key Protected Wild Plants—Based on an analysis of existing conservation lists [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 22622-. |
| [15] | Cheng Du, Yuan Wang, Xiaoling Yan, Jing Yan, Huiru Li, Qingfei Zhang, Yonghong Hu. Composition and historical changes of plant species diversity in Shanghai and the updated checklist of Shanghai vascular plants (2022) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 23093-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()