



Biodiv Sci ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (2): 143-150. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08286 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2009.08286
• Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xuelan Yan, Wenqiao Tang, Jinquan Yang**( )
)
Received:2008-11-06
Accepted:2009-03-05
Online:2009-03-20
Published:2009-03-20
Contact:
Jinquan Yang*
Xuelan Yan, Wenqiao Tang, Jinquan Yang*. Population genetic structure of tapertail anchovy (Coilia mystus) in coastal waters of southeast China based on mtDNA control region sequences[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(2): 143-150.
| 采集地 Location | 样本数Sample size | 单元型数 Haplotype number | 单元型 Haplotype | 单元型多样性Haplotype diversity (h) | 核苷酸多样性 Nucleotide diversity (π) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闽江 Minjiang River (MJ) | 17 | 6 | H1(1)、H2(1)、H4(2)、H5(1)、H7(1)、H8(11) | 0.5882 ± 0.1348 | 0.0015 ± 0.0013 |
| 九龙江 Jiulong River (JL) | 16 | 7 | H1(1)、H3(1)、H6(1)、H8(10)、H9(1)、H10(1)、H11(1) | 0.6250 ± 0.1390 | 0.0037 ± 0.0024 |
| 长江 Yangtze River (CJ) | 18 | 11 | H12(4)、H13(1)、H14(1)、H15(1)、H19(3)、H20(1)、H21(1)、H22(1)、H23(3)、H25(1)、 H27(1) | 0.9216 ± 0.0417 | 0.0080 ± 0.0046 |
| 钱塘江 Qiantang River (QT) | 14 | 10 | H14(1)、H16(1)、H17(1)、H18(1)、H19(3)、H22(2)、H23(2)、H24(1)、H26(1)、H28(1) | 0.9451 ± 0.0451 | 0.0077 ± 0.0046 |
| 总计 Total | 65 | 28 | 0.9433 ± 0.0168 | 0.0317 ± 0.0158 |
Table 1 Sample information, distribution frequency of 28 haplotypes (H1-H28), haplotype diversity (h) and nucleotide diversity (π) of Coilia mystus
| 采集地 Location | 样本数Sample size | 单元型数 Haplotype number | 单元型 Haplotype | 单元型多样性Haplotype diversity (h) | 核苷酸多样性 Nucleotide diversity (π) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闽江 Minjiang River (MJ) | 17 | 6 | H1(1)、H2(1)、H4(2)、H5(1)、H7(1)、H8(11) | 0.5882 ± 0.1348 | 0.0015 ± 0.0013 |
| 九龙江 Jiulong River (JL) | 16 | 7 | H1(1)、H3(1)、H6(1)、H8(10)、H9(1)、H10(1)、H11(1) | 0.6250 ± 0.1390 | 0.0037 ± 0.0024 |
| 长江 Yangtze River (CJ) | 18 | 11 | H12(4)、H13(1)、H14(1)、H15(1)、H19(3)、H20(1)、H21(1)、H22(1)、H23(3)、H25(1)、 H27(1) | 0.9216 ± 0.0417 | 0.0080 ± 0.0046 |
| 钱塘江 Qiantang River (QT) | 14 | 10 | H14(1)、H16(1)、H17(1)、H18(1)、H19(3)、H22(2)、H23(2)、H24(1)、H26(1)、H28(1) | 0.9451 ± 0.0451 | 0.0077 ± 0.0046 |
| 总计 Total | 65 | 28 | 0.9433 ± 0.0168 | 0.0317 ± 0.0158 |
| 种群 Population | 闽江 MJ | 九龙江 JL | 长江 CJ | 钱塘江 QT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闽江 MJ | 0.002 | |||
| 九龙江 JL | 0.003 | 0.004 | ||
| 长江 CJ | 0.060 | 0.060 | 0.007 | |
| 钱塘江 QT | 0.060 | 0.059 | 0.008 | 0.008 |
Table 2 The average K2P distance between and within Coilia mystus populations
| 种群 Population | 闽江 MJ | 九龙江 JL | 长江 CJ | 钱塘江 QT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闽江 MJ | 0.002 | |||
| 九龙江 JL | 0.003 | 0.004 | ||
| 长江 CJ | 0.060 | 0.060 | 0.007 | |
| 钱塘江 QT | 0.060 | 0.059 | 0.008 | 0.008 |
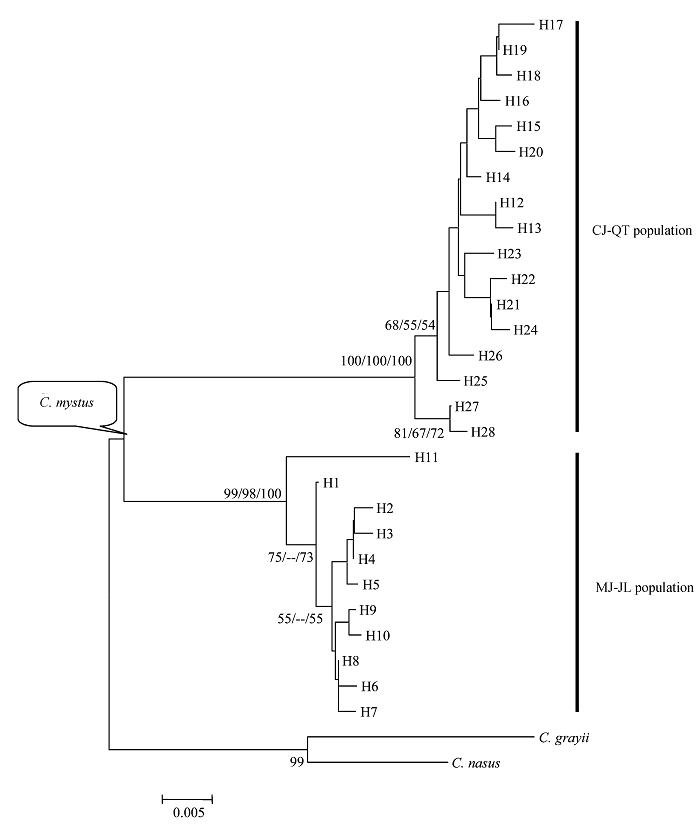
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic trees of four Coilia mystus populations resulted from mtDNA control region sequence. Numbers at nodes are percent recovery in bootstrap analysis. Given for bootstrap values greater than 50% (Neighbor-joining left, maximum likelihood middle, maximum parsimony right (only shows Ti/Tv 2:1weighted; tree length = 137, CI = 0.8248 and HI = 0.1752)).
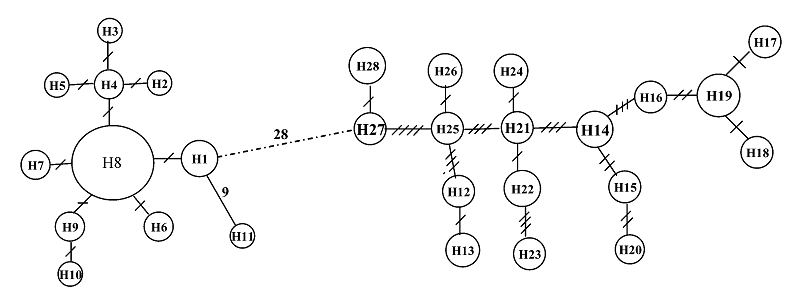
Fig. 2 Minimum spanning networks showing genetic relationship among control region haplotypes for the four Coilia mystus populations. The characters within circles are haplotype codes. Slashes on the lines joining haplotypes denote number of observed mutations.
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 变异分量 Variance components | 变异百分比 Percentage of variation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 组间 Among groups | 1 | 14.59231 | 90.77 |
| 组内种群间 Among populations within group | 2 | 0.03239 | 0.20 |
| 种群内 Within population | 61 | 1.45064 | 9.02 |
| 总计 Total | 64 | 16.07535 |
Table 3 AMOVA of 561 bp mtDNA control region sequences for 65 individuals of Coilia mystus
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 变异分量 Variance components | 变异百分比 Percentage of variation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 组间 Among groups | 1 | 14.59231 | 90.77 |
| 组内种群间 Among populations within group | 2 | 0.03239 | 0.20 |
| 种群内 Within population | 61 | 1.45064 | 9.02 |
| 总计 Total | 64 | 16.07535 |
| 种群 Population | 闽江 MJ | 九龙江 JL | 长江 CJ | 钱塘江 QT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闽江 MJ | 82.96 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
| 九龙江 JL | 0.0030 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
| 长江 CJ | 0.9245 | 0.9060 | 19.91 | |
| 钱塘江 QT | 0.9183 | 0.8998 | 0.0120 |
Table 4 Matrix of pairwise FST (below diagonal) and Nm (above diagonal) between four populations of Coilia mystus
| 种群 Population | 闽江 MJ | 九龙江 JL | 长江 CJ | 钱塘江 QT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闽江 MJ | 82.96 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
| 九龙江 JL | 0.0030 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
| 长江 CJ | 0.9245 | 0.9060 | 19.91 | |
| 钱塘江 QT | 0.9183 | 0.8998 | 0.0120 |
| [1] | Avise JC (2000) Phylogeography: The History and Formation of Species, pp. 9-32. Harvard University Press, London. |
| [2] | Bekessy SA, Ennos RA, Burgman MA, Newton AC, Ades PK (2003) Neutral DNA markers fail to detect genetic divergence in an ecologically important trait. Biological Conservation, 110, 267-275. |
| [3] |
Bowen BW, Grant WS (1997) Phylogeography of the sardines (Sardinops spp.): assessing biogeographic models and population histories in temperate upwelling zones. Evolution, 51, 1601-1610.
URL PMID |
| [4] | Cheng QQ (程起群), Ma CY (马春艳), Miu T (缪烔), Lu X (陆星), Sha ZX (沙珍霞) (2007) Genetic diversity in two wild populations of tapertail anchovy Coilia mystus via 12S ribosomal segment sequences of mitochondrial DNA. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University (大连水产学院学报), 22, 387-391. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Cheng QQ (程起群), Ma CY (马春艳), Zhuang P (庄平), Sha ZX (沙珍霞), Lu X (陆星), Miu T (缪烔) (2008) Genetic structure and evolution characters in three populations of Coilia mystus based on cytochrome b gene segment sequence of mitochondrial DNA. Journal of Fisheries of China (水产学报), 32, 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] |
Drummond AJ, Rambaut A (2007) BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 7, 214.
URL PMID |
| [7] |
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin ver. 3.0: An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evolutionary Bioinformatics Online, 1, 47-50.
URL PMID |
| [8] | Frankham R, Ballou JD, Briscoe DA (2002) Introduction to Conservation Genetics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [9] | Galtier N, Gouy M, Gautier C (1996) SEAVIEW and PHYLO_WIN: two graphic tools for sequence alignment and molecular phylogeny. Computer Applications in the Biosciences, 12, 543-548. |
| [10] | Grant WS, Bowen BW (1998) Shallow population histories in deep evolutionary lineages of marine fishes: insights from sardines and anchovies and lessons for conservation. Journal of Heredity, 89, 415-426. |
| [11] | Liu JX, Gao TX, Zhuang ZM, Jin XS, Yokogawa K, Zhang YP (2006) Late Pleistocene divergence and subsequent population expansion of two closely related fish species, Japanese anchovy (Engraulis japonicus) and Australian anchovy (E. australis). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 40, 712-723. |
| [12] | Liu WB (刘文斌) (1995) Biochemical and morphological comparison and interspecific relationships of four species of the genus Coilia in China. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (海洋与湖沼), 26, 558-565. (in Chinese) |
| [13] | Ni Y (倪勇) (1999) Fishery resources conservation for Coilia mystus in the Changjiang estuary. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China (中国水产科学), 6(5), 75-77. (in Chinese) |
| [14] | Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics, 14, 817-818. |
| [15] | Rambaut A, Drummond AJ (2007) Tracer v1.4. http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer. |
| [16] | Randi E, Lucchini V (1998) Organization and evolution of the mitochondrial DNA control region in the avian genus Alectoris. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 47, 149-162. |
| [17] | Rozas J, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Messeguer X, Rozas R (2003) DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics, 19, 2496-2497. |
| [18] | Shi WG (施炜纲), Wang B (王博) (2002) Status quo of tapertail anchovy resource in the estuaries of the Yangtze River. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica (水生生物学报), 26, 648-653. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Swofford DL (2002) PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (* and other Methods) (version 4.0). Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA. |
| [20] | Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 1596-1599. |
| [21] | Tang QY, Liu HZ, Mayden R, Xiong BX (2006) Comparison of evolutionary rates in the mitochondrial DNA cytochrome b gene and control region and their implications for phylogeny of the Cobitoidea (Teleostei: Cypriniformes). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 39, 347-357. |
| [22] | Tang WQ (唐文乔), Hu XL (胡雪莲), Yang JQ (杨金权) (2007) Species validities of Coilia brachygnathus and C. nasus taihuensis based on sequence variations of complete mtDNA control region. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 15, 224-231. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] |
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 4876-4882.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | van Tienderen PH, de Haan AA, van der Linden CG, Vosman B (2002) Biodiversity assessment using markers for ecologically important trait. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 17, 577-582. |
| [25] |
Verheyen E, Salzburger W, Snoeks J, Meyer A (2003) Origin of the superflock of cichlid fishes from lake Victoria, East Africa. Science, 300, 325-329.
URL PMID |
| [26] | Vrijenhoek RC (1994) Genetic diversity and fitness in small populations. In: Conservation Genetics (eds Loeschcke V, Tomiuk J, Jian SK), pp. 37-53, Birkhäuser-Verlag, Basel. |
| [27] | Whitehead PJP, Nelson GJ, Wongratana T (1988) FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 7. Clupeoid Fishes of the World (Suborder Clupeoidei). Part 2: Engraulididae. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(7/2), 305-579. |
| [28] | Yang JQ (杨金权), Hu XL (胡雪莲), Tang WQ (唐文乔), Lin HD (林弘都) (2008) mtDNA control region sequence variation and genetic diversity of Coilia nasus in Yangtze River estuary and its adjacent waters. Chinese Journal of Zoology (动物学杂志), 43(1), 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Yu ZN, Kong XY, Guo TH, Jiang YY, Zhuang ZM, Jin XS (2005) Mitochondrial DNA sequence variation of Japanese anchovy Engraulis japonicus from the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Fisheries Science, 71, 299-307. |
| [30] | Yuan CM (袁传宓), Lin JB (林金榜), Qin AL (秦安舲), Liu RH (刘仁华) (1976) Historical and present taxonomic status about the genus Coilia in China. Journal of Nanjing University Mathematical Biquarterly (南京大学学报数学半年刊), (2), 1-12. (in Chinese) |
| [31] | Zhang SY (张世义) (2001) Fauna Sinica (Osteichthyes): Acipenseriformes, Elopiformes, Clupeiformes, Gonorhynch- iformes (中国动物志(硬骨鱼纲): 鲟形目, 海鲢目, 鲱形目, 鼠鳝目), pp. 148-154. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [32] | Zhang YP, Ge S (2007) Molecular evolution study in China: progress and future promise. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Science, 362, 973-986. |
| [1] | Jiachen Wang, Tangjun Xu, Wei Xu, Gaoji Zhang, Yijin You, Honghua Ruan, Hongyi Liu. Impact of urban landscape pattern on the genetic structure of Thereuopoda clunifera population in Nanjing, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | Kexin Cao, Jingwen Wang, Guo Zheng, Pengfeng Wu, Yingbin Li, Shuyan Cui. Effects of precipitation regime change and nitrogen deposition on soil nematode diversity in the grassland of northern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [3] | Shiyi Long, Bobo Zhang, Yuchen Xia, Yangfan Fei, Yani Meng, Bingwei Lü, Yueqing Song, Pu Zheng, Taoran Guo, Jian Zhang, Shaopeng Li. Effects of diversity and temporal stability of native communities on the biomass of invasive species Solidago canadensis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24263-. |
| [4] | Linjun He, Wenjing Yang, Yuhao Shi, Kezhemo Ashuo, Yu Fan, Guoyan Wang, Jingji Li, Songlin Shi, Guihua Yi, Peihao Peng. Effects of plant community phylogeny and functional diversity on Ageratina adenophora invasion under fire disturbance [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24269-. |
| [5] | Qingduo Li, Dongmei Li. Analysis for the prevalence of global bat-borne Bartonella [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [6] | Chen Feng, Jie Zhang, Hongwen Huang. Parallel situ conservation: A new plant conservation strategy to integrate in situ and ex situ conservation of plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [7] | Hailing Qi, Pengzhen Fan, Yuehua Wang, Jie Liu. Genetic diversity and population structure of Juglans regia from six provinces in northern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [8] | Yuanyuan Xiao, Wei Feng, Yangui Qiao, Yuqing Zhang, Shugao Qin. Effects of soil microbial community characteristics on soil multifunctionality in sand-fixation shrublands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22585-. |
| [9] | Fei Xiong, Hongyan Liu, Dongdong Zhai, Xinbin Duan, Huiwu Tian, Daqing Chen. Population genetic structure of Pelteobagrus vachelli in the upper Yangtze River based on genome re-sequencing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [10] | Yiyue He, Yuying Liu, Fubin Zhang, Qiang Qin, Yu Zeng, Zhenyu Lü, Kun Yang. Genetic diversity and population structure of Saurogobio dabryi under cascade water conservancy projects in the Jialing River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [11] | Weiyue Sun, Jiangping Shu, Yufeng Gu, Morigengaowa, Xiajin Du, Baodong Liu, Yuehong Yan. Conservation genomics analysis revealed the endangered mechanism of Adiantum nelumboides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [12] | Xiaoyan Jiang, Shengjie Gao, Yan Jiang, Yun Tian, Xin Jia, Tianshan Zha. Species diversity, functional diversity, and phylogenetic diversity in plant communities at different phases of vegetation restoration in the Mu Us sandy grassland [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21387-. |
| [13] | Togtokh Mongke, Dongyi Bai, Tugeqin Bao, Ruoyang Zhao, Tana An, Aertengqimike Tiemuqier, Baoyindeligeer Mongkejargal, Has Soyoltiin, Manglai Dugarjaviin, Haige Han. Assessment of SNPs-based genomic diversity in different populations of Eastern Asian landrace horses [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [14] | Jing Cui, Mingfang Xu, Qun Zhang, Yao Li, Xiaoshu Zeng, Sha Li. Differences in genetic diversity of Pleuronichthys cornutus in the coastal water of China and Japan based on three mitochondrial markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [15] | Xinyu Cai, Xiaowei Mao, Yiqiang Zhao. Methods and research progress on the origin of animal domestication [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(4): 21457-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()