



Biodiv Sci ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (4): 455-462. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019403 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019403
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Mengke Jia1,2,3,Yili Guo1,3,*( ),Dongxing Li1,3,Bin Wang1,3,Wusheng Xiang1,3,Ailong Wang4,Shengyuan Liu4,Tao Ding1,3,Fuzhao Huang1,3,Shujun Wen1,3,Shuhua Lu1,3,Xiankun Li1,3,*(
),Dongxing Li1,3,Bin Wang1,3,Wusheng Xiang1,3,Ailong Wang4,Shengyuan Liu4,Tao Ding1,3,Fuzhao Huang1,3,Shujun Wen1,3,Shuhua Lu1,3,Xiankun Li1,3,*( )
)
Received:2019-12-19
Accepted:2020-03-31
Online:2020-04-20
Published:2020-06-15
Contact:
Yili Guo,Xiankun Li
Mengke Jia,Yili Guo,Dongxing Li,Bin Wang,Wusheng Xiang,Ailong Wang,Shengyuan Liu,Tao Ding,Fuzhao Huang,Shujun Wen,Shuhua Lu,Xiankun Li. Spatio-temporal dynamics of leaf litter in a karst seasonal rainforest in southwest Guangxi[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(4): 455-462.
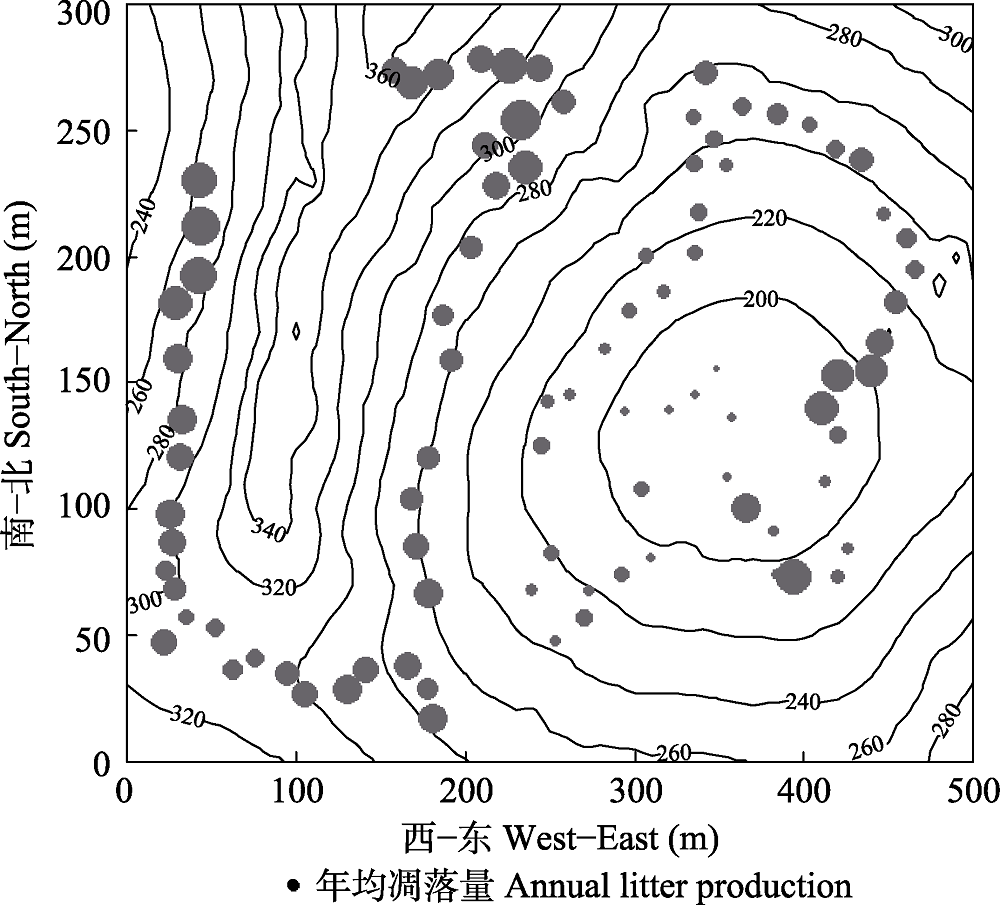
Fig. 2 The contour map and perennial annual leaf litter fall production of 90 litter fall traps of the 15 ha forest dynamics plot in Nonggang, Guangxi. Black dots size indicate the production of litter fall.
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 平均值 Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.578** | 0.670** | 0.644** | 0.394** | 0.491** | 0.697** | 0.682** |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.447** | 0.400** | 0.421** | 0.422** | 0.314** | 0.255* | 0.411** |
| 凹凸度 Convexity | 0.276** | 0.223* | 0.302** | 0.286** | 0.238* | 0.139 | 0.262* |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.141 | 0.296** | 0.095 | 0.01 | 0.046 | 0.222* | 0.172 |
| 岩石裸露率 Rock-bareness rate | 0.183* | 0.223* | 0.192* | 0.289** | 0.268** | 0.334** | 0.255** |
| 湿润度指数 Topographic wetness index | -0.461** | -0.494** | -0.509** | -0.446** | -0.400** | -0.363** | -0.497** |
| 干旱度指数 Altitude above channel | 0.2 | 0.264* | 0.324** | 0.220* | 0.343** | 0.294** | 0.316** |
| 胸径变异系数 DBH variation | -0.281** | -0.352** | -0.284** | -0.137 | -0.114 | -0.326** | -0.299** |
| 胸高断面积之和 Total basal area | 0.229** | 0.218** | 0.229** | 0.243* | 0.145* | 0.196* | 0.234** |
| 物种丰富度 Species richness | 0.089 | 0.112 | 0.091 | 0.132 | 0.103 | 0.078 | 0.097 |
Table 1 Correlations between leaf litter fall production and ecological factors in different years of the 15 ha forest dynamics plot in Nonggang, Guangxi. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 平均值 Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.578** | 0.670** | 0.644** | 0.394** | 0.491** | 0.697** | 0.682** |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.447** | 0.400** | 0.421** | 0.422** | 0.314** | 0.255* | 0.411** |
| 凹凸度 Convexity | 0.276** | 0.223* | 0.302** | 0.286** | 0.238* | 0.139 | 0.262* |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.141 | 0.296** | 0.095 | 0.01 | 0.046 | 0.222* | 0.172 |
| 岩石裸露率 Rock-bareness rate | 0.183* | 0.223* | 0.192* | 0.289** | 0.268** | 0.334** | 0.255** |
| 湿润度指数 Topographic wetness index | -0.461** | -0.494** | -0.509** | -0.446** | -0.400** | -0.363** | -0.497** |
| 干旱度指数 Altitude above channel | 0.2 | 0.264* | 0.324** | 0.220* | 0.343** | 0.294** | 0.316** |
| 胸径变异系数 DBH variation | -0.281** | -0.352** | -0.284** | -0.137 | -0.114 | -0.326** | -0.299** |
| 胸高断面积之和 Total basal area | 0.229** | 0.218** | 0.229** | 0.243* | 0.145* | 0.196* | 0.234** |
| 物种丰富度 Species richness | 0.089 | 0.112 | 0.091 | 0.132 | 0.103 | 0.078 | 0.097 |
| 模型因子 Environmental parameters | r2adj | 累计解释率 Cumulative explained deviation (%) | AIC | 贡献拟合值 Fitted contribution values | 卡方检验 Pr(χ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.425 | 46.5 | 116.366 | 9.344 | 0.000 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.256 | 29.1 | 1,137.742 | 6.254 | 0.000 |
| 凹凸度 Convexity | 0.210 | 25.9 | 1,144.322 | 4.041 | 0.001 |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.114 | 16.7 | 1,154.586 | 2.161 | 0.056 |
| 岩石裸露率 Rock-bareness rate | 0.171 | 22.8 | 1,149.297 | 2.848 | 0.008 |
| 湿润度指数 Topographic wetness index | 0.257 | 27.2 | 1,135.356 | 13.75 | 0.000 |
| 干旱度指数 Altitude above channel | 0.071 | 8.15 | 1,154.644 | 7.809 | 0.006 |
| 胸径变异系数 DBH variation | 0.042 | 5.32 | 1,157.379 | 4.943 | 0.029 |
| 胸高断面积之和 Total basal area | 0.162 | 22.9 | 1,151.089 | 2.598 | 0.015 |
| 物种丰富度 Species richness | 0.044 | 7.87 | 1,159.372 | 1.437 | 0.229 |
Table 2 Test of generalized additive models (GAMs) for modeling leaf annual litter fall production of the 15 ha forest dynamics plot in Nonggang, Guangxi with different indices, respectively
| 模型因子 Environmental parameters | r2adj | 累计解释率 Cumulative explained deviation (%) | AIC | 贡献拟合值 Fitted contribution values | 卡方检验 Pr(χ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.425 | 46.5 | 116.366 | 9.344 | 0.000 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.256 | 29.1 | 1,137.742 | 6.254 | 0.000 |
| 凹凸度 Convexity | 0.210 | 25.9 | 1,144.322 | 4.041 | 0.001 |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.114 | 16.7 | 1,154.586 | 2.161 | 0.056 |
| 岩石裸露率 Rock-bareness rate | 0.171 | 22.8 | 1,149.297 | 2.848 | 0.008 |
| 湿润度指数 Topographic wetness index | 0.257 | 27.2 | 1,135.356 | 13.75 | 0.000 |
| 干旱度指数 Altitude above channel | 0.071 | 8.15 | 1,154.644 | 7.809 | 0.006 |
| 胸径变异系数 DBH variation | 0.042 | 5.32 | 1,157.379 | 4.943 | 0.029 |
| 胸高断面积之和 Total basal area | 0.162 | 22.9 | 1,151.089 | 2.598 | 0.015 |
| 物种丰富度 Species richness | 0.044 | 7.87 | 1,159.372 | 1.437 | 0.229 |
| 模型因子 Environmental parameters | r2adj | 累计解释率 Cumulative explained deviation (%) | AIC | F检验 Pr(F) | 贡献拟合值 Fitted contribution values | 卡方检验 Pr(χ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.425 | 46.5 | 1,116.366 | 0.000 | 6.108 | 0.000 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.458 | 49.2 | 1,110.539 | 0.000 | 0.025 | 0.874 |
| 凹凸度 Convexity | 0.513 | 57.7 | 1,106.171 | 0.000 | 1.289 | 0.260 |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.525 | 58.9 | 1,104.41 | 0.000 | 2.215 | 0.033 |
| 岩石裸露率 Rock-bareness rate | 0.596 | 67.5 | 1,093.937 | 0.000 | 2.631 | 0.109 |
| 湿润度指数 Topographic wetness index | 0.602 | 69.3 | 1,094.793 | 0.000 | 0.887 | 0.349 |
| 干旱度指数 Altitude above channel | 0.593 | 68.1 | 1,095.75 | 0.000 | 0.821 | 0.368 |
| 胸径变异系数 DBH variation | 0.591 | 68.4 | 1,096.955 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.963 |
| 胸高断面积之和 Total basal area | 0.594 | 69.1 | 1,097.032 | 0.000 | 1.312 | 0.256 |
Table 3 Test of generalized additive models (GAMs) for modeling annual leaf litter fall production of the 15 ha forest dynamics plot in Nonggang, Guangxi with all of the indices
| 模型因子 Environmental parameters | r2adj | 累计解释率 Cumulative explained deviation (%) | AIC | F检验 Pr(F) | 贡献拟合值 Fitted contribution values | 卡方检验 Pr(χ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.425 | 46.5 | 1,116.366 | 0.000 | 6.108 | 0.000 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.458 | 49.2 | 1,110.539 | 0.000 | 0.025 | 0.874 |
| 凹凸度 Convexity | 0.513 | 57.7 | 1,106.171 | 0.000 | 1.289 | 0.260 |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.525 | 58.9 | 1,104.41 | 0.000 | 2.215 | 0.033 |
| 岩石裸露率 Rock-bareness rate | 0.596 | 67.5 | 1,093.937 | 0.000 | 2.631 | 0.109 |
| 湿润度指数 Topographic wetness index | 0.602 | 69.3 | 1,094.793 | 0.000 | 0.887 | 0.349 |
| 干旱度指数 Altitude above channel | 0.593 | 68.1 | 1,095.75 | 0.000 | 0.821 | 0.368 |
| 胸径变异系数 DBH variation | 0.591 | 68.4 | 1,096.955 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.963 |
| 胸高断面积之和 Total basal area | 0.594 | 69.1 | 1,097.032 | 0.000 | 1.312 | 0.256 |
| [1] | Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002) Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach, 2nd edn. Springer, New York. |
| [2] | Cao KF, Fu PL, Chen YJ, Jiang YJ, Zhu SD (2014) Implications of the ecophysiological adaptation of plants on tropical karst habitats for the ecological restoration of desertified rocky lands in southern China. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 44, 238-247. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 曹坤芳, 付培立, 陈亚军, 姜艳娟, 朱师丹 (2014) 热带岩溶植物生理生态适应性对于南方石漠化土地生态重建的启示. 中国科学: 生命科学, 44, 238-247.] | |
| [3] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and A Comparison with Other Plots. Springer, Berlin. |
| [4] |
Du YJ, Mi XC, Liu XJ, Chen L, Ma KP (2009) Seed dispersal phenology and dispersal syndromes in a subtropical broad-leaved forest of China. Forest Ecology and Management, 258, 1147-1152.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Guan LL, Zhou GY, Zhang DQ, Liu JX, Zhang QM (2004) Twenty years of litter fall dynamics in subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests at the Dinghushan Forest Ecosystem Research Station. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 28, 449-456. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 官丽莉, 周国逸, 张德强, 刘菊秀, 张倩媚 (2004) 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林凋落物量20年动态研究. 植物生态学报, 28, 449-456.] | |
| [6] |
Guisan A, Edwards Jr TC, Hastie T (2002) Generalized linear and generalized additive models in studies of species distributions: Setting the scene. Ecological Modelling, 157, 89-100.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Guo K, Liu CC, Dong M (2011) Ecological adaptation of plants and control of rocky-desertification on karst region of Southwest China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 35, 991-999. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 郭柯, 刘长成, 董鸣 (2011) 我国西南喀斯特植物生态适应性与石漠化治理. 植物生态学报, 35, 991-999.]
DOI URL |
|
| [8] | Guo LB, Sims REH (1999) Litter production and nutrient return in New Zealand eucalypt short-rotation forest: Implications for land management. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 73, 93-100. |
| [9] | Guo YL, Chen HYC, Mallik AU, Wang B, Li DX, Xiang WS, Li XK (2019) Predominance of abiotic drivers in the relationship between species diversity and litterfall production in a tropical karst seasonal rainforest. Forest Ecology and Management, 449, 117452. |
| [10] | Guo YL, Li DX, Wang B, He YL, Xiang WS, Jiang YL, Li XK (2017) Composition and spatio-temporal dynamics of litter fall in a northern tropical karst seasonal rainforest in Nonggang, Guangxi, southern China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 265-274. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭屹立, 李冬兴, 王斌, 何运林, 向悟生, 蒋裕良, 李先琨 (2017) 北热带喀斯特季节性雨林凋落物组分构成及时空动态特征. 生物多样性, 25, 265-274.] | |
| [11] | Guo YL, Wang B, Li DX, Mallik AU, Xiang WS, Ding T, Wen SJ, Lu SH, Huang FZ, He YL, Li XK (2017) Effects of topography and spatial processes on structuring tree species composition in a diverse heterogeneous tropical karst seasonal rainforest. Flora, 231, 21-28. |
| [12] |
Guo YL, Wang B, Xiang WS, Ding T, Lu SH, Huang FZ, Wen SJ, Li DX, He YL, Li XK (2016) Responses of spatial pattern of woody plants’ basal area to topographic factors in a tropical karst seasonal rainforest in Nonggang, Guangxi, southern China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 30-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 郭屹立, 王斌, 向悟生, 丁涛, 陆树华, 黄甫昭, 文淑均, 李冬兴, 何运林, 李先琨 (2016) 喀斯特季节性雨林木本植物胸高断面积分布格局及其对地形因子的响应. 生物多样性, 24, 30-39.]
DOI URL |
|
| [13] |
Guo YL, Wang B, Xiang WS, Ding T, Lu SH, Huang YS, Huang FZ, Li DX, Li XK (2015) Spatial distribution of tree species in a tropical karst seasonal rainforest in Nonggang, Guangxi, southern China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 183-191. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 郭屹立, 王斌, 向悟生, 丁涛, 陆树华, 黄俞淞, 黄甫昭, 李冬兴, 李先琨 (2015) 广西弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林监测样地种群空间点格局分析. 生物多样性, 23, 183-191.]
DOI URL |
|
| [14] | Guo YL, Xiang WS, Wang B, Li DX, Mallik AU, Chen HYC, Huang FZ, Ding T, Wen SJ, Lu SH, Li XK (2018) Partitioning beta diversity in a tropical karst seasonal rainforest in Southern China. Scientific Reports, 8, 17408. |
| [15] | Han XY, Zhao FX, Li WY (2007) A review of researches on forest litterfall. Forestry Science and Technology Information, 39, 12-13, 16. |
| [16] |
Ingwell LL, Wright JS, Becklund KK, Hubbell SP, Schnitzer SA (2010) The impact of lianas on 10 years of tree growth and mortality on Barro Colorado Island, Panama. Journal of Ecology, 98, 879-887.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Jiang YL, Li XK, Guo YL, Ding T, Wang B, Xiang WS (2017) Diversity of climbing seed plants and their reproductive habit in a karst seasonal rain forest in Nonggang, Guangxi, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 41, 716-728. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 蒋裕良, 李先琨, 郭屹立, 丁涛, 王斌, 向悟生 (2017) 广西弄岗喀斯特季节性雨林藤本种子植物多样性及繁殖习性. 植物生态学报, 41, 716-728.]
DOI URL |
|
| [18] | Jiang ZC, Yuan DX (1999) Dynamics features of the epikarst zone and their significance in environment sand resources. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 20, 302-308. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋忠诚, 袁道先 (1999) 表层岩溶带的岩溶动力学特征及其环境和资源意义. 地球学报, 20, 302-308.] | |
| [19] | Li XK, He CX, Tang JS, Jiang ZC, Huang YQ (2008) Evolution and ecological processes of karst ecosystem of Guangxi. Guangxi Sciences, 15, 80-86, 91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李先琨, 何成新, 唐建生, 蒋忠诚, 黄玉清 (2008) 广西岩溶山地生态系统特征与恢复重建. 广西科学, 15, 80-86, 91.] | |
| [20] | Liu CJ, Westman CJ, Berg B, Kutsch W, Wang GZ, Man RZ, Ilvesniemi H (2004) Variation in litterfall-climate relationships between coniferous and broadleaf forests in Eurasia. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 13, 105-114. |
| [21] | Malhi Y (2012) The productivity, metabolism and carbon cycle of tropical forest vegetation. Journal of Ecology, 100, 65-75. |
| [22] | Poorter L, van der Sande MT, Thompson J, Arets EJMM, Alarcón A, Álvarez-Sánchez J, Ascarrunz N, Balvanera P, Barajas-Guzmán G, Boit A, Bongers F, Carvalho FA, Casanoves F, Cornejo-Tenorio G, Costa FRC, de Castilho CV, Duivenvoorden JF, Dutrieux LP, Enquist BJ, Fernández Méndez F, Finegan B, Gormley LHL, Healey JR, Hoosbeek MR, Ibarra-Manríquez G, Junqueira AB, Levis C, Licona JC, Lisboa LS, Magnusson WE, Martínez-Ramos M, Martínez-Yrizar A, Martorano LG, Maskell LC, Mazzei L, Meave JA, Mora F, Muñoz R, Nytch C, Pansonato MP, Parr TW, Paz H, Pérez-García EA, Rentería LY, Rodríguez- Velazquez J, Rozendaal DMA, Ruschel AR, Sakschewski B, Salgado-Negret B, Schietti J, Simões M, Sinclair FL, Souza PF, Souza FC, Stropp J, ter Steege H, Swenson NG, Thonicke K, Toledo M, Uriarte M, van der Hout P, Walker P, Zamora N, Peña-Claros M (2015) Diversity enhances carbon storage in tropical forests. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 24, 1314-1328. |
| [23] | R Core Team (2019) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. https://www.R-project.org/. (accessed on 2019-11-15) |
| [24] | Reiners WA, Lang GE (1987) Changes in litterfall along a gradient in altitude. Journal of Ecology, 5, 629-638. |
| [25] | Sharma S, Hoque ATMR, Analuddin K, Hagihara A (2012) Litterfall dynamics in an overcrowded mangrove Kandelia obovata (S., L.) Yong stand over five years. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 98, 31-41. |
| [26] | Swartzman G, Huang CH, Kaluzny S (1992) Spatial analysis of Bering Sea groundfish survey data using generalized additive models. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 49, 1366-1378. |
| [27] |
Vasconcelos HL, Luizão FJ (2004) Litter production and litter nutrient concentrations in a fragmented Amazonian landscape. Ecological Applications, 14, 884-892.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Wang B, Huang YS, Li XK, Xiang WS, Ding T, Huang FZ, Lu SH, Han WH, Wen SJ, He LJ (2014) Species composition and spatial distribution of the 15 ha northern tropical karst seasonal rain forest dynamic plot in Nonggang of Guangxi, southern China. Biodiversity Science, 22, 141-156. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 王斌, 黄俞淞, 李先琨, 向悟生, 丁涛, 黄甫昭, 陆树华, 韩文衡, 文淑均, 何兰军 (2014) 弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林15 ha监测样地的树种组成与空间分布. 生物多样性, 22, 141-156.]
DOI URL |
|
| [29] | Wang FY (1989) Review on the study of forest litterfall. Advances in Ecology, 6(2), 82-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王凤友 (1989) 森林凋落量研究综述. 生态学进展, 6(2), 82-89.] | |
| [30] | Wood SN (2006) Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R. Chapman and Hall/CRC Press, London. |
| [31] | Yan ER, Wang XH, Zhou W (2008) Characteristics of litterfall in relation to soil nutrients in mature and degraded evergreen broad-leaved forests of Tiantong, East China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 阎恩荣, 王希华, 周武 (2008) 天童常绿阔叶林演替系列植物群落的N:P化学计量特征. 植物生态学报, 32, 1-12.] | |
| [32] |
Yu GS, Wang SJ, Rong L, Ran JC (2011) Litter dynamics of major successional communities in Maolan karst forest of China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 35, 1019-1028. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 俞国松, 王世杰, 容丽, 冉景丞 (2011) 茂兰喀斯特森林主要演替群落的凋落物动态. 植物生态学报, 35, 1019-1028.]
DOI URL |
|
| [33] | Yuan DX (1991) Karst of China. Geological Publishing House, Beijing. |
| [34] |
Zhang H, Yuan W, Dong W, Liu S (2014) Seasonal patterns of litterfall in forest ecosystem worldwide. Ecological Complexity, 20, 240-247.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Zhang Y, Chen HYH (2015) Individual size in equality links forest diversity and above-ground biomass. Journal of Ecology, 103, 1245-1252.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn