



Biodiv Sci ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (7): 769-778. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019367 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019367
Special Issue: 传粉生物学
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Next Articles
Yuanjun Yu1,2, Huolin Luo1, Nannan Liu1, Dongjin Xiong1, Yibo Luo2, Boyun Yang1,*( )
)
Received:2019-11-20
Accepted:2020-03-23
Online:2020-07-20
Published:2020-09-29
Contact:
Boyun Yang
Yuanjun Yu, Huolin Luo, Nannan Liu, Dongjin Xiong, Yibo Luo, Boyun Yang. Influence of the climate change on suitable areas of Calanthe sieboldii and its pollinators in China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(7): 769-778.
| 编号 Number | 变量描述 Variable description | 方差膨胀因子 Variance inflation factor | 校正判定系数 Adjusted R2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bio1 | 年平均气温 Annual mean temperature | 2,162.4 | 13.2 |
| Bio2 | 昼夜温差月均值 Mean diurnal range | 968.6 | 22.1 |
| Bio3 | 等温性 Isothermality | 231.1 | 9.6 |
| Bio4 | 温度季节性 Temperature seasonality | 3,230.3 | 19.3 |
| Bio5 | 最暖月最高温 Max temperature of warmest month | 27,969.6 | 8.1 |
| Bio6 | 最冷月最低温 Min temperature of coldest month | 127,767.6 | 12.9 |
| Bio7 | 年均温差 Temperature annual range | 146,914.7 | 21.1 |
| Bio8 | 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of wettest quarter | 11.5 | 21.5 |
| Bio9 | 最干季均温 Mean temperature of driest quarter | 42.8 | 11.3 |
| Bio10 | 最暖季均温 Mean temperature of warmest quarter | 2,009.7 | 6.3 |
| Bio11 | 最冷季均温 Mean temperature of coldest quarter | 11,340.5 | 12.5 |
| Bio12 | 年均降水量 Annual precipitation | 105.3 | 29.9 |
| Bio13 | 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month | 207.9 | 27.8 |
| Bio14 | 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month | 332.1 | 26.6 |
| Bio15 | 降水季节性 Precipitation seasonality | 20.2 | 17.7 |
| Bio16 | 最湿季降水量 Precipitation of wettest quarter | 228.8 | 29.9 |
| Bio17 | 最干季降水量 Precipitation of driest quarter | 382.3 | 27.0 |
| Bio18 | 最暖季降水量 Precipitation of warmest quarter | 54.5 | 15.4 |
| Bio19 | 最冷季降水量 Precipitation of coldest quarter | 40.4 | 28.6 |
Table 1 Assessment of biological environmental variables of Calanthe sieboldii (Bold font mean variables used for modeling)
| 编号 Number | 变量描述 Variable description | 方差膨胀因子 Variance inflation factor | 校正判定系数 Adjusted R2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bio1 | 年平均气温 Annual mean temperature | 2,162.4 | 13.2 |
| Bio2 | 昼夜温差月均值 Mean diurnal range | 968.6 | 22.1 |
| Bio3 | 等温性 Isothermality | 231.1 | 9.6 |
| Bio4 | 温度季节性 Temperature seasonality | 3,230.3 | 19.3 |
| Bio5 | 最暖月最高温 Max temperature of warmest month | 27,969.6 | 8.1 |
| Bio6 | 最冷月最低温 Min temperature of coldest month | 127,767.6 | 12.9 |
| Bio7 | 年均温差 Temperature annual range | 146,914.7 | 21.1 |
| Bio8 | 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of wettest quarter | 11.5 | 21.5 |
| Bio9 | 最干季均温 Mean temperature of driest quarter | 42.8 | 11.3 |
| Bio10 | 最暖季均温 Mean temperature of warmest quarter | 2,009.7 | 6.3 |
| Bio11 | 最冷季均温 Mean temperature of coldest quarter | 11,340.5 | 12.5 |
| Bio12 | 年均降水量 Annual precipitation | 105.3 | 29.9 |
| Bio13 | 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month | 207.9 | 27.8 |
| Bio14 | 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month | 332.1 | 26.6 |
| Bio15 | 降水季节性 Precipitation seasonality | 20.2 | 17.7 |
| Bio16 | 最湿季降水量 Precipitation of wettest quarter | 228.8 | 29.9 |
| Bio17 | 最干季降水量 Precipitation of driest quarter | 382.3 | 27.0 |
| Bio18 | 最暖季降水量 Precipitation of warmest quarter | 54.5 | 15.4 |
| Bio19 | 最冷季降水量 Precipitation of coldest quarter | 40.4 | 28.6 |
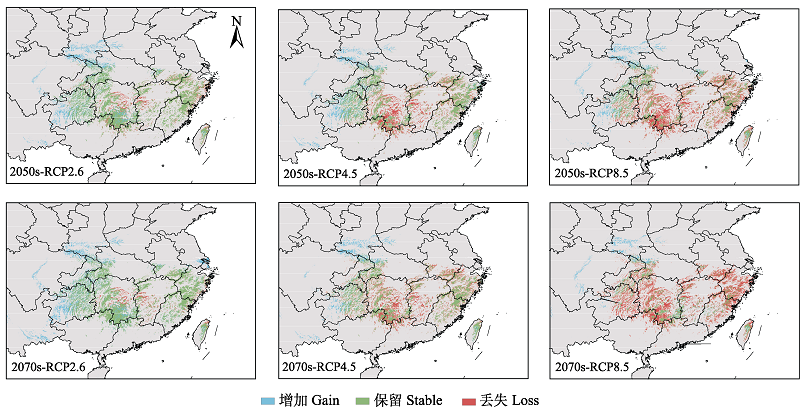
Fig. 2 Predicted suitable habitats change of Calanthe sieboldii by ensembled model of weighted mean of probabilities under different climate change scenarios
| 气候模式 Climate models | 年代 Time | 气候情景 Scenarios | 当前分布区 Current range (km2) | 丢失 Loss (km2) | 增加 Gain (km2) | 未来分布区 Future range (km2) | 适生区净变化率 Net changes in suitable area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCSM4 | 2050 | RCP2.6 | 424,281 | 64,782 | 138,733 | 498,232 | 17.4 |
| RCP4.5 | 424,281 | 148,569 | 121,545 | 397,257 | -6.4 | ||
| RCP8.5 | 424,281 | 242,163 | 100,146 | 282,264 | -33.5 | ||
| 2070 | RCP2.6 | 424,281 | 40,928 | 188,254 | 571,607 | 34.7 | |
| RCP4.5 | 424,281 | 176,090 | 92,036 | 340,227 | -19.8 | ||
| RCP8.5 | 424,281 | 303,405 | 79,212 | 200,088 | -52.8 | ||
| HadGEM2-AO | 2050 | RCP2.6 | 424,281 | 120,838 | 185,188 | 488,631 | 15.2 |
| RCP4.5 | 424,281 | 188,459 | 149,785 | 385,607 | -9.1 | ||
| RCP8.5 | 424,281 | 223,285 | 138,763 | 339,759 | -19.9 | ||
| 2070 | RCP2.6 | 424,281 | 135,160 | 196,285 | 485,406 | 14.4 | |
| RCP4.5 | 424,281 | 267,545 | 120,198 | 276,934 | -34.7 | ||
| RCP8.5 | 424,281 | 330,576 | 80,286 | 173,991 | -59.0 | ||
| FGOALS-g2 | 2050 | RCP2.6 | 424,281 | 94,930 | 153,479 | 482,830 | 13.8 |
| RCP4.5 | 424,281 | 148,569 | 121,545 | 397,257 | -6.4 | ||
| RCP8.5 | 424,281 | 242,163 | 100,146 | 282,264 | -33.5 | ||
| 2070 | RCP2.6 | 424,281 | 40,928 | 188,254 | 571,607 | 34.7 | |
| RCP4.5 | 424,281 | 176,090 | 92,036 | 340,227 | -19.8 | ||
| RCP8.5 | 424,281 | 303,405 | 79,212 | 200,088 | -52.8 |
Table 2 Changes of suitable areas of Calanthe sieboldii under different global climate models and climatic scenarios
| 气候模式 Climate models | 年代 Time | 气候情景 Scenarios | 当前分布区 Current range (km2) | 丢失 Loss (km2) | 增加 Gain (km2) | 未来分布区 Future range (km2) | 适生区净变化率 Net changes in suitable area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCSM4 | 2050 | RCP2.6 | 424,281 | 64,782 | 138,733 | 498,232 | 17.4 |
| RCP4.5 | 424,281 | 148,569 | 121,545 | 397,257 | -6.4 | ||
| RCP8.5 | 424,281 | 242,163 | 100,146 | 282,264 | -33.5 | ||
| 2070 | RCP2.6 | 424,281 | 40,928 | 188,254 | 571,607 | 34.7 | |
| RCP4.5 | 424,281 | 176,090 | 92,036 | 340,227 | -19.8 | ||
| RCP8.5 | 424,281 | 303,405 | 79,212 | 200,088 | -52.8 | ||
| HadGEM2-AO | 2050 | RCP2.6 | 424,281 | 120,838 | 185,188 | 488,631 | 15.2 |
| RCP4.5 | 424,281 | 188,459 | 149,785 | 385,607 | -9.1 | ||
| RCP8.5 | 424,281 | 223,285 | 138,763 | 339,759 | -19.9 | ||
| 2070 | RCP2.6 | 424,281 | 135,160 | 196,285 | 485,406 | 14.4 | |
| RCP4.5 | 424,281 | 267,545 | 120,198 | 276,934 | -34.7 | ||
| RCP8.5 | 424,281 | 330,576 | 80,286 | 173,991 | -59.0 | ||
| FGOALS-g2 | 2050 | RCP2.6 | 424,281 | 94,930 | 153,479 | 482,830 | 13.8 |
| RCP4.5 | 424,281 | 148,569 | 121,545 | 397,257 | -6.4 | ||
| RCP8.5 | 424,281 | 242,163 | 100,146 | 282,264 | -33.5 | ||
| 2070 | RCP2.6 | 424,281 | 40,928 | 188,254 | 571,607 | 34.7 | |
| RCP4.5 | 424,281 | 176,090 | 92,036 | 340,227 | -19.8 | ||
| RCP8.5 | 424,281 | 303,405 | 79,212 | 200,088 | -52.8 |
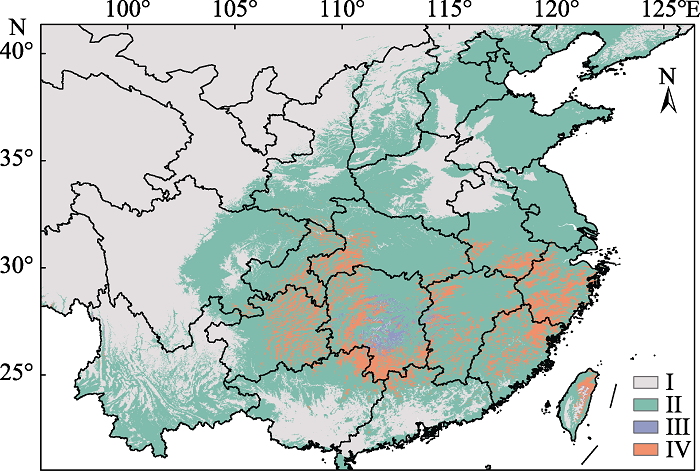
Fig. 3 Predicted current suitable habitats of Calanthe sieboldii and Xylocopa spp. by ensembled model of weighted mean of probabilities. I, Non-suitable habitats; II, suitable habitats of Xylocopa spp.; III, suitable habitats of Calanthe sieboldii; IV, Co-distribution areas.
| 年代 Time | 气候情景 Scenarios | 大黄花虾脊兰适生区 Suitable areas of Calanthe sieboldii (km2) | 木蜂适生区 Suitable areas of Xylocopa spp. (km2) | 共同分布区 Co-distribution areas (km2) | 共同分布区占大黄花虾脊兰适生区比例 Proportion of co-distribution areas among suitable areas of Calanthe sieboldii (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 当前 Current | - | 424,281 | 3,326,189 | 382,189 | 90.0 |
| 2050 | RCP2.6 | 498,232 | 2,725,353 | 460,145 | 92.4 |
| RCP4.5 | 397,257 | 2,672,072 | 347,495 | 87.5 | |
| RCP8.5 | 282,264 | 2,780,090 | 255,319 | 90.4 | |
| 2070 | RCP2.6 | 571,607 | 2,895,034 | 511,387 | 89.5 |
| RCP4.5 | 340,227 | 2,747,877 | 294,294 | 86.5 | |
| RCP8.5 | 200,088 | 2,561,470 | 157,259 | 78.6 |
Table 3 Predicted habitats overlap change of Calanthe sieboldii and Xylocopa spp. by ensembled model of CCSM4 climate models under different future climate scenarios
| 年代 Time | 气候情景 Scenarios | 大黄花虾脊兰适生区 Suitable areas of Calanthe sieboldii (km2) | 木蜂适生区 Suitable areas of Xylocopa spp. (km2) | 共同分布区 Co-distribution areas (km2) | 共同分布区占大黄花虾脊兰适生区比例 Proportion of co-distribution areas among suitable areas of Calanthe sieboldii (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 当前 Current | - | 424,281 | 3,326,189 | 382,189 | 90.0 |
| 2050 | RCP2.6 | 498,232 | 2,725,353 | 460,145 | 92.4 |
| RCP4.5 | 397,257 | 2,672,072 | 347,495 | 87.5 | |
| RCP8.5 | 282,264 | 2,780,090 | 255,319 | 90.4 | |
| 2070 | RCP2.6 | 571,607 | 2,895,034 | 511,387 | 89.5 |
| RCP4.5 | 340,227 | 2,747,877 | 294,294 | 86.5 | |
| RCP8.5 | 200,088 | 2,561,470 | 157,259 | 78.6 |
| [1] |
Aguilar R, Ashworth L, Galetto L, Aizen MA (2006) Plant reproductive susceptibility to habitat fragmentation: Review and synthesis through a meta-analysis. Ecology Letters, 9, 968-980.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] | Allouche O, Tsoar A, Kadmon R (2006) Assessing the accuracy of species distribution models: Prevalence, Kappa and the true skill statistic (TSS). Journal of Applied Ecology, 43, 1223-1232. |
| [3] | Alsos IG, Ehrich D, Thuiller W, Eidesen PB, Tribsch A, Schönswetter P, Lagaye C, Taberlet P, Brochmann C (2012) Genetic consequences of climate change for northern plants. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 279, 2042-2051. |
| [4] | Araujo M, Luoto M (2010) The importance of biotic interactions for modelling species distributions under climate change. Global Ecology & Biogeography, 16, 743-753. |
| [5] | Arditti J, Ghani AKA (2000) Numerical and physical properties of orchid seeds and their biological implications. New Phytologist, 145, 367-421. |
| [6] | Austin MP (1999) A silent clash of paradigms: Some inconsistencies in community ecology. Oikos, 86, 170-178. |
| [7] | Biesmeijer JC, Roberts SPM, Reemer M, Ohlemüller R, Edwards M, Peeters T, Schaffers AP, Potts SG, Kleukers R, Thomas CD, Settele J, Kunin WE (2006) Parallel declines in pollinators and insect-pollinated plants in Britain and the Netherlands. Science, 313, 351-354. |
| [8] | Bond WJ, Lawton JH, May RM (1994) Do mutualisms matter? Assessing the impact of pollinator and disperser disruption on plant extinction. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B: Biological Sciences, 344, 83-90. |
| [9] | Bourg NA, Mcshea WJ, Gill DE (2005) Putting a CART before the search: Successful habitat prediction for a rare forest herb. Ecology, 86, 2793-2804. |
| [10] | Chappell MA (1982) Temperature regulation of carpenter bees (Xylocopa californica) foraging in the Colorado Desert of southern California. Physiological Zoology, 55, 267-280. |
| [11] | Chen XC, Xu Y, Xu CH, Yao Y (2014) Assessment of precipitation simulations in China by CMIP5 multi-models. Progressus Inquisitiones De Mutatione Climatis, 10, 217-225. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈晓晨, 徐影, 许崇海, 姚遥 (2014) CMIP5 全球气候模式对中国地区降水模拟能力的评估. 气候变化研究进展, 10, 217-225.] | |
| [12] | Chen ZD, Ying JS, Lu AM (2012) Disjunct distribution of seed plants between southwestern China and Taiwan Island of China. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 47, 551-570. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈之端, 应俊生, 路安民 (2012) 中国西南地区与台湾种子植物间断分布现象. 植物学报, 47, 551-570.] | |
| [13] | Danabasoglu G, Bates SC, Briegleb BP, Jayne SR, Jochum M, Large WG, Peacock S, Yeager SG (2012) The CCSM4 ocean component. Journal of Climate, 25, 1361-1389. |
| [14] | DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL (1988) Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics, 44, 837-845. |
| [15] | Dormann CF, Elith J, Bacher S, Buchmann C, Carl G, Carré G, Marquéz JRG, Gruber B, Lafourcade B, Leitão PJ (2013) Collinearity: A review of methods to deal with it and a simulation study evaluating their performance. Ecography, 36, 27-46. |
| [16] | Elith J, Leathwick JR (2009) Species distribution models: Ecological explanation and prediction across space and time. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, & Systematics, 40, 677-697. |
| [17] | Friedman JH (1991) Multivariate adaptive regression splines. The Annals of Statistics, 19, 1-67. |
| [18] | GBIF.org (2019) GBIF occurrence download. https://doi.org/10.15468/dl.8fcyvs/. (accessed on 2019-01-20) |
| [19] | Guisan A, Thuiller W (2005) Predicting species distribution: Offering more than simple habitat models. Ecology Letters, 8, 993-1009. |
| [20] | Guisan A, Thuiller W, Zimmermann NE (2017) Habitat Suitability and Distribution Models: With Applications in R. Cambridge University Press, Cornwall. |
| [21] | Guisan A, Zimmermann NE (2000) Predictive habitat distribution models in ecology. Ecological Modelling, 135, 147-186. |
| [22] | Guo C, Lek S, Ye S, Wei L, Liu J, Li Z (2015) Uncertainty in ensemble modelling of large-scale species distribution: Effects from species characteristics and model techniques. Ecological Modelling, 306, 67-75. |
| [23] |
Hegland SJ, Nielsen A, Lázaro A, Bjerknes AL, Totland Ø (2009) How does climate warming affect plant-pollinator interactions? Ecology Letters, 12, 184-195.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | Heinrich B, Buchmann SL (1986) Thermoregulatory physiology of the carpenter bee, Xylocopa varipuncta. Journal of Comparative Physiology B, 156, 557-562. |
| [25] | Heusser LE (2000) Rapid oscillations in western North America vegetation and climate during oxygen isotope stage 5 inferred from pollen data from Santa Barbara Basin (Hole 893A). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 161, 407-421. |
| [26] | Ignasi B, Ascher JS, David W, Danforth BN, Sheila C, Sarah K, Rachael W (2011) Climate-associated phenological advances in bee pollinators and bee-pollinated plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 20645-20649. |
| [27] |
Jane M, Craze PG, Waser NM, Price MV (2007) Global warming and the disruption of plant-pollinator interactions. Ecology Letters, 10, 710-717.
URL PMID |
| [28] | Johnson SD, Steiner KE (2000) Generalization versus specialization in plant pollination systems. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 15, 140-143. |
| [29] |
Jones-Farrand DT, Fearer TM, Thogmartin WE, Thompson FR, Nelson MD, Tirpak JM (2011) Comparison of statistical and theoretical habitat models for conservation planning: The benefit of ensemble prediction. Ecological Applications, 21, 2269-2282.
URL PMID |
| [30] | Karger DN, Conrad O, Böhner J, Kawohl T, Kreft H, Soria-Auza RW, Zimmermann NE, Linder HP, Kessler M (2017) Climatologies at high resolution for the earth’s land surface areas. Scientific Data, 4, 170122. |
| [31] | Liaw A, Wiener M (2002) Classification and regression by randomForest. R News, 2, 18-22. |
| [32] | Lomba A, Pellissier L, Randin C, Vicente J, Moreira F, Honrado J, Guisan A (2010) Overcoming the rare species modelling paradox: A novel hierarchical framework applied to an Iberian endemic plant. Biological Conservation, 143, 2647-2657. |
| [33] |
Luo M, Wang H, Lü Z (2017) Evaluating the performance of species distribution models Biomod2 and MaxEnt using the giant panda distribution data. Journal of Applied Ecology, 28, 4001-4006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL PMID |
|
[ 罗玫, 王昊, 吕植 (2017) 使用大熊猫数据评估Biomod2和MaxEnt分布预测模型的表现. 应用生态学报, 28, 4001-4006.]
PMID |
|
| [34] | Maschinski J, Baggs JE, Quintana-Ascencio PF, Menges ES (2010) Using population viability analysis to predict the effects of climate change on the extinction risk of an endangered limestone endemic shrub, Arizona cliffrose. Conservation Biology, 20, 218-228. |
| [35] | McCaffrey DF, Ridgeway G, Morral AR (2004) Propensity score estimation with boosted regression for evaluating causal effects in observational studies. Psychological Methods, 9, 403-425. |
| [36] | McCullagh P (1989) Generalized Linear Models. Routledge, New York. |
| [37] | Miller JR, Turner MG, Smithwick EA, Dent CL, Stanley EH (2004) Spatial extrapolation: The science of predicting ecological patterns and processes. BioScience, 54, 310-320. |
| [38] | Ozinga WA, Schaminée JH, Bekker RM, Bonn S, Poschlod P, Tackenberg O, Bakker J, Groenendael JMV (2005) Predictability of plant species composition from environmental conditions is constrained by dispersal limitation. Oikos, 108, 555-561. |
| [39] | Parmesan C, Duarte C, Poloczanska E, Richardson AJ, Singer MC (2011) Overstretching attribution. Nature Climate Change, 1, 2-4. |
| [40] | Pearson RG, Dawson TP (2003) Predicting the impacts of climate change on the distribution of species: Are bioclimate envelope models useful? Global Ecology and Biogeography, 12, 361-371. |
| [41] | Phillips SJ, Anderson RP, Schapire RE (2006) Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecological Modelling, 190, 231-259. |
| [42] | R Core Team (2019) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing https://www.R-project.org/. (accessed on 2019-05-13) |
| [43] | Sheth SN, Angert AL (2014) The evolution of environmental tolerance and range size: A comparison of geographically restricted and widespread Mimulus. Evolution, 68, 2917-2931. |
| [44] | Sipes SD, Tepedino VJ (1995) Reproductive biology of the rare orchid, Spiranthes diluvialis: Breeding system, pollination, and implications for conservation. Conservation Biology, 9, 929-938. |
| [45] | Suggitt AJ, Wilson RJ, August TA, Beale CM, Bennie JJ, Dordolo A, Fox R, Hopkins JJ, Isaac NJB, Jorieux P (2014) Climate Change Refugia for the Flora and Fauna of England. Natural England Commissioned Reports NECR162, London. |
| [46] | Sugiura N (2013) Specialized pollination by carpenter bees in Calanthe striata (Orchidaceae), with a review of carpenter bee pollination in orchids. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 171, 730-743. |
| [47] |
Sun M, Gross K, Schiestl FP (2014) Floral adaptation to local pollinator guilds in a terrestrial orchid. Annals of Botany, 113, 289-300.
DOI URL PMID |
| [48] | Tremblay RL, Ackerman JD, Zimmerman JK, Calvo RN (2004) Variation in sexual reproduction in orchids and its evolutionary consequences: A spasmodic journey to diversification. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 84, 1-54. |
| [49] | van der Cingel N(2001) An Atlas of Orchid Pollination: European Orchids. CRC Press, Rotterdam. |
| [50] | van Vuuren DP, Edmonds J, Kainuma M, Riahi K, Thomson A, Hibbard K, Hurtt GC, Kram T, Krey V, Lamarque JF, Masui T, Meinshausen M, Nakicenovic N, Smith SJ, Rose SK (2011) The representative concentration pathways: An overview. Climatic Change, 109, 5-31. |
| [51] | Wilfried T, Damien G, Robin E, Frank B (2019) biomod2: Ensemble Platform for Species Distribution Modeling. R package version 3.3-7.1. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package= biomod2/. (accessed on 2019-05-27) |
| [52] | Xie D, Zhang C, Zhang MH, Wu MH, Zhang DG (2017) New records of monocotyledon plants in Hubei. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 37, 815-819. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谢丹, 张成, 张梦华, 吴名鹤, 张代贵 (2017) 湖北单子叶植物新记录. 西北植物学报, 37, 815-819.] | |
| [53] | Yoder JA, Zettler LW, Stewart SL (2000) Water requirements of terrestrial and epiphytic orchid seeds and seedlings, and evidence for water uptake by means of mycotrophy. Plant Science, 156, 145-150. |
| [54] | Zhang XR, Pu Z, Huang ZH, Zhou X, Xing SH (2017) Habitat characteristics and niche analysis of Calanthe sieboldii Decne. survival community. Plant Science Journal, 35, 799-806. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张孝然, 蒲真, 黄治昊, 周鑫, 邢韶华 (2017) 大黄花虾脊兰生境特征及生存群落物种生态位分析. 植物科学学报, 35, 799-806.] | |
| [55] |
Zhao MS, Running SW (2010) Drought-induced reduction in global terrestrial net primary production from 2000 through 2009. Science, 329, 940-943.
URL PMID |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()