



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 23212. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023212 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023212
彭昀月1,*( )(
)( ), 罗永梅1(
), 罗永梅1( ), 徐泽楠2, 靳彤1(
), 徐泽楠2, 靳彤1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-21
接受日期:2023-11-26
出版日期:2024-02-20
发布日期:2023-12-07
通讯作者:
E-mail:
Yunyue Peng1,*( )(
)( ), Yongmei Luo1(
), Yongmei Luo1( ), Zenan Xu2, Tong Jin1(
), Zenan Xu2, Tong Jin1( )
)
Received:2023-06-21
Accepted:2023-11-26
Online:2024-02-20
Published:2023-12-07
Contact:
E-mail: 摘要:
在“碳达峰”和“碳中和”目标的驱动下, 我国可再生能源增长势头迅猛, 而随着光伏、风电的大规模发展, 其生态影响问题也引发关注, 但缺乏系统性的研究综述。本文回顾了国内外集中式光伏和陆上风电电场对环境、物种多样性和生态系统服务功能影响的研究, 发现: 光伏的生态影响主要体现在对土壤、植被和栖息地质量的改变, 对部分物种有不利影响, 在较为干旱的地区, 光伏设施能起到降温增湿的作用, 促进植被恢复, 在荒漠地区可以发挥防风固沙的生态作用; 风电电场的生态影响集中在对土壤植被的扰动、造成鸟类碰撞死亡和栖息地破碎化等方面, 影响物种迁徙和区域生态系统服务功能。但目前的研究在生态影响机制和生态系统整体影响方面还存在不足, 对此, 本文提出了完善与统一调查方法、采用先进的生态环境调查技术、加强在物种和生态系统水平上的系统性影响研究等建议。未来需要进一步研究光伏、风电电场的生态影响, 在能源规划初期关注生态本底调查和生物多样性评估, 并制定相应的生态影响减缓策略。
彭昀月, 罗永梅, 徐泽楠, 靳彤 (2024) 集中式大型光伏及风电电场生态影响: 进展与展望. 生物多样性, 32, 23212. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023212.
Yunyue Peng, Yongmei Luo, Zenan Xu, Tong Jin (2024) Ecological impacts of centralized large-scale photovoltaics and wind farms: Progress and prospects. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23212. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023212.
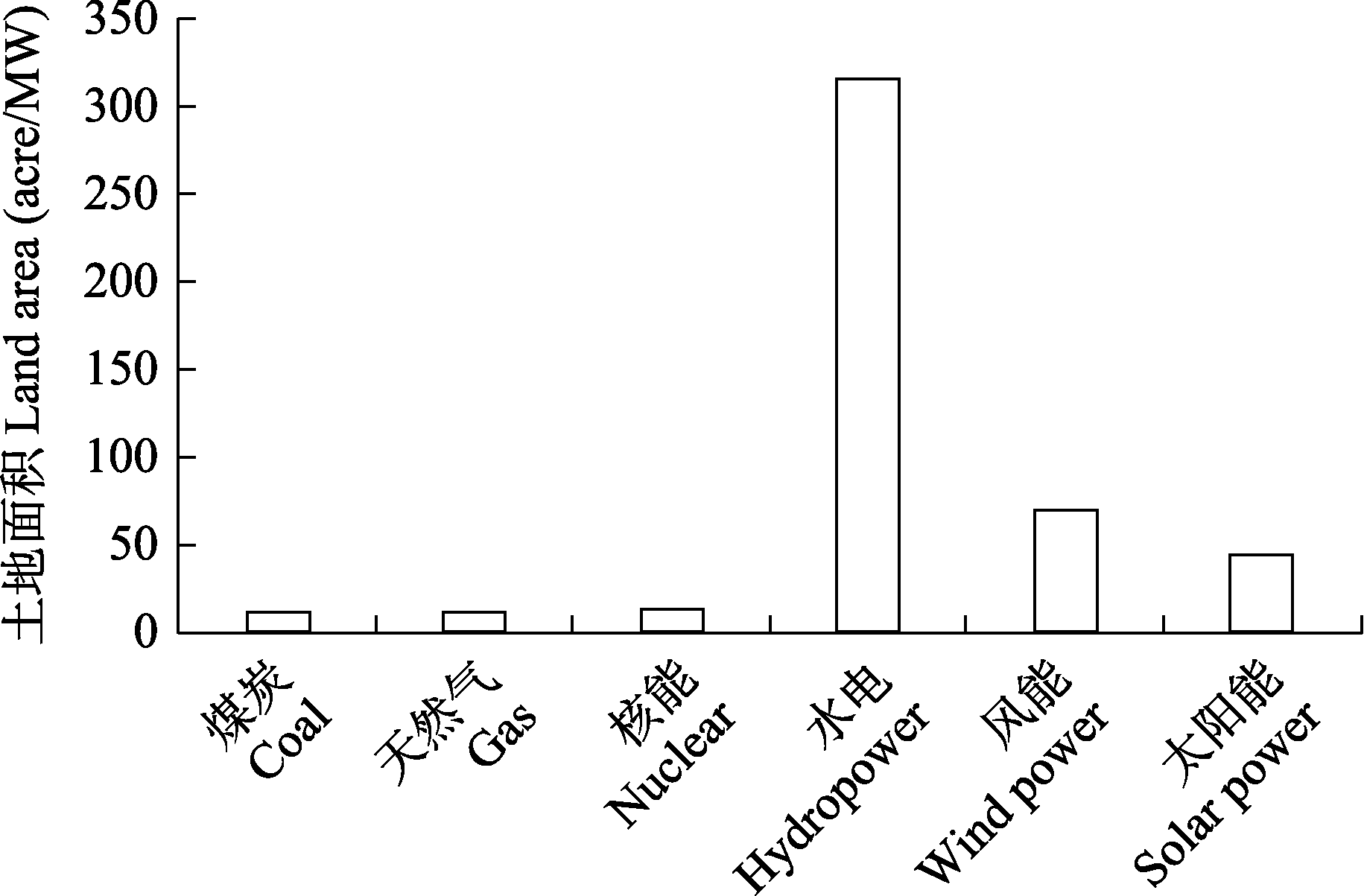
图1 不同类型能源生产、加工、运输及废弃物处理全过程所需土地面积。根据Stevens等(2017)重绘。
Fig. 1 The land area required for the entire process of energy production, processing, transportation, and waste disposal among different types of energy. Redrawn from Stevens et al (2017).
| [1] | Ai JW, Yu KY, Huang RX, Geng JW, Xie Z, Liu J (2023) The impact of wind power projects on potential ecological corridors based on the MSPA-MCR Model. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43, 3665-3676. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [艾婧文, 余坤勇, 黄茹鲜, 耿建伟, 谢祯, 刘健 (2023) 基于MSPA-MCR模型的风电项目对潜在生态廊道影响研究. 生态学报, 43, 3665-3676.] | |
| [2] |
Allison TD, Cochrane JF, Lonsdorf E, Sanders-Reed C (2017) A review of options for mitigating take of golden eagles at wind energy facilities. Journal of Raptor Research, 51, 319-333.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Armstrong A, Ostle NJ, Whitaker J (2016) Solar park microclimate and vegetation management effects on grassland carbon cycling. Environmental Research Letters, 7, 74016. |
| [4] | AWWI American Wind and Wildlife Institute (2017) Wind Turbine Interactions with Wildlife and Their Habitats: A Summary of Research Results and Priority Questions. https://rewi.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/AWWI-Wind-Wildlife-Interactions-Summary-June-2017.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-11) |
| [5] |
Battany MC, Grismer ME (2000) Rainfall runoff and erosion in Napa Valley vineyards: Effects of slope, cover and surface roughness. Hydrological Processes, 14, 1289-1304.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Bennun L, Bochove JV, Ng C, Fletcher C, Carbone G (2021) Mitigating Biodiversity Impacts Associated with Solar and Wind Energy Development: Guidelines for Project Developers. IUCN, Gland & The Biodiversity Consultancy, Cambridge. https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/2021-004-En.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-11) |
| [7] |
Bopucki R, Klich D, Gielarek S (2017) Do terrestrial animals avoid areas close to turbines in functioning wind farms in agricultural landscapes? Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189, 1-11.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Chang ZF, Wang Q, Liu SZ, Wang FL, Liu SJ, Wang F, Sun T, Zhan KJ (2018) Preliminary study on the effect of desert Gobi photovoltaic farms on sand consolidation—A case study of Gansu Hexi Corridor. Soil and Water Conservation in China, (8), 18-22. (in Chinese) |
| [常兆丰, 王祺, 刘世增, 王芳琳, 刘淑娟, 王飞, 孙涛, 詹科杰 (2018) 沙漠戈壁光伏电场固沙效应初步研究——以甘肃河西走廊为例. 中国水土保持, (8), 18-22.] | |
| [9] | Chen ZQ (2017) Eco-environmental impact in EIA of wind power generation project. Journal of Environment & Development, 29(6), 27, 29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈志强 (2017) 风力发电项目环评中的生态环境影响. 环境与发展, 29(6), 27, 29.] | |
| [10] |
Cheng K, Yue Q, Xu XR, Yan M, Pan GX (2015) Characterizing and quantifying soil resilience for ecosystem services. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 48, 4621-4629. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[程琨, 岳骞, 徐向瑞, 闫明, 潘根兴 (2015) 土壤生态系统服务功能表征与计量. 中国农业科学, 48, 4621-4629.]
DOI |
|
| [11] | Chock RY, Clucas B, Peterson EK, Blackwell BF, Blumstein DT, Church K, Fernández-Juricic E, Francescoli G, Greggor AL, Kemp P (2021) Evaluating potential effects of solar power facilities on wildlife from an animal behavior perspective. Conservation Science and Practice, 3, e319. |
| [12] |
Conkling T, Loss S, Diffendorfer J, Duerr A, Katzner T (2021) Limitations, lack of standardization, and recommended best practices in studies of renewable energy effects on birds and bats. Conservation Biology, 35, 64-76.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Copeland HE, Pocewicz A, Kiesecker JM (2011) Geography of energy development in Western North America:Potential impacts on terrestrial ecosystems. In: Energy Development and Wildlife Conservation in Western North America (ed. Naugle DE), pp. 7-22. Island Press, Washington, DC. |
| [14] | Cypher BL, Boroski BB, Burton RK, Meade DE, Phillips SE, Leitner P, Kelly EC, Westall TL, Dart J (2021) Photovoltaic solar farms in California: Can we have renewable electricity and our species, too? California Fish and Wildlife, 107, 231-248. |
| [15] |
Dahl EL, May R, Hoel PL, Bevanger K, Pedersen HC, Røskaft E, Stokke BG (2013) White-tailed eagles (Haliaeetus albicilla) at the Smøla wind-power plant, Central Norway, lack behavioral flight responses to wind turbines. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 37, 66-74.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
De Lucas M, Ferrer M, Bechard MJ, Muñoz AR (2012) Griffon vulture mortality at wind farms in southern Spain: Distribution of fatalities and active mitigation measures. Biological Conservation, 147, 184-189.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Denholm P, Hand M, Jackson M, Ong S (2009) Land Use Requirements of Modern Wind Power Plants in the United States. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden. https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy09osti/45834.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-11) |
| [18] | Devault T, Seamans T, Schmidt J, Belant J, Blackwell B, Mooers N, Tyson L, Pelt L (2014) Bird use of solar photovoltaic installations at US airports: Implications for aviation safety. Landscape and Urban Planning, 122, 122-128. |
| [19] |
Dhar A, Naeth M, Jennings P, El-Din M (2020) Perspectives on environmental impacts and a land reclamation strategy for solar and wind energy systems. Science of the Total Environment, 718, 134602.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Ding CX, Liu Y (2021) Impact of photovoltaic park construction on soil prokaryotic microbial communities in alpine desert grasslands on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 29, 1061-1069. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[丁成翔, 刘禹 (2021) 光伏园区建设对青藏高原高寒荒漠草地土壤原核微生物群落的影响. 草地学报, 29, 1061-1069.]
DOI |
|
| [21] |
Drewitt A, Langston R (2006) Assessing the impacts of wind farms on birds. Ibis, 148, 29-42.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Du WJ, Guan JJ (2019) Environmental impact and countermeasures of wind power construction in Yunnan. Environmental Science Survey, 38, 79-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杜文静, 关佳杰 (2019) 云南省风电建设项目对环境的影响及对策措施. 环境科学导刊, 38, 79-81.] | |
| [23] | Everaert J (2003) Windturbines en vogels in Vlaanderen: Voorlopige onderzoeksresultaten en aanbevelingen. Natuur Oriolus, 69, 145-155. |
| [24] |
Fthenakis V, Kim HC (2009) Land use and electricity generation: A life-cycle analysis. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 13, 1465-1474.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Gamboa G, Munda G (2007) The problem of windfarm location: A social multi-criteria evaluation framework. Energy Policy, 35, 1564-1583.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Gao XQ, Yang LW, Lü F, Ma LY, Li HL, Hui XY, Hou XH (2016) Observational study on the impact of the large solar farm on air temperature and humidity in desert areas of Golmud. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 37, 2909-2915. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高晓清, 杨丽薇, 吕芳, 马丽云, 李海玲, 惠小英, 侯旭宏 (2016) 光伏电站对格尔木荒漠地区空气温湿度影响的观测研究. 太阳能学报, 37, 2909-2915.] | |
| [27] |
Gasparatos A, Doll C, Esteban M, Ahmed A, Olang T (2017) Renewable energy and biodiversity: Implications for transitioning to a green economy. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 70, 161-184.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Gelbard J, Belnap J (2003) Roads as conduits for exotic plant invasions in a semiarid landscape. Conservation Biology, 17, 420-432.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Greif S, Siemers B (2010) Innate recognition of water bodies in echolocating bats. Nature Communications, 1, 107.
PMID |
| [30] |
Grodsky SM, Jennelle CS, Drake D (2013) Bird mortality at a wind-energy facility near a wetland of international importance. The Condor, 115, 700-711.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Guerrero-Campo J, Montserrat-Marti G (2004) Comparison of floristic changes on vegetation affected by different levels of soil erosion in Miocene clays and Eocene marls from Northeast Spain. Plant Ecology, 173, 83-93.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Hall R, João E, Knapp CW (2020) Environmental impacts of decommissioning: Onshore versus offshore wind farms. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 83, 106404.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Hamed TA, Alshare A (2021) Environmental impact of solar and wind energy—A review. Journal of Sustainable Development of Energy, Water and Environment Systems, 10, 1090387. |
| [34] |
Hastik R, Basso S, Geitner C, Haida C, Poljanec A, Portaccio A, Vrščaj B, Walzer C (2015) Renewable energies and ecosystem service impacts. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 48, 608-623.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Hau E, Renouard H (2006) Wind Turbines: Fundamentals, Technologies, Application, Economics, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin. |
| [36] | Hernandez R, Easter S, Murphy-Mariscal M, Maestre F, Tavassoli M, Allen EB, Barrows C, Belnap J, Ochoa-Hueso R, Ravi S, Allen M (2014) Environmental impacts of utility-scale solar energy. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 29, 766-779. |
| [37] | Hernandez RR, Hoffacker MK, Murphy-Mariscal ML, Wu GC, Allen MF (2015) Solar energy development impacts on land cover change and protected areas. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 13579-13584. |
| [38] |
Horváth G, Blahó M, Egri Á, Kriska G, Seres I, Robertson B (2010) Reducing the maladaptive attractiveness of solar panels to polarotactic insects. Conservation Biology, 24, 1644-1653.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Hötker H, Thomsen K, Jeromin H (2006) Impacts on Biodiversity of Exploitation of Renewable Energy Sources: The Example of Birds and Bats. Nature and Biodiversity Conservation Union (NABU), Bergenhusen. https://eolien-biodiversite.com/IMG/pdf/englischewindkraftstudie_1252510701.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-11) |
| [40] | Hu J, Wang S (2018) Impact of large-scale wind power base located in Gansu Jiuquan on regional climate. Global Energy Interconnection, 1(2), 120-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [胡菊, 王姝 (2018) 甘肃酒泉大型风电基地对区域气候的影响研究. 全球能源互联网, 1(2), 120-128.] | |
| [41] | Huang YJ, Zhao YY, Wen YG, Sun DJ, Gao H, Liang J, Zhu J, Zhou XG (2022) Birds diversity and their influence by wind turbines in autumn at Xing’an area wind farms, Xing’an County, Guangxi. Journal of Guangxi Academy of Sciences, 38, 304-310. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄勇杰, 赵岩岩, 温远光, 孙冬婧, 高惠, 梁佳, 朱健, 周晓果 (2022) 广西兴安县兴安片区风电场秋季鸟类多样性及其受风机的影响. 广西科学院学报, 38, 304-310.] | |
| [42] | Hui JX, Han X, Cui C, Luo YM (2020) Eco-friendly onshore wind power development policy recommendations. Electric Power Equipment Management, (9), 27-28, 37. (in Chinese) |
| [惠婧璇, 韩雪, 崔成, 罗永梅 (2020) 生态友好的陆上风电发展政策建议. 电力设备管理, (9), 27-28, 37.] | |
| [43] | Hunt WG (2001) Continuing studies of golden eagles at Altamont Pass. In:Proceedings of the National Avian-Wind Power Planning Meeting IV, p. 15, Carmel. |
| [44] | Hunt WG, Jackman RE, Hunt TL, Driscoll DE, Culp L (1999) A Population Study of Golden Eagles in the Altamont Pass Wind Resource Area: Population Trend Analysis, 1994-1997. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden & Predatory Bird Research Group, University of California, Santa Cruz. https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy99osti/26092.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-11) |
| [45] | Jiang JX, Yang LW, Li ZC, Gao XQ (2019) Progress in the research on the impact of wind farms on climate and environment. Advances in Earth Science, 34, 1038-1049. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[蒋俊霞, 杨丽薇, 李振朝, 高晓清 (2019) 风电场对气候环境的影响研究进展. 地球科学进展, 34, 1038-1049.]
DOI |
|
| [46] | Jin SP, Chen ZQ, Zhao L, Guo J, Hou YJ (2020) Analysis on prevention and control of ecological environment impact of photovoltaic power generation construction projects. Energy and Energy Conservation, (11), 59-60, 106. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [靳绍鹏, 陈智清, 赵龙, 国洁, 侯永江 (2020) 光伏发电建设项目生态环境影响防控分析. 能源与节能, (11), 59-60, 106.] | |
| [47] |
Josimović B, Pucar M (2010) The strategic environmental impact assessment of electric wind energy plants: Case study ‘Bavanište’ (Serbia). Renewable Energy, 35, 1509-1519.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Kagan RA, Viner TC, Trail PW, Espinoza EO (2014) Avian Mortality at Solar Energy Facilities in Southern California: A Preliminary Analysis. National Fish and Wildlife Forensics Laboratory, Ashland, Oregon. https://usiraq.procon.org/sourcefiles/avian-mortality-solar-energy-ivanpah-apr-2014.PDF. (accessed on 2024-02-11) |
| [49] |
Kim JY, Koide D, Ishihama F, Kadoya T, Nishihiro J (2021) Current site planning of medium to large solar power systems accelerates the loss of the remaining semi-natural and agricultural habitats. Science of the Total Environment, 779, 146475.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Kitano M, Smallwood KS, Fukaya K (2023) Bird carcass detection from integrated trials at multiple wind farms. The Journal of Wildlife Management, 87, e22326. |
| [51] | Kosciuch K, Riser-Espinoza D, Gerringer M, Erickson W (2020) A summary of bird mortality at photovoltaic utility scale solar facilities in the Southwestern U.S. PLoS ONE, 15, e232034. |
| [52] | Kruckenberg H, Jaene J (1999) Zum Einfluss eines Windparks auf die Verteilung weidender Bläßgänse im Rheiderland (Landkreis Leer, Niedersachsen). Natur und Landschaft, 74, 420-427. |
| [53] | Kumara HN, Babu S, Rao GB, Mahato S, Bhattacharya M, Rao NVR, Tamiliniyan D, Parengal H, Deepak D, Balakrishnan A (2022) Responses of birds and mammals to long-established wind farms in India. Scientific Reports, 12, 1339. |
| [54] |
Kunz T, Arnett E, Erickson W, Hoar A, Johnson G, Larkin R, Strickland M, Thresher R, Tuttle M (2007) Ecological impacts of wind energy development on bats: Questions, research needs, and hypotheses. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 5, 315-324.
DOI URL |
| [55] | Laffta S (2014) Environmental impacts of wind energy. Journal of Clean Energy Technologies, 1, 251-254. |
| [56] |
Larsen JK, Madsen J (2000) Effects of wind turbines and other physical elements on field utilization by pink-footed geese (Anser brachyrhynchus): A landscape perspective. Landscape Ecology, 15, 755-764.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Li Y, Kalnay E, Motesharrei S, Rivas J, Kucharski F, Kirk-Davidoff D, Bach E, Zeng N (2018) Climate model shows large-scale wind and solar farms in the Sahara increase rain and vegetation. Science, 361, 1019-1022.
DOI PMID |
| [58] | Li ZL (2015) Effect of wind power site construction on soil nutrients and vegetation of the surrounding disturbed region. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 22(6), 61-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李智兰 (2015) 风电场建设对周边扰动区域土壤养分和植被的影响. 水土保持研究, 22(6), 61-66.] | |
| [59] | Liu DX (2020) Management of solar photovoltaic power plants in the context of eco-environmental protection. Regional Governance, (3), 176-178. (in Chinese) |
| [刘冬晓 (2020) 生态环境保护视域下的太阳能光伏发电站管理. 区域治理, (3), 176-178.] | |
| [60] |
Liu Y, Zhang R, Huang Z, Cheng Z, López-Vicente M, Ma XR, Wu G (2019) Solar photovoltaic panels significantly promote vegetation recovery by modifying the soil surface microhabitats in arid sandy ecosystem. Land Degradation & Development, 30, 2177-2186.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Liu Y, Zhang R, Ma X, Wu G (2020) Combined ecological and economic benefits of the solar photovoltaic industry in arid sandy ecosystems. Journal of Cleaner Production, 262, 121376.
DOI URL |
| [62] | Liu YQ, Zhao H (2017) Investigation on bird strike in wind farm in bird sensitive area in Yunnan Province. Environmental Science Survey, 36, 167-169. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘越强, 赵华 (2017) 云南鸟类敏感区域已建风电场鸟撞影响调查. 环境科学导刊, 36, 167-169.] | |
| [63] |
Lovich JE, Ennen JR (2011) Wildlife conservation and solar energy development in the desert southwest, United States. Bioscience, 61, 982-992.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Marques A, Santos C, Hanssen F, Muñoz A, Onrubia A, Wikelski M, Moreira F, Palmeirim J, Silva J (2020) Wind turbines cause functional habitat loss for migratory soaring birds. Journal of Animal Ecology, 89, 93-103.
DOI PMID |
| [65] | Montag H, Parker DG, Clarkson T (2016) The Effects of Solar Farms on Local Biodiversity: A Comparative Study. Clarkson and Woods, Somerset & Wychwood Biodiversity, Devon. https://helapco.gr/wp-content/uploads/Solar_Farms_Biodiversity_Study.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-11) |
| [66] | Muñoz AR, Farfán MÁ (2020) European free-tailed bat fatalities at wind farms in southern Spain. Biodiversity and Conservation, 43, 37-41. |
| [67] | Munson S, Belnap J, Okin G (2011) Responses of wind erosion to climate-induced vegetation changes on the Colorado Plateau. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 3854-3859. |
| [68] |
Nazir MS, Bilal M, Sohail HM, Liu B, Chen W, Iqbal H (2020) Impacts of renewable energy atlas: Reaping the benefits of renewables and biodiversity threats. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 45, 22113-22124.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Nekola J (2012) The impact of a utility corridor on terrestrial gastropod biodiversity. Biodiversity and Conservation, 21, 781-795.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Newton I, Little B (2009) Assessment of wind-farm and other bird casualties from carcasses found on a Northumbrian beach over an 11-year period. Bird Study, 56, 158-167.
DOI URL |
| [71] | Ong C (2013) Land-use Requirements for Solar Power Plants in the United States. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden. https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy13osti/56290.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-11) |
| [72] |
Pearce-Higgins J, Stephen L, Douse A, Langston R (2012) Greater impacts of wind farms on bird populations during construction than subsequent operation: Results of a multi-site and multi-species analysis. Journal of Applied Ecology, 49, 386-394.
DOI URL |
| [73] | Poot H, De Vries H, Donners M, Wernand M, Marquenie J (2008) Green light for nocturnally migrating birds. Ecology and Society, 13(2), 47. |
| [74] |
Poulsen AH, Raaschou-Nielsen O, Peña A, Hahmann AN, Nordsborg RB, Ketzel M, Brandt J, Sørensen M (2018) Short-term nighttime wind turbine noise and cardiovascular events: A nationwide case-crossover study from Denmark. Environment International, 114, 160-166.
DOI PMID |
| [75] | Ralston-Paton S, Smallie J, Pearson A, Ramalho R (2017) Wind Energy’s Impacts on Birds in South Africa: A Preliminary Review of the Results of Operational Monitoring at the First Wind Farms of the Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement Programme in South Africa. BirdLife South Africa, Johannesburg. https://www.birdlife.org.za/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Wind-Energy-and-Birds-Impacts.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-11) |
| [76] |
Reid T, Krüger S, Whitfield DP, Amar A (2015) Using spatial analyses of bearded vulture movements in southern Africa to inform wind turbine placement. Journal of Applied Ecology, 52, 881-892.
DOI URL |
| [77] | Ren XC, Yi KP, Cao L (2022) Optimizing layout of wind farms and power grids to avoid bird strikes. Environmental Protection Science, 48(3), 13-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [任西婵, 伊坤朋, 曹垒 (2022) 优化风电场和电网布局以避免鸟撞. 环境保护科学, 48(3), 13-19.] | |
| [78] |
Rushworth I, Krüger S (2014) Wind farms threaten southern Africa’s cliff-nesting vultures. Ostrich, 85, 13-23.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
Salguero MM, De la Cruz A, Muñoz A, Arroyo GM (2023) Bat mortality in wind farms of southern Europe: Temporal patterns and implications in the current context of climate change. Biodiversity and Conservation, 32, 3953-3971.
DOI |
| [80] |
Santos M, Bastos R, Travassos P, Bessa Santos R, Repas M, Cabral J (2010) Predicting the trends of vertebrate species richness as a response to wind farms installation in mountain ecosystems of northwest Portugal. Ecological Indicators, 10, 192-205.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
Sayed E, Wilberforce Awotwe T, Elsaid K, Rabaia M, Abdelkareem M, Chae K, Olabi AG (2020) A critical review on environmental impacts of renewable energy systems and mitigation strategies: Wind, hydro, biomass and geothermal. Science of the Total Environment, 766, 144505.
DOI URL |
| [82] | Shang W, Zhang ZP, Fu GQ, Wan X, Zhang WX, Xiao B, Yang XM, Man DQ, Jin HX, Li YQ (2020) Effects of Photovoltaic Farm Construction on Vegetation and Soil Microorganisms in the Desert Area of Hexi Corridor. Gansu Research Institute of Sand Control, Lanzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [尚雯, 张芝萍, 付贵全, 万翔, 张卫星, 肖斌, 杨雪梅, 满多清, 金红喜, 李玉强 (2020) 光伏电场建设对河西走廊荒漠区植被和土壤微生物的影响. 甘肃省治沙研究所, 兰州.] | |
| [83] | Sharifian M (2015) The Paths of Clean Technology: From Innovation to Commercialization. PhD dissertation, Faculty of Business, University of Alberta, Alberta. |
| [84] | Shi J, Yang QM, Li JA, Tang PC (2022) An overview of the environmental impact issues and implications of wastewater generated by photovoltaic panel cleaning. Cleaning World, 38(5), 47-49. (in Chinese) |
| [石杰, 杨乔木, 李继安, 唐鹏程 (2022) 浅谈光伏板清洁产生污水的环境影响问题及启示. 清洗世界, 38(5), 47-49.] | |
| [85] | Sinha P, Hoffman B, Sakers J, Althouse L (2018) Best practices in responsible land use for improving biodiversity at a utility-scale solar facility. Case Studies in the Environment, 2(1), 1-12. |
| [86] |
Skarin A, Nellemann C, Rönnegård L, Sandström P, Lundqvist H (2015) Wind farm construction impacts reindeer migration and movement corridors. Landscape Ecology, 30, 1527-1540.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
Skarin A, Sandström P, Alam M (2018) Out of sight of wind turbines—Reindeer response to wind farms in operation. Ecology and Evolution, 8, 9906-9919.
DOI PMID |
| [88] | Song NN (2022) Effects of Wind Farm and Its Sounding Landscape Factors on Magpie (Pica pica) Nest in Agroforestry System: A Case Study of Chongming Beihu Wind Farm. PhD dissertation, East China Normal University, Shanghai. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋宁宁 (2022) 农林复合生态系统中风电场及其周边景观因子对喜鹊巢的影响. 博士学位论文, 华东师范大学, 上海.] | |
| [89] |
Sovacool B (2009) Contextualizing avian mortality: A preliminary appraisal of bird and bat fatalities from wind, fossil-fuel, and nuclear electricity. Energy Policy, 37, 2241-2248.
DOI URL |
| [90] | Stevens L, Anderson B, Cowan C, Colton K, Johnson D (2017) The Footprint of Energy: Land Use of U. S. Electricity Production. https://docs.wind-watch.org/US-footprints-Strata-2017.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-11) |
| [91] |
Stoms D, Dashiell S, Davis F (2013) Siting solar energy development to minimize biological impacts. Renewable Energy, 57, 289-298.
DOI URL |
| [92] | Tang B, Wu D, Zhao X, Zhou T, Zhao W, Wei H (2017) The observed impacts of wind farms on local vegetation growth in Northern China. Remote Sensing, 9(4), 332. |
| [93] | Taylor R (2014) Potential Ecological Impacts of Ground- mounted Photovoltaic Solar Panels in the UK: An Introduction and Literature Review. BSG Ecology, Newport. https://www.bsg-ecology.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Solar-Panels-and-Wildlife-Review-2019.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-11) |
| [94] | TBC The Biodiversity Consultancy (2019) Wind Energy: Managing Biodiversity Risks. The Biodiversity Consultancy, Cambridge. ttps://www.thebiodiversityconsultancy.com/fileadmin/uploads/tbc/Documents/Resources/Wind-energy-TBC-IBN-August-2019-1.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-11) |
| [95] |
Tesfahunegny W, Datiko D, Wale M, Hailay GE, Hunduma T (2020) Impact of wind energy development on birds and bats: The case of Adama wind farm, Central Ethiopia. The Journal of Basic and Applied Zoology, 81, 1-9.
DOI |
| [96] |
Turney D, Fthenakis V (2011) Environmental impacts from the installation and operation of large-scale solar power plants. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15, 3261-3270.
DOI URL |
| [97] | Uldrijan D, Cerny M, Winkler J (2022) Solar park: Opportunity or threat for vegetation and ecosystem. Journal of Ecological Engineering, 23, 1-10. |
| [98] | US-BLM United States Bureau of Land Management (2010) California Desert Conservation Area Plan Amendment and Final Environmental Impact Statement for the Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System Project. United States Department of the Interior, Needles. |
| [99] | Villegas-Patraca R, Cabrera-Cruz SA, Herrera-Alsina L (2014) Soaring migratory birds avoid wind farm in the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, southern Mexico. PLoS ONE, 9, e92462. |
| [100] |
Walsh-Thomas JM, Cervone G, Agouris P, Manca G (2012) Further evidence of impacts of large-scale wind farms on land surface temperature. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 16, 6432-6437.
DOI URL |
| [101] |
Wang LM, Li HQ, Cheng SK (2012) A study of the ecological effects of solar energy development in Tibet. Mountain Research and Development, 32, 83-91.
DOI URL |
| [102] | Wang G, Zhao YM, Dong L, Li GQ (2021) Effects of wind turbines on land surface temperature and evapotranspiration in a desert steppe. Geomatics World, 28(2), 74-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王刚, 赵玉梅, 董丽, 李国庆 (2021) 风力发电机对荒漠草原地表温度及蒸散发的影响. 地理信息世界, 28(2), 74-81.] | |
| [103] | Wang Q, Luo K, Wu CL, Fan JR (2019) Wind resource assessment of weather research and forecasting model coupled with wind farm parameterization model. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 53, 1572-1581. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王强, 罗坤, 吴春雷, 樊建人 (2019) 耦合风电场参数化模型的天气预报模式对风资源的评估和验证. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 53, 1572-1581.] | |
| [104] |
Wang SF, Wang SC, Smith P (2015) Ecological impacts of wind farms on birds: Questions, hypotheses, and research needs. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 44, 599-607.
DOI URL |
| [105] | Wang T, Wang DX, Guo TD, Zhang GG, Zhao SX, Niu HC, Lu SY, Lin H (2016) The impact of photovoltaic power construction on soil and vegetation. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 23(3), 90-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王涛, 王得祥, 郭廷栋, 张岗岗, 赵世雄, 牛怀诚, 卢舜瑜, 林虎 (2016) 光伏电站建设对土壤和植被的影响. 水土保持研究, 23(3), 90-94.] | |
| [106] | Wang Y, Li GQ, Zhou J, Wang MY, Song Y (2021) Research on influence of PV array on soil moisture. Solar Energy, (7), 53-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王颖, 李国庆, 周洁, 王梦瑶, 宋媛 (2021) 光伏阵列对土壤水分的影响研究. 太阳能, (7), 53-58.] | |
| [107] | Wang ZY, Wang J, Gao Y, Dang XH, Meng ZJ (2019) Impacts of photovoltaic power station construction on ecology environment in sandy area. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 39, 191-196. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王祯仪, 汪季, 高永, 党晓宏, 蒙仲举 (2019) 光伏电站建设对沙区生态环境的影响. 水土保持通报, 39, 191-196.] | |
| [108] | Winkelman JE (1994) Bird/Wind Turbine Investigations in Europe. In:Proceedings of the National Avian-Wind Power Planning Meeting, pp. 20-21, Denver. |
| [109] |
Wu JG, Gong Q, Wang Y (2023) The impacts of wind farms on ecosystems, biodiversity, and the environments. Ecological Economy, 39(9), 167-178. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [吴建国, 巩倩, 王阳 (2023) 风电场对生态系统、生物多样性及环境的影响. 生态经济, 39(9), 167-178.] | |
| [110] |
Wu W, Yue S, Zhou X, Guo M, Wang J, Ren L, Yuan B (2020) Observational study on the impact of large-scale photovoltaic development in deserts on local air temperature and humidity. Sustainability, 12, 3403.
DOI URL |
| [111] | Xu XY, Xiao YZ (2021) Wind power development in the Pearl River Delta and its threat to birds and related countermeasures. Modern Vocational Education, (33), 178-181. (in Chinese) |
| [徐晓羽, 肖懿芝 (2021) 珠三角风电发展及其对鸟类威胁和相关应对措施. 现代职业教育, (33), 178-181.] | |
| [112] | Yang SB (2023) Environmental impact assessment and pollution prevention for photovoltaic projects. Low Carbon World, 13(8), 19-21. (in Chinese) |
| [杨松波 (2023) 光伏项目环境影响评价及污染防治. 低碳世界, 13(8), 19-21.] | |
| [113] | Zhang JH, Ke T, Jiang HB, Liu L (2017) Analysis of the impact of wind power on migratory birds. Green Environmental Protection Building Materials, (7), 23. (in Chinese) |
| [张建华, 柯涛, 姜洪波, 刘玲 (2017) 风力发电对候鸟的影响分析. 绿色环保建材, (7), 23.] | |
| [114] | Zhao PY, Gao Y, Chen X, Gao L (2016) Effect of desert photovoltaic power plant on air temperature and humidity. Western Resources, (3), 125-128. (in Chinese) |
| [赵鹏宇, 高永, 陈曦, 高亮 (2016) 沙漠光伏电站对空气温湿度影响研究. 西部资源, (3), 125-128.] | |
| [115] |
Zhao S, Xu H, Song N, Wang Z, Li B, Wang T (2020) Effect of wind farms on wintering ducks at an important wintering ground in China along the East Asian-Australasian Flyway. Ecology and Evolution, 10, 9567-9580.
DOI PMID |
| [116] | Zhao SS (2022) Study on the Impact of Onshore Wind Farm Developments on the Wintering Waterbirds and Their Conservation Strategies in the Coast of Yangtze River Delta, China. PhD dissertation, East China Normal University, Shanghai. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵闪闪 (2022) 长江三角洲海岸带风电开发对越冬水鸟的影响及其保育策略研究. 博士学位论文, 华东师范大学, 上海.] | |
| [117] | Zhao YJ (2020) Impact of photovoltaic power stations on ecological environment and relevant countermeasures. Journal of Environment & Development, 32(11), 25-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵彦军 (2020) 光伏电站对生态环境的影响与相关对策. 环境与发展, 32(11), 25-26.] | |
| [118] | Zhao ZW (2021) Impact of wind farm construction on surface vegetation in Northern Shanxi. Environmental Science and Management, 46(5), 160-164. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵珍伟 (2021) 山西北部风电场建设对地表植被的影响研究. 环境科学与管理, 46(5), 160-164.] | |
| [119] | Zheng JQ, Luo Y, Chang R, Gao XQ (2023) Study on impact of large-scaled photovotaic development on local climate and ecosystem. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 44, 253-265. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[郑隽卿, 罗勇, 常蕊, 高晓清 (2023) 大规模光伏开发对局地气候生态影响研究. 太阳能学报, 44, 253-265.]
DOI |
|
| [120] |
Zhou L, Tian Y, Baidya Roy S, Thorncroft C, Bosart LF, Hu Y (2012) Impacts of wind farms on land surface temperature. Nature Climate Change, 2, 539-543.
DOI |
| [121] | Zhu YK, Li YD, Lou YQ, Zhou J, Sun YH (2016) Impact of wind farm on birds and mitigation strategies. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 51, 682-691. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱永可, 李阳端, 楼瑛强, 周江, 孙悦华 (2016) 风力发电对鸟类的影响以及应对措施. 动物学杂志, 51, 682-691.] |
| [1] | 彭昀月, 罗永梅, 靳彤, 李佳颖, 陈玉峰. 减缓陆上集中式光伏及风电电场生态影响的早期选址规划方法与工具[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24063-. |
| [2] | 王彦平, 张敏楚, 詹成修. 嵌套分布格局研究进展: 分析方法、影响机制及保护应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23314-. |
| [3] | 刘向, 张鹏, 刘建全. 无机肥料是青海塔拉滩光伏电站植被恢复过程中的限制性因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 22100-. |
| [4] | 齐月, 李俊生, 闫冰, 邓贞贞, 付刚. 化学除草剂对农田生态系统野生植物多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(2): 228-236. |
| [5] | 干晓静, 李博, 陈家宽, 马志军. 生物入侵对鸟类的生态影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(5): 548-557. |
| [6] | 彭羽, 刘雪华. 城市化对植物多样性影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(5): 558-562. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn