



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (4): 355-363. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017037 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017037
所属专题: 生物多样性与生态系统功能
收稿日期:2017-02-15
接受日期:2017-04-07
出版日期:2017-04-20
发布日期:2017-04-20
通讯作者:
张健
基金资助:Received:2017-02-15
Accepted:2017-04-07
Online:2017-04-20
Published:2017-04-20
Contact:
Zhang Jian
摘要:
高质量的生物多样性数据是认知生物多样性的起源和维持机制及应对其丧失风险的科学基础。当前, 在新物种发现、已知物种的地理分布、种群数量与时空动态、物种进化史、功能性状、物种与环境之间以及物种与物种之间的相互作用等7个方面都存在着知识上的空缺。大数据时代的到来为弥补这些知识空缺提供了可能,大数据的挖掘及其应用最近已成为国际生物多样性与宏生态学研究的前沿内容。如何有效地利用和分析不断增长的生物多样性大数据是生物多样性研究面临的一个极大挑战。本文通过全球、大陆和区域尺度上的研究案例展示了大数据在生物多样性研究中应用的新进展, 内容涉及森林覆盖变化、保护生态学、生物多样性与生态系统功能、气候变化对生物多样性的影响等。最后, 对大数据在生物多样性研究中存在的数据采集、处理和分析等方面的问题进行了总结, 并对其潜在应用前景进行了探讨。
张健 (2017) 大数据时代的生物多样性科学与宏生态学. 生物多样性, 25, 355-363. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017037.
Jian Zhang (2017) Biodiversity science and macroecology in the era of big data. Biodiversity Science, 25, 355-363. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017037.
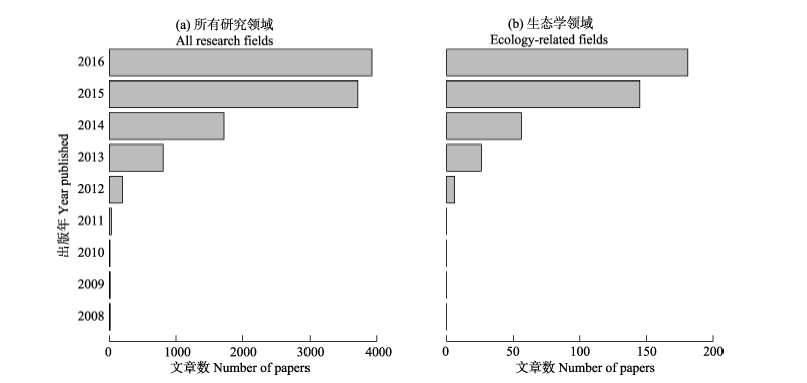
图1 基于Web of Science核心数据库以“big data”为主题的年度论文数量变化(2008-2016)
Fig. 1 The number of papers between 2008 and 2016 using “big data” as the topic in the Web of Science Core database
| 知识空缺 Knowledge shortfalls | 生物多样性的不同方面 Aspect of biodiversity | 定义 Definition | 相关文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linnean shortfall | 物种 Species | 缺乏对世界上很多现存和已灭绝物种描述的知识。Lack of knowledge about the description of most of living and extinct species on Earth. | Brown & Lomolino, 1998; Brito, 2010 |
| Wallacean shortfall | 地理分布 Geographic distribution | 缺乏有关大多数物种在各个时间尺度上的地理分布的知识。Lack of knowledge about the geographic distribution of most species at all scales most of the time. | Lomolino, 2004 |
| Prestonian shortfall | 种群 Populations | 缺乏在时空尺度上的物种多度和种群动态的知识。Lack of knowledge about species abundance and population dynamics in space and time. | Cardoso et al, 2011 |
| Darwinian shortfall | 进化 Evolution | 缺乏关于生命之树以及物种和它们的性状进化的信息。Lack of knowledge about the tree of life and the evolution of species and their traits. | Diniz-Filho et al, 2013 |
| Raunkiaeran shortfall | 功能性状和生态功能 Functional traits and ecological functions | 缺乏物种的性状及其生态功能的知识。Lack of knowledge about species’ traits and their ecological functions. | Hortal et al, 2015 |
| Hutchinsonian shortfall | 非生物耐性因子 Abiotic tolerances | 缺乏物种如何应对和忍耐非生物因子的知识。Lack of knowledge about the responses and tolerances of species to abiotic conditions. | Cardoso et al, 2011 |
| Eltonian shortfall | 生态的相互作用 Ecological interactions | 缺乏物种相互作用及其影响个体存活和适合度的知识。Lack of knowledge on species’ interactions and these interactions’ effects on individual survival and fitness. | Hortal et al, 2015 |
表1 生物多样性研究中存在的7个主要知识空缺(基于Hortal et al, 2015修改)
Table 1 Definitions for seven main shortfalls (or gaps) of current biodiversity knowledge (Adopted from Hortal et al, 2015)
| 知识空缺 Knowledge shortfalls | 生物多样性的不同方面 Aspect of biodiversity | 定义 Definition | 相关文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linnean shortfall | 物种 Species | 缺乏对世界上很多现存和已灭绝物种描述的知识。Lack of knowledge about the description of most of living and extinct species on Earth. | Brown & Lomolino, 1998; Brito, 2010 |
| Wallacean shortfall | 地理分布 Geographic distribution | 缺乏有关大多数物种在各个时间尺度上的地理分布的知识。Lack of knowledge about the geographic distribution of most species at all scales most of the time. | Lomolino, 2004 |
| Prestonian shortfall | 种群 Populations | 缺乏在时空尺度上的物种多度和种群动态的知识。Lack of knowledge about species abundance and population dynamics in space and time. | Cardoso et al, 2011 |
| Darwinian shortfall | 进化 Evolution | 缺乏关于生命之树以及物种和它们的性状进化的信息。Lack of knowledge about the tree of life and the evolution of species and their traits. | Diniz-Filho et al, 2013 |
| Raunkiaeran shortfall | 功能性状和生态功能 Functional traits and ecological functions | 缺乏物种的性状及其生态功能的知识。Lack of knowledge about species’ traits and their ecological functions. | Hortal et al, 2015 |
| Hutchinsonian shortfall | 非生物耐性因子 Abiotic tolerances | 缺乏物种如何应对和忍耐非生物因子的知识。Lack of knowledge about the responses and tolerances of species to abiotic conditions. | Cardoso et al, 2011 |
| Eltonian shortfall | 生态的相互作用 Ecological interactions | 缺乏物种相互作用及其影响个体存活和适合度的知识。Lack of knowledge on species’ interactions and these interactions’ effects on individual survival and fitness. | Hortal et al, 2015 |
| 1 | ABMI (Alberta Biodiversity Monitoring Institute) (2016) Alberta Wall-to-Wall Vegetation Layer Including “Backfilled” Vegetation in Human Footprints (Version 6). http: abmi.ca/. (accessed on 2017-03-22) |
| 2 | Asner GP, Martin RE, Knapp DE, Tupayachi R, Anderson CB, Sinca F, Vaughn NR, Llactayo W (2017) Airborne laser-guided imaging spectroscopy to map forest trait diversity and guide conservation. Science, 355, 385-389. |
| 3 | Bechtold WA, Patterson PL (2005) The Enhanced Forest Inventory and Analysis Program: National Sampling Design and Estimation Procedures. General Techinical Report, SRS-80. USDA Forest Service, Southern Research Station, Asheville, NC. |
| 4 | Brown JH (1995) Macroecology. Chicago University Press, Chicago. |
| 5 | Brown JH, Lomolino MV (1998) Biogeography. Sinauer Press, Sunderland, Massachusetts. |
| 6 | Brito D (2010) Overcoming the Linnean shortfall: data deficiency and biological survey priorities. Basic and Applied Ecology, 11, 709-713. |
| 7 | Cardoso P, Erwin TL, Borges PA, New TR (2011) The seven impediments in invertebrate conservation and how to overcome them. Biological Conservation, 144, 2647-2655. |
| 8 | Diniz-Filho JAF, Loyola RD, Raia P, Mooers AO, Bini LM (2013) Darwinian shortfalls in biodiversity conservation. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 28, 689-695. |
| 9 | Dai SQ, Zhao B (2016) Trends and challenges of ecosystem observations in the age of big data. Biodiversity Science, 24, 85-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戴圣骐, 赵斌 (2016) 大数据时代下的生态系统观测发展趋势与挑战. 生物多样性, 24, 85-94.] | |
| 10 | Dobson LL, La Sorte FA, Manne LL, Hawkins BA (2015) The diversity and abundance of North American bird assemblages fail to track changing productivity. Ecology, 96, 1105-1114. |
| 11 | Enquist BJ, Condit R, Peet RK, Schildhauer M, Thiers BM (2017) Cyberinfrastructure for an integrated botanical information network to investigate the ecological impacts of global climate change on plant biodiversity. PeerJ, 4, e2615v2. |
| 12 | Falchi F, Cinzano P, Duriscoe D, Kyba CCM, Elvidge CD, Baugh K, Portnov BA, Rybnikova NA, Furgoni R (2016) The new world atlas of artificial night sky brightness. Science Advances, 2, e1600377. |
| 13 | Fei S, Guo Q, Potter K (2016) Macrosystems ecology: novel methods and new understanding of multi-scale patterns and processes. Landscape Ecology, 31, 1-6. |
| 14 | Gantz J, Reinsel D (2012) The Digital Universe in 2020: Big Data, Bigger Digital Shadows, and Biggest Growth in the Far East. IDC (International Data Corporation), Framingham. |
| 15 | Gaston KJ, Visser ME, Hölker F (2015) The biological impacts of artificial light at night: the research challenge. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 370, 20140133. |
| 16 | Hampton SE, Strasser CA, Tewksbury JJ, Gram WK, Budden AE, Batcheller AL, Duke CS, Porter JH (2013) Big data and the future of ecology. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 11, 156-162. |
| 17 | Hansen MC, Potapov PV, Moore R, Hancher M, Turubanova SA, Tyukavina A, Thau D, Stehman SV, Goetz SJ, Loveland TR, Kommareddy A, Egorov A, Chini L, Justice CO, Townshend JRG (2013) High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science, 342, 850-853. |
| 18 | Heffernan JB, Soranno PA, Angilletta MJ, Buckley LB, Gruner DS, Keitt TH, Kellner JR, Kominoski JS, Rocha AV, Xiao J, Harms TK, Goring SJ, Koenig LE, McDowell WH, Powell H, Richardson AD, Stow CA, Vargas R, Weathers KC (2014) Macrosystems ecology: understanding ecological patterns and processes at continental scales. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 12, 5-14. |
| 19 | Hey T, Tansley S, Tolle K (translated by Pan XF, Zhang XL) (2012) The Fourth Paradigm: Data-Intensive Scientific Discovery. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [潘教峰, 张晓林等(译) (2012) 第四范式: 数据密集型科学发现. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 20 | Hinchliff CE, Smith SA, Allman JF, Burleigh JG, Chaudhary R, Coghill LM, Crandall KA, Deng J, Drew BT, Gazis R, Gude K, Hibbett DS, Katz LA, Laughinghouse HD, McTavish EJ, Midford PE, Owen CL, Ree RH, Rees JA, Soltis DE, Williams T, Cranston KA (2015) Synthesis of phylogeny and taxonomy into a comprehensive tree of life. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 12764-12769. |
| 21 | Hortal J, Bello F, Diniz-Filho JAF, Lewinsohn TM, Lobo JM, Ladle RJ (2015) Seven shortfalls that beset large-scale knowledge of biodiversity. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 46, 523-549. |
| 22 | Houlahan JE, McKinney ST, Anderson TM, McGill BJ (2017) The priority of prediction in ecological understanding. Oikos, 26, 1-7. |
| 23 | Hu HJ, Jiang ZG, Wang ZW (2003) Macroecology: concept and progresses. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 23, 1192-1199. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [胡慧建, 蒋志刚, 王祖望 (2003) 宏生态学(Macroecology)及其研究. 生态学报, 23, 1192-1199.] | |
| 24 | Ibisch PL, Hoffmann MT, Kreft S, Pe’er G, Kati V, Biber- Freudenberger L, DellaSala DA, Vale MM, Hobson PR, Selva N (2016) A global map of roadless areas and their conservation status. Science, 354, 1423-1427. |
| 25 | Jetz W, Thomas GH, Joy JB, Hartmann K, Mooers AO (2012) The global diversity of birds in space and time. Nature, 491, 444-448. |
| 26 | Jones MB, Schildhauer MP, Reichman OJ, Bowers S (2006) The new bioinformatics: integrating ecological data from the gene to the biosphere. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 37, 519-544. |
| 27 | Keitt TH, Stanley HE (1998) Dynamics of North American breeding bird populations. Nature, 393, 257-260. |
| 28 | LaDeau SL, Kilpatrick AM, Marra PP (2007) West Nile virus emergence and large-scale declines of North American bird populations. Nature, 447, 710-713. |
| 29 | Lawton JH (1999) Are there general laws in ecology? Oikos, 84, 177-192. |
| 30 | Liang JJ, Crowther TW, Picard N, Wiser S, Zhou M, Alberti G, Schulze ED, McGuire AD, Bozzato F, Pretzsch H, de-Miguel S, Paquette A, Hérault B, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Barrett CB, Glick HB, Hengeveld GM, Nabuurs GJ, Pfautsch S, Viana H, Vibrans AC, Ammer C, Schall P, Verbyla D, Tchebakova N, Fischer M, Watson JV, Chen HYH, Lei X, Schelhaas MJ, Lu H, Gianelle D, Parfenova EI, Salas C, Lee E, Lee B, Kim HS, Bruelheide H, Coomes DA, Piotto D, Sunderland T, Schmid B, Gourlet-Fleury S, Sonké B, Tavani R, Zhu J, Brandl S, Vayreda J, Kitahara F, Searle EB, Neldner VJ, Ngugi MR, Baraloto C, Frizzera L, Bałazy R, Oleksyn J, Zawiła-Niedźwiecki T, Bouriaud O, Bussotti F, Finér L, Jaroszewicz B, Jucker T, Valladares F, Jagodzinski AM, Peri PL, Gonmadje C, Marthy W, O’Brien T, Martin EH, Marshall AR, Rovero F, Bitariho R, Niklaus PA, Alvarez-Loayza P, Chamuya N, Valencia R, Mortier F, Wortel V, Engone-Obiang NL, Ferreira LV, Odeke DE, Vasquez RM, Lewis SL, Reich PB (2016) Positive biodiversity-productivity relationship predominant in global forests. Science, 354, aaf8957. |
| 31 | Liu XJ, Ma KP (2015) Plant functional traits—concepts, applications and future directions. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 45, 325-339. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘晓娟, 马克平 (2015) 植物功能性状研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学, 45, 325-339.] | |
| 32 | Lomolino MV (2004) Conservation biogeography. In: Frontiers of Biogeography: New Directions in the Geography of Nature (eds Lomolino MV, Heaney LR), pp. 293-296. Sinauer Press, Sunderland, Massachusetts. |
| 33 | Ma KP (2014) Rapid development of biodiversity informatics in China. Biodiversity Science, 22, 251-252. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (2014) 生物多样性信息学在中国快速发展. 生物多样性, 22, 251-252.] | |
| 34 | Ma KP (2016) Hot topics for biodiversity science. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1-2. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (2016) 生物多样性科学的热点问题. 生物多样性, 24, 1-2.] | |
| 35 | Ma KP (2017) Mapping Asia Plants: a cyberinfrastructure for plant diversity in Asia. Biodiversity Science, 25, 1-2. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (2017) 亚洲生物多样性数字化计划. 生物多样性, 25, 1-2.] | |
| 36 | Mayer-Schönberger V, Cukier K (2013) Big Data: A Revolution that Will Transform How We Live, Work, and Think. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, Boston. |
| 37 | Mayor S, Cahill J, He F, Sólymos P, Boutin S (2012) Regional boreal biodiversity peaks at intermediate human disturbance. Nature Communications, 3, 1142. |
| 38 | Meyer C, Kreft H, Guralnick R, Jetz W (2015) Global priorities for an effective information basis of biodiversity distributions. Nature Communications, 6, 8221. |
| 39 | Meyer C, Weigelt P, Kreft H (2016) Multidimensional biases, gaps and uncertainties in global plant occurrence information. Ecology Letters, 19, 992-1006. |
| 40 | Pennisi E (2005) What determines species diversity? Science, 309, 90. |
| 41 | Roughgarden J (2009) Is there a general theory of community ecology? Biology & Philosophy, 24, 521-529. |
| 42 | Soberon J, Peterson T (2004) Biodiversity informatics: managing and applying primary biodiversity data. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 359, 689-698. |
| 43 | Soranno PA, Schimel DS (2014) Macrosystems ecology: big data, big ecology. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 12, 3. |
| 44 | Stralberg D, Matsuoka SM, Hamann A, Bayne EM, Sólymos P, Schmiegelow F, Wang X, Cumming SG, Song SJ (2015) Projecting boreal bird responses to climate change: the signal exceeds the noise. Ecological Applications, 25, 52-69. |
| 45 | Sun H, Deng T, Chen YS, Zhou Z (2017) Current research and development trends in floristic geography. Biodiversity Science, 25, 111-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙航, 邓涛, 陈永生, 周卓 (2017) 植物区系地理研究现状及发展趋势. 生物多样性, 25, 111-122.] | |
| 46 | Sutherland WJ, Adams WM, Aronson RB, Aveling R, Blackburn TM, Broad S, Ceballos G, Côté IM, Cowling RM, Dafonseca GAB, Dinerstein E, Ferraro PJ, Fleishman E, Gascon C, Hunter Jr M, Hutton J, Kareiva P, Kuria A, MacDonald DW, Mackinnon K, Madgwick FJ, Mascia MB, Mcneely J, Milner-Gulland EJ, Moon S, Morley CG, Nelson S, Osborn D, Pai M, Parsons ECM, Peck LS, Possingham H, Prior SV, Pullin AS, Rands MRW, Ranganathan J, Redford KH, Rodriguez JP, Seymour F, Sobel J, Sodhi NS, Stott A, Vance-Borland K, Watkinson AR (2009) One hundred questions of importance to the conservation of global biological diversity. Conservation Biology, 23, 557-567. |
| 47 | Terborgh JW (2015) Toward a trophic theory of species diversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 11415-11422. |
| 48 | Violle C, Reich PB, Pacala SW, Enquist BJ, Kattge J (2014) The emergence and promise of functional biogeography. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, 13690-13696. |
| 49 | Wang LS, Chen B, Ji LQ, Ma KP (2010) Progress in biodiversity informatics. Biodiversity Science, 18, 429-443. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王利松, 陈彬, 纪力强, 马克平 (2010) 生物多样性信息学研究进展. 生物多样性, 18, 429-443.] | |
| 50 | Wu JG, Shen WJ (2002) The sciences of complexity and ecological applications. In: Lectures in Modern Ecology (II): From Basic Ecology to Environmental Issues (eds Wu JG, Han XG, Huang JH), pp. 6-15. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [邬建国, 申卫军 (2002) 复杂性科学及其生态学应用. 见: 现代生态学讲座 (二): 基础研究与环境问题(邬建国, 韩兴国, 黄建辉主编), 6-15页. 中国科学技术出版社, 北京.] | |
| 51 | Yang WJ, Ma KP, Kreft H (2013) Geographical sampling bias in a large distributional database and its effects on species richness-environment models. Journal of Biogeography, 40, 1415-1426. |
| 52 | Zanne AE, Tank DC, Cornwell WK, Eastman JM, Smith SA, FitzJohn RG, McGlinn DJ, O’Meara BC, Moles AT, Reich PB, Royer DL, Soltis DE, Stevens PF, Westoby M, Wright IJ, Aarssen L, Bertin RI, Calaminus A, Govaerts R, Hemmings F, Leishman MR, Oleksyn J, Soltis PS, Swenson NG, Warman L, Beaulieu JM (2014) Three keys to the radiation of angiosperms into freezing environments. Nature, 506, 89-92. |
| 53 | Zhang J, Chen SB, Chen B, Du YJ, Huang XL, Pan XB, Zhang Q (2013) Citizen science: integrating scientific research, ecological conservation and public participation. Biodiversity Science, 21, 738-749. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张健, 陈圣宾, 陈彬, 杜彦君, 黄晓磊, 潘绪斌, 张强 (2013) 公众科学: 整合科学研究, 生态保护和公众参与. 生物多样性, 21, 738-749.] | |
| 54 | Zhang J, Huang S, Hogg E, Lieffers V, Qin Y, He F (2014a) Estimating spatial variation in Alberta forest biomass from a combination of forest inventory and remote sensing data. Biogeosciences, 11, 2793-2808. |
| 55 | Zhang J, Kissling WD, He F (2013) Local forest structure, climate and human disturbance determine regional distribution of boreal bird species richness in Alberta, Canada. Journal of Biogeography, 40, 1131-1142. |
| 56 | Zhang J, Mayor SJ, He F (2014b) Does disturbance regime change community assembly of angiosperm plant communities in the boreal forest? Journal of Plant Ecology, 7, 188-201. |
| 57 | Zhang J, Nielsen SE, Chen Y, Georges D, Qin Y, Wang SS, Svenning JC, Thuiller W (2017) Extinction risk of North American seed plants elevated by climate and land-use change. Journal of Applied Ecology, 54, 303-312. |
| 58 | Zhang J, Nielsen SE, Stolar J, Chen Y, Thuiller W (2015) Gains and losses of plant species and phylogenetic diversity for a northern high-latitude region. Diversity and Distributions, 21, 1441-1454. |
| [1] | 顾燚芸, 薛嘉祈, 高金会, 谢心仪, 韦铭, 雷进宇, 闻丞. 一种基于公众科学数据的区域性鸟类多样性评价方法[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24080-. |
| [2] | 徐文轩, 徐峰, 马伟, 汪沐阳, 王建成, 杨维康. 基于层次分析法的旗舰物种遴选方法[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21536-. |
| [3] | 丁晨晨, 梁冬妮, 信文培, 李春旺, 蒋志刚. 中国哺乳动物形态、生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21520-. |
| [4] | 刘童祎, 陈静, 姜立云, 乔格侠. 中国半翅目等29目昆虫2020年新分类单元[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(8): 1050-1057. |
| [5] | 顾伯健, 王放. 野生绿孔雀生态学及保护生物学研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1554-1564. |
| [6] | 刘炎林, 宋大昭, 刘蓓蓓, 夏凡, 陈月龙, 王一晴, 黄巧雯. 中国猫科动物红外相机监测平台介绍: 民间环保机构的数据整合[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(9): 1067-1074. |
| [7] | 庄文颖,李熠,郑焕娣,曾昭清,王新存. 中国非地衣型大型子囊菌受威胁现状评估及致危因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(1): 26-40. |
| [8] | 张凤麟, 王昕, 张健. 生物多样性信息资源.II.环境类型数据[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(1): 53-65. |
| [9] | 徐诗涛, 宋希强, 凌鹏, 陈元君, 任明迅. 日本演习林制度对中国生物多样性保护与国家公园建设的启示[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(1): 96-104. |
| [10] | 商辉, 严岳鸿. 自然杂交与生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(6): 683-688. |
| [11] | 王昕, 张凤麟, 张健. 生物多样性信息资源. I. 物种分布、编目、系统发育与生活史性状[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(11): 1223-1238. |
| [12] | 周喜乐, 张宪春, 孙久琼, 严岳鸿. 中国石松类和蕨类植物的多样性与地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(1): 102-107. |
| [13] | 黄卫昌, 周翔宇, 倪子轶, 邵丽. 基于标本和分布信息评估中国虾脊兰属植物的濒危状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(4): 493-498. |
| [14] | 宋大昭, 王卜平, 蒋进原, 万绍平, 崔士明, 王天明, 冯利民. 山西晋中庆城林场华北豹及其主要猎物种群的红外相机监测[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(6): 733-736. |
| [15] | 邵广昭, 李瀚, 林永昌, 赖昆祺. 海洋生物多样性信息资源[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(3): 253-263. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()
