



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 567-575. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018211 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018211
李诣远*( ),DavidC.Molik,MichaelE.Pfrender
),DavidC.Molik,MichaelE.Pfrender
收稿日期:2018-08-01
接受日期:2019-03-05
出版日期:2019-05-20
发布日期:2019-05-20
Li Yiyuan( )*,C. Molik David,E. Pfrender Michael
)*,C. Molik David,E. Pfrender Michael
Received:2018-08-01
Accepted:2019-03-05
Online:2019-05-20
Published:2019-05-20
摘要:
基于宏条形码技术的物种快速检测有助于生物多样性的评估、预测和保护。本文介绍了常用宏条形码分析的步骤和参数设定方法。我们利用Nextflow搭建了一款宏条形码分析流程EPPS, 可以自动化地运行从原始数据的质量控制到环境多样性的比较。Nextflow软件还拥有流程监控的功能, 可视化输出每个进程所消耗的时间与内存。本文还使用测试数据和已发表数据证明该平台能够有效地分析宏条形码数据并可靠地分析环境生物多样性的相似性。
李诣远, DavidC.Molik, MichaelE.Pfrender (2019) 基于Nextflow构建的宏条形码自动化分析流程EPPS. 生物多样性, 27, 567-575.
DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018211.
Li Yiyuan, C. Molik David, E. Pfrender Michael (2019) EPPS, a metabarcoding bioinformatics pipeline using Nextflow. Biodiversity Science, 27, 567-575. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018211.
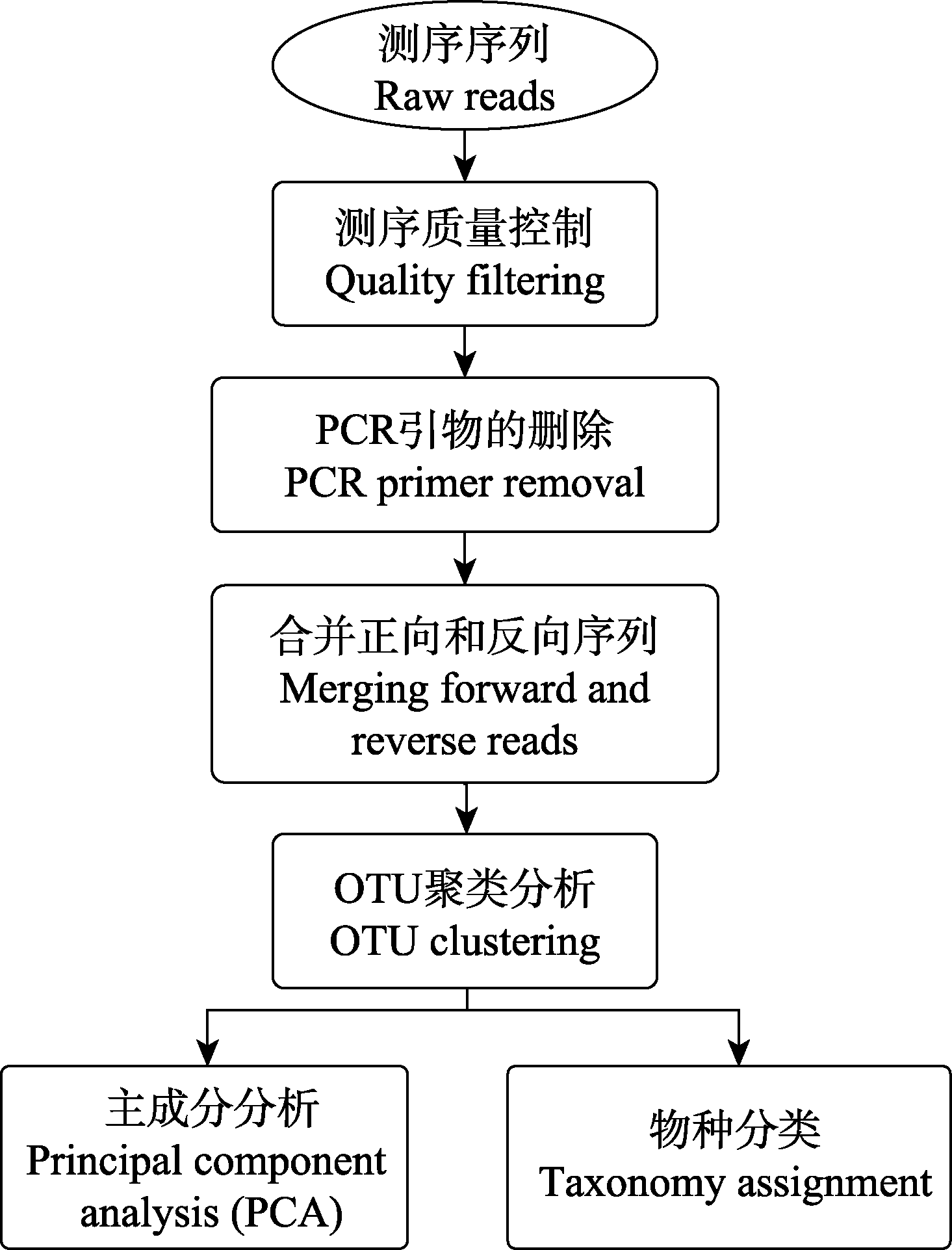
图1 EPPS的主要分析步骤。OTU聚类分析还包括去除重复序列、OTU聚类和嵌合体的检测。
Fig. 1 The workflow of EPPS. OTU clustering step includes, dereplication, OTU clustering and chimera detection.
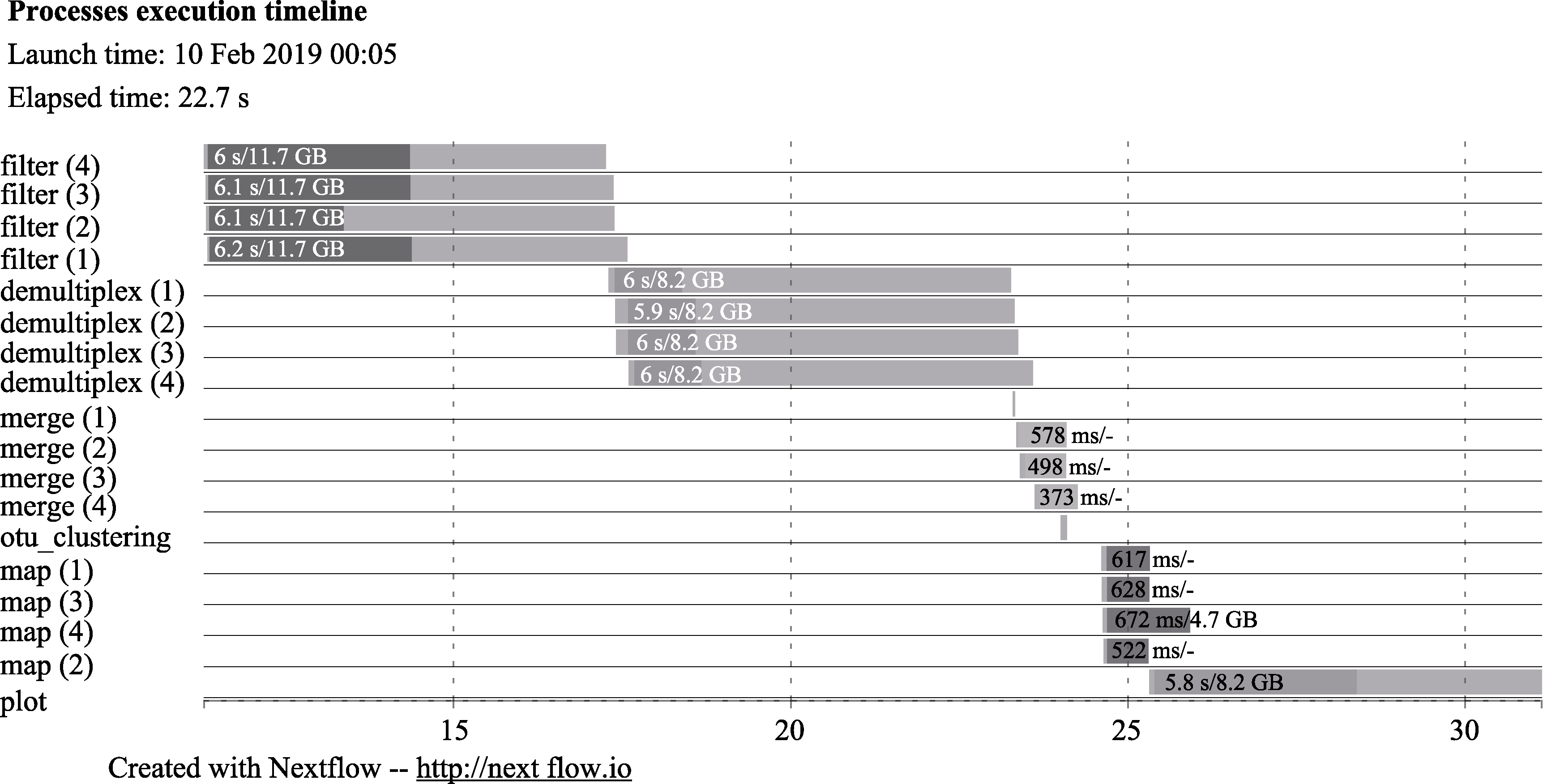
图2 EPPS流程每一个进程的时间消耗。横坐标代表时间, 单位是秒。最左列的名称分别对应了宏条形码分析的流程。filter: 测序质量控制; demultiplex: PCR引物的删除, 如果有多个引物则将各个引物分开; merge: 合并正向和反向序列; otu_clustering/map: OTU聚类分析; plot: 主成分分析。由于测试数据有4个样品, 因此每个进程的右侧括号里有1-4的序号。浅色进度条代表进程所消耗的系统时间。深色进度条代表的是每个进程的CPU时间。每个进度条包含有两个数字, 第1个数字代表每个进度的系统时间, 第2个数字代表虚拟内存的峰值。
Fig. 2 The timeline chart of EPPS. The x-axis is the amount of time for each process in seconds. Each row indicates the name of different stages of the analysis. filter, Data filtering; demultiplex, Primer removal and demultiplex if there are multiple primers; merge, Merging of forward and reverse reads; otu_clustering and map, OTU clustering and mapping of reads; plot, Plotting PCA plot. As there are four samples in the testing data set, there are four processes (1 to 4) for filter, demultiplex, merge, and map steps. Each bar indicates the time for each process. The dark area in each bar represents the real execution time. Each bar displays two numbers: the task duration time and the virtual memory size peak.
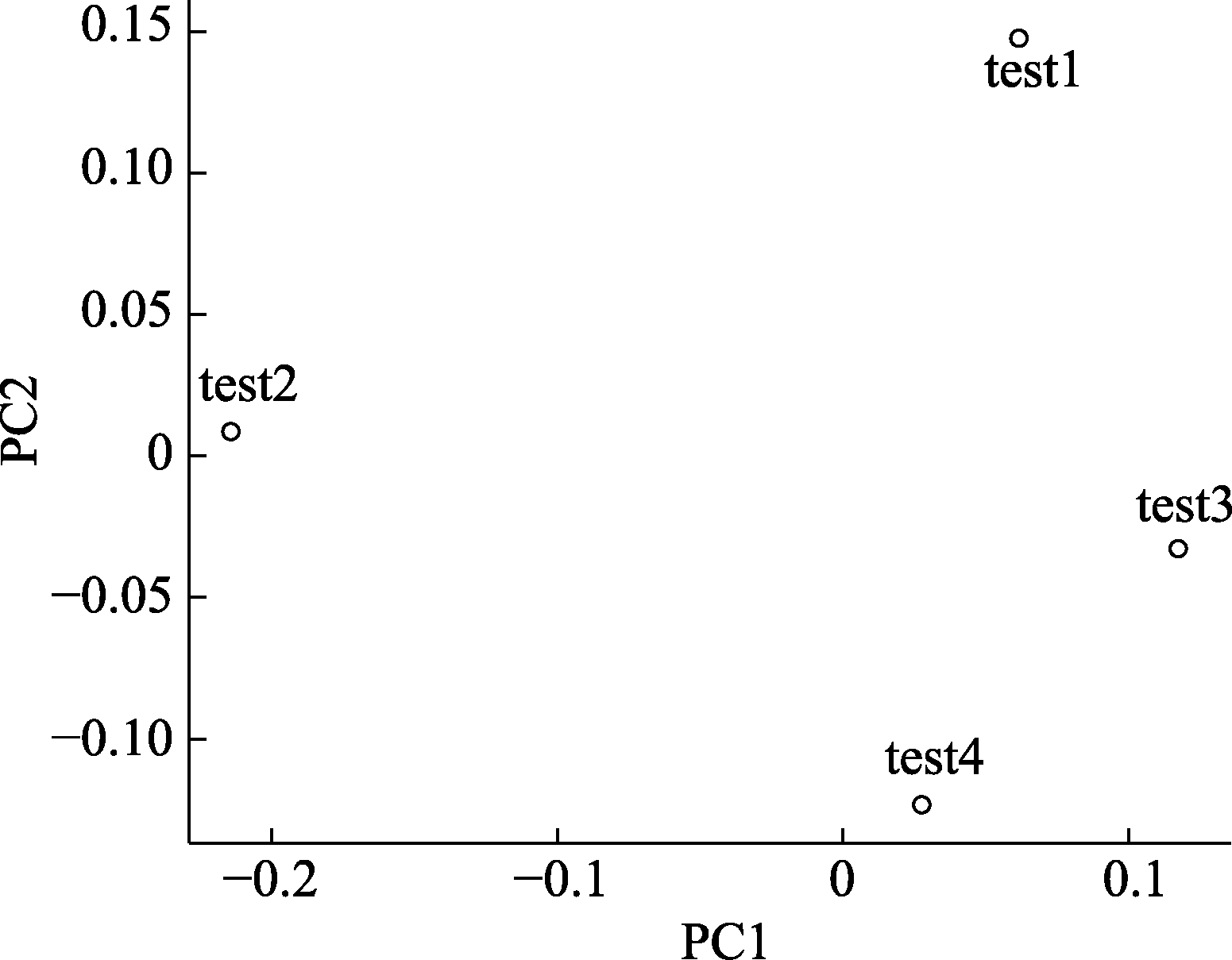
图3 基于测试数据的主成分分析结果。图中每一个点代表一个测试数据的样品。点与点之间距离越近代表样品之间的物种组成相似度越高。例如, test3和test4的相似度大于test3和test1的相似度。
Fig. 3 PCA plot based on testing data. Each dot in the figure represents a test sample. The distance between dots indicates the dissimilarity between samples. For example, the similarity between test3 and test4 is higher than test1 and test2.
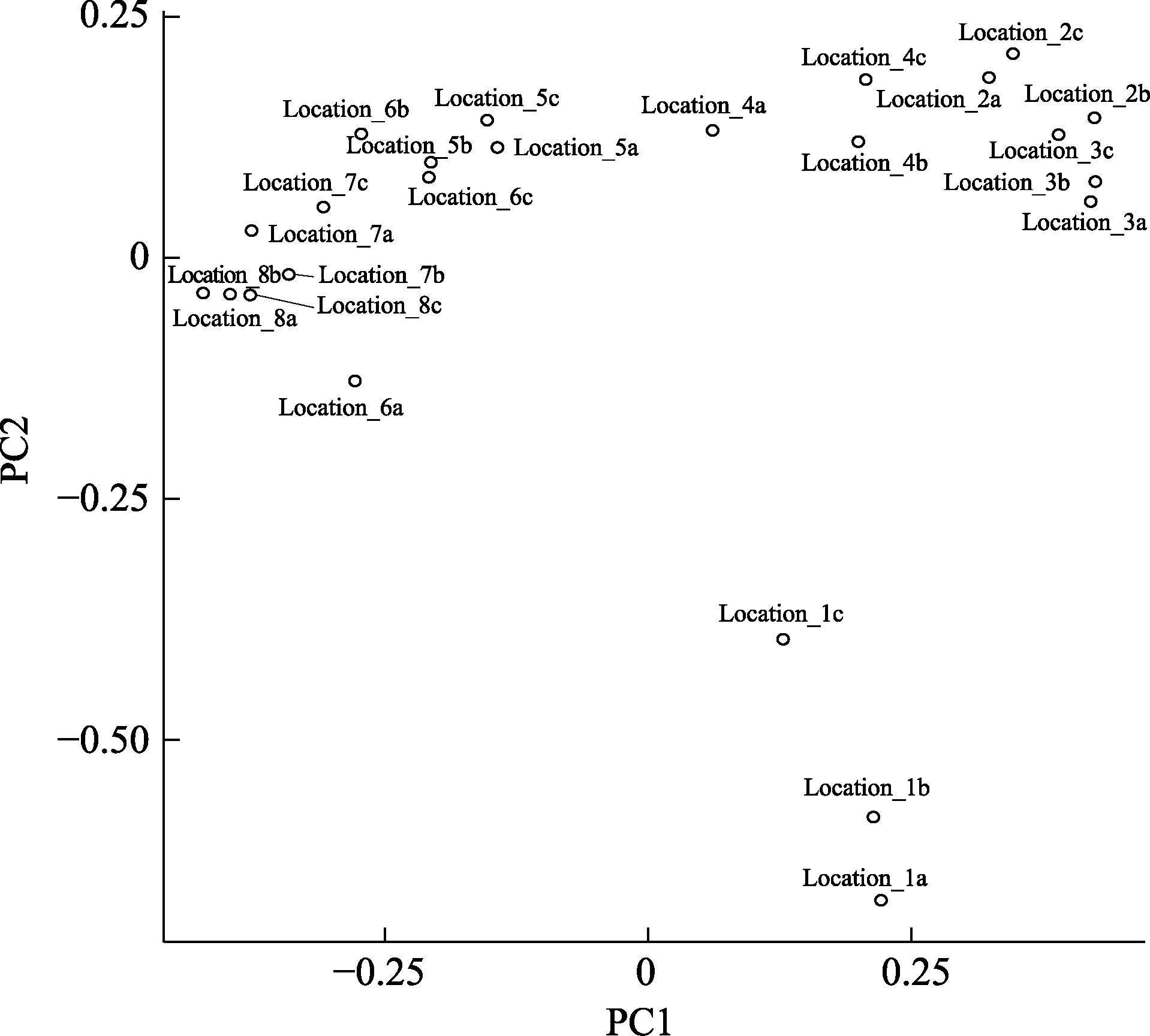
图4 公共数据的分析结果。样品的名称编号1-8分别代表从最上游到下游的8个采样点。编号的后缀a, b, c分别代表同一个采样地点的3次独立的重复取样。基于图中的结果, 最上游的样品Location1有独特的鱼类多样性组成。Location 3-6有类似的鱼类多样性组成。最下游的样品Location 7-8有类似的鱼类多样性组成。
Fig. 4 EPPS result based on public data set. Samples are named from 1 to 8 from upstream to downstream. The suffix “a”, “b” and “c” indicate three replicates of the same sampling location. Based on the PCA, the most upstream sample (Location 1) has unique fish composition. Location 3-6 have similar fish composition. The downstream samples (Location 7-8) share similar fish composition.
| [1] |
Bazinet AL, Cummings MP ( 2012) A comparative evaluation of sequence classification programs. BMC Bioinformatics, 13, 92.
DOI |
| [2] |
Berger SA, Krompass D, Stamatakis A ( 2011) Performance, accuracy, and web server for evolutionary placement of short sequence reads under maximum likelihood. Systematic Biology, 60, 291-302.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Bik HM, Interactive Pitch Inc . ( 2014) Phinch: An interactive, exploratory data visualization framework for-Omic datasets. bioRxiv, 009944. |
| [4] |
Bista I, Carvalho GR, Tang M, Walsh K, Zhou X, Hajibabaei M, Shokralla S, Seymour M, Bradley D, Liu S, Christmas M ( 2018) Performance of amplicon and shotgun sequencing for accurate biomass estimation in invertebrate community samples. Molecular Ecology Resources, 18, 1020-1034.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Bohmann K, Evans A, Gilbert MT, Carvalho GR, Creer S, Knapp M, Douglas WY, De Bruyn M ( 2014) Environmental DNA for wildlife biology and biodiversity monitoring. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 29, 358-367. |
| [6] |
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B ( 2014) Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics, 30, 2114-2120.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Boyer F, Mercier C, Bonin A, Le Bras Y, Taberlet P, Coissac E ( 2016) obitools: A unix-inspired software package for DNA metabarcoding. Molecular Ecology Resources, 16, 176-182.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Brady A, Salzberg SL ( 2009) Phymm and PhymmBL: Metagenomic phylogenetic classification with interpolated Markov models. Nature Methods, 6, 673.
DOI |
| [9] |
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJ, Holmes SP ( 2016) DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nature Methods, 13, 581.
DOI |
| [10] |
Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V, Ma N, Papadopoulos J, Bealer K, Madden TL ( 2009) BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics, 10, 421.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Lozupone CA, Turnbaugh PJ, Fierer N, Knight R ( 2011) Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 4516-4522.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA ( 2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods, 7, 335.
DOI |
| [13] |
Cardoso P, Borges PA, Veech JA ( 2009) Testing the performance of beta diversity measures based on incidence data: The robustness to undersampling. Diversity and Distributions, 15, 1081-1090.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Collen B, Whitton F, Dyer EE, Baillie JE, Cumberlidge N, Darwall WR, Pollock C, Richman NI, Soulsby AM, Böhm M ( 2014) Global patterns of freshwater species diversity, threat and endemism. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 23, 40-51.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Crampton-Platt A, Timmermans MJ, Gimmel ML, Kutty SN, Cockerill TD, Vun Khen C, Vogler AP ( 2015) Soup to tree: The phylogeny of beetles inferred by mitochondrial metagenomics of a Bornean rainforest sample. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 32, 2302-2316.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Crampton-Platt A, Douglas WY, Zhou X, Vogler AP ( 2016) Mitochondrial metagenomics: Letting the genes out of the bottle. GigaScience, 5, 15.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Deiner K, Bik HM, Mächler E, Seymour M, Lacoursière- Roussel A, Altermatt F, Creer S, Bista I, Lodge DM, de Vere N, Pfrender ME ( 2017 a) Environmental DNA metabarcoding: Transforming how we survey animal and plant communities. Molecular Ecology, 26, 5872-5895.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Deiner K, Renshaw MA, Li Y, Olds BP, Lodge DM, Pfrender ME ( 2017 b) Long-range PCR allows sequencing of mitochondrial genomes from environmental DNA. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 8, 1888-1898.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Di Tommaso P, Chatzou M, Floden EW, Barja PP, Palumbo E, Notredame C ( 2017) Nextflow enables reproducible computational workflows. Nature Biotechnology, 35, 316.
DOI |
| [20] |
Dowle EJ, Pochon X, Banks JC, Shearer K, Wood SA ( 2016) Targeted gene enrichment and high-throughput sequencing for environmental biomonitoring: A case study using freshwater macroinvertebrates. Molecular Ecology Resources, 16, 1240-1254.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Edgar RC ( 2016) SINTAX: A simple non-Bayesian taxonomy classifier for 16S and ITS sequences. bioRxiv, 074161. |
| [22] |
Edgar RC ( 2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics, 26, 2460-2461.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Edgar RC ( 2013) UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nature Methods, 10, 996.
DOI |
| [24] |
Evans NT, Li Y, Renshaw MA, Olds BP, Deiner K, Turner CR, Jerde CL, Lodge DM, Lamberti GA, Pfrender ME ( 2017) Fish community assessment with eDNA metabarcoding: Effects of sampling design and bioinformatic filtering. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 74, 1362-1374.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Evans NT, Olds BP, Renshaw MA, Turner CR, Li Y, Jerde CL, Mahon AR, Pfrender ME, Lamberti GA, Lodge DM ( 2016) Quantification of mesocosm fish and amphibian species diversity via environmental DNA metabarcoding. Molecular Ecology Resources, 16, 29-41.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Gerlach W, Stoye J ( 2011) Taxonomic classification of metagenomic shotgun sequences with CARMA3. Nucleic Acids Research, 39, e91.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Huson DH, Auch AF, Qi J, Schuster SC ( 2007) MEGAN analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Research, 17, 377-386.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Ji Y, Ashton L, Pedley SM, Edwards DP, Tang Y, Nakamura A, Kitching R, Dolman PM, Woodcock P, Edwards FA, Larsen TH ( 2013) Reliable, verifiable and efficient monitoring of biodiversity via metabarcoding. Ecology Letters, 16, 1245-1257.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Li Y, Evans NT, Renshaw MA, Jerde CL, Olds BP, Shogren AJ, Deiner K, Lodge DM, Lamberti GA, Pfrender ME ( 2018) Estimating fish alpha- and beta-diversity along a small stream with environmental DNA metabarcoding. Metabarcoding and Metagenomics, 2, e24262.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Liu B, Gibbons T, Ghodsi M, Pop M ( 2010) MetaPhyler: Taxonomic profiling for metagenomic sequences. In: Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), 2010 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), pp. 95-100. |
| [31] |
Liu S, Wang X, Xie L, Tan M, Li Z, Su X, Zhang H, Misof B, Kjer KM, Tang M, Niehuis O ( 2016) Mitochondrial capture enriches mito-DNA 100 fold, enabling PCR-free mitogenomics biodiversity analysis. Molecular Ecology Resources, 16, 470-479.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Liu S, Li Y, Lu J, Su X, Tang M, Zhang R, Zhou L, Zhou C, Yang Q, Ji Y, Yu DW ( 2013) SOAPBarcode: Revealing arthropod biodiversity through assembly of Illumina shotgun sequences of PCR amplicons. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 4, 1142-1150.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Lodge DM, Turner CR, Jerde CL, Barnes MA, Chadderton L, Egan SP, Feder JL, Mahon AR, Pfrender ME ( 2012) Conservation in a cup of water: Estimating biodiversity and population abundance from environmental DNA. Molecular Ecology, 21, 2555-2558.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Martin M ( 2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. journal, 17, 10-12. |
| [35] |
Masella AP, Bartram AK, Truszkowski JM, Brown DG, Neufeld JD ( 2012) PANDAseq: Paired-end assembler for Illumina sequences. BMC Bioinformatics, 13, 31.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Matsen FA, Kodner RB, Armbrust EV ( 2010) pplacer: Linear time maximum-likelihood and Bayesian phylogenetic placement of sequences onto a fixed reference tree. BMC Bioinformatics, 11, 538.
DOI |
| [37] | Millennium Ecosystem Assessment ( 2005) Ecosystem and Human Well-being: Biodiversity Synthesis. World Resources Institute, Washington, DC. |
| [38] |
Munch K, Boomsma W, Huelsenbeck JP, Willerslev E, Nielsen R ( 2008) Statistical assignment of DNA sequences using Bayesian phylogenetics. Systematic Biology, 57, 750-757.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Newbold T, Hudson LN, Hill SL, Contu S, Lysenko I, Senior RA, Börger L, Bennett DJ, Choimes A, Collen B, Day J ( 2015) Global effects of land use on local terrestrial biodiversity. Nature, 520, 45.
DOI |
| [40] | Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MH, Wagner H ( 2013) Package ‘vegan’. Community Ecology Package, version. 2. ( accessed on 2018-08-01) |
| [41] |
Olds BP, Jerde CL, Renshaw MA, Li Y, Evans NT, Turner CR, Deiner K, Mahon AR, Brueseke MA, Shirey PD, Pfrender ME ( 2016) Estimating species richness using environmental DNA. Ecology and Evolution, 6, 4214-4226.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Patil KR, Roune L, McHardy AC ( 2012) The PhyloPythiaS web server for taxonomic assignment of metagenome sequences. PLoS ONE, 7, e38581.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Pfrender M, Hawkins C, Bagley M, Courtney G, Creutzburg B, Epler J, Fend S, Ferrington L Jr, Hartzell P, Jackson S, Larsen D ( 2010) Assessing macroinvertebrate biodiversity in freshwater ecosystems: Advances and challenges in DNA-based approaches. The Quarterly Review of Biology, 85, 319-340.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Pimm SL, Jenkins CN, Abell R, Brooks TM, Gittleman JL, Joppa LN, Raven PH, Roberts CM, Sexton JO ( 2014) The biodiversity of species and their rates of extinction, distribution, and protection. Science, 344, 1246752.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Piro VC, Matschkowski M, Renard BY ( 2017) MetaMeta: Integrating metagenome analysis tools to improve taxonomic profiling. Microbiome, 5, 101.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP ( 2009) FastTree: Computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 26, 1641-1650.
DOI URL |
| [47] | R Core Team ( 2016) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. https://www.R-project.org/. ( accessed on 2018-08-01) |
| [48] |
Rognes T, Flouri T, Nichols B, Quince C, Mahé F ( 2016) VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ, 4, e2584.
DOI URL |
| [49] | Rosen GL, Reichenberger ER, Rosenfeld AM ( 2010) NBC: The Naive Bayes Classification tool webserver for taxonomic classification of metagenomic reads. Bioinformatics, 27, 127-129. |
| [50] |
Sato Y, Miya M, Fukunaga T, Sado T, Iwasaki W ( 2018) MitoFish and MiFish pipeline: A mitochondrial genome database of fish with an analysis pipeline for environmental DNA metabarcoding. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35, 1553-1555.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW ( 2009) Introducing Mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 7537-7541.
DOI URL |
| [52] | Simon TP, Evans NT ( 2017) Environmental quality assessment using stream fishes. In: Methods in Stream Ecology, 3rd edn. (eds Hauer FR, Lamberti G), pp. 319-334. Elsevier, London. |
| [53] | Slowikowski K ( 2018) ggrepel: Automatically Position Non- Overlapping Text Labels with ‘ggplot2’. https://CRAN.R- project.org/package=ggrepel. ( accessed on 2018-08-01) |
| [54] |
Taberlet P, Coissac E, Hajibabaei M, Rieseberg LH ( 2012) Environmental DNA. Molecular Ecology, 21, 1789-1793.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Tang M, Hardman CJ, Ji Y, Meng G, Liu S, Tan M, Yang S, Moss ED, Wang J, Yang C, Bruce C ( 2015) High-throughput monitoring of wild bee diversity and abundance via mitogenomics. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 6, 1034-1043.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Thomsen PF, Kielgast JO, Iversen LL, Wiuf C, Rasmussen M, Gilbert MT, Orlando L, Willerslev E ( 2012) Monitoring endangered freshwater biodiversity using environmental DNA. Molecular Ecology, 21, 2565-2573.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Thomsen PF, Willerslev E ( 2015) Environmental DNA—An emerging tool in conservation for monitoring past and present biodiversity. Biological Conservation, 183, 4-18.
DOI URL |
| [58] | Uritskiy GV, DiRuggiero J, Taylor J ( 2018) MetaWRAP—A flexible pipeline for genome-resolved metagenomic data analysis. bioRxiv, 277442. |
| [59] | Visconti A, Martin TC, Falchi M ( 2018) YAMP: A containerised workflow enabling reproducibility in metagenomics research. GigaScience, 7, giy072. |
| [60] |
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR ( 2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 5261-5267.
DOI URL |
| [61] | Wickham H ( 2016) ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Springer-Verlag, New York. 2016) ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Springer-Verlag, New York. |
| [62] |
Wilcox TM, Zarn KE, Piggott MP, Young MK, McKelvey KS, Schwartz MK ( 2018) Capture enrichment of aquatic environmental DNA: A first proof of concept. Molecular Ecology Resources, 18, 1392-1401.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Worm B, Barbier EB, Beaumont N, Duffy JE, Folke C, Halpern BS, Jackson JB, Lotze HK, Micheli F, Palumbi SR, Sala E ( 2006) Impacts of biodiversity loss on ocean ecosystem services. Science, 314, 787-790.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Zhou HW, Li DF, Tam NF, Jiang XT, Zhang H, Sheng HF, Qin J, Liu X, Zou F ( 2011) BIPES, a cost-effective high-throughput method for assessing microbial diversity. The ISME Journal, 5, 741.
DOI |
| [65] |
Zhou X, Li Y, Liu S, Yang Q, Su X, Zhou L, Tang M, Fu R, Li J, Huang Q ( 2013) Ultra-deep sequencing enables high-fidelity recovery of biodiversity for bulk arthropod samples without PCR amplification. GigaScience, 2, 4.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 姜熠辉, 刘岳, 曾旭, 林喆滢, 王楠, 彭吉豪, 曹玲, 曾聪. 东海六个国家级海洋保护区鱼类多样性和连通性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24128-. |
| [2] | 董志远, 陈琳琳, 张乃鹏, 陈莉, 孙德斌, 倪艳梅, 李宝泉. 基于环境DNA宏条形码技术研究黄河三角洲典型潮沟系统鱼类多样性及其对水文连通性的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23073-. |
| [3] | 叶俊伟, 田斌. 中国西南地区重要木本油料植物扁核木的遗传结构及成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1629-1637. |
| [4] | 徐承香, 李子忠, 黎道洪. 贵州织金洞洞穴动物群落多样性与光照强度及土壤重金属含量的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(1): 62-70. |
| [5] | 王玉, 高光彩, 付必谦, 吴专. 北京野鸭湖湿地地表甲虫群落组成与空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(1): 30-42. |
| [6] | 周志强, 魏晓雪, 刘彤. 新疆奇台荒漠植物群落的数量分类及土壤环境解释[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(3): 264-270. |
| [7] | 金伟栋, 洪德林. 太湖流域粳稻地方品种遗传多样性研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(6): 479-487. |
| [8] | 王正寰, 王小明. 资源选择函数拟合藏狐洞穴生境利用特征的有效性分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(5): 382-391. |
| [9] | 吴陆生, 吴孝兵, 江红星, 王朝林. 野生扬子鳄生境特征分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2005, 13(2): 156-161. |
| [10] | 龚志莲, 郭辉军, 盛才余, 周开元. 西双版纳社区旱稻品种多样性与就地保护初探[J]. 生物多样性, 2004, 12(4): 427-434. |
| [11] | 吴海荣, 强胜. 南京市秋季外来杂草定量调查研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2003, 11(5): 432-438. |
| [12] | 张文辉, 王延平, 刘国彬. 独叶草构件生长及其与环境的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2003, 11(2): 132-140. |
| [13] | 李欣海, 马志军, 李典谟, 丁长青, 翟天庆, 路宝忠. 应用资源选择函数研究朱鹮的巢址选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2001, 09(4): 352-358. |
| [14] | 刘志斌, 郑哲民, 王青川. 东亚飞蝗与亚洲飞蝗的主成分及判别式分析*[J]. 生物多样性, 1997, 05(1): 67-71. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn