



Biodiv Sci ›› 2012, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (2): 184-192. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.09211 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2012.09211
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Fang Li, Yilin Shu, Hailong Wu*( )
)
Received:2011-11-22
Accepted:2012-02-28
Online:2012-03-20
Published:2012-04-09
Contact:
Hailong Wu
Fang Li, Yilin Shu, Hailong Wu. Polymorphism of exon 2 of MHC Class II B gene in the Chinese concave- eared torrent frog (Odorrana tormota)[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(2): 184-192.
| 引物 Primer | 序列 Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| X1 | CGTTGGATATACGATCTGGAGG |
| X2 | GTACTTCGACAGTGATAAGGGATT |
| S1 | GGGTTTCTGTTCCAGGAGTCAG |
| S2 | AGCACTTGGTCTCCCCAGCTCGGT |
| IIQ1BU | GTACGGAGGATATCAGGTTTC |
| IIQ1BD | CAGGTGCAGTATATTCCTTCAT |
Table 1 Sequences of the primers used in the study of MHC II B genes variation in the Chinese concave-eared torrent frog
| 引物 Primer | 序列 Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| X1 | CGTTGGATATACGATCTGGAGG |
| X2 | GTACTTCGACAGTGATAAGGGATT |
| S1 | GGGTTTCTGTTCCAGGAGTCAG |
| S2 | AGCACTTGGTCTCCCCAGCTCGGT |
| IIQ1BU | GTACGGAGGATATCAGGTTTC |
| IIQ1BD | CAGGTGCAGTATATTCCTTCAT |
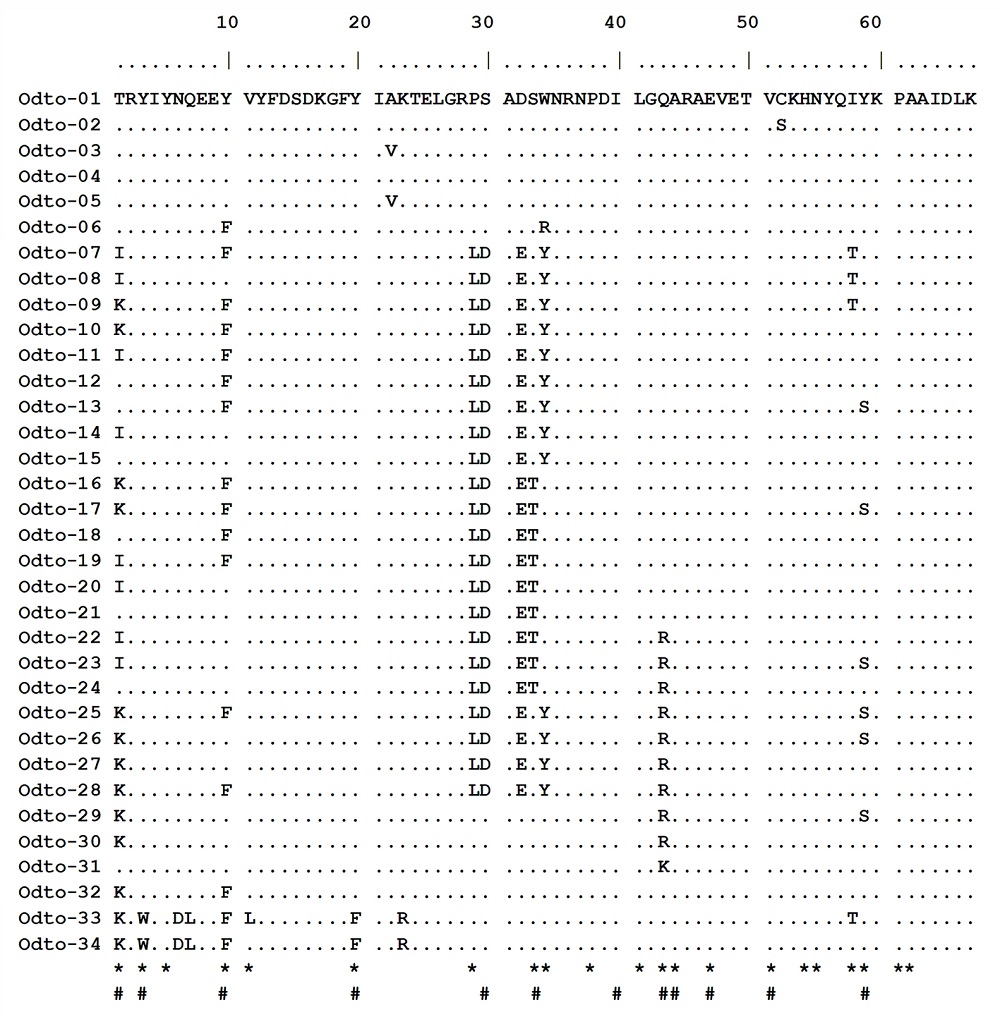
Fig. 1 Amino acid alignment of MHC II alleles of the Chinese concave-eared torrent frog. Sites involved in putative antigen binding sites are indicated by * (according to Brown et al., 1993) or by # (according to Tong et al., 2006), respectively.
| 位点 Sites | 同义替换率dN | 非同义替换率dS | dN/dS | Z检验P值 P(Z-test) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 0.047(0.014) | 0.050(0.018) | 0.710 | 0.909 |
| ABS ( | 0.116(0.037) | 0.046(0.029) | 1.081 | 0.028 |
| Non-ABS ( | 0.020(0.011) | 0.051(0.025) | 0.510 | 0.075 |
| ABS ( | 0.167(0.056) | 0.081(0.066) | 1.480 | 0.032 |
| Non-ABS ( | 0.025(0.011) | 0.044(0.018) | 0.491 | 0.176 |
Table 2 The average rates of nonsynonymous substitutions per nonsynonymous site (dN) and synonymous substitutions per synonymous site (dS) as well as the resulting ratio dN/dS for the sequenced section, the ABS (putative antigen binding sites) and non-ABS of MHC II B genes exon 2 of the Chinese concave-eared torrent frog.
| 位点 Sites | 同义替换率dN | 非同义替换率dS | dN/dS | Z检验P值 P(Z-test) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 0.047(0.014) | 0.050(0.018) | 0.710 | 0.909 |
| ABS ( | 0.116(0.037) | 0.046(0.029) | 1.081 | 0.028 |
| Non-ABS ( | 0.020(0.011) | 0.051(0.025) | 0.510 | 0.075 |
| ABS ( | 0.167(0.056) | 0.081(0.066) | 1.480 | 0.032 |
| Non-ABS ( | 0.025(0.011) | 0.044(0.018) | 0.491 | 0.176 |
| 模型 Model | 似然值 Likelihood | 估计参数 Estimate parameters | (LRT) 2△L | 受正选择位点 Positively selected sites |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | -655.027 | p0= 0.69482 p1=0.30518 ω0=0.02484 ω1=1.00000 | 52.322 (P<0.001) | None |
| M2 | -628.866 | p0=0.48425 p1=0.43958 p2=0.07617 ω0=0.00000 ω1=1.00000 ω2=15.77201 | 1T**, 10Y**, 34W**, 43Q*, 59Y** | |
| M7 | -655.106 | p= 0.01273 q= 0.02500 | 52.454 (P<0.001) | None |
| M8 | -628.879 | p0=0.92380 p=0.00503 q=0.00516 (p1= 0.07620) ω= 16.20861 | 1T**, 10Y**, 33S, 34W**, 43Q*, 59Y** |
Table 3 Summary of parameter estimates and likelihood values of different models of codon evolution for exon 2 of MHC II B gene in the Chinese concave-eared torrent frog
| 模型 Model | 似然值 Likelihood | 估计参数 Estimate parameters | (LRT) 2△L | 受正选择位点 Positively selected sites |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | -655.027 | p0= 0.69482 p1=0.30518 ω0=0.02484 ω1=1.00000 | 52.322 (P<0.001) | None |
| M2 | -628.866 | p0=0.48425 p1=0.43958 p2=0.07617 ω0=0.00000 ω1=1.00000 ω2=15.77201 | 1T**, 10Y**, 34W**, 43Q*, 59Y** | |
| M7 | -655.106 | p= 0.01273 q= 0.02500 | 52.454 (P<0.001) | None |
| M8 | -628.879 | p0=0.92380 p=0.00503 q=0.00516 (p1= 0.07620) ω= 16.20861 | 1T**, 10Y**, 33S, 34W**, 43Q*, 59Y** |
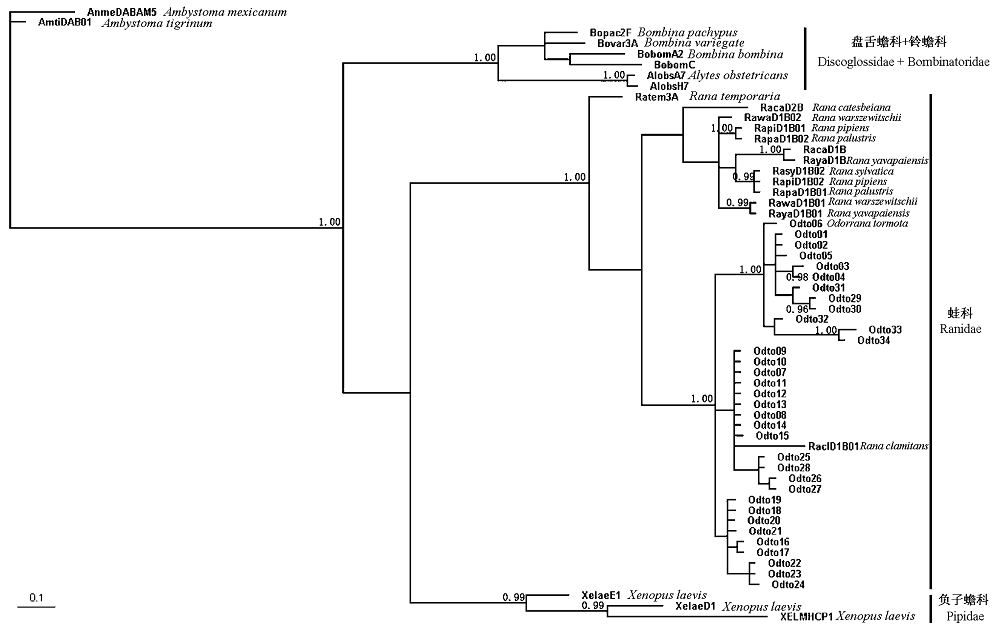
Fig. 2 Phylogenetic relationship of anuran MHC class II B exon 2 nucleotide sequences constructed with Bayesian inference with two outgroup sequences from the caudate amphibian, Ambystoma tigrinum and Ambystoma mexicanum. Posterior probabilities above 0.95 are indicated on branches.
| [1] |
Alcaide M, Edwards SV, Negro JJ (2007) Characterization, polymorphism, and evolution of MHC class II B genes in birds of prey. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 65, 541-554.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] |
Babik W, Pabijan M, Radwan J (2008) Contrasting patterns of variation in MHC loci in the Alpine newt. Molecular Ecology, 17, 2339-2355.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] |
Bai CM, Garner TWJ, Li YM (2010) First evidence of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in China: discovery of chytridiomycosis in introduced American bullfrogs and native amphibians in the Yunnan Province, China. EcoHealth, 7, 127-134.
URL PMID |
| [4] |
Bos DH, DeWoody JA (2005) Molecular characterization of major histocompatibility complex class II alleles in wild tiger salamanders (Ambystoma tigrinum). Immunogenetics, 57, 775-781.
URL PMID |
| [5] |
Bos DH, Waldman B (2006) Evolution by recombination and transspecies polymorphism in the MHC class I gene of Xenopus laevis. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 23, 137-143.
URL PMID |
| [6] |
Brown JH, Jardetzky TS, Gorga JC, Stern LJ, Urban RG, Strominger JL, Wiley DC (1993) Three-dimensional structure of the human class II histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR1. Nature, 364, 33-39.
URL PMID |
| [7] | Chen BH (陈璧辉) (1991) The Amphibian and Reptilian Fauna of Anhui (安徽两栖爬行动物志). Anhui Science and Technology Publishing House, Hefei. (in Chinese) |
| [8] | Cottage A, Yang AP, Maunders H, de Lacy RC, Ramsay NA (2001) Identification of DNA sequences flanking T-DNA insertions by PCR-walking. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 19, 321-327. |
| [9] | Daszak P, Cunningham AA, Hyatt AD (2003) Infectious disease and amphibian population decline. Diversity and Distributions, 9, 141-150. |
| [10] | Fei L (费梁), Hu SQ (胡淑琴), Ye CY (叶昌媛), Huang YZ (黄永昭) (2009) Fauna Sinica: Amphibia (Vol. 2. Anura) (中国动物志: 两栖纲(中卷无尾目)). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [11] |
Feng AS, Narins PM, Xu CH, Lin WY, Yu ZL, Qiu Q, Xu ZM, Shen JX (2006) Ultrasonic communication in frogs. Nature, 440, 333-336.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
Feng AS, Narins PM, Xu CH (2002) Vocal acrobatics in a Chinese frog, Amolops tormotus. Naturwissenschaften, 89, 352-356.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
Harf R, Sommer S (2005) Association between major histocompatibility complex class II DRB alleles and parasite load in the hairy-footed gerbil, Gerbillurus paeba, in the southern Kalahari. Molecular Ecology, 14, 85-91.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] |
Hauswaldt JS, Stuckas H, Pfautsch S, Tiedemann R (2007) Molecular characterization of MHC class II in a nonmodel anuran species, the fire-bellied toad Bombina bombina. Immunogenetics, 59, 479-491.
URL PMID |
| [15] |
Hedrick PW, Parker KM (1998) MHC variation in the endangered gila topminnow. Evolution, 52, 194-199.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] |
Hovhannisyan Z, Weiss A, Martin A, Wiesner M, Tollefsen S, Yoshida K, Ciszewski C, Curran SA, Murray JA, David CS, Sollid LM, Koning F, Teyton L, Jabri B (2008) The role of HLA-DQ8 β57 polymorphism in the anti-gluten T-cell response in coeliac disease. Nature, 456, 534-538.
URL PMID |
| [17] |
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics, 17, 754-755.
URL PMID |
| [18] | Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Mammalian Protein Metabolism (ed. Munro HN), pp. 21-132. Academic Press, New York. |
| [19] |
Kiemnec-Tyburczy KM, Richmond JD, Savage AE, Zamudio KR (2010) Selection, trans-species polymorphism, and locus identification of major histocompatibility complex class IIβ alleles of New World ranid frogs. Immunogenetics, 62, 741-751.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] | Klein J (1986) Natural History of the Major Histocompatibility Complex, 1st edn. John Wiley and Sons, New York, Chichester, Brisbane, Toronto, Singapore. |
| [21] |
Klein J, Sato A (1998) Birth of the major histocompatibility complex. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology, 47, 199-209.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] | Langefors Å, Lohm J, Grahn M, Andersen Ø, Von Schantz T (2001) Association between major histocompatibility complex class II B alleles and resistance to Aeromonas salmonicida in Atlantic salmon. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 268, 479-485. |
| [23] |
Laurens V, Chapusot C, del Rosario Ordonez M, Bentrari F, Padros MR, Tournefier A (2001) Axolotl MHC class II beta chain: predominance of one allele and alternative splicing of the beta 1 domain. European Journal of Immunology, 31, 506-515.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | Li PP, Lu YY, Li A, Yu LN (2008) The tadpole of a little-known frog, Rana tormotus Wu, 1977. Asiatic Herpetological Research, 11, 71-75. |
| [25] | May S, Beebee TJC (2009) Characterisation of major histocompatibility complex class II alleles in the natterjack toad, Bufo calamita. Conservation Genetics Resources, 1, 415-417. |
| [26] |
Nei M, Gojobori T (1986) Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 3, 418-426.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] |
Nielsen R, Yang Z (1998) Likelihood models for detecting positively selected amino acid sites and applications to the HIV-1 envelope gene. Genetics, 148, 929-936.
URL PMID |
| [28] |
Ohta Y, Goetz W, Hossain MZ, Nonaka M, Flajnik MF (2006) Ancestral organization of the MHC revealed in the amphibian Xenopus. The Journal of Immunology, 176, 3674-3685.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] | Padgett-Flohr GE (2008) Pathogenicity of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in two threatened California amphibians: Rana draytonii and Ambystoma californiense. Herpetological Conservation and Biology, 3, 182-191. |
| [30] |
Parham P, Ohta T (1996) Population biology of antigen presentation by MHC class I molecules. Science, 272, 67-74.
URL PMID |
| [31] |
Paterson S, Wilson K, Pemberton JM (1998) Major hist- ocompatibility-complex variation associated with juvenile survival and parasite resistance in a large unmanaged ungulate population (Ovis aries L.). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 95, 3714-3719.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Pounds JA, Bustamante MR, Coloma LA, Consuegra JA, Fogden MPL, Foster PN, Marca EL, Masters KL, Merino-Viteri A, Puschendorf R, Ron SR, Sánchez-Azofeifa GA, Still CJ, Young BE (2006) Widespread amphibian extinctions from epidemic disease driven by global warming. Nature, 439, 161-167.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] |
Richardson DS, Westerdahl H (2003) MHC diversity in two Acrocephalus species: the outbred great reed warble and the inbred Seychelles warbler. Molecular Ecology, 12, 3523-3529.
DOI URL PMID |
| [34] |
Sato A, Figueroa F, O’Huigin C, Steck N, Klein J (1998) Cloning of major histocompatibility complex (Mhc) genes from three spine stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology, 7, 221-231.
URL PMID |
| [35] |
Shen JX, Feng AS, Xu ZM, Yu ZL, Arch VS, Yu XJ, Narins PM (2008) Ultrasonic frogs show hyperacute phonotaxis to female courtship calls. Nature, 453, 914-916.
URL PMID |
| [36] |
Shen JX, Xu ZM, Yu ZL, Wang SA, Zheng DZ, Fan SC (2011) Ultrasonic frogs show extraordinary sex differences in auditory frequency sensitivity. Nature Communications, 2, 342. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1339.
URL PMID |
| [37] |
Su X, Wu XB, Yan P, Cao SY, Hu YL (2007) Rearrangement of a mitochondrial tRNA gene of the concave-eared torrent frog, Amolops tormotus. Gene, 394, 25-34.
DOI URL PMID |
| [38] |
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA 4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA4) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 1596-1599.
DOI URL PMID |
| [39] |
Teacher AGF, Garner TWJ, Nichols RA (2009) Evidence for directional selection at a novel major histocompatibility class I marker in wild common frogs (Rana temporaria) exposed to a viral pathogen (Ranavirus). PLoS ONE, 4, e4616.
DOI URL PMID |
| [40] |
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 4876-4882.
URL PMID |
| [41] |
Tong JC, Bramson J, Kanduc D, Chow S, Sinha AA, Ranganathan S (2006) Modeling the bound conformation of pemphigus vulgaris-associated peptides to MHC Class II DR and DQ alleles. Immunome Research, 2, 1.
DOI URL PMID |
| [42] | Westerdahl H, Waldenstrom J, Hansson B, Hasselquist D, von Schantz T, Bensch S (2005) Associations between malaria and MHC genes in a migratory songbird. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 272, 1511-1518. |
| [43] |
Wong WSW, Yang ZH, Goldman N, Nielsen R (2004) Accuracy and power of statistical methods for detecting adaptive evolution in protein coding sequences and for identifying positively selected sites. Genetics, 168, 1041-1051.
URL PMID |
| [44] | Yan JC, Luo TL, Wu HL (2011) Development and charac- terization of twelve polymorphic microsatellite loci for the Chinese concave-eared frog (Odorrana tormota). Conser- vation Genetics Resource, 3, 225-227. |
| [45] |
Yang ZH (1997) PAML: a program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Computer Applications in the Biosciences, 13, 555-556.
URL PMID |
| [46] |
Zeisset I, Beebee TJC (2009) Molecular characterization of major histocompatibility complex class II alleles in the common frog, Rana temporaria. Molecular Ecology Resources, 9, 738-745.
URL PMID |
| [1] | Li Hualiang, Zhang Mingjun, Zhang Xibin, Tan Rong, Li Shichuan, Feng Erhui, Lin Xueyun, Chen Min, Yan enbo, Zeng Zhigao. Composition and influencing factors of the amphibian community in Hainan Dongzhaigang National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24350-. |
| [2] | Yixin Jiang, Yingying Shi, Shuo Gao, Supen Wang. The impact of anthropogenic noise, artificial light at night and road kills on amphibians [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22427-. |
| [3] | Cheng Li, Jianping Jiang, Feng Xie, Tian Zhao, Jing Che, Yiming Li, Weiguo Du, Weikang Yang, Feng Xu. Progress and prospect of Chinese biodiversity monitoring of amphibians and reptiles [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(12): 23382-. |
| [4] | Hao Dong, Ziyi Ke, Yatao Wu, Junqi Miao, Fang Zhang. Changes in vocal characteristics of male concave-eared torrent frogs (Odorrana tormota) in different chorus tides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22217-. |
| [5] | Yunfeng Song, Chuanwu Chen, Yanping Wang. A dataset on the life-history and ecological traits of Chinese amphibians [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(3): 22053-. |
| [6] | Zhiwei Gao, Tianyu Qian, Jianping Jiang, Dejia Hou, Xuejian Deng, Daode Yang. Species diversity and distribution of amphibians and reptiles in Hunan Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(2): 21290-. |
| [7] | Cunlu Wang,Hu Chen,Hua Xiao,Hongmei Zhang,Linzhi Li,Cheng Guo,Jing Chen,Qiang Wei. Diversity and habitat selection of amphibians in rocky desertification area in northwestern Guizhou [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(4): 485-495. |
| [8] | Kai Wang, Jinlong Ren, Hongman Chen, Zhitong Lyu, Xianguang Guo, Ke Jiang, Jinmin Chen, Jiatang Li, Peng Guo, Yingyong Wang, Jing Che. The updated checklists of amphibians and reptiles of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(2): 189-218. |
| [9] | Cheng Li, Feng Xie, Jing Che, Jianping Jiang. Monitoring and research of amphibians and reptiles diversity in key areas of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(3): 246-254. |
| [10] | Zhigang Jiang, Zhenhua Luo. Assessing species endangerment status: progress in research and an example from China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(5): 612-622. |
| [11] | GENG Bao-Rong. Evaluation of amphibian species diversity in Fujian [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2004, 12(6): 618-625. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn