



Biodiv Sci ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (5): 605-616. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020326 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020326
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiyang Hao1, Cha He1, Kelin Chu2, Zhixin Shen3, Qiang Zhao1, Wei Gao1, Da Pan1,*( ), Hongying Sun1,*(
), Hongying Sun1,*( )
)
Received:2020-08-12
Accepted:2020-10-16
Online:2021-05-20
Published:2021-01-17
Contact:
Da Pan,Hongying Sun
Xiyang Hao, Cha He, Kelin Chu, Zhixin Shen, Qiang Zhao, Wei Gao, Da Pan, Hongying Sun. The distribution pattern and biodiversity conservation of freshwater crabs in Hainan Island[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(5): 605-616.
| 分类地位 Classification | 物种名 Species name |
|---|---|
| 溪蟹科 Potamidae | |
| 非仿溪蟹属 Apotamonautes* | 海南非仿溪蟹泮水亚种 Apotamonautes hainanensis banshuiensis* |
| 海南非仿溪蟹霸王岭亚种 Apotamonautes hainanensis bawanglingensis* | |
| 海南非仿溪蟹指名亚种 Apotamonautes hainanensis hainanensis* | |
| 海南非仿溪蟹南林亚种 Apotamonautes hainanensis nanlinensis* | |
| 海南溪蟹属 Hainanpotamon | 戴氏海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon daiae* |
| 府城海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon fuchengense* | |
| 和乐海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon helense* | |
| 东方海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon orientale* | |
| 新内溪蟹属 Neotiwaripotamon* | 白氏新内溪蟹 Neotiwaripotamon whiteheadi* |
| 尖峰新内溪蟹 Neotiwaripotamon jianfengense* | |
| 岩溪蟹属 Calcipotamon* | 紫光岩溪蟹 Calcipotamon puglabrum* |
| 拟地蟹科 Gecarcinucidae | |
| 束腰蟹属 Somanniathelphusa | 坝王束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa bawangensis* |
| 海南束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa hainanensis* | |
| 琼山束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa qiongshanensis* | |
| 通什束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa tongzhaensis* |
Table 1 A checklist of the freshwater crabs in Hainan Island, China
| 分类地位 Classification | 物种名 Species name |
|---|---|
| 溪蟹科 Potamidae | |
| 非仿溪蟹属 Apotamonautes* | 海南非仿溪蟹泮水亚种 Apotamonautes hainanensis banshuiensis* |
| 海南非仿溪蟹霸王岭亚种 Apotamonautes hainanensis bawanglingensis* | |
| 海南非仿溪蟹指名亚种 Apotamonautes hainanensis hainanensis* | |
| 海南非仿溪蟹南林亚种 Apotamonautes hainanensis nanlinensis* | |
| 海南溪蟹属 Hainanpotamon | 戴氏海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon daiae* |
| 府城海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon fuchengense* | |
| 和乐海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon helense* | |
| 东方海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon orientale* | |
| 新内溪蟹属 Neotiwaripotamon* | 白氏新内溪蟹 Neotiwaripotamon whiteheadi* |
| 尖峰新内溪蟹 Neotiwaripotamon jianfengense* | |
| 岩溪蟹属 Calcipotamon* | 紫光岩溪蟹 Calcipotamon puglabrum* |
| 拟地蟹科 Gecarcinucidae | |
| 束腰蟹属 Somanniathelphusa | 坝王束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa bawangensis* |
| 海南束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa hainanensis* | |
| 琼山束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa qiongshanensis* | |
| 通什束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa tongzhaensis* |
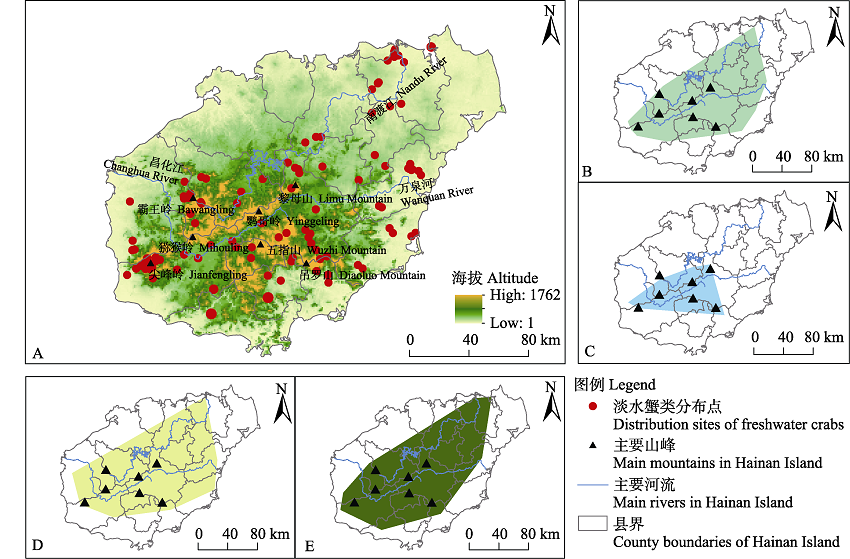
Fig. 1 Distribution area of different genera of freshwater crabs in Hainan Island. A, Distribution sites of freshwater crabs; B, Apotamonautes species distribution area; C, Newtiwaripotamon and Calcipotamon species distribution area; D, Hainanpotamon species distribution area; E, Somanniathephusa species distribution area.
| 种名 Species name | 受胁等级 Threatened categories | 所依据的标准 IUCN Redlist Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| 海南非仿溪蟹 Apotamonautes hainanensis | LC | |
| 戴氏海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon daiae | LC | |
| 府城海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon fuchengense | VU | B1ab(i, ii, iii) + 2ab(i, ii, iii) |
| 和乐海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon helense | LC | |
| 东方海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon orientale | VU | B1ab(iii) + 2ab(iii) |
| 白氏新内溪蟹 Neotiwaripotamon whiteheadi | NT | |
| 尖峰新内溪蟹 Neotiwaripotamon jianfengense | LC | |
| 紫光岩溪蟹 Calcipotamon puglabrum | NT | |
| 坝王束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa bawangensis | LC | |
| 海南束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa hainanensis | LC | |
| 琼山束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa qiongshanensis | LC | |
| 通什束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa tongzhaensis | LC |
Table 2 Threatened categories of freshwater crabs in Hainan Island
| 种名 Species name | 受胁等级 Threatened categories | 所依据的标准 IUCN Redlist Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| 海南非仿溪蟹 Apotamonautes hainanensis | LC | |
| 戴氏海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon daiae | LC | |
| 府城海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon fuchengense | VU | B1ab(i, ii, iii) + 2ab(i, ii, iii) |
| 和乐海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon helense | LC | |
| 东方海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon orientale | VU | B1ab(iii) + 2ab(iii) |
| 白氏新内溪蟹 Neotiwaripotamon whiteheadi | NT | |
| 尖峰新内溪蟹 Neotiwaripotamon jianfengense | LC | |
| 紫光岩溪蟹 Calcipotamon puglabrum | NT | |
| 坝王束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa bawangensis | LC | |
| 海南束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa hainanensis | LC | |
| 琼山束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa qiongshanensis | LC | |
| 通什束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa tongzhaensis | LC |
| 种名 Species name | 分布区像元数 Pixel of presence | NRs覆盖像元数 Pixel of presence covered by NRs | NRs覆盖比例 Coverage of NRs (%) | NP覆盖的像元数 Pixel of presence covered by NP | NP覆盖比例 Coverage of NP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 紫光岩溪蟹 Calcipotamon puglabrum* | 203 | 55 | 27.09 | 203 | 100.00 |
| 府城海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon fuchengense* | 1,125 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 |
| 白氏新内溪蟹 Neotiwaripotamon whiteheadi* | 2,233 | 328 | 14.69 | 1,312 | 58.76 |
| 和乐海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon helense* | 3,752 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 |
| 尖峰新内溪蟹 Neotiwaripotamon jianfengense* | 5,729 | 1,534 | 26.78 | 3,354 | 58.54 |
| 东方海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon orientale* | 6,317 | 1,338 | 21.18 | 2,694 | 42.65 |
| 琼山束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa qiongshanensis | 6,853 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 |
| 海南束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa hainanensis | 7,023 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 |
| 坝王束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa bawangensis | 7,872 | 65 | 0.83 | 441 | 5.60 |
| 通什束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa tongzhaensis | 12,175 | 1,254 | 10.30 | 3,190 | 26.20 |
| 海南非仿溪蟹 Apotamonautes hainanensis | 12,323 | 1,835 | 14.89 | 4,621 | 37.50 |
| 戴氏海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon daiae | 14,331 | 2,044 | 14.26 | 5,073 | 35.40 |
| 均值 Average | 6,661.33 | 704 | 10.83 | 1,741 | 30.39 |
Table 3 The coverage of nature reserves and Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park on the distribution of Hainan freshwater crab species
| 种名 Species name | 分布区像元数 Pixel of presence | NRs覆盖像元数 Pixel of presence covered by NRs | NRs覆盖比例 Coverage of NRs (%) | NP覆盖的像元数 Pixel of presence covered by NP | NP覆盖比例 Coverage of NP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 紫光岩溪蟹 Calcipotamon puglabrum* | 203 | 55 | 27.09 | 203 | 100.00 |
| 府城海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon fuchengense* | 1,125 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 |
| 白氏新内溪蟹 Neotiwaripotamon whiteheadi* | 2,233 | 328 | 14.69 | 1,312 | 58.76 |
| 和乐海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon helense* | 3,752 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 |
| 尖峰新内溪蟹 Neotiwaripotamon jianfengense* | 5,729 | 1,534 | 26.78 | 3,354 | 58.54 |
| 东方海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon orientale* | 6,317 | 1,338 | 21.18 | 2,694 | 42.65 |
| 琼山束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa qiongshanensis | 6,853 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 |
| 海南束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa hainanensis | 7,023 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 |
| 坝王束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa bawangensis | 7,872 | 65 | 0.83 | 441 | 5.60 |
| 通什束腰蟹 Somanniathelphusa tongzhaensis | 12,175 | 1,254 | 10.30 | 3,190 | 26.20 |
| 海南非仿溪蟹 Apotamonautes hainanensis | 12,323 | 1,835 | 14.89 | 4,621 | 37.50 |
| 戴氏海南溪蟹 Hainanpotamon daiae | 14,331 | 2,044 | 14.26 | 5,073 | 35.40 |
| 均值 Average | 6,661.33 | 704 | 10.83 | 1,741 | 30.39 |
| [1] |
Bryant JV, Gottelli D, Zeng X, Hong X, Chan BPL, Fellowes JR, Zhang Y, Luo J, Durrant C, Geissmann T, Chatterjee HJ, Turvey ST (2016) Assessing current genetic status of the Hainan gibbon using historical and demographic baselines: Implications for conservation management of species of extreme rarity. Molecular Ecology, 25, 3540-3556.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Chen CW, Chen CS, Wang YP (2019) Ecological correlates of extinction risk in Chinese amphibians. Diversity and Distributions, 25, 1586-1598.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Cheng TH, Tan YK (1973) On the birds of Hainan. II. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 19, 405-416. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郑作新, 谭耀匡 (1973) 海南岛的鸟类. II. 动物学报, 19, 405-416.] | |
| [4] | Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences (1986) The Freshwater and Estuary Fishes of Hainan Island. Guangdong Science and Technology Press, Guangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 中国水产科学研究院 (1986) 海南岛淡水及河口鱼类志. 广东科技出版社, 广州.] | |
| [5] |
Chu KL, Ma XP, Zhang ZW, Wang PF, Lü LN, Zhao Q, Sun HY (2018) A checklist for the classification and distribution of China’s freshwater crabs. Biodiversity Science, 26, 274-282. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 楚克林, 马晓萍, 张泽伟, 王鹏飞, 吕琳娜, 赵强, 孙红英 (2018) 中国淡水蟹分类与分布名录(十足目: 拟地蟹科, 溪蟹科). 生物多样性, 26, 274-282.] | |
| [6] |
Cumberlidge N, Ng PKL, Yeo DCJ, Magalhães C, Campos MR, Alvarez F, Naruse T, Daniels SR, Esser LJ, Attipoe FYK, Clotilde-Ba FL, Darwall W, McIvor A, Baillie JEM, Collen B, Ram M (2009) Freshwater crabs and the biodiversity crisis: Importance, threats, status, and conservation challenges. Biological Conservation, 142, 1665-1673.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Dai AY (1995) On a new genus and two new species of freshwater crabs from Hainan Island, China (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura: Potamidae). Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica, 20, 391-397. |
| [8] | Dai AY (1999) Fauna Sinica · Arthropoda · Crustacea ·Malacostraca · Decapoda · Parathelphusidae, Potamidae. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴爱云 (1999) 中国动物志·节肢动物门·甲壳动物亚门·软甲纲·十足目·束腹蟹科, 溪蟹科. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [9] | Dai AY, Naiyanetr P (1994) A revision of genus Tiwaripotamon Bott, 1970, the freshwater crabs from China (Decapoda: Brachyura: Potamidae). Sinozoologia, 11, 47-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴爱云, 拍文·乃亚内 (1994) 中国淡水蟹类内溪蟹属的修订(十足目: 短尾派: 溪蟹科). 动物学集刊, 11, 47-72.] | |
| [10] | Dai AY, Xing DJ (1993) A study on Apotamonautes from Hainan Island, China (Decapods: Brachyura). Sinozoologia, 10, 63-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴爱云, 邢定介 (1993) 海南岛非仿溪蟹的研究(十足目, 短尾派). 动物学集刊, 10, 63-72.] | |
| [11] | Dai AY, Xing DJ (1994) On Somanniathephusa from Hainan Island, China (Decapods: Parathelphusidae). In: Memorial Volume Dedicated to the Hundredth Anniversary of the Birthday of the Late Prof. Sisan CHEN (Z. CHEN) (ed. Chen YZ), pp. 97-108. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴爱云, 邢定介 (1994) 海南岛束腰蟹属的研究. 见: 纪念陈祯教授诞辰一百周年论文集(陈阅增主编), 97-108页. 中国科学技术出版社, 北京.] | |
| [12] | Esser L, Cumberlidge N (2008) Hainanpotamon orientale. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008: e. T134773A4011437. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/134773/4011437.html. (accessed on 2020-06-08) |
| [13] |
Fielding AH, Bell JF (1997) A review of methods for the assessment of prediction errors in conservation presence/ absence models. Environmental Conservation, 24, 38-49.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Heiner M, Higgins J, Li XB (2011) Identifying freshwater conservation priorities in the Upper Yangtze River Basin. Freshwater Biology, 56, 89-105.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Hou P, Zhai J, Cao W, Yang M, Cai MY, Li J (2018) Evaluation on ecosystem changes and protection of the national key ecological function zones in mountainous areas of central Hainan Island. Acta Geographica Sinica, 73, 429-441. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 侯鹏, 翟俊, 曹巍, 杨旻, 蔡明勇, 李静 (2018) 国家重点生态功能区生态状况变化与保护成效评估——以海南岛中部山区国家重点生态功能区为例. 地理学报, 73, 429-441.] | |
| [16] |
Huang C, Huang SZ, Shen ZX (2020) A new long-legged terrestrial freshwater crab, Calcipotamon puglabrum gen. nov. et sp. nov. (Crustacea: Decapoda: Potamidae), from Hainan Island, China. Zootaxa, 4766, 447-456.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Huang Y, Wang YZ (2011) Progress in the biogeography of amphibian and reptile in Hainan Island. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 30, 304-309. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄勇, 王跃招 (2011) 海南岛两栖爬行动物生物地理学研究进展. 四川动物, 30, 304-309.] | |
| [18] | IUCN (2001) IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria: Version 3.1. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland & Cambridge, UK. |
| [19] | IUCN (2012a) IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria, Version 3.1, 2nd edn. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland & Cambridge, UK. |
| [20] | IUCN (2012b) Guidelines for Application of IUCN Red List Criteria at Regional and National Levels, Version 4.0. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland & Cambridge, UK. |
| [21] | IUCN Standards and Petitions Committee (2019) Guidelines for Using the IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria. Version 14. http://www.iucnredlist.org. (accessed on 2020-06-01) |
| [22] | Jiang ZG, Ma KP, Han XG (1997) Conservation Biology. Zhejiang Science and Technology Press, Hangzhou. (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 马克平, 韩兴国 (1997) 保护生物学. 浙江科学技术出版社, 杭州.] | |
| [23] | Kawai T, Cumberlidge N (2016) Conservation First: Strategic Planning to Save the Critically Endangered Singapore Freshwater Crab, Johora singaporensis. Springer International Publishing, Cham, Switzerland. |
| [24] |
Lehner B, Grill G (2013) Global river hydrography and network routing: Baseline data and new approaches to study the world’s large river systems. Hydrological Processes, 27, 2171-2186.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Li TJ, Lim WH, Cai YX (2015) A new locality of the Singapore freshwater crab Johora singaporensis (Crustacea: Brachyura: Potamidae) in the Bukit Timah Nature Reserve. Nature in Singapore, 8, 53-56. |
| [26] | Lin MZ, Zhang YL (2000) Dynamic changes of forest resources in Hainan and its sustainable development. Ecological Science, 19, 84-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 林媚珍, 张镱锂 (2000) 海南岛森林资源的动态变化及其可持续发展. 生态科学, 19, 84-89.] | |
| [27] |
Liu CR, White M, Newell G (2011) Measuring and comparing the accuracy of species distribution models with presence- absence data. Ecography, 34, 232-243.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Liu MG (2010) Atlas of Physical Geography of China. SinoMaps Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘明光 (2010) 中国自然地理图集. 中国地图出版社, 北京.] | |
| [29] |
Manel S, Williams HC, Ormerod SJ (2001) Evaluating presence-absence models in ecology: The need to account for prevalence. Journal of Applied Ecology, 38, 921-931.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Ng DJJ, Sivasothi N, Cai YX, Davison GWH, Yeo DCJ (2015a) A new locality of the Singapore freshwater crab, Johora singaporensis (Crustacea: Brachyura: Potamidae). Nature in Singapore, 8, 31-35. |
| [31] |
Ng DJJ, Yeo DCJ, Sivasothi N, Ng PKL (2015b) Conservation challenges and action for the Critically Endangered Singapore freshwater crab Johora singaporensis. Oryx, 49, 345-351.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Pearce J, Ferrier S (2000) Evaluating the predictive performance of habitat models developed using logistic regression. Ecological Modelling, 133, 225-245.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Phillips SJ, Anderson RP, Schapire RE (2006) Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecological Modelling, 190, 231-259.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Stephen FE, Hijmans RJ (2017) WorldClim 2: New 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. International Journal of Climatology, 37, 4302-4315.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Tognelli MF, Anderson EP, Jiménez SLF, Chuctaya J, Chocano L, Maldonado OJA, Mesa SL, Mojica JI, Carvajal VFM, Correa V, Ortega H, Rivadeneira RJF, Sánchez DP, Cox NA, Hidalgo M, Jiménez PP, Lasso CA, Sarmiento J, Velásquez MA, Villa NFA (2019) Assessing conservation priorities of endemic freshwater fishes in the Tropical Andes region. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 29, 1123-1132.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Wang S, Xie Y (2005) China Species Red List, Vol. III. Invertebrates. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 汪松, 解焱 (2005) 中国物种红色名录(第三卷): 无脊椎动物. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [37] | Warren DL, Matzke N, Cardillo M, Baumgartner J, Beaumont L, Huron N, Simões M, Iglesias TL, Dinnage R (2019) ENMTools. https://github.com/danlwarren/ENMTools. (accessed on 2020-05-01) |
| [38] | Xu HG, Cao MC, Wu J, Ding H (2013) An Inventory of Biodiversity of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 徐海根, 曹铭昌, 吴军, 丁晖 (2013) 中国生物多样性本底评估报告. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [39] |
Yeo DCJ, Naruse T (2007) A revision of the freshwater crab genus Hainanpotamon Dai, 1995 (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura: Potamidae: Potamiscinae), with a redescription of Potamon (Potamon) orientale (Parisi, 1916) and descriptions of three new species. Zoological Science, 24, 1143-1158.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Yu SB, Zhai PM, Zhang Q (2006) Variation of characteristics of drought in Hainan Island during 1961-2004. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 27, 113-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 俞胜宾, 翟盘茂, 张强 (2006) 1961-2004海南岛干旱演变特征分析. 热带作物学报, 27, 113-115.] | |
| [41] | Zhang LS (2012) Paleogeography of China: The Formation of China’s Natural Environment. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张兰生 (2012) 中国古地理: 中国自然环境的形成. 科学出版社, 北京.] |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn