



Biodiv Sci ›› 2008, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (6): 607-612. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.08179 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2008.08179
• Research Bulletins • Previous Articles Next Articles
Huifang Li1,*( ), Wenjuan Xu1, Wenqi Zhu1, Sumei Xue2, Kuanwei Chen1
), Wenjuan Xu1, Wenqi Zhu1, Sumei Xue2, Kuanwei Chen1
Received:2008-07-28
Accepted:2008-10-17
Online:2008-11-20
Published:2008-11-20
Contact:
Huifang Li
About author:* E-mail: lhfxf_002@yahoo.com.cnHuifang Li, Wenjuan Xu, Wenqi Zhu, Sumei Xue, Kuanwei Chen. Genetic diversity and evolution of Fujian domestic duck breeds[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2008, 16(6): 607-612.
| 品种 Breed | 样本量 Sample size | 单倍型数 No. of haplotypes | 单倍型比例 Haplotype ratio (%) | 单倍型多样度 Haplotype diversity Hd | 平均核苷酸差异数Mean number of nucleotide differences K | 核苷酸多样度 Nucleotide diversity Pi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 莆田黑鸭 PT | 8 | 3 | 37.5 | 0.46429 | 0.75000 | 0.00112 |
| 金定鸭 JD | 8 | 3 | 37.5 | 0.75000 | 0.96429 | 0.00145 |
| 连城白鸭 LC | 8 | 3 | 37.5 | 0.60714 | 0.78571 | 0.00118 |
| 山麻鸭 SM | 8 | 2 | 25.0 | 0.42857 | 0.42857 | 0.00064 |
Table 1 Genetic diversity in four domestic duck breeds
| 品种 Breed | 样本量 Sample size | 单倍型数 No. of haplotypes | 单倍型比例 Haplotype ratio (%) | 单倍型多样度 Haplotype diversity Hd | 平均核苷酸差异数Mean number of nucleotide differences K | 核苷酸多样度 Nucleotide diversity Pi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 莆田黑鸭 PT | 8 | 3 | 37.5 | 0.46429 | 0.75000 | 0.00112 |
| 金定鸭 JD | 8 | 3 | 37.5 | 0.75000 | 0.96429 | 0.00145 |
| 连城白鸭 LC | 8 | 3 | 37.5 | 0.60714 | 0.78571 | 0.00118 |
| 山麻鸭 SM | 8 | 2 | 25.0 | 0.42857 | 0.42857 | 0.00064 |
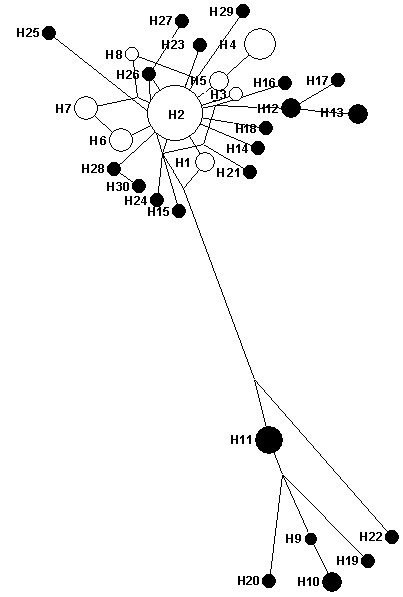
Fig. 3 Reduced median-joining networks of mtDNA D-loop haplotypes. The hollow circles represent the haplotypes of Fujian domestic ducks, and the solid circles represent the haplotypes of mallard.
| [1] |
Avise JC, Ankney CD, Nelson WS (1990) Mitochondrial gene trees and the evolutionary relationship of mallard and black ducks. Evolution, 44,1109-1119.
URL PMID |
| [2] | Chen Q (陈巧), Huang ZY (黄周英), Yan FH (鄢绯寰), Lü LJ (吕良炬) (2006) Analysis of genetic relationship among some local domestic ducks in Fujian Province. Journal of Quanzhou Normal University (Natural Science) (泉州师范学院学报(自然科学)), 24,90-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Chen YX (陈奕欣), Chen XL (陈小麟), Lü LJ (吕良炬), Zhao Y (赵扬), Zuo ZH (左正宏), Lai YZ (赖垣忠) (2001) Research for domestic duck resources and the strain breeding. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science) (厦门大学学报(自然科学版)), 40,642-646. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] |
Gray MW, Burger G, Lang BE (1999) Mitochondrial evolution. Science, 283,1476-1481.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] | He DQ (何大乾) (2007) Study on the Genetic Diversity of the mtDNA Partial Sequences and Its Evolution for the Main Chinese Domestic Ducks (中国主要地方鸭种线粒体DNA部分序列的遗传多样性及其起源进化研究). PhD dissertation, Sichuan Agricultural University, Chengdu. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Ji WL (吉文林), Qian K (钱凯), Li HF (李慧芳), Ge HW (葛洪伟), Zhao XT (赵旭庭), Duan XJ (段修军), Chen KW (陈宽维) (2006) Analysis of genetic diversity of 7 domestic duck populations conserved in national waterfowl gene pool. China Poultry (中国家禽), 28,72-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Johnson KP, Sorenson MD (1999) Phylogeny and biogeography of dabbling ducks (Genus: Anas): a comparison of molecular and morphological evidence. Auk, 116,792-805. |
| [8] | Kulikova IV, Zhuravlev YN, McCracken KG (2004) Asymmetric hybridization and sex-biased gene flow between eastern spot-billed ducks (Anas zonorhyncha) and mallards (Anas platyrhynchos) in the Russian Far East. Auk, 121,930-949. |
| [9] | Kulikova IV, Drovetski SV, Gibson DD, Harrigan RJ, Rohwer S, Sorenson MD, Winker K, Zhuravlev YN, McCracken KG (2005) Phylogeography of the mallard (Anas platyrhynchos): hybridization, dispersal, and lineage sorting contribute to complex geographic structure. Auk, 122,949-965. |
| [10] |
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 5,150-163.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] | Lai SJ (赖松家), Wang L (王玲), Liu YP (刘益平), Li XW (李学伟) (2005) Study on mitochondrial DNA genetic polymorphism of some yak breeds in China. Acta Genetica Sinica (遗传学报), 32,463-470. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Lai YZ (赖垣忠), Zhang SZ (张松踪) (1989) Studies on the serum prealbumin types of the ducks. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica (畜牧兽医学报), 20,129-133. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Lan H (兰宏), Wang W (王文), Shi LM (施立明) (1995) The mitochondrial DNA diversity of pigs in southwest China. Acta Genetica Sinica (遗传学报), 22,28-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Li QF (李齐发), Li YX (李隐侠), Zhao XB (赵兴波), Pan ZX (潘增祥), Liu ZS (刘振山), Zhang QB (张庆波), Qu XG (屈旭光), Song DW (宋大伟), Dong LY (董丽艳), Li N (李宁), Xie Z (谢庄) (2008) Sequencing D-loop region of mitochondrial DNA in yak and study on its taxonomic status in Bovinae. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica (畜牧兽医学报), 39,1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Li HF (李慧芳), Li BC (李碧春), Chen KW (陈宽维), Yang N (杨宁), Ma YH (马月辉), Tang QP (汤青萍), Tu YJ (屠云洁) (2006) Study on molecular genetic diversity of native duck breeds in China. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica (畜牧兽医学报), 37,1107-1113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Li HF (李慧芳), Li BC (李碧春), Ma YH (马月辉), Tang QP (汤青萍), Chen KW (陈宽维), Tu YJ (屠云洁) (2007) Molecular genetic diversity of Fujian domestic duck breeds. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 18,463-466. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Liu RY (刘若余), Xia XL (夏先林), Lei CZ (雷初朝), Zhang MZ (张明忠), Chen H (陈宏), Yang GS (杨公社) (2006) Genetic diversity of mitochondrial DNA D-loop sequences in cattle breeds in Guizhou. Hereditas (Beijing) (遗传), 28,279-284. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Mahanta JD, Jalaludeen A (1999) Studies on certail haematological constituents of native ducks of Kerala. Indian Journal of Poultry Science, 34,20-206. |
| [19] | Nei M (1982) Evolution of human races at the gene level. In: Human Genetics, Part A: The Unfolding Genome (eds Bonne Tamir B, Cohen T, Goodman RM), Alan R.pp.167-181. Liss, New York. |
| [20] | Randi E, Lueehini V (1998) Organization and evolution of the mitochondrial DNA control region in the avian genus Alectoris. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 4,449-462. |
| [21] |
Rozas J, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Messeguer X, Rozas R (2003) DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics, 19,2496-2497.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] |
Saccone C, Gissi C, Lanave C, Pesole G, Reyes A (2000) Evolution of the mitochondrial genetic system: an overview. Gene, 261,153-159.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] |
Sorenson MD, Ast JC, Dimcheff DE, Yuri T, Mindell DP (1999) Primers for a PCR-based approach to mitochondrial genome sequencing in birds and other vertebrates. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 12,105-114.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | Wakana S, Watanabe T, Hayashi Y, Tomita T (1986) A variant in the restriction endonuclease cleavage pattern of mitochondrial DNA in the domestic fowl, Gallus gallus domesticus. Animal Genetics, 2,159-168. |
| [25] | Yan FH (鄢绯寰), Zuo ZH (左正宏), Chen M (陈美), Song YQ (宋岳强), Lü LJ (吕良炬), Chen YX (陈奕欣) (2005) Analysis of genetic diversity and relationship among some chinese domestic ducks and wild ducks using AFLP. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science) (厦门大学学报(自然科学版)), 44,729-733. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Zhang TJ (张汤杰), Li HF (李慧芳), Chen KW (陈宽维), Chang H (常洪), Tang QP (汤青萍), Zhang JX (张晶鑫) (2007) Analysis on the genetic polymorphism and systematic evolution in domestic ducks by mitochondrial DNA D-loop region. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica (畜牧兽医学报), 38,1168-1175. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [2] | Jiachen Wang, Tangjun Xu, Wei Xu, Gaoji Zhang, Yijin You, Honghua Ruan, Hongyi Liu. Impact of urban landscape pattern on the genetic structure of Thereuopoda clunifera population in Nanjing, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [3] | Yajun Sun. What do higher or lower organisms mean—Clarify the meaning and validity of the biological ladder implied by On the Origin of Species [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24394-. |
| [4] | Nan Chen, Quan-Guo Zhang. The experimental evolution approach [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24171-. |
| [5] | Hua He, Dunyan Tan, Xiaochen Yang. Cryptic dioecy in angiosperms: Diversity, phylogeny and evolutionary significance [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 24149-. |
| [6] | Yingli Cai, Hongge Zhu, Jiaxin Li. Biodiversity conservation in China: Policy evolution, main measures and development trends [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23386-. |
| [7] | Rui Qu, Zhenjun Zuo, Youxin Wang, Liangjian Zhang, Zhigang Wu, Xiujuan Qiao, Zhong Wang. The biogeochemical niche based on elementome and its applications in different ecosystems [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23378-. |
| [8] | Kexin Cao, Jingwen Wang, Guo Zheng, Pengfeng Wu, Yingbin Li, Shuyan Cui. Effects of precipitation regime change and nitrogen deposition on soil nematode diversity in the grassland of northern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [9] | Shiyi Long, Bobo Zhang, Yuchen Xia, Yangfan Fei, Yani Meng, Bingwei Lü, Yueqing Song, Pu Zheng, Taoran Guo, Jian Zhang, Shaopeng Li. Effects of diversity and temporal stability of native communities on the biomass of invasive species Solidago canadensis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24263-. |
| [10] | Linjun He, Wenjing Yang, Yuhao Shi, Kezhemo Ashuo, Yu Fan, Guoyan Wang, Jingji Li, Songlin Shi, Guihua Yi, Peihao Peng. Effects of plant community phylogeny and functional diversity on Ageratina adenophora invasion under fire disturbance [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24269-. |
| [11] | Chen-Kun Jiang, Wen-Bin Yu, Guang-Yuan Rao, Huaicheng Li, Julien B. Bachelier, Hartmut H. Hilger, Theodor C. H. Cole. Plant Phylogeny Posters—An educational project on plant diversity from an evolutionary perspective [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24210-. |
| [12] | Qingduo Li, Dongmei Li. Analysis for the prevalence of global bat-borne Bartonella [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [13] | Chen Feng, Jie Zhang, Hongwen Huang. Parallel situ conservation: A new plant conservation strategy to integrate in situ and ex situ conservation of plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [14] | Hailing Qi, Pengzhen Fan, Yuehua Wang, Jie Liu. Genetic diversity and population structure of Juglans regia from six provinces in northern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [15] | Zhaoyang Jing, Keguang Cheng, Heng Shu, Yongpeng Ma, Pingli Liu. Whole genome resequencing approach for conservation biology of endangered plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22679-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()