



Biodiv Sci ›› 2010, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (1): 50-59. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.050 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2010.050
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yongjiu Cai1,2, Zhijun Gong1,*( ), Boqiang Qin1
), Boqiang Qin1
Received:2009-08-26
Accepted:2009-12-31
Online:2010-01-20
Published:2010-01-20
Contact:
Zhijun Gong
Yongjiu Cai, Zhijun Gong, Boqiang Qin. Community structure and diversity of macrozoobenthos in Lake Taihu, a large shallow eutrophic lake in China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(1): 50-59.
| 物种 Species | 相对重要性指数 IRI | 物种 Species | 相对重要性指数 IRI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 寡毛纲 Oligochaeta | 椎实螺科 Lymnaeidae | ||
| 仙女虫科 Naididae | 椭圆萝卜螺 Radix swinhoei | <1 | |
| 七鳃管盘虫 Aulophorus heptabranchiata | 17 | 扁蜷螺科 Planorbidae | |
| 指鳃尾盘虫 Dero digitata | 21 | 凸旋螺 Gyraulus convexiusculus | <1 |
| 参差仙女虫 Nais variabilis | 10 | 黑螺科 Melaniidae | |
| 颤蚓科 Tubificidae | 方格短沟蜷 Semisulcospira cancellata | 12 | |
| 苏氏尾鳃蚓 Branchiura sowerbyi | 36 | 田螺科 Viviparidae | |
| 霍甫水丝蚓 Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri | 2,077 | 铜锈环棱螺 Bellamya aeruginosa | 535 |
| 巨毛水丝蚓 L. grandisetosus | 6 | 摇蚊幼虫 Chironomidae | |
| 水丝蚓属一种 Limnodrilus sp. | 7 | 半折摇蚊 Chironomus semireductus | 8 |
| 中华河蚓 Rhyacodrilus sinicus | 109 | 羽摇蚊 C. plumosus | <1 |
| 嫩丝蚓属一种 Teneridrilus sp. | <1 | 褐斑菱跗摇蚊 Clinotanypus sugiyamai | <1 |
| 颤蚓科一种 Tubificidae sp. | 三带环足摇蚊 Cricotopus trifasciatus | <1 | |
| 软体动物 Mollusca | 指突隐摇蚊 Cryptochironomus digitatus | <1 | |
| 双壳纲 Bivalvia | 侧叶雕翅摇蚊 Glyptotendipes lobiferus | <1 | |
| 蚬科 Corbiculidae | 小摇蚊属一种 Microchironomus sp. | 1 | |
| 河蚬 Corbicula fluminea | 1,788 | 多足摇蚊属一种 Polypedilum sp. | <1 |
| 截蛏科 Solecurtidae | 花翅前突摇蚊 Proclakius choreus | 2 | |
| 中国淡水蛏 Novaculina chinensis | <1 | 中国长足摇蚊 Tanypus chinensis | 46 |
| 球蚬科 Sphaeriidae | 长跗摇蚊属一种 Tanytarsus sp. | <1 | |
| 湖球蚬 Sphaerium lacustre | 4 | 其他 Others | |
| 蚌科 Unionidae | 端足目一种 Amphipoda sp. | 4 | |
| 背角无齿蚌 Anodonta woodiana woodiana | * | 虫怱属一种 Caenagrion sp. | <1 |
| 背瘤丽蚌 Lamprotula leai | * | 扁舌蛭 Glossiphonia complanata | <1 |
| 腹足纲 Gastropod | 钩虾属一种 Gammarus sp. | 137 | |
| 觿螺科 Hydrobiidae | 寡鳃齿吻沙蚕 Nephtys oligobranchia | 7 | |
| 长角涵螺 Alocinma longicornis | 13 | 多毛纲一种 Polychatea sp.1 | 41 |
| 纹沼螺 Parafossarulus striatulus | 6 | 多毛纲一种 Polychatea sp.2 | 3 |
| 光滑狭口螺 Stenothyra glabra | 6 |
Table 1 Species composition of macrozoobenthos in Lake Taihu and showing the index of relative importance (IRI)
| 物种 Species | 相对重要性指数 IRI | 物种 Species | 相对重要性指数 IRI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 寡毛纲 Oligochaeta | 椎实螺科 Lymnaeidae | ||
| 仙女虫科 Naididae | 椭圆萝卜螺 Radix swinhoei | <1 | |
| 七鳃管盘虫 Aulophorus heptabranchiata | 17 | 扁蜷螺科 Planorbidae | |
| 指鳃尾盘虫 Dero digitata | 21 | 凸旋螺 Gyraulus convexiusculus | <1 |
| 参差仙女虫 Nais variabilis | 10 | 黑螺科 Melaniidae | |
| 颤蚓科 Tubificidae | 方格短沟蜷 Semisulcospira cancellata | 12 | |
| 苏氏尾鳃蚓 Branchiura sowerbyi | 36 | 田螺科 Viviparidae | |
| 霍甫水丝蚓 Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri | 2,077 | 铜锈环棱螺 Bellamya aeruginosa | 535 |
| 巨毛水丝蚓 L. grandisetosus | 6 | 摇蚊幼虫 Chironomidae | |
| 水丝蚓属一种 Limnodrilus sp. | 7 | 半折摇蚊 Chironomus semireductus | 8 |
| 中华河蚓 Rhyacodrilus sinicus | 109 | 羽摇蚊 C. plumosus | <1 |
| 嫩丝蚓属一种 Teneridrilus sp. | <1 | 褐斑菱跗摇蚊 Clinotanypus sugiyamai | <1 |
| 颤蚓科一种 Tubificidae sp. | 三带环足摇蚊 Cricotopus trifasciatus | <1 | |
| 软体动物 Mollusca | 指突隐摇蚊 Cryptochironomus digitatus | <1 | |
| 双壳纲 Bivalvia | 侧叶雕翅摇蚊 Glyptotendipes lobiferus | <1 | |
| 蚬科 Corbiculidae | 小摇蚊属一种 Microchironomus sp. | 1 | |
| 河蚬 Corbicula fluminea | 1,788 | 多足摇蚊属一种 Polypedilum sp. | <1 |
| 截蛏科 Solecurtidae | 花翅前突摇蚊 Proclakius choreus | 2 | |
| 中国淡水蛏 Novaculina chinensis | <1 | 中国长足摇蚊 Tanypus chinensis | 46 |
| 球蚬科 Sphaeriidae | 长跗摇蚊属一种 Tanytarsus sp. | <1 | |
| 湖球蚬 Sphaerium lacustre | 4 | 其他 Others | |
| 蚌科 Unionidae | 端足目一种 Amphipoda sp. | 4 | |
| 背角无齿蚌 Anodonta woodiana woodiana | * | 虫怱属一种 Caenagrion sp. | <1 |
| 背瘤丽蚌 Lamprotula leai | * | 扁舌蛭 Glossiphonia complanata | <1 |
| 腹足纲 Gastropod | 钩虾属一种 Gammarus sp. | 137 | |
| 觿螺科 Hydrobiidae | 寡鳃齿吻沙蚕 Nephtys oligobranchia | 7 | |
| 长角涵螺 Alocinma longicornis | 13 | 多毛纲一种 Polychatea sp.1 | 41 |
| 纹沼螺 Parafossarulus striatulus | 6 | 多毛纲一种 Polychatea sp.2 | 3 |
| 光滑狭口螺 Stenothyra glabra | 6 |
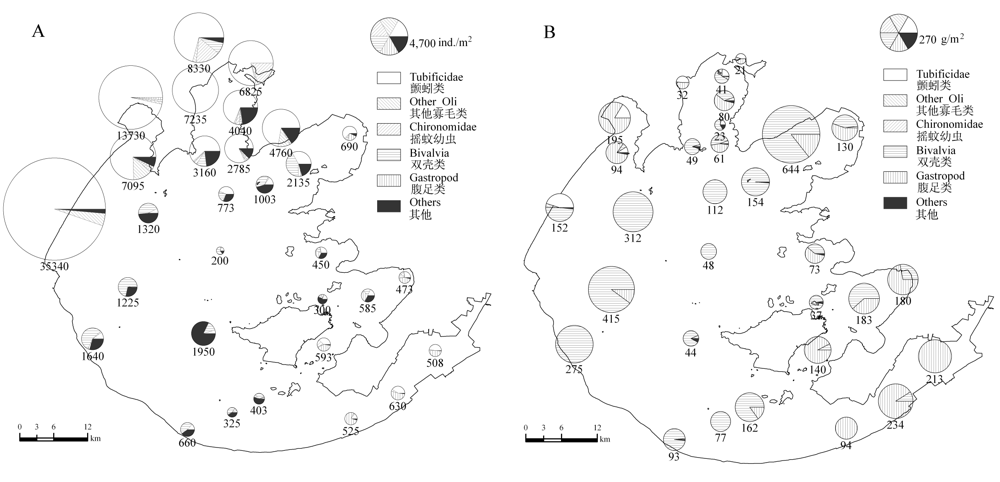
Fig. 2 Spatial distribution of mean density (A, ind./m2) and biomass (B, g/m2) and the proportion of different groups in 30 sampling sites. Other_Oli: species of Oligochaeta excluding Tubificidae.
| 物种 Species | Group A | Group B | Group C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 寡毛类 Oligochaeta | |||
| 霍甫水丝蚓 Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri | 7,883(50.29%) | 242(10.08%) | 115(18.46%) |
| 中华河蚓 Rhyacodrilus sinicus | 621(14.6%) | ||
| 苏氏尾鳃蚓 Branchiura sowerbyi | 51(4.97%) | 23(5.69%) | 44(10.12%) |
| 指鳃尾盘虫 Dero digitata | 211(5.79%) | ||
| 软体动物 Mollusca | |||
| 河蚬 Corbicula fluminea | 386(30.34%) | 36(6.8%) | |
| 铜锈环棱螺 Bellamya aeruginosa | 102(19.73%) | ||
| 方格短沟蜷 Semisulcospira cancellata | 19(5.43%) | ||
| 光滑狭口螺 Stenothyra glabra | 11(3.56%) | ||
| 长角涵螺 Alocinma longicornis | 50(14.13%) | ||
| 纹沼螺 Parafossarulus striatulus | 31(6.57%) | ||
| 摇蚊幼虫 Chironomidae | |||
| 中国长足摇蚊 Tanypus chinensis | 302(5.31%) | ||
| 半折摇蚊 Chironomus semireductus | 46(3.04%) | ||
| 其他 Others | |||
| 钩虾属一种 Gammarus sp. | 357(7.22%) | 195(16.39%) | |
| 多毛类一种 Polychaeta sp.1 | 200(17.80%) | ||
| 合计 Total | 9,471(91.20%) | 1,046(80.30%) | 408(84.80%) |
Table 2 Mean density (ind./m2) of dominant species for each affinity group and the contribution (%) to with-in group similarity
| 物种 Species | Group A | Group B | Group C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 寡毛类 Oligochaeta | |||
| 霍甫水丝蚓 Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri | 7,883(50.29%) | 242(10.08%) | 115(18.46%) |
| 中华河蚓 Rhyacodrilus sinicus | 621(14.6%) | ||
| 苏氏尾鳃蚓 Branchiura sowerbyi | 51(4.97%) | 23(5.69%) | 44(10.12%) |
| 指鳃尾盘虫 Dero digitata | 211(5.79%) | ||
| 软体动物 Mollusca | |||
| 河蚬 Corbicula fluminea | 386(30.34%) | 36(6.8%) | |
| 铜锈环棱螺 Bellamya aeruginosa | 102(19.73%) | ||
| 方格短沟蜷 Semisulcospira cancellata | 19(5.43%) | ||
| 光滑狭口螺 Stenothyra glabra | 11(3.56%) | ||
| 长角涵螺 Alocinma longicornis | 50(14.13%) | ||
| 纹沼螺 Parafossarulus striatulus | 31(6.57%) | ||
| 摇蚊幼虫 Chironomidae | |||
| 中国长足摇蚊 Tanypus chinensis | 302(5.31%) | ||
| 半折摇蚊 Chironomus semireductus | 46(3.04%) | ||
| 其他 Others | |||
| 钩虾属一种 Gammarus sp. | 357(7.22%) | 195(16.39%) | |
| 多毛类一种 Polychaeta sp.1 | 200(17.80%) | ||
| 合计 Total | 9,471(91.20%) | 1,046(80.30%) | 408(84.80%) |
| 密度 Density | 生物量 Biomass | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | Group B | Group C | Group A | Group B | Group C | ||||
| 直接收集者 Gatherers | 8,771(94.73%) | 604(57.91%) | 306(51.09%) | 18.14(24.35%) | 1.64(0.83%) | 1.08(0.69%) | |||
| 过滤收集者 Filterers | 138(1.49%) | 392(37.58%) | 37(6.18%) | 21.55(28.92%) | 182.58(92.40%) | 34.71(22.27%) | |||
| 捕食者 Predators | 294(3.18%) | 27(2.59%) | 20(3.34%) | 0.83(1.11%) | 0.13(0.07%) | 0.09(0.06%) | |||
| 刮食者 Scrapers | 44(0.48%) | 20(1.92%) | 232(38.73%) | 33.99(45.62%) | 13.24(6.70%) | 119.95(76.97%) | |||
| 撕食者 Shredders | 12(0.13%) | 0 | 4(0.67%) | 0 | 0 | 0.01(0.01%) | |||
Table 3 Mean density (ind./m2), biomass (g/m2) and the proportion of different functional feeding group in each affinity group
| 密度 Density | 生物量 Biomass | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | Group B | Group C | Group A | Group B | Group C | ||||
| 直接收集者 Gatherers | 8,771(94.73%) | 604(57.91%) | 306(51.09%) | 18.14(24.35%) | 1.64(0.83%) | 1.08(0.69%) | |||
| 过滤收集者 Filterers | 138(1.49%) | 392(37.58%) | 37(6.18%) | 21.55(28.92%) | 182.58(92.40%) | 34.71(22.27%) | |||
| 捕食者 Predators | 294(3.18%) | 27(2.59%) | 20(3.34%) | 0.83(1.11%) | 0.13(0.07%) | 0.09(0.06%) | |||
| 刮食者 Scrapers | 44(0.48%) | 20(1.92%) | 232(38.73%) | 33.99(45.62%) | 13.24(6.70%) | 119.95(76.97%) | |||
| 撕食者 Shredders | 12(0.13%) | 0 | 4(0.67%) | 0 | 0 | 0.01(0.01%) | |||
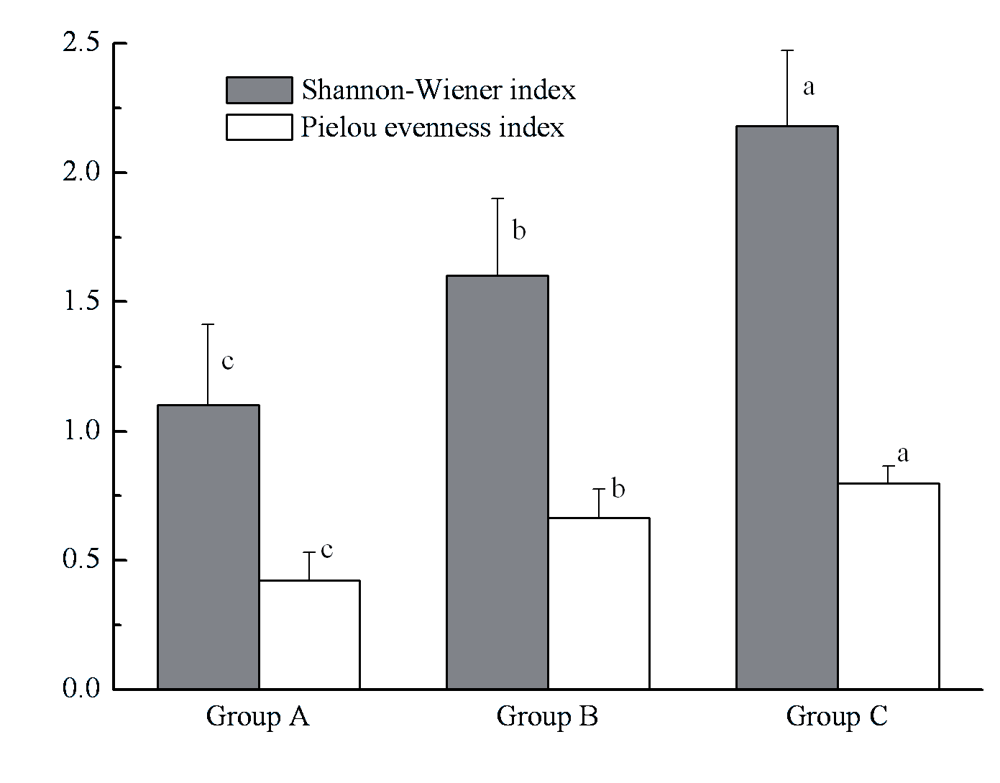
Fig. 6 Shannon-Wiener index and Pielou index of macrozoobenthos for each affinity group in Lake Taihu. Different letters indicate significant differences among the groups (one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post-hoc test, P < 0.05)
| [1] | Brönmark C (1985) Interactions between macrophytes, epiphytes and herbivores: an experimental approach. Oikos, 45, 26-30. |
| [2] | Brönmark C (1990) How do herbivorous freshwater snails affect macrophyte? A comment. Ecology, 71, 1212-1215. |
| [3] | Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Australian Journal of Ecology, 18, 117-143. |
| [4] | Covich AP, Palmer MA, Crowl TA (1999) The role of benthic invertebrate species in freshwater ecosystems: zoobenthic species influence energy flows and nutrient cycling. BioScience, 49, 119-127. |
| [5] | Duan HT, Ma RH, Xu XF, Kong FX, Zhang SX, Kong WJ, Hao JY, Shang LL (2009) Two-decade reconstruction of algal blooms in China’s Lake Taihu. Environmental Science & Technology, 43, 3522-3528. |
| [6] | Duan XH (段学花), Wang ZY (王兆印), Tian SM (田世民) (2007) Field experiment on the effect of streambed substrate on macroinvertebrate diversity. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology) ( 清华大学学报(自然科学版)), 9, 1553-1556. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Frouin P (2000) Effects of anthropogenic disturbances of tropical soft-bottom benthic communities. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 194, 39-53. |
| [8] | Galuppo N, Maci S, Pinna M, Basset A (2007) Habitat types and distribution of benthic macroinvertebrates in a transitional water ecosystem: Alimini Grande (Puglia, Italy). Transitional Waters Bulletin, 4, 9-19. |
| [9] | Gong ZJ, Xie P (2001) Impact of eutrophication on biodiversity of the macrozoobenthos community in a Chinese shallow lake. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 16, 171-178. |
| [10] | Gu XH (谷孝鸿), Zhang SZ (张圣照), Bai XL (白秀玲), Hu WP (胡维平), Hu YH (胡耀辉), Wang XR (王晓蓉) (2005) Evolution of community structure of aquatic macrophytes in East Taihu Lake and its wetlands. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 25, 1541-1548. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Han J (韩洁), Zhang ZN (张志南), Yu ZS (于子山) (2004) Macrobenthic community structure in the southern and central Bohai Sea, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 24, 531-537. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Huang YP (黄漪平) (2001) The Water Environment and Pollution Control in Lake Taihu (太湖水环境及其污染控制). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [13] | Jones JI, Sayer CD (2003) Does the fish-invertebrate-periphy- ton cascade precipitate plant loss in shallow lakes? Ecology, 84, 2155-2167. |
| [14] | Li J (李江), Jin XC (金湘灿), Jiang X (姜霞), Liu LJ (刘利军) (2007) Vertical changes of physiochemical characteristics and phosphorus concentrations of sediments from different trophic regions of Taihu Lake. Research of Environmental Sciences (环境科学研究), 20(4), 64-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Liang YL (梁彦龄), Wang HZ (王洪铸) (2000) Zoobenthos. In: Advanced Hydrobiology (高级水生生物学) (ed. Liu JK (刘建康)), pp. 241-259. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [16] | Lindegaard C (1994) The role of zoobenthos in energy flow in two shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia, 275/276, 313-322. |
| [17] | Liu WL (刘伟龙), Hu WP (胡维平), Chen YG (陈永根), Gu XH (谷孝鸿), Hu ZX (胡志新), Chen YW (陈宇炜), Ji J (季江) (2007) Temporal and spatial variation of aquatic macrophytes in West Taihu Lake. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 27, 159-170. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Liu XQ (刘学勤) (2006) Food Composition and Food Webs of Zoobenthos in Yangtze Lakes (湖泊底栖动物食物组成与食物网研究). PhD dissertation, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan. (in Chinese) |
| [19] | Liu YY (刘月英), Zhang WZ (张文珍), Wang YX (王跃先), Wang EY (王恩义) (1979) Economic Fauna of China: Freshwater Mollusca (中国经济动物志·淡水软体动物). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [20] | Morse JC, Yang LF, Tian LX (1994) Aquatic Insects of China Useful for Monitoring Water Quality. Hohai University Press, Nanjing. |
| [21] | Nanjing Institute of Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院南京地理研究所) (1965) Preliminary Reports of Comprehensive Investigation on Lake Taihu (太湖综合调查初步报告). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [22] | Pielou EC (1975) Ecological Diversity. Wiley-Inters, New York. |
| [23] | Qin BQ (秦伯强) (2002) Approaches to mechanisms and control of eutrophication of shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Journal of Lake Sciences (湖泊科学), 14, 193-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Qin BQ (秦伯强), Hu WP (胡维平), Chen WM (陈伟民) (2004) The Processes and Mechanism of Lake Taihu Environment (太湖水环境演化过程与机理). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [25] | Qin BQ, Xu PZ, Wu QL, Luo LC, Zhang YL (2007) Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia, 581, 3-4. |
| [26] | Reavell PE (1980) A study on the diets of some British freshwater gastropods. Journal of Conchology, 30, 253-271. |
| [27] | Shannon CE, Wiener WJ (1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication, p. 117. University of Illinois Press, Urbana. |
| [28] | Shostell JM, Williams BS (2007) Habitat complexity as a determinate of benthic macroinvertebrate community structure in cypress tree reservoirs. Hydrobiologia, 575, 389-399. |
| [29] | Sun CB (孙超白), Zhou FF (周凤帆) (1983) Benthic assessment. Journal of Shanghai Normal College (上海师范学院学报) (Suppl.), 71-82. (in Chinese) |
| [30] | Tews J, Brose U, Grimm V, Tielbörger K, Wichmann MC, Schwager M, Jeltsch F (2004) Animal species diversity driven by habitat heterogeneity/diversity: the importance of keystone structures. Journal of Biogeography, 31, 79-92. |
| [31] | Thomas JD (1990) Mutualistic interactions in freshwater modular systems with molluscan components. Advances in Ecological Research, 20, 125-178. |
| [32] | Tolonen KT, Hämäläinen H, Holopainen IJ, Karjalainen J (2001) Influences of habitat type and environmental variables on littoral macroinvertebrate communities in a large lake system. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 152, 39-67. |
| [33] | Wang HZ (王洪铸) (2002) Studies on Taxonomy, Distribution and Ecology of Microdrile Oligochaetes of China, with Descriptions of Two New Species from the Vicinity of the Great Wall Station of China, Antarctica (中国小蚓类研究—附中国南极长城站附近地区两新种). Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [34] | Vanni MJ (2002) Nutrient cycling by animals in freshwater ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 33, 341-370. |
| [35] | Warwick RM (1986) A new method for detecting pollution effects on marine macrobenthic communities. Marine Biology, 92, 557-562. |
| [36] | Xiong JL (熊金林), Mei XG (梅兴国), Hu CL (胡传林) (2003) Comparative study on the community structure and biodiversity of zoobenthos in lakes of different pollution states. Journal of Lake Sciences (湖泊科学), 15, 161-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [37] | Yan YJ (闫云君), Li XY (李晓宇), Liang YL (梁彦龄) (2005) A comparative study on community structure of macrozoobenthos between macrophtic and algal lakes. Journal of Lake Sciences (湖泊科学), 17, 176-182. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [38] | Zhou H (周红), Zhang ZN (张志南) (2002) Rationale of the multivariate statistical software primer and its application in benthic community ecology. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao (青岛海洋大学学报), 33, 58-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [39] | Zhu GW (朱广伟) (2008) Eutrophic status and causing factors for a large, shallow and subtropical Lake Taihu, China. Journal of Lake Sciences (湖泊科学), 20, 21-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()