



Biodiv Sci ›› 2015, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (6): 759-766. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015109 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2015109
Special Issue: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhenjie Ding, Dan Yu, Xinwei Xu*( )
)
Received:2015-05-03
Accepted:2015-11-09
Online:2015-11-20
Published:2015-12-02
Contact:
Xu Xinwei
Zhenjie Ding, Dan Yu, Xinwei Xu. Phylogeography of Typha laxmannii in the northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and adjacent areas[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(6): 759-766.
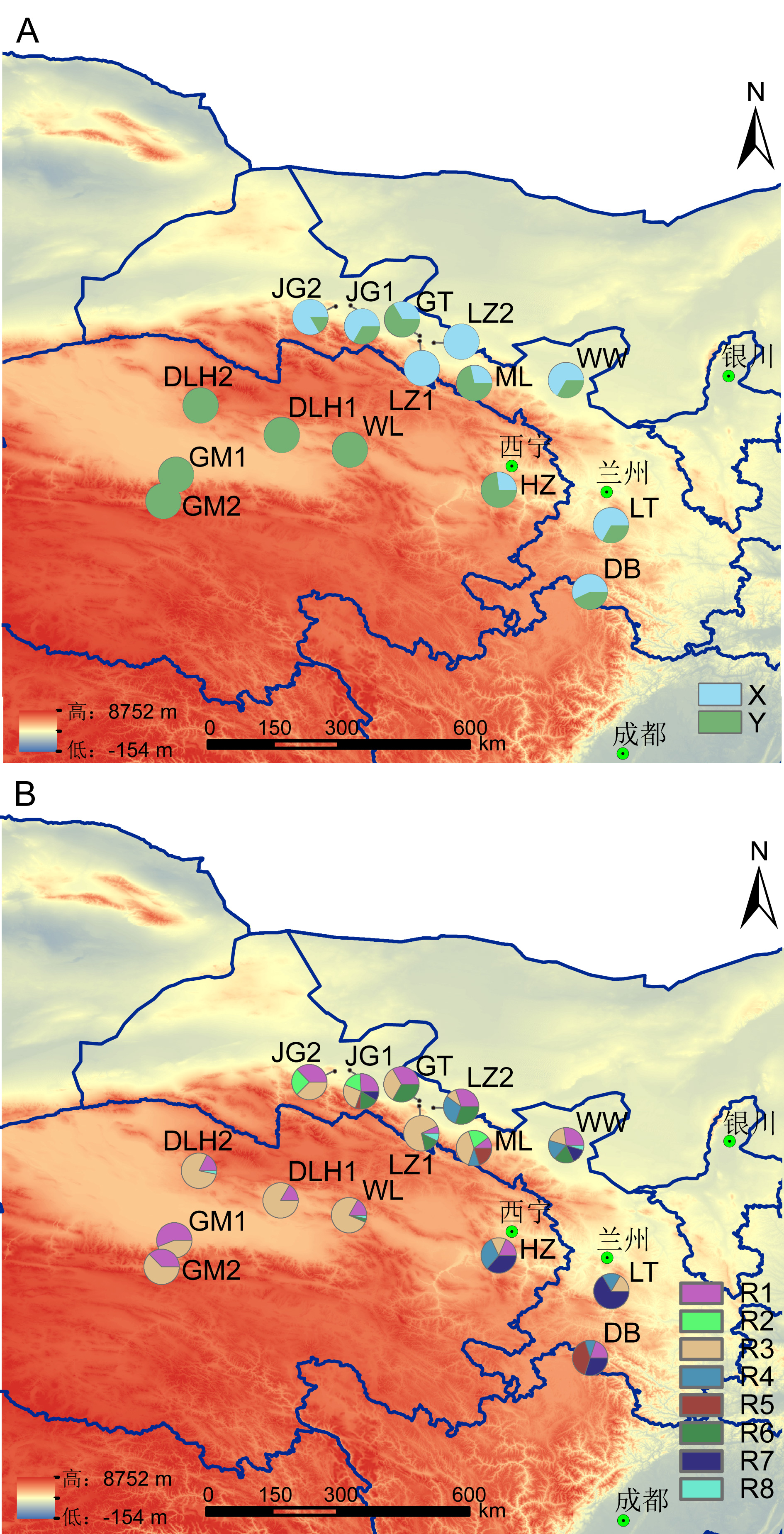
Fig. 1 The distribution of cpDNA haplotypes (A) and nDNA haplotypes (B) for Typha laxmannii populations. The population codes are the same as those in Table 1.
| 区域 Regions | 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 Degrees of freedom | 方差 Sum of squares | 变异成分 Variance components | 变异比率 Percentage of variation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶绿体DNA cpDNA | ||||||
| 高原台面 Plateau platform | 种群间 Among populations | 5 | 0.876 | 0.010 | 0.210 | |
| 种群内 Within population | 78 | 2.933 | 0.038 | 0.790 | ||
| 邻近地区 Adjacent areas | 种群间 Among populations | 8 | 3.014 | 0.025 | 0.111 | |
| 种群内 Within population | 55 | 11.095 | 0.202 | 0.889 | ||
| 高原台面及其邻近地区 Plateau platform and adjacent areas | 地区间 Among groups | 1 | 14.155 | 0.190 | 0.602 | |
| 地区内的种群之间 Among populations within group | 13 | 3.890 | 0.020 | 0.064 | ||
| 种群内 Within population | 133 | 14.029 | 0.105 | 0.334 | ||
| 核DNA nDNA | ||||||
| 高原台面 Plateau platform | 种群间 Among populations | 6 | 47.282 | 0.348 | 0.402 | |
| 种群内 Within population | 147 | 76.231 | 0.519 | 0.598 | ||
| 邻近地区 Adjacent areas | 种群间 Among populations | 8 | 43.106 | 0.304 | 0.169 | |
| 种群内 Within population | 109 | 162.911 | 1.495 | 0.831 | ||
| 高原台面及其邻近地区 Plateau platform and adjacent areas | 地区间 Among groups | 1 | 24.261 | 0.122 | 0.087 | |
| 地区内的种群之间 Among populations within group | 13 | 89.515 | 0.338 | 0.243 | ||
| 种群内 Within population | 257 | 240.015 | 0.934 | 0.670 | ||
Table 2 Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) of PS and rpl32-trnL sequences from Typha laxmannii populations
| 区域 Regions | 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 Degrees of freedom | 方差 Sum of squares | 变异成分 Variance components | 变异比率 Percentage of variation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶绿体DNA cpDNA | ||||||
| 高原台面 Plateau platform | 种群间 Among populations | 5 | 0.876 | 0.010 | 0.210 | |
| 种群内 Within population | 78 | 2.933 | 0.038 | 0.790 | ||
| 邻近地区 Adjacent areas | 种群间 Among populations | 8 | 3.014 | 0.025 | 0.111 | |
| 种群内 Within population | 55 | 11.095 | 0.202 | 0.889 | ||
| 高原台面及其邻近地区 Plateau platform and adjacent areas | 地区间 Among groups | 1 | 14.155 | 0.190 | 0.602 | |
| 地区内的种群之间 Among populations within group | 13 | 3.890 | 0.020 | 0.064 | ||
| 种群内 Within population | 133 | 14.029 | 0.105 | 0.334 | ||
| 核DNA nDNA | ||||||
| 高原台面 Plateau platform | 种群间 Among populations | 6 | 47.282 | 0.348 | 0.402 | |
| 种群内 Within population | 147 | 76.231 | 0.519 | 0.598 | ||
| 邻近地区 Adjacent areas | 种群间 Among populations | 8 | 43.106 | 0.304 | 0.169 | |
| 种群内 Within population | 109 | 162.911 | 1.495 | 0.831 | ||
| 高原台面及其邻近地区 Plateau platform and adjacent areas | 地区间 Among groups | 1 | 24.261 | 0.122 | 0.087 | |
| 地区内的种群之间 Among populations within group | 13 | 89.515 | 0.338 | 0.243 | ||
| 种群内 Within population | 257 | 240.015 | 0.934 | 0.670 | ||
| 1 | Avise JC, Arnold J, Ball RM, Bermingham E, Lamb T, Neigel JE, Reeb CA, Saunders NC (1987) Intraspecific phylogeography: the mitochondrial DNA bridge between population genetics and systematics.Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 18, 489-522. |
| 2 | Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Röhl A (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies.Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 37-48. |
| 3 | Beheregaray LB (2008) Twenty years of phylogeography: the state of the field and the challenges for the Southern Hemisphere.Molecular Ecology, 17, 3754-3774. |
| 4 | Chen JM, Du ZY, Sun SS, Gituru RW, Wang QF (2013) Chloroplast DNA phylogeography reveals repeated range expansion in a widespread aquatic herb Hippuris vulgaris in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and adjacent areas.PLoS ONE, 8, e60948. |
| 5 | Chen JM, Du ZY, Yuan YY, Wang QF (2014) Phylogeography of an alpine aquatic herb Ranunculus bungei (Ranunculaceae) on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 52, 313-325. |
| 6 | Ekstam B, Forseby Å (1999) Germination response of Phragmites australis and Typha latifolia to diurnal fluctua- tions in temperature.Seed Science Research, 9, 157-163. |
| 7 | Excoffier L, Lischer HEL (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows.Molecular Ecology Resources, 10, 564-567. |
| 8 | Jia DR, Liu TL, Wang LY, Zhou DW, Liu JQ (2011) Evolutionary history of an alpine shrub Hippophae tibetana (Elaeagnaceae): allopatric divergence and regional expansion.Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 102, 37-50. |
| 9 | Katoh K, Misawa K, Kuma KI, Miyata T (2002) MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform.Nucleic Acids Research, 30, 3059-3066. |
| 10 | Keane B, Pelikan S, Toth GP, Smith MK, Rogstad SH (1999) Genetic diversity of Typha latifolia (Typhaceae) and the impact of pollutants examined with tandem-repetitive DNA probes.American Journal of Botany, 86, 1226-1238. |
| 11 | Kim C, Choi HK (2011) Molecular systematics and character evolution of Typha (Typhaceae) inferred from nuclear and plastid DNA sequence data.Taxon, 60, 1417-1428. |
| 12 | Krattinger K (1975) Genetic mobility in Typha.Aquatic Botany, 1, 57-70. |
| 13 | Lamote V, De Loose M, Van Bockstaele E, Roldán-Ruiz I (2005) Evaluation of AFLP markers to reveal genetic diversity in Typha.Aquatic Botany, 83, 296-309. |
| 14 | Lee DW, Fairbrothers DE (1973) Enzyme differences between adjacent hybrid and parent populations of Typha.Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club, 100, 3-11. |
| 15 | Li L, Abbott RJ, Liu B, Sun Y, Li L, Zou J, Wang X, Miehe G, Liu J (2013) Pliocene intraspecific divergence and Plio- Pleistocene range expansions within Picea likiangensis (Lijiang spruce), a dominant forest tree of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Molecular Ecology, 22, 5237-5255. |
| 16 | Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP V5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data.Bioinformatics, 25, 1451-1452. |
| 17 | Liu JQ, Sun YS, Ge XJ, Gao LM, Qiu YX (2012) Phylogeographic studies of plants in China: advances in the past and directions in the future.Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 50, 267-275. |
| 18 | Liu YP, Su X, He YH, Han LM, Huang YY, Wang ZZ (2015) Evolutionary history of Orinus thoroldii (Poaceae), endemic to the western Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau in China.Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 59, 159-167. |
| 19 | Mashburn SJ, Sharitz RR, Smith MH (1978) Genetic variation among Typha populations of the southeastern United States.Evolution, 32, 681-685. |
| 20 | McNaughton S (1966) Ecotype function in the Typha community-type.Ecological Monographs, 36, 298-325. |
| 21 | Meng L, Yang R, Abbott RJ, Miehe G, Hu T, Liu J (2007) Mitochondrial and chloroplast phylogeography of Picea crassifolia Kom. (Pinaceae) in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and adjacent highlands.Molecular Ecology, 16, 4128-4137. |
| 22 | Na HR, Kim C, Choi HK (2010) Genetic relationship and genetic diversity among Typha taxa from East Asia based on AFLP markers.Aquatic Botany, 92, 207-213. |
| 23 | Pons O, Petit RJ (1996) Measuring and testing genetic differentiation with ordered versus unordered alleles.Genetics, 144, 1237-1245. |
| 24 | Qiu YX, Fu CX, Comes HP (2011) Plant molecular phylogeography in China and adjacent regions: tracing the genetic imprints of Quaternary climate and environmental change in the world’s most diverse temperate flora.Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 59, 225-244. |
| 25 | Sharitz RR, Wineriter SA, Smith MH, Liu EH (1980) Comparison of isozymes among Typha species in the eastern United States.American Journal of Botany, 67, 1297-1303. |
| 26 | Shaw J, Lickey EB, Schilling EE, Small RL (2007) Comparison of whole chloroplast genome sequences to choose noncoding regions for phylogenetic studies in angiosperms: the tortoise and the hare III.American Journal of Botany, 94, 275-288. |
| 27 | Sun K, Simpson D (2010) Typhaceae. In: Flora of China (eds Wu ZY, Raven PH, Hong DY), Vol. 23, pp. 158-163. Science Press, Beijing, China and Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, Missouri, USA. |
| 28 | Sun YS, Ikeda H, Wang YJ, Liu JQ (2010) Phylogeography of Potentilla fruticosa (Rosaceae) in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau revisited: a reappraisal and new insights.Plant Ecology & Diversity, 3, 249-257. |
| 29 | Sun YS, Li L, Li L, Zou JB, Liu JQ (2014) Distributional dynamics and interspecific gene flow in Picea likiangensis and P. wilsonii triggered by climate change on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Journal of Biogeography, 42, 475-484. |
| 30 | Tsyusko OV, Smith MH, Sharitz RR, Glenn TC (2005) Genetic and clonal diversity of two cattail species, Typha latifolia and T. angustifolia (Typhaceae), from Ukraine.American Journal of Botany, 92, 1161-1169. |
| 31 | Wang GN, He XY, Miehe G, Mao KS (2014) Phylogeography of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau endemic alpine herb Pomato- sace filicula (Primulaceae).Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 52, 289-302. |
| 32 | Yang FS, Li YF, Ding X, Wang XQ (2008) Extensive population expansion of Pedicularis longiflora (Orobanchaceae) on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and its correlation with the Quaternary climate change.Molecular Ecology, 17, 5135-5145. |
| 33 | Zhang Q, Chiang TY, George M, Liu JQ, Abbott RJ (2005) Phylogeography of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau endemic Juniperus przewalskii (Cupressaceae) inferred from chloroplast DNA sequence variation.Molecular Ecology, 14, 3513-3524. |
| 34 | Zhang TC, Comes HP, Sun H (2011) Chloroplast phylogeography of Terminalia franchetii (Combretaceae) from the eastern Sino-Himalayan region and its correlation with historical river capture events. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 60, 1-12. |
| 35 | Zhang XH, Tapia M, Webb JB, Huang YH, Miao S (2008) Molecular signatures of two cattail species, Typha domingensis and Typha latifolia (Typhaceae), in South Florida.Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 49, 368-376. |
| 36 | Zhao CX, Ma G, Liang QL, Wang CB, He XJ (2013) Phylogeography of an alpine plant (Bupleurum smithii, Apiaceae) endemic to the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and adjacent regions inferred from chloroplast DNA sequence variation.Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 51, 382-395. |
| [1] | Hu Ying, Wang Xi, Zhang Xinxin, Zhou Wei, Chen Xiaoyang, Hu Xinsheng. Advancing phylogeography with chloroplast DNA markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(2): 219-234. |
| [2] | Yingxiong Qiu, Qixiang Lu, Yonghua Zhang, Yanan Cao. Phylogeography of East Asia’s Tertiary relict plants: current progress and future prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(2): 136-146. |
| [3] |
Keping Ma.
New opportunities for mainstreaming biodiversity conservation [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(5): 557-558. |
| [4] | Dexing Zhang. Unorthodox reflections on molecular ecology research in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(5): 559-569. |
| [5] | Hongyu Niu, Hao Shen, Wanhui Ye. Whole-range studies on alien plant invasion: recent progress and future prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(6): 559-568. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()