



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 23409. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023409 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023409
收稿日期:2023-10-31
接受日期:2024-01-29
出版日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2024-03-24
通讯作者:
*E-mail: zdhxyh@163.com
基金资助:Received:2023-10-31
Accepted:2024-01-29
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2024-03-24
Contact:
*E-mail: zdhxyh@163.com
摘要:
跟踪野生动物可以了解它们的生态习性和种群动态。自动化的、高效准确的目标跟踪算法对于野生动物保护具有重要意义。由于东北虎(Panthera tigris altaica)生存环境复杂, 行动方式隐蔽且具有快速运动的特点, 拍摄到的图像可能存在运动模糊问题, 难以捕获清晰稳定的画面。因此, 监测东北虎种群的难点在于实现自动准确地跟踪东北虎个体。在实际环境中, 由于光照变化、遮挡、相似性干扰等问题的存在, 导致错误跟踪东北虎个体。针对这些问题, 本文提出了一种基于注意力特征融合的孪生网络跟踪框架, 旨在实现对实际复杂场景中东北虎个体的准确跟踪。基于孪生网络的视觉目标跟踪框架将目标跟踪视为相似性学习问题, 本文对传统基于孪生网络的跟踪架构进行改进, 将注意力特征融合嵌入主干网络ResNet50中进行特征提取。为了增强模型对跟踪场景中发生极端尺度变化的东北虎个体的关注度, 本文在注意力特征融合模块中引入了多尺度通道注意力机制, 以适应不同的东北虎个体状态和环境变化。实验结果表明, 本文的方法与当前的先进跟踪器相比取得了更优的跟踪性能, 跟踪成功率和精确度分别达到了72.5%和93.9%, 相比基准跟踪算法分别提高了4.1%和2.3%, 证明本文的跟踪方法可以在复杂的实际场景下为自动高效地监测东北虎提供一种有效的方案。
许群, 谢永华 (2024) 基于注意力机制融合多特征的东北虎个体自动跟踪方法. 生物多样性, 32, 23409. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023409.
Qun Xu, Yonghua Xie (2024) Automatic individual tracking method of Amur tiger based on attention mechanism fusion of multiple features. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23409. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023409.
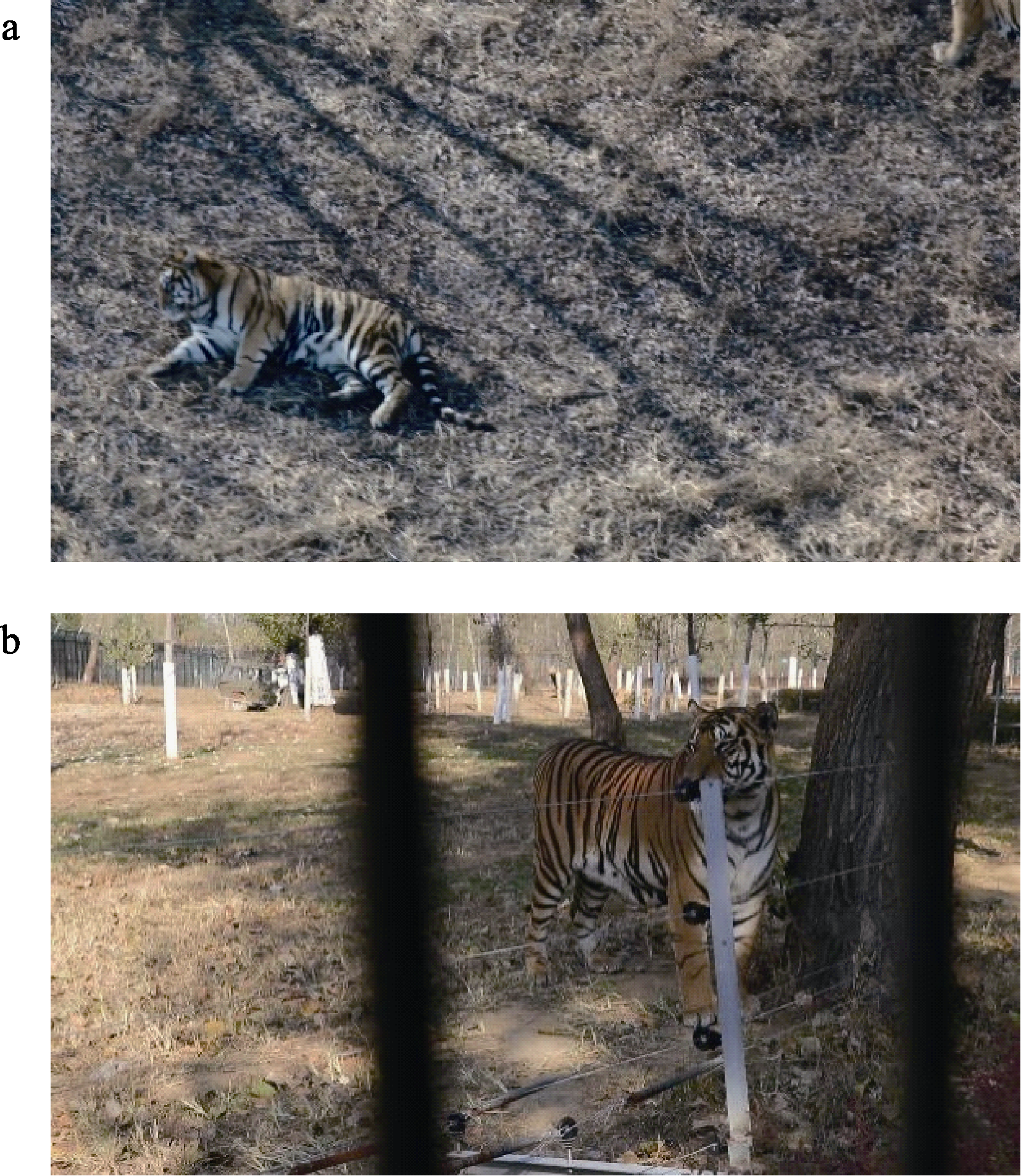

图1 东北虎目标跟踪训练数据集样本示例。(a)无人机拍摄的图像样本; (b)野生东北虎重识别数据集中的图像样本。
Fig. 1 Samples of Amur tiger target tracking training dataset. (a) Image sample taken by unmanned aerial vehicle; (b) Image sample in a benchmark for Amur tiger re-identification in the wild.
| 视频 Video | 光照变化 Illumination variation | 目标旋转 Object rotation | 部分遮挡 Partial occlusion | 相似干扰 Similarity interference | 目标形变 Object deformation | 尺度变化 Scale variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiger_01 | √ | √ | - | √ | - | - |
| Tiger_02 | - | √ | - | - | √ | √ |
| Tiger_03 | - | - | - | √ | - | - |
| Tiger_04 | - | √ | - | - | - | - |
| Tiger_05 | - | √ | - | - | - | - |
| Tiger_06 | √ | √ | - | - | - | - |
| Tiger_07 | - | √ | √ | √ | - | - |
| Tiger_08 | - | - | - | √ | - | - |
表1 图2各视频序列面对的挑战
Table 1 The challenges of each video sequence in Fig. 2
| 视频 Video | 光照变化 Illumination variation | 目标旋转 Object rotation | 部分遮挡 Partial occlusion | 相似干扰 Similarity interference | 目标形变 Object deformation | 尺度变化 Scale variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiger_01 | √ | √ | - | √ | - | - |
| Tiger_02 | - | √ | - | - | √ | √ |
| Tiger_03 | - | - | - | √ | - | - |
| Tiger_04 | - | √ | - | - | - | - |
| Tiger_05 | - | √ | - | - | - | - |
| Tiger_06 | √ | √ | - | - | - | - |
| Tiger_07 | - | √ | √ | √ | - | - |
| Tiger_08 | - | - | - | √ | - | - |
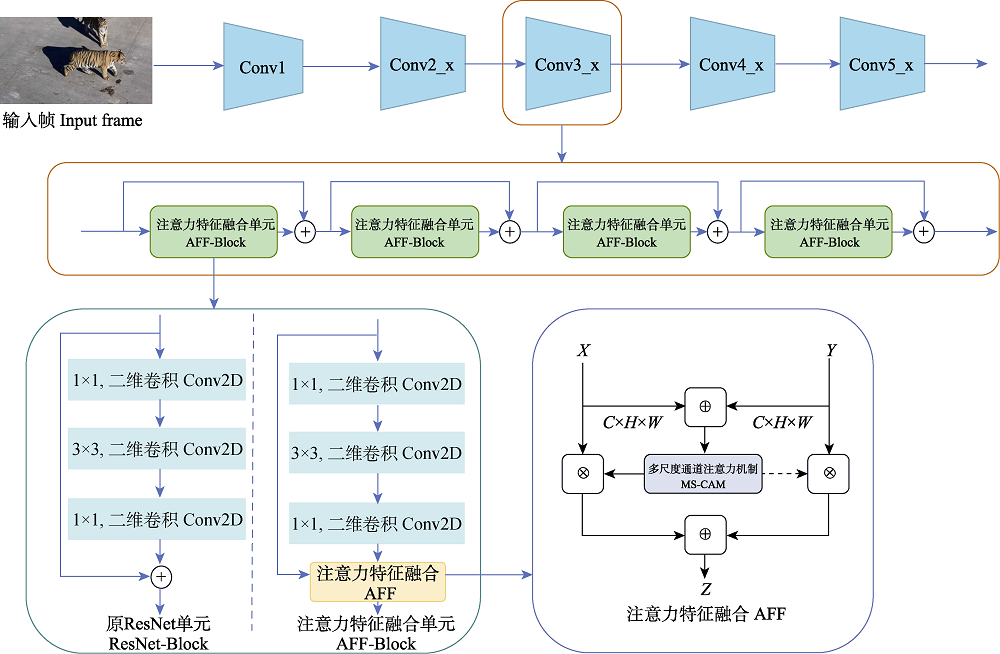
图5 基于注意力特征融合的AFF-ResNet50网络的整体结构。C、H、W分别为输入特征图的通道数、高度、宽度; X: ResNet单元中从上一层直接传递过来的原始输入; Y: ResNet单元中残差函数的输出; Z: 融合后的输出特征。
Fig. 5 Overall structure of AFF-ResNet50 network based on attention feature fusion. C, H, W represent the channels, height, and width of the input feature map respectively; X, The original input directly passed from the previous layer in the ResNet block; Y, The output of the residual function in the ResNet block; Z, The fused output feature.
| 跟踪器 Tracker | 平均像素误差 Average pixel error | 平均重叠率 Average overlap rate |
|---|---|---|
| 本文 This study | 9.016 | 0.737 |
| SiamFC | 15.380 | 0.730 |
| SiamRPN++ | 9.889 | 0.688 |
| SiamCAR | 19.630 | 0.692 |
| SiamBAN | 10.495 | 0.694 |
| SiamGAT | 11.828 | 0.719 |
表2 本文算法与当前5种先进跟踪方法在8个跟踪视频序列(Tiger_01-Tiger_08)下的平均像素误差与平均重叠率
Table 2 Average pixel error and average overlap rate of this study and five current state-of-the-art tracking methods on eight video sequences (Tiger_01-Tiger_08)
| 跟踪器 Tracker | 平均像素误差 Average pixel error | 平均重叠率 Average overlap rate |
|---|---|---|
| 本文 This study | 9.016 | 0.737 |
| SiamFC | 15.380 | 0.730 |
| SiamRPN++ | 9.889 | 0.688 |
| SiamCAR | 19.630 | 0.692 |
| SiamBAN | 10.495 | 0.694 |
| SiamGAT | 11.828 | 0.719 |
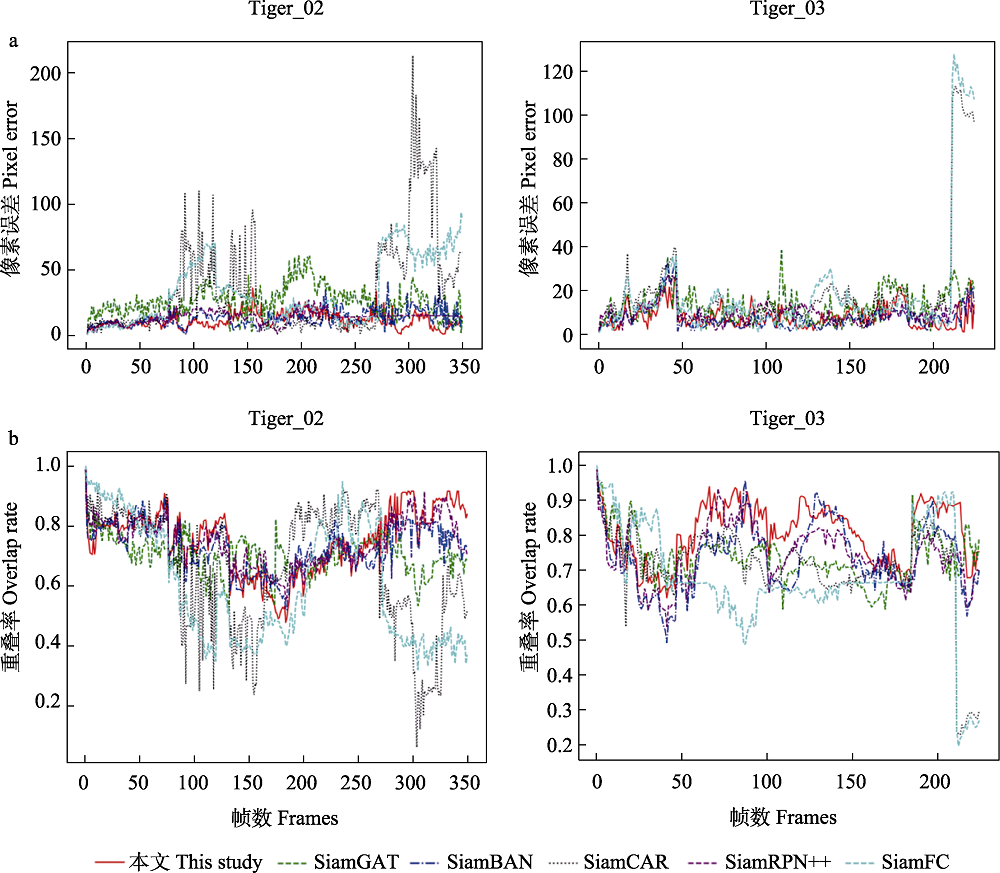
图6 本文算法与当前5种先进跟踪方法在视频序列Tiger_02和Tiger_03下的像素误差结果(a)和重叠率结果(b)的曲线图
Fig. 6 A graph of the pixel error results (a) and the overlap rate results (b) of this study and five current state-of-the-art tracking methods on the video sequences Tiger_02 and Tiger_03
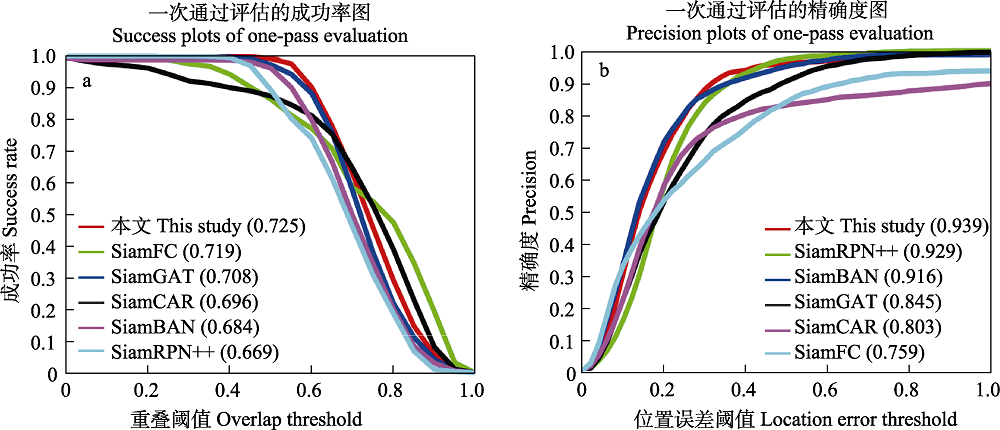
图7 本文算法与当前5种先进跟踪方法在东北虎目标跟踪测试数据集上的跟踪成功率与精确度对比
Fig. 7 Comparison of tracking success rate and precision of this study and five current state-of-the-art tracking methods on the Amur tiger target tracking test dataset
| 跟踪器 Tracker | 光照变化 Illumination variation | 目标旋转 Object rotation | 部分遮挡 Partial occlusion | 相似干扰 Similarity interference | 目标形变 Object deformation | 尺度变化 Scale variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 本文 This Study | 0.719 | 0.723 | 0.728 | 0.711 | 0.740 | 0.755 |
| SiamFC | 0.794 | 0.694 | 0.750 | 0.673 | 0.734 | 0.743 |
| SiamRPN++ | 0.663 | 0.651 | 0.728 | 0.649 | 0.728 | 0.711 |
| SiamCAR | 0.694 | 0.680 | 0.712 | 0.680 | 0.709 | 0.719 |
| SiamBAN | 0.672 | 0.672 | 0.722 | 0.656 | 0.722 | 0.718 |
| SiamGAT | 0.681 | 0.683 | 0.729 | 0.728 | 0.728 | 0.744 |
表3 本文算法与当前5种先进跟踪方法在东北虎目标跟踪测试数据集中6种挑战的成功率
Table 3 Tracking success rate of this study and five current state-of-the-art tracking methods on six types of challenges in the Amur tiger target tracking test dataset
| 跟踪器 Tracker | 光照变化 Illumination variation | 目标旋转 Object rotation | 部分遮挡 Partial occlusion | 相似干扰 Similarity interference | 目标形变 Object deformation | 尺度变化 Scale variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 本文 This Study | 0.719 | 0.723 | 0.728 | 0.711 | 0.740 | 0.755 |
| SiamFC | 0.794 | 0.694 | 0.750 | 0.673 | 0.734 | 0.743 |
| SiamRPN++ | 0.663 | 0.651 | 0.728 | 0.649 | 0.728 | 0.711 |
| SiamCAR | 0.694 | 0.680 | 0.712 | 0.680 | 0.709 | 0.719 |
| SiamBAN | 0.672 | 0.672 | 0.722 | 0.656 | 0.722 | 0.718 |
| SiamGAT | 0.681 | 0.683 | 0.729 | 0.728 | 0.728 | 0.744 |
| 跟踪器 Tracker | 光照变化 Illumination variation | 目标旋转 Object rotation | 部分遮挡 Partial occlusion | 相似干扰 Similarity interference | 目标形变 Object deformation | 尺度变化 Scale variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 本文 This study | 0.972 | 0.970 | 0.887 | 0.849 | 0.904 | 0.982 |
| SiamFC | 0.864 | 0.748 | 0.724 | 0.563 | 0.745 | 0.916 |
| SiamRPN++ | 0.964 | 0.959 | 0.880 | 0.840 | 0.897 | 0.982 |
| SiamCAR | 0.767 | 0.786 | 0.753 | 0.776 | 0.769 | 0.894 |
| SiamBAN | 0.924 | 0.944 | 0.878 | 0.829 | 0.892 | 0.973 |
| SiamGAT | 0.937 | 0.841 | 0.756 | 0.853 | 0.773 | 0.918 |
表4 本文算法与当前5种先进跟踪方法在东北虎目标跟踪测试数据集中6种挑战的精确度
Table 4 Tracking precision of this study and five current state-of-the-art tracking methods on six types of challenges in the Amur tiger target tracking test dataset
| 跟踪器 Tracker | 光照变化 Illumination variation | 目标旋转 Object rotation | 部分遮挡 Partial occlusion | 相似干扰 Similarity interference | 目标形变 Object deformation | 尺度变化 Scale variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 本文 This study | 0.972 | 0.970 | 0.887 | 0.849 | 0.904 | 0.982 |
| SiamFC | 0.864 | 0.748 | 0.724 | 0.563 | 0.745 | 0.916 |
| SiamRPN++ | 0.964 | 0.959 | 0.880 | 0.840 | 0.897 | 0.982 |
| SiamCAR | 0.767 | 0.786 | 0.753 | 0.776 | 0.769 | 0.894 |
| SiamBAN | 0.924 | 0.944 | 0.878 | 0.829 | 0.892 | 0.973 |
| SiamGAT | 0.937 | 0.841 | 0.756 | 0.853 | 0.773 | 0.918 |

图8 在6种挑战下的东北虎跟踪结果定性比较。a-e分别表示光照变化、目标旋转、部分遮挡、相似干扰、目标形变和尺度变化挑战。
Fig. 8 Qualitative comparison of tracking results of Amur tigers under six types of challenges. a-e represent illumination variation, object rotation, partial occlusion, similarity interference, object deformation, and scale variation challenges, respectively.
| 模型 Model | 成功率 Success rate (%) | 精确度 Precision (%) |
|---|---|---|
| SiamBAN | 68.4 | 91.6 |
| SiamBAN + 多尺度通道注意力机制 SiamBAN + Multi-scale channel attention module (MS-CAM) | 67.0 | 93.5 |
| SiamBAN + 注意力特征融合 SiamBAN + Attentional feature fusion (AFF) | 72.5 | 93.9 |
| SiamBAN + 特征金字塔网络 SiamBAN + Feature pyramid networks (FPN) | 63.6 | 94.1 |
表5 SiamBAN以及其采用不同特征融合方法的跟踪成功率与精确度对比
Table 5 Comparison of tracking success rate and precision of SiamBAN with various feature fusion methods
| 模型 Model | 成功率 Success rate (%) | 精确度 Precision (%) |
|---|---|---|
| SiamBAN | 68.4 | 91.6 |
| SiamBAN + 多尺度通道注意力机制 SiamBAN + Multi-scale channel attention module (MS-CAM) | 67.0 | 93.5 |
| SiamBAN + 注意力特征融合 SiamBAN + Attentional feature fusion (AFF) | 72.5 | 93.9 |
| SiamBAN + 特征金字塔网络 SiamBAN + Feature pyramid networks (FPN) | 63.6 | 94.1 |
| [1] | Altobel MZ, Sah M (2021) Tiger detection using Faster R-CNN for wildlife conservation. In: 14thInternational Conference on Theory and Application of Fuzzy Systems and Soft Computing-ICAFS- 2020, pp. 572-579. Springer, Cham. |
| [2] | Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Henriques JF, Vedaldi A, Torr PHS (2016) Fully-convolutional Siamese networks for object tracking. In: Computer Vision - ECCV 2016 Workshops, pp. 850-865. Springer, Cham. |
| [3] | Bhattacharya S, Sultana M, Das B, Roy B (2022) A deep neural network framework for detection and identification of Bengal tigers. Innovations in Systems and Software Engineering, 18, 1-9. |
| [4] | Chen X, Yan B, Zhu JW, Wang D, Yang XY, Lu HC (2021) Transformer tracking. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp.8122-8131. Nashville, TN, USA. |
| [5] | Chen ZD, Zhong BN, Li GR, Zhang SP, Ji RR (2020) Siamese box adaptive network for visual tracking. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6667-6676. Seattle, WA, USA. |
| [6] | Dai YM, Gieseke F, Oehmcke S, Wu YQ, Barnard K (2021) Attentional feature fusion.In: 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 3559-3568. Waikoloa, HI, USA. |
| [7] |
Gong YN, Tan MY, Wang Z, Zhao GJ, Jiang PL, Jiang SM, Zhang DJ, Ge JP, Feng LM (2019) AI recognition of infrared camera image of wild animals based on deep learning: Northeast Tiger and Leopard National Park for example. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 39, 458-465. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [ 宫一男, 谭孟雨, 王震, 赵国静, 蒋沛林, 蒋仕铭, 张鼎基, 葛剑平, 冯利民 (2019) 基于深度学习的红外相机动物影像人工智能识别: 以东北虎豹国家公园为例. 兽类学报, 39, 458-465.] | |
| [8] | Guo DY, Shao YY, Cui Y, Wang ZH, Zhang LY, Shen CH (2021) Graph attention tracking. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 9538-9547. Nashville, TN, USA. |
| [9] | Guo DY, Wang J, Cui Y, Wang ZH, Chen SY (2020) SiamCAR:Siamese fully convolutional classification and regression for visual tracking. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6268-6276. Seattle, WA, USA. |
| [10] | Hayward GD, Miquelle DG, Smirnov EN, Nations C (2002) Monitoring Amur tiger populations: Characteristics of track surveys in snow. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 30, 1150-1159. |
| [11] | He KM, Zhang XY, Ren SQ, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770-778. Las Vegas, NV, USA. |
| [12] | Karanth KU, Nichols JD, Kumar NS, Link WA, Hines JE (2004) Tigers and their prey: Predicting carnivore densities from prey abundance. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 101, 4854-4858. |
| [13] | Kays R, Crofoot MC, Jetz W, Wikelski M (2015) Terrestrial animal tracking as an eye on life and planet. Science, 348, eaaa2478. |
| [14] | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2017) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Communications of the ACM, 60, 84-90. |
| [15] | Li B, Wu W, Wang Q, Zhang FY, Xing JL, Yan JJ (2019) SiamRPN:Evolution of Siamese visual tracking with very deep networks. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp.4277-4286. Long Beach, CA, USA. |
| [16] | Li B, Yan JJ, Wu W, Zhu Z, Hu XL (2018) High performance visual tracking with siamese region proposal network. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp.8971-8980. Salt Lake City, UT, USA. |
| [17] | Li SY, Li JG, Tang HL, Qian R, Lin WY (2020) ATRW: A benchmark for Amur tiger re-identification in the wild. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 2590-2598. Seattle, WA, USA. |
| [18] | Lin TY, Dollár P, Girshick R, He KM, Hariharan B, Belongie S (2017) Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 936-944. Honolulu, HI, USA. |
| [19] | Liu PJ, Fu XF, Sun HF, He L, Liu SJ (2023) A highly robust target tracking algorithm merging a CNN and Transformer. Journal of System Simulation, 35, 1-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘沛津, 付雪峰, 孙浩峰, 何林, 刘淑婕 (2023) 一种融合CNN与Transformer的高鲁棒性目标跟踪算法. 系统仿真学报, 35, 1-15.] | |
| [20] | Palanisamy V, Ratnarajah N (2021) Detection of wildlife animals using deep learning approaches:A systematic review.In: 2021 21st International Conference on Advances in ICT for Emerging Regions (ICter), pp. 153-158. Colombo, Sri Lanka. |
| [21] | Qi JZ, Gu JY, Ning Y, Miquelle DG, Holyoak M, Wen DS, Liang X, Liu SY, Roberts NJ, Yang EY, Lang JM, Wang FY, Li C, Liang Z, Liu PQ, Ren Y, Zhou SC, Zhang MH, Ma JZ, Chang J, Jiang GS (2021) Integrated assessments call for establishing a sustainable meta-population of Amur tigers in northeast Asia. Biological Conservation, 261, 109250. |
| [22] | Rai P, Golchha V, Srivastava A, Vyas G, Mishra S (2016) An automatic classification of bird species using audio feature extraction and support vector machines. In: 2016 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), pp. 1-5. Coimbatore, India. |
| [23] | Riordan P (1998) Unsupervised recognition of individual tigers and snow leopards from their footprints. Animal Conservation, 1, 253-262. |
| [24] | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net:Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (eds Goos G, Hartmanis J), pp. 234-241. Springer International Publishing, Cham. |
| [25] | Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma SA, Huang ZH, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M, Berg AC, Li FF (2015) ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 115, 211-252. |
| [26] | Scanes CG (2018) Human activity and habitat loss:Destruction, fragmentation, and degradation. In: Animals and Human Society (eds Scanes CG, Toukhsati SR), pp. 451-482. Elsevier, Amsterdam. |
| [27] | Schindler F, Steinhage V (2021) Identification of animals and recognition of their actions in wildlife videos using deep learning techniques. Ecological Informatics, 61, 101215. |
| [28] | Shi CM, Liu D, Cui YL, Xie JJ, Roberts NJ, Jiang GS (2020) Amur tiger stripes: Individual identification based on deep convolutional neural network. Integrative Zoology, 15, 461-470. |
| [29] | Su QG, Tang JL, Zhai MX, He DJ (2022) An intelligent method for dairy goat tracking based on Siamese network. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 193, 106636. |
| [30] | Vo XT, Hoang VD, Nguyen DL, Jo K (2022) Pedestrian head detection and tracking via global vision transformer. In: Frontiers of Computer Vision, IW-FCV 2022, pp. 155-167. Springer, Cham. |
| [31] | Wan P, Zhao JW, Zhu M, Tan HQ, Deng ZY, Huang YY, Wu WJ, Ding AZ (2021) Freshwater fish species identification method based on improved ResNet 50 model. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 37(12), 159-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 万鹏, 赵竣威, 朱明, 谭鹤群, 邓志勇, 黄毓毅, 吴文锦, 丁安子 (2021) 基于改进ResNet50模型的大宗淡水鱼种类识别方法. 农业工程学报, 37(12), 159-168.] | |
| [32] | Wang C, Chen HQ, Zhang XB, Meng CY (2016) Evaluation of a laying-hen tracking algorithm based on a hybrid support vector machine. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology, 7, 1-10. |
| [33] |
Wang D, Hu YB, Ma TX, Nie YG, Xie Y, Wei FW (2016) Noninvasive genetics provides insights into the population size and genetic diversity of an Amur tiger population in China. Integrative Zoology, 11, 16-24.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | Xie JJ, Li AQ, Zhang JG, Cheng ZA (2019) An integrated wildlife recognition model based on multi-branch aggregation and squeeze-and-excitation network. Applied Sciences, 9, 2794. |
| [35] | Xie YH, Jiang JZ, Bao H, Zhai PH, Zhao Y, Zhou XY, Jiang GS (2023) Recognition of big mammal species in airborne thermal imaging based on YOLO V5 algorithm. Integrative Zoology, 18, 333-352. |
| [36] | Zhang J, Yang SQ, Hu SR, Ning JF, Lan XY, Wang YS (2023) A dairy goat tracking method via lightweight fusion and Kullback Leibler divergence. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 213, 108189. |
| [37] | Zhao TT, Zhou ZF, Li DX, Liu S, Li M (2018) Individual identification of leopard based on improved Cifar-10 deep learning model. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 49, 585-591, 598. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵婷婷, 周哲峰, 李东喜, 刘松, 李明 (2018) 基于改进的Cifar-10深度学习模型的金钱豹个体识别研究. 太原理工大学学报, 49, 585-591, 598.] | |
| [38] | Zheng ZY, Zhang XQ, Qin LF, Yue S, Zeng PB (2023) Cows’ legs tracking and lameness detection in dairy cattle using video analysis and Siamese neural networks. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 205, 107618. |
| [39] |
Zhou ZY, Hou JP, Liu P, Chen P, Duan C (2023) Giant panda head image segmentation based on dual model fusion. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 43, 82-88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 周章玉, 侯佳萍, 刘鹏, 陈鹏, 段昶 (2023) 基于双模型融合的大熊猫头部图像分割. 兽类学报, 43, 82-88.]
DOI |
|
| [40] |
Zhu YX, Wang DW, Li ZL, Feng JW, Wang TM (2022) Restoring tiger population in Asia: Challenges, opportunities, and future prospects. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22421. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 朱逸晓, 王大伟, 李治霖, 冯佳伟, 王天明 (2022) 亚洲虎种群恢复的机遇与挑战. 生物多样性, 30, 22421.]
DOI |
| [1] | 杜宇晨, 刘蓓萌, 陈俊峰, 王浩, 谢屹. 基于结构方程模型的农户保护意愿影响因素分析: 以东北虎豹国家公园珲春片区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23155-. |
| [2] | 蔡建民, 何培宇, 杨智鹏, 李露莹, 赵启军, 潘帆. 基于深度特征融合的鸟鸣识别方法及其可解释性分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23087-. |
| [3] | 孙翊斐, 王士政, 冯佳伟, 王天明. 东北虎豹国家公园森林声景的昼夜和季节变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(1): 22523-. |
| [4] | 谢卓钒, 李鼎昭, 孙海信, 张安民. 面向鸟鸣声识别任务的深度学习技术[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(1): 22308-. |
| [5] | 蒋亚芳, 田静, 赵晶博, 唐小平. 国家公园生态系统完整性的内涵及评价框架: 以东北虎豹国家公园为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(10): 1279-1287. |
| [6] | 王天明, 冯利民, 杨海涛, 鲍蕾, 王红芳, 葛剑平. 东北虎豹生物多样性红外相机监测平台概述[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(9): 1059-1066. |
| [7] | 田瑜, 邬建国, 寇晓军, 李钟汶, 王天明, 牟溥, 葛剑平. 东北虎种群的时空动态及其原因分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(3): 211-225. |
| [8] | 吴平, 周开亚, 王亚明, 黄恭情, 徐麟木. 用RFLP和PCR-RFLP技术研究东北虎和华南虎线粒体DNA多态性*[J]. 生物多样性, 1997, 05(3): 173-178. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn

