



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 25112. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025112 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2025112
收稿日期:2025-03-30
接受日期:2025-07-07
出版日期:2025-08-20
发布日期:2025-09-17
通讯作者:
*E-mail: aiying@bjfu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Aiying Wang1,*( )(
)( ), Wanjin Liao2(
), Wanjin Liao2( )
)
Received:2025-03-30
Accepted:2025-07-07
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-09-17
Contact:
*E-mail: aiying@bjfu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
协同演化是推动和维持地球生物多样性的重要驱动力, 其产生的演化结果与关系模式对于揭示生物多样性的产生和维持机制十分关键。协同系统发育分析作为推断物种间相互作用或相互作用网络协同演化过程所产生结果模式的重要方法, 可以建立在两个或多个类群的系统发育树之间, 通过全局拟合或基于事件的分析方法, 推断类群间的系统发育一致性及协同宏演化事件。本文首先介绍了协同演化的基本概念。其次, 系统阐述了协同系统发育分析在两个类群和多个类群之间的常用分析方法, 并对全局拟合和基于事件分析的两大类方法进行了比较。随后, 综述了协同系统发育分析方法在物种间相互作用及群落构建的协同演化研究中的应用。最后, 本文综合该领域中现有的研究方法和进展, 探讨了当前方法的局限性, 并对协同系统发育分析方法在协同演化中的研究发展方向提出了展望。
王蔼英, 廖万金 (2025) 协同演化研究: 协同系统发育分析方法与进展. 生物多样性, 33, 25112. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025112.
Aiying Wang, Wanjin Liao (2025) Coevolutionary processes: Methods and advances in cophylogenetic analysis. Biodiversity Science, 33, 25112. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025112.
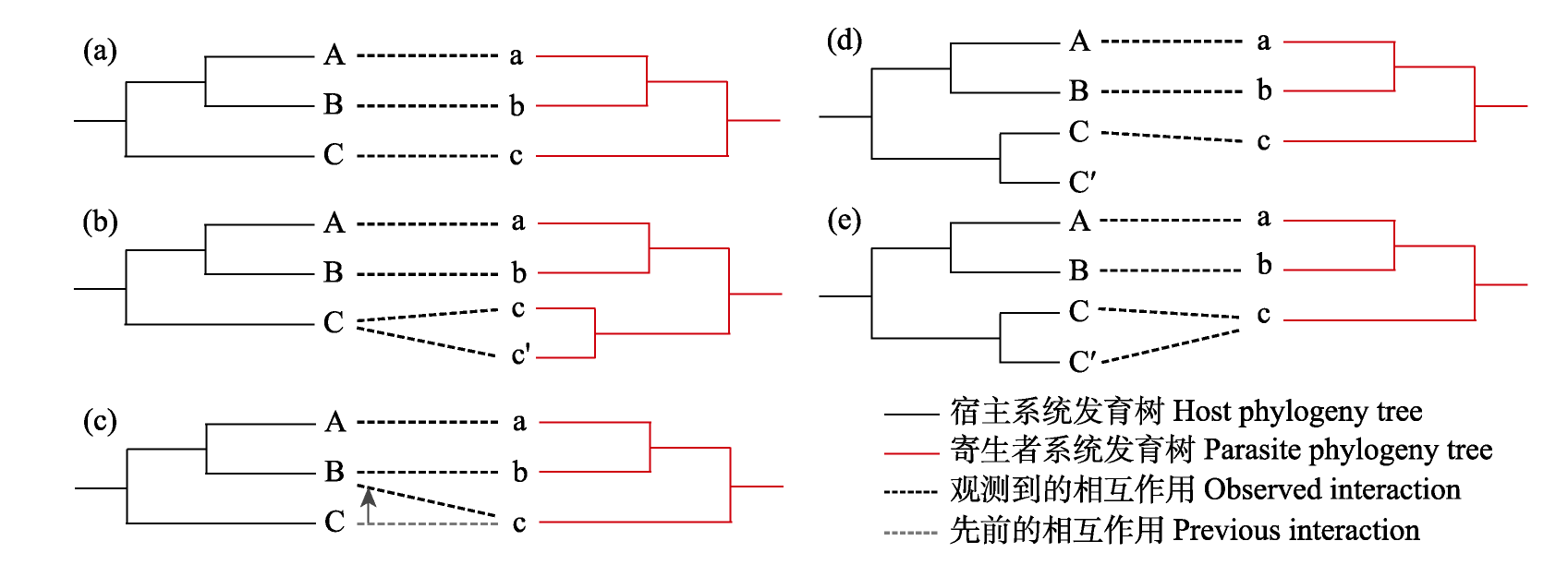
图1 协同系统发育分析中的协同宏演化事件。(a)协同物种形成, 宿主与寄生者支系同步发生物种形成, 产生完全一致的拓扑结构; (b)物种加倍, 仅在寄生者支系发生物种形成(寄生者物种c和c')而对应的宿主支系没有发生物种形成, 并且新形成的寄生者物种仍然对应原本的宿主物种; (c)宿主转移, 一个寄生者物种从一个宿主物种转移到另一个宿主物种的过程(寄生者物种c从宿主C转移到宿主B); (d)丢失, 仅在宿主支系发生物种形成(宿主物种C和C')而现存的寄生者支系上的物种仅对应一种宿主支系的物种; (e)分化失败, 仅在宿主支系发生物种形成(宿主物种C和C'), 并且现存的寄生者支系上的物种同时对应发生物种形成后新的两种宿主物种。本图根据Conow等(2010)和Dismukes等(2022)改编绘制。
Fig. 1 Macroevolutionary events in cophylogenetic analysis. (a) Cospeciation, where speciation occurs concurrently in the host and parasite clades, resulting in a completely congruent topological structure; (b) Duplication, where speciation in the parasite clade occurs (parasite species c and c') without speciation in the host clade and both new parasite species remain associated with the ancestral host species; (c) Host switch, the process in which a parasite species switched from one host species to another (parasite species c switches from host C to host B); (d) Loss, where speciation occurs in only the host clade (host species C and C') and the existing parasite species associates with only one new host species; (e) Failure to diverge, where speciation occurs in only the host clade (host species C and C') and the existing parasite species associates with both new host species. This figure was modified from the illustrations and descriptions in Conow et al (2010) and Dismukes et al (2022).
| [1] |
Agrawal AA, Zhang XN (2021) The evolution of coevolution in the study of species interactions. Evolution, 75, 1594-1606.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Alcala N, Jenkins T, Christe P, Vuilleumier S (2017) Host shift and cospeciation rate estimation from co-phylogenies. Ecology Letters, 20, 1014-1024.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Althoff DM, Segraves KA (2022) Evolution of antagonistic and mutualistic traits in the yucca-yucca moth obligate pollination mutualism. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 35, 100-108.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Althoff DM, Segraves KA, Johnson MTJ (2014) Testing for coevolutionary diversification: Linking pattern with process. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 29, 82-89.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Anderson RM, Hennessy AB, Kowalski K, Kessler A, Bagchi R, Singer MS (2024) Phloem-feeding insects create parasitoid-free space for caterpillars. Current Biology, 34, 3665-3672.e3.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Assis APA, Thompson JN, Santana PC, Jordano P, Bascompte J, Guimarães PR Jr (2020) Genetic correlations and ecological networks shape coevolving mutualisms. Ecology Letters, 23, 1789-1799.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Balbuena JA, Míguez-Lozano R, Blasco-Costa I (2013) PACo: A novel Procrustes application to cophylogenetic analysis. PLoS ONE, 8, e61048. |
| [8] |
Balbuena JA, Pérez-Escobar ÓA, Llopis-Belenguer C, Blasco-Costa I (2020) Random tanglegram partitions (random TaPas): An Alexandrian approach to the cophylogenetic Gordian knot. Systematic Biology, 69, 1212-1230.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Barraclough TG (2015) How do species interactions affect evolutionary dynamics across whole communities? Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 46, 25-48.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Baudet C, Donati B, Sinaimeri B, Crescenzi P, Gautier C, Matias C, Sagot MF (2015) Cophylogeny reconstruction via an approximate Bayesian computation. Systematic Biology, 64, 416-431.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Blasco-Costa I, Hayward A, Poulin R, Balbuena JA (2021) Next-generation cophylogeny: Unravelling eco-evolutionary processes. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 36, 907-918.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Boyd BM, Nguyen NP, Allen JM, Waterhouse RM, Vo KB, Sweet AD, Clayton DH, Bush SE, Shapiro MD, Johnson KP (2022) Long-distance dispersal of pigeons and doves generated new ecological opportunities for host-switching and adaptive radiation by their parasites. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 289, 20220042. |
| [13] | Bracewell RR, Vanderpool D, Good JM, Six DL (2018) Cascading speciation among mutualists and antagonists in a tree-beetle-fungi interaction. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 285, 20180694. |
| [14] |
Braga MP, Janz N, Nylin S, Ronquist F, Landis MJ (2021) Phylogenetic reconstruction of ancestral ecological networks through time for pierid butterflies and their host plants. Ecology Letters, 24, 2134-2145.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Braga MP, Landis MJ, Nylin S, Janz N, Ronquist F (2020) Bayesian inference of ancestral host-parasite interactions under a phylogenetic model of host repertoire evolution. Systematic Biology, 69, 1149-1162.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Bronstein MM, Bruna J, Cohen T, Veličković P (2021) Geometric deep learning: Grids, groups, graphs, geodesics, and gauges. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2104.13478. |
| [17] |
Brooks DR (1979) Testing the context and extent of host-parasite coevolution. Systematic Biology, 28, 299-307.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Brooks DR, Dowling APG, Van Veller MGP, Hoberg EP (2004) Ending a decade of deception: A valiant failure, a not-so-valiant failure, and a success story. Cladistics, 20, 32-46. |
| [19] |
Caudill V, Ralph P (2025) Genetic architecture, spatial heterogeneity, and the arms race between newts and snakes: Exploring coevolution with simulations. The American Naturalist, 205, 184-202.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Charleston MA (1998) Jungles: A new solution to the host/ parasite phylogeny reconciliation problem. Mathematical Biosciences, 149, 191-223.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Charleston MA, Page RDM (2002) TreeMap 2.0β. A Macintosh R program for the Analysis of How Dependent Phylogenies are Related, by Cophylogeny Mapping. University of Glasgow, Scotland. |
| [22] | Clayton DH, Bush SE, Goates BM, Johnson KP (2003) Host defense reinforces host-parasite cospeciation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 100, 15694-15699. |
| [23] |
Cogni R, Quental TB, Guimarães PR Jr (2022) Ehrlich and Raven escape and radiate coevolution hypothesis at different levels of organization: Past and future perspectives. Evolution, 76, 1108-1123.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Conow C, Fielder D, Ovadia Y, Libeskind-Hadas R (2010) Jane: A new tool for the cophylogeny reconstruction problem. Algorithms for Molecular Biology, 5, 16.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Cornwallis CK, Griffin AS (2024) A guided tour of phylogenetic comparative methods for studying trait evolution. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 55, 181-204.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Cruaud A, Rønsted N, Chantarasuwan B, Chou LS, Clement WL, Couloux A, Cousins B, Genson G, Harrison RD, Hanson PE, Hossaert-McKey M, Jabbour-Zahab R, Jousselin E, Kerdelhué C, Kjellberg F, Lopez-Vaamonde C, Peebles J, Peng YQ, Pereira RAS, Schramm T, Ubaidillah R, van Noort S, Weiblen GD, Yang DR, Yodpinyanee A, Libeskind-Hadas R, Cook JM, Rasplus JY, Savolainen V (2012) An extreme case of plant-insect codiversification: Figs and fig-pollinating wasps. Systematic Biology, 61, 1029-1047.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Cuthill JH, Charleston M (2012) Phylogenetic codivergence supports coevolution of mimetic Heliconius butterflies. PLoS ONE, 7, e36464. |
| [28] | Darwin C (1862) Fertilisation of Orchids. John Murray, London. |
| [29] | Dawkins R, Krebs JR (1979) Arms races between and within species. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 205, 489-511. |
| [30] |
de Andreazzi CS, Astegiano J, Guimarães PR Jr (2020) Coevolution by different functional mechanisms modulates the structure and dynamics of antagonistic and mutualistic networks. Oikos, 129, 224-237.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
de Vienne DM, Giraud T, Shykoff JA (2007) When can host shifts produce congruent host and parasite phylogenies? A simulation approach. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 20, 1428-1438.
PMID |
| [32] |
de Vienne DM, Refrégier G, López-Villavicencio M, Tellier A, Hood ME, Giraud T (2013) Cospeciation vs host-shift speciation: Methods for testing, evidence from natural associations and relation to coevolution. New Phytologist, 198, 347-385.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Dismukes W, Braga MP, Hembry DH, Heath TA, Landis MJ (2022) Cophylogenetic methods to untangle the evolutionary history of ecological interactions. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 53, 275-298.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Dismukes W, Heath TA (2021) Treeducken: An R package for simulating cophylogenetic systems. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 12, 1358-1364.
DOI |
| [35] |
Dormann CF, Fründ J, Schaefer HM (2017) Identifying causes of patterns in ecological networks: Opportunities and limitations. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 48, 559-584.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Ehrlich PR, Raven PH (1964) Butterflies and plants: A study in coevolution. Evolution, 18, 586-608.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Farenholz H (1913) Ectoparasiten und Abstammungslehre. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 41, 371-374. |
| [38] |
Feder JL, Forbes AA (2010) Sequential speciation and the diversity of parasitic insects. Ecological Entomology, 35, 67-76.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Forister ML, Feldman CR (2011) Phylogenetic cascades and the origins of tropical diversity. Biotropica, 43, 270-278.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Fox LR (1988) Diffuse coevolution within complex communities. Ecology, 69, 906-907.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Fuzessy L, Silveira FAO, Culot L, Jordano P, Verdú M (2022) Phylogenetic congruence between Neotropical primates and plants is driven by frugivory. Ecology Letters, 25, 320-329.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Gause GF (1934) The Struggle for Existence. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore. |
| [43] |
Goslee SC, Niering WA, Urban DL, Christensen NL (2005) Influence of environment, history and vegetative interactions on stand dynamics in a Connecticut forest. The Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society, 132, 471-482.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Groussin M, Mazel F, Sanders JG, Smillie CS, Lavergne S, Thuiller W, Alm EJ (2017) Unraveling the processes shaping mammalian gut microbiomes over evolutionary time. Nature Communications, 8, 14319.
DOI PMID |
| [45] | Hafner MS, Nadler SA (1990) Cospeciation in host-parasite assemblages: Comparative analysis of rates of evolution and timing of cospeciation events. Systematic Biology, 39, 192-204. |
| [46] |
Hafner MS, Sudman PD, Villablanca FX, Spradling TA, Demastes JW, Nadler SA (1994) Disparate rates of molecular evolution in cospeciating hosts and parasites. Science, 265, 1087-1090.
PMID |
| [47] |
Harmon LJ, Andreazzi CS, Débarre F, Drury J, Goldberg EE, Martins AB, Melián CJ, Narwani A, Nuismer SL, Pennell MW, Rudman SM, Seehausen O, Silvestro D, Weber M, Matthews B (2019) Detecting the macroevolutionary signal of species interactions. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 32, 769-782.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Hayward A, Poulin R, Nakagawa S (2021) A broadscale analysis of host-symbiont cophylogeny reveals the drivers of phylogenetic congruence. Ecology Letters, 24, 1681-1696.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Hembry DH, Weber MG (2020) Ecological interactions and macroevolution: A new field with old roots. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 51, 215-243.
DOI |
| [50] |
Hembry DH, Yoder JB, Goodman KR (2014) Coevolution and the diversification of life. The American Naturalist, 184, 425-438.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
Hommola K, Smith JE, Qiu Y, Gilks WR (2009) A permutation test of host-parasite cospeciation. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 26, 1457-1468.
DOI PMID |
| [52] | Hutchinson MC, Cagua EF, Balbuena JA, Stouffer DB, Poisot T (2017) paco: Implementing Procrustean approach to cophylogeny in R. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 8, 932-940. |
| [53] | Ives AR, Godfray HCJ (2006) Phylogenetic analysis of trophic associations. The American Naturalist, 168, E1-E14. |
| [54] |
Janzen DH (1980) When is it coevolution? Evolution, 34, 611-612.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
Kawatsu K, Ushio M, van Veen FJF, Kondoh M (2021) Are networks of trophic interactions sufficient for understanding the dynamics of multi-trophic communities? Analysis of a tri-trophic insect food-web time-series. Ecology Letters, 24, 543-552.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Laine AL, Tylianakis JM (2024) The coevolutionary consequences of biodiversity change. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 39, 745-756.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Legendre P, Desdevises Y, Bazin E (2002) A statistical test for host-parasite coevolution. Systematic Biology, 51, 217-234.
PMID |
| [58] |
Llaberia-Robledillo M, Lucas-Lledó JI, Pérez-Escobar OA, Krasnov BR, Balbuena JA (2023) Rtapas: An R package to assess cophylogenetic signal between two evolutionary histories. Systematic Biology, 72, 946-954.
DOI PMID |
| [59] |
Lopez-Vaamonde C, Godfray HCJ, West SA, Hansson C, Cook JM (2005) The evolution of host use and unusual reproductive strategies in Achrysocharoides parasitoid wasps. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 18, 1029-1041.
PMID |
| [60] | Lynch M (2023) Mutation pressure, drift, and the pace of molecular coevolution. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 120, e2306741120. |
| [61] |
Maliet O, Loeuille N, Morlon H (2020) An individual-based model for the eco-evolutionary emergence of bipartite interaction networks. Ecology Letters, 23, 1623-1634.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Mayfield MM, Levine JM (2010) Opposing effects of competitive exclusion on the phylogenetic structure of communities. Ecology Letters, 13, 1085-1093.
DOI PMID |
| [63] |
Medina M, Baker DM, Baltrus DA, Bennett GM, Cardini U, Correa AMS, Degnan SM, Christa G, Kim E, Li JC, Nash DR, Marzinelli E, Nishiguchi M, Prada C, Roth MS, Saha M, Smith CI, Theis KR, Zaneveld J (2022) Grand challenges in coevolution. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 618251.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Merkle D, Middendorf M (2005) Reconstruction of the cophylogenetic history of related phylogenetic trees with divergence timing information. Theory in Biosciences, 123, 277-299.
DOI PMID |
| [65] | Merkle D, Middendorf M, Wieseke N (2010) A parameter- adaptive dynamic programming approach for inferring cophylogenies. BMC Bioinformatics, 11 (Suppl. 1), S60. |
| [66] |
Morlon H, Andréoletti J, Barido-Sottani J, Lambert S, Perez-Lamarque B, Quintero I, Senderov V, Veron P (2024) Phylogenetic insights into diversification. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 55, 1-21.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Morlon H, Lewitus E, Condamine FL, Manceau M, Clavel J, Drury J (2016) RPANDA: An R package for macroevolutionary analyses on phylogenetic trees. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 589-597.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Mramba LK, Barber S, Hommola K, Dyer LA, Wilson JS, Forister ML, Gilks WR (2013) Permutation tests for analyzing cospeciation in multiple phylogenies: Applications in tri-trophic ecology. Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology, 12, 679-701.
DOI PMID |
| [69] |
Nooney C, Barber S, Gusnanto A, Gilks WR (2017) A statistical method for analysing cospeciation in tritrophic ecology using electrical circuit theory. Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology, 16, 313-331.
DOI PMID |
| [70] |
Nuismer SL, Harmon LJ (2015) Predicting rates of interspecific interaction from phylogenetic trees. Ecology Letters, 18, 17-27.
DOI PMID |
| [71] |
Nuismer SL, Week B, Aizen MA (2018) Coevolution slows the disassembly of mutualistic networks. The American Naturalist, 192, 490-502.
DOI PMID |
| [72] |
Page RDM (1989) Comments on component-compatibility in historical biogeography. Cladistics, 5, 167-182.
DOI PMID |
| [73] | Page RDM (1994) Parallel phylogenies: Reconstructing the history of host-parasite assemblages. Cladistics, 10, 155-173. |
| [74] | Page RDM (2003) Tangled Trees:Phylogeny, Cospeciation, and Coevolution. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [75] |
Pang XX, Zhang DY (2023) Impact of ghost introgression on coalescent-based species tree inference and estimation of divergence time. Systematic Biology, 72, 35-49.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Perez-Lamarque B, Morlon H (2023) Comparing different computational approaches for detecting long-term vertical transmission in host-associated microbiota. Molecular Ecology, 32, 6671-6685.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Perez-Lamarque B, Morlon H (2024) Distinguishing cophylogenetic signal from phylogenetic congruence clarifies the interplay between evolutionary history and species interactions. Systematic Biology, 73, 613-622.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
Poisot T, Canard E, Mouillot D, Mouquet N, Gravel D (2012) The dissimilarity of species interaction networks. Ecology Letters, 15, 1353-1361.
DOI PMID |
| [79] | Prediger C, Ferreira EA, Zorzato SV, Hua-Van A, Klasson L, Miller WJ, Yassin A, Madi-Ravazzi L (2024) Saltational episodes of reticulate evolution in the Drosophila saltans species group. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 41, msae250. |
| [80] | R Core Team (2022) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. |
| [81] | Rolland J, Henao-Diaz LF, Doebeli M, Germain R, Harmon LJ, Knowles LL, Liow LH, Mank JE, Machac A, Otto SP, Pennell M, Salamin N, Silvestro D, Sugawara M, Uyeda J, Wagner CE, Schluter D (2023) Conceptual and empirical bridges between micro- and macroevolution. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 7, 1181-1193. |
| [82] |
Ronquist F (1995) Reconstructing the history of host-parasite associations using generalised parsimony. Cladistics, 11, 73-89.
DOI PMID |
| [83] |
Ronquist F (1997) Phylogenetic approaches in coevolution and biogeography. Zoologica Scripta, 26, 313-322.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
Russo L, Miller AD, Tooker J, Bjornstad ON, Shea K (2018) Quantitative evolutionary patterns in bipartite networks: Vicariance, phylogenetic tracking or diffuse co-evolution? Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 761-772.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
Santichaivekin S, Yang Q, Liu JY, Mawhorter R, Jiang J, Wesley T, Wu YC, Libeskind-Hadas R (2021) eMPRess: A systematic cophylogeny reconciliation tool. Bioinformatics, 37, 2481-2482.
DOI PMID |
| [86] |
Segar ST, Fayle TM, Srivastava DS, Lewinsohn TM, Lewis OT, Novotny V, Kitching RL, Maunsell SC (2020) The role of evolution in shaping ecological networks. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 35, 454-466.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
Siddall ME, Perkins SL (2003) Brooks parsimony analysis: A valiant failure. Cladistics, 19, 554-564.
DOI PMID |
| [88] |
Sinaimeri B, Urbini L, Sagot MF, Matias C (2023) Cophylogeny reconstruction allowing for multiple associations through approximate Bayesian computation. Systematic Biology, 72, 1370-1386.
DOI PMID |
| [89] |
Sweet AD, Boyd BM, Johnson KP (2016) Cophylogenetic patterns are uncorrelated between two lineages of parasites on the same hosts. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 118, 813-828.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
Szidat L (1956) Zoogeographische beziehungen zwischen fischen und ihren parasiten. Zeitschrift für Parasitenkunde, 17, 237-268.
DOI URL |
| [91] | Szöllõsi GJ, Boussau B, Abby SS, Tannier E, Daubin V (2012) Phylogenetic modeling of lateral gene transfer reconstructs the pattern and relative timing of speciations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 109, 17513-17518. |
| [92] |
Szöllõsi GJ, Rosikiewicz W, Boussau B, Tannier E, Daubin V (2013) Efficient exploration of the space of reconciled gene trees. Systematic Biology, 62, 901-912.
DOI PMID |
| [93] |
Tong ZY, Huang SQ (2019) The development, misuse and evidence of the concept “coevolution”. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 49, 421-435. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [童泽宇, 黄双全 (2019) 协同演化概念的发展、使用误区与研究证据. 中国科学: 生命科学, 49, 421-435.] | |
| [94] | Tsang CTT, Hui TKL, Chung NM, Yuen WT, Tsang LM (2024) Comparative analysis of gut microbiome of mangrove brachyuran crabs revealed patterns of phylosymbiosis and codiversification. Molecular Ecology, 33, e17377. |
| [95] |
Van Dam MH, Parisotto A, Medina MN, Cabras AA, Gutiérrez-Trejo N, Wilts BD, Lam AW (2024) Biogeography confounds the signal of cospeciation in Batesian mimicry. Current Biology, 34, 5554-5563.e4.
DOI URL |
| [96] |
Van der Niet T, Peakall R, Johnson SD (2014) Pollinator-driven ecological speciation in plants: New evidence and future perspectives. Annals of Botany, 113, 199-211.
DOI PMID |
| [97] | van Valen L (1973) A new evolutionary law. Evolutionary Theory, 1, 1-30. |
| [98] | Wang AY, Peng YQ, Cook JM, Yang DR, Zhang DY, Liao WJ (2023) Host insect specificity and interspecific competition drive parasitoid diversification in a plant-insect community. Ecology, 104, e4062. |
| [99] |
Wang AY, Peng YQ, Harder LD, Huang JF, Yang DR, Zhang DY, Liao WJ (2019) The nature of interspecific interactions and co-diversification patterns, as illustrated by the fig microcosm. New Phytologist, 224, 1304-1315.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
Wang G, Zhang XT, Herre EA, McKey D, Machado CA, Yu WB, Cannon CH, Arnold ML, Pereira RAS, Ming R, Liu YF, Wang YB, Ma DN, Chen J (2021) Genomic evidence of prevalent hybridization throughout the evolutionary history of the fig-wasp pollination mutualism. Nature Communications, 12, 718.
DOI PMID |
| [101] |
Ward AKG, Zhang YM, Brown GE, Hippee AC, Prior KM, Rollins S, Sierra N, Sheikh SI, Tribull CM, Forbes AA (2024) Speciation in kleptoparasites of oak gall wasps often correlates with shifts into new tree habitats, tree organs, or gall morphospace. Evolution, 78, 174-187.
DOI URL |
| [102] |
Weiblen GD (2002) How to be a fig wasp. Annual Review of Entomology, 47, 299-330.
PMID |
| [103] |
Wilson JS, Forister ML, Dyer LA, O’connor JM, Burls K, Feldman CR, Jaramillo MA, Miller JS, Rodríguez- Castañeda G, Tepe EJ, Whitfield JB, Young B (2012) Host conservatism, host shifts and diversification across three trophic levels in two Neotropical forests. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 25, 532-546.
DOI PMID |
| [104] |
Yoder JB, Dang A, MacGregor C, Plaza M (2022) Plant-associate interactions and diversification across trophic levels. Evolution Letters, 6, 375-389.
DOI PMID |
| [105] |
Yoder JB, Nuismer SL (2010) When does coevolution promote diversification? The American Naturalist, 176, 802-817.
DOI PMID |
| [106] |
Yu H, Zhang ZW, Liu L, Cheng YF, Deng XX, Segar ST, Compton SG (2022) Asymmetric sharing of pollinator fig wasps between two sympatric dioecious fig trees: A reflection of supply and demand or differences in the size of their figs? Botanical Studies, 63, 7.
DOI PMID |
| [107] |
Zeng YC, Hembry DH (2024) Coevolution-induced selection for and against phenotypic novelty shapes species richness in clade co-diversification. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 37, 1510-1522.
DOI PMID |
| [108] |
Zeng YC, Wiens JJ (2021) Species interactions have predictable impacts on diversification. Ecology Letters, 24, 239-248.
DOI PMID |
| [109] | Zhang WP, Cao L, Lin XR, Ding YM, Liang Y, Zhang DY, Pang EL, Renner SS, Bai WN (2022) Dead-end hybridization in walnut trees revealed by large-scale genomic sequence data. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 39, msab308. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn