



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (5): 24056. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024056 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024056
李柏灿1,2,3, 张军国1,2,3,*( ), 张长春1,2,3, 王丽凤1,2,3, 徐基良4, 刘利5,*(
), 张长春1,2,3, 王丽凤1,2,3, 徐基良4, 刘利5,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-02-16
接受日期:2024-04-12
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-04-19
通讯作者:
E-mail: 基金资助:
Baican Li1,2,3, Junguo Zhang1,2,3,*( ), Changchun Zhang1,2,3, Lifeng Wang1,2,3, Jiliang Xu4, Li Liu5,*(
), Changchun Zhang1,2,3, Lifeng Wang1,2,3, Jiliang Xu4, Li Liu5,*( )
)
Received:2024-02-16
Accepted:2024-04-12
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-04-19
Contact:
E-mail: 摘要:
北京地区珍稀鸟类的保护对维护当地生物多样性具有重要意义。随着人工智能技术的发展, 利用深度学习技术自动识别鸟类成为鸟类调查保护的重要手段。实际鸟类图像存在背景复杂以及相近科属鸟类具有外观相似等特点, 导致模型识别精度不佳。针对以上问题, 本文提出一种基于TC-YOLO模型的鸟类识别方法。首先, 为解决鸟类识别中复杂背景导致的漏检问题, 本文方法结合CARAFE (content-aware reassembly of features)机制, 自适应生成不同特征点所对应的上采样核, 在更大的感受野内聚合上下文语义信息, 有效聚焦鸟类前景区域。其次, 为解决鸟类识别中相似外观导致的误检问题, 本文方法引入TSCODE (task-specific context decoupling)解耦定位和分类任务, 通过获取多层级特征图的信息以回归目标边界, 并利用包含底层纹理和高层语义的特征进行物种分类, 进而提高模型的鸟类识别精度。最后, 本文开展对比实验以验证模型的性能。实验结果表明, TC-YOLO模型的平均精度均值在包含北京地区28种国家一级保护鸟类的自建数据集Beijing-28和鸟类公开数据集CUB200-2011上分别达到78.7%和75.3%, 均优于已有方法, 而且在公开数据集MS COCO上验证了TC-YOLO模型拥有较强的泛化性。本文提出的TC-YOLO模型对背景复杂或外观相似的鸟类图像都能有效识别, 漏检率和误检率较低, 能够为鸟类保护提供重要技术支撑。
李柏灿, 张军国, 张长春, 王丽凤, 徐基良, 刘利 (2024) 基于TC-YOLO模型的北京珍稀鸟类识别方法. 生物多样性, 32, 24056. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024056.
Baican Li, Junguo Zhang, Changchun Zhang, Lifeng Wang, Jiliang Xu, Li Liu (2024) Rare bird recognition method in Beijing based on TC-YOLO model. Biodiversity Science, 32, 24056. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024056.
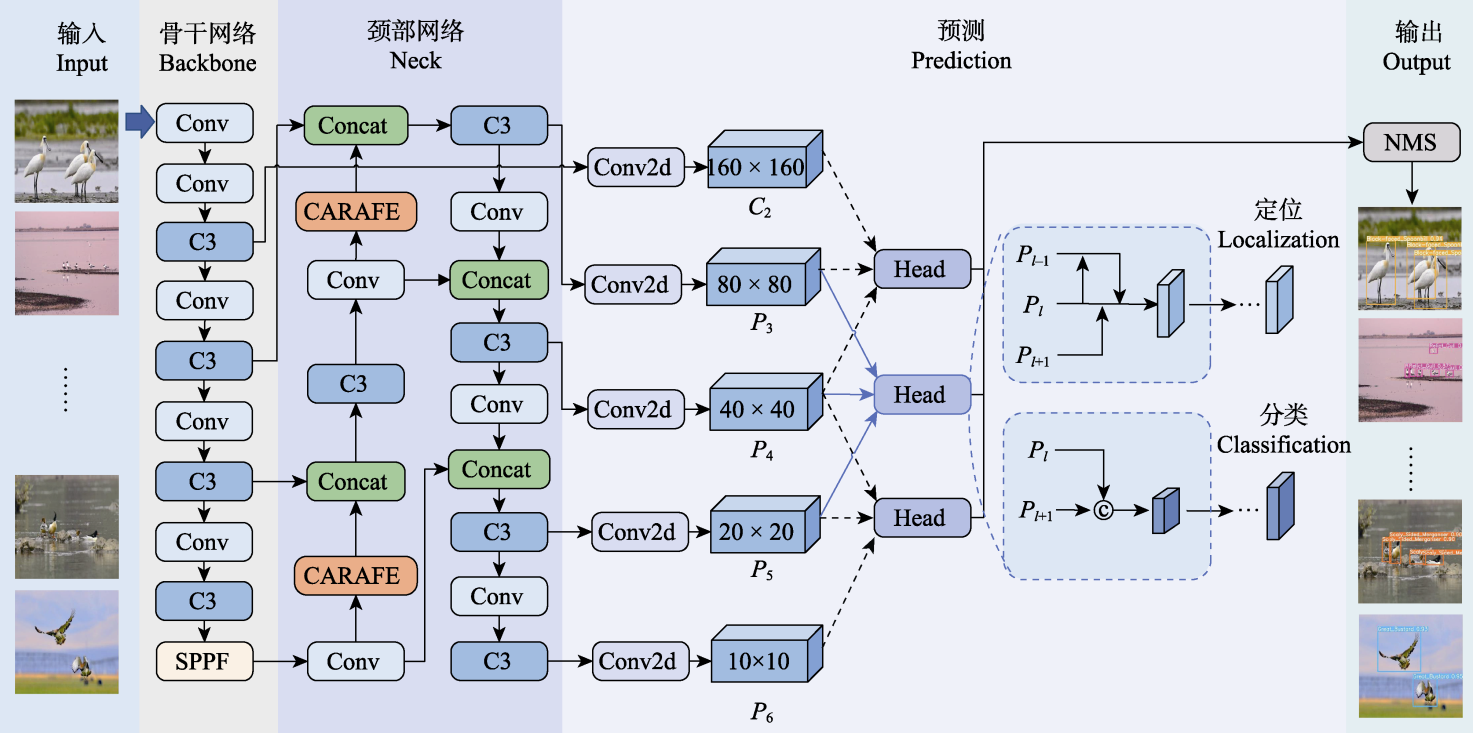
图3 TC-YOLO模型结构。Conv和Conv2d: 卷积; C3: 特征提取; SPPF: 空间金字塔池化结构; Concat和c: 特征融合; CARAFE: CARAFE上采样; C2: 第2层特征提取的特征图; Pl: 第l层金字塔层级的特征图; Head: TSCODE解耦头; NMS: 非极大值抑制。
Fig. 3 TC-YOLO model structure. Conv and Conv2d, Convolution; C3, Feature extraction; SPPF, Space pyramid pool structure; Concat and c, Feature fusion; CARAFE, CARAFE upsampling; C2, The feature map of layer 2 feature extraction; Pl, The feature map of the l-th pyramid level; Head, TSCODE decoupling header; NMS, Non-maximum suppression.
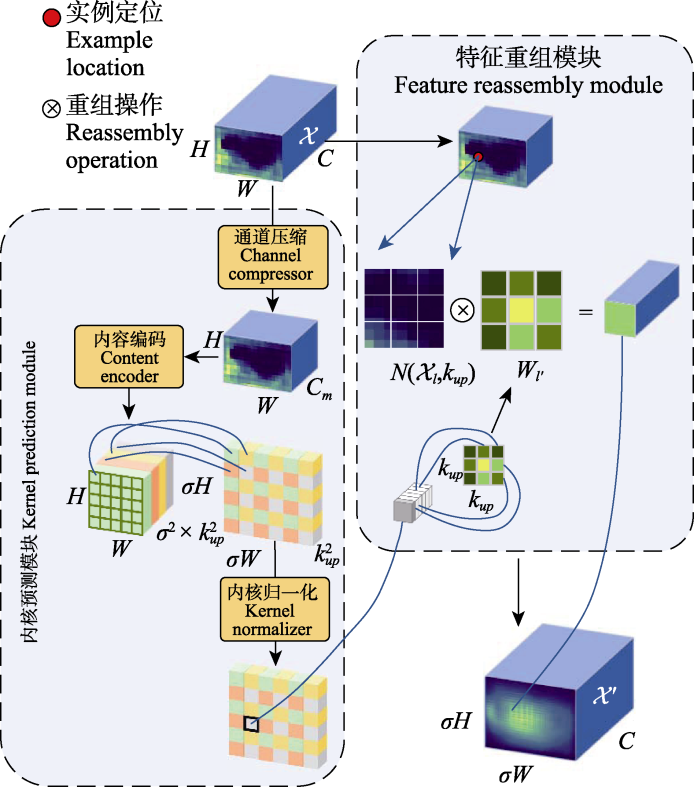
图4 CARAFE模型结构。$\mathcal{X}$: 输入特征图; C: 特征图的通道数; H: 输入特征图的高; W: 输入特征图的宽; Cm: 降维后的通道数; σ: 上采样率; σ 2 × k u p 2: 内容编码后的输出通道数; k u p 2: 预测的上采样核大小; l: 原始位置; l°: 目标位置; $N\left(\mathcal{X}_{l}, \boldsymbol{k}_{u p}\right)$: 以原始位置为中心的正方形区域; Wl°:重组上采样核; $\mathcal{X}^{\prime}$: 输出特征图; σH: 输出特征图的高; σW: 输出特征图的宽。
Fig. 4 CARAFE model structure. $\mathcal{X}$, Input feature map; C, The number of channels of the input feature map; H, The height of the input feature map; W, The width of the input feature map; Cm, Number of channels after channel compression; σ, Upsample ratio; σ 2 × k u p 2, Number of output channels after content encoding; k u p 2, Predicted upsampling kernel size; l, Source location; l°, Target location; $N\left(\mathcal{X}_{l}, \boldsymbol{k}_{u p}\right)$, A square area centered on the source position; Wl°, Reassembly upsampling kernel; $\mathcal{X}^{\prime}$, Output feature map; σH, The height of the output feature map; σW, The width of the output feature map.
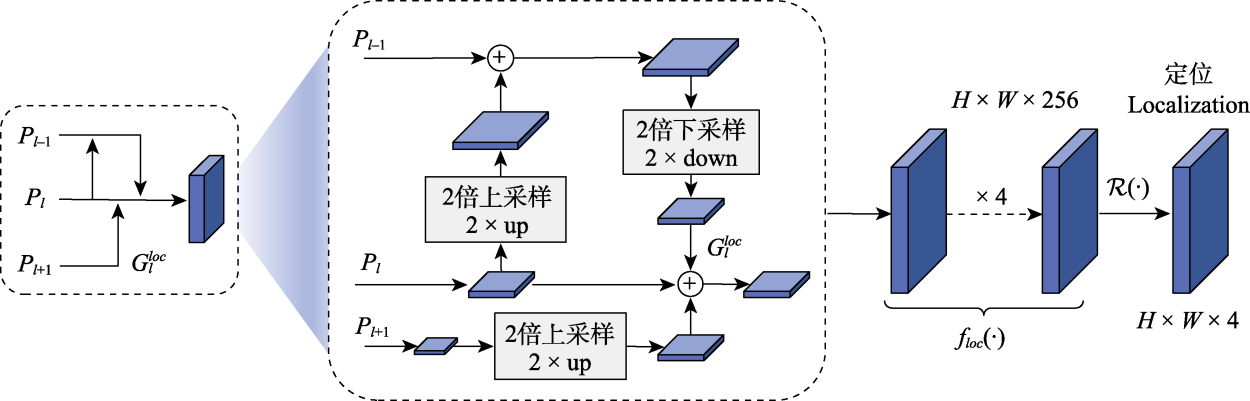
图5 细节保留编码结构。Pl: 第l层金字塔层级的特征图; Gloc l: 定位的特征图; H: 特征图的高; W: 特征图的宽; floc(·): 定位的特征投影函数; $\mathcal{R}(\cdot)$: 定位的最终层。
Fig. 5 Detail-preserving encoding structure. Pl, The feature map of the l-th pyramid level; Gloc l, The feature map for localization; H, The height of the feature map; W, The width of the feature map; floc(·), The feature projection functions for localization; $\mathcal{R}(\cdot)$, The final layer in localization.
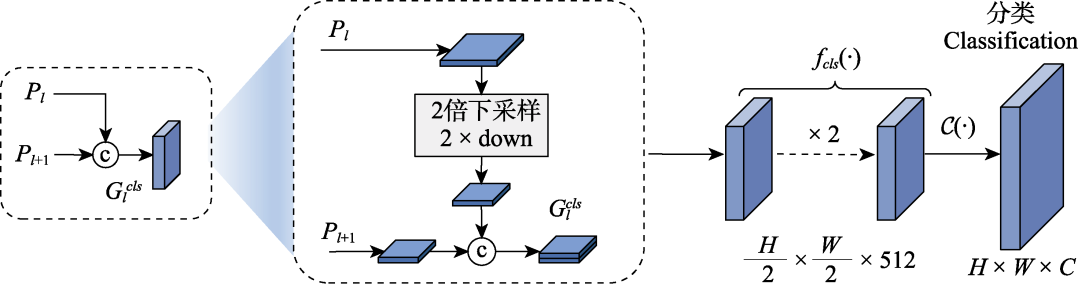
图6 语义上下文编码结构。Pl: 第l层金字塔层级的特征图; Gcls l: 分类的特征图; H: 特征图的高; W: 特征图的宽; C: 特征图的通道数; fcls(·): 分类的特征投影函数; C(·): 分类的最终层。
Fig. 6 Semantic context encoding structure. Pl, The feature map of the l-th pyramid level; Gcls l, The feature map for localization; H, The height of the feature map; W, The width of the feature map; C, The number of channels of the feature map; fcls(·), The feature projection functions for localization; C(·), The final layer in localization.
| 算法模型 Algorithm model | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5 (%) | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5:0.9 (%) | 参数量 Parameters (×106 M) | 帧率 Frames per second (帧/s) | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC-YOLO | 90.6 | 78.7 | 28.89 | 56 | 本文 This study |
| Faster R-CNN | 67.9 | 45.2 | 28.56 | 16 | Ren et al, |
| SSD | 85.3 | 68.3 | 26.29 | 47 | Liu et al, |
| YOLOv3-tiny | 80.9 | 54.8 | 8.73 | 86 | Adarsh et al, |
| YOLOv4-tiny | 75.1 | 48.6 | 6.06 | 70 | Wang et al, |
| YOLOv5s | 90.2 | 76.3 | 7.09 | 85 | Jocher, |
| YOLOv6n | 76.6 | 67.6 | 4.64 | 67 | Li et al, |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 81.4 | 66.1 | 6.09 | 64 | Wang CY et al, |
| YOLOv8n | 84.9 | 74.5 | 3.01 | 67 | Jocher, |
表1 Comparison of experimental results on the Beijing-28 dataset among different models①(①洪洋 (2022) 森林野火预警的小目标检测算法研究. 硕士学位论文, 电子科技大学, 成都.)
Table 1
| 算法模型 Algorithm model | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5 (%) | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5:0.9 (%) | 参数量 Parameters (×106 M) | 帧率 Frames per second (帧/s) | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC-YOLO | 90.6 | 78.7 | 28.89 | 56 | 本文 This study |
| Faster R-CNN | 67.9 | 45.2 | 28.56 | 16 | Ren et al, |
| SSD | 85.3 | 68.3 | 26.29 | 47 | Liu et al, |
| YOLOv3-tiny | 80.9 | 54.8 | 8.73 | 86 | Adarsh et al, |
| YOLOv4-tiny | 75.1 | 48.6 | 6.06 | 70 | Wang et al, |
| YOLOv5s | 90.2 | 76.3 | 7.09 | 85 | Jocher, |
| YOLOv6n | 76.6 | 67.6 | 4.64 | 67 | Li et al, |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 81.4 | 66.1 | 6.09 | 64 | Wang CY et al, |
| YOLOv8n | 84.9 | 74.5 | 3.01 | 67 | Jocher, |
| 方法 Methods | 模型构成 Model composition | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5 (%) | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC-YOLO | YOLOv5s + CARAFE + TSCODE | 90.6 | 78.7 | 本文 This study |
| 方法1 Method 1 | YOLOv5s | 90.2 | 76.3 | Jocher, |
| 方法2 Method 2 | YOLOv5s + CBAM | 89.9 | 76.2 | Xue et al, |
| 方法3 Method 3 | YOLOv5s + SA | 89.8 | 75.2 | Hao et al, |
| 方法4 Method 4 | YOLOv5s + CA | 89.3 | 74.4 | Zhang et al, |
| 方法5 Method 5 | YOLOv5s + WioUv3 | 89.9 | 76.1 | Zhao et al, |
表2 不同改进YOLOv5s方法在Beijing-28数据集实验结果对比
Table 2 Comparison of experimental results on the Beijing-28 dataset among different improved YOLOv5s methods
| 方法 Methods | 模型构成 Model composition | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5 (%) | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC-YOLO | YOLOv5s + CARAFE + TSCODE | 90.6 | 78.7 | 本文 This study |
| 方法1 Method 1 | YOLOv5s | 90.2 | 76.3 | Jocher, |
| 方法2 Method 2 | YOLOv5s + CBAM | 89.9 | 76.2 | Xue et al, |
| 方法3 Method 3 | YOLOv5s + SA | 89.8 | 75.2 | Hao et al, |
| 方法4 Method 4 | YOLOv5s + CA | 89.3 | 74.4 | Zhang et al, |
| 方法5 Method 5 | YOLOv5s + WioUv3 | 89.9 | 76.1 | Zhao et al, |

图9 YOLOv5s改进前后算法识别效果对比图(漏检情况)
Fig. 9 Comparison of recognition performance between before and after improvement in YOLOv5s (missed detection situations)
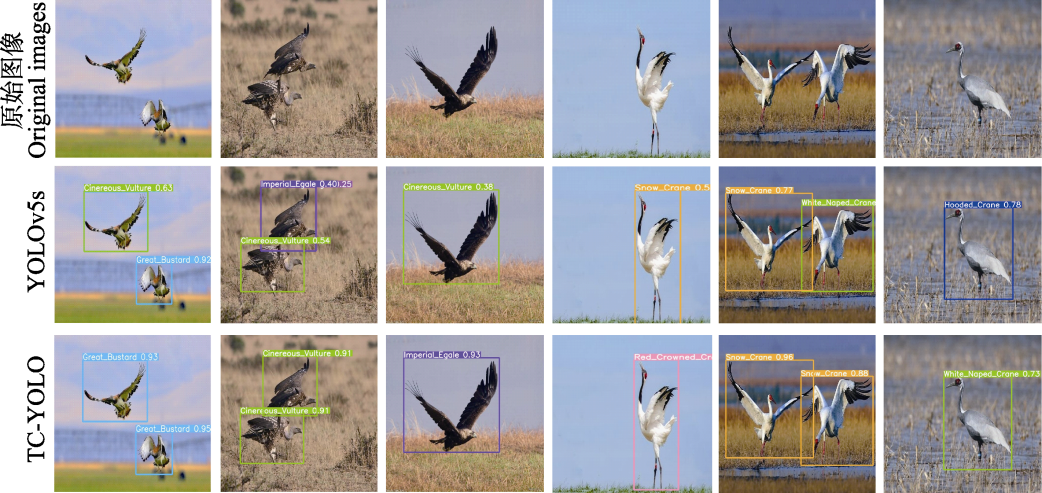

图10 YOLOv5s改进前后算法识别效果对比图(误检情况)
Fig. 10 Comparison of recognition performance between before and after improvement in YOLOv5s (false detection situations)
| 数据集 Datasets | 算法模型 Algorithm model | 精确率 Precision (%) | 召回率 Recall (%) | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5 (%) | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing-28 | YOLOv5s | 86.8 | 87.4 | 90.2 | 76.3 |
| C-YOLO | 87.5 | 88.3 | 90.3 | 77.3 | |
| T-YOLO | 87.3 | 88.1 | 90.2 | 77.4 | |
| TC-YOLO | 89.4 | 89.5 | 90.6 | 78.7 | |
| CUB200-2011 | YOLOv5s | 81.7 | 82.2 | 85.4 | 72.8 |
| C-YOLO | 81.9 | 82.5 | 85.6 | 73.5 | |
| T-YOLO | 84.7 | 82.0 | 85.4 | 74.7 | |
| TC-YOLO | 85.1 | 82.5 | 85.5 | 75.3 |
表3 TC-YOLO模型的消融实验结果
Table 3 Ablation experimental results of TC-YOLO model
| 数据集 Datasets | 算法模型 Algorithm model | 精确率 Precision (%) | 召回率 Recall (%) | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5 (%) | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing-28 | YOLOv5s | 86.8 | 87.4 | 90.2 | 76.3 |
| C-YOLO | 87.5 | 88.3 | 90.3 | 77.3 | |
| T-YOLO | 87.3 | 88.1 | 90.2 | 77.4 | |
| TC-YOLO | 89.4 | 89.5 | 90.6 | 78.7 | |
| CUB200-2011 | YOLOv5s | 81.7 | 82.2 | 85.4 | 72.8 |
| C-YOLO | 81.9 | 82.5 | 85.6 | 73.5 | |
| T-YOLO | 84.7 | 82.0 | 85.4 | 74.7 | |
| TC-YOLO | 85.1 | 82.5 | 85.5 | 75.3 |
| 算法模型 Algorithm model | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5 (%) | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
| TC-YOLO | 61.0 | 42.1 | 本文 This study |
| Faster R-CNN* | 59.2 | 39.8 | Ren et al, |
| SSD* | 43.1 | 25.1 | Liu et al, |
| YOLOv4-tiny* | 42.1 | 24.9 | Wang et al, |
| YOLOv5s* | 56.8 | 37.4 | Jocher, |
| YOLOv6n* | 52.7 | 37.0 | Li et al, |
| YOLOv7-tiny* | 52.8 | 35.2 | Wang CY et al, |
| YOLOv8n* | 52.6 | 37.3 | Jocher, |
表4 不同模型在MS COCO数据集上的实验结果对比(*代表论文中的实验结果)
Table 4 Comparison of experimental results on the MS COCO dataset among different models (* represents experimental results in the paper)
| 算法模型 Algorithm model | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5 (%) | 平均精度均值 mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
| TC-YOLO | 61.0 | 42.1 | 本文 This study |
| Faster R-CNN* | 59.2 | 39.8 | Ren et al, |
| SSD* | 43.1 | 25.1 | Liu et al, |
| YOLOv4-tiny* | 42.1 | 24.9 | Wang et al, |
| YOLOv5s* | 56.8 | 37.4 | Jocher, |
| YOLOv6n* | 52.7 | 37.0 | Li et al, |
| YOLOv7-tiny* | 52.8 | 35.2 | Wang CY et al, |
| YOLOv8n* | 52.6 | 37.3 | Jocher, |
| [1] | Adarsh P, Rathi P, Kumar M (2020) YOLO v3-Tiny: Object detection and recognition using one stage improved model. In: 2020 International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), pp. 687-694. IEEE, Coimbatore. |
| [2] | Alqaysi H, Fedorov I, Qureshi FZ, O’Nils M (2021) A temporal boosted YOLO-based model for birds detection around wind farms. Journal of Imaging, 7, 227. |
| [3] |
Cai JM, He PY, Yang ZP, Li LY, Zhao QJ, Pan F (2023) A deep feature fusion-based method for bird sound recognition and its interpretability analysis. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23087. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[蔡建民, 何培宇, 杨智鹏, 李露莹, 赵启军, 潘帆 (2023) 基于深度特征融合的鸟鸣识别方法及其可解释性分析. 生物多样性, 31, 23087.]
DOI |
|
| [4] | Cheng G, Yuan X, Yao XW, Yan KB, Zeng QH, Xie XX, Han JW (2023) Towards large-scale small object detection: Survey and benchmarks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 45, 13467-13488. |
| [5] | Feng CJ, Zhong YJ, Gao Y, Scott MR, Huang WL (2021) Tood: Task-aligned one-stage object detection. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 3490-3499. IEEE, Montreal. |
| [6] | Ge Z, Liu ST, Wang F, Li ZM, Sun J (2021) Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv, doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2107.08430. |
| [7] | Gou JP, Xiong XS, Yu BS, Du L, Zhan YB, Tao DC (2023) Multi-target knowledge distillation via student self- reflection. International Journal of Computer Vision, 131, 1857-1874. |
| [8] | Hao WL, Zhang L, Han M, Zhang K, Li FZ, Yang GQ, Liu ZY (2023) YOLOv5-SA-FC: A novel pig detection and counting method based on shuffle attention and focal complete intersection over union. Animals, 13, 3201. |
| [9] | Hong YY, Lu XL, Zhao HP (2021) Bird diversity and interannual dynamics in different habitats of agricultural landscape in Huanghuai Plain. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 2045-2055. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [洪咏怡, 卢训令, 赵海鹏 (2021) 黄淮平原农业景观不同生境鸟类多样性特征及年际动态. 生态学报, 41, 2045-2055.] | |
| [10] | Huang RR, Wang Y, Yang HZ (2022) Cross-layer attention network for fine-grained visual categorization. arXiv, doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2210.08784. |
| [11] | Jocher G (2022) YOLOv5 Release v6.0. https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/tag/v6.0. (accessed on 2022-11-22) |
| [12] | Jocher G (2023) YOLOv8 Release v8.1.0. https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/releases/tag/v8.1.0. (accessed on 2023-01-10) |
| [13] | Lei JL, Gao SH, Rasool MA, Fan R, Jia YF, Lei GC (2023) Optimized small waterbird detection method using surveillance videos based on YOLOv7. Animals, 13, 1929. |
| [14] | Li CY, Li LL, Jiang HL, Weng KH, Geng YF, Li L, Ke ZD, Li QY, Cheng M, Nie WQ, Li YD, Zhang B, Liang YF, Zhou LY, Xu XM, Chu XX, Wei XX, Wei XL (2022) YOLOv6: A single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications. arXiv, doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2209.02976. |
| [15] | Lin TY, Dollár P, Girshick R, He KM, Hariharan B, Belongie S (2017) Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2117-2125. IEEE, Honolulu. |
| [16] | Lin TY, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, Dollár P, Zitnick C (2014) Microsoft coco:Common objects in context. In: 2014 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 740-755. Springer International Publishing, Zurich. |
| [17] | Liu S, Qi L, Qin HF, Shi JP, Jia JY (2018) Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 8759-8768. IEEE, Salt Lake City, UT. |
| [18] | Liu SL, Li YL, Qu JY, Wu RB (2022) Airport UAV and birds detection based on deformable DETR. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2253, 012024. |
| [19] | Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu CY, Berg AC (2016) SSD:Single shot MultiBox detector. In: 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 21-37. Springer International Publishing, Amsterdam. |
| [20] | Mokany K, Ware C, Harwood TD, Schmidt RK, Ferrier S (2022) Habitat-based biodiversity assessment for ecosystem accounting in the Murray-Darling Basin. Conservation Biology, 36, e13915. |
| [21] | Ren SQ, He KM, Girshick R, Sun J (2016) Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 39, 1137-1149. |
| [22] | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net:Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), pp. 234-241. Springer International Publishing, Munich. |
| [23] | Roth K, Vinyals O, Akata Z (2022) Non-isotropy regularization for proxy-based deep metric learning. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7420-7430. IEEE, New Orleans. |
| [24] | Song GL, Liu Y, Wang XG (2020) Revisiting the sibling head in object detector. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 11563-11572. IEEE, Seattle. |
| [25] | Sun HB, He XT, Peng YX (2022) Sim-trans: Structure information modeling transformer for fine-grained visual categorization. In: 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM), pp. 5853-5861. ACM, Lisboa. |
| [26] | Wah C, Branson S, Welinder P, Perona P, Belongie S (2011) The Caltech-UCSD Birds-200-2011 Dataset, Technical Report CNS-TR-2011-001. California Institute of Technology, California, USA. |
| [27] | Wang CY, Bochkovskiy A, Liao HYM (2021) Scaled-yolov4: Scaling cross stage partial network. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 13029-13038. IEEE, Nashville. |
| [28] | Wang CY, Bochkovskiy A, Liao HYM (2023) YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7464-7475. IEEE, Vancouver. |
| [29] | Wang JQ, Chen K, Xu R, Liu ZW, Loy CC, Lin DH (2019) Carafe: Content-aware reassembly of features. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 3007-3016. IEEE, Seoul. |
| [30] | Wang JX, Su YH, Yao JH, Liu M, Du YR, Wu X, Huang L, Zhao MH (2023) Apple rapid recognition and processing method based on an improved version of YOLOv5. Ecological Informatics, 77, 102196. |
| [31] | Wang K, Yang F, Chen ZB, Chen YX, Zhang Y (2023) A fine-grained bird classification method based on attention and decoupled knowledge distillation. Animals, 13, 264. |
| [32] |
Wu KY, Ruan WD, Zhou DF, Chen QC, Zhang CY, Pan XY, Yu S, Liu Y, Xiao RB (2023) Syllable clustering analysis-based passive acoustic monitoring technology and its application in bird monitoring. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22370. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[吴科毅, 阮文达, 周棣锋, 陈庆春, 张承云, 潘新园, 余上, 刘阳, 肖荣波 (2023) 基于音节聚类分析的被动声学监测技术及其在鸟类监测中的应用. 生物多样性, 31, 22370.]
DOI |
|
| [33] | Wu Y, Chen YP, Yuan L, Liu ZC, Wang LJ, Li HZ, Fu Y (2020) Rethinking classification and localization for object detection. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 10186-10195. IEEE, Seattle. |
| [34] | Xiang WB, Song ZY, Zhang GX, Wu XC (2022) Birds detection in natural scenes based on improved faster RCNN. Applied Sciences, 12, 6094. |
| [35] |
Xiao ZS, Xiao WH, Wang TM, Li S, Lian XM, Song DZ, Deng XQ, Zhou QH (2022) Wildlife monitoring and research using camera-trapping technology across China: The current status and future issues. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22451. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[肖治术, 肖文宏, 王天明, 李晟, 连新明, 宋大昭, 邓雪琴, 周岐海 (2022) 中国野生动物红外相机监测与研究: 现状及未来. 生物多样性, 30, 22451.]
DOI |
|
| [36] | Xie JJ, Zhong YJ, Zhang JG, Liu S, Ding CQ, Triantafyllopoulos A (2023a) A review of automatic recognition technology for bird vocalizations in the deep learning era. Ecological Informatics, 73, 101927. |
| [37] | Xie JJ, Zhong YJ, Zhang JG, Zhang CC, Schuller BW (2023b) A weakly supervised spatial group attention network for fine-grained visual recognition. Applied Intelligence, 53, 23301-23315. |
| [38] |
Xie ZF, Li DZ, Sun HX, Zhang AM (2023) Deep learning techniques for bird chirp recognition task. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22308. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[谢卓钒, 李鼎昭, 孙海信, 张安民 (2023) 面向鸟鸣声识别任务的深度学习技术. 生物多样性, 31, 22308.]
DOI |
|
| [39] | Xue ZY, Lin HF, Wang F (2022) A small target forest fire detection model based on YOLOv5 improvement. Forests, 13, 1332. |
| [40] | Yang CHY, Huang ZH, Wang NY (2022) QueryDet: Cascaded sparse query for accelerating high-resolution small object detection. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 13668-13677. IEEE, New Orleans. |
| [41] | Zhang H, Shao FM, He XH, Zhang ZH, Cai YG, Bi SH (2023) Research on object detection and recognition method for UAV aerial images based on improved YOLOv5. Drones, 7, 402. |
| [42] | Zhao Q, Wei HL, Zhai XY (2023) Improving tire specification character recognition in the YOLOv5 network. Applied Sciences, 13, 7310. |
| [43] | Zhao YF, Li J, Chen XW, Tian YH (2021) Part-guided relational transformers for fine-grained visual recognition. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 30, 9470-9481. |
| [44] | Zhu JY, Park T, Isola P, Efros AA (2017) Unpaired image-to- image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 2223-2232. IEEE, Venice. |
| [45] | Zhu SM (2024) The Number of Terrestrial Wild Animals in the City Has Increased to 612 Species. (in Chinese) |
| [朱松梅 (2024) 全市陆生野生动物种类增至612种.] https://www.beijing.gov.cn/ywdt/yaowen/202404/t20240414_3617537.html. (accessed on 2024-04-14) | |
| [46] | Zhuang JY, Qin Z, Yu H, Chen XC (2023) Task-Specific context decoupling for object detection. arXiv, doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2303.01047. |
| [47] | Zou C, Liang YQ (2021) Bird detection of transmission line based on YOLO V3 algorithm. Computer Applications and Software, 38(10), 164-167, 241. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邹聪, 梁永全 (2021) 基于YOLO V3算法的输电线路鸟类检测. 计算机应用与软件, 38(10), 164-167, 241.] |
| [1] | 巴苏艳, 赵春艳, 刘媛, 方强. 通过虫体花粉识别构建植物‒传粉者网络: 人工模型与AI模型高度一致[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24088-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn