



生物多样性 ›› 2010, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (2): 182-187. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.195 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2010.195
刘琳1, 孙磊1,*( ), 张瑞英1, 姚娜2, 李潞滨2,*
), 张瑞英1, 姚娜2, 李潞滨2,*
收稿日期:2009-09-15
接受日期:2009-12-16
出版日期:2010-03-20
发布日期:2010-03-20
通讯作者:
孙磊,李潞滨
基金资助:
Lin Liu1, Lei Sun1,*( ), Ruiying Zhang1, Na Yao2, Lubin Li2,*
), Ruiying Zhang1, Na Yao2, Lubin Li2,*
Received:2009-09-15
Accepted:2009-12-16
Online:2010-03-20
Published:2010-03-20
Contact:
Lei Sun, Lubin Li
摘要:
植物内生细菌可通过分泌吲哚乙酸(Indole-3-acetic acid, IAA)等方式促进植物生长。本研究以温室盆栽春兰(Cymbidium goeringii)为材料, 采用分离培养方法对春兰根中可分泌IAA的内生细菌多样性进行了研究。从春兰根组织中共分离纯化得到了256株内生细菌, 其中57株具有分泌IAA的能力, 占总菌数的22.3%。根据ARDRA(amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis)及16S rDNA系统发育分析结果, 将57株内生细菌划分为25个组, 分属于6大类群, 分别为变形菌门的α-变形菌纲(35.1%)、γ-变形菌纲(14.0%)和β-变形菌纲(8.8%)、厚壁菌门(33.3%)、放线菌门(7.0%)及拟杆菌门(1.8%)。其中变形菌门的α-变形菌纲和厚壁菌门为优势类群, 类芽孢杆菌属(Paenibacillus)为优势菌属, 且为高产IAA的主体菌属。另外, 测序结果显示有4个菌株的序列与已知细菌的最高序列相似性低于97.0%, 可能为潜在的新种或新属。研究结果表明春兰根中分泌IAA的内生细菌具有丰富的多样性。这一结果可为研究和开发植物促生细菌提供基础资料。
刘琳, 孙磊, 张瑞英, 姚娜, 李潞滨 (2010) 春兰根中可分泌吲哚乙酸的内生细菌多样性. 生物多样性, 18, 182-187. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.195.
Lin Liu, Lei Sun, Ruiying Zhang, Na Yao, Lubin Li (2010) Diversity of IAA-producing endophytic bacteria isolated from the roots of Cymbidium goeringii. Biodiversity Science, 18, 182-187. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.195.
| 类群 Group | 分型测序菌株Isolate | 菌株数 No.of strains | IAA分泌量 IAA production (mg·L-1· (OD600)-1) | 最相近菌种(登录号) Nearest strain (accession no.) | 序列相似性Similarity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-变形菌纲Alphaproteobacteria (35.1%) | R209 | 7 | 1.0#-26.3# | Rhizobium miluonense (EF061096) | 100.0 |
| R128-2 | 1 | 5.8# | R. huautlense (AF025852) | 97.1 | |
| R141 | 1 | 3.6# | R. giardinii (U86344) | 97.3 | |
| R224-3 | 4 | 10.0#-43.1# | Skermanella aerolata (DQ672568) | 90.1 | |
| R120 | 2 | 23.9*-47.1# | Devosia insulae (EF012357) | 97.8 | |
| R90 | 2 | 0.5*-1.7# | Sphingopyxis macrogoltabida (AB372254) | 99.8 | |
| R83-1 | 1 | 2.3# | Altererythrobacter epoxidivorans (DQ304436) | 96.3 | |
| R178 | 1 | 14.9# | Mesorhizobium opportunistum (AY601515) | 97.5 | |
| R191 | 1 | 25.8* | Agrobacterium tumefaciens (EU445236) | 100.0 | |
| β-变形菌纲Betaproteobacteria (8.8%) | R94 | 2 | 0.7#-5.3# | Variovorax paradoxus (AJ420329) | 99.0 |
| R199 | 1 | 1.9# | V. soli (DQ432053) | 98.4 | |
| R163 | 1 | 18.9# | Burkholderia caribensis (Y17009) | 99.1 | |
| R235-1 | 1 | 13.1* | Herbaspirillum chlorophenolicum (NR_024804) | 99.4 | |
| γ-变形菌纲 Gammaproteobacteria (14.0%) | R215-2 | 7 | 10.1*-14.6# | Dyella yeojuensis (DQ181549) | 100.0 |
| R192 | 1 | 3.3* | Pseudoxanthomonas japonensis (AB008507) | 99.7 | |
| 厚壁菌门 Firmicutes (33.33%) | R138 | 11 | 1.1*-114.8# | Paenibacillus agaridevorans (NR_025490) | 98.0 |
| R172 | 4 | 37.6#-44.0# | P. contaminans (EF626690) | 94.6 | |
| R12-2 | 2 | 26.3#-26.4# | P. alkaliterrae (AY960748) | 96.3 | |
| R59 | 1 | 7.7# | Bacillus aerophilus (AJ831844) | 100.0 | |
| R95 | 1 | 11.6# | B. niabensis (DQ176422) | 99.8 | |
| 放线菌门 Actinobacteria (7.0%) | R73-1 | 1 | 1.7# | Nocardioides aquiterrae (AF529063) | 98.3 |
| R100 | 1 | 15.3# | Brachybacterium paraconglomeratum (AJ415377) | 100.0 | |
| R152 | 1 | 9.6# | Arthrobacter niigatensis (AB248526) | 100.0 | |
| R205 | 1 | 1.6# | Streptomyces albaduncus (AY999757) | 98.7 | |
| 拟杆菌门 Bacteroidetes (1.8%) | R156-1 | 1 | 2.1* | Chitinophaga terrae (AB267724) | 97.4 |
表1 分泌IAA的春兰根内生细菌的16S rDNA序列相似性分析
Table 1 Identity analysis of the 16S rDNA partial sequences of IAA-producing endophytic bacteria fromCymbidium goeringii roots
| 类群 Group | 分型测序菌株Isolate | 菌株数 No.of strains | IAA分泌量 IAA production (mg·L-1· (OD600)-1) | 最相近菌种(登录号) Nearest strain (accession no.) | 序列相似性Similarity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-变形菌纲Alphaproteobacteria (35.1%) | R209 | 7 | 1.0#-26.3# | Rhizobium miluonense (EF061096) | 100.0 |
| R128-2 | 1 | 5.8# | R. huautlense (AF025852) | 97.1 | |
| R141 | 1 | 3.6# | R. giardinii (U86344) | 97.3 | |
| R224-3 | 4 | 10.0#-43.1# | Skermanella aerolata (DQ672568) | 90.1 | |
| R120 | 2 | 23.9*-47.1# | Devosia insulae (EF012357) | 97.8 | |
| R90 | 2 | 0.5*-1.7# | Sphingopyxis macrogoltabida (AB372254) | 99.8 | |
| R83-1 | 1 | 2.3# | Altererythrobacter epoxidivorans (DQ304436) | 96.3 | |
| R178 | 1 | 14.9# | Mesorhizobium opportunistum (AY601515) | 97.5 | |
| R191 | 1 | 25.8* | Agrobacterium tumefaciens (EU445236) | 100.0 | |
| β-变形菌纲Betaproteobacteria (8.8%) | R94 | 2 | 0.7#-5.3# | Variovorax paradoxus (AJ420329) | 99.0 |
| R199 | 1 | 1.9# | V. soli (DQ432053) | 98.4 | |
| R163 | 1 | 18.9# | Burkholderia caribensis (Y17009) | 99.1 | |
| R235-1 | 1 | 13.1* | Herbaspirillum chlorophenolicum (NR_024804) | 99.4 | |
| γ-变形菌纲 Gammaproteobacteria (14.0%) | R215-2 | 7 | 10.1*-14.6# | Dyella yeojuensis (DQ181549) | 100.0 |
| R192 | 1 | 3.3* | Pseudoxanthomonas japonensis (AB008507) | 99.7 | |
| 厚壁菌门 Firmicutes (33.33%) | R138 | 11 | 1.1*-114.8# | Paenibacillus agaridevorans (NR_025490) | 98.0 |
| R172 | 4 | 37.6#-44.0# | P. contaminans (EF626690) | 94.6 | |
| R12-2 | 2 | 26.3#-26.4# | P. alkaliterrae (AY960748) | 96.3 | |
| R59 | 1 | 7.7# | Bacillus aerophilus (AJ831844) | 100.0 | |
| R95 | 1 | 11.6# | B. niabensis (DQ176422) | 99.8 | |
| 放线菌门 Actinobacteria (7.0%) | R73-1 | 1 | 1.7# | Nocardioides aquiterrae (AF529063) | 98.3 |
| R100 | 1 | 15.3# | Brachybacterium paraconglomeratum (AJ415377) | 100.0 | |
| R152 | 1 | 9.6# | Arthrobacter niigatensis (AB248526) | 100.0 | |
| R205 | 1 | 1.6# | Streptomyces albaduncus (AY999757) | 98.7 | |
| 拟杆菌门 Bacteroidetes (1.8%) | R156-1 | 1 | 2.1* | Chitinophaga terrae (AB267724) | 97.4 |
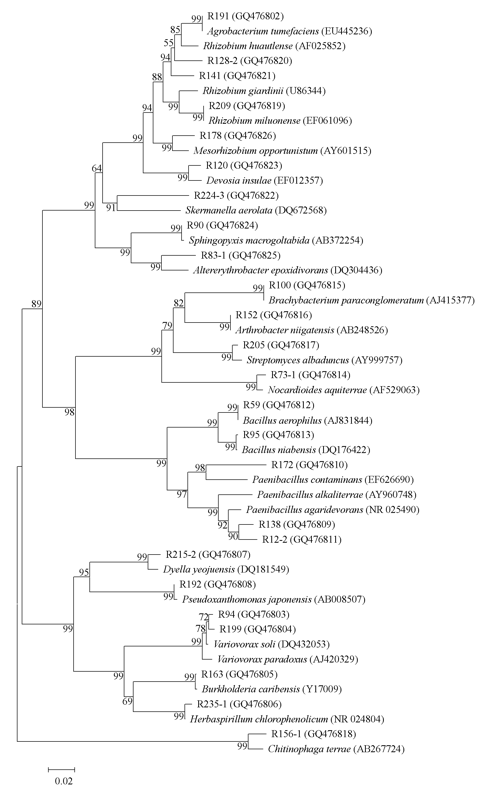
图1 可分泌IAA的春兰根内生细菌的16S rDNA系统发育树(图中分枝上数字为1,000次抽样的Bootstrap百分值, 括号内为序列登录号)
Fig. 1 A dendrogram based on the 16S rDNA partial sequences of IAA-producing endophytic bacteria from the roots of Cymbidium goeringii. Bootstrap values (percent) calculated from 1,000 resamplings are shown at branch nodes. GenBank accession numbers are given in parentheses.
| [1] |
Aagot N, Nybroe O, Nielsen P, Johnsen K (2001) An altered Pseudomonas diversity is recovered from soil by using nutrient-poor Pseudomonas-selective soil extract media . Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67,5233-5239.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] | Arshad M, Frankenberger WT (1991) Microbial production of plant hormones. Plant and Soil, 133,1-8. |
| [3] |
Berge O, Guinebretière MH, Achouak W, Normand P, Heulin T (2002) Paenibacillus graminis sp. nov. and Paenibacillus odorifer sp. nov., isolated from plant roots, soil and food . International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 52,607-616.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] | Currah RS, Zelmer CD, Hambleton S, Richardson KA (1997) Fungi from orchid mycorrhizas. In: Orchid Biology: Reviews and Perspectives. VII (eds Arditti J, Pridgeon AM),pp.117-170. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht. |
| [5] | Da Mota FF, Gomes EA, Seldin L (2008) Auxin production and detection of the gene coding for the Auxin Efflux Carrier (AEC) protein in Paenibacillus polymyxa. Journal of Microbiology, 46,257-264. |
| [6] | Dias ACF, Costa FEC, Andreote FD, Lacava PT, Teixeira MA, Assumpção LC, Araújo WL, João L, Azevedo JL, Melo IS (2008) Isolation of micropropagated strawberry endophytic bacteria and assessment of their potential for plant growth promotion. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 25,189-195. |
| [7] | Du RQ (杜荣骞) (1999) Biostatistics (生物统计学). Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [8] |
Edwards U, Rogall T, Blöker H, Emde M, Böttger EC (1989) Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes: characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Research, 17,7843-7853.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] | Glickmann E, Dessaux Y (1995) A critical examination of the specificity of the salkowski reagent for indolic compounds produced by phytopathogenic bacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2,793-796. |
| [10] | Kado CI (1991) Plant pathogenic bacteria. In: The Prokaryotes (eds Balows A, Truper HG, Dworkin M, Schleifer KH)pp.659-674. Springer-Verlag, New York. |
| [11] | Kamneva SV, Muronets EM (1999) Genetic control of the processes of interaction of bacteria with plants in associations. Genetika, 35,1480-1494. |
| [12] |
Kawai M, Matsutera E, Kanda H, Yamaguchi N, Tani K, Nasu M (2002) 16S ribosomal DNA-based analysis of bacterial diversity in purified water used in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes by PCR and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68,699-704.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
Kuklinsky-Sobral J, Araujo WL, Mendes R, Geraldi IO, Pizzirani-Kleiner AA, Azevedo JL (2004) Isolation and characterization of soybean-associated bacteria and their potential for plant growth promotion. Environmental Microbiology, 6,1244-1251.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] | Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics (eds Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M),pp.115-175. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, United Kingdom. |
| [15] | Li JH, Wang ET, Chen WF, Chen WX (2008) Genetic diversity and potential for promotion of plant growth detected in nodule endophytic bacteria of soybean grown in Heilongjiang Province of China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40,238-246. |
| [16] | Libbert E, Risch H (1969) Interactions between plants and epiphytic bacteria regarding their auxin metabolism.V. Isolation and identification of the IAA-producing and destroying bacteria from pea plants. Physiologia Plantarum, 22,51-58. |
| [17] | Lodewyckx C, Vangronsveld J, Porteous F, Moore ERB, Taghavi S, Mezgeay M, van der Lelie D (2002) Endophytic bacteria and their potential application. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 86,583-606. |
| [18] |
Long HH, Schmidt DD, Baldwin IT (2008) Native bacterial endophytes promote host growth in a species-specific manner; phytohormone manipulations do not result in common growth responses. PLoS ONE, 3,e2702.
URL PMID |
| [19] |
Mendes R, Pizzirani-Kleiner AA, Araujo WL, Raaijmakers JM (2007) Diversity of cultivated endophytic bacteria from sugarcane: genetic and biochemical characterization of Burkholderia cepacia complex isolates . Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73,7259-7267.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] | Rasmussen HN (2002) Recent developments in the study of orchid mycorrhiza. Plant and Soil, 244,149-163. |
| [21] | Sarwar M, Frankenberger WT (1994) Tryptophan dependent biosynthesis of auxins in soil. Plant and Soil, 160,97-104. |
| [22] | Selim S, Negrel J, Govaerts C, Gianinazzi S, Tuinen DV (2005) Isolation and partial characterization of antagonistic peptides produced by Paenibacillus sp. strain B2 isolated from the sorghum mycorrhizosphere . Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71,6501-6507. |
| [23] | Sun L (孙磊), Bi XB (毕晓宝), Li LB (李潞滨), Liu L (刘琳), Han JG (韩继刚), Yang K (杨凯) (2009) Primary research on the isolation method of root endophytic bacteria of Cymbidium goeringii. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei (河北农业大学学报), 32,42-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] |
Taghavi B, Garafola C, Monchy S, Newman L, Hoffman A, Weyens N, Barac T, Vangronsveld J,van der Lelie D (2009) Genome survey and characterization of endophytic bacteria exhibiting a beneficial effect on growth and development of poplar trees. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75,748-757.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] |
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24,1596-1599.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Tsavkelova EA, Cherdyntseva TA, Netrusov AI (2005) Auxin production by bacteria associated with orchid roots. Microbiology, 74,46-53. |
| [27] |
Tsavkelova EA, Cherdyntseva TA, Botina SG, Netrusov AI (2007) Bacteria associated with orchid roots and microbial production of auxin. Microbiological Research, 162,69-76.
URL PMID |
| [1] | 何建瑜, 刘雪珠, 赵荣涛, 吴方伟, 王健鑫. 东海表层沉积物纯培养与非培养细菌多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(1): 28-37. |
| [2] | 朱德锐, 刘建, 韩睿, 沈国平, 杨芳, 龙启福, 刘德立. 青海湖嗜盐微生物系统发育与种群多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2012, 20(4): 495-504. |
| [3] | 罗明, 韩剑, 蒋平安, 武红旗. 新疆罗布泊地区可培养嗜盐细菌多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(3): 288-295. |
| [4] | 徐琳, 徐佳洁, 刘巧莉, 谢瑞美, 韦革宏. 西北部分地区苦马豆根瘤菌的遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(1): 69-75. |
| [5] | 张建萍, 董乃源, 余浩滨, 周勇军, 陆永良, 耿锐梅, 余柳青. 应用16S rDNA-RFLP方法分析宁夏地区稻田土壤细菌的多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2008, 16(6): 586-592. |
| [6] | 滕齐辉, 曹慧, 崔中利, 王英, 孙波, 郝红涛, 李顺鹏. 太湖地区典型菜地土壤微生物16S rDNA的PCR-RFLP分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(4): 345-351. |
| [7] | 樊昊心, Derek J. Fairley, Christopher Rensing, Ian L. Pepper, 王革娇. 中国和美国原始土壤中非高温泉古菌的发现和鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(3): 181-187. |
| [8] | 东秀珠, 沈德龙, 辛玉华. 16S rDNA同源性所揭示的双歧杆菌与有关细菌的亲缘关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2000, 08(2): 146-152. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn