



Biodiv Sci ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 23273. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023273 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023273
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Haidi Qi1, Dinghai Zhang1,*( ), Lishan Shan2, Guopeng Chen2, Bo Zhang3
), Lishan Shan2, Guopeng Chen2, Bo Zhang3
Received:2023-07-31
Accepted:2023-10-18
Online:2023-11-20
Published:2023-11-09
Contact:
* E-mail: Haidi Qi, Dinghai Zhang, Lishan Shan, Guopeng Chen, Bo Zhang. Advances in the mechanisms of entomopathogenic fungi infecting insect hosts and the defense strategies of insects[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23273.
| 门 Phylum | 纲 Class | 目 Order | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 子囊菌门 Ascomycota | 散囊菌纲 Eurotiomycetes | 爪甲团囊菌目 Onygenales | 圆球囊菌科 Ascosphaeraceae | 球囊菌属 Ascosphaera | 蜜蜂球囊菌 A. apis |
| 粪壳菌纲 Sordariomycetes | 肉座菌目 Hypocreales | 线虫草科 Ophiocordycipitaceae | 线虫草属 Ophiocordyceps | 偏侧蛇虫草菌 O. unilateralis | |
| 麦角菌科 | 白僵菌属 Beauveria | 球孢白僵菌 B. bassiana | |||
| Clavicipitaceae | 座壳孢属 Aschersonia | 粉虱座壳孢 A. aleyroids | |||
| 绿僵菌属 Metarhizium | 金龟子绿僵菌 M. anisopliae | ||||
| 莱氏绿僵菌 M. rileyi | |||||
| 虫霉门 Entomophthoromycota | 虫霉纲 Entomophthoromycetes | 虫霉目 Entomophthorales | 虫霉科 Entomophthoraceae | 虫霉属 Entomophthora | 蝇虫霉 E. muscae |
| 团孢霉属 Massospora | 蝉团孢霉 M. cicadina | ||||
| 拟虫疫霉属 Eryniopsis | 萤拟虫疫霉 E. lampyridarum | ||||
| 噬虫霉属 Entomophaga | 蝗噬虫霉 E. grylli | ||||
| 虫疠霉属 Pandora | 新蚜虫疠霉 P. neoaphidis |
Table1 Insect pathogenic fungi and their classification
| 门 Phylum | 纲 Class | 目 Order | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 子囊菌门 Ascomycota | 散囊菌纲 Eurotiomycetes | 爪甲团囊菌目 Onygenales | 圆球囊菌科 Ascosphaeraceae | 球囊菌属 Ascosphaera | 蜜蜂球囊菌 A. apis |
| 粪壳菌纲 Sordariomycetes | 肉座菌目 Hypocreales | 线虫草科 Ophiocordycipitaceae | 线虫草属 Ophiocordyceps | 偏侧蛇虫草菌 O. unilateralis | |
| 麦角菌科 | 白僵菌属 Beauveria | 球孢白僵菌 B. bassiana | |||
| Clavicipitaceae | 座壳孢属 Aschersonia | 粉虱座壳孢 A. aleyroids | |||
| 绿僵菌属 Metarhizium | 金龟子绿僵菌 M. anisopliae | ||||
| 莱氏绿僵菌 M. rileyi | |||||
| 虫霉门 Entomophthoromycota | 虫霉纲 Entomophthoromycetes | 虫霉目 Entomophthorales | 虫霉科 Entomophthoraceae | 虫霉属 Entomophthora | 蝇虫霉 E. muscae |
| 团孢霉属 Massospora | 蝉团孢霉 M. cicadina | ||||
| 拟虫疫霉属 Eryniopsis | 萤拟虫疫霉 E. lampyridarum | ||||
| 噬虫霉属 Entomophaga | 蝗噬虫霉 E. grylli | ||||
| 虫疠霉属 Pandora | 新蚜虫疠霉 P. neoaphidis |
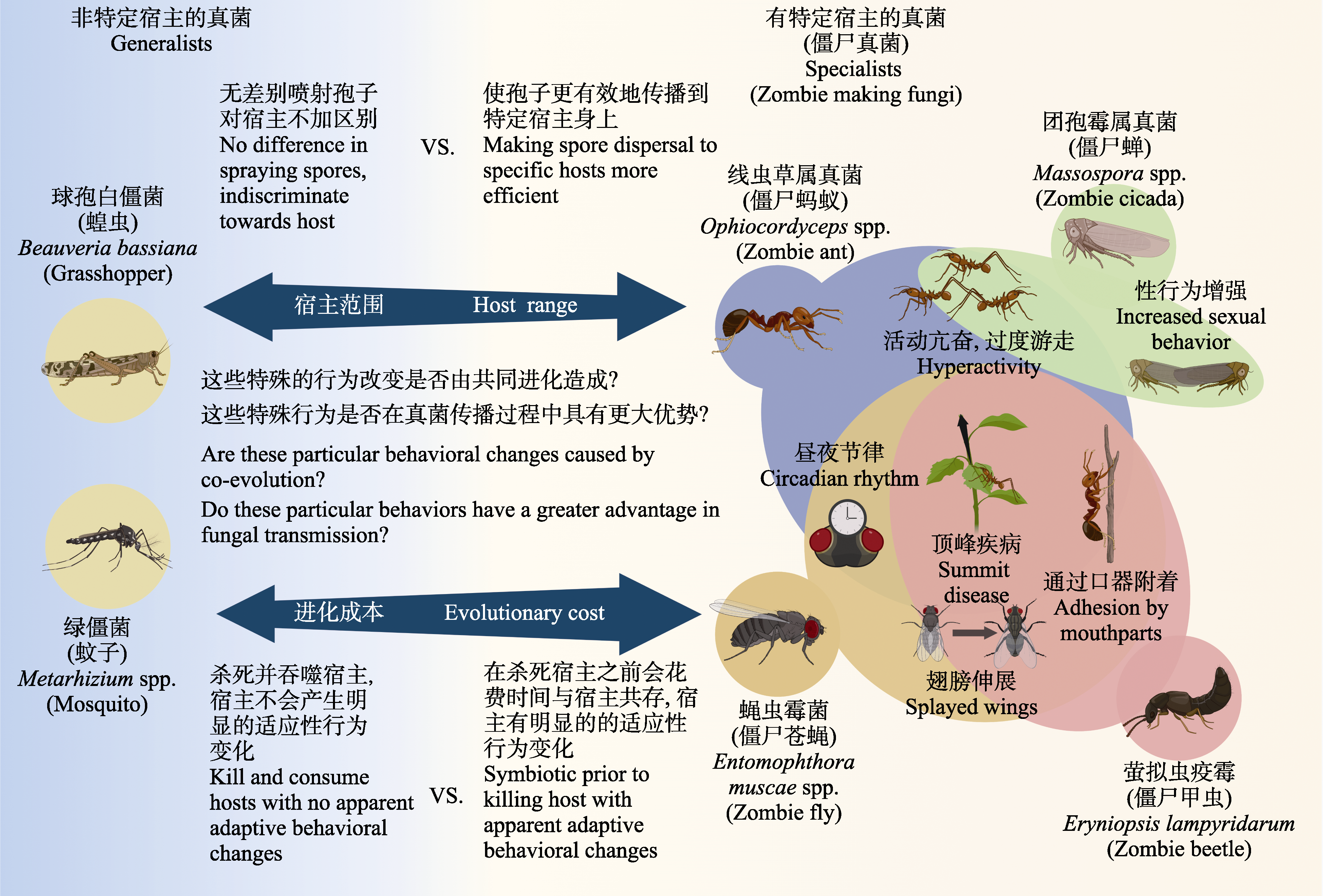
Fig. 2 Differences in the process of host infection by different types of fungi and the overlapping behavior of “zombie making fungi” hosts. Adapted by de Bekker et al (2021).
| [1] |
Altincicek B, Berisha A, Mukherjee K, Spengler B, Römpp A, Vilcinskas A (2009) Identification of collagen IV derived danger/alarm signals in insect immunity by nanoLC- FTICRMS. Biological Chemistry, 390, 1303-1311.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Andersen SB, Ferrari M, Evans HC, Elliot SL, Boomsma JJ, Hughes DP (2012) Disease dynamics in a specialized parasite of ant societies. PLoS ONE, 7, e36352. |
| [3] |
Andersen SB, Gerritsma S, Yusah KM, Mayntz D, Hywel-Jones NL, Billen J, Boomsma JJ, Hughes DP (2009) The life of a dead ant: The expression of an adaptive extended phenotype. The American Naturalist, 174, 424-433.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Aronstein KA, Murray KD (2010) Chalkbrood disease in honey bees. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 103, S20-S29. |
| [5] | Audoin V (1837) Nouvelles expe´riences sur la nature de la maladie contagieuse qui attaque les Vers a` soie, et qu’on de´signe sous le nom de Muscardine. Annales des Sciences Naturelles, 8, 257-270. (in French) |
| [6] |
Bamisile BS, Akutse KS, Siddiqui JA, Xu YJ (2021) Model application of entomopathogenic fungi as alternatives to chemical pesticides: Prospects, challenges, and insights for next-generation sustainable agriculture. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12, 741804.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Barelli L, Padilla-Guerrero IE, Bidochka MJ (2011) Differential expression of insect and plant specific adhesin genes, Mad1 and Mad2, in Metarhizium robertsii. Fungal Biology, 115, 1174-1185.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Bilgo E, Lovett B, St. Leger RJ, Sanon A, Dabiré RK, Diabaté A (2018) Native entomopathogenic Metarhizium spp. from Burkina Faso and their virulence against the malaria vector Anopheles coluzzii and non-target insects. Parasites & Vectors, 11, 209. |
| [9] |
Blum MS (1992) Ant venoms: Chemical and pharmacological properties. Journal of Toxicology: Toxin Reviews, 11, 115-164.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Bojke A, Tkaczuk C, Stepnowski P, Gołębiowski M (2018) Comparison of volatile compounds released by entomopathogenic fungi. Microbiological Research, 214, 129-136.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Boomsma JJ, Jensen AB, Meyling NV, Eilenberg J (2014) Evolutionary interaction networks of insect pathogenic fungi. Annual Review of Entomology, 59, 467-485.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Boyce GR, Gluck-Thaler E, Slot JC, Stajich JE, Davis WJ, James TY, Cooley JR, Panaccione DG, Eilenberg J, De Fine Licht HH, Macias AM, Berger MC, Wickert KL, Stauder CM, Spahr EJ, Maust MD, Metheny AM, Simon C, Kritsky G, Hodge KT, Humber RA, Gullion T, Short DPG, Kijimoto T, Mozgai D, Arguedas N, Kasson MT (2019) Psychoactive plant- and mushroom-associated alkaloids from two behavior modifying cicada pathogens. Fungal Ecology, 41, 147-164.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Brütsch T, Chapuisat M (2014) Wood ants protect their brood with tree resin. Animal Behaviour, 93, 157-161.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Bundey S, Raymond S, Dean P, Roberts SK, Dillon RJ, Charnley AK (2003) Eicosanoid involvement in the regulation of behavioral fever in the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 52, 183-192.
PMID |
| [15] |
Carruthers RI, Larkin TS, Firstencel H, Feng ZD (1992) Influence of thermal ecology on the mycosis of a rangeland grasshopper. Ecology, 73, 190-204.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Carruthers RI, Ramos ME, Larkin TS, Hostetter DL, Soper RS (1997) The entomophaga grylli (Fresenius) Batko species complex: Its biology, ecology, and use for biological control of pest grasshoppers. The Memoirs of the Entomological Society of Canada, 129, 329-353.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Charnley AK St. Leger RJ (1991) The role of cuticle-degrading enzymes in fungal pathogenesis in insects. In: TheFungal Spore and Disease Initiation in Plants and Animals (ColeGT,eds Hoch HC), pp.267-286. Springer, Boston, MA. |
| [18] | Chen ZH, Chen K, Xu L, Liu Q, Zhang YJ, Shi LM, Peng XY, Chen JF (2022) Species diversity of entomogenous fungi for 4 types of field ecosystems in Baoshan City in Western Yunnan Province. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 35, 209-216. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈自宏, 陈凯, 徐玲, 柳青, 张云娇, 石龙敏, 彭兴艳, 陈家富 (2022) 滇西保山地区4种农田生态系统土壤中虫生真菌物种多样性. 西南农业学报, 35, 209-216.] | |
| [19] |
Chung TY, Sun PF, Kuo JI, Lee YI, Lin CC, Chou JY (2017) Zombie ant heads are oriented relative to solar cues. Fungal Ecology, 25, 22-28.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Cooley JR, Marshall DC, Hill KBR (2018) A specialized fungal parasite (Massospora cicadina) hijacks the sexual signals of periodical cicadas (Hemiptera: Cicadidae: Magicicada). Scientific Reports, 8, 1432.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Cremer S, Armitage-Sophie AO, Schmid-Hempel P (2007) Social immunity. Current Biology, 17, R693-R702. |
| [22] | Culliney TW (2014) Crop Losses to Arthropods: Integrated Pest Management. Springer, Dordrecht. |
| [23] | de Bekker C, Beckerson WC, Elya C (2021) Mechanisms behind the madness: How do zombie-making fungal entomopathogens affect host behavior to increase transmission? mBio, 12, e01872-21. |
| [24] | de Bekker C, Das B (2022) Hijacking time: How Ophiocordyceps fungi could be using ant host clocks to manipulate behavior. Parasite Immunology, 44, e12909. |
| [25] |
de Bekker C, Ohm RA, Evans HC, Brachmann A, Hughes DP (2017) Ant-infecting Ophiocordyceps genomes reveal a high diversity of potential behavioral manipulation genes and a possible major role for enterotoxins. Scientific Reports, 7, 12508.
DOI |
| [26] |
de Bekker C, Ohm RA, Loreto RG, Sebastian A, Albert I, Merrow M, Brachmann A, Hughes DP (2015) Gene expression during zombie ant biting behavior reflects the complexity underlying fungal parasitic behavioral manipulation. BMC Genomics, 16, 620.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
de Bekker C, Quevillon LE, Smith PB, Fleming KR, Ghosh D, Patterson AD, Hughes DP (2014) Species-specific ant brain manipulation by a specialized fungal parasite. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 14, 166.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
de Faria MR, Wraight SP (2007) Mycoinsecticides and Mycoacaricides: A comprehensive list with worldwide coverage and international classification of formulation types. Biological Control, 43, 237-256.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
de Roode JC, Lefèvre T (2012) Behavioral immunity in insects. Insects, 3, 789-820.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Ebani VV, Mancianti F (2021) Entomopathogenic fungi and bacteria in a veterinary perspective. Biology, 10, 479.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Elliot SL, Blanford S, Thomas MB (2002) Host-pathogen interactions in a varying environment:Temperature, behavioural fever and fitness. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 269, 1599-1607. |
| [32] | Elya C, Lok TC, Spencer QE, McCausland H, Martinez CC, Eisen M (2018) Robust manipulation of the behavior of Drosophila melanogaster by a fungal pathogen in the laboratory. eLife, 7, 34414. |
| [33] | Fernández-Marín H, Zimmerman JK, Rehner SA, Wcislo WT (2006) Active use of the metapleural glands by ants in controlling fungal infection. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 273, 1689-1695. |
| [34] |
Fronza E, Specht A, Heinzen H, de Barros NM (2017) Metarhizium (Nomuraea) rileyias biological control agent. Biocontrol Science and Technology, 27, 1243-1264.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Gao Q, Jin K, Ying SH, Zhang YJ, Xiao GH, Shang YF, Duan ZB, Hu X, Xie XQ, Zhou G, Peng GX, Luo ZB, Huang W, Wang B, Fang WG, Wang SB, Zhong Y, Ma LJ, St. Leger RJ, Zhao GP, Pei Y, Feng MG, Xia YX, Wang CS (2011) Genome sequencing and comparative transcriptomics of the model entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium anisopliae and M. acridum. PLoS Genetics, 7, e1001264. |
| [36] |
Gilliam M, Taber S III, Richardson GV (1983) Hygienic behavior of honey bees in relation to chalkbrood disease. Apidologie, 14, 29-39.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Glare T, Caradus J, Gelernter W, Jackson T, Keyhani N, Köhl J, Marrone P, Morin L, Stewart A (2012) Have biopesticides come of age? Trends in Biotechnology, 30, 250-258. |
| [38] |
Greenfield BPJ, Lord AM, Dudley ED, Butt TM (2014) Conidia of the insect pathogenic fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae, fail to adhere to mosquito larval cuticle. Royal Society Open Science, 1, 140193.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Griesch J, Vilcinskas A (1998) Proteases released by entomopathogenic fungi impair phagocytic activity, attachment and spreading of plasmatocytes isolated from haemolymph of the greater wax moth Galleria mellonella. Biocontrol Science and Technology, 8, 517-531.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Gryganskyi AP, Mullens BA, Gajdeczka MT, Rehner SA, Vilgalys R, Hajek AE (2017) Hijacked: Co-option of host behavior by entomophthoralean fungi. PLoS Pathogens, 13, e1006274. |
| [41] |
Hajek AE, Steinkraus DC, Castrillo LA (2018) Sleeping beauties: Horizontal transmission via resting spores of species in the entomophthoromycotina. Insects, 9, 102.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Hibbett DS, Binder M, Bischoff JF, Blackwell M, Cannon PF, Eriksson OE, Huhndorf S, James T, Kirk PM, Lücking R, Thorsten Lumbsch H, Lutzoni F, Matheny PB, McLaughlin DJ, Powell MJ, Redhead S, Schoch CL, Spatafora JW, Stalpers JA, Vilgalys R, Aime MC, Aptroot A, Bauer R, Begerow D, Benny GL, Castlebury LA, Crous PW, Dai YC, Gams W, Geiser DM, Griffith GW, Gueidan C, Hawksworth DL, Hestmark G, Hosaka K, Humber RA, Hyde KD, Ironside JE, Kõljalg U, Kurtzman CP, Larsson KH, Lichtwardt R, Longcore J, Miądlikowska J, Miller A, Moncalvo JM, Mozley-Standridge S, Oberwinkler F, Parmasto E, Reeb V, Rogers JD, Roux C, Ryvarden L, Sampaio JP, Schüßler A, Sugiyama J, Thorn RG, Tibell L, Untereiner WA, Walker C, Wang Z, Weir A, Weiss M, White MM, Winka K, Yao YJ, Zhang N (2007) A higher-level phylogenetic classification of the fungi. Mycological Research, 111, 509-547.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
Holder DJ, Keyhani NO (2005) Adhesion of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria (Cordyceps) bassiana to substrata. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 5260-5266.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Holder DJ, Kirkland BH, Lewis MW, Keyhani NO (2007) Surface characteristics of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria (Cordyceps) bassiana. Microbiology, 153, 3448-3457.
DOI PMID |
| [45] | Hou CX, Qin GX, Liu T, Guo XJ (2012) Advances in defense mechanism of insects against pathogenic fungi. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 40, 11649-11652. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [侯成香, 覃光星, 刘挺, 郭锡杰 (2012) 昆虫对病原真菌的防御机制研究进展. 安徽农业科学, 40, 11649-11652.] | |
| [46] | Hu X, Xiao GH, Zheng P, Shang YF, Su Y, Zhang XY, Liu XZ, Zhan S, St. Leger RJ, Wang CS (2014) Trajectory and genomic determinants of fungal-pathogen speciation and host adaptation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, 16796-16801. |
| [47] |
Hughes DP, Andersen SB, Hywel-Jones NL, Himaman W, Billen J, Boomsma JJ (2011) Behavioral mechanisms and morphological symptoms of zombie ants dying from fungal infection. BMC Ecology, 11, 13.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Hughes DP, Araújo JPM, Loreto RG, Quevillon L, de Bekker C, Evans HC (2016) From so simple a beginning: the evolution of behavioral manipulation by fungi. Advances in Genetics, 94, 437-469.
DOI PMID |
| [49] |
Humber RA (2012) Entomophthoromycota: A new phylum and reclassification for entomophthoroid fungi. Mycotaxon, 120, 477-492.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Ingle YV, Bhosale DN, Karande VD, Bramhankar SB, Mane SS, Paithankar DH, Sadawarte AK (2022) Identification, pathogenesis and compatibility of Aschersonia aleyrodis (Webber) with selected fungicides and insecticides. International Journal of Tropical Insect Science, 42, 2093-2101.
DOI |
| [51] | Inglis DG, Enkerli J, Goettel MS (2012) Manual of techniques in invertebrate pathology. In: LaboratoryTechniques Used for Entomopathogenic Fungi (ed. Lacey LA), pp.189-253. Elsevier, Amsterdam. |
| [52] |
Islam W, Adnan M, Shabbir A, Naveed H, Abubakar YS, Qasim M, Tayyab M, Noman A, Nisar MS, Ali Khan K, Ali H (2021) Insect-fungal-interactions: A detailed review on entomopathogenic fungi pathogenicity to combat insect pests. Microbial Pathogenesis, 159, 105122.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Jensen AB, Thomsen L, Eilenberg J (2006) Value of host range, morphological, and genetic characteristics within the Entomophthora muscae species complex. Mycological Research, 110, 941-950.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Kalsbeek V, Mullens BA, Jespersen JB (2001) Field studies of Entomophthora (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales)— Induced behavioral fever in Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae) in Denmark. Biological Control, 21, 264-273.
DOI URL |
| [55] | Khan S, Somerville D, Frese M, Nayudu M (2020) Environmental gut bacteria in European honey bees (Apis mellifera) from Australia and their relationship to the chalkbrood disease. PLoS ONE, 15, e0238252. |
| [56] | Knight K (2019) Invading fungus forces zombie ant’s death grip. Journal of Experimental Biology, 222, jeb208538. |
| [57] |
Kramm KR, West DF, Rockenbach PG (1982) Termite pathogens: Transfer of the entomopathogen Metarhizium anisopliae between Reticulitermes sp. termites. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 40, 1-6.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Litwin A, Nowak M, Różalska S (2020) Entomopathogenic fungi: Unconventional applications. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 19, 23-42.
DOI |
| [59] |
Liu L, Zhao XY, Tang QB, Lei CL, Huang QY (2019) The mechanisms of social immunity against fungal infections in eusocial insects. Toxins, 11, 244.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Loreto RG, Elliot SL, Freitas-Mayara LR, Pereira TM, Hughes DP (2014) Long-term disease dynamics for a specialized parasite of ant societies: A field study. PLoS ONE, 9, e103516. |
| [61] |
Loreto RG, Hughes DP (2019) The metabolic alteration and apparent preservation of the zombie ant brain. Journal of Insect Physiology, 118, 103918.
DOI URL |
| [62] | Lovett B, Macias A, Stajich JE, Cooley J, Eilenberg J, de Fine Licht HH, Kasson MT (2020) Behavioral betrayal: How select fungal parasites enlist living insects to do their bidding. PLoS Pathogens, 16, e1008598. |
| [63] | Lu HL St. Leger RJ (2016) Insect immunity to entomopathogenic fungi. In: Advancesin Genetics (Lovett BSt.eds Leger RJ), pp. 251-285. Academic Press, Cambridge. |
| [64] | Maina UM, Galadima IB, Gambo FM, Zakaria D (2018) A review on the use of entomopathogenic fungi in the management of insect pests of field crops. Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies, 6, 27-32. |
| [65] |
Małagocka J, Grell MN, Lange L, Eilenberg J, Jensen AB (2015) Transcriptome of an entomophthoralean fungus (Pandora formicae) shows molecular machinery adjusted for successful host exploitation and transmission. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 128, 47-56.
DOI PMID |
| [66] | Mangold CA, Ishler MJ, Loreto RG, Hazen ML, Hughes DP (2019) Zombie ant death grip due to hypercontracted mandibular muscles. Journal of Experimental Biology, 222, jeb200683. |
| [67] |
Mannino MC, Huarte-Bonnet C, Davyt-Colo B, Pedrini N (2019) Is the insect cuticle the only entry gate for fungal infection? Insights into alternative modes of action of entomopathogenic fungi. Journal of Fungi, 5, 33.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Mantzoukas S, Eliopoulos PA (2020) Endophytic entomopathogenic fungi: A valuable biological control tool against plant pests. Applied Sciences, 10, 360.
DOI URL |
| [69] | Moller AP (1993) A fungus infecting domestic flies manipulates sexual behaviour of its host. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 33, 403-407. |
| [70] | Money NP (2016) Spore production, discharge, and dispersal. In: TheFungi (WatkinsonSC, BoddyL,eds Money NP), pp.67-97. Elsevier, Amsterdam. |
| [71] | Morgan ED (2008) Chemical sorcery for sociality: Exocrine secretions of ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecological News, 11, 79-90. |
| [72] | Mullens BA, Rodriguez JL, Meyer JA (1987) An epizootiological study of Entomophthora muscae in muscoid fly populations on Southern California poultry facilities, with emphasis on Musca domestica. Hilgardia, 55, 1-41. |
| [73] |
Oi DH, Pereira RM (1993) Ant behavior and microbial pathogens (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). The Florida Entomologist, 76, 63-74.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Ortiz-Urquiza A, Keyhani NO (2013) Action on the surface: Entomopathogenic fungi versus the insect cuticle. Insects, 4, 357-374.
DOI PMID |
| [75] | Pei XY, Arachchige MNJ, Zhu CH, Wang D (2020) Diversity of entomopathogenic fungi in Western Sichuan Plateau. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 56(8), 73-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [裴晓亚, Arachchige MNJ, 朱晨慧, 王敦 (2020) 川西高原昆虫病原真菌的多样性. 林业科学, 56(8), 73-79.] | |
| [76] |
Pell JK, Pluke R, Clark SJ, Kenward MG, Alderson PG (1997) Interactions between two aphid natural enemies, the entomopathogenic fungus Erynia neoaphidis Remaudière & Hennebert (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales) and the predatory beetle Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 69, 261-268.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Qazi SS, Khachatourians GG (2007) Hydrated conidia of Metarhizium anisopliae release a family of metalloproteases. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 95, 48-59.
DOI URL |
| [78] | Qu S, Wang SB (2018) Interaction of entomopathogenic fungi with the host immune system. Developmental & Comparative Immunology, 83, 96-103. |
| [79] | Raghukumar S (2017) Fungi:Characteristics and classification. In: Fungiin Coastal and Oceanic Marine Ecosystems (ed. Raghukumar S), pp.1-15. Springer, Cham. |
| [80] |
Rajula J, Rahman A, Krutmuang P (2020) Entomopathogenic fungi in Southeast Asia and Africa and their possible adoption in biological control. Biological Control, 151, 104399.
DOI URL |
| [81] | Rohrlich C, Merle I, Mze Hassani I, Verger M, Zuin M, Besse S, Robène I, Nibouche S, Costet L (2018) Variation in physiological host range in three strains of two species of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria. PLoS ONE, 13, e0199199. |
| [82] |
Rosengaus RB, Jordan C, Lefebvre ML, Traniello JFA (1999) Pathogen alarm behavior in a termite: A new form of communication in social insects. Naturwissenschaften, 86, 544-548.
PMID |
| [83] |
Rosengaus RB, Traniello JF (2001) Disease susceptibility and the adaptive nature of colony demography in the dampwood termite Zootermopsis angusticollis. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 50, 546-556.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
Roy HE, Pell JK, Alderson PG (1999) Effects of fungal infection on the alarm response of pea aphids. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 74, 69-75.
PMID |
| [85] |
Roy HE, Pell JK, Clark SJ, Alderson PG (1998) Implications of predator foraging on aphid pathogen dynamics. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 71, 236-247.
PMID |
| [86] |
Roy HE, Steinkraus DC, Eilenberg J, Hajek AE, Pell JK (2006) Bizarre interactions and endgames: Entomopathogenic fungi and their arthropod hosts. Annual Review of Entomology, 51, 331-357.
PMID |
| [87] | Ryder LS, Cruz-Mireles N, Molinari C, Eisermann I, Eseola AB, Talbot NJ (2022) The appressorium at a glance. Journal of Cell Science, 135, jcs259857. |
| [88] |
Santi L, da Silva WOB, Berger M, Guimarães JA, Schrank A, Vainstein MH (2010) Conidial surface proteins of Metarhizium anisopliae: Source of activities related with toxic effects, host penetration and pathogenesis. Toxicon, 55, 874-880.
DOI URL |
| [89] |
Schabel HG (1976) Oral infection of Hylobius pales by Metarrhizium anisopliae. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 27, 377-383.
DOI URL |
| [90] | Scorsetti AC, Jensen AB, López LC, Humber RA (2012) First report of Pandora neoaphidis resting spore formation in vivo in aphid hosts. Fungal Biology, 116, 196-203. |
| [91] | Shang YF, Feng P, Wang CS (2015) Fungi that infect insects: Altering host behavior and beyond. PLoS Pathogens, 11, e1005037. |
| [92] | Sharma A, Sharma S, Yadav PK (2023) Entomopathogenic fungi and their relevance in sustainable agriculture: A review. Cogent Food & Agriculture, 9, 2180857. |
| [93] | Sharma L, Bohra N, Singh RK, Marques G (2019) Potential of entomopathogenic bacteria and fungi. In: Microbes for Sustainable Insect Pest Management: An Eco-friendly Approach, Vol. 1 (eds Khan MA, Ahmad W), pp. 115-149. Springer, Cham. |
| [94] | Sinha KK, Choudhary AK, Kumari P (2016) Entomopathogenic fungi. In: EcofriendlyPest Management for Food Security (ed. Omkar), pp. 475-505. Elsevier, Amsterdam. |
| [95] | Skinner M, Parker BL, Kim JS (2014) Role of entomopathogenic fungi in integrated pest management. In: IntegratedPest Management (RadcliffeEB,eds Hutchison WD), pp.169-191. Elsevier, Amsterdam. |
| [96] |
Speare AT (1921) Massospora cicadina Peck. Mycologia, 13, 72-82.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
Steinkraus DC, Hajek AE, Liebherr JK (2017) Zombie soldier beetles: Epizootics in the goldenrod soldier beetle, Chauliognathus pensylvanicus (Coleoptera: Cantharidae) caused by Eryniopsis lampyridarum (Entomophthoro- mycotina: Entomophthoraceae). Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 148, 51-59.
DOI PMID |
| [98] | Stock SP, Kaya HK, Lacey LA (2009) Field manual of techniques in invertebrate pathology. Journal of Economic Entomology, 102, 1726. |
| [99] |
Toledo AV, Alippi AM, de Remes Lenicov AMM (2011) Growth inhibition of Beauveria bassiana by bacteria isolated from the cuticular surface of the corn leafhopper, Dalbulus maidis and the planthopper, Delphacodes kuscheli, two important vectors of maize pathogens. Journal of Insect Science, 11, 29.
DOI PMID |
| [100] | Tripathi AD, Mishra R, Maurya KK, Singh RB, Wilson DW (2019) Estimates for world population and global food availability for global health. In: TheRole of Functional Food Security in Global Health (ed. Isaza A), pp.3-24. Elsevier, Amsterdam. |
| [101] |
Umaru FF, Simarani K (2022) Efficacy of entomopathogenic fungal formulations against Elasmolomus pallens (Dallas) (Hemiptera: Rhyparochromidae) and their extracellular enzymatic activities. Toxins, 14, 584.
DOI URL |
| [102] | van Seventer JM, Hochberg NS (2017) Principles of infectious diseases: Transmission, diagnosis, prevention, and control. In: International Encyclopedia of Public Health (ed. Quah SR), pp. 22-39. Elsevier, Amsterdam. |
| [103] |
Vega FE (2018) The use of fungal entomopathogens as endophytes in biological control: A review. Mycologia, 110, 4-30.
DOI PMID |
| [104] |
Vega FE, Goettel MS, Blackwell M, Chandler D, Jackson MA, Keller S, Koike M, Maniania NK, Monzón A, Ownley BH, Pell JK, Rangel DEN, Roy HE (2009) Fungal entomopathogens: New insights on their ecology. Fungal Ecology, 2, 149-159.
DOI URL |
| [105] |
Vilcinskas A (2010) Coevolution between pathogen-derived proteinases and proteinase inhibitors of host insects. Virulence, 1, 206-214.
DOI PMID |
| [106] | Vilcinskas A, Jegorov A, Landa Z, Götz P, Matha V (1999) Effects of beauverolide L and cyclosporin A on humoral and cellular immune response of the greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology (Part C): Pharmacology, Toxicology and Endocrinology, 122, 83-92. |
| [107] |
Vilcinskas A, Matha V, Götz P (1997a) Effects of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae and its secondary metabolites on morphology and cytoskeleton of plasmatocytes isolated from the greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella. Journal of Insect Physiology, 43, 1149-1159.
DOI URL |
| [108] |
Vilcinskas A, Matha V, Götz P (1997b) Inhibition of phagocytic activity of plasmatocytes isolated from Galleria mellonella by entomogenous fungi and their secondary metabolites. Journal of Insect Physiology, 43, 475-483.
DOI URL |
| [109] |
Vilcinskas A, Wedde M (2002) Insect inhibitors of metalloproteinases. IUBMB Life, 54, 339-343.
PMID |
| [110] |
Wang CS St. Leger RJ (2007) The MAD 1 adhesin of Metarhizium anisopliae links adhesion with blastospore production and virulence to insects, and the MAD2 adhesin enables attachment to plants. Eukaryotic Cell, 6, 808-816.
DOI URL |
| [111] | Wang J, Zhang K, Zhang X, Liu L, Ning SY, Chen C, Wan Y (2021) Isolation, identification and diversity analysis of entomogenous fungi in Qinba Mountains. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 49, 122-129. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王军, 张琨, 张绪, 刘柳, 宁硕瀛, 陈川, 万一 (2021) 秦巴山区虫生真菌的分离鉴定与多样性分析. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 49, 122-129.] | |
| [112] | Wang LL, Wang H, Xiong Y, Zhou X, Wang J, Wang JH, Wu SR (2022) Research progress on insect-borne fungi for control of crop pests. Journal of Tropical Biology, 13, 309-314. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王露露, 王辉, 熊焰, 周霞, 王军, 王健华, 伍苏然 (2022) 虫生真菌防治农作物害虫的研究进展. 热带生物学报, 13, 309-314.] | |
| [113] | Wang Y, Cui CL, Wang GD, Li YF, Wang SB (2021) Insects defend against fungal infection by employing microRNAs to silence virulence-related genes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 118, e2023802118. |
| [114] |
Watson DW, Mullens BA, Petersen JJ (1993) Behavioral fever response of Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae) to infection by Entomophthora muscae (Zygomycetes: Entomophthorales). Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 61, 10-16.
DOI URL |
| [115] |
White J, Lloyd M (1983) A pathogenic fungus, Massospora cicadina peck (Entomophthorales), in emerging nymphs of periodical cicadas 1 (Homoptera: Cicadidae). Environmental Entomology, 12, 1245-1252.
DOI URL |
| [116] | Will I, Das B, Trinh T, Brachmann A, Ohm RA, Bekker DC (2020) Genetic underpinnings of host manipulation by Ophiocordyceps as revealed by comparative transcriptomics. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics, 10, 2275-2296. |
| [117] | Yassine H, Kamareddine L, Osta MA (2012) The mosquito melanization response is implicated in defense against the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. PLoS Pathogens, 8, e1003029. |
| [118] | Zhao L, Teng Y, Luo YM (2017) Present pollution status and control strategy of pesticides in agricultural soils in China: A review. Soils, 49, 417-427. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明 (2017) 中国农田土壤农药污染现状和防控对策. 土壤, 49, 417-427.] | |
| [119] | Zhao YX, Chen QZ, Du GZ, Chen B (2022) Study on diversity of entomogenous fungi in Pinus kesiya var. langbianensis forest in Lancang County, Yunnan Province. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 53, 2161-2174. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵永鑫, 陈玘喆, 杜广祖, 陈斌 (2022) 云南澜沧县思茅松林虫生真菌多样性研究. 南方农业学报, 53, 2161-2174.] | |
| [120] |
Zurek L, Wes WD, Krasnoff SB, Schal C (2002) Effect of the entomopathogenic fungus, Entomophthora muscae (Zygomycetes: Entomophthoraceae), on sex pheromone and other cuticular hydrocarbons of the house fly, Musca domestica. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 80, 171-176.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()