



Biodiv Sci ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 23079. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023079 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023079
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Next Articles
Fuhua Zhang, Fei Xi, Xinrui Tang, Peng Cen, Shibao Wu( )
)
Received:2023-03-19
Accepted:2023-08-23
Online:2023-10-20
Published:2023-09-18
Contact:
*E-mail: wushibao@163.com
Fuhua Zhang, Fei Xi, Xinrui Tang, Peng Cen, Shibao Wu. The illegal trade network of pangolin meat in Chinese mainland and its implications for the implementation of key interventions[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(10): 23079.
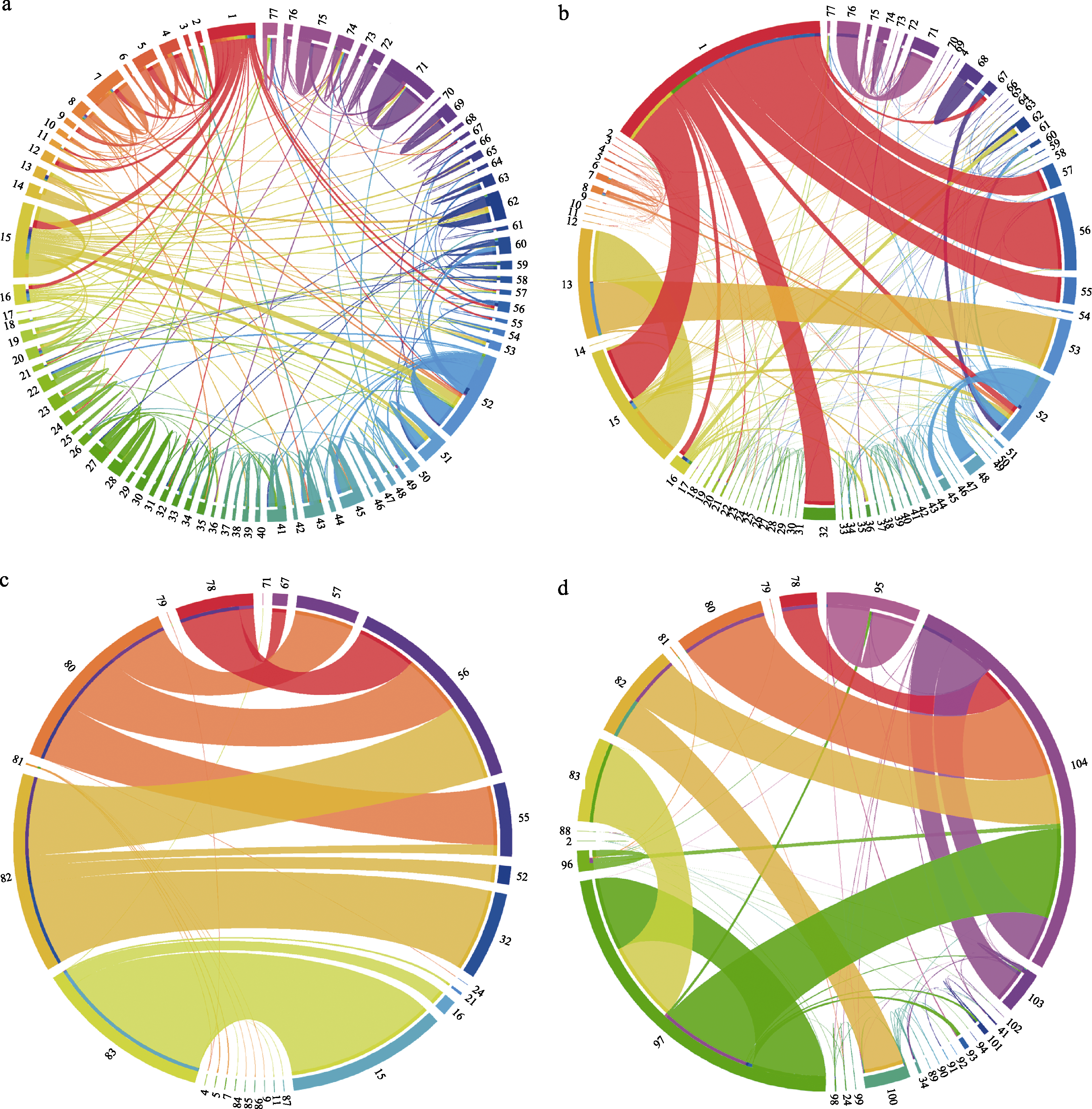
Fig. 3 A circular map of the illegal trade in pangolin meat between different regions seized in China from 2001 to 2021. (a) The number of seized incidences in pangolin meat between regions; (b) Number of seized individuals in pangolin meat between regions; (c) Number of individuals illegally traded into different cities of Chinese mainland from different countries; (d) Number of individuals in illegal trade between different provinces in China and between different provinces in China and other countries. The gap between the connection band and the edge colored ring bar represents the import, the edge colored ring bar and the same color connection band indicates the exit, and the colored ring bar filling the gap between the two represents the destination of the goods export. The width of the connection band indicates the number of seized incidences (a) or individuals (b, c and d). The numbers in the figure represent the cities as follow: 1. Abroad; 2. Chongqing; 3. Liupanshui, Mianyang, Chengdu, Panzhihua; 4. Xishuangbanna; 5. Baoshan; 6. Chuxiong; 7. Dehong; 8. Kunming; 9. Pu’er; 10. Qujing; 11. Wenshan; 12. Lijiang, Nujiang, Dali, Honghe, Lincang; 13. Beihai; 14. Chongzuo; 15. Fangchenggang; 16. Unknown cities in Guangxi, Wuzhou, Hezhou, Baise; 17. Guilin; 18. Liuzhou; 19. Nanning; 20. Qinzhou; 21. Yulin; 22. Ganzhou; 23. Yingtan, Nanchang, Fuzhou (Jiangxi), Shangrao, Ji’an, Jiujiang; 24. Hainan; 25. Jingzhou, Enshi; 26. Unknown cities in Fujian, Putian, Nanping; 27. Fuzhou (Fujian); 28. Longyan; 29. Ningde; 30. Quanzhou; 31. Sanming; 32. Xiamen; 33, Zhangzhou; 34. Beijing; 35. Unknown cities in Shandong, Xi’an, Jilin, Shijiazhuang, Qingdao; 36. Zhengzhou; 37. Changzhou; 38. Suzhou, Taizhou (Jiangsu); 39. Nanjing; 40. Wuxi; 41. Shanghai; 42. Fuyang, Xuancheng, Wuhu; 43. Changsha; 44. Chenzhou; 45. Hengyang; 46. Huaihua; 47. Unknown cities in Hunan, Xiangxi, Yongzhou; 48. Yiyang; 49. Zhuzhou; 50. Dongguan; 51. Foshan; 52. Guangzhou; 53. Unknown cities in Guangdong, Chaozhou, Shantou, Shanwei; 54. Heyuan; 55. Huizhou; 56. Jiangmen; 57. Jieyang; 58. Maoming; 59. Meizhou; 60. Qingyuan; 61. Shaoguan; 62. Shenzhen; 63. Yangjiang; 64. Yunfu; 65. Zhanjiang; 66. Zhaoqing; 67. Zhongshan; 68. Zhuhai; 69. Hangzhou; 70. Jiaxing; 71. Jinhua; 72. Lishui; 73. Ningbo; 74. Quzhou; 75. Shaoxing; 76. Taizhou (Zhejiang); 77. Wenzhou; 78. Indonesia; 79. Laos; 80. Malaysia; 81. Myanmar; 82. Abroad unknown; 83. Vietnam; 84. Honghe; 85. Lincang; 86. Nujiang ; 87. Baise; 88. Sichuan; 89. Jilin; 90. Shandong; 91. Hebei; 92. Shaanxi; 93. Henan; 94. Guizhou; 95. Zhejiang; 96. Yunnan; 97. Guangxi; 98. Jiangxi; 99. Hubei; 100. Fujian; 101. Jiangsu; 102. Anhui; 103. Hunan; 104. Guangdong.
| 序号 No. | 总贸易量中介值 Betw. (ind.) | 贸易个体来源 Borgatti’s source betw. (ind.) | 贸易个体去向 Borgatti’s destination betw. (ind.) | 总案件量中介值 Betw. (inc) | 贸易案件来源 Borgatti’s source betw. (inc.) | 贸易案件去向 Borgatti’s destination betw. (inc.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou |
| 2 | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 衢州 Quzhou | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 佛山 Foshan |
| 3 | 金华 Jinhua | 衢州 Quzhou | 金华 Jinhua | 昆明 Kunming | 衢州 Quzhou | 昆明 Kunming |
| 4 | 昆明 Kunming | 北海 Beihai | 昆明 Kunming | 上海 Shanghai | 上海 Shanghai | 深圳 Shenzhen |
| 5 | 衢州 Quzhou | 昆明 Kunming | 深圳 Shenzhen | 佛山 Foshan | 长沙 Changsha | 衢州 Quzhou |
Table 1 Betweenness centrality of the number of seized individuals and incidences in the illegal trade of pangolin meat in different cities
| 序号 No. | 总贸易量中介值 Betw. (ind.) | 贸易个体来源 Borgatti’s source betw. (ind.) | 贸易个体去向 Borgatti’s destination betw. (ind.) | 总案件量中介值 Betw. (inc) | 贸易案件来源 Borgatti’s source betw. (inc.) | 贸易案件去向 Borgatti’s destination betw. (inc.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou |
| 2 | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 衢州 Quzhou | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 佛山 Foshan |
| 3 | 金华 Jinhua | 衢州 Quzhou | 金华 Jinhua | 昆明 Kunming | 衢州 Quzhou | 昆明 Kunming |
| 4 | 昆明 Kunming | 北海 Beihai | 昆明 Kunming | 上海 Shanghai | 上海 Shanghai | 深圳 Shenzhen |
| 5 | 衢州 Quzhou | 昆明 Kunming | 深圳 Shenzhen | 佛山 Foshan | 长沙 Changsha | 衢州 Quzhou |
| 序号 No. | 总贸易量 Degree value (ind.) | 输入数量 Indegree value (ind.) | 输出数量 Outdegree value (ind.) | 总案件数量 Degree value (inc.) | 输入案件量 Indegree value (inc.) | 输出案件量 Outdegree value (inc.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 江门 Jiangmen | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 防城港 Fangchenggang |
| 2 | 北海 Beihai | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 北海 Beihai | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 佛山 Foshan | 广州 Guangzhou |
| 3 | 江门 Jiangmen | 北海 Beihai | 广州 Guangzhou | 德宏 Dehong | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 德宏 Dehong |
| 4 | 广州 Guangzhou | 厦门 Xiamen | 台州 Taizhou | 昆明 Kunming | 保山 Baoshan | 长沙 Changsha |
| 5 | 厦门 Xiamen | 惠州 Huizhou | 中山 Zhongshan | 佛山 Foshan | 衡阳 Hengyang | 昆明 Kunming |
Table 2 Degree centrality of the number of seized individuals and incidences in the illegal trade of pangolin meat in different cities
| 序号 No. | 总贸易量 Degree value (ind.) | 输入数量 Indegree value (ind.) | 输出数量 Outdegree value (ind.) | 总案件数量 Degree value (inc.) | 输入案件量 Indegree value (inc.) | 输出案件量 Outdegree value (inc.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 江门 Jiangmen | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 防城港 Fangchenggang |
| 2 | 北海 Beihai | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 北海 Beihai | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 佛山 Foshan | 广州 Guangzhou |
| 3 | 江门 Jiangmen | 北海 Beihai | 广州 Guangzhou | 德宏 Dehong | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 德宏 Dehong |
| 4 | 广州 Guangzhou | 厦门 Xiamen | 台州 Taizhou | 昆明 Kunming | 保山 Baoshan | 长沙 Changsha |
| 5 | 厦门 Xiamen | 惠州 Huizhou | 中山 Zhongshan | 佛山 Foshan | 衡阳 Hengyang | 昆明 Kunming |
| 分组 No. | 关键节点 Key players | 破碎化指数 Fragmentation index |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 中国上海 China’s Shanghai | 0.394 |
| 2 | 中国福州、上海 China’s Fuzhou, Shanghai | 0.46 |
| 3 | 中国长沙、广州、昆明 China’s Changsha, Guangzhou, Kunming | 0.511 |
| 4 | 中国防城港、广州、深圳、广西未知城市 China’s Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi | 0.546 |
| 5 | 中国防城港、广州、深圳、广西未知城市; 越南 China’s Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam | 0.583 |
| 6 | 中国防城港、福州、广州、上海、广西未知城市; 越南 China’s Fangchenggang, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Shanghai, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam | 0.771 |
| 7 | 中国长沙、防城港、广州、昆明、衢州、深圳、广西未知城市 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Kunming, Quzhou, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi | 0.886 |
| 8 | 中国长沙、防城港、福州、广州、上海、昆明、广西未知城市; 越南 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Shanghai, Kunming, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam | 0.923 |
| 9 | 中国长沙、防城港、广州、昆明、上海、深圳、广西未知城市; 越南; 马来西亚 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Kunming, Shanghai, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam; Malaysia | 0.943 |
| 10 | 中国长沙、防城港、广州、昆明、上海、深圳、广西未知城市; 越南; 马来西亚; 缅甸 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Kunming, Shanghai, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam; Malaysia; Myanmar | 0.953 |
Table 3 Removal or isolation of the destruction of the illegal trade network of pangolin meat by a group of nodes composed of 1 to 10 cities
| 分组 No. | 关键节点 Key players | 破碎化指数 Fragmentation index |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 中国上海 China’s Shanghai | 0.394 |
| 2 | 中国福州、上海 China’s Fuzhou, Shanghai | 0.46 |
| 3 | 中国长沙、广州、昆明 China’s Changsha, Guangzhou, Kunming | 0.511 |
| 4 | 中国防城港、广州、深圳、广西未知城市 China’s Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi | 0.546 |
| 5 | 中国防城港、广州、深圳、广西未知城市; 越南 China’s Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam | 0.583 |
| 6 | 中国防城港、福州、广州、上海、广西未知城市; 越南 China’s Fangchenggang, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Shanghai, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam | 0.771 |
| 7 | 中国长沙、防城港、广州、昆明、衢州、深圳、广西未知城市 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Kunming, Quzhou, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi | 0.886 |
| 8 | 中国长沙、防城港、福州、广州、上海、昆明、广西未知城市; 越南 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Shanghai, Kunming, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam | 0.923 |
| 9 | 中国长沙、防城港、广州、昆明、上海、深圳、广西未知城市; 越南; 马来西亚 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Kunming, Shanghai, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam; Malaysia | 0.943 |
| 10 | 中国长沙、防城港、广州、昆明、上海、深圳、广西未知城市; 越南; 马来西亚; 缅甸 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Kunming, Shanghai, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam; Malaysia; Myanmar | 0.953 |
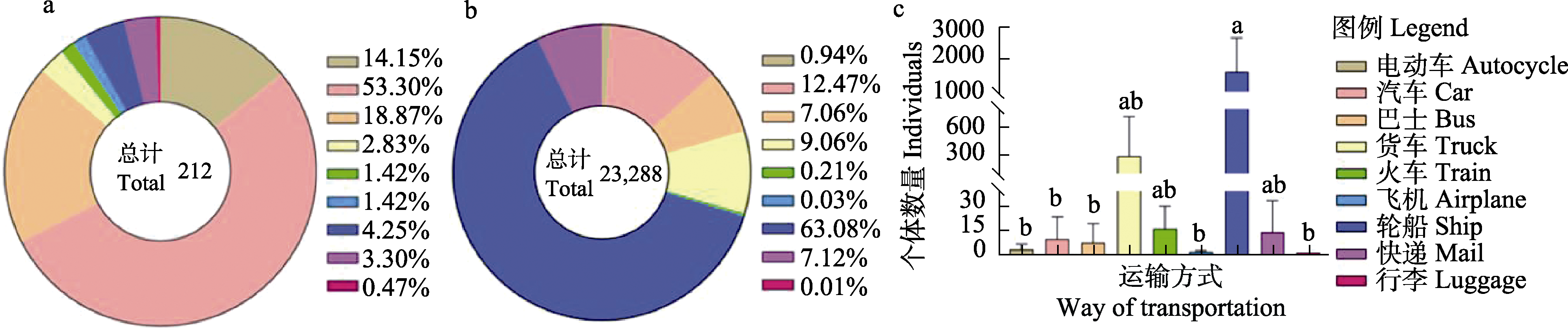
Fig. 4 Different ways of transportation used in the illegal trade of pangolin meat. (a) Frequency of different modes of transportation; (b) The total volume of transportation and; (c) Volume of single transportation mode (mean ± SD). In Fig. (c), there are no significant differences between those labeled with the same letter and those with different letters represent a significant difference.
| [1] | Allen GM (1938) The Mammals of China and Mongolia (Part 1). The American Museum of Natural History, New York. |
| [2] | Borgatti SP (2014) Key Player Program. http://www.analytictech.com/keyplayer/keyplayer.htm. (accessed on 2021-04-15) |
| [3] | Broad S, Mulliken T, Roe D (2014) The nature and extent of legal and illegal trade in wildlife. In: The Trade in Wildlife: Regulation for Conservation (ed. Oldfield S), pp. 25-44. Routledge, London. |
| [4] | Burgess G, Olmedo A, Cerissimo D, Waterman C (2020) Changing consumer behavior for pangolin products. In: Pangolins: Science, Society and Conservation (eds Challender DWS, Nash HC, Waterman C), pp. 349-366. Academic Press, London. |
| [5] | Butts CT (2010) sna: Tools for Social Network Analysis. R package version 2.2-0. |
| [6] | Challender DWS, Waterman C, Baillie JEM (2014a) Scaling up Pangolin Conservation. IUCN SSC Pangolin Specialist Group Conservation Action Plan, Zoological Society of London, London. |
| [7] | Challender DWS, Nguyen VT, Shepherd C, Krishnasamy K, Wang A, Lee B, Panjang E, Fletcher L, Heng S, Seah HMJ, Olsson A, Nguyen TTA, Nguyen VQ, Chung Y (2014b) Manis javanica. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2014. 3. https://www.iucnredlist.org. (accessed on 2015-05-08) |
| [8] |
Challender DWS, Harrop SR, MacMillan DC (2015) Understanding markets to conserve trade-threatened species in CITES. Biological Conservation, 187, 249-259.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Challender DWS, Baillie J, Waterman C, Pietersen D, Nash H, Wicker L, Parker K, Thomson P, Nguyen TV, Hywood L, Shepherd C (2016) On scaling up pangolin conservation. TRAFFIC Bulletin, 28, 19-21. |
| [10] | Challender DWS, Heinrich S, Shepherd CR, Katsis LKD (2020) International trade and trafficking in pangolins, 1900-2019. In: Pangolins: Science, Society and Conservation (eds Challender DWS, Nash HC, Waterman C), pp. 259-276. Academic Press, London. |
| [11] |
Cheng W, Xing S, Bonebrake TC (2017) Recent pangolin seizures in China reveal priority areas for intervention. Conservation Letters, 10, 757-764.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Emogor CA, Ingram DJ, Coad L, Worthington TA, Dunn A, Imong I, Balmford A (2021) The scale of Nigeria’s involvement in the trans-national illegal pangolin trade: Temporal and spatial patterns and the effectiveness of wildlife trade regulations. Biological Conservation, 264, 109365.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Heinrich S, Wittmann TA, Prowse TAA, Ross JV, Delean S, Shepherd CR, Cassey P (2016) Where did all the pangolins go? International CITES trade in pangolin species. Global Ecology and Conservation, 8, 241-253.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Heinrich S, Wittman TA, Ross JV, Shepherd CR, Challender DWS, Cassey P (2017) The global trafficking of pangolins: A comprehensive summary of seizures and trafficking routes from 2010-2015. TRAFFIC, Southeast Asia Regional Office, Petaling Jaya, Selangor, Malaysia. |
| [15] | Heinrich S, Ross JV, Cassey P (2019) Of cowboys, fish and pangolins: US trade in exotic leather. Conservation Science and Practice, 1, e75. |
| [16] | Huang XQ, Newman C, Buesching CD, Shao ML, Ye YC, Liu S, MacDonald DW, Zhou ZM (2021) Prosecution records reveal pangolin trading networks in China, 2014-2019. Zoological Research, 42, 666-670. |
| [17] | Ingram DJ, Cronin DT, Challender DWS, Venditti DM, Gonder MK (2019) Characterising trafficking and trade of pangolins in the Gulf of Guinea. Global Ecology and Conservation, 17, e00576. |
| [18] | IUCN SSC Pangolin Specialist Group (2019) Pangolin. https://pangolinsg.org/pangolins/. (accessed on 2022-04-05) |
| [19] | IUCN (2014) Eating Pangolins to Extinction. http://www.iucnredlist.org/news/eating-pangolins-to-extinction. (accessed on 2014-08-05) |
| [20] |
Mendiratta U, Sheel V, Singh S (2017) Enforcement seizures reveals large-scale illegal trade in India’s tortoise and freshwater turtles. Biological Conservation, 207, 100-105.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Mozer A, Prost S (2023) An introduction to illegal wildlife trade and its effects on biodiversity and society. Forensic Science International: Animals and Enviroments, 3, 100064. |
| [22] | Nellemann C, Henriksen R, Kreilhuber A, Stewart D, Kotsovou M, Raxter P, Mrema E, Barrat S (2016) The Rise of Environmental Crime—A Growing Threat to Natural Resources, Peace, Development and Security. United Nations Environment and Development Forum (UNED), Norwegian Center for Global Analyses, http://www.unep.org/resources/report/rise-environmental-crime-growing-threat-natural-resources-peace-development-and. (accessed on 2021-05-17) |
| [23] | Omifolaji JK, Hughes AC, Ibrahim AS, Zhou J, Zhang S, Ikyaagba ET, Luan X (2022) Dissecting the illegal pangolin trade in China: An insight from seizures data reports. Nature Conservation, 45, 17-38. |
| [24] | Patel NG, Rorres C, Joly DO, Brownstein JS, Boston R, Levy MZ, Smith G (2015) Quantitative methods of identifying the key nodes in the illegal wildlife trade network. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 7948-7953. |
| [25] | R Core Development Team (2014) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. |
| [26] | Riski P (2015) Customs officials seize 455 pangolins hidden in crates of fish in Indonesia. https://news.mongabay.com/2015/07/customs-officials-seize-455-pangolins-hidden-in-crates-of-fish-in-indonesia/. (accessed on 2023-02-05) |
| [27] | Schoppe S, Katsis LKD, Alvarado D, Acosta-Lagrada L (2020) Philippine pangolin Manis culionensis (de Elera, 1915). In: Pangolins: Science, Society and Conservation (eds Challender DWS, Nash HC, Waterman C), pp. 109-122. Academic Press, London. |
| [28] |
Sulaiman MH, Azmi WA, Hassan M, Chong JL (2017) Current updates on the morphological measurements of the Malayan pangolin (Manis javanica). Folia Zoologica, 66, 262-266.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Wang Y, Turvey ST, Leader-Williams N (2020) Knowledge and attitudes about the use of pangolin scale products in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) within China. People and Nature, 2, 903-912.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Wang RH (1985) Need to protect rare wild animals—Pangolins. Sichuan Environment, (2), 78-79. (in Chinese) |
| [王荣怀 (1985) 要保护稀有野生动物——穿山甲. 四川环境, (2), 78-79.] | |
| [31] | Wu SB, Liu NF, Zhang YM, Ma GZ (2004a) Assessment of threatened status of Chinese pangolin. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 10, 456-461. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴诗宝, 刘廼发, 张迎梅, 马广智 (2004a) 中国穿山甲受危状况评估. 应用与环境生物学报, 10, 456-461.] | |
| [32] | Wu SB, Liu NF, Zhang YN, Ma GZ (2004b) Physical measurement and comparison for two species of pangolin. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 24, 361-364. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴诗宝, 刘廼发, 张迎梅, 马广智 (2004b) 两种穿山甲外形量衡度的测定及比较. 兽类学报, 24, 361-364.] | |
| [33] | Wu SB, Ma GZ, Liao QX, Lu KH (2005) Studies of Conservation Biology on Chinese Pangolin (Manis pentadactyla). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [吴诗宝, 马广智, 廖庆祥, 卢开和 (2005) 中国穿山甲(Manis pentadactyla)保护生物学研究. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [34] | Wyatt T (2013) Wildlife Trafficking: A Deconstruction of the Crime, the Victims, and the Offenders. Palgrave Macmillan. London. |
| [35] | Xing S, Bonebrake TC, Cheng W, Zhang M, Ades G, Shaw D, Zhou Y (2020) Meat and medicine:Historic and contemporary use in Asia. In: Pangolins: Science, Society and Conservation (eds Challender DWS, Nash HC, Waterman C), pp. 227-239. Academic Press, London. |
| [36] | Xu J, Yee E, Zhang K (2019) The Pangolin Reports: Trafficked to Extinction. https://globalstory.pangolinreports.com/#lede. (accessed on 2022-04-05) |
| [37] | Yang L, Zou JJ, Zhang FH, Su C, Ma GZ, Wu SB (2010) Estimation of number of individuals of Malayan pangolin with number of their scales. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 31(4), 180-181. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨立, 邹洁建, 张富华, 苏超, 马广智, 吴诗宝 (2010) 用鳞片估计马来穿山甲个体数量. 野生动物, 31(4), 180-181.] | |
| [38] | Yu DY, Gao EH, Lin YH, Qin XY (2001) The status and countermeasures for protection of Chinese pangolin. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 29(2), 79-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [遇达祎, 郜二虎, 林英华, 秦秀云 (2001) 中国穿山甲的现状与保护对策. 东北林业大学学报, 29(2), 79-82.] | |
| [39] |
Zhang M, Gouveia A, Qin T, Quan R, Nijman V (2017) Illegal pangolin trade in northernmost Myanmar and its links to India and China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 10, 23-31.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Zhang F, Yu Y, Wu S, Mahmood A, Yu J, Min Y (2020) Reducing pangolin demand by understanding motivations for human consumption in Guangdong, China. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 8, 574161.
DOI URL |
| [41] | Zhang F, Wang W, Mahmood A, Wu S, Li J, Xu N (2021) Observations of Chinese pangolins (Manis pentadactyla) in mainland China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 26, e01460. |
| [42] | Zhang F, Wu S, Cen P (2022a) The past, present and future of the pangolin in mainland China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 33, e01995. |
| [43] | Zhang F, Tang X, Cen P, Wu S (2022b) Illegal Trade of Pangolins Meat in China [Data set]. Zenodo, https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6809243. |
| [44] |
Zhou ZM, Zhou Y, Newman C, MacDonald DW (2014) Scaling up pangolin protection in China. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 12(2), 97-98.
DOI URL |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn