



Biodiv Sci ›› 2016, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (11): 1203-1219. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015313 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2015313
• Special Feature: Chinese Biodiversity Monitoring and Research Network (Sino BON) • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiangcheng Mi1, Jing Guo1, Zhanqing Hao2, Zongqiang Xie1,*( ), Ke Guo1, Keping Ma1
), Ke Guo1, Keping Ma1
Received:2015-11-12
Accepted:2016-08-10
Online:2016-11-20
Published:2016-12-14
Contact:
Xie Zongqiang
Xiangcheng Mi, Jing Guo, Zhanqing Hao, Zongqiang Xie, Ke Guo, Keping Ma. Chinese forest biodiversity monitoring: scientific foundations and strategic planning[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(11): 1203-1219.
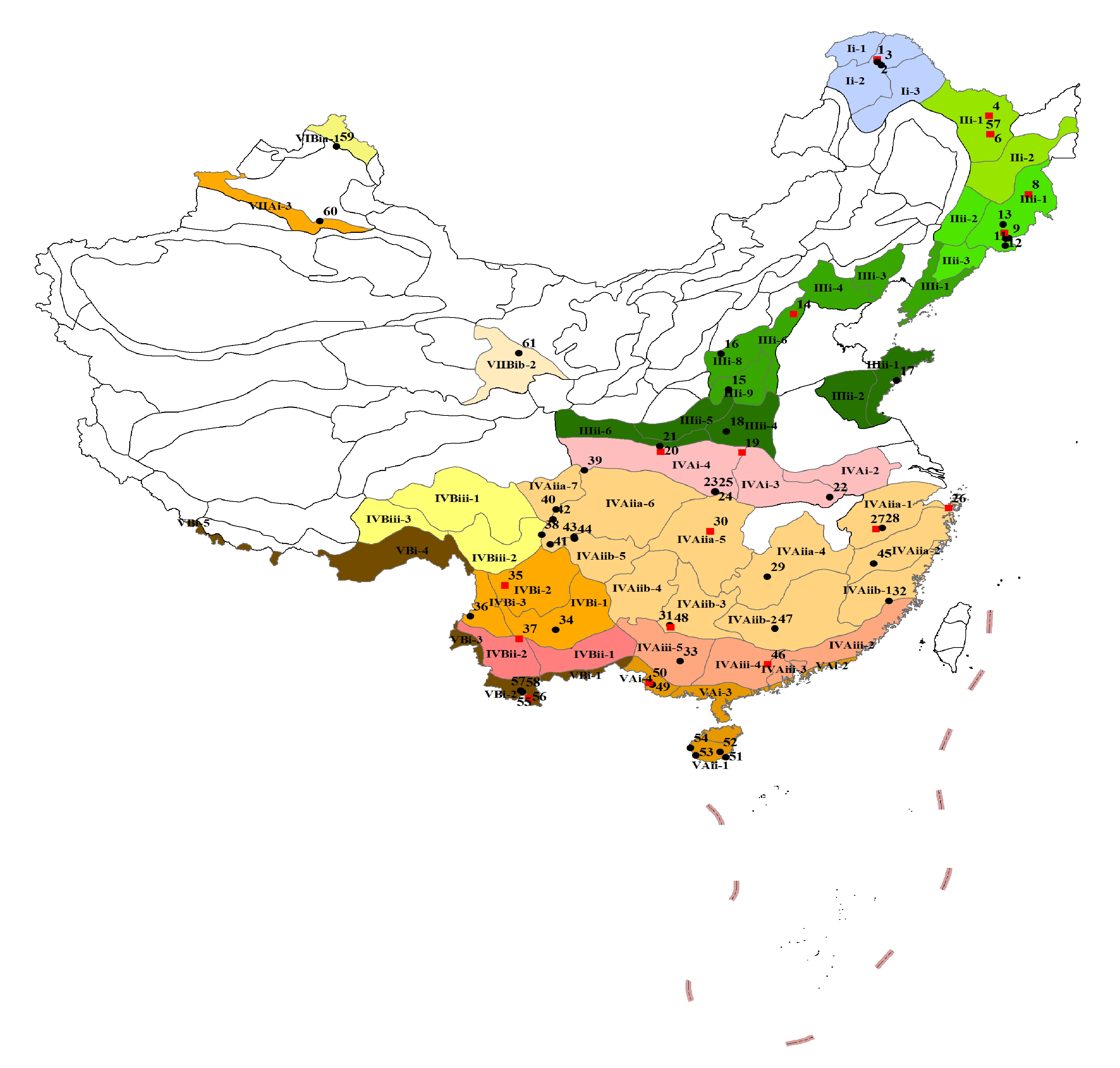
Fig. 1 Samples distribution of representative forest communities in China. The black circles stand for representative forest communities, and the red squares for being constructed or constructed large forest dynamic plots. The code from Ii-1 to VIIBib-2 represents different forest areas in Appendix 2.
| 1 | Ahumada JA, Silva CE, Gajapersad K, Hallam C, Hurtado J, Martin E, McWilliam A, Mugerwa B, O’Brien T, Rovero F (2011) Community structure and diversity of tropical forest mammals: data from a global camera trap network. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 366, 2703-2711. |
| 2 | Anderson-Teixeira KJ, Davies SJ, Bennett AC, Gonzalez-Akre EB, Muller-Landau HC, Wright SJ, Abu Salim K, Almeyda Zambrano AM, Alonso A, Baltzer JL, Basset Y, Bourg NA, Broadbent EN, Brockelman WY, Bunyavejchewin S, Burslem DFRP, Butt N, Cao M, Cardenas D, Chuyong GB, Clay K, Cordell S, Dattaraja HS, Deng X, Detto M, Du X, Duque A, Erikson DL, Ewango CEN, Fischer GA, Fletcher C, Foster RB, Giardina CP, Gilbert GS, Gunatilleke N, Gunatilleke S, Hao Z, Hargrove WW, Hart TB, Hau BCH, He F, Hoffman FM, Howe RW, Hubbell SP, Inman-Narahari FM, Jansen PA, Jiang M, Johnson DJ, Kanzaki M, Kassim AR, Kenfack D, Kibet S, Kinnaird MF, Korte L, Kral K, Kumar J, Larson AJ, Li Y, Li X, Liu S, Lum SKY, Lutz JA, Ma K, Maddalena DM, Makana JR, Malhi Y, Marthews T, Mat Serudin R, McMahon SM, McShea WJ, Memiaghe HR, Mi X, Mizuno T, Morecroft M, Myers JA, Novotny V, de Oliveira AA, Ong PS, Orwig DA, Ostertag R, den Ouden J, Parker GG, Phillips RP, Sack L, Sainge MN, Sang W, Sri-ngernyuang K, Sukumar R, Sun IF, Sungpalee W, Suresh HS, Tan S, Thomas SC, Thomas DW, Thompson J, Turner BL, Uriarte M, Valencia R, Vallejo MI, Vicentini A, Vrška T, Wang X, Wang X, Weiblen G, Wolf A, Xu H, Yap S, Zimmerman J (2015) CTFS-ForestGEO: a worldwide network monitoring forests in an era of global change. Global Change Biology, 21, 528-549. |
| 3 | Bai XJ, Queenborough S, Wang XG, Zhang J, Li B, Yuan ZQ, Xing DL, Lin F, Ye J, Hao ZQ (2012) Effects of local biotic neighbors and habitat heterogeneity on tree and shrub seedling survival in an old-growth temperate forest. Oecologia, 170, 755-765. |
| 4 | Bai Y, Han X, Wu J, Chen Z, Li L (2004) Ecosystem stability and compensatory effects in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Nature, 431, 181-184. |
| 5 | Barlow J, Ewers RM, Anderson L, Aragao LEOC, Baker TR, Boyd E, Feldpausch TR, Gloor E, Hall A, Malhi Y, Milliken W, Mulligan M, Parry L, Pennington T, Peres CA, Phillips OL, Roman-Cuesta RM, Tobias JA, Gardner TA (2011) Using learning networks to understand complex systems: a case study of biological, geophysical and social research in the Amazon. Biological Reviews, 86, 457-474. |
| 6 | Barnosky AD, Matzke N, Tomiya S, Wogan GOU, Swartz B, Quental TB, Marshall C, McGuire JL, Lindsey EL, Maguire KC, Mersey B, Ferrer EA (2011) Has the Earth’s sixth mass extinction already arrived? Nature, 471, 51-57. |
| 7 | Baru C, Fegraus EH, Andelman SJ, Chandra S, Kaya K, Lin K, Youn C (2012) Cyberinfrastructure for observatory and monitoring networks: a case study from the TEAM Network. BioScience, 62, 667-675. |
| 8 | Bin Y, Lin G, Li B, Wu L, Shen Y, Ye WH (2012) Seedling recruitment patterns in a 20 ha subtropical forest plot: hints for niche-based processes and negative density dependence. European Journal of Forest Research, 131, 453-461. |
| 9 | Bin Y, Wang Z, Wang Z, Ye WH, Cao H, Lian JY (2010) The effects of dispersal limitation and topographic heterogeneity on beta diversity and phylobetadiversity in a subtropical forest. Plant Ecology, 209, 237-256. |
| 10 | Board M (1990) Managing Troubled Waters:The Role of Marine Environmental Monitoring. National Academies Press, Washington. |
| 11 | Brienen RJW, Phillips OL, Feldpausch TR, Gloor E, Baker TR, Lloyd J, Lopez-Gonzalez G, Monteagudo-Mendoza A, Malhi Y, Lewis SL, Vasquez Martinez R, Alexiades M, Alvarez Davila E, Alvarez-Loayza P, Andrade A, Aragao LEOC, Araujo-Murakami A, Arets EJMM, Arroyo L, Aymard C GA, Banki OS, Baraloto C, Barroso J, Bonal D, Boot RGA, Camargo JLC, Castilho CV, Chama V, Chao KJ, Chave J, Comiskey JA, Cornejo Valverde F, da Costa L, de Oliveira EA, Di Fiore A, Erwin TL, Fauset S, Forsthofer M, Galbraith DR, Grahame ES, Groot N, Herault B, Higuchi N, Honorio Coronado EN, Keeling H, Killeen TJ, Laurance WF, Laurance S, Licona J, Magnussen WE, Marimon BS, Marimon-Junior BH, Mendoza C, Neill DA, Nogueira EM, Nunez P, Pallqui Camacho NC, Parada A, Pardo-Molina G, Peacock J, Pena-Claros M, Pickavance GC, Pitman NCA, Poorter L, Prieto A, Quesada CA, Ramirez F, Ramirez- Angulo H, Restrepo Z, Roopsind A, Rudas A, Salomao RP, Schwarz M, Silva N, Silva-Espejo JE, Silveira M, Stropp J, Talbot J, ter Steege H, Teran-Aguilar J, Terborgh J, Thomas-Caesar R, Toledo M, Torello-Raventos M, Umetsu RK, van der Heijden GMF, van der Hout P, Guimaraes Vieira IC, Vieira SA, Vilanova E, Vos VA, Zagt RJ (2015) Long-term decline of the Amazon carbon sink. Nature, 519, 344-348. |
| 12 | Bruelheide H, Nadrowski K, Assmann T, Bauhus J, Both S, Buscot F, Chen XY, Ding B, Durka W, Erfmeier A, Gutknecht JLM, Guo D, Guo LD, Härdtle W, He J-S, Klein A-M, Kühn P, Liang Y, Liu X, Michalski S, Niklaus PA, Pei K, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Scholten T, Schuldt A, Seidler G, Trogisch S, von Oheimb G, Welk E, Wirth C, Wubet T, Yang X, Yu M, Zhang S, Zhou H, Fischer M, Ma K, Schmid B (2014) Designing forest biodiversity experiments: general considerations illustrated by a new large experiment in subtropical China. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 5, 74-89. |
| 13 | Bubb P, Chenery A, Herkenrath P, Kapos V, Mapendembe A, Stanwell-Smith D, Wal-pole M (2011) National indicators, monitoring and reporting for the strategic plan for biodiversity 2011-2020. UNEP-WCMC: Cambridge, UK. |
| 14 | Carnicer J, Coll M, Ninyerola M, Pons X, Sánchez G, Peñuelas J (2011) Widespread crown condition decline, food web disruption, and amplified tree mortality with increased climate change-type drought. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 1474-1478. |
| 15 | Cavanaugh KC, Gosnell JS, Davis SL, Ahumada J, Boundja P, Clark DB, Mugerwa B, Jansen PA, O’Brien TG, Rovero F, Sheil D, Vasquez R, Andelman S (2014) Carbon storage in tropical forests correlates with taxonomic diversity and functional dominance on a global scale. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 23, 563-573. |
| 16 | Chave J, Condit R, Muller-Landau HC, Thomas SC, Ashton PS, Bunyavejchewin S, Co LL, Dattaraja HS, Davies SJ, Esufali S, Ewango CEN, Feeley KJ, Foster RB, Gunatilleke N, Gunatilleke S, Hall P, Hart TB, Hernández C, Hubbell SP, Itoh A, Kiratiprayoon S, LaFrankie JV, Loo de Lao S, Makana JR, Noor MNS, Kassim AR, Samper C, Sukumar R, Suresh HS, Tan S, Thompson J, Tongco MDC, Valencia R, Vallejo M, Villa G, Yamakura T, Zimmerman JK, Losos EC (2008) Assessing Evidence for a Pervasive Alteration in Tropical Tree Communities. PLoS Biology, 6, e45. |
| 17 | Chen L, Mi XC, Comita LS, Zhang L, Ren HB, Ma KP (2010) Community-level consequences of density dependence and habitat association in a subtropical broad-leaved forest. Ecology Letters, 13, 695-704. |
| 18 | Chisholm RA, Condit R, Rahman KA, Baker PJ, Bunyavejchewin S, Chen YY, Chuyong G, Dattaraja HS, Davies S, Ewango CEN, Gunatilleke CVS, Nimal Gunatilleke IAU, Hubbell S, Kenfack D, Kiratiprayoon S, Lin Y, Makana JR, Pongpattananurak N, Pulla S, Punchi-Manage R, Sukumar R, Su SH, Sun IF, Suresh HS, Tan S, Thomas D, Yap S (2014) Temporal variability of forest communities: empirical estimates of population change in 4000 tree species. Ecology Letters, 17, 855-865. |
| 19 | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and Comparison with Other Plots. Springer, Berlin. |
| 20 | Dong SX, Davies SJ, Ashton PS, Bunyavejchewin S, Supardi MN, Kassim AR, Tan S, Moorcroft PR (2012) Variability in solar radiation and temperature explains observed patterns and trends in tree growth rates across four tropical forests. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 279, 3923-3931. |
| 21 | Editorial Board of Forest in China(2000) Forest in China . China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国森林编辑委员会(2000) 中国森林. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 22 | Editorial Board of the Vegetation Atlas of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences(2009) 1: 1000000 Vegetation Atlas of China. Geology Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国科学院中国植被图编辑委员会(2009) 中华人民共和植被图(1:1000000). 地质出版社, 北京.] | |
| 23 | Elzinga CL, Salzer DW, Willoughby JW, Gibbs JP (2009) Monitoring Plant and Animal Populations: A Handbook for Field Biologists. John Wiley & Sons, New York. |
| 24 | Feeley KJ, Joseph Wright S, Nur Supardi MN, Kassim AR, Davies SJ (2007) Decelerating growth in tropical forest trees. Ecology Letters, 10, 461-469. |
| 25 | Ferretti M (2010) Harmonizing forest inventories and forest condition monitoring—the rise or the fall of harmonized forest condition monitoring in Europe? iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, 3, 1-4. |
| 26 | Ferretti M, Chiarucci A (2003) Design concepts adopted in long-term forest monitoring programs in Europe—problems for the future? Science of the Total Environment, 310, 171-178. |
| 27 | Ferretti M, Fischer R (2013) Forest Monitoring: Methods for Terrestrial Investigations in Europe with an Overview of North America and Asia. Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. |
| 28 | Fraenkel AA (1989) Convention on long-range transboundary air pollution: meeting the challenge of international cooperation, The Harvard International Law Journal, 30, 447-476. |
| 29 | Gardner T (2012) Monitoring forest biodiversity: improving conservation through ecologically-responsible management. Management of Environmental Quality, 37, e16-e17. |
| 30 | Gong LC (1988)The publication of book series of Chinese Forest. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 10(2), 78. (in Chinese) |
| [宫连城 (1988) 《中国森林》编辑出版概况. 北京林业大学学报, 10(2), 78] | |
| 31 | Guo Y, Lu J, Franklin SB, Wang Q, Xu Y, Zhang K, Bao D, Qiao X, Huang H, Lu Z, Jiang M (2013) Spatial distribution of tree species in a species-rich subtropical mountain forest in central China. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 43, 826-835. |
| 32 | Han Y, Yu X, Wang X, Wang Y, Tian J, Xu L, Wang C (2013) Net anthropogenic phosphorus inputs (NAPI) index application in Mainland China. Chemosphere, 90, 329-337. |
| 33 | Hao ZQ, Zhang J, Song B, Ye J, Li B (2007) Vertical structure and spatial associations of dominant tree species in an old- growth temperate forest. Forest Ecology and Management, 252, 1-11. |
| 34 | He JS, Liu CR, Ma KP (2000) Standards and methods of forest biodiversity monitoring. In: China’s Biodiversity Conserva- tion Toward the 21st Century: Proceedings of the Third National Symposium on the Conservation and Sustainable Use of Biological Diversity (ed. Xu ZH), pp. 331-347. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [贺金生, 刘灿然, 马克平 (2000)森林生物多样性监测规范和方法. 见:面向21世纪的中国生物多样性保护—第三届全国生物多样性保护与持续利用研讨会论文集(许智宏主编), pp. 331-347. 林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 35 | Hooper DU, Adair EC, Cardinale BJ, Byrnes JEK, Hungate BA, Matulich KL, Gonzalez A, Duffy JE, Gamfeldt L, O'Connor MI (2012) A global synthesis reveals biodiversity loss as a major driver of ecosystem change. Nature, 486, 105-108. |
| 36 | Ingwell LL, Joseph Wright S, Becklund KK, Hubbell SP, Schnitzer SA (2010) The impact of lianas on 10 years of tree growth and mortality on Barro Colorado Island, Panama. Journal of Ecology, 98, 879-887. |
| 37 | Lai J, Mi X, Ren H, Ma K (2009) Species-habitat associations change in a subtropical forest of China. Journal of Vegetation Science, 20, 415-423. |
| 38 | Legendre P, Mi X, Ren H, Ma K, Yu M, Sun IF, He F (2009) Partitioning beta diversity in a subtropical broad-leaved forest of China. Ecology, 90, 663-674. |
| 39 | Leigh E (2004) The neutral theory of forest ecology. Tropical Forest Diversity and Dynamism: Findings From a Large- Scale Plot Network (eds Losos E, Leigh E), pp. 244-263. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| 40 | Li L, Huang Z, Ye W, Cao H, Wei S, Wang Z, Lian J, Sun IF, Ma K, He F (2009) Spatial distributions of tree species in a subtropical forest of China. Oikos, 118, 495-502. |
| 41 | Lin L, Comita LS, Zheng Z, Cao M (2012) Seasonal differ- entiation in density-dependent seedling survival in a tropical rain forest. Journal of Ecology, 100, 905-914. |
| 42 | Lin LX, Yue XH (2007) The overview, directions and trends of development of Chinese forest resources inventory. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 13(15), 112-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [林来仙, 岳祥华 (2007) 我国森林资源清查概况、发展方向和趋势. 安徽农学通报, 13(15), 112-113.] | |
| 43 | Lindenmayer DB, Franklin JF, Fischer J (2006) General management principles and a checklist of strategies to guide forest biodiversity conservation. Biological Conservation, 131, 433-445. |
| 44 | Liu XJ, Swenson NG, Zhang JL, Ma KP (2013) The environ- ment and space, not phylogeny, determine trait dispersion in a subtropical forest. Functional Ecology, 27, 264-272. |
| 45 | Lorenz M, Nagel HD, Granke O, Kraft P (2008) Critical loads and their exceedances at intensive forest monitoring sites in Europe. Environmental Pollution, 155, 426-435. |
| 46 | Lu J, Johnson DJ, Qiao X, Lu Z, Wang Q, Jiang M (2015) Density dependence and habitat preference shape seedling survival in a subtropical forest in central China. Journal of Plant Ecology, 8, 568-577. |
| 47 | Ma KP (1994) A workshop of biodiversity monitoring held in USA. Biodiversity Science, 2, 184-186. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (1994) 生物多样性监测研讨班在美国举办. 生物多样性, 2, 184-186]. | |
| 48 | Malhi Y, Aragão LEOC, Galbraith D, Huntingford C, Fisher R, Zelazowski P, Sitch S, McSweeney C, Meir P (2009) Exploring the likelihood and mechanism of a climate- change-induced dieback of the Amazon rainforest. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 106, 20610-20615. |
| 49 | Malhi Y, Grace J (2000) Tropical forests and atmospheric carbon dioxide. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 15, 332-337. |
| 50 | Malhi Y, Phillips OL, Lloyd J, Baker T, Wright J, Almeida S, Arroyo L, Frederiksen T, Grace J, Higuchi N, Killeen T, Laurance WF, Leaño C, Lewis S, Meir P, Monteagudo A, Neill D, Núñez Vargas P, Panfil SN, Patiño S, Pitman N, Quesada CA, Rudas-Ll A, Salomão R, Saleska S, Silva N, Silveira M, Sombroek WG, Valencia R, Vásquez Martínez R, Vieira ICG, Vinceti B, Canadell J, White PS (2002) An international network to monitor the structure, composition and dynamics of Amazonian forests (RAINFOR). Journal of Vegetation Science, 13, 439-450. |
| 51 | McMahon SM, Parker GG, Miller DR (2010) Evidence for a recent increase in forest growth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 107, 3611-3615. |
| 52 | Mi XC, Swenson NG, Valencia R, Kress WJ, Erickson DL, Pérez ÁJ, Ren HB, Su SH, Gunatilleke N, Gunatilleke S, Hao ZQ, Ye WH, Cao M, Suresh HS, Dattaraja HS, Sukumar R, Ma KP (2012) The contribution of rare species to community phylogenetic diversity across a global network of forest plots. The American Naturalist, 180, e17-e30. |
| 53 | Niu X, Wang B (2013) Assessment of forest ecosystem services in China: a methodology. Journal of Food, Agriculture & Environment, 11, 2249-2254. |
| 54 | Pereira HM, Ferrier S, Walters M, Geller G, Jongman R, Scholes R, Bruford MW, Brummitt N, Butchart S, Cardoso A (2013) Essential biodiversity variables. Science, 339, 277-278. |
| 55 | Phillips OL, Lewis SL, Baker TR, Chao KJ, Higuchi N (2008) The changing Amazon forest. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 363, 1819-1827. |
| 56 | Phillips OL, Malhi Y, Vinceti B, Baker T, Lewis SL, Higuchi N, Laurance WF, Vargas PN, Martinez RV, Laurance S, Ferreira LV, Stern M, Brown S, Grace J (2002) Changes in growth of tropical forests: evaluating potential biases. Ecological Applications, 12, 576-587. |
| 57 | Phillips OL, Vásquez Martínez R, Núñez Vargas P, Lorenzo Monteagudo A, Chuspe Zans ME, Galiano Sánchez W, Peña Cruz A, Timaná M, Yli-Halla M, Rose S (2003) Efficient plot-based floristic assessment of tropical forests. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 19, 629-645. |
| 58 | Ricklefs RE, He F (2016) Region effects influence local tree species diversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 113, 674-679. |
| 59 | Schnitzer SA, Bongers F (2011) Increasing liana abundance and biomass in tropical forests: emerging patterns and putative mechanisms. Ecology Letters, 14, 397-406. |
| 60 | Scholes RJ, Mace GM, Turner W, Geller GN, Jürgens N, Larigauderie A, Muchoney D, Walther BA, Mooney HA (2008) Toward a Global Biodiversity Observing System. Science, 321, 1044-1045. |
| 61 | Scholes RJ, Walters M, Turak E, Saarenmaa H, Heip CHR, Tuama ÉÓ, Faith DP, Mooney HA, Ferrier S, Jongman RHG, Harrison IJ, Yahara T, Pereira HM, Larigauderie A, Geller G (2012) Building a global observing system for biodiversity. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 4, 139-146. |
| 62 | Shen G, Yu M, Hu XS, Mi X, Ren H, Sun IF, Ma K (2009) Species-area relationships explained by the joint effects of dispersal limitation and habitat heterogeneity. Ecology, 90, 3033-3041. |
| 63 | van Dobben H, de Vries W (2010) Relation between forest vegetation, atmospheric deposition and site conditions at regional and European scales. Environmental Pollution, 158, 921-933. |
| 64 | Vos P, Meelis E, Ter Keurs WJ (2000) A framework for the design of ecological monitoring programs as a tool for environmental and nature management. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 61, 317-344. |
| 65 | Wang B, Cui XH, Yang FW (2004) Chinese Forest Ecosystem Research Network (CFERN) and its development. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 23(4), 84-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王兵, 崔向慧, 杨锋伟 (2004) 中国森林生态系统定位研究网络的建设与发展. 生态学杂志, 23(4), 84-91.] | |
| 66 | Wang D, Wang B, Niu X (2013) Forest carbon sequestration in China and its benefits. Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research, 29, 51-59. |
| 67 | Wang Q, Bao D, Guo Y, Lu J, Lu Z, Xu Y, Zhang K, Liu H, Meng H, Jiang M, Qiao X, Huang H (2014a) Species associations in a species-rich subtropical forest were not well-explained by stochastic geometry of biodiversity. PLoS ONE, 9, e97300. |
| 68 | Wang Q, Xu Y, Lu Z, Bao D, Guo Y, Lu J, Zhang K, Liu H, Meng H, Qiao X, Huang H, Jiang M (2014b) Disentangling the effects of topography and space on the distributions of dominant species in a subtropical forest. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 5113-5122. |
| 69 | Wang SY, Lin SS (1995) Progress in studies of long-term forest ecological research in China. World Forestry Research, (4), 44-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王淑元, 林升寿 (1995) 我国森林生态系统定位研究的进展. 世界林业研究, (4), 44-49.] | |
| 70 | Wang XG, Swenson NG, Wiegand T, Wolf A, Howe R, Lin F, Ye J, Yuan ZQ, Shi S, Bai XJ, Xing DL, Hao ZQ (2013) Phylogenetic and functional diversity area relationships in two temperate forests. Ecography, 36, 883-893. |
| 71 | Wang XG, Wiegand T, Hao ZQ, Li B, Ye J, Lin F (2010) Species associations in an old-growth temperate forest in north-eastern China. Journal of Ecology, 98, 674-686. |
| 72 | Wang XG, Wiegand T, Swenson NG, Wolf AT, Howe RW, Hao ZQ, Lin F, Ye J, Yuan ZQ (2015) Mechanisms underlying local functional and phylogenetic beta diversity in two temperate forests. Ecology, 96, 1062-1073. |
| 73 | Wang XG, Wiegand T, Wolf A, Howe R, Davies SJ, Hao ZQ (2011) Spatial patterns of tree species richness in two temperate forests. Journal of Ecology, 99, 1382-1393. |
| 74 | Wang Z, Ye WH, Cao H, Huang Z, Lian JY, Li L, Wei S, Sun IF (2009) Species-topography association in a species-rich subtropical forest of China. Basic and Applied Ecology, 10, 648-655. |
| 75 | Wright SJ, Calderón O (2006) Seasonal, El Niño and longer term changes in flower and seed production in a moist tropical forest. Ecology Letters, 9, 35-44. |
| 76 | Wu ZY (1980) Vegetation of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [吴征镒 (1980) 中国植被. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 77 | Xu CD (2014) Forest management in China from eight forest resources inventories. Forest Economics, (4), 8-11 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [许传德 (2014) 从连续八次森林资源清查数据看我国森林经营. 生态经济, (4), 8-11.] | |
| 78 | Yang P, Yu XB, Zhuang XL, Niu D (2008) Present status and train of thought of future development of Chinese Ecosystem Research Network (CERN) of CAS. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 23, 555-561. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨萍, 于秀波, 庄绪亮, 牛栋 (2008) 中国科学院中国生态系统研究网络(CERN)的现状及未来发展思路. 中国科学院院刊, 23, 555-561.] | |
| 79 | Yang J, Swenson NG, Cao M, Chuyong GB, Ewango CEN, Howe R, Kenfack D, Thomas D, Wolf A, Lin L (2013) A phylogenetic perspective on the individual species-area relationship in temperate and tropical tree communities. PLoS ONE, 8, e63192. |
| 80 | Yang J, Zhang G, Ci X, Swenson NG, Cao M, Sha L, Li J, Baskin CC, Slik JWF, Lin L (2014) Functional and phylogenetic assembly in a Chinese tropical tree community across size classes, spatial scales and habitats. Functional Ecology, 28, 520-529. |
| 81 | Youn C, Chandra S, Fegraus EH, Lin K, Baru C (2011) TEAM Network: building web-based data access and analysis environments for ecosystem services. Procedia Computer Science, 4, 146-155. |
| 82 | Yu GR, Yu XB (2013) Chinese ecological research network and conservation of natural ecosystem. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 28, 275-283. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于贵瑞, 于秀波 (2013) 中国生态系统研究网络与自然生态系统保护. 中国科学院院刊, 28, 275-283.] | |
| 83 | Yuan ZQ, Gazol A, Lin F, Ye J, Shi S, Wang XG, Wang M, Hao ZQ (2013) Soil organic carbon in an old-growth temperate forest: spatial pattern, determinants and bias in its quantification. Geoderma, 195-196, 48-55. |
| 84 | Zhang L, Mi XC, Shao H, Ma KP (2011) Strong plant-soil associations in a heterogeneous subtropical broad-leaved forest. Plant and Soil, 347, 211-220. |
| 85 | Zhou G, Liu S, Li Z, Zhang D, Tang X, Zhou C, Yan J, Mo J (2006) Old-growth forests can accumulate carbon in soils. Science, 314, 1417. |
| 86 | Zhu Y, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP (2010) Density dependence is prevalent in a heterogeneous subtropical forest. Oikos, 119, 109-119. |
| [1] | Yu Ren, Shengli Tao, Tianyu Hu, Haitao Yang, Hongcan Guan, Yanjun Su, Kai Cheng, Mengxi Chen, Huawei Wan, Qinghua Guo. The outlook and system construction for monitoring Essential Biodiversity Variables based on remote sensing: The case of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(10): 22530-. |
| [2] | Cheng Li, Feng Xie, Jing Che, Jianping Jiang. Monitoring and research of amphibians and reptiles diversity in key areas of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(3): 246-254. |
| [3] | WANG Li-Xia, LI Ying-Hui, LI Wei, ZHU Li, GUAN Yuan, NING Xue-Cheng, GUAN Rong-Xia, LIU Zhang-Xiong, CHANG Ru-Zhen, QIU Li-Juan. Establishment of a core collection of Changjiang spring sowing soybean [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2004, 12(6): 578-585. |
| [4] | FANG Jing-Yun, LI Yi-De, ZHU Biao, LIU Guo-Hua, ZHOU Guang-Yi. Community structures and species richness in the montane rain forest of Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2004, 12(1): 29-43. |
| [5] | Wang Hongxin, Hu Zhiang. Plant breeding system, genetic structure and conservation of genetic diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 1996, 04(2): 92-96. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn