



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 25195. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025195 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2025195
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaoqian Zhao1,2,3( ), Zheping Xu4,5,*(
), Zheping Xu4,5,*( )(
)( ), Hui Wu1,2,3,*(
), Hui Wu1,2,3,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2025-05-27
Accepted:2025-09-02
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-11-21
Contact:
* Co-authors for correspondence. E-mail: Supported by:Xiaoqian Zhao, Zheping Xu, Hui Wu. Development path and implications of the Global Biodiversity Information Facility[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(10): 25195.
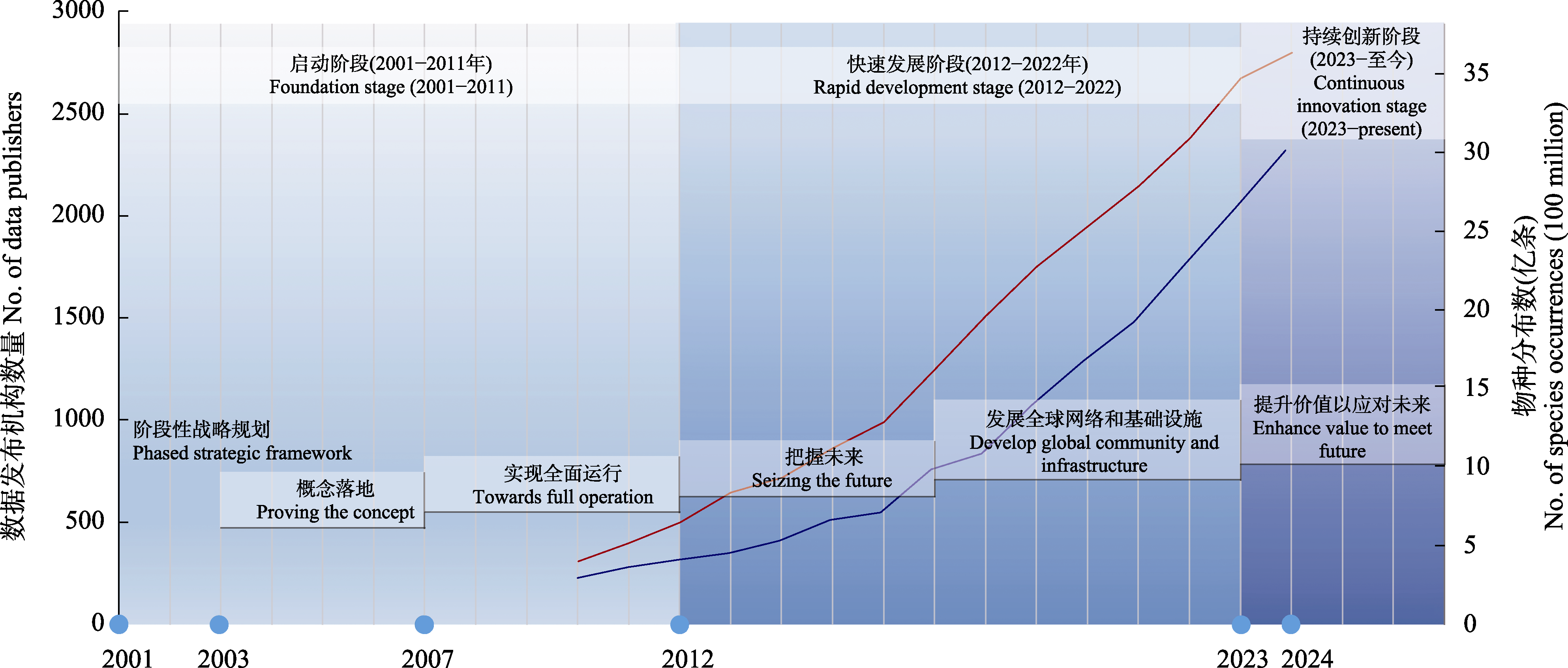
Fig. 1 Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) phased strategic framework, the number of data publishers (in red) and species occurrence records (in blue). Annual statistics on data publishers and records before 2010 are missing (GBIF, 2025a).
| 合作伙伴 Partners | 类型 Type | 伙伴关系 Partnership | 合作内容及成效 Collaboration content and achievements |
|---|---|---|---|
| 联合国生物多样性公约 United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) | 全球治理框架与政策协调机构 Global governance frameworks and policy coordination organization | 观察员 Observer | 数据支撑爱知生物多样性目标中15个目标(CBD, |
| 联合国可持续发展目标 United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) | 全球治理框架与政策协调机构 Global governance frameworks and policy coordination organization | 数据合作 Data partnership | 数据支撑SDG 13、14、15多个指标 Data underpin multiple indicators of SDG 13, 14, and 15 |
| 世界卫生组织 World Health Organization (WHO) | 全球治理框架与政策协调机构 Global governance frameworks and policy coordination organization | 数据合作 Data partnership | 合作协调全球人类疫病相关的生物多样性数据70万条 Collaboratively coordinate 700,000 global biodiversity data related to human infectious diseases |
| 政府间气候变化专门委员会Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) | 科学评估机构 Science-based assessment organization | 观察员 Observer | 3.8亿条数据支持IPCC特别报告的生物多样性调查结果(Warren et al, |
| 生物多样性和生态系统服务政府间科学政策平台 Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) | 科学评估机构 Science-based assessment organization | 观察员、数据和知识工作组和能力建设工作组成员 Observer; task group member: knowledge and data, capacity-building | 数据支撑生物多样性丧失的关键驱动因子评估(IPBES, |
| 全球生物多样性监测网络 Group on Earth Observations Biodiversity Observation Network (GEO BON) | 科学评估机构 Science-based assessment organization | 咨询委员会成员 Advisory Committee member | 数据支撑基本生物多样性变量(essential biodiversity variables, EBVs)指标生成 Data underpins the generation of indicators for essential biodiversity variables (EBVs) |
| 世界自然保护联盟 International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) | 科学评估机构 Science-based assessment organization | 数据合作 Data partnership | 数据支撑IUCN 15,000份单独评估、2022年IUCN红色名录更新; 区域节点参与名录评估工作 Data underpin 15,000 separate assessments conducted by IUCN and the 2022 update of the IUCN Red List, with regional nodes involved in the assessment process |
Table 1 Brief introduction to GBIF international partners
| 合作伙伴 Partners | 类型 Type | 伙伴关系 Partnership | 合作内容及成效 Collaboration content and achievements |
|---|---|---|---|
| 联合国生物多样性公约 United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) | 全球治理框架与政策协调机构 Global governance frameworks and policy coordination organization | 观察员 Observer | 数据支撑爱知生物多样性目标中15个目标(CBD, |
| 联合国可持续发展目标 United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) | 全球治理框架与政策协调机构 Global governance frameworks and policy coordination organization | 数据合作 Data partnership | 数据支撑SDG 13、14、15多个指标 Data underpin multiple indicators of SDG 13, 14, and 15 |
| 世界卫生组织 World Health Organization (WHO) | 全球治理框架与政策协调机构 Global governance frameworks and policy coordination organization | 数据合作 Data partnership | 合作协调全球人类疫病相关的生物多样性数据70万条 Collaboratively coordinate 700,000 global biodiversity data related to human infectious diseases |
| 政府间气候变化专门委员会Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) | 科学评估机构 Science-based assessment organization | 观察员 Observer | 3.8亿条数据支持IPCC特别报告的生物多样性调查结果(Warren et al, |
| 生物多样性和生态系统服务政府间科学政策平台 Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) | 科学评估机构 Science-based assessment organization | 观察员、数据和知识工作组和能力建设工作组成员 Observer; task group member: knowledge and data, capacity-building | 数据支撑生物多样性丧失的关键驱动因子评估(IPBES, |
| 全球生物多样性监测网络 Group on Earth Observations Biodiversity Observation Network (GEO BON) | 科学评估机构 Science-based assessment organization | 咨询委员会成员 Advisory Committee member | 数据支撑基本生物多样性变量(essential biodiversity variables, EBVs)指标生成 Data underpins the generation of indicators for essential biodiversity variables (EBVs) |
| 世界自然保护联盟 International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) | 科学评估机构 Science-based assessment organization | 数据合作 Data partnership | 数据支撑IUCN 15,000份单独评估、2022年IUCN红色名录更新; 区域节点参与名录评估工作 Data underpin 15,000 separate assessments conducted by IUCN and the 2022 update of the IUCN Red List, with regional nodes involved in the assessment process |
| [1] | Abarenkov K, Andersson AF, Bissett A, Finstad AG, Fossøy F, Grosjean M, Hope M, Jeppesen TS, Kõljalg U, Lundin D, Nilsson RN, Prager M, Provoost P, Schigel D, Suominen S, Svenningsen C, Frøslev TG (2023) Publishing DNA-derived Data through Biodiversity Data Platforms v1.3.3. Secretariat. https://docs.gbif.org/publishing-dna-derived-data. (accessed on 2025-03-22) |
| [2] |
Blair J, Gwiazdowski R, Borrelli A, Hotchkiss M, Park C, Perrett G, Hanner R (2020) Towards a catalogue of biodiversity databases: An ontological case study. Biodiversity Data Journal, 8, e32765.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Bloom DA, Zermoglio P, Guralnick R (2021) Analysis of Biodiversity Data needs in the Post-2020 Framework Version 1a247a5. https://docs.gbif.org/post-2020-data-needs. (accessed on 2024-12-06) |
| [4] | CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity) (2016) CSP Members’ Contribution to the Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011-2020 and the Aichi Biodiversity Targets. https://www.cbd.int/csp/survey/gbif.pdf. (accessed on 2024-12-20) |
| [5] | CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity) (2022) Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. https://www.cbd.int/doc/decisions/cop-15/cop-15-dec-04-en.pdf. (accessed on 2024-12-20) |
| [6] | CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity) (2024) List of Key Initiatives and Partnerships Supporting the Implementation of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. https://www.cbd.int/sbstta/sbstta-24/post2020-monitoring-en.pdf. (accessed on 2025-02-19) |
| [7] | CCSA TC601 Big Data Technology and Standard Committee (2025) Practice Guide for High-Quality Datasets (Version 1.0). China Communications Standards Association, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [CCSA TC601大数据技术标准推进委员会 (2025) 高质量数据集实践指南(1.0). 中国通信标准化协会, 北京.] | |
| [8] |
Chandler M, See L, Copas K, Bonde AMZ, López BC, Danielsen F, Legind JK, Masinde S, Miller-Rushing AJ, Newman G, Rosemartin A, Turak E (2017) Contribution of citizen science towards international biodiversity monitoring. Biological Conservation, 213, 280-294.
DOI URL |
| [9] | CODATA (Committee on Data of the International Science Council) (2020) Twenty-year Review of GBIF. https://zenodo.org/records/3779922. (accessed on 2025-02-19) |
| [10] |
Costello MJ, Appeltans W, Bailly N, Berendsohn WG, de Jong Y, Edwards M, Froese R, Huettmann F, Los W, Mees J, Segers H, Bisby FA (2014) Strategies for the sustainability of online open-access biodiversity databases. Biological Conservation, 173, 155-165.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Edwards JL, Lane MA, Nielsen ES (2000) Interoperability of biodiversity databases: Biodiversity information on every desktop. Science, 289, 2312-2314.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | ESFRI (European Strategy Forum on Research Infrastructures) (2018) Roadmap 2018:Strategy Report on Research Infrastructures. http://roadmap2018.esfri.eu/media/1066/esf ri-roadmap-2018.pdf. (accessed on 2025-05-04) |
| [13] | GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) (2002) GBIF Ebbe Nielsen Challenge. https://www.gbif.org/ebbe. (accessed on 2024-12-04) |
| [14] | GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) (2010) GBIF Graduate Researchers Award. https://www.gbif.org/graduate-researchers-award. (accessed on 2024-12-04) |
| [15] | GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) (2011) GBIF Annual Report 2011. http://links.gbif.org/ar2011.pdf. (accessed on 2024-12-04) |
| [16] | GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) (2012) GBIF Funders. https://www.gbif.org/funders. (accessed on 2024-12-04) |
| [17] | GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) (2017a) GBIF Committee Handbooks. https://www.gbif.org/committee-handbooks. (accessed on 2024-12-04) |
| [18] | GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) (2017b) Citation Guidelines. https://www.gbif.org/citation-guidelines. (accessed on 2024-12-30) |
| [19] | GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) (2021) GBIF Strategic Framework 2023-2027. https://assets.ctfassets.net/uo17ejk9rkwj/4syMySXpjvR7ZABffjJx2g/d6c0e77cc72d7e3429f3c248ec50eef2/gbif-strategic-framework-23-27.pdf. (accessed on 2024-12-04) |
| [20] | GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) (2024a) Literature Tracking. https://www.gbif.org/literature-tracking. (accessed on 2024-12-04) |
| [21] | GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) (2024b) ChatIPT System Wins the 2024 Ebbe Nielsen Challenge. https://www.gbif.org/news/6aw2VFiEHYlqb48w86uKSf/chatipt-system-wins-the-2024-ebbe-nielsen-challenge. (accessed on 2025-05-04) |
| [22] | GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) (2024c) GBIF Nodes Implementation Plan 2024. https://docs.gbif.org/nodes-implementation-2024/en/. (accessed on 2024-12-04) |
| [23] | GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) (2025a) GBIF Home Page. https://www.gbif.org. (accessed on 2025-01-10) |
| [24] | GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) (2025b) GBIF Work Programme 2025: Annual Update and Implementation Plan to Strategic Framework 2023-2027. https://docs.gbif.org/2025-work-programme/en/. (accessed on 2025-05-04) |
| [25] | GBIF Secretariat, Deloitte Access Economics (2023) Economic Valuation and Assessment of the Impact of the GBIF Network. https://www.deloitte.com/content/dam/assets-zone1/au/en/docs/services/economics/deloitte-economics-global-biodiversity-information-facility-260623.pdf. (accessed on 2024-12-04) |
| [26] | Global Environment Facility (2023) New Global Biodiversity Fund Launched in Vancouver. https://www.thegef.org/newsroom/press-releases/new-global-biodiversity-fund-launched-vancouver. (accessed on 2024-08-22) |
| [27] | Guerra C, Wall DH (2023) SoilBON Final Report: Joint Call for Soil Biodiversity Data Mobilization. https://assets.ctfassets.net/uo17ejk9rkwj/5DPz0lKQK3kKptc6AZrHVM/4e0e2577b452d2ef14ec4ab831a55ea8/SoilBON-report_v0.pdf. (accessed on 2025-05-04) |
| [28] |
Güntsch A, Overmann J, Ebert B, Bonn A, Le Bras Y, Engel T, Hovstad KA, Lange Canhos DA, Newman P, van Ommen Kloeke E, Ratcliffe S le Roux M, Smith VS, Triebel D, Fichtmueller D, Luther K (2025) National biodiversity data infrastructures: Ten essential functions for science, policy, and practice. BioScience, 75, 139-151.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Hampton SE, Strasser CA, Tewksbury JJ, Gram WK, Budden AE, Batcheller AL, Duke CS, Porter JH (2013) Big data and the future of ecology. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 11, 156-162.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Heberling JM, Miller JT, Noesgaard D, Weingart SB, Schigel DS (2021) Data integration enables global biodiversity synthesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 118, e2018093118. |
| [31] | Hobern D, Apostolico A, Arnaud E, Bello JC, Canhos D, Dubois G, Field D, Alonso Garcia E, Hardisty A, Harrison J, Heidorn B, Krishtalka L, Mata E, Page RDM, Parr C, Price J, Willoughby S (2012) Global Biodiversity Informatics Outlook: Delivering Biodiversity Knowledge in the Information Age. Global Biodiversity Information Facility, Copenhagen. |
| [32] | Hodson S (2024) WorldFAIR (D2.2) WorldFAIR’s Experience with FIPs (Second Set of FAIR Implementation Profiles for Each Case Study) (V1). https://zenodo.org/records/11236094. (accessed on 2025-05-04) |
| [33] | IPBES (Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services) (2023) Thematic Assessment Report on Invasive Alien Species and Their Control. https://www.ipbes.net/ias. (accessed on 2025-05-04) |
| [34] | Ji LQ, Qiao HJ, Xie BG, Zhang SW, Lin B, Zhu H, Deng H, Li N, Han Y (2004) Introduction to Global Biodiversity Information Network (GBIF): Organization, activities, projects and information services. In: Progress in Biodiversity Conservation and Research in China VI—Proceedings of the Sixth National Symposium on Biodiversity Conservation and Sustainable Utilization, pp. 79-141. China Meteorological Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [纪力强, 乔慧捷, 谢本贵, 张尚武, 林斌, 朱慧, 邓浩, 李诺, 韩艳 (2004) 全球生物多样性信息网络(GBIF)介绍: 组织、活动、项目和信息服务. 见: 中国生物多样性保护与研究进展Ⅵ——第六届全国生物多样性保护与持续利用研讨会论文集, pp. 79-141. 气象出版社, 北京.] | |
| [35] | Kamburska L, Fontaneto D, Rogora M, Schigel D (2023) Preface: Georeferenced freshwater biodiversity data. Journal of Limnology, 82, 2138. |
| [36] | Kenyon G (2001) Network aims to link species data from global collections. Nature, 410, 290. |
| [37] |
Lahti K (2022) The role and the purpose of national biodiversity data infrastructures in between the local and international data services. Biodiversity Information Science and Standards, 6, e91489.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Liu HY, Qin HN, Bao BJ, Chen TX, Han GX, Liu QR (2022) Analysis of digitized specimens of higher plants in China. Guihaia, 42(Z1), 29-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘慧圆, 覃海宁, 包伯坚, 陈天翔, 韩国霞, 刘全儒 (2022) 中国高等植物数字化标本分析. 广西植物, 42(增刊1), 29-45.] | |
| [39] |
Liu YL, Song DZ, Liu BB, Xia F, Chen YL, Wang YQ, Huang QW (2020) Overview of the camera-trapping platform for felid species in China: Data integration by a conservation NGO. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1067-1074. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [刘炎林, 宋大昭, 刘蓓蓓, 夏凡, 陈月龙, 王一晴, 黄巧雯 (2020) 中国猫科动物红外相机监测平台介绍: 民间环保机构的数据整合. 生物多样性, 28, 1067-1074.] | |
| [40] |
Luther K, Güntsch A, Koenig-Ries B, Fichtmueller D (2022) NFDI4Biodiversity: A German infrastructure for biodiversity data. Biodiversity Information Science and Standards, 6, e93869.
DOI URL |
| [41] | Ma KP, Zhu M, Ji LQ, Ma JC, Guo QH, Ouyang ZY, Zhu L (2018) Establishing China infrastructure for big biodiversity data. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 33, 838-845. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马克平, 朱敏, 纪力强, 马俊才, 郭庆华, 欧阳志云, 朱丽 (2018) 中国生物多样性大数据平台建设. 中国科学院院刊, 33, 838-845.] | |
| [42] | Mi XC, Feng G, Hu YB, Zhang J, Chen L, Corlett RT, Hughes AC, Pimm S, Schmid B, Shi SH, Svenning JC, Ma KP (2021) The global significance of biodiversity science in China: An overview. National Science Review, 8, nwab032. |
| [43] | Ministry of the Environment, Government of Japan (2022) BIFA Impact Infographic Summary. https://assets.ctfassets.net/uo17ejk9rkwj/6DRgLpJTNqPI4kvraYlTwr/d717b5d9c86f338484fb9072b3164794/A4BIFA-summary-vf.pdf. (accessed on 2025-05-07) |
| [44] |
Pollock LJ, Kitzes J, Beery S, Gaynor KM, Jarzyna MA, Mac Aodha O, Meyer B, Rolnick D, Taylor GW, Tuia D, Berger-Wolf T (2025) Harnessing artificial intelligence to fill global shortfalls in biodiversity knowledge. Nature Reviews Biodiversity, 1, 166-182.
DOI |
| [45] | Rafiq K, Beery S, Palmer MS, Harchaoui Z, Abrahms B (2025) Generative AI as a tool to accelerate the field of ecology. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 9, 378-385. |
| [46] |
Reynolds SA, Beery S, Burgess N, Burgman M, Butchart SHM, Cooke SJ, Coomes D, Danielsen F, Di Minin E, Durán AP, Gassert F, Hinsley A, Jaffer S, Jones JPG, Li BV, Mac Aodha O, Madhavapeddy A, O’Donnell SAL, Oxbury WM, Peck L, Pettorelli N, Rodríguez JP, Shuckburgh E, Strassburg B, Yamashita H, Miao ZQ, Sutherland WJ (2025) The potential for AI to revolutionize conservation: A horizon scan. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 40, 191-207.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Royaux C, Sananikone J, Arnaud E, Norvez O, Ainsa A, Morin S, Pamerlon S, Archambeau AS, Le Bras Y, (2022) French Biodiversity Data Hub: Linking local to global biodiversity through international initiatives and open science clouds. Biodiversity Information Science and Standards, 6, e91374.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Shimabukuro P, Groom Q, Fouque F, Campbell L, Chareonviriyaphap T, Etang J, Manguin S, Sinka M, Schigel D, Ingenloff K (2024) Bridging biodiversity and health: The Global Biodiversity Information Facility’s initiative on open data on vectors of human diseases. Gigabyte, 2024, gigabyte117. |
| [49] |
Silvestro D, Goria S, Sterner T, Antonelli A (2022) Improving biodiversity protection through artificial intelligence. Nature Sustainability, 5, 415-424.
DOI PMID |
| [50] | Stevens S, Wu J, Thompson MJ, Campolongo EG, Song CH, Carlyn DE, Dong L, Dahdul WM, Stewart C, Berger-Wolf T, Chao WL, Su Y (2024) Bioclip: A vision foundation model for the tree of life. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 19412-19424. IEEE, Seattle, Washington. |
| [51] |
Tang XM, Qin T (2025) Chinese enterprises’ biodiversity disclosure index construction and financing effects. Biodiversity Science, 33, 24264. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[汤心萌, 秦涛 (2025) 中国企业生物多样性信息披露指数构建及融资效应. 生物多样性, 33, 24264.]
DOI |
|
| [52] |
Thomas C (2009) Biodiversity databases spread, prompting unification call. Science, 324, 1632-1633.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
van Klink R, August T, Bas Y, Bodesheim P, Bonn A, Fossøy F, Høye TT, Jongejans E, Menz MHM, Miraldo A, Roslin T, Roy HE, Ruczyński I, Schigel D, Schäffler L, Sheard JK, Svenningsen C, Tschan GF, Wäldchen J, Zizka VMA, Åström J, Bowler DE (2022) Emerging technologies revolutionise insect ecology and monitoring. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 37, 872-885.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Warren R, Price J, Graham E, Forstenhaeusler N, VanDerWal J (2018) The projected effect on insects, vertebrates, and plants of limiting global warming to 1.5°C rather than 2°C. Science, 360, 791-795.
DOI PMID |
| [55] | Wei FW, Ping XG, Hu YB, Nie YG, Zeng Y, Huang GP (2021) Main achievements, challenges, and recommendations of biodiversity conservation in China. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 36, 375-383. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [魏辅文, 平晓鸽, 胡义波, 聂永刚, 曾岩, 黄广平 (2021) 中国生物多样性保护取得的主要成绩、面临的挑战与对策建议. 中国科学院院刊, 36, 375-383.] | |
| [56] |
Wilkinson MD, Dumontier M, Aalbersberg IJ, Appleton G, Axton M, Baak A, Blomberg N, Boiten JW, da Silva Santos LB, Bourne PE, Bouwman J, Brookes AJ, Clark T, Crosas M, Dillo I, Dumon O, Edmunds S, Evelo CT, Finkers R, Gonzalez-Beltran A, Gray AJG, Groth P, Goble C, Grethe JS, Heringa J ’t Hoen PAC, Hooft R, Kuhn T, Kok R, Kok J, Lusher SJ, Martone ME, Mons A, Packer AL, Persson B, Rocca-Serra P, Roos M, van Schaik R, Sansone SA, Schultes E, Sengstag T, Slater T, Strawn G, Swertz MA, Thompson M, van der Lei J, van Mulligen E, Velterop J, Waagmeester A, Wittenburg P, Wolstencroft K, Zhao J, Mons B (2016) The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Scientific Data, 3, 160018.
DOI |
| [57] |
Wu H, Xu XH, Feng XJ, Mi XC, Su YJ, Xiao ZS, Zhu CD, Cao L, Gao X, Song CY, Guo LD, Wu DH, Jiang JP, Shen H, Ma KP (2022) Progress and prospect of China biodiversity monitoring from a global perspective. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22434. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[吴慧, 徐学红, 冯晓娟, 米湘成, 苏艳军, 肖治术, 朱朝东, 曹垒, 高欣, 宋创业, 郭良栋, 吴东辉, 江建平, 沈浩, 马克平 (2022) 全球视角下的中国生物多样性监测进展与展望. 生物多样性, 30, 22434.]
DOI |
|
| [58] | Xu ZP, Piao ML, Liu QQ, Peng X, Liu YN, Wu YL (2025) 2024 Asia Biodiversity Data Use Guide: Linking to the UN 17 Sustainable Development Goals and Open Science. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15422533. (accessed on 2025-07-06) |
| [59] |
Zhang J (2017) Biodiversity science and macroecology in the era of big data. Biodiversity Science, 25, 355-363. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张健 (2017) 大数据时代的生物多样性科学与宏生态学. 生物多样性, 25, 355-363.]
DOI |
|
| [60] |
Zhang J, Kong HZ, Huang XL, Fu SL, Guo LD, Guo QH, Lei FM, Lü Z, Zhou YR, Ma KP (2022) Thirty key questions for biodiversity science in China. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22609. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张健, 孔宏智, 黄晓磊, 傅声雷, 郭良栋, 郭庆华, 雷富民, 吕植, 周玉荣, 马克平 (2022) 中国生物多样性研究的30个核心问题. 生物多样性, 30, 22609.]
DOI |
|
| [61] |
Zhao LN, Li JY, Barrett RL, Liu B, Hu HH, Lu LM, Chen ZD (2024) Spatial heterogeneity of extinction risk for flowering plants in China. Nature Communications, 15, 6352.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | Kaiying He, Xinhui Xu, Chengyun Zhang, Zezhou Hao, Zhishu Xiao, Yingying Guo. Bioacoustics data archives management standards and management technology progress [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24266-. |
| [2] | Wenna Tu, Jiawei Yi, Yunyan Du, Nan Wang, Jiale Qian, Sheng Huang, Xiaoyue Wang. A spatiotemporal analysis of human digital footprint and the human activities exposure of grassland biomass in Qinghai Lake National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(6): 21310-. |
| [3] | Yuxi Zhong, Chuanwu Chen, Yanping Wang. A dataset on the life-history and ecological traits of Chinese lizards [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(4): 22071-. |
| [4] | Junjie Li, Huanhuan Liu, Yangxue Wu, Lingda Zeng, Xiaolei Huang. A dataset on the diversity and geographical distributions of hemipteran insects in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(9): 1154-1158. |
| [5] | Rongzhou Qiu, Jian Zhao, Hong Chen, Xiaoqing Xian, Meixiang Chi, Qiyong Weng. Research and application of a big data collection method for invasive species surveys [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(10): 1377-1385. |
| [6] | Jia Li, Xiulei Wang, Mingwei Yang, Daxiang Chen, Xiaoju Wang, Ping Luo, Fang Liu, Yadong Xue, Guangliang Li, Yuguang Zhang, Yu Zhang, Diqiang Li. Construction progress of camera-trapping database from the Nature Reserves Biological Specimen Resources Sharing Sub-platform [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(9): 1081-1089. |
| [7] | Fenglin Zhang,Xin Wang,Jian Zhang. Biodiversity information resources. II. Environmental data [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(1): 53-65. |
| [8] | Jian Zhang. Biodiversity science and macroecology in the era of big data [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(4): 355-363. |
| [9] | Hang Sun, Tao Deng, Yongsheng Chen, Zhuo Zhou. Current research and development trends in floristic geography [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(2): 111-122. |
| [10] | Xin Wang, Fenglin Zhang, Jian Zhang. Biodiversity information resources. I. Species distribution, catalogue, phylogeny, and life history traits [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(11): 1223-1238. |
| [11] | Junjie Li, Xiaolei Huang. Analysis of publication trends of biodiversity data papers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(12): 1317-1324. |
| [12] | QIAO Hui-Jie, HAN Yan, LI Nuo, JI Li-Qiang. A model of biodiversity information integration [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2004, 12(5): 553-561. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()