



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 24168. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024168 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024168
• Technology and Methodology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhang Shuxin1, Jia Zixuan2, Fang Tao1, Liu Yifan1, Zhao Wei1, Wang Rong3, Chang Haichao1, Luo Fangli1,4,*( )(
)( ), Zhu Yaojun5,6, Yu Feihai7,8
), Zhu Yaojun5,6, Yu Feihai7,8
Received:2024-05-07
Accepted:2025-01-06
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-03-17
Contact:
*E-mail: ecoluofangli@bjfu.edu.cn
Supported by:Zhang Shuxin, Jia Zixuan, Fang Tao, Liu Yifan, Zhao Wei, Wang Rong, Chang Haichao, Luo Fangli, Zhu Yaojun, Yu Feihai. Methods to evaluate plant tolerance to environmental stresses[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24168.
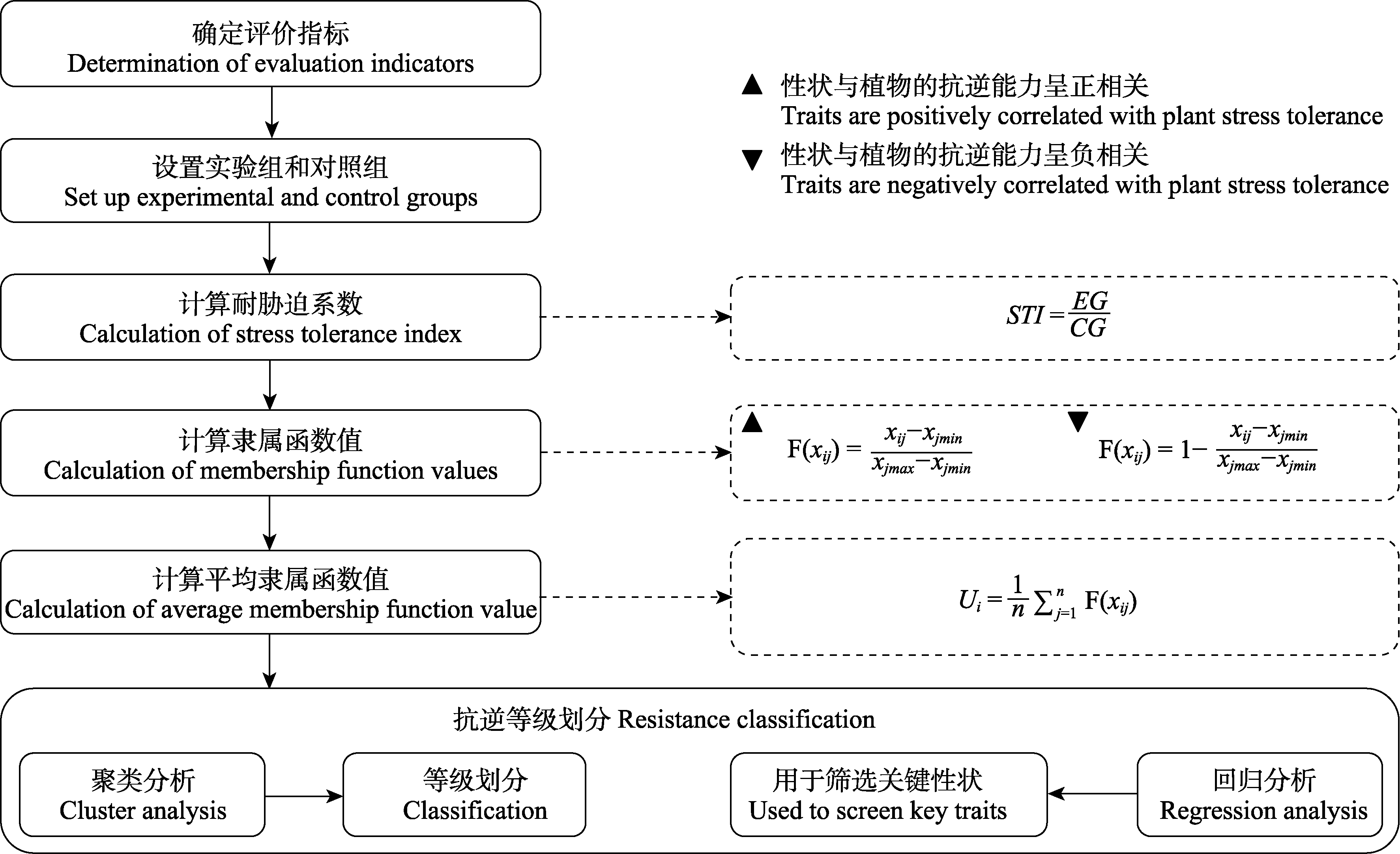
Fig. 1 Main process in the evaluation of plant resilience using the average membership function value. STI, Stress tolerance index; EG, Average value of trait under stress; CG, Average value of trait under control; F(xij), Membership function value of the j trait of the i plant; Ui, Average membership function value of the ith plant; xij, Measured value of the j trait of the i plant; xjmax, Maximum value of the j trait; xjmin, Minimum value of the j trait. Packages such as cluster and factoextra in R and Analysis-Category-Cluster in IBM SPSS Statistics can perform cluster analysis. Packages such as stats and glmulti in R and Analysis-regression in IBM SPPS Statistics can perform regression analysis.
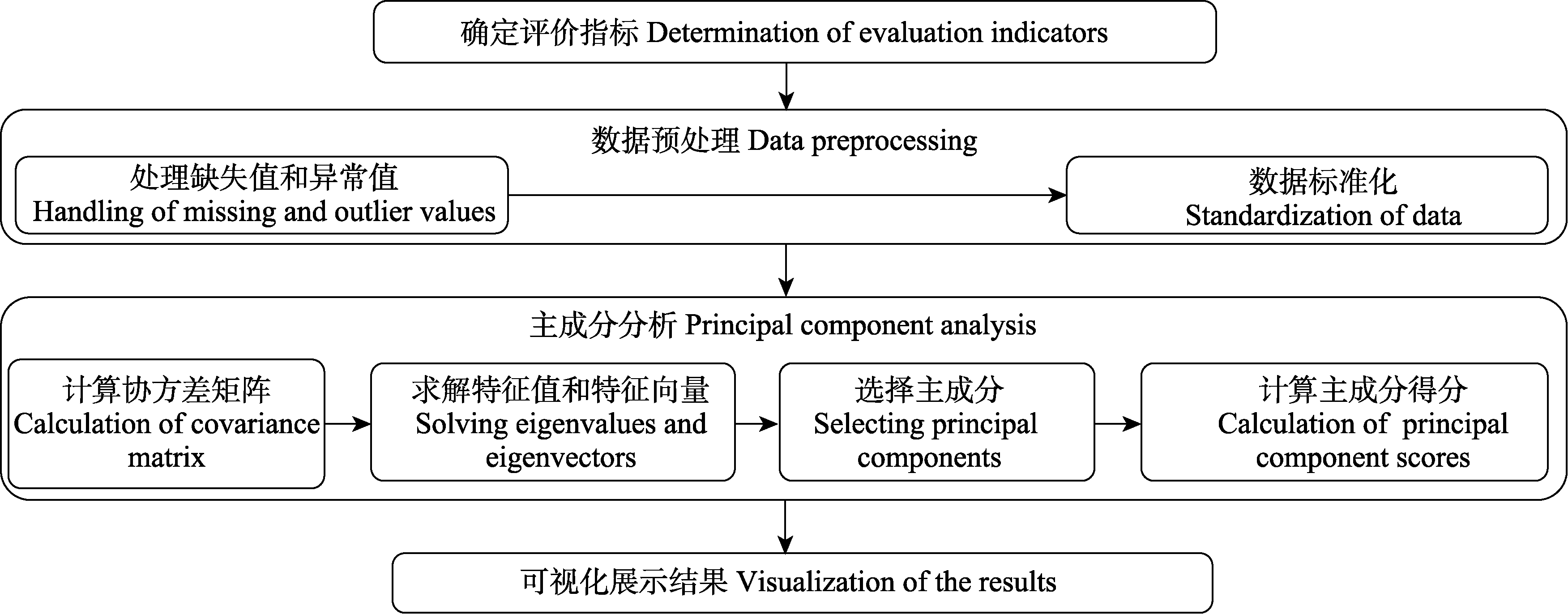
Fig. 2 Main processes in the evaluation of plant resilience using principal component analysis. Packages such as FactoMineR and stats in R and analysis-dimensionality reduction-factor analysis in IBM SPSS Statistics can perform principal component analysis.
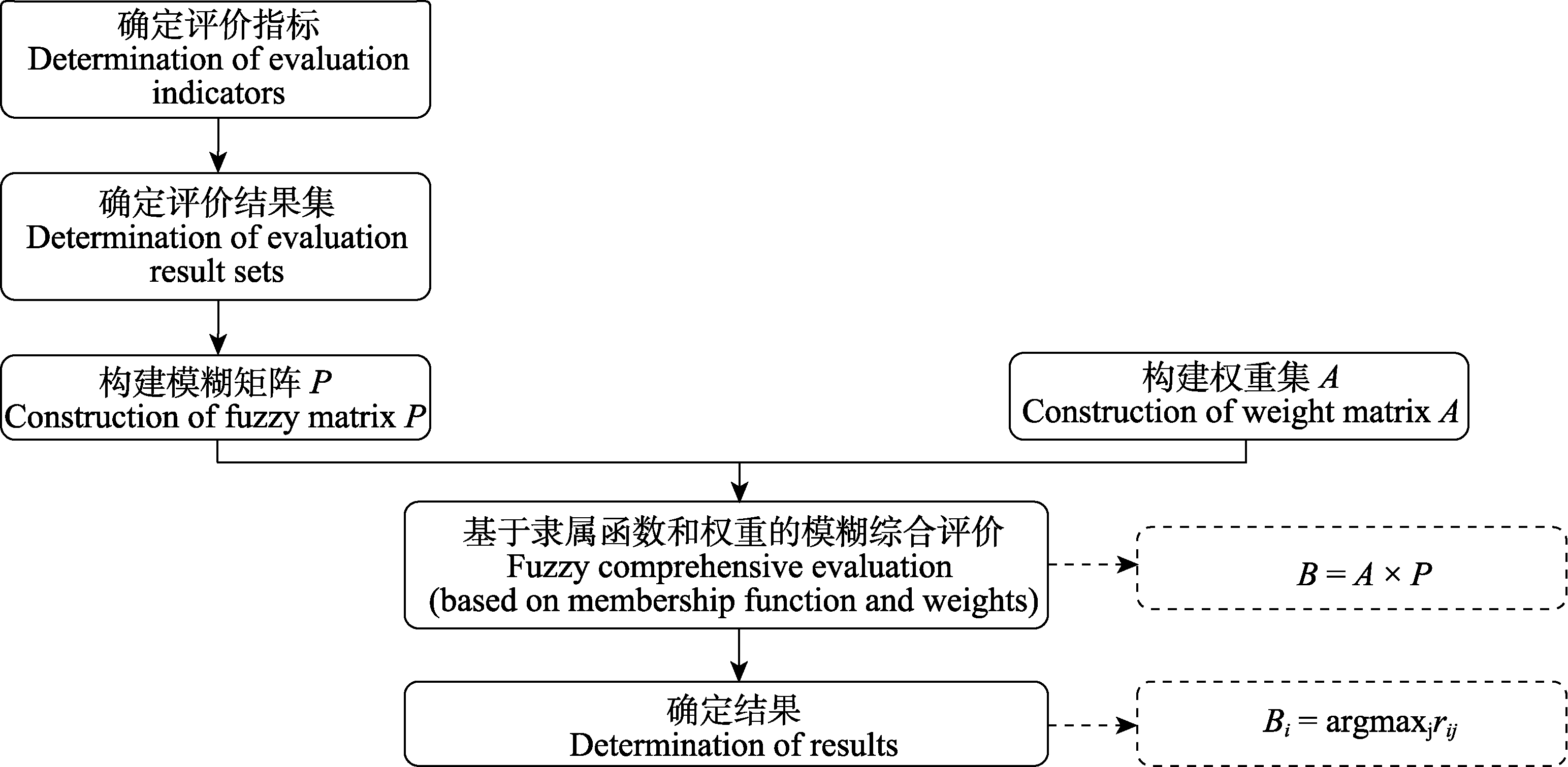
Fig. 3 Main processes of in the evaluation of plant resilience using fuzzy comprehensive evaluation (based on membership function and weights). rij, Membership degree of single trait i in evaluation grade j; P, Fuzzy matrix composed of rij; B, Result matrix; ×, Common fuzzy operators; argmaxj, The index of evaluation grade that maximized membership degree rij; Bi, For the i element, choose the j rank that maximizes rij.
| 特点 Features | M(˄, ˅) | M(×, ˅) | M(˄, +) | M(×, +) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体现权重作用 Reflecting the influence of weights | 不明显 Not apparent | 明显 Apparent | 不明显 Not apparent | 明显 Apparent |
| 综合程度 Comprehensive degree | 弱 Weak | 弱 Weak | 强 Strong | 强 Strong |
| 利用隶属矩阵的信息 Utilizing information from the membership matrix | 不充分 Insufficient | 不充分 Insufficient | 比较充分 Sufficient comparison | 充分 Sufficient |
| 类型 Category | 主因素突出 Principal factor prominence | 主因素突出 Principal factor prominence | 加权平均 Weighted average | 加权平均 Weighted average |
Table 1 Common fuzzy operators
| 特点 Features | M(˄, ˅) | M(×, ˅) | M(˄, +) | M(×, +) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体现权重作用 Reflecting the influence of weights | 不明显 Not apparent | 明显 Apparent | 不明显 Not apparent | 明显 Apparent |
| 综合程度 Comprehensive degree | 弱 Weak | 弱 Weak | 强 Strong | 强 Strong |
| 利用隶属矩阵的信息 Utilizing information from the membership matrix | 不充分 Insufficient | 不充分 Insufficient | 比较充分 Sufficient comparison | 充分 Sufficient |
| 类型 Category | 主因素突出 Principal factor prominence | 主因素突出 Principal factor prominence | 加权平均 Weighted average | 加权平均 Weighted average |
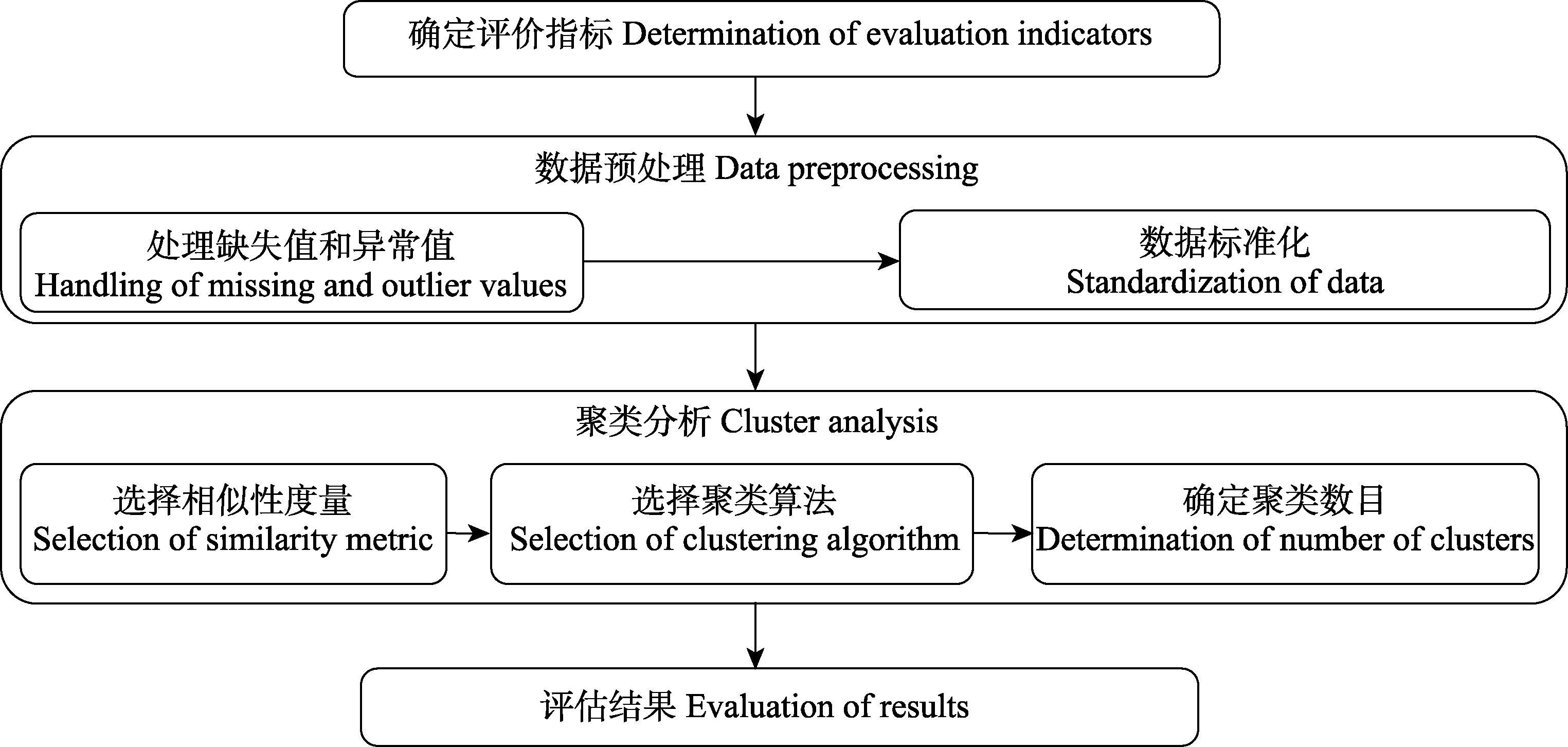
Fig. 4 Main processes in the evaluation of plant resilience using cluster analysis. Packages such as cluster and stats in R and IBM SPSS Statistics can perform cluster analysis.
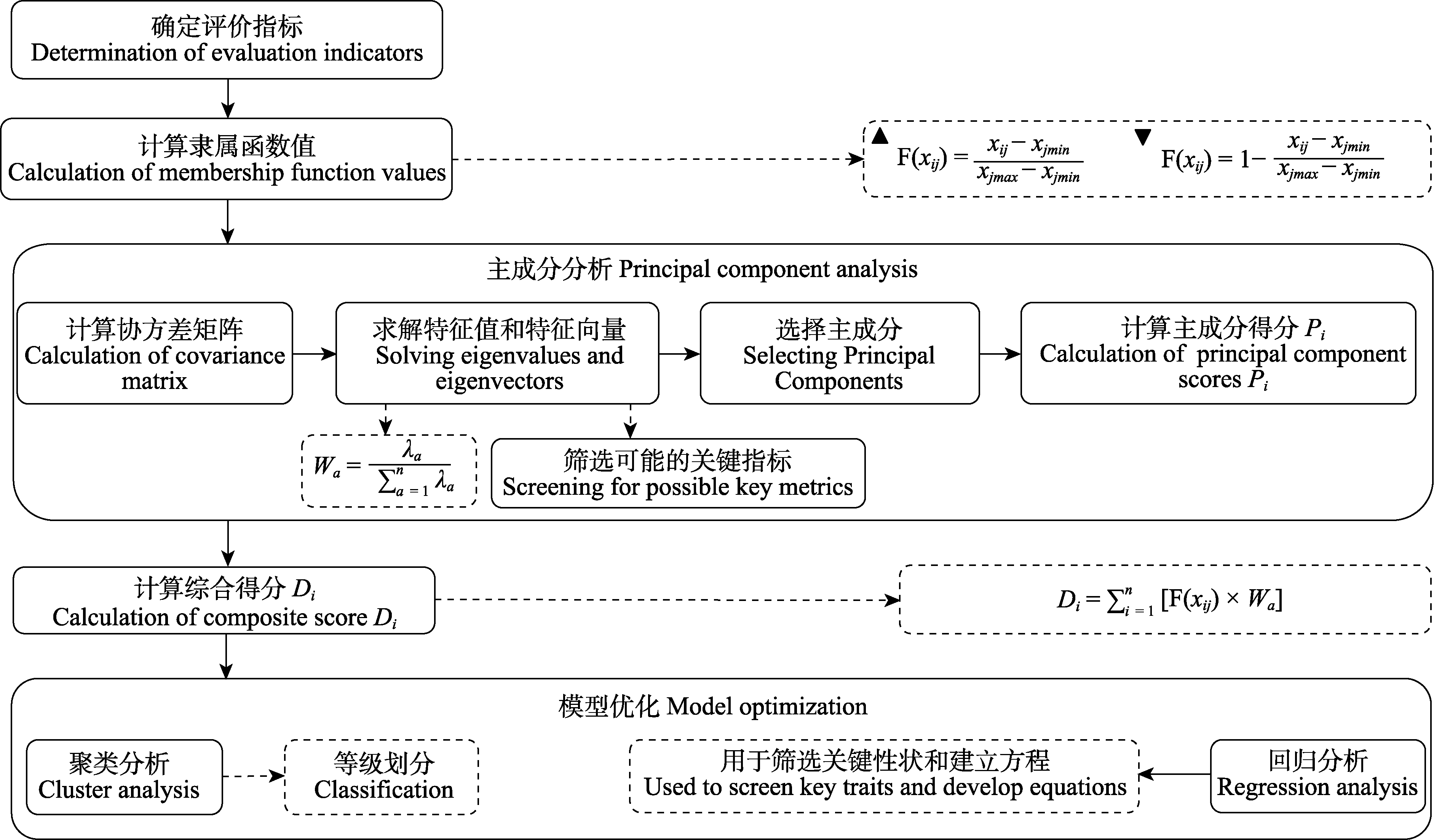
Fig. 5 Main processes in the evaluation of plant resilience using composite evaluation (combining membership function and principal component analysis). F(xij), Membership function value of the j trait of the i plant, xij: Measured value of the j trait of the i plant; xjmax, Maximum value of the j trait; xjmin, Minimum value of the j trait; Wa, Weight of the ath principal component, is the contribution rate of the a principal component; Di, Comprehensive score of the i plant.
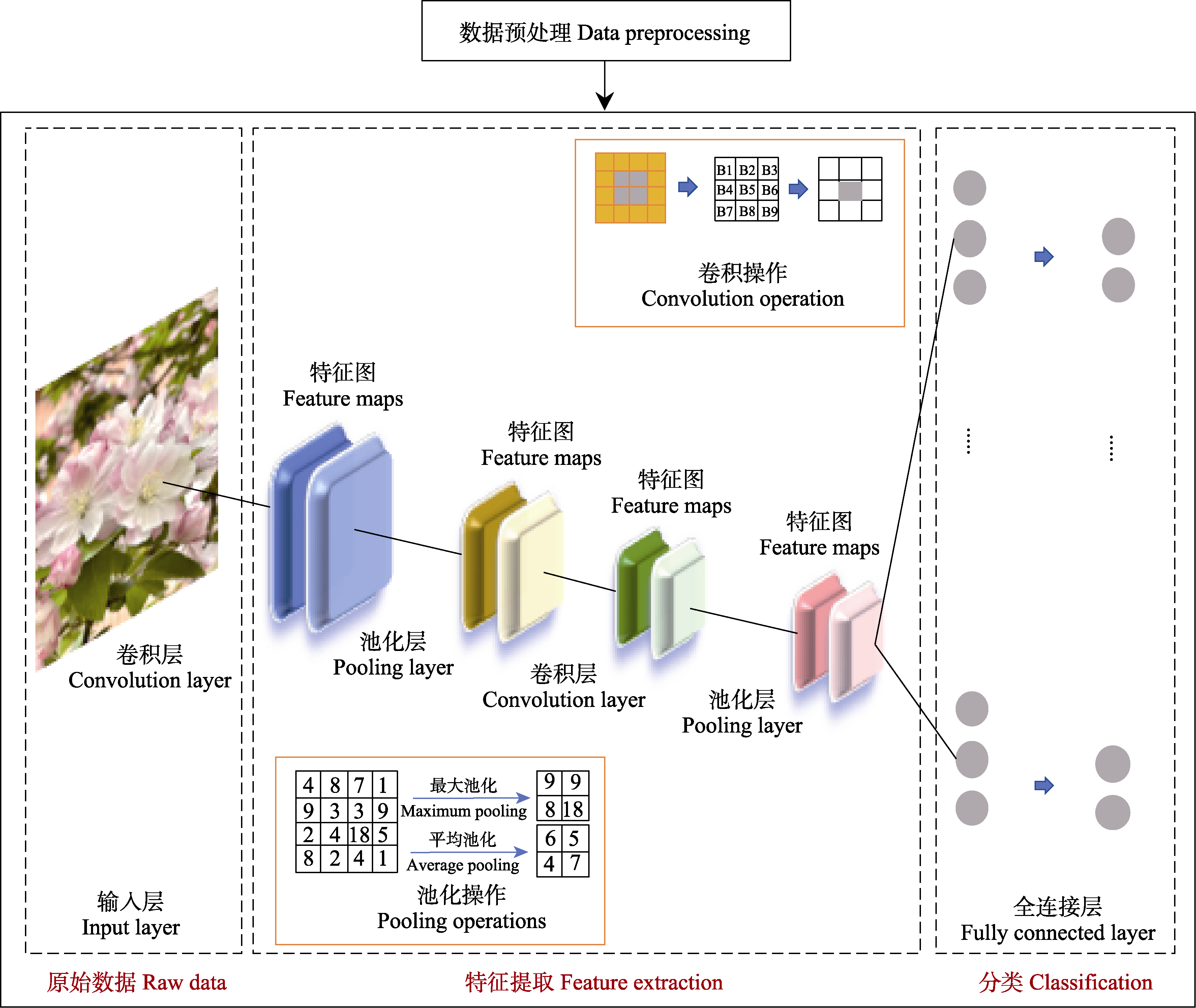
Fig. 6 The structure of typical convolutional neural network model for plant stress evaluation. Input layer, Receives the original image; Convolution layer, Performs convolution operation on the input data through the convolution kernel, extracts the local features, and forms a new feature map; Pooling layer, Down samples the feature map, reduces the size of the feature map and the number of parameters, and combines the similar features into a single one; Fully-connected layer, Performs linear transformation and nonlinear activation on the pooled feature map, spreads it into a one-dimensional vector, and performs classification, regression and other tasks. Deep learning frameworks such as Keras, Caffe, and TensorFlow all implement convolutional neural networks.
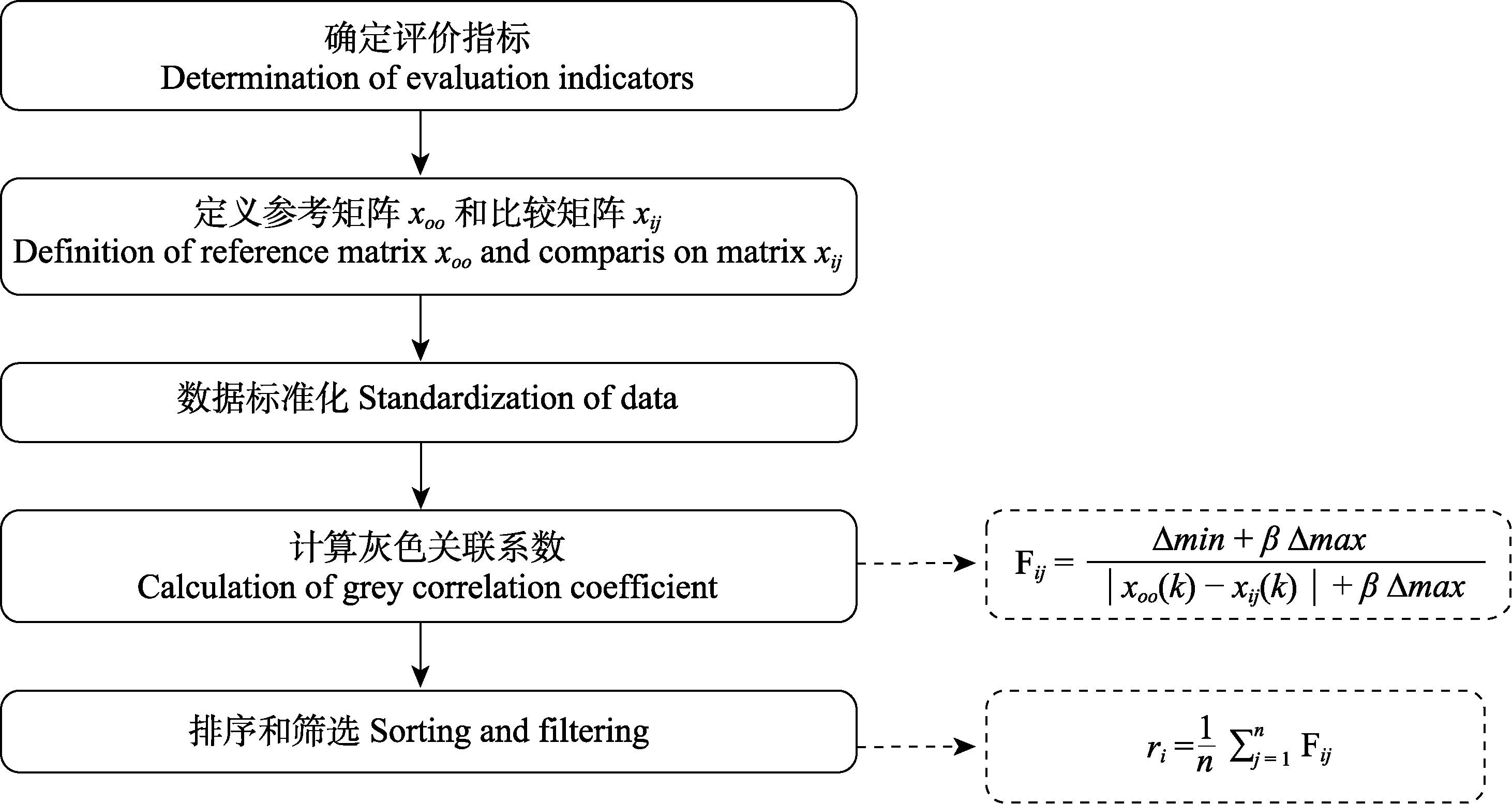
Fig. 7 Main processes in the evaluation of plant resilience using grey relational analysis. Fij, Grey correlation degree of j trait of the i plant; Δmin, The minimum absolute grey correlation coefficient between xoj and xij; β, Discrimination coefficient, generally 0.5; Δmax, The maximum absolutegrey correlation coefficient between xoj and xij; xoj(k), K data of reference sequence; xij(k), k data of the comparison sequence; rj, Degree of association between the j trait and the reference sequence. This can be done in packages such as greybox in R and Pandas in Python.
| [1] | Aala WF, Gregorio GB (2019) Morphological and molecular characterization of novel salt-tolerant rice germplasms from the Philippines and Bangladesh. Rice Science, 26, 178-188. |
| [2] | Abdelrahman M, Mostofa MG, Tran CD, El-Sayed M, Li WQ, Sulieman S, Tanaka M, Seki M, Tran LP (2023) The karrikin receptor karrikin insensitive 2 positively regulates heat stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant & Cell Physiology, 63, 1914-1926. |
| [3] | Alam MS, Tester M, Fiene G, Mousa MAA (2021) Early growth stage characterization and the biochemical responses for salinity stress in tomato. Plants, 10, 712. |
| [4] | Allel D, Ben-Amar A, Badri M, Abdelly C (2016) Salt tolerance in barley originating from harsh environment of North Africa. Australian Journal of Crop Science, 10, 438-451. |
| [5] | Azimi S, Kaur T, Gandhi TK (2021) A deep learning approach to measure stress level in plants due to nitrogen deficiency. Measurement, 173, 108650. |
| [6] | Cao X, Jiang FL, Wang X, Zang YW, Wu Z (2015) Comprehensive evaluation and screening for chilling- tolerance in tomato lines at the seedling stage. Euphytica, 205, 569-584. |
| [7] | Chen XJ, Min DH, Ahmad Yasir T, Hu YG (2012) Evaluation of 14 morphological, yield-related and physiological traits as indicators of drought tolerance in Chinese winter bread wheat revealed by analysis of the membership function value of drought tolerance (MFVD). Field Crops Research, 137, 195-201. |
| [8] | Deng J (1989) Introduction to grey system theory. Journal of Grey System, 1, 1-24. |
| [9] | Deng Y, Sun XJ, Zhang Q, Anwar S, Lu JY, Guo HX, Qin LX, Zhang LG, Wang CY (2023) Comprehensive evaluation and physiological response of quinoa genotypes to low nitrogen. Agronomy, 13, 1597. |
| [10] | Dhaka VS, Meena SV, Rani G, Sinwar D, Kavita K, Ijaz MF, Woźniak M (2021) A survey of deep convolutional neural networks applied for prediction of plant leaf diseases. Sensors, 21, 4749. |
| [11] | Dong ZX, Xiong Y, Xiong YL, Zhao JM, Zhang JB, Peng JH, Chen SM, Min W, Yu QQ, Ma X (2024) Evaluation of production performance and nutritional value of eleven forage sorghum varieties in Liangshan Prefecture. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 32, 2934-2942. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 董志晓, 熊毅, 熊艳丽, 赵俊茗, 张建波, 彭靖涵, 陈书明, 敏伟, 余青青, 马啸 (2024) 11份饲用甜高粱品种在凉山州的生产性能及营养价值评价. 草地学报, 32, 2934-2942.]
DOI |
|
| [12] | Ezugwu AE, Ikotun AM, Oyelade OO, Abualigah L, Agushaka JO, Eke CI, Akinyelu AA (2022) A comprehensive survey of clustering algorithms: State-of-the-art machine learning applications, taxonomy, challenges, and future research prospects. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 110, 104743. |
| [13] | Fu XQ, Han B, Liu SY, Zhou JY, Zhang HW, Wang HB, Zhang H, Ouyang ZQ (2022) WSVAS: A YOLOv4-based phenotyping platform for automatically detecting the salt tolerance of wheat based on seed germination vigour. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13, 1074360. |
| [14] | Guo CC, Zhu LX, Sun HC, Han QC, Wang SJ, Zhu JJ, Zhang YJ, Zhang K, Bai ZY, Li AC, Liu LT, Li CD (2024) Evaluation of drought-tolerant varieties based on root system architecture in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). BMC Plant Biology, 24, 127. |
| [15] | Han W, Yang ZQ, Huang LD, Sun CX, Yu XJ, Zhao MF (2019) Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of the effects of relative air humidity on the morpho-physiological traits of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) under high temperature. Scientia Horticulturae, 246, 971-978. |
| [16] | Hao SX, Cao HX, Wang HB, Pan XY (2019) Effects of water stress at different growth stages on comprehensive fruit quality and yield in different bunches of tomatoes in greenhouses. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 12, 67-76. |
| [17] | Hartigan JA, Wong MA (1979) Algorithm AS 136: A K-means clustering algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society C: Applied Statistics, 28, 100-108. |
| [18] | Huang YS, Shen L, Liu H (2019) Grey relational analysis, principal component analysis and forecasting of carbon emissions based on long short-term memory in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 209, 415-423. |
| [19] | Ibrahim Ibrahim S, Naawe EK, Çaliskan ME (2024) Effect of drought stress on morphological and yield characteristics of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) breeding lines. Potato Research, 67, 529-543. |
| [20] |
Kakar N, Jumaa SH, Redoña ED, Warburton ML, Reddy KR (2019) Evaluating rice for salinity using pot-culture provides a systematic tolerance assessment at the seedling stage. Rice, 12, 57.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Khan MIR, Kumari S, Nazir F, Khanna RR, Gupta R, Chhillar H (2023) Defensive role of plant hormones in advancing abiotic stress-resistant rice plants. Rice Science, 30, 15-35. |
| [22] | Iosa M, Demeyere N, Abbruzzese L, Zoccolotti P, Mancuso M (2022) Principal component analysis of Oxford cognitive screen in patients with stroke. Frontiers in Neurology, 13, 779679. |
| [23] |
Jiang B, Wang ST, Sun ZB, Zhang HR, Wang J, Liu Y (2023) Evaluation of cultivated land soil fertility based on membership function and principal component analysis. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 39(2), 22-27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 姜冰, 王松涛, 孙增兵, 张海瑞, 王建, 刘阳 (2023) 基于隶属度函数和主成分分析的耕地土壤肥力评价. 中国农学通报, 39(2), 22-27.]
DOI |
|
| [24] | LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature, 521, 436-444. |
| [25] | Li AM, Fan M, Qin GD, Wang HL, Xu YC (2023) Water quality parameter COD retrieved from remote sensing based on convolutional neural network model. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 43, 651-656. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李爱民, 范猛, 秦光铎, 王海隆, 许有成 (2023) 卷积神经网络模型的遥感反演水质参数COD. 光谱学与光谱分析, 43, 651-656.] | |
| [26] | Li FX (2023) Research on the application of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation in teaching performance appraisal of college teachers. Packaging Engineering, 44(S1), 663-669. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李付星 (2023) 模糊综合评价在高校教师教学绩效考核中的应用研究. 包装工程, 44(S1), 663-669.] | |
| [27] | Li JL, Xue Y, Wang XY, Xu BB, Guo ST (2024) Judgment technique for over-exploration of water-conducting channel based on process analysis and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. Coal Science and Technology, 52(7), 178-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李建林, 薛杨, 王心义, 徐博博, 郭水涛 (2024) 基于模糊综合评价的导水通道超前探查判识技术. 煤炭科学技术, 52(7), 178-186.] | |
| [28] | Li WH, Zhang HZ, Zeng YL, Xiang LJ, Lei ZH, Huang QX, Li TY, Shen F, Cheng Q (2020) A salt tolerance evaluation method for sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) at the seed germination stage. Scientific Reports, 10, 10626. |
| [29] | Liu ZL, Li XY, Wang ZL, Qin JF (2020) Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of diseases and pests resistance of sweet potato varieties based on combination weighting. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 48(12), 93-97. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘忠玲, 李小艳, 王自力, 秦家范 (2020) 基于组合赋权的甘薯品种抗病性模糊综合评价. 江苏农业科学, 48(12), 93-97.] | |
| [30] | Mbarki S, Skalicky M, Vachova P, Hajihashemi S, Jouini L, Zivcak M, Tlustos P, Brestic M, Hejnak V, Zoghlami Khelil A, (2020) Comparing salt tolerance at seedling and germination stages in local populations of Medicago ciliaris L. to Medicago intertexta L. and Medicago scutellata L. Plants, 9, 526. |
| [31] | Meng XY, Zhang PL, Zheng YT, Qin K (2023) Research on the satisfaction of talent cultivation quality of nursing academic degree postgraduates based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. Chinese Nursing Research, 37, 4021-4024. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孟欣玉, 张培莉, 郑玉婷, 覃凯 (2023) 基于模糊综合评价法的护理硕士学术学位研究生人才培养质量满意度研究. 护理研究, 37, 4021-4024.] | |
| [32] |
Mills G, Sharps K, Simpson D, Pleijel H, Frei M, Burkey K, Emberson L, Uddling J, Broberg M, Feng ZZ, Kobayashi K, Agrawal M (2018) Closing the global ozone yield gap: Quantification and cobenefits for multistress tolerance. Global Change Biology, 24, 4869-4893.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Nasser M, Yusof UK (2023) Deep learning based methods for breast cancer diagnosis: A systematic review and future direction. Diagnostics, 13, 161. |
| [34] |
Negrão S, Schmöckel SM, Tester M (2017) Evaluating physiological responses of plants to salinity stress. Annals of Botany, 119, 1-11.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Niu Y, Wang F, Liu L, Zhang GL, Qi B, Liu XH, Zhao HL, Huang ZW, Fan S, Zhang LQ (2023) Comprehensive evaluation and screening for 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene tolerance in rice cultivars at different growth stages. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 42, 154-167. |
| [36] | Pathania S, Singh H (2021) Evaluation and prediction of salinity tolerance behavior of citrus rootstocks. Scientia Horticulturae, 289, 110422. |
| [37] | Qin XH, Wang ZY, Yao JP, Zhou Q, Zhao PF, Wang ZY, Huang L (2020) Using a one-dimensional convolutional neural network with a conditional generative adversarial network to classify plant electrical signals. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 174, 105464. |
| [38] |
Radanielson AM, Angeles O, Li T, Ismail AM, Gaydon DS (2018) Describing the physiological responses of different rice genotypes to salt stress using sigmoid and piecewise linear functions. Field Crops Research, 220, 46-56.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Reddy INBL, Kim SM, Kim BK, Yoon IS, Kwon TR (2017) Identification of rice accessions associated with K+/Na+ ratio and salt tolerance based on physiological and molecular responses. Rice Science, 24, 360-364. |
| [40] | Ruan DW, Wang J, Yan JP, Gühmann C (2023) CNN parameter design based on fault signal analysis and its application in bearing fault diagnosis. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 55, 101877. |
| [41] | Saxena A, Prasad M, Gupta A, Bharill N, Patel OP, Tiwari A, Er MJ, Ding WP, Lin CT (2017) A review of clustering techniques and developments. Neurocomputing, 267, 664-681. |
| [42] | Sikder RK, Wang XR, Jin DS, Zhang HH, Gui HP, Dong Q, Pang NC, Zhang XL, Song MZ (2020) Screening and evaluation of reliable traits of upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) genotypes for salt tolerance at the seedling growth stage. Journal of Cotton Research, 3, 11. |
| [43] | Sivakumar J, Prashanth JEP, Rajesh N, Reddy SM, Pinjari OB (2020) Principal component analysis approach for comprehensive screening of salt stress-tolerant tomato germplasm at the seedling stage. Journal of Biosciences, 45, 141. |
| [44] | Tan ZW, Wang WL, Zong R, Pan JH, Yang HB (2019) Classification of heart sound signals in congenital heart disease based on convolutional neural network. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 36, 728-736, 744. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谭朝文, 王威廉, 宗容, 潘家华, 杨宏波 (2019) 基于卷积神经网络的先心病心音信号分类算法. 生物医学工程学杂志, 36, 728-736, 744.] | |
| [45] | Tang Z, Yang JL, Li Z, Qi F (2020) Grape disease image classification based on lightweight convolution neural networks and channelwise attention. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 178, 105735. |
| [46] | Tian HJ, Ding SQ, Zhang D, Wang JB, Hu MT, Yang KZ, Hao Y, Qiao N, Du WT, Li RF, Yang XD, Xu RH (2024) Sodium bicarbonate tolerance during seedling stages of maize (Zea mays L.) lines. Food and Energy Security, 13, e70013. |
| [47] | Tong CY, Yang GT, AoenBolige, Terigen, Li HW, Li B, Li ZS, Zheng Q (2022) Screening of salt-tolerant Thinopyrum ponticum under two coastal region salinity stress levels. Frontiers in Genetics, 13, 832013. |
| [48] | Wang JY, Li CN, Li L, Reynolds M, Mao XG, Jing RL (2021) Exploitation of drought tolerance-related genes for crop improvement. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22, 10265. |
| [49] | Wang XT, Liu XN, Tang JW, Jia SB, Ma L (2022) Comparison of yield and nutritional quality of 4 graminaceous forages on plateau under arid environment. Grassland and Turf, 42(1), 57-61, 68. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王晓彤, 柳小妮, 唐俊伟, 贾顺斌, 马力 (2022) 干旱环境下4种高原禾本科牧草产量及营养品质比较. 草原与草坪, 42(1), 57-61, 68.] | |
| [50] | Wang ZY, Qin XH, Li JH, Fan LF, Zhou Q, Wang YQ, Zhao X, Xie CJ, Wang ZY, Huang L (2019) Highly reproducible periodic electrical potential changes associated with salt tolerance in wheat plants. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 160, 120-130. |
| [51] | Ward JH Jr (1963) Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 58, 236-244. |
| [52] | Wassie M, Zhang WH, Zhang Q, Ji K, Chen L (2019) Effect of heat stress on growth and physiological traits of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) and a comprehensive evaluation for heat tolerance. Agronomy, 9, 597. |
| [53] | Wu H, Guo JR, Wang CF, Li KL, Zhang XW, Yang Z, Li MT, Wang BS (2019) An effective screening method and a reliable screening trait for salt tolerance of Brassica napus at the germination stage. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10, 530. |
| [54] |
Yan CJ, Song SH, Wang WB, Wang CL, Li HB, Wang F, Li SY, Sun XG (2020) Screening diverse soybean genotypes for drought tolerance by membership function value based on multiple traits and drought-tolerant coefficient of yield. BMC Plant Biology, 20, 321.
DOI PMID |
| [55] | Yang XF, Ye YM, Li XT, Lau RYK, Zhang XF, Huang XH (2018) Hyperspectral image classification with deep learning models. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 56, 5408-5423. |
| [56] |
Yang ZL, Shi YQ, Li PL, Pan KH, Li GQ, Li XG, Yao S, Zhang DH (2022) Application of principal component analysis (PCA) to the evaluation and screening of multiactivity fungi. Journal of Ocean University of China, 21, 763-772.
DOI PMID |
| [57] | Yao JP, Wang ZY, de Oliveira RF, Wang ZY, Huang L (2021) A deep learning method for the long-term prediction of plant electrical signals under salt stress to identify salt tolerance. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 190, 106435. |
| [58] | Zhang CN, Luo T, Liu JH, Xian MZ, Yuan JZ, Hu LY, Xu ZH (2019) Evaluation of the low-temperature tolerance of rapeseed genotypes at the germination and seedling emergence stages. Crop Science, 59, 1709-1717. |
| [59] | Zhang JX, Zhang AW, Liu ZX, He WT, Yang SY (2023) Multi-index fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model with information entropy of alfalfa salt tolerance based on LiDAR data and hyperspectral image data. Frontiers in Plant Science, 14, 1200501. |
| [60] |
Zhang WF, Zhu SK, He S, Wang YX (2015) Screening of oil sources by using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry and multivariate statistical analysis. Journal of Chromatography A, 1380, 162-170.
DOI PMID |
| [61] | Zhang ZQ, Dong R, Tan DL, Duan L, Jiang F, Yao XX, Yang DX, Hu JY, Zhang J, Zhong WH, Zhao ZH (2023) Effect of structural parameters on diesel particulate filter trapping performance of heavy-duty diesel engines based on grey correlation analysis. Energy, 271, 127025. |
| [62] | Zhao J, Pan FJ, Li ZM, Lan YB, Lu LQ, Yang DJ, Wen YT (2021) Detection of cotton waterlogging stress based on hyperspectral images and convolutional neural network. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 14, 167-174. |
| [63] | Zhao T, Pan XJ, Ou ZG, Li Q, Zhang WE (2022) Comprehensive evaluation of waterlogging tolerance of eleven Canna cultivars at flowering stage. Scientia Horticulturae, 296, 110890. |
| [64] | Zhou J, Zhou JF, Ye H, Ali ML, Chen PY, Nguyen HT (2021) Yield estimation of soybean breeding lines under drought stress using unmanned aerial vehicle-based imagery and convolutional neural network. Biosystems Engineering, 204, 90-103. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()