



生物多样性 ›› 2008, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (4): 362-368. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07314 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2008.07314
收稿日期:2007-10-19
接受日期:2008-04-01
出版日期:2008-07-20
发布日期:2008-07-20
通讯作者:
张启翔
基金资助:
Ruili Zhang, Yin Jia, Qixiang Zhang*( )
)
Received:2007-10-19
Accepted:2008-04-01
Online:2008-07-20
Published:2008-07-20
Contact:
Qixiang Zhang
摘要:
滇北球花报春(Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata)的早春蓝紫色球状花序具有独特的观赏价值, 但由于多种因素的影响, 其天然群体正在逐渐减少。为评价其遗传多样性水平, 我们对滇北球花报春10个天然群体进行了表型性状变异研究。结果表明: 滇北球花报春8个表型性状在群体间和群体内均存在极显著差异, 变异系数(CV)在4.73-9.90%之间, 表型分化系数(Vst)在0.1541-0.4069之间, 平均值为0.2854, 群体内的变异是表型变异的主要来源。根据8个表型性状的UPGMA聚类分析将10个天然群体划分为3类。依本研究结果, 在对滇北球花报春种质资源保护时进行就地保护是十分必要的, 并且应该优先保护表型变异较为丰富的天然群体。
张睿鹂, 贾茵, 张启翔 (2008) 滇北球花报春天然群体表型变异研究. 生物多样性, 16, 362-368. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07314.
Ruili Zhang, Yin Jia, Qixiang Zhang (2008) Phenotypic variation of natural populations of Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata. Biodiversity Science, 16, 362-368. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07314.
| 群体编号 Population No. | 地点 Origin | 经纬度 Locality | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 生境 Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSM 1 | 大理苍山 Cangshan Mountains, Dali | 25°41'165" N 100°06'403" E | 3,330 | 山坡杜鹃林下, 北向 Slope, under Rhododendron shrubs, facing north |
| CSM 2 | 大理苍山 Cangshan Mountains, Dali | 25°41'749" N 100°06'557" E | 2,800 | 干燥山坡坡地, 杜鹃林缘, 西向 Dry slope, beneath Rhododendron shrubs, facing west |
| MX | 漾濞美翕 Meixi, Yangbi | 25°43'213" N 100°03'175" E | 3,050 | 山间开敞坡地, 林缘, 西向 Grassy slope, beneath the woodlands, facing west |
| TCL | 云龙天池 Tianchi Lake, Yunlong | 25°51'422" N 99°19'389" E | 2,330 | 干燥坡地, 乔木林下, 东南向 Dry slope, under the woodlands, facing southeast |
| LDP | 丽江梨地坪 Lidiping, Lijiang | 27°12'389" N 99°24'478" E | 3,400 | 山坡坡地, 南向 Grassy slope, facing south |
| PTG | 维西攀天阁 Pantiange, Weixi | 27°20'983" N 99°11'976" E | 2,900 | 开阔缓坡, 沼泽地, 南向 Moist meadow, facing south |
| SBM | 双柏百竹山 Baizhu Mountain, Shuangbai | 24°33'404" N 100°48'615" E | 2,500 | 山顶开阔地带, 潮湿林缘, 东南向 Open forest, moist, beneath the woodlands, facing southeast |
| YLM | 丽江玉龙雪山 Yulong Mountains, Lijiang | 27°07'791'' N 100°15'114'' E | 2,800 | 山坡杜鹃林下, 东北向 Slope, under Rhododendron shrubs, facing northeast |
| SCH | 景东山厂河 Shanchanghe, Jingdong | 24°18'151" N 100°43'882" E | 2,210 | 干燥的开阔地带, 北向 Dry slope, facing north |
| ZZ | 腾冲自治 Zizhi, Tengchong | 26°34'309" N 99°53'572" E | 2,500 | 开阔地带, 干燥, 南向 Open forest, dry, facing south |
表1 滇北球花报春天然群体的地理位置及生态因子
Table 1 Locations and ecological factors of the sampled populations of Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata
| 群体编号 Population No. | 地点 Origin | 经纬度 Locality | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 生境 Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSM 1 | 大理苍山 Cangshan Mountains, Dali | 25°41'165" N 100°06'403" E | 3,330 | 山坡杜鹃林下, 北向 Slope, under Rhododendron shrubs, facing north |
| CSM 2 | 大理苍山 Cangshan Mountains, Dali | 25°41'749" N 100°06'557" E | 2,800 | 干燥山坡坡地, 杜鹃林缘, 西向 Dry slope, beneath Rhododendron shrubs, facing west |
| MX | 漾濞美翕 Meixi, Yangbi | 25°43'213" N 100°03'175" E | 3,050 | 山间开敞坡地, 林缘, 西向 Grassy slope, beneath the woodlands, facing west |
| TCL | 云龙天池 Tianchi Lake, Yunlong | 25°51'422" N 99°19'389" E | 2,330 | 干燥坡地, 乔木林下, 东南向 Dry slope, under the woodlands, facing southeast |
| LDP | 丽江梨地坪 Lidiping, Lijiang | 27°12'389" N 99°24'478" E | 3,400 | 山坡坡地, 南向 Grassy slope, facing south |
| PTG | 维西攀天阁 Pantiange, Weixi | 27°20'983" N 99°11'976" E | 2,900 | 开阔缓坡, 沼泽地, 南向 Moist meadow, facing south |
| SBM | 双柏百竹山 Baizhu Mountain, Shuangbai | 24°33'404" N 100°48'615" E | 2,500 | 山顶开阔地带, 潮湿林缘, 东南向 Open forest, moist, beneath the woodlands, facing southeast |
| YLM | 丽江玉龙雪山 Yulong Mountains, Lijiang | 27°07'791'' N 100°15'114'' E | 2,800 | 山坡杜鹃林下, 东北向 Slope, under Rhododendron shrubs, facing northeast |
| SCH | 景东山厂河 Shanchanghe, Jingdong | 24°18'151" N 100°43'882" E | 2,210 | 干燥的开阔地带, 北向 Dry slope, facing north |
| ZZ | 腾冲自治 Zizhi, Tengchong | 26°34'309" N 99°53'572" E | 2,500 | 开阔地带, 干燥, 南向 Open forest, dry, facing south |
| 株高 Plant height | 冠幅 Rosette width | 叶丛高 Rosette height | 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 花序直径 Flower diameter | 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冠幅 Rosette width | 0.122 | ||||||
| 叶丛高 Rosette height | 0.056 | -0.511 | |||||
| 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | -0.157 | 0.053 | 0.645* | ||||
| 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 0.562 | -0.399 | -0.017 | -0.335 | |||
| 花序直径 Flower diameter | -0.396 | -0.448 | 0.281 | 0.100 | -0.417 | ||
| 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 0.696* | -0.006 | 0.193 | 0.079 | 0.496 | -0.219 | |
| 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 0.316 | 0.079 | 0.293 | 0.140 | -0.069 | 0.016 | 0.463 |
表2 滇北球花报春10个天然群体8个性状Pearson相关系数(r)及其显著性检验
Table 2 Pearson correlation coefficient (r) for eight morphological traits and their significance in the Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata populations
| 株高 Plant height | 冠幅 Rosette width | 叶丛高 Rosette height | 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 花序直径 Flower diameter | 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冠幅 Rosette width | 0.122 | ||||||
| 叶丛高 Rosette height | 0.056 | -0.511 | |||||
| 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | -0.157 | 0.053 | 0.645* | ||||
| 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 0.562 | -0.399 | -0.017 | -0.335 | |||
| 花序直径 Flower diameter | -0.396 | -0.448 | 0.281 | 0.100 | -0.417 | ||
| 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 0.696* | -0.006 | 0.193 | 0.079 | 0.496 | -0.219 | |
| 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 0.316 | 0.079 | 0.293 | 0.140 | -0.069 | 0.016 | 0.463 |
| 群体编号 Population | 变异系数 CV (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height | 冠幅 Rosette width | 叶丛高 Rosette height | 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 花序直径 Flower diameter | 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 平均 Average | |
| CSM 1 | 11.51 | 10.28 | 6.88 | 10.12 | 6.62 | 16.64 | 5.17 | 5.04 | 9.03 |
| CSM 2 | 8.56 | 9.45 | 6.32 | 5.26 | 4.57 | 11.43 | 3.98 | 3.77 | 6.67 |
| MX | 5.92 | 4.92 | 5.32 | 4.78 | 6.82 | 3.34 | 3.76 | 2.95 | 4.73 |
| TCL | 8.65 | 13.47 | 7.18 | 6.51 | 7.34 | 17.68 | 4.77 | 6.07 | 8.96 |
| LDP | 8.16 | 9.05 | 5.98 | 4.77 | 3.49 | 10.57 | 4.99 | 3.52 | 6.32 |
| PTG | 15.26 | 12.62 | 8.76 | 7.99 | 6.48 | 15.24 | 6.14 | 6.68 | 9.90 |
| SBM | 4.55 | 4.17 | 4.75 | 4.14 | 3.49 | 12.58 | 3.59 | 4.02 | 5.16 |
| YLM | 7.96 | 8.14 | 7.82 | 4.62 | 2.32 | 7.78 | 2.86 | 3.25 | 5.59 |
| SCH | 8.54 | 8.26 | 6.51 | 3.35 | 4.48 | 4.39 | 4.09 | 3.88 | 5.44 |
| ZZ | 13.49 | 10.86 | 8.13 | 9.33 | 4.58 | 13.46 | 5.61 | 6.29 | 8.97 |
表3 滇北球花报春天然群体表型性状变异系数
Table 3 Coefficients of variance (CV) of morphological traits within each population of Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata
| 群体编号 Population | 变异系数 CV (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height | 冠幅 Rosette width | 叶丛高 Rosette height | 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 花序直径 Flower diameter | 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 平均 Average | |
| CSM 1 | 11.51 | 10.28 | 6.88 | 10.12 | 6.62 | 16.64 | 5.17 | 5.04 | 9.03 |
| CSM 2 | 8.56 | 9.45 | 6.32 | 5.26 | 4.57 | 11.43 | 3.98 | 3.77 | 6.67 |
| MX | 5.92 | 4.92 | 5.32 | 4.78 | 6.82 | 3.34 | 3.76 | 2.95 | 4.73 |
| TCL | 8.65 | 13.47 | 7.18 | 6.51 | 7.34 | 17.68 | 4.77 | 6.07 | 8.96 |
| LDP | 8.16 | 9.05 | 5.98 | 4.77 | 3.49 | 10.57 | 4.99 | 3.52 | 6.32 |
| PTG | 15.26 | 12.62 | 8.76 | 7.99 | 6.48 | 15.24 | 6.14 | 6.68 | 9.90 |
| SBM | 4.55 | 4.17 | 4.75 | 4.14 | 3.49 | 12.58 | 3.59 | 4.02 | 5.16 |
| YLM | 7.96 | 8.14 | 7.82 | 4.62 | 2.32 | 7.78 | 2.86 | 3.25 | 5.59 |
| SCH | 8.54 | 8.26 | 6.51 | 3.35 | 4.48 | 4.39 | 4.09 | 3.88 | 5.44 |
| ZZ | 13.49 | 10.86 | 8.13 | 9.33 | 4.58 | 13.46 | 5.61 | 6.29 | 8.97 |
| 性状 Traits | 均方(自由度) MS (df) | F | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | 机误 Random error | 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | ||
| 株高 Plant height | 207.53 (9) | 9.99 (290) | 1.3962 | 20.76** | 7.16** | |
| 冠幅 Rosette width | 13.31 (9) | 1.42 (290) | 0.5663 | 9.35** | 2.51** | |
| 叶丛高 Rosette height | 280.42 (9) | 17.5 (290) | 2.5684 | 15.97** | 6.84** | |
| 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 23.90 (9) | 2.36 (290) | 0.2382 | 10.14** | 9.89** | |
| 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 118.23 (9) | 13.52 (290) | 0.7212 | 8.75** | 18.74** | |
| 花序直径 Flower diameter | 21.31 (9) | 1.35 (290) | 0.2076 | 15.74** | 6.52** | |
| 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 43.41 (9) | 5.23 (290) | 1.7746 | 8.3** | 2.94** | |
| 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 0.1525 (9) | 0.0325 (290) | 0.0115 | 4.69** | 2.83** | |
表4 滇北球花报春群体间和群体内表型性状方差分析
Table 4 Variance analysis of morphological traits among and within populations of Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata
| 性状 Traits | 均方(自由度) MS (df) | F | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | 机误 Random error | 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | ||
| 株高 Plant height | 207.53 (9) | 9.99 (290) | 1.3962 | 20.76** | 7.16** | |
| 冠幅 Rosette width | 13.31 (9) | 1.42 (290) | 0.5663 | 9.35** | 2.51** | |
| 叶丛高 Rosette height | 280.42 (9) | 17.5 (290) | 2.5684 | 15.97** | 6.84** | |
| 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 23.90 (9) | 2.36 (290) | 0.2382 | 10.14** | 9.89** | |
| 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 118.23 (9) | 13.52 (290) | 0.7212 | 8.75** | 18.74** | |
| 花序直径 Flower diameter | 21.31 (9) | 1.35 (290) | 0.2076 | 15.74** | 6.52** | |
| 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 43.41 (9) | 5.23 (290) | 1.7746 | 8.3** | 2.94** | |
| 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 0.1525 (9) | 0.0325 (290) | 0.0115 | 4.69** | 2.83** | |
| 性状 Traits | 方差分量 Variance component | 方差分量百分比 % of variation | 表型分化系数 Vst | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | 机误 Random error | 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | 机误 Random error | |||
| 株高 Plant height | 2.1948 | 3.1992 | 1.3962 | 32.32 | 47.11 | 20.56 | 0.4069 | |
| 冠幅 Rosette width | 0.1321 | 0.2858 | 0.5663 | 13.43 | 29.05 | 57.53 | 0.3161 | |
| 叶丛高 Rosette height | 2.9207 | 4.9973 | 2.5684 | 27.84 | 47.67 | 24.50 | 0.3017 | |
| 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 0.2394 | 0.7058 | 0.2382 | 19.42 | 57.25 | 19.32 | 0.2533 | |
| 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 1.1635 | 4.2651 | 0.7212 | 18.94 | 69.43 | 11.74 | 0.2143 | |
| 花序直径 Flower diameter | 0.2219 | 0.3821 | 0.2076 | 27.34 | 47.08 | 25.58 | 0.3674 | |
| 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 0.4242 | 1.1521 | 1.7746 | 12.66 | 34.38 | 52.96 | 0.2691 | |
| 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 0.0004 | 0.0021 | 0.0115 | 2.72 | 14.93 | 82.34 | 0.1541 | |
| 平均值 Mean | 19.33 | 43.36 | 37.31 | 0.2854 | ||||
表5 滇北球花报春群体间和群体内方差分量与群体间表型分化系数
Table 5 Variance portions and differentiation coefficients of variance of morphological traits among and within populations of Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata
| 性状 Traits | 方差分量 Variance component | 方差分量百分比 % of variation | 表型分化系数 Vst | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | 机误 Random error | 群体间 Among populations | 群体内 Within population | 机误 Random error | |||
| 株高 Plant height | 2.1948 | 3.1992 | 1.3962 | 32.32 | 47.11 | 20.56 | 0.4069 | |
| 冠幅 Rosette width | 0.1321 | 0.2858 | 0.5663 | 13.43 | 29.05 | 57.53 | 0.3161 | |
| 叶丛高 Rosette height | 2.9207 | 4.9973 | 2.5684 | 27.84 | 47.67 | 24.50 | 0.3017 | |
| 最长叶长 Longest leaf length | 0.2394 | 0.7058 | 0.2382 | 19.42 | 57.25 | 19.32 | 0.2533 | |
| 最长叶宽 Longest leaf width | 1.1635 | 4.2651 | 0.7212 | 18.94 | 69.43 | 11.74 | 0.2143 | |
| 花序直径 Flower diameter | 0.2219 | 0.3821 | 0.2076 | 27.34 | 47.08 | 25.58 | 0.3674 | |
| 花梗长度 Flower stalk length | 0.4242 | 1.1521 | 1.7746 | 12.66 | 34.38 | 52.96 | 0.2691 | |
| 种子千粒重 Thousand seeds mass | 0.0004 | 0.0021 | 0.0115 | 2.72 | 14.93 | 82.34 | 0.1541 | |
| 平均值 Mean | 19.33 | 43.36 | 37.31 | 0.2854 | ||||
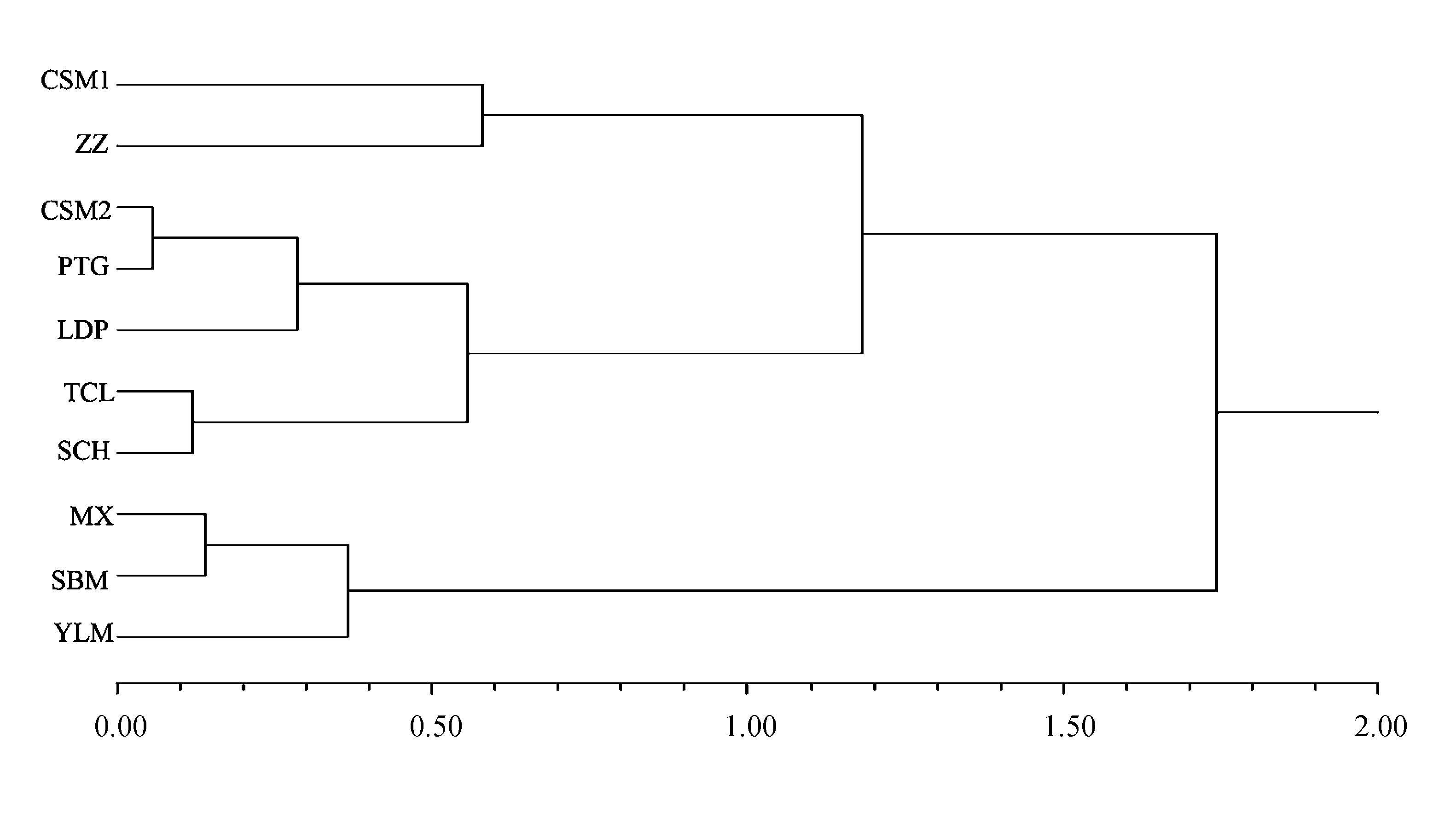
图1 滇北球花报春天然群体UPGMA聚类图。群体编号同表1。
Fig. 1 UPGMA dendrogram of ten natural populations of Primula denticulatassp. sinodenticulata based on eight morphological traits. Population codes are the same as in Table 1.
| [1] | Antrobus S, Lack AJ (1993) Genetics of colonizing and established populations of Primula veris. Heredity, 71,252-258. |
| [2] | Christoph R, Anja A, Markus R (2005) Molecular variation within and between ten populations of Primula farinosa (Primulaceae) along an altitudinal gradient in the north Alps. Basic and Applied Ecology, 6,35-45. |
| [3] | Ge S (葛颂), Wang MX (王明庥), Chen YW (陈岳武) (1988) An analysis of population genetic structure of masson pine by isozyme technique. Scientia Silvae Sinicae (林业科学), 24,399-409. (in Chinese with English abstract ). |
| [4] | Gu WC (顾万春), Li WY (李文英) (2007) Analysis and suggestions of benefit sharing policies relating to forest tree germplasm resources in China. World Forestry Research (世界林业研究), 20 (1),66-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Hamrick JL, Godt MJW (1990) Allozyme diversity in plant species. In:Plant Population Genetics, Breeding, and Genetic Resources (eds Brown AHD, Clegg MT, Kahler AL),pp.43-63. Sinauer Association Inc.,Massachusetts. |
| [6] | Hamrick JL, Godt MJW (1992) Factors influencing levels of genetic diversity in woody plant species. New Forest, 6,95-124. |
| [7] | Honjo M, Ueno S, TsumuraY, Washitani I, Ohsawa R (2004) Phylogeographic study based on intraspecific sequence variation of chloroplast DNA for the conservation of genetic diversity in the Japanese endangered species Primula sieboldii. Biological Conservation, 120,215-224. |
| [8] | Hu QM (胡启明) (1994) On the geographical distribution of the Primulaceae. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany(热带亚热带植物学报), 2 (4),1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Ishihama F, Nakano C, Ueno S, Ajima M, Tsumura Y, Washitani I (2003) Seed set and gene flow patterns in an experimental population of an endangered heterostylous herb with controlled local opposite-morph density. Functional Ecology, 17,680-689. |
| [10] |
Jacquemyn H, Honnay O, Galbusera P, Roldan-Ruiz I (2004) Genetic structure of the forest herb Primula elatior in a changing landscape. Molecular Ecology, 13,211-219.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] | Jin Y (金燕), Lu BR (卢宝荣) (2003) Sampling strategy of genetic diversity. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 11,155-161. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] |
Kitamoto N, Honjo M, Ueno S, Takenaka A,TsumuraY, Washitani I, Ohsawa R (2005) Spatial genetic structure among and within populations of Primula sieboldii growing beside separate streams. Molecular Ecology, 14,149-157.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] | Liang SL (梁树乐), Zhang QX (张启翔) (2004) Investigation on resources of the Primula L. in the Cangshan Mountains of Dali. Journal of Laiyang Agricultural College (莱阳农学院学报), 21,63-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Liang SL (梁树乐) (2006) Studies on the Introduction and Crossbreeding of Wild Primula L. from the Southwest of China (我国西南地区部分野生报春的引种与杂交育种研究). PhD dissertation, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [15] | Li B (李斌), Gu WC (顾万春), Lu BM (卢宝明) (2002) A study on phenotypic diversity of seeds and cones characteristics in Pinus bungeana. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 10,181-188. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Li J (李进), Chen KY (陈可咏), Li BS (李渤生) (1998) The variation of genetic diversity of Quercus aquifolioides in different elevations. Acta Botanica Sinica(植物学报), 40,761-767. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Luo SB (罗少波), Li ZJ (李智军), Zhou WB (周微波), Kenichihida , Takehiko (1996) Technique for identification of heat tolerance in heading Chinese cabbage (中国蔬菜), 2,16-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Ming J (明军), Gu WC (顾万春) (2006a) Genetic diversity in natural populations of Syringa oblata detected by AFLP markers. Acta Horticulturae Sinica (园艺学报), 33,1269-1274. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Ming J (明军), Gu WC (顾万春) (2006b) Phenotypic variation of Syringa oblata Lindl. Forest Research (林业科学研究), 19,199-204. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] |
Nan P, Shi SH, Peng SL, Tian CJ, Zhong Y (2003) Genetic diversity in Primula obconica (Primulaceae) from central and south-west China as revealed by ISSR markers. Annals of Botany, 91,329-333.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] | Richards J (1993) Primula. B. T. Bastford Ltd., London. |
| [22] | Rossum F, Echchgadda G, Szabadi I, Triest L (2002) Commonness and long-term survival in fragmented habitats: Primula elatior as a study case . Conservation Biology, 16,1286-1295. |
| [23] | Van Rossum F, Echchgadda G, Szabadi I, Triest L (2002) Commonness and long-term survival in fragmented habitats: Primula elatior as a study case. Conservation Biology, 16,1286-1295. |
| [24] | Wang FY (王凤英), Ge XJ (葛学军), Hao G (郝刚), Hu QM (胡启明) (2005) Genetic diversity and differentiation in Primula sikkimensis (Primulaceae) in Himalyan- Hengduan Mountains. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany (热带亚热带植物学报), 13,149-153. (in the Chinese with English abstract). |
| [25] | Wsahitani I, Ishihama F, Matsumura C, Nagai M, Nishihiro J, Ajima M (2005) Conservation ecology of Primula sieboldii: synthesis of information towards the prediction of the genetic/demographic fate of a population. Plant Species Biology, 20,3-15. |
| [26] | Xue DW, Ge XJ, Hao G, Zhang CQ (2004) High genetic diversity in a rare, narrowly endemic Primrose species: Primula interjacens by ISSR analysis. Acta Botanica Sinica, 46,1163-1169. |
| [1] | 李斌, 顾万春, 卢宝明. 白皮松天然群体种实性状表型多样性研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2002, 10(2): 181-188. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn