



Biodiv Sci ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 549-560. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017045 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017045
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles
Xue Zhang1, Yurui Wang1, Yangbo Fan1,2, Xiaotian Luo1, Xiaozhong Hu1, Feng Gao1,*( )
)
Received:2017-02-18
Accepted:2017-04-17
Online:2017-05-20
Published:2017-06-06
Contact:
Gao Feng
Xue Zhang, Yurui Wang, Yangbo Fan, Xiaotian Luo, Xiaozhong Hu, Feng Gao. Morphology, ontogeny and molecular phylogeny of Euplotes aediculatus Pierson, 1943 (Ciliophora, Euplotida)[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(5): 549-560.
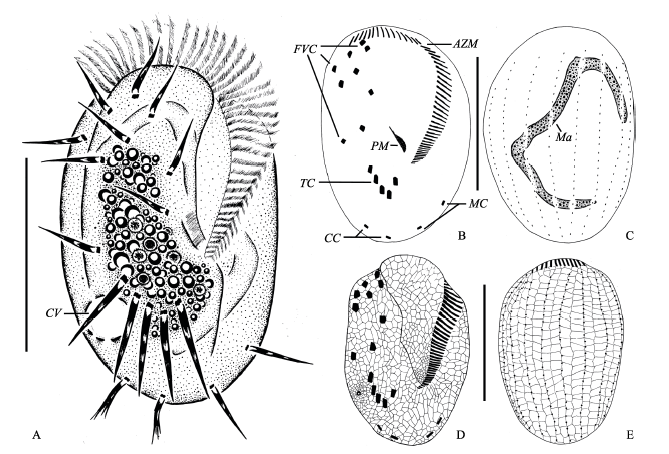
Fig. 1 Morphology of Euplotes aediculatus in vivo, after protargol and silver nitrate impregnation. A, Ventral view of a representative individual; B and C, Ventral (B) and dorsal (C) view of the infraciliature and nuclear apparatus; D and E, Silverline system on ventral (D) and dorsal side (E); AZM, Adoral zone of membranelles; CC, Caudal cirri; CV, Contractile vacuole; FVC, Frontoventral cirri; Ma, Macronucleus; MC, Marginal cirri; PM, Paroral membrane; TC, Transverse cirri. Scale bar = 100 µm.
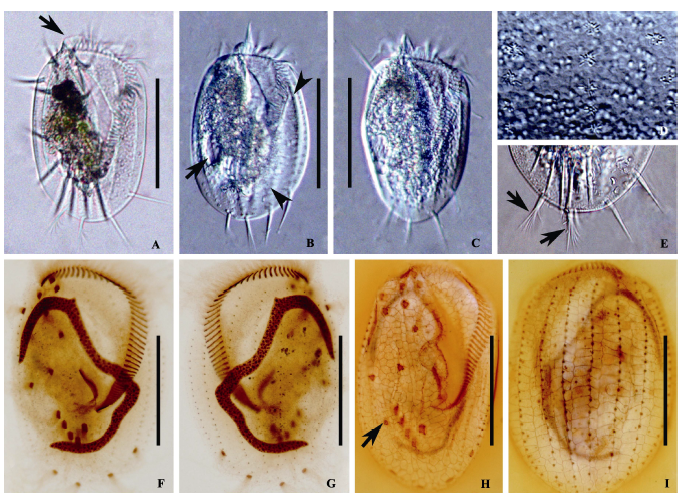
Fig. 2 Morphology of Euplotes aediculatus. A-E, Photomicrographs in vivo; F and G, Photomicrographs after protargol; H and I, Photomicrographs after silver nitrate impregnation. A, Ventral view of a representative individual, arrow points to collar; B and C, Ventral views, showing different body shapes, arrow in picture B points to contractile vacuole, arrowheads in picture B point to ribs in the back; D, Dorsal view, showing the cortical granules arranged around the dorsal cilia; E, Posterior portion of an individual, showing the caudal cirri (arrows) and the left marginal cirri; F and G, Ventral (F) and dorsal (G) view of the infraciliature and nuclear apparatus; H and I, Silverline system on ventral (H) and dorsal side (I), arrow in picture H points to contractile vacuole. Scale bar = 100 µm.
| 特征 Character | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 平均值 Mean | 中值 Median | 标准差 Standard deviation | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | 个体数 Number of cells |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体长 Length of body (μm) | 115 | 142 | 128.3 | 129 | 7.25 | 5.7 | 20 |
| 体宽 Width of body (μm) | 76 | 101 | 92.2 | 93.5 | 6.28 | 6.8 | 20 |
| 口区长 Length of adoral zone (μm) | 79 | 98 | 86.3 | 86.5 | 4.74 | 5.5 | 20 |
| 口围带小膜数目 Number of adoral membranelles | 47 | 55 | 51.1 | 51.5 | 1.90 | 3.7 | 20 |
| 额腹棘毛数目 Number of frontoventral cirri | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9.0 | 0 | 0 | 19 |
| 横棘毛数目 Number of transverse cirri | 5 | 5 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| 缘棘毛数目 Number of marginal cirri | 2 | 2 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| 尾棘毛数目 Number of caudal cirri | 2 | 2 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| 背触毛列数 Number of dorsal kineties | 8 | 8 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| 中央背触毛列毛基体数目 Number of dikinetids in mid-dorsal kinety | 21 | 26 | 21.9 | 21.0 | 1.36 | 6.2 | 20 |
| 最左侧背触毛列毛基体数目 Number of dikinetids in the leftmost dorsal kinety | 15 | 23 | 18.5 | 18.0 | 1.73 | 9.4 | 20 |
Table 1 Morphometric characterizations of Euplotes aediculatus from Small West Lake of Qingdao based on protargol-stained specimens
| 特征 Character | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 平均值 Mean | 中值 Median | 标准差 Standard deviation | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | 个体数 Number of cells |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体长 Length of body (μm) | 115 | 142 | 128.3 | 129 | 7.25 | 5.7 | 20 |
| 体宽 Width of body (μm) | 76 | 101 | 92.2 | 93.5 | 6.28 | 6.8 | 20 |
| 口区长 Length of adoral zone (μm) | 79 | 98 | 86.3 | 86.5 | 4.74 | 5.5 | 20 |
| 口围带小膜数目 Number of adoral membranelles | 47 | 55 | 51.1 | 51.5 | 1.90 | 3.7 | 20 |
| 额腹棘毛数目 Number of frontoventral cirri | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9.0 | 0 | 0 | 19 |
| 横棘毛数目 Number of transverse cirri | 5 | 5 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| 缘棘毛数目 Number of marginal cirri | 2 | 2 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| 尾棘毛数目 Number of caudal cirri | 2 | 2 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| 背触毛列数 Number of dorsal kineties | 8 | 8 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| 中央背触毛列毛基体数目 Number of dikinetids in mid-dorsal kinety | 21 | 26 | 21.9 | 21.0 | 1.36 | 6.2 | 20 |
| 最左侧背触毛列毛基体数目 Number of dikinetids in the leftmost dorsal kinety | 15 | 23 | 18.5 | 18.0 | 1.73 | 9.4 | 20 |
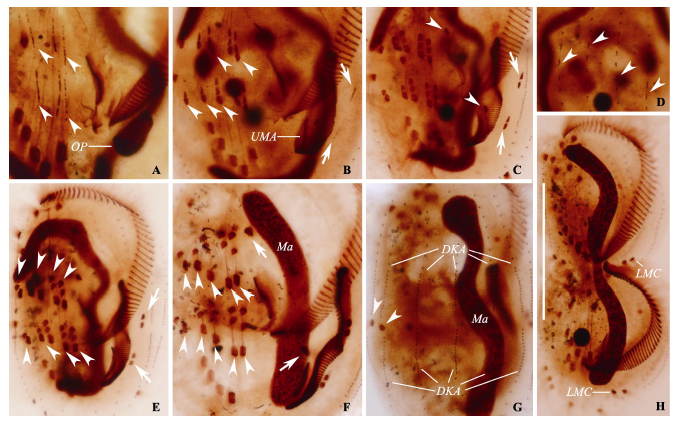
Fig. 3 Photomicrographs of Euplotes aediculatus during morphogenesis after protargol impregnation. A, Ventral view of an early divider, showing the oral primordium in opisthe, arrowheads mark the frontal-ventral-transverse cirral streaks of both dividers; B, Ventral view of an early-middle divider, arrowheads show the differentiation of frontal-ventral-transverse cirral anlagen, arrows marks the marginal anlagen; C, Ventral view of a mid-stage divider, arrowheads demonstrate the leftmost frontal cirrus (I/1) in both proter and opisthe, arrows marks the differentiation of marginal anlagen; D, Dorsal view of an early-middle divider, arrowheads show the formation of dorsal kineties anlagen; E, Ventral view of another mid-stage divider, arrowheads show the differentiation of frontal-ventral-transverse cirral anlagen almost complete, arrows point to the new marginal cirri of both daughter cells; F, Ventral view of a late divider, noting the macronucleus become a short strand, arrowheads show the transverse cirri, arrows mark the leftmost frontal cirri (I/1); G, Dorsal view of another late divider, arrowheads show the newly formed caudal cirri in the proter; H, Ventral view of a last stage divider, showing cirri almost in their final position and the division of the macronucleus. DKA, Dorsal kineties anlagen; LMC, Left marginal cirri; Ma, Macronucleus; OP, Opisthe’s oral primordium; UMA, Undulating membrane anlagen. Scale bar = 70 µm.
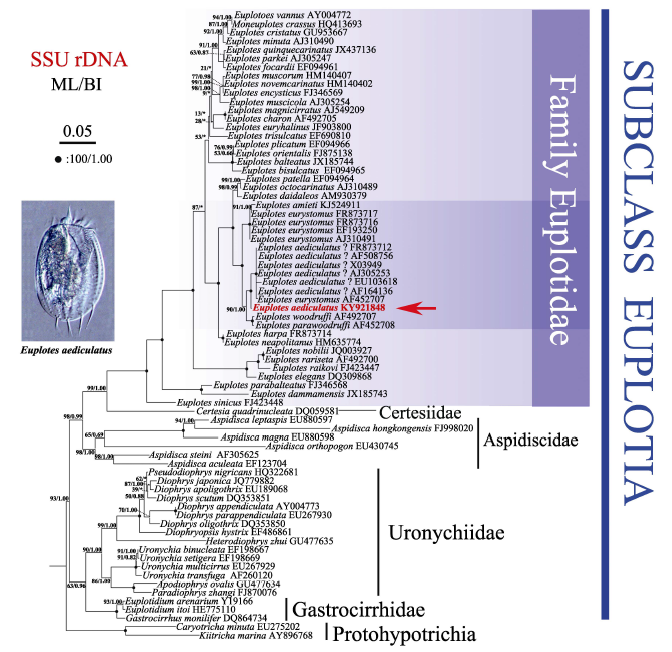
Fig. 4 Maximum likelihood (ML) tree based on small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Newly characterized sequence in this study is shown in bold. The numbers at the nodes represent the support values of ML/Bayesian inference (BI). Fully supported (100/1.00) branches are marked with solid circles. Asterisks reflect the disagreement between ML and BI. All branches are drawn to scale. The scale bar corresponds to five substitutions per 100 nucleotide positions.
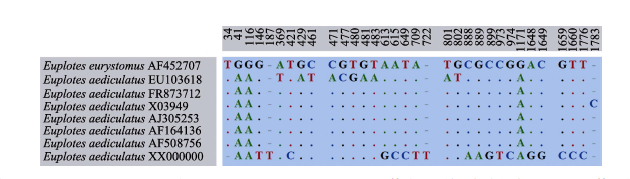
Fig. 5 Unmatched sites from SSU rDNA sequence alignment of seven Euplotes aediculatus populations and one E. eurystomus population. Numbers indicate the positions of nucleotides in the alignment, missing sites are represented by dashes (-), and matching sites are marked with dots (.).
| [1] | Adl SM, Simpson AG, Lane CE, Lukes J, Bass D, Bowser SS, Brown MW, Burki F, Dunthorn M, Hampl V, Heiss A, Hoppenrath M, Lara E, Le Gall L, Lynn DH, McManus H, Mitchell EA, Mozley-Stanridge SE, Parfrey LW, Pawlowski J, Rueckert S, Shadwick L, Schoch CL, Smirnov A, Spiegel FW (2012) The revised classification of eukaryotes. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 59, 429-493. |
| [2] | Borror AC (1972) Revision of the order Hypotrichida (Ciliophora, Protozoa). Journal of Protozoology, 19, 1-23. |
| [3] | Borror AC, Hill BF (1995) The order Euplotida (Ciliophora): taxonomy, with division of Euplotes into several genera. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 42, 457-466. |
| [4] | Carter HP (1972) Infraciliature of eleven species of the genus Euplotes. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society, 91, 466-492. |
| [5] | Chen XM, Zhao Y, Al-Farraj SA, Saleh AQ, El-Serehy HA, Shao C, Al-Rasheid KAS (2015) Taxonomic descriptions of two marine ciliates, Euplotes dammamensis n. sp. and Euplotes balteatus (Dujardin, 1841) Kahl, 1932 (Ciliophora, Spirotrichea, Euplotida), collected from the Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Acta Protozoologica, 52, 73-87. |
| [6] | Corliss JO (1979) The Ciliated Protozoa:Characterization, Classification and Guide to the Literature.Pergamon Press, Oxford. |
| [7] | Curds RC (1975) A guide to the species of Euplotes (Hypotrichida, Ciliatea). Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History) Zoology, 28, 3-61. |
| [8] | Curds RC, Wu ICH (1983) A review of the Euplotidae (Hypotrichida, Ciliophora). Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History) Zoology, 44, 191-247. |
| [9] | Dai RH, Xu KD, He YY (2013) Morphological, physiological, and molecular evidences suggest that Euplotes parawoodruffi is a junior synonym of Euplotes woodruffi (Ciliophora, Euplotida). Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 60, 70-78. |
| [10] | Di Giuseppe G, Erra F, Frontini F, Dini F, Vallesi A, Luporini P (2014) Improved description of the bipolar ciliate, Euplotes petzi, and definition of its basal position in the Euplotes phylogenetic tree. European Journal of Protistology, 50, 402-411. |
| [11] | Dong JY, Lu XT, Shao C, Huang J, Alrasheid KA (2016) Morphology, morphogenesis and molecular phylogeny of a novel saline soil ciliate, Lamtostyla salina n. sp. (Ciliophora, Hypotricha). European Journal of Protistology, 56, 219-231. |
| [12] | Dragesco J (1970) Ciliés Libres du Cameroun. Annales de la Faculté des Sciences (Numéro hors série). Université Fédérale du Cameroun, Yaoundé. (in French) |
| [13] | Dragesco J (2003) Infraciliature et morphometrie de vingt espèces de ciliés hypotriches recoltés au Rwanda et Burundi, comprenant Kahliella quadrinucleata n. sp., Pleurotricha multinucleata n. sp. et Laurentiella bergeri n. sp. Travaux du Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle “Grigore Antipa”, 45, 7-59. (in French) |
| [14] | Foissner W (1982) Ecology and taxonomy of the Hypotrichida (Protozoa: Ciliophora) of some Austrian soils. Archiv Für Protistenkunde, 126, 19-143. (in French with English abstract) |
| [15] | Foissner W (1991) Basic light and scanning electron microscopic methods for taxonomic studies of ciliated protozoa. European Journal of Protistology, 27, 313-330. |
| [16] | Foissner W (2014) An update of ‘basic light and scanning electron microscopic methods for taxonomic studies of ciliated Protozoa’. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 64, 271-292. |
| [17] | Fotedar R, Stoeck T, Filker S, Fell JW, Agatha S, Al Marri M, Jiang JM (2016) Description of the halophile Euplotes qatarensis nov. spec. (Ciliophora, Spirotrichea, Euplotida) isolated from the hypersaline Khor Al-Adaid Lagoon in Qatar. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 63, 578-590. |
| [18] | Gao F, Warren A, Zhang QQ, Gong J, Miao M, Sun P, Xu DP, Huang J, Yi ZZ, Song WB (2016) The all-data-based evolutionary hypothesis of ciliated protists with a revised classification of the phylum Ciliophora (Eukaryota, Alveolata). Scientific Reports, 6, 24874. |
| [19] | Hewitt EA, Müller KM, Cannone J, Hogan DJ, Gutell R, Prescott DM (2003) Phylogenetic relationships among 28 spirotrichous ciliates documented by rDNA. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 29, 258-267. |
| [20] | Jiang JM, Zhang QQ, Hu XZ, Shao C, Al-Rasheid KAS, Song WB (2010a) Two new marine ciliates, Euplotes sinicus sp. nov. and Euplotes parabalteatus sp. nov., and a new small subunit rRNA gene sequence of Euplotes rariseta (Ciliophora, Spirotrichea, Euplotida). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 60, 1241-1251. |
| [21] | Jiang JM, Zhang QQ, Warren A, Al-Rasheid KAS, Song WB (2010b) Morphology and SSU rRNA gene-based phylogeny of two marine Euplotes species, E. orientalis spec. nov. and E. raikovi (Ciliophora, Euplotida). European Journal of Protistology, 46, 121-132. |
| [22] | Kahl A (1932) Urtiere oder Protozoa. I: Wimpertiere oder Ciliata (Infusoria), 3. Spirotricha. Tierwelt Dtl., 25, 399-650. (in German) |
| [23] | Lahr DJG, Laughinghouse HD, Oliverio A, Gao F, Katz LA (2014) How discordant morphological and molecular evolution among microorganisms can revise our notions of biodiversity on Earth. Bioessays, 36, 950-959. |
| [24] | Li LQ, Zhao XL, Ji DD, Hu XZ, Al-Rasheid KA, Al-Farraj SA, Song WB (2016) Description of two marine amphisiellid ciliates, Amphisiella milnei (Kahl, 1932) Horváth, 1950 and A. sinica sp. nov. (Ciliophora: Hypotrichia), with notes on their ontogenesis and SSU rDNA-based phylogeny. European Journal of Protistology, 54, 59-73. |
| [25] | Liu MJ, Fan YB, Miao M, Hu XZ, Al-Rasheid KAS, Al-Farraj SA, Ma HG (2015) Morphological and morphogenetic redescriptions and SSU rRNA gene-based phylogeny of the poorly-known species Euplotes amieti Dragesco, 1970 (Ciliophora, Euplotida). Acta Protozoologica, 54, 171. |
| [26] | Lynn DH (2008) The Ciliated Protozoa: Characterization, Classification and Guide to the Literature, 3rd edn. Springer-Verlag, Dordrecht. |
| [27] | Ma HG, Jiang JM, Hu XZ, Shao C, Song WB (2008) Morphology and morphogenesis of the marine ciliate, Euplotes rariseta (Ciliophora, Euplotida). Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 32, 57-62. |
| [28] | Medlin L, Elwood HJ, Stickel S, Sogin ML (1988) The characterization of enzymatically amplified eukaryotic 16S-like rRNA-coding regions. Gene, 71, 491-499. |
| [29] | Nylander JA (2004) MrModeltest 2. 2. Department of Systematic Zoology, Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University, Uppsala. |
| [30] | Pan HB, Hu JX, Jiang JM, Wang LQ, Hu XZ (2015) Morphology and phylogeny of three Pleuronema species (Ciliophora, Scuticociliatia) from Hangzhou Bay, China, with description of two new species, P. binucleatum n. sp. and P. parawiackowskii n. sp. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 63, 287-298. |
| [31] | Pang YB, Wei HB (1999) Studies on the morphology and morphogenesis in Euplotes aediculatus. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), (1), 103-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [庞延斌, 魏红兵 (1999) 小腔游仆虫Euplotes aediculatus形态和形态发生的研究. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (1), 103-109.] | |
| [32] | Petroni G, Dini F, Verni F, Rosati G (2002) A molecular approach to the tangled intrageneric relationships underlying phylogeny in Euplotes (Ciliophora, Spirotrichea). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 22, 118-130. |
| [33] | Pierson BF (1943) A comparative morphological study of several species of Euplotes closely related to Euplotes patella. Journal of Morphology, 72, 125-165. |
| [34] | Pierson BF, Gierke R, Fisher AL (1968) Clarification of the taxonomic identification of Euplotes eurystomus Kahl and E. aediculatus Pierson. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society, 87, 306-316. |
| [35] | Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics, 14, 817-818. |
| [36] | Qu ZS, Pan HB, Hu XZ, Li JQ, Al-Farraj SA, Al-Rasheid KAS, Yi ZZ (2015) Morphology and molecular phylogeny of three cyrtophorid ciliates (Protozoa, Ciliophora) from China, including two new species, Chilodonella parauncinata sp. n. and Chlamydonella irregularis sp. n. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 62, 267-279. |
| [37] | Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MRBAYES 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics, 19, 1572-1574. |
| [38] | Ruffolo JJ (1976) Cortical morphogenesis during the cell division cycle in Euplotes: an integrated study using light optical, scanning electron and transmission electron microscopy. Journal of Morphology, 148, 489-527. |
| [39] | Shao C, Ma HG, Gao S, Khaled ARA, Song WB (2010) Reevaluation of cortical developmental patterns in Euplotes (s. l.), including a morphogenetic redescription of E. charon (Protozoa, Ciliophora, Euplotida). Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 28, 593-602. |
| [40] | Sogin ML, Swanton MT, Gunderson JH, Elwood HJ (1986) Sequence of the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene from the hypotrichous ciliate Euplotes aediculatus. Journal of Protozoology, 33, 26-29. |
| [41] | Song WB, Warren A, Hu XZ (2009)Free-living Ciliates in the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese and in English) [宋微波, Warren A., 胡晓钟 (2009) 中国黄渤海的自由生纤毛虫. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [42] | Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J (2008) A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML web servers. Systematic Biology, 57, 758-771. |
| [43] | Syberg-Olsen MJ, Irwin NAT, Vannini C, Erra F, Di Giuseppe G, Boscaro V, Keeling PJ (2016) Biogeography and character evolution of the ciliate genus Euplotes (Spirotrichea, Euplotia), with description of Euplotes curdsi sp. nov. PLoS ONE, 11, e0165442. |
| [44] | Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 1596-1599. |
| [45] | Tuffrau M (1960) Révision du genre Euplotes, fondée sur la comparaison des structures superficielles. Hydrobiologia, 15, 1-77. (in French) |
| [46] | Vannini C, Ferrantini F, Ristori A, Verni F, Petroni G (2012) Betaproteobacterial symbionts of the ciliate Euplotes: origin and tangled evolutionary path of an obligate microbial association. Environmental Microbiology, 14, 2553-2563. |
| [47] | Washburn ES, Borror AC (1972) Euplotes raikovi Agamaliev, 1966 (Ciliophora, Hypotrichida) from New Hampshire: description and morphogenesis. Journal of Protozoology, 19, 604-608. |
| [48] | Wilbert N (1975) Eine verbesserte Technik der Protargolimprä gnation für Ciliaten. Mikrokosmos, 64, 171-179. (in German) |
| [49] | Xie DM, Fan XP, Ni B, Gu FK (2016) Morphogenesis of the cortical silver-line system in the ciliate genus Euplotes (Protozoa, Ciliophora). Periodical of Ocean University of China (Natural Science), 46, 41-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谢冬梅, 范鑫鹏, 倪兵, 顾福康 (2016) 游仆虫(原生动物, 纤毛门)皮层银线系的形态发生模式. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 46, 41-50.] | |
| [50] | Yi ZZ, Katz LA, Song WB (2012) Assessing whether alpha-tubulin sequences are suitable for phylogenetic reconstruction of Ciliophora with insights into its evolution in euplotids. PLoS ONE, 7, e40635. |
| [51] | Yi ZZ, Song WB, Clamp JC, Chen ZG, Gao S, Zhang QQ (2009) Reconsideration of systematic relationships within the order Euplotida (Protista, Ciliophora) using new sequences of the gene coding for small-subunit rRNA and testing the use of combined data sets to construct phylogenies of the Diophrys-complex. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 50, 599-607. |
| [1] | Hong Deyuan. A brief discussion on methodology in taxonomy [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24541-. |
| [2] | Yajun Sun. What do higher or lower organisms mean—Clarify the meaning and validity of the biological ladder implied by On the Origin of Species [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24394-. |
| [3] | Hua He, Dunyan Tan, Xiaochen Yang. Cryptic dioecy in angiosperms: Diversity, phylogeny and evolutionary significance [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 24149-. |
| [4] | Yanyu Ai, Haixia Hu, Ting Shen, Yuxuan Mo, Jinhua Qi, Liang Song. Vascular epiphyte diversity and the correlation analysis with host tree characteristics: A case in a mid-mountain moist evergreen broad-leaved forest, Ailao Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24072-. |
| [5] | Yanwen Lv, Ziyun Wang, Yu Xiao, Zihan He, Chao Wu, Xinsheng Hu. Advances in lineage sorting theories and their detection methods [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23400-. |
| [6] | Chen-Kun Jiang, Wen-Bin Yu, Guang-Yuan Rao, Huaicheng Li, Julien B. Bachelier, Hartmut H. Hilger, Theodor C. H. Cole. Plant Phylogeny Posters—An educational project on plant diversity from an evolutionary perspective [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24210-. |
| [7] | Huiyin Song, Zhengyu Hu, Guoxiang Liu. Assessing advances in taxonomic research on Chlorellaceae (Chlorophyta) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22083-. |
| [8] | Zhizhong Li, Shuai Peng, Qingfeng Wang, Wei Li, Shichu Liang, Jinming Chen. Cryptic diversity of the genus Ottelia in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22394-. |
| [9] | Yajun Sun. Why do we believe in Darwin’s theory of evolution—On the 25 folds of aesthetic parsimony of On the Origin of Species [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(9): 22243-. |
| [10] | Ting Wang, Jiangping Shu, Yufeng Gu, Yanqing Li, Tuo Yang, Zhoufeng Xu, Jianying Xiang, Xianchun Zhang, Yuehong Yan. Insight into the studies on diversity of lycophytes and ferns in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(7): 22381-. |
| [11] | Jianming Wang, Mengjun Qu, Yin Wang, Yiming Feng, Bo Wu, Qi Lu, Nianpeng He, Jingwen Li. The drivers of plant taxonomic, functional, and phylogenetic β-diversity in the gobi desert of northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(6): 21503-. |
| [12] | Yangkang Chen, Yi Wang, Jialiang Li, Wentao Wang, Duanyu Feng, Kangshan Mao. Principles, error sources and application suggestions of prevailing molecular dating methods [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(5): 629-646. |
| [13] | Wei Wang, Yang Liu. The current status, problems, and policy suggestions for reconstructing the plant tree of life [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(2): 176-188. |
| [14] | Bin Cao, Guojie Li, Ruilin Zhao. Species diversity and geographic components of Russula from the Greater and Lesser Khinggan Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(8): 854-866. |
| [15] | Chen Zuoyi, Xu Xiaojing, Zhu Suying, Zhai Mengyi, Li Yang. Species diversity and geographical distribution of the Chaetoceros lorenzianus complex along the coast of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(2): 149-158. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()