



Biodiv Sci ›› 2018, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (7): 678-689. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017132 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017132
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xu Xiang, Zhang Huayong*( ), Xie Ting, Sun Qingqing, Tian Yonglan
), Xie Ting, Sun Qingqing, Tian Yonglan
Received:2018-03-08
Accepted:2018-05-26
Online:2018-07-20
Published:2018-09-11
Contact:
Zhang Huayong
Xu Xiang, Zhang Huayong, Xie Ting, Sun Qingqing, Tian Yonglan. Elevational pattern of seed plant diversity in Xishuangbanna and its mechanisms[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(7): 678-689.
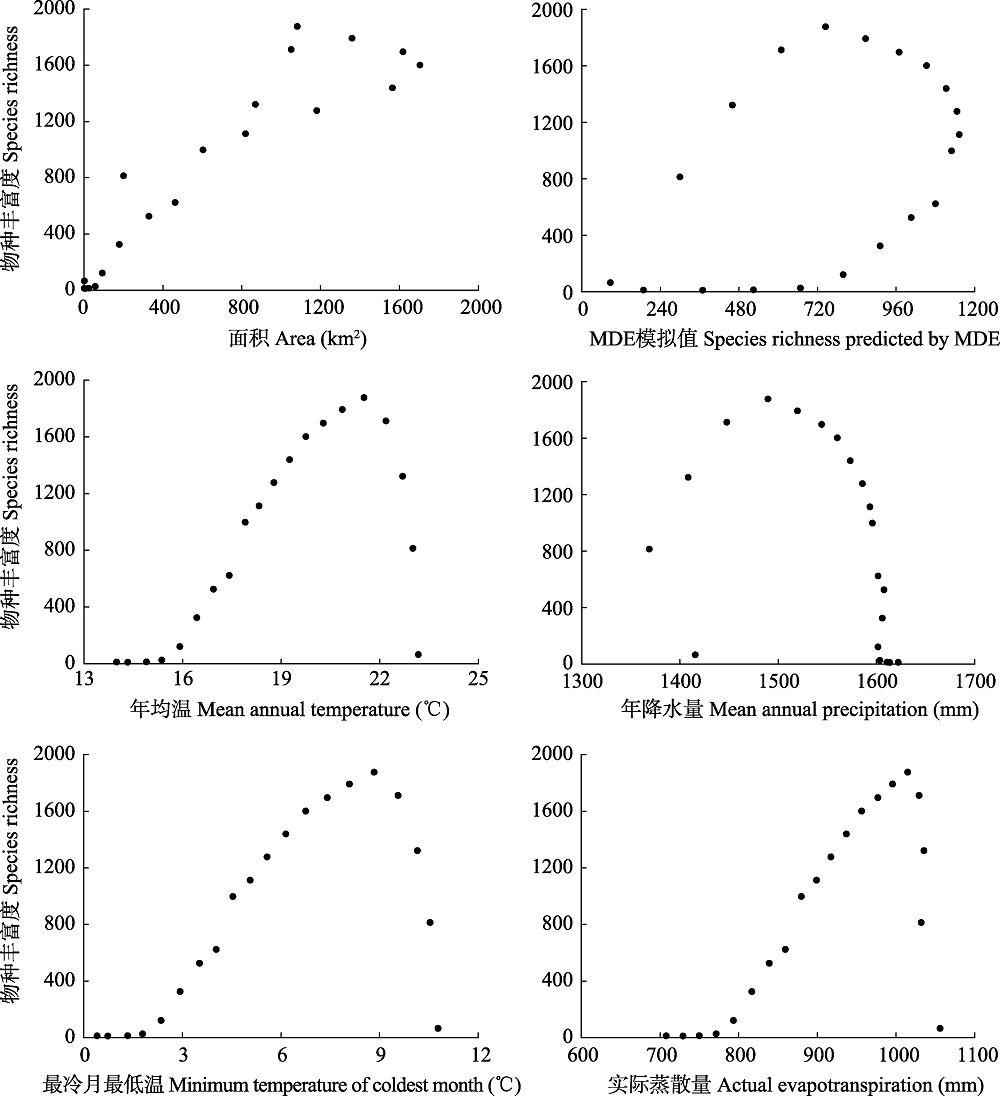
Fig. 4 Relationship between species richness of seed plants and area, species richness predicted by mid-domain effect (MDE), mean annual temperature, mean annual precipitation, minimum temperature of coldest month and actual evapotranspiration in Xishuangbanna
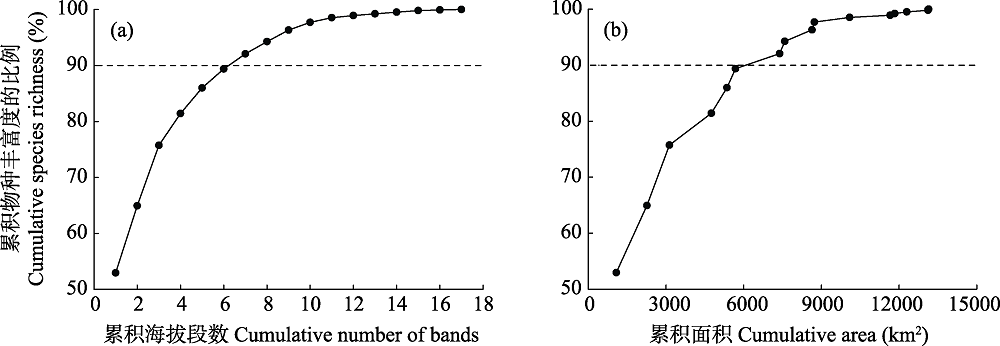
Fig. 5 Relationship between cumulative species richness and cumulative number of bands (a), cumulative area (b) in plant diversity hotspots identified using the complementary algorithm in Xishuangbanna
| 热点地区海拔段 Hotspot elevational band (m) | 保护区覆盖的热点地区面积 Hotspot area covered by nature reserves (km2) | 保护区覆盖的热点地区比例 Percentage of hotspot area covered by nature reserves (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 800-900 | 312.63 | 28.90 |
| 1,300-1,400 | 303.45 | 25.70 |
| 600-700 | 57.16 | 6.58 |
| 1,000-1,100 | 585.83 | 36.20 |
| 1,500-1,600 | 129.96 | 21.53 |
| 1,700-1,800 | 61.78 | 18.76 |
| 1,100-1,200 | 529.49 | 31.08 |
| 合计 Total | 1,980.30 | 26.81 |
Table 1 Spatial regression between plant diversity hotspots and nature reserves in Xishuangbanna
| 热点地区海拔段 Hotspot elevational band (m) | 保护区覆盖的热点地区面积 Hotspot area covered by nature reserves (km2) | 保护区覆盖的热点地区比例 Percentage of hotspot area covered by nature reserves (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 800-900 | 312.63 | 28.90 |
| 1,300-1,400 | 303.45 | 25.70 |
| 600-700 | 57.16 | 6.58 |
| 1,000-1,100 | 585.83 | 36.20 |
| 1,500-1,600 | 129.96 | 21.53 |
| 1,700-1,800 | 61.78 | 18.76 |
| 1,100-1,200 | 529.49 | 31.08 |
| 合计 Total | 1,980.30 | 26.81 |
| [1] | Acharya BK, Chettri B, Vijayan L (2011) Distribution pattern of trees along an elevation gradient of Eastern Himalaya, India. Acta Oecologica, 37, 329-336. |
| [2] | Adams JM, Woodward FI (1989) Patterns in tree species richness as a test of the glacial extinction hypothesis. Nature, 339, 699-701. |
| [3] | Allen AP, Brown JH, Gillooly JF (2002) Global biodiversity, biochemical kinetics, and the energetic-equivalence rule. Science, 297, 1545-1548. |
| [4] | Arrhenius O (1921) Species and area. Journal of Ecology, 9, 95-99. |
| [5] | Bachman S, Baker WJ, Brummitt N, Dransfield J, Moat J (2004) Elevational gradients, area and tropical island diversity: An example from the palms of New Guinea. Ecography, 27, 299-310. |
| [6] | Borcard D, Legendre P, Drapeau P (1992) Partialling out the spatial component of ecological variation. Ecology, 73, 1045-1055. |
| [7] | Brown JH, Gillooly JF, Allen AP, Savage VM, West GB (2004) Toward a metabolic theory of ecology. Ecology, 85, 1771-1789. |
| [8] | Chen J, Ban YF, Li SN (2014) China: Open access to earth land-cover map. Nature, 514, 434. |
| [9] | Chen J, Liao AP, Chen J, Peng S, Chen LJ, Zhang HW (2017) 30-meter global land cover data product-GlobeLand30. Geomatics World, 24, 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈军, 廖安平, 陈晋, 彭舒, 陈利军, 张宏伟 (2017) 全球30 m地表覆盖遥感数据产品-GlobeLand30. 地理信息世界, 24, 1-8.] | |
| [10] | Chi XL, Tang ZY (2011) Effects of area, temperature and geometric constraints on elevational patterns of species richness: A case study in the Mountain Taibai, Qinling Mountains, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 35, 362-370. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [池秀莲, 唐志尧 (2011) 面积、温度及分布区限制对物种丰富度海拔格局的影响: 以秦岭太白山为例. 植物生态学报, 35, 362-370.] | |
| [11] | Clarke A, Gaston KJ (2006) Climate, energy and diversity. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 273, 2257-2266. |
| [12] | Colwell RK (2008) RangeModel: Tools for exploring and assessing geometric constraints on species richness (the mid-domain effect) along transects. Ecography, 31, 4-7. |
| [13] | Colwell RK, Hurtt GC (1994) Nonbiological gradients in species richness and a spurious Rapoport effect. The American Naturalist, 144, 570-595. |
| [14] | Colwell RK, Lees DC (2000) The mid-domain effect: Geometric constraints on the geography of species richness. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 15, 70-76. |
| [15] | Colwell RK, Rahbek C, Gotelli NJ (2004) The mid-domain effect and species richness patterns: What have we learned so far? The American Naturalist, 163, E1-E23. |
| [16] | Currie DJ (1991) Energy and large-scale patterns of animal- and plant-species richness. The American Naturalist, 137, 27-49. |
| [17] | Currie DJ, Paquin V (1987) Large-scale biogeographical patterns of species richness of trees. Nature, 329, 326-327. |
| [18] | Diniz-Filho JAF, Bini LM, Hawkins BA (2003) Spatial autocorrelation and red herrings in geographical ecology. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 12, 53-64. |
| [19] | Dobson AP (1997) Geographic distribution of endangered species in the United States. Science, 275, 550-553. |
| [20] | Evans KL, James NA, Gaston KJ (2006) Abundance, species richness and energy availability in the North American avifauna. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 15, 372-385. |
| [21] | Feng CG, Tong C, Zhang RY, Li GG, Wang HKY, Tang YT, Zhang CF, Zhao K (2017) Biodiversity and distribution patterns of Triplophysa species in the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 25, 53-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [冯晨光, 童超, 张仁意, 李国刚, 王贺崐元, 汤永涛, 张存芳, 赵凯 (2017) 青藏高原东北部边缘高原鳅属鱼类的多样性与分布格局. 生物多样性, 25, 53-61.] | |
| [22] | Feng JM, Wang XP, Li J, Fang JY (2006) Effects of area and mid-domain effect on altitudinal pattern of seed plants richness in Lijiang, Yunnan, China. Biodiversity Science, 14, 107-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [冯建孟, 王襄平, 李晶, 方精云 (2006) 面积和中间膨胀效应对丽江地区种子植物物种丰富度垂直分布格局的影响. 生物多样性, 14, 107-113.] | |
| [23] | Gillooly JF, Brown JH, West GB, Savage VM, Charnov EL (2001) Effects of size and temperature on metabolic rate. Science, 293, 2248-2251. |
| [24] | Grytnes JA, Beaman JH, Romdal TS, Rahbek C (2010) The mid-domain effect matters: Simulation analyses of range-size distribution data from Mount Kinabalu, Borneo. Journal of Biogeography, 35, 2138-2147. |
| [25] | Hawkins BA (2001) Ecology’s oldest pattern? Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 16, 470. |
| [26] | Hawkins BA, DeVries PJ (2009) Tropical niche conservatism and the species richness gradient of North American butterflies. Journal of Biogeography, 36, 1698-1711. |
| [27] | Hawkins BA, Field R, Cornell HV, Currie DJ, Guegan JF, Kaufman DM, Kerr JT, Mittelbach GG, Oberdorff T, O’Brien EM, Porter EE, Turner JRG (2003) Energy, water, and broad-scale geographic patterns of species richness. Ecology, 84, 3105-3117. |
| [28] | He X, Du F, Yang YM, Yin WY, Zhuang CZ, Yan XS, Zhao MX (2011) Pattern of species richness along altitudinal gradient in Tongbiguan Nature Reserve, Southwest China and with a discussion on calculation methods of species density. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 19, 543-548. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [和霞, 杜凡, 杨宇明, 尹伍元, 庄翠珍, 岩香甩, 赵明旭 (2011) 铜壁关自然保护区种子植物物种丰富度的海拔梯度格局——兼论物种密度的计算方法. 热带亚热带植物学报, 19, 543-548.] | |
| [29] | Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL, Jones PG, Jarvis A (2005) Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. International Journal of Climatology, 25, 1965-1978. |
| [30] | Jetz W, Rahbek C (2002) Geographic range size and determinants of avian species richness. Science, 297, 1548-1551. |
| [31] | Karger DN, Kluge J, Krömer T, Hemp A, Lehnert M, Kessler M (2011) The effect of area on local and regional elevational patterns of species richness. Journal of Biogeography, 38, 1177-1185. |
| [32] | Kati V, Devillers P, Dufr M, Vokou D, Lebrun P (2004) Hotspots, complementarity or representativeness? Designing optimal small-scale reserves for biodiversity conservation. Biological Conservation, 120, 471-480. |
| [33] | Lan GY, Hu YH, Cao M, Zhu H, Wang H, Zhou SX, Deng XB, Cui JY, Huang JG, Liu LY (2008) Establishment of Xishuangbanna tropical forest dynamics plot: Species compositions and spatial distribution patterns. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 287-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [兰国玉, 胡跃华, 曹敏, 朱华, 王洪, 周仕顺, 邓晓保, 崔景云, 黄建国, 刘林云 (2008) 西双版纳热带森林动态监测样地——树种组成与空间分布格局. 植物生态学报, 32, 287-298.] | |
| [34] | Li D, Tang JW, Luo CK, Li JS, Liu ZA (2006) Analysis on the coenological characteristics of monsoonal evergreen broad-leaved forest communities in Xishuangbanna. Journal of Mountain Science, 24, 257-267. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李冬, 唐建维, 罗成坤, 李俊松, 刘正安 (2006) 西双版纳季风常绿阔叶林的群落学特征. 山地学报, 24, 257-267.] | |
| [35] | Li DQ, Song YL (2000) Review on hot spot and GAP analysis. Chinese Biodiversity, 8, 208-214. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [李迪强, 宋延龄 (2000) 热点地区与GAP分析研究进展. 生物多样性, 8, 208-214.] | |
| [36] | Li QY, Wang XP (2013) Elevational pattern of species richness in the Three Gorges region of the Yangtze River: Effect of climate, geometric constraints, area and topographical heterogeneity. Biodiversity Science, 21, 141-152. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李巧燕, 王襄平 (2013) 长江三峡库区物种多样性的垂直分布格局: 气候、几何限制、面积及地形异质性的影响. 生物多样性, 21, 141-152.] | |
| [37] | Liu KM, Zheng Z, Gong DJ (2017) Elevational patterns of species richness and their underlying mechanism. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36, 541-554. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘开明, 郑智, 龚大洁 (2017) 物种丰富度的垂直分布格局及其形成机制. 生态学杂志, 36, 541-554.] | |
| [38] | Liu QF, Liu Y, Sun XL, Zhang XF, Kang SRL, Ding Y, Zhang Q, Niu JM (2015) The explanation of climatic hypotheses to community species diversity patterns in Inner Mongolia grasslands. Biodiversity Science, 23, 463-470. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘庆福, 刘洋, 孙小丽, 张雪峰, 康萨如拉, 丁勇, 张庆, 牛建明 (2015) 气候假说对内蒙古草原群落物种多样性格局的解释. 生物多样性, 23, 463-470.] | |
| [39] | Liu Y, Zhang YP, He DM, Cao M, Zhu H (2007) Elevational patterns of species richness and climate interpretation of longitudinal range-gorge region. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52, 43-50. (in Chinese) |
| [刘洋, 张一平, 何大明, 曹敏, 朱华 (2007) 纵向岭谷区山地植物物种丰富度垂直分布格局及气候解释. 科学通报, 52, 43-50.] | |
| [40] | Lomolino MV (2001) Elevation gradients of species-density: Historical and prospective views. Global Ecology & Biogeography, 10, 3-13. |
| [41] | McCain CM (2007) Area and mammalian elevational diversity. Ecology, 88, 76-86. |
| [42] | Myers N (1988) Threatened biotas: “Hot spots” in tropical forests. Environmentalist, 8, 187-208. |
| [43] | Nogués-Bravo D, Araújo MB, Romdal T, Rahbek C (2008) Scale effects and human impact on the elevational species richness gradients. Nature, 453, 216-219. |
| [44] | O’Brien EM (1993) Climatic gradients in woody plant species richness: Towards an explanation based on an analysis of southern Africa’s woody flora. Journal of Biogeography, 20, 181-198. |
| [45] | O’Brien EM (1998) Water-energy dynamics, climate, and prediction of woody plant species richness: An interim general model. Journal of Biogeography, 25, 379-398. |
| [46] | Pouteau R, Bayle É, Blanchard É, Birnbaum P, Cassan J, Hequet V, Ibanez T, Vandrot H (2015) Accounting for the indirect area effect in stacked species distribution models to map species richness in a montane biodiversity hotspot. Diversity & Distributions, 21, 1329-1338. |
| [47] | Qian H (1998) Large-scale biogeographic patterns of vascular plant richness in North America: An analysis at the generic level. Journal of Biogeography, 25, 829-836. |
| [48] | Rahbek C (1997) The relationship among area, elevation, and regional species richness in neotropical birds. The American Naturalist, 149, 875-902. |
| [49] | Rahbek C (2005) The role of spatial scale and the perception of large-scale species-richness patterns. Ecology Letters, 8, 224-239. |
| [50] | Sanders NJ (2002) Elevational gradients in ant species richness: Area, geometry, and Rapoport’s rule. Ecography, 25, 25-32. |
| [51] | Tang LL, Li TB, Li DW, Meng XX (2014) Elevational patterns of plant richness in the Taibai Mountain, China. The Scientific World Journal, 2014, 309053. |
| [52] | Vetaas OR, Grytnes JA (2002) Distribution of vascular plant species richness and endemic richness along the Himalayan elevation gradient in Nepal. Global Ecology & Biogeography, 11, 291-301. |
| [53] | Wang ZH, Chen AP, Fang JY (2004a) Richness of seed plants in relation with topography in Hunan Province. Acta Geographica Sinica, 59, 889-894. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王志恒, 陈安平, 方精云 (2004a) 湖南省种子植物物种丰富度与地形的关系. 地理学报, 59, 889-894.] | |
| [54] | Wang ZH, Chen AP, Piao SL, Fang JY (2004b) Pattern of species richness along an altitudinal gradient on Gaoligong Mountains, Southwest China. Biodiversity Science, 12, 82-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王志恒, 陈安平, 朴世龙, 方精云 (2004b) 高黎贡山种子植物物种丰富度沿海拔梯度的变化. 生物多样性, 12, 82-88.] | |
| [55] | Wang ZH, Tang ZY, Fang JY (2007) Altitudinal patterns of seed plant richness in the Gaoligong Mountains, south-east Tibet, China. Diversity & Distributions, 13, 845-854. |
| [56] | Wang ZH, Tang ZY, Fang JY (2009a) The species-energy hypothesis as a mechanism for species richness patterns. Biodiversity Science, 17, 613-624. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王志恒, 唐志尧, 方精云 (2009a) 物种多样性地理格局的能量假说. 生物多样性, 17, 613-624.] | |
| [57] | Wang ZH, Tang ZY, Fang JY (2009b) Metabolic theory of ecology: An explanation for species richness patterns based on the metabolic processes of organisms. Biodiversity Science, 17, 625-634. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王志恒, 唐志尧, 方精云 (2009b) 生态学代谢理论: 基于个体新陈代谢过程解释物种多样性的地理格局. 生物多样性, 17, 625-634.] | |
| [58] | Wen C, Gu L, Wang H, Lü Z, Hu RC, Zhong J (2015) GAP analysis on national nature reserves in China based on the distribution of endangered species. Biodiversity Science, 23, 591-600. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [闻丞, 顾垒, 王昊, 吕植, 胡若成, 钟嘉 (2015) 基于最受关注濒危物种分布的国家级自然保护区空缺分析. 生物多样性, 23, 591-600.] | |
| [59] | Woodward FI, Lomas MR, Kelly CK (2004) Global climate and the distribution of plant biomes. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 359, 1465-1476. |
| [60] | Xu X, Zhang HY, Luo J, Zhang DJ, Ma A (2017) Area-corrected species richness patterns of vascular plants along a tropical elevational gradient. Journal of Mountain Science, 14, 694-704. |
| [61] | Zhang YB, Du HD, Jin XH, Ma KP (2015) Species diversity and geographic distribution of wild Orchidaceae in China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 60, 179-188. (in Chinese) |
| [张殷波, 杜昊东, 金效华, 马克平 (2015) 中国野生兰科植物物种多样性与地理分布. 科学通报, 60, 179-188.] | |
| [62] | Zhang ZJ, Yan YJ, Tian Y, Li JS, He JS, Tang ZY (2015) Distribution and conservation of orchid species richness in China. Biological Conservation, 181, 64-72. |
| [63] | Zheng Z, Gong DJ, Zhang Q, Zhao HB (2014) Vertical patterns of plant species diversity in the Baishuijiang Nature Reserve: Explanation of area, climate and boundary constraint. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25, 3390-3398. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑智, 龚大洁, 张乾, 赵海斌 (2014) 白水江自然保护区植物物种多样性的垂直格局: 面积、气候、边界限制的解释. 应用生态学报, 25, 3390-3398.] | |
| [64] | Zhu H (2007) On the classification of forest vegetation in Xishuangbanna, southern Yunnan. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 29, 377-387. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱华 (2007) 论滇南西双版纳的森林植被分类. 云南植物研究, 29, 377-387.] | |
| [65] | Zhu H (2006) A discussion on plant diversity of tropical montane rain forests in Xishuangbanna, Yunnan. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 30, 184-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱华 (2006) 西双版纳热带山地雨林的植物多样性研究的一些问题讨论. 植物生态学报, 30, 184-186.] | |
| [66] | Zhu H, Wang H, Li BG, Zhou SX, Zhang JH (2015) Studies on the forest vegetation of Xishuangbanna. Plant Science Journal, 33, 641-726. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱华, 王洪, 李保贵, 周仕顺, 张建侯 (2015) 西双版纳森林植被研究. 植物科学学报, 33, 641-726.] | |
| [67] | Zhu H, Yan LC (2012) Native Seed Plants in Xishuangbanna of Yunnan. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [朱华, 闫丽春 (2012) 云南西双版纳野生种子植物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [68] | Zhu Y, Jiang Y, Liu QR, Xiong M, Kang MY (2007) Altitudinal pattern of vascular plant species richness based on equal-area belts in Mt. Helan. Biodiversity Science, 15, 408-418. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱源, 江源, 刘全儒, 熊敏, 康慕谊 (2007) 基于等面积高度带划分的贺兰山维管植物物种丰富度的海拔分布格局. 生物多样性, 15, 408-418.] |
| [1] | Jia Zhenni, Zhang Yicen, Du Yanjun, Ren Haibao. Influences of disturbances on successional dynamics of species diversity in mid- subtropical forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [2] | Xinyi He, Yumei Pan, Yan Zhu, Jiayi Chen, Sirong Zhang, Naili Zhang. Impact of ectomycorrhizal tree dominance and species richness on soil nitrogen turnover in a warm temperate forest [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24173-. |
| [3] | Rongjiao Li, Jianghai Dong, Wenfang Zheng, Ruyuan Liu, Lijuan Zhao, Ruihe Gao. Soil faunal diversity characteristics and influencing factors across the altitude gradient in the poplar-birch forest of Guandi Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24070-. |
| [4] | Yiyun Gu, Jiaqi Xue, Jinhui Gao, Xinyi Xie, Ming Wei, Jinyu Lei, Cheng Wen. A public science data-based regional bird diversity assessment method [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 24080-. |
| [5] | Yao Zhang, Junyao Sun, Wei Li. Temporal and spatial trends in NDVI of vegetation in water level fluctuation zone and drivers along an altitude gradient in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23432-. |
| [6] | Bin Li, Pengfei Song, Haifeng Gu, Bo Xu, Daoxin Liu, Feng Jiang, Chengbo Liang, Meng Zhang, Hongmei Gao, Zhenyuan Cai, Tongzuo Zhang. Bird community diversity patterns and their drivers in the Qinghai region of Kunlun Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23406-. |
| [7] | Jingci Meng, Guodong Wang, Guanglan Cao, Nanlin Hu, Meiling Zhao, Yantong Zhao, Zhenshan Xue, Bo Liu, Wenhua Piao, Ming Jiang. Patterns and drivers of plant species richness in Phragmites australis marshes in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23194-. |
| [8] | Guoshan Shi, Feng Liu, Guanghong Cao, Dian Chen, Shangwen Xia, Yun Deng, Bin Wang, Xiaodong Yang, Luxiang Lin. Beta diversity of woody plants in a tropical seasonal rainforest at Xishuangbanna: Roles of space, environment, and forest stand structure [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24285-. |
| [9] | Fangfang Wu, Na Liu, Chunmei He, Zuoqiang Yuan, Zhanqing Hao, Qiulong Yin. Elevational gradient pattern of woody plant community structure and diversity in the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [10] | Jia Yao, Congling Zhang, Shixuan Li, Yang Lin, Zhen Wang, Yuhan Zhang, Weilong Zhou, Xinhe Pan, Shan Zhu, Yiqing Wu, Dan Wang, Jinliang Liu, Shanshan Tan, Guochun Shen, Mingjian Yu. Characteristics of plant communities in the Baishanzu continuous elevational transect [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24052-. |
| [11] | Liyuan Wang, Huijian Hu, Jie Jiang, Yiming Hu. Species richness patterns of mammals and birds and their drivers in the Nanling Mountain Range [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23026-. |
| [12] | Xiaoyan Luo, Qiang Li, Xiaolei Huang. DNA barcode reference dataset for flower-visiting insects in Daiyun Mountain National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23236-. |
| [13] | Zhifa Liu, Xincai Wang, Yuening Gong, Daojian Chen, Qiang Zhang. Diversity and elevational distribution of birds and mammals based on infrared camera monitoring in Guangdong Nanling National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 22689-. |
| [14] | Shengwen Chen, Haibao Ren, Guangrong Tong, Ningning Wang, Wenchao Lan, Jianhua Xue, Xiangcheng Mi. Spatial patterns in woody species diversity in the Qianjiangyuan National Park [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 22587-. |
| [15] | Yanqiu Xie, Hui Huang, Chunxiao Wang, Yaqin He, Yixuan Jiang, Zilin Liu, Chuanyuan Deng, Yushan Zheng. Determinants of species-area relationship and species richness of coastal endemic plants in the Fujian islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22345-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()