物种多样性是生物多样性在物种水平上的表现形式, 也是生态系统恢复与重建的重要特性之一(刘晓丽等, 2020)。较高的多样性水平能够增加地下生物量的比例, 形成空间分布和形态特征多样化的根系网络, 从而扩大植物根系与土壤的接触面积, 减少土壤流失(李慧等, 2021; 李惠珍等, 2022; Lou et al, 2023)。而单一物种由于根系参数的局限性常难以充分利用土壤空间以形成稳定的根-土复合体, 缓解土壤侵蚀的能力较弱(郭洋楠等, 2022)。土壤抗冲性是评价土壤结构稳定性的重要指标, 表征其抵抗地表径流机械破坏的能力(沙小燕等, 2022)。丰富的物种多样性和良好的根系特征可以改善土壤性质并促进土壤团聚体形成, 提高土壤抗侵蚀能力(Lou et al, 2023)。尤其是草本植物群落, 其较高的密度与物种多样性以及较短的根系成型周期, 在提高表土抗性和稳定性方面具有重要作用(郭洋楠等, 2022)。
干扰可能导致局部生境丧失或斑块化, 改变植物群落物种的资源利用能力和相关种群的功能关系。人工维护措施会影响植被的发展与演替, 促进物种与环境之间的选择与适应, 使群落内各物种在相互影响的情况下也有稳定共存的机遇(刘晓丽等, 2020; 尹才佳等, 2022)。物种多样性的改变进一步影响根系垂直分布差异和土壤抗冲性能的变化(李慧等, 2021)。已有研究表明, 土壤抗冲性强弱受土地利用类型、根系特征、土壤性质等因素综合影响, 根系和物种多样性对提高土壤抗冲性有积极作用(肖鹏等, 2019; 沙小燕等, 2022; Lou et al, 2023)。在植被恢复过程中, 环境变化导致的生境资源异质性和人为干预在一定程度上可对植物群落的物种组成与多样性维持产生积极影响, 加快植被恢复及生态环境改善(刘晓丽等, 2020)。人工植草、灌木去除、覆土等措施可改善群落结构和水养供应, 促进草本植物的补充和根系发育(Johnson et al, 2018; 田曼等, 2019; Wang et al, 2022; 李彩弟等, 2023)。但不合理的维护措施可能形成较为单一的植被和脆弱的土壤结构, 导致土壤抗冲性变差(肖鹏等, 2019; 侯星辰等, 2022; 资如毅等, 2022)。长期以来, 维护措施在草本群落上的应用多集中在全球草地典型分布区及石灰岩山地、半干旱草原等生态较脆弱的区域(Evju et al, 2015; Harpole et al, 2016; 赵月丹等, 2019; 刘晓丽等, 2020), 而对易遭受雨水冲刷和人为破坏的湿润地区土遗址的植被生态学研究则鲜少涉及。我国土遗址的生态恢复多通过博物馆式、防风化加固等工程措施进行维护, 采用植物保护土遗址的理念在秦始皇陵、寒窑遗址公园、汉魏洛阳城等地有不同程度的应用, 但仅简单提及植被可改善遗址环境, 未深究其加固土体、减缓雨水冲刷等的保护作用(王菲等, 2013)。三星堆遗址城墙多数呈倾斜状斜行夯层, 素土堆积的夯筑方式较为随意, 土体本身强度和稳定性差。再加上其位于暴雨多、雨期长的成都平原, 水土流失、边坡垮塌等问题难以避免(张跃辉等, 2005; 许丹阳, 2021)。研究草本植物物种多样性及其根系与土壤抗冲性的关系对防止遗址城墙水土流失、发挥原生植被的水土保持作用意义重大。
三星堆遗址城墙是中华文明探源工程的重要组成部分。不同维护措施下草本植物物种多样性与土壤抗冲性的关系是现阶段遗址城墙保护关注的焦点。鉴于此, 本研究以三星堆遗址城墙5种维护措施(自然更新、种植、弃耕、灌木去除、修剪)下形成的典型草本群落为研究对象, 探讨了不同措施下的草本植物多样性、根系和土壤抗冲性及其相关性, 以期科学评价不同维护措施下植被的恢复和重建状况, 为三星堆遗址城墙保护及申遗工作实施提供科学依据, 为全国具有类似植被覆盖的湿润地区土遗址保护提供经验。
1 材料与方法
1.1 研究区概况
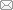
三星堆遗址城墙(30°42′-30°59′ N, 103°12′- 103°51′ E)位于四川省广汉市三星堆遗址内(图1), 是5,000年古蜀文明的辉煌例证。该地海拔约500 m, 属亚热带湿润气候, 年均气温16-17℃, 年均降水量890.8 mm, 暴雨多。年均日照时数1,229.2 h, 年均相对湿度82% (张跃辉等, 2005)。研究区位于三星堆遗址东、西、南城墙和祭祀坑, 城墙宽40-50 m, 长约495-1,200 m (张跃辉等, 2005)。遗址城墙均遭受同等耕作破坏, 自2012年退耕禁种, 设立核心保护区。主要土壤类型为冲积土或水稻土。主要草本植物有丝茅(Imperata cylindrica var. major)、积雪草(Centella asiatica)、喜旱莲子草(Alternanthera philoxeroides)、钻叶紫菀(Symphyotrichum subulatum)、马蹄金(Geranium nepalense)等。
图1
1.2 样地设置与群落调查
在三星堆遗址城墙上选择生境相似的种植、弃耕、灌木去除、修剪4种人为干扰或人工维护措施处理后的典型样地, 同时以东城墙接近无干扰的自然更新样地作为对照。(1)自然更新样地(natural regeneration plots, NR): 东城墙, 2012年以来无任何维护措施, 以原生植被自然更新为主, 现已形成相对稳定的草本群落。(2)种植样地(planting plots, PL): 西城墙, 因历代耕种导致墙体松散、土体裸露, 于2012年栽种丝茅, 无维护, 现丝茅广布。(3)弃耕样地(abandoned field plots, AF): 南城墙, 2012年限制耕作后, 城墙附近仍有少量居民点未迁出, 偶有种植豆类、瓜类及少量蔬菜, 以浅耕为主。(4)灌木去除样地(shrub removal plots, SR): 祭祀坑城墙, 2012年覆素土, 土层厚度约20 cm, 每年秋季割除高度超过20 cm的灌木及大型草本。(5)修剪样地(pruning plots, PR): 西城墙北侧, 2012年人工种植结缕草(Zoysia japonica)、马蹄金、蛇莓(Duchesnea indica)等多年生草本, 每年秋季修剪。
依据方精云等(2009)的研究方法, 在全面踏查的基础上, 于2022年10月采用典型样地法选取三星堆遗址城墙5种样地类型, 各类型均设置4个20 m × 30 m的样地, 共计20个, 总面积12,000 m2。在各样地中运用对角线法设置12个1 m × 1 m草本样方, 共计240个样方。记录样方内草本的种名、高度、盖度、株数(丛数)。
1.3 物种多样性计算
用如下公式计算草本层α多样性指数(马克平和刘玉明, 1994):
式中, S为物种数, Pi为第i种的个体数ni占所有物种个体总数n的比例, 即Pi = ni/n。
1.4 土壤取样及测定
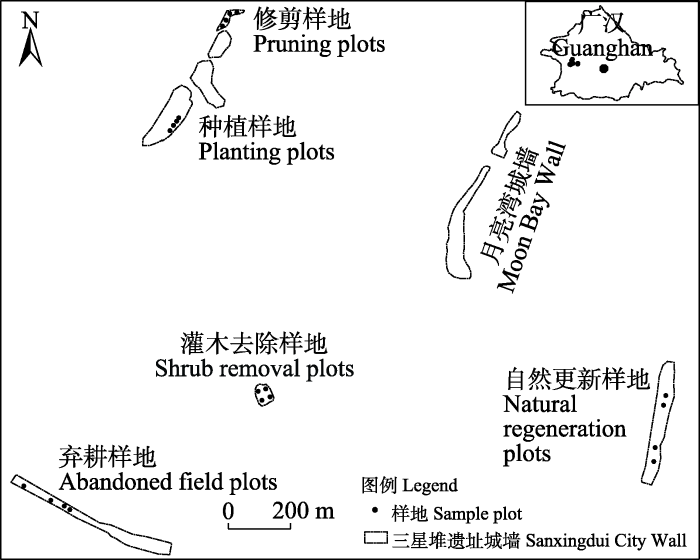
土壤抗冲试验采用改进的原状土冲刷试验法(鱼舜尧等, 2022), 装置如图2所示。选取样地内植物生长均匀的地带, 用取样器(长10 cm、宽10 cm、高8 cm)取表层土(0-20 cm)及草本植物细根, 于上述每个典型样地中随机取4个重复, 共计80份土样。将取样器去掉上盖放入盆中, 加水至取样器上沿, 浸泡18 h后装入土样槽, 使土样表面和土样槽面齐平, 将冲刷槽坡度调节至样地平均坡度25°, 通过恒压水箱控制流量(2.84 L/min)为暴雨条件后放水冲刷。冲刷总时长15 min, 在0-5 min内以1 min为一个时段, 5-15 min内以2 min为一个时段, 各时段收集一次泥沙量。冲刷结束后静置沉淀, 沉淀后的泥沙转入铝盒, 置于烘箱中烘干并称取泥沙质量(g)。
图2
土壤抗冲系数(AS)计算公式如下:
式中, Q为冲刷槽每分钟的水流量(L/min); t为冲刷历时(min); m为被冲刷土壤干重(g)。
1.5 根系测定
参照张荣等(2020)的研究方法, 在冲刷实验后将土样放置在筛孔100目(0.15 mm)的不锈钢网筛上以流水冲洗, 获取土壤中的草本植物细根, 将其置于65℃烘箱烘干至恒重。采用Epson数字化扫描仪(Expression 10000XL 1.0)和根系图像分析系统软件(Win RHIZO Pro2009c)对细根形态特征指标进行扫描和定量分析。细根之间无重叠堆积, 扫描出细根的根长、根径、根表面积、根体积、分叉数, 将各土样的根长度、根表面积、根体积除以土样体积, 获得根长密度(root length density, RLD)、根表面积密度(root surface area density, RSAD)和根体积密度(root volume density, RVD)。
1.6 数据处理
使用Microsoft Excel 2021、SPSS 26软件整理分析数据。采用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA)和最小显著差异法(LSD)分析不同维护措施下草本植物多样性指数、土壤抗冲性及细根特征之间的差异(α = 0.05)。运用Pearson相关性分析计算物种多样性和土壤抗冲性及细根指标之间的相关性。使用Origin 2021完成绘图。
2 结果
2.1 草本植物群落物种组成
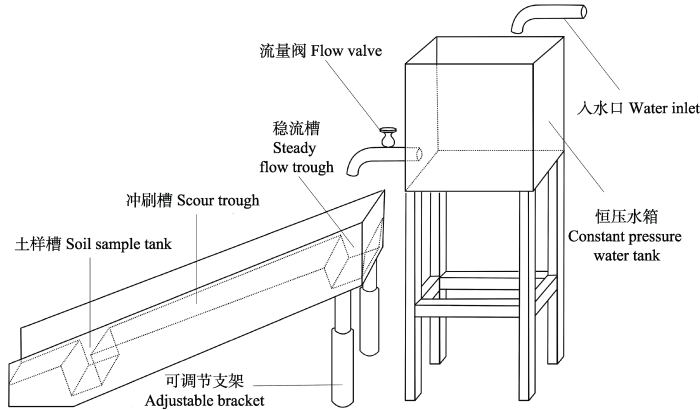
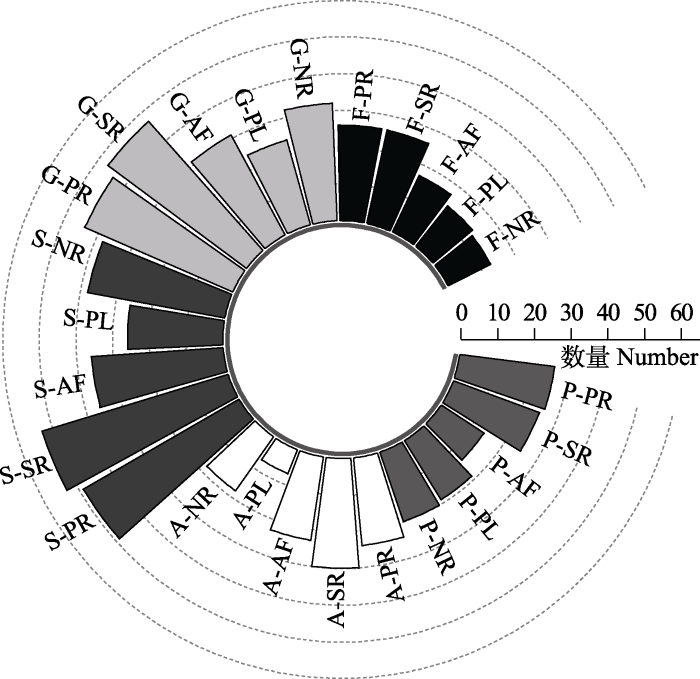
实际调查结果显示(图3), 研究区内共记录草本植物103种, 隶属40科81属, 以菊科及禾本科植物占优且在各类型样地中均有分布。自然更新样地、种植样地、弃耕样地、灌木去除样地、修剪样地中分别记录草本植物38种(13科32属)、26种(14科24属)、36种(17科31属)、53种(26科47属)、49种(26科44属)。从生活型上看, 除弃耕样地外, 其余样地以多年生草本植物占优且差异不显著(P > 0.05), 多年生草本的物种数占比依次为种植样地(73%) > 自然更新样地(53%) > 修剪样地(52%) > 灌木去除样地(45%) > 弃耕样地(38%), 其中弃耕样地多年生草本植物显著少于其余样地(P < 0.05), 仍以一年生草本为主。
图3
图3
三星堆遗址城墙不同维护措施下草本植物群落物种组成和生活型。F: 科; G: 属; S: 种; A: 一年生草本; P: 多年生草本; NR: 自然更新样地; PL: 种植样地; AF: 弃耕样地; SR: 灌木去除样地; PR: 修剪样地。
Fig. 3
Species composition and life form of herbaceous plant community under different maintenance measures at Sanxingdui City Wall. F, Family; G, Genus; S, Species; A, Annual herb; P, Perennial herb; NR, Natural regeneration plots; PL, Planting plots; AF, Abandoned field plots; SR, Shrub removal plots; PR, Pruning plots.
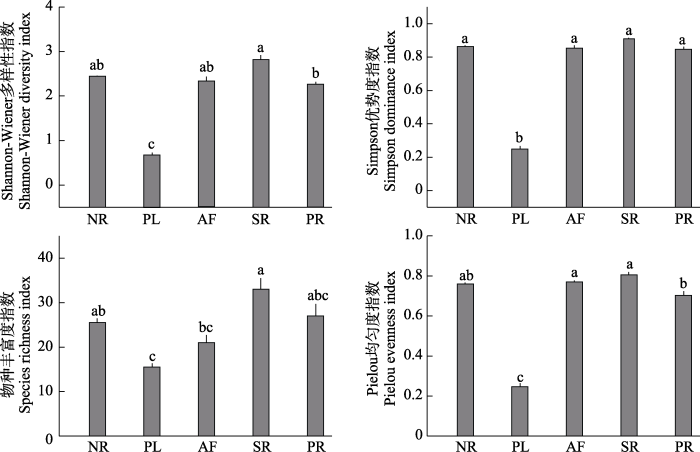
2.2 草本植物群落物种多样性指数
不同维护措施对草本植物群落物种多样性的影响不同(图4)。各样地的Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Simpson优势度指数从大到小排序为灌木去除样地 > 自然更新样地 > 弃耕样地 > 修剪样地 > 种植样地, 物种丰富度指数和Pielou均匀度指数为灌木去除样地 > 弃耕样地 > 修剪样地 > 自然更新样地 > 种植样地。4种多样性指数均表现出灌木去除样地最大, 种植样地最小, 且种植样地的Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Simpson优势度指数、Pielou均匀度指数显著低于其余4种类型(P < 0.05), 物种丰富度指数与自然更新样地、灌木去除样地差异显著(P < 0.05)。自然更新样地、弃耕样地、灌木去除样地、修剪样地的Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Simpson优势度指数、Pielou均匀度指数较接近, 无显著差异(P > 0.05)。
图4
图4
三星堆遗址城墙不同维护措施下草本植物群落物种多样性比较。NR: 自然更新样地; PL: 种植样地; AF: 弃耕样地; SR: 灌木去除样地; PR: 修剪样地。不同小写字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 4
Comparison of species diversity of herbaceous plant communities under different maintenance measures at Sanxingdui City Wall. NR, Natural regeneration plots; PL, Planting plots; AF, Abandoned field plots; SR, Shrub removal plots; PR, Pruning plots. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 level.
2.3 不同维护措施下土壤抗冲性及细根特征
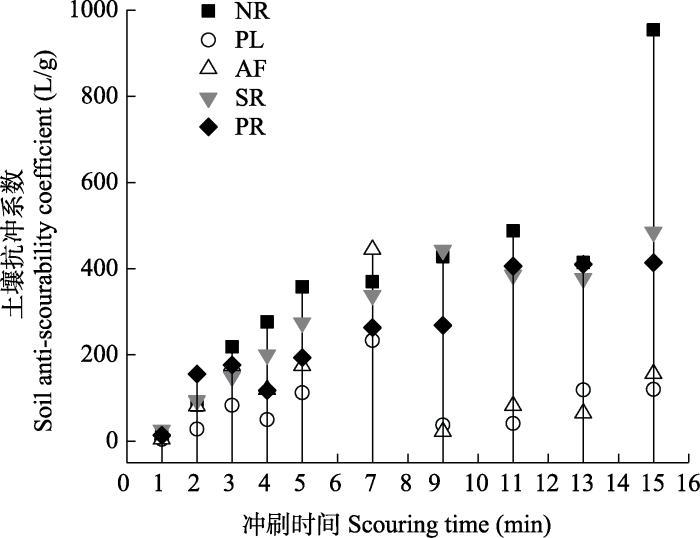
2.3.1 不同维护措施下冲刷过程中土壤抗冲系数变化特征
由图5可知, 各类型群落初始土壤抗冲系数均无显著差异(P > 0.05)。前7 min内, 各类型群落土壤抗冲系数随时间延长呈上升趋势; 冲刷7 min后, 自然更新样地、灌木去除样地、修剪样地的土壤抗冲系数呈波动式增长, 其中自然更新样地的土壤抗冲系数增幅较大。弃耕样地、种植样地的土壤抗冲系数在7-9 min内陡降(P < 0.05), 随后又恢复缓慢上升态势。从整体上看, 各类型群落的土壤抗冲性随冲刷的进行而逐渐增强, 其中自然更新样地和修剪样地的土壤抗冲系数变化显著(P < 0.05)。当15 min的冲刷结束时, 自然更新样地的土壤抗冲系数最大, 土壤抵抗径流冲刷优势明显, 其次是灌木去除样地、修剪样地, 而弃耕样地、种植样地土壤抗冲性系数较小且与自然更新样地差异显著(P < 0.05)。
图5
图5
三星堆遗址城墙不同维护措施下冲刷过程土壤抗冲性变化特征。NR: 自然更新样地; PL: 种植样地; AF: 弃耕样地; SR: 灌木去除样地; PR: 修剪样地。
Fig. 5
The variation characteristics of soil anti-scourability in the process of erosion under different maintenance measures at Sanxingdui City Wall. NR, Natural regeneration plots; PL, Planting plots; AF, Abandoned field plots; SR, Shrub removal plots; PR, Pruning plots.
2.3.2 不同维护措施下土壤抗冲性及细根指标比较
由表1可知, 不同维护措施下土壤抗冲系数和细根指标差异显著(P < 0.05)。5种样地类型根表面积密度为0.0749-0.4055 cm2/cm3, 根长密度为0.3706-0.8659 cm/cm3, 根体积密度为0.0017- 0.0164 cm3/cm3, 平均根径介于0.73-1.63 mm。土壤抗冲系数和细根指标均在灌木去除样地达到峰值, 且灌木去除样地的根表面积密度、根体积密度、平均根径与其他样地类型差异显著(P < 0.05)。此外, 土壤抗冲系数和根长密度在种植样地最小, 根表面积密度、根体积密度、平均根径、分叉数在弃耕样地最小。种植样地与弃耕样地的土壤抗冲系数、根长密度、分叉数无显著差异(P > 0.05); 种植样地与修剪样地的根表面积密度、根体积密度及平均根径无显著差异(P > 0.05)。
表1 三星堆遗址城墙不同维护措施下土壤抗冲系数及细根指标。不同小写字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Table 1
| 抗冲系数 Anti-scourability coefficient (L/g) | 根表面积密度 Root surface area density (cm2/cm3) | 根长密度 Root length density (cm/cm3) | 根体积密度 Root volume density (cm3/cm3) | 平均根径 Average root diameter (mm) | 分叉数 Root forks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然更新样地 Natural regeneration plots | 118.31 ± 10.94ab | 0.1577 ± 0.0183c | 0.6448 ± 0.0139b | 0.0049 ± 0.0005b | 1.19 ± 0.11b | 1,238 ± 185b |
| 种植样地 Planting plots | 18.81 ± 2.09c | 0.2350 ± 0.0119b | 0.3706 ± 0.0230c | 0.0074 ± 0.0005b | 1.20 ± 0.04b | 583 ± 98c |
| 弃耕样地 Abandoned field plots | 22.11 ± 2.41c | 0.0749 ± 0.0116d | 0.4168 ± 0.0866c | 0.0017 ± 0.0002c | 0.73 ± 0.06c | 394 ± 80c |
| 灌木去除样地 Shrub removal plots | 138.86 ± 13.03a | 0.4055 ± 0.0369a | 0.8659 ± 0.0490ab | 0.0164 ± 0.002a | 1.63 ± 0.15a | 1,793 ± 129a |
| 修剪样地 Pruning plots | 99.26 ± 0.72b | 0.2304 ± 0.0158b | 0.7745 ± 0.0386ab | 0.0051 ± 0.0005b | 0.91 ± 0.04bc | 1,592 ± 65ab |
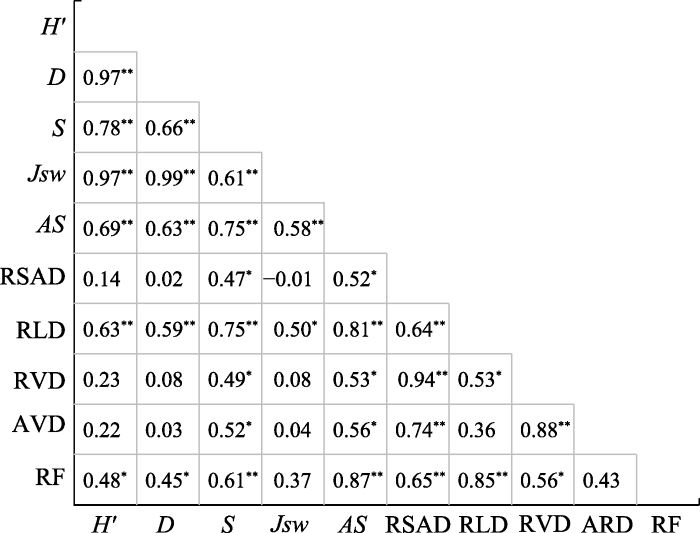
2.4 不同维护措施下物种多样性与抗冲系数及细根指标的关系
Pearson相关性分析结果表明(图6), 4种多样性指数均与土壤抗冲系数呈极显著正相关(P < 0.01)。可见随着物种多样性水平提高, 土壤抗冲能力增强。4种多样性指数之间正相关性极显著(P < 0.01), 相互影响程度高, 应综合考量。Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Simpson优势度指数分别与根长密度和分叉数显著正相关(P < 0.05), 物种丰富度指数与根长密度和分叉数极显著正相关(P < 0.01), 与根表面积密度、根体积密度和平均根径呈显著正相关(P < 0.05)。根长密度、平均根径、分叉数与土壤抗冲系数极显著正相关(P < 0.01), 根表面积密度、根体积密度与土壤抗冲系数亦显著正相关(P < 0.05)。
图6
图6
三星堆遗址城墙草本植物群落物种多样性指数与抗冲系数及细根指标的相关性。H': Shannon-Wiener多样性指数; D: Simpson优势度指数; S: 物种丰富度指数; JSW: Pielou均匀度指数; AS: 土壤抗冲系数; RSAD: 根表面积密度: RLD: 根长密度; RVD: 根体积密度; ARD: 平均根径; RF: 分叉数。* P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01。
Fig. 6
Correlation of species diversity index, soil anti-scourability coefficient and fine root index of herbaceous plant communities at Sanxingdui City Wall. H', Shannon-Wiener diversity index; D, Simpson dominance index; S, species richness index; JSW, Pielou evenness index; AS, Soil anti-scourability coefficient; RSAD, Root surface area density; RLD, Root length density; RVD, Root volume density; ARD, Average root diameter; RF, Root forks. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01.
3 讨论
3.1 不同维护措施对三星堆草本植物群落物种组成及多样性的影响
人为因素可能改变群落中的植物组成与相对丰度, 产生积极的植物相互作用, 进而影响物种多样性的空间分布(Arroyo et al, 2021; Blowes et al, 2022)。本研究是在三星堆遗址城墙设置核心保护区10年后进行的实地调查, 发现不同维护措施下草本植物群落的物种组成与多样性存在分异。各样地类型物种组成不同但均以菊科及禾本科等先锋植物占优势, 这可能与其较强的繁殖速率和适应能力有关(尹才佳等, 2022)。除弃耕样地外, 其余样地均以多年生草本为主, 在相似环境下维持稳定的物种多样性、减弱土壤侵蚀的潜力更大(Wang et al, 2022)。Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Simpson优势度指数、物种丰富度指数和Pielou均匀度指数在灌木去除样地最高, 在种植样地最低, 物种组成也表现出同样的规律。这可能是因为灌木去除样地覆土后使土壤养分增加, 灌木及高大草本的去除为低矮草本接受光照提供机遇, 利于原生草本的补充。经过环境与物种的双向选择和适应, 植物类型渐趋多样化(李彩弟等, 2023)。这与赵月丹等(2019)在内蒙古灌丛化草原的平茬实验结果类似。他们发现灌丛平茬后显著提高了相邻植物群落的多样性和均匀度。与之相反, 种植样地大面积栽植丝茅后无进一步维护措施, 再加上丝茅耐受性强和繁殖速度快的特性, 其重要值达93.84%, 可在群落中迅速获取竞争优势以促进自身生长, 从而限制了其他物种的定殖(Parker et al, 2019), 使群落物种组成单一化, 多样性水平较低。
植物群落物种多样性反映了群落物种组成的结构水平, 能够直接或间接体现群落和生态系统的稳定程度和生境差异。更高的物种多样性通常与更高的群落生产力、抗入侵能力和生态系统多功能性相关联(李霞等, 2020; 侯星辰等, 2022)。本研究发现自然更新样地的多样性指数和物种组成次于灌木去除样地, 但差异均不显著。说明原生植被经过长期调整优化, 自然恢复较好。弃耕样地的多样性水平较低, 主要归因于城墙附近居民的耕作活动对遗址环境的破坏, 豆类、瓜类等植物因其传播特征和蔓生性延缓了邻近草本的恢复。修剪样地经过长期修剪维护, 物种组成与自然更新样地无显著差异, 但多样性水平较低, 可能是不适宜的修剪频率和强度影响了植物生长与更新, 导致了物种多样性水平的分异(孙玉真等, 2023)。
3.2 不同维护措施对三星堆草本植物群落土壤抗冲性的影响
不同维护措施影响草本植物物种多样性水平。相对多元化的植被可以提高群落的稳定性和持续性, 挖掘植物资源高效利用的潜力(张建贵等, 2019); 此外, 具有更高物种多样性和复杂根系特征的植物群落也有利于形成更稳定的团聚体以增强土壤抗冲性(李霞等, 2020; 李慧等, 2021; 李惠珍等, 2022)。本研究中, 灌木去除样地的土壤抗冲性较大且与自然更新样地无显著差异, 可能是削弱了上层灌木的竞争优势, 利于草本植物的生长与根系的发育。弃耕样地限制耕作后, 城墙附近仍有部分居民未迁出, 偶有耕作等人为干扰, 导致某些结构松散的土块易被冲刷移动, 表现出较差的抗冲性能。这与已有研究发现的耕作等扰动减弱土壤抗冲能力的结果类似(肖鹏等, 2019; 资如毅等, 2022)。种植样地的土壤抗冲性较差, 同样与种植单一植被导致多样性水平降低及根系指标排序靠后有关。
本研究中土壤抗冲性与根系指标正相关性明显, 各指标能很好地描述根系与土壤颗粒间接触的紧密程度。已有研究表明, 根长、根表面积和根体积越大, 根系与土壤的结合效果越好, 内聚力和加固力越强, 土壤抗冲性也有所增强(Zegeye et al, 2018; 肖鹏等, 2019; 张扬等, 2021; Wang et al, 2022)。分叉数包含植物所有主根和侧根, 表征根系在土壤中的发育状况及空间分布范围, 是植物固土保水能力的体现, 且与其总根长、总表面积和总体积关联性强(李思诗等, 2018)。叶鑫等(2020)对河岸带不同生境草本植物群落特征的研究发现物种多样性和土壤抗冲性呈负相关, 本研究结果与之相反, 可能是本研究区的特殊生境、地表覆盖差异和人为干扰等复杂因素所致。
3.3 关于三星堆遗址城墙植被恢复的建议
三星堆遗址城墙的保护是推动中华文明探源工程的关键, 城墙表面的植被状况对遗址区风貌展现的重要性不言而喻。根据物种多样性调查结果, 原生草本自然更新状况较好, 多样性水平有随时间延长而增加的趋势且对土壤抗冲性提升有积极作用, 其物种多样性的配置组合可为遗址城墙表面原生植被恢复提供参考。实地调查中发现部分草本植物具有花果等物候变化规律(如野菊(Chrysanthemum indicum)、马蹄金等), 建议重点保护以增强遗址城墙的景观价值。此外, 覆土能填平遗址城墙表面沟壑且为草本植物重新定殖提供生长空间, 后期适度去除灌木可提高草本植物多样性和土壤抗冲性, 并能控制其根系在覆土厚度范围内, 良好的根系指标与地上植被多样性的相互协调有利于维持遗址城墙的稳态。某些生根性强、生长迅速的草本植物, 如种植样地的丝茅广布, 导致观察到的物种多样性较低, 且在实地调查中发现较多根系已延伸至60-80 cm, 必须及时去除以减轻根系对遗址的破坏和对原生植被的排挤。
综上, 不同维护措施下草本植物物种多样性与根系特征可显著影响土壤抗冲性, 灌木去除样地和自然更新样地的草本植物物种多样性指数、根系特征与土壤抗冲性较好。结合三星堆遗址城墙的文化属性与发展要求, 建议实行原生境保护措施, 促进适应性强、根系浅的原生草本植物自然更新以形成良好的植被覆盖。必要时辅以灌木去除、修剪等维护措施, 有效提升物种多样性和土壤抗冲性。由于植被生长与当地气候及土壤养分条件密切相关, 本研究的理念和实践还需深入探讨。但在当下土遗址保护的探索阶段, 仍可为原有植被较多的湿润地区土遗址保护提供新思路。
参考文献
Plant-plant interactions and local patterns of diversity from semi-arid to subalpine Mediterranean plant communities
DOI:10.1007/s10531-021-02257-w
[本文引用: 1]

An understanding of the diversity spatial organization in plant communities provides essential information for management and conservation planning. In this study we investigated, using a multi-species approach, how plant–plant interactions determine the local structure and composition of diversity in a set of Mediterranean plant communities, ranging from semi-arid to subalpine habitats. Specifically, we evaluated the spatial pattern of diversity (i.e., diversity aggregation or segregation) in the local neighborhood of perennial plant species using the ISAR (individual species–area relationship) method. We also assessed the local pattern of beta-diversity (i.e., the spatial heterogeneity in species composition among local assemblages), including the contribution of species turnover (i.e., species replacement) and nestedness (i.e., differences in species richness) to the overall local beta-diversity. Our results showed that local diversity segregation decreased in the less productive plant communities. Also, we found that graminoids largely acted as diversity segregators, while forbs showed more diverse neighborhoods than expected in less productive study sites. Interestingly, not all shrub and dwarf shrub species aggregated diversity in their surroundings. Finally, an increase in nestedness was associated with less segregated diversity patterns in the local neighborhood of shrub species, underlining their role in creating diversity islands in less productive environmental conditions. Our results provide further insights into the effect of plant–plant interactions in shaping the structure and composition of diversity in Mediterranean plant communities, and highlight the species and groups of species that management and conservation strategies should focus on in order to prevent a loss of biodiversity.
Local biodiversity change reflects interactions among changing abundance, evenness, and richness
Plant species occurrence in a fragmented grassland landscape: The importance of species traits
DOI:10.1007/s10531-014-0835-y URL [本文引用: 1]
Methods and protocols for plant community inventory
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09253
[本文引用: 1]

A plant community is an assemblage of plant populations that live in certain area, and interact with and adapt to one another in the context of long-term environmental changes. Plant communities maintain global ecosystem functions, and provide food and habitats for animals and other organisms. Plant communities also provide primary resources for human survival and development, and are therefore indispensable to human societies. China is among the countries with the most diverse plant communities in the world. However, no systematic national inventory has been conducted for Chinese plant communities. This fact obstructs exploitation and protection of China’s plant resources, and also hampers the development of the fields of Chinese ecology and geography. There is an urgent need to survey Chinese plant communities using consis-tent methods and protocols. In this paper, we review major concepts in plant community ecology, and pro-pose a framework for developing plant community inventories based on recent progress in community ecol-ogy and our own experience with long-term field surveys. Our framework provides protocols for site selec-tion and plot design, items to be measured in a plot, and measurements of functional traits of dominant spe-cies. We also review protocols for field surveys of large, long-term plots. The protocols proposed in this pa-per are expected to be a base for standardizing methodology for inventory of Chinese plant communities.
植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09253
[本文引用: 1]

植物群落是不同植物在长期环境变化中相互作用、相互适应而形成的组合。它提供着人类赖以生存的主要物质资源, 维系着地球生态系统的健康和功能, 也为各种动物和其他生物提供食物来源和栖息地, 是人类生存和发展不可或缺的物质基础, 具有不可替代的作用。我国植物群落类型多样, 在世界上首屈一指, 但我国至今尚没有一次全面和系统的植物群落清查, 不仅影响了人们对我国植物资源的了解、利用和保护, 也不利于我国生态学、环境科学和地理学等相关学科的发展。采用统一的方法体系和技术规范开展我国植物群落的清查工作势在必行, 并具有紧迫性。本文基于作者长期的野外工作实践和国内外的群落调查方法, 首先简要定义了与植物群落清查有关的重要概念, 在此基础上, 论述了调查样地的设置原则和体系、群落清查的技术指标和方法、主要优势种生态属性的测定方法和规范, 并介绍了大样地调查的主要步骤。通过本文的介绍、归纳和总结, 试图为制定我国植物群落清查的技术规范提供基础材料和技术储备。
Research progress on influence of herbaceous vegetation on slope stability
DOI:10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2022.04.009
[本文引用: 2]

Shallow slope damage is one of the important factors leading to ecological damage.This paper discusses the slope stabilization mechanism of herbaceous plants in terms of their effects on habitat and root parameters,and summarizes the practical experience of herbaceous plants in ecological slope engineering in terms of species configuration and management measures.Finally,the directions of herbaceous plant slope stabilization research are proposed:to improve the concept of herbaceous plant slope stability enhancement,to clarify the specific slope stabilization mechanism of herbaceous plants,to establish ecological processes and quantitative models,and to improve the species allocation patterns,spatial layout strategies,and sustainable management measures in specific habitats.
草本植物对边坡稳定性影响研究进展
DOI:10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2022.04.009
[本文引用: 2]

边坡浅层破坏是导致生态环境破坏的重要因素之一。本文针对草本植物的边坡稳定性提升效果与潜力,从对生境的影响和根系参数方面讨论了草本植物的固坡机理;总结了生态边坡工程中草本植物在物种配置与管理措施方面的实践经验。最后,提出了草本植物固坡研究的方向:完善草本植物的边坡稳定性提升概念,探清草本植物的具体固坡机理,建立生态过程和定量化模型,提升特定生境下的物种配置模式、空间布局策略与可持续管理措施。
Addition of multiple limiting resources reduces grassland diversity
DOI:10.1038/nature19324 [本文引用: 1]
Responses of plant community diversity to human disturbance in temperate grassland with different soil parent materials
不同母质温带草地植物群落多样性对人为干扰的响应
DOI:10.13287/j.1001-9332.202208.015
[本文引用: 2]

本研究以赛罕乌拉保护区2种不同土壤母质(黄土和沙母质)与3种利用方式(围栏打草、季节性放牧和自由放牧)草地为对象,基于群落组成调查数据,计算人为干扰指数与物种多样性指数,研究草地植物群落物种多样性与草地退化程度间的关系。结果表明: 土壤母质与人为利用方式的差异使草地处于不同的退化状态,黄土与沙母质类型草地退化程度均随人为利用强度的增加而上升,且当人为利用方式相同时,黄土母质草地人为干扰指数(均值1.21)比沙母质草地(均值1.48)低。各样地物种多样性指数总体随土壤母质的砂质化和人为利用强度的增加而下降,其中Margalef丰富度指数为1.57~4.27,Shannon多样性指数为1.16~2.39,Simpson优势度指数为0.76~0.87,Pielou均匀度指数为0.71~0.80。随着人为干扰指数增加,丰富度指数、多样性指数和优势度指数均下降,而均匀度指数有上升趋势。过度放牧对2种土壤母质草地均会造成严重威胁,黄土与沙母质草地最适宜的利用方式分别为围封打草和季节性放牧。在今后生物多样性保护的实施过程中,需兼顾草地不同土壤母质与人为利用方式的影响,针对不同土壤母质条件规划不同的草地利用方式,实现因地制宜的草地恢复与管理。
Seed addition and biomass removal key to restoring native forbs in degraded temperate grassland
DOI:10.1111/avsc.2018.21.issue-2 URL [本文引用: 1]
Effects of planting patterns on vegetation and soil characteristics of artificial pasture in the Qinghai Lake Basin
种植方式对青海湖流域人工草地植被和土壤养分特征的影响
DOI:10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2023.02.021
[本文引用: 2]

为探究多年生人工草地在青海湖流域的适应性和稳定性,本研究以青海草地早熟禾(Poa pratensis.Qinghai)和青海中华羊茅(Festuca sinensis.Qinghai)单播及混播人工草地为研究对象,分析不同种植方式下人工草地植被和土壤养分特征的变化。结果表明:青海草地早熟禾+青海中华羊茅混播草地和青海草地早熟禾单播草地的生物量和盖度高于青海中华羊茅单播草地,且在生长旺期(8月),青海草地早熟禾+青海中华羊茅混播草地生物量最高,为586.2 g·m<sup>-2</sup>;青海草地早熟禾单播、青海中华羊茅单播和青海草地早熟禾+青海中华羊茅混播草地间土壤有机质、全氮、全磷、硝态氮、铵态氮和土壤含水量在相同土壤深度下差异不显著,但土壤氮、磷及有机质间存在显著的相关性。综上所述,在青海湖流域建植青海草地早熟禾+青海中华羊茅混播型人工草地可以获得较高的产量,但需在种植和管理过程中协调好土壤氮、磷间的关系。
Research progress on the effects of root niche differences on ecosystems
根系生态位差异对生态系统的影响
Effects of plant diversity on root morphology and leaf area index of legume-grass mixture community
植物多样性水平对豆禾混播群落根系形态及叶面积指数的影响
Root architecture of eight Gramineae plant species in the Benggang Area of Changting County
DOI:10.11686/cyxb2017490
[本文引用: 1]

In order to explore the root architecture of herbaceous plants in the Benggang area, eight Gramineae species were studied (<em>Imperata cylindrica</em>, <em>Eulalia speciosa</em>, <em>Miscanthus floridulus</em>, <em>Eriachne pallescens</em>, <em>Cynodon dactylon</em>, <em>Paspalum wettsteinii</em>, <em>Pennisetum</em> sp. and <em>Vetiveria zizanioides</em>). Six root architecture parameters were analyzed and comprehensively evaluated using principal component analysis. The results showed that the average diameter of the tested herbaceous roots was between 0.36 and 0.63 mm. There were no significant differences in the total root length of <em>E. speciosa</em>, <em>M. floridulus</em>, <em>E. pallescens</em>, <em>P. wettsteinii</em> and <em>V. zizanioides</em>. The total root surface area, total root volume, root tip numbers and crossing numbers varied by plant species. The total root surface area of <em>Pennisetum</em> sp. was the largest and that of <em>I. cylindrica</em> the smallest. The root tips and crossing numbers of <em>Pennisetum</em> sp. were also the largest. Average diameter, total root surface area and total root volume were the main factors influencing root architecture. The composite score order of the eight species’ roots was <em>Pennisetum</em> sp.><em>P. wettsteinii</em>><em>E. speciosa</em>><em>M. floridulus</em>><em>V. zizanioides</em>><em>E. pallescens</em>><em>C. dactylon</em>><em>I. cylindrica</em>. These results help to provide a scientific basis for the screening, allocating and popularizing of herbaceous plants for the control of erosion.
长汀县崩岗区8种禾本科植物根系构型特征
DOI:10.11686/cyxb2017490
[本文引用: 1]

为探究崩岗区草本植物根系构型特征,以8种禾本科植物:白茅、金茅、五节芒、鹧鸪草、狗牙根、宽叶雀稗、巨菌草和香根草为研究对象,运用主成分分析法对其6个根系构型参数进行分析和综合评分。结果表明:试验草本根系平均直径为0.36~0.63 mm;金茅、五节芒、鹧鸪草、宽叶雀稗和香根草总根长无显著差异;总根表面积、总根体积、根尖数和交叉数均不同,巨菌草的总根表面积最大,白茅的最小,巨菌草的根尖数和交叉数均最大。根系构型的主要影响因子是平均直径、总根表面积和总根体积。8种植物根系综合得分依次为:巨菌草>宽叶雀稗>金茅>五节芒>香根草>鹧鸪草>狗牙根>白茅。研究成果可为崩岗治理中草本植物的筛选、配置和推广提供科学依据。
Influence of habitat on the distribution pattern and diversity of plant community in dry and warm valleys of the middle reaches of the Dadu River, China
DOI:10.17520/biods.2019202
[本文引用: 2]

In the dry and warm valleys of the middle reaches of the Dadu River, landslides and debris flows occur frequently. Studying vegetation on these slopes is valuable in understanding vegetation succession in regards to ecological restoration of highly disturbed landscapes. In this study, plots were selected along the Dadu River every 5 km to investigate species composition, distribution, topography, soil characteristics, and vegetation change in the middle reaches of the Dadu River valley. Plant communities were classified, compared and sorted using multiple regression tree (MRT), alpha diversity index and canonical correspondence analysis (CCA). The results showed that the landscape were divided into four communities based on three factors: soil carbon, pH and C : N, i.e. Lespedeza floribunda-Arthraxon hispidus-Elsholtzia ciliate, Ficus tikoua-Dodonaea viscosa-Carex schneideri, Pinus yunnanensis-Quercus variabilis and Arthraxon hispidus-Heteropogon contortus. Shrub and grass dominate this area, with occasional areas of bare ground which is liable to debris flow disasters. The species richness, dominance and diversity of shrub-grass (Lespedeza floribunda) community are consistently higher than arbor and grass communities, although species diversity values are not significant. The shrub and grass community is widely distributed, although fragile and unstable as alien species reached 8.33% within these communities. MRT and CCA analysis showed that pH, C : N, slope direction and soil bulk density are the main factors influencing vegetation distribution pattern as soil influences are more important than topography.
大渡河中游干暖河谷区生境对植物群落分布格局和多样性的影响
DOI:10.17520/biods.2019202
[本文引用: 2]

大渡河中游干暖河谷区滑坡和泥石流灾害频发, 对该区域坡面植物群落的研究有助于揭示植被演替的方向, 为坡面植被生态恢复提供基本依据。本研究沿大渡河中游河谷区每隔约5 km设置典型样地, 调查了植被的物种组成和分布以及样地的地形、土壤等10个生境因子, 探讨河谷区植被的连续性变化, 并通过多元回归树(multivariate regression trees, MRT)、多样性指数和典范对应分析(canonical correspondence analysis, CCA)等方法对植物群落进行分类、比较和排序。结果表明: 大渡河中游干暖河谷植被以土壤碳含量、pH值和C : N等3个因子为节点, 可划分为多花胡枝子(Lespedeza floribunda)-荩草(Arthraxon hispidus)-香薷(Elsholtzia ciliate)(群落A)、地果(Ficus tikoua)-车桑子(Dodonaea viscosa)-川滇薹草(Carex schneideri)(群落B)、云南松(Pinus yunnanensis)-栓皮栎(Quercus variabilis)(群落C)和荩草-扭黄茅(Heteropogon contortus)(群落D)等4种群落。该区域以灌木和草本为主要植被类型(群落A、B、C), 间或有裸地分布, 易成为泥石流灾害产生的物源区; 以多花胡枝子为主的灌草群落A的物种丰富度、优势度与多样性表现一致, 均高于以乔木和草本为主的群落C和D, 但物种多样性优势并不显著, 灌草群落分布广而结构单一, 外来物种占比为8.33%, 是生态系统脆弱和不稳定的表现。多元回归树和典范对应分析结果表明, pH值、C : N、坡向和土壤容重等4个因子对植物群落组成和分布影响最大, 且土壤因子的影响大于地形因子。
Effects of vegetation restoration on the species composition and diversity of plant communities in the limestone mountains in northern Anhui Province
皖北石灰岩山地不同植被恢复模式对植物群落物种组成及多样性的影响
Vertical distribution of vegetation roots and its influence on soil erosion resistance along gully headwalls in the gullied Loess Plateau
DOI:10.1007/s11368-022-03395-6 [本文引用: 3]
Measurement of biotic community diversity. I. α diversity (Part 2)
生物群落多样性的测度方法. I. α多样性的测度方法(下)
Plant species natural abundances are determined by their growth and modification of soil resources in monoculture
DOI:10.1007/s11104-019-04299-0 [本文引用: 1]
Characteristics of soil anti-scouribility in gully head wall of grass-covering on the gullied Loess Plateau, Northwest China
黄土高塬沟壑区草地沟头立壁土壤抗冲性特征
DOI:10.13287/j.1001-9332.202201.027
[本文引用: 2]

黄土高原植被恢复使沟头立璧土壤侵蚀过程发生显著变化。为明确黄土高塬沟壑区草地沟头立壁土壤抗冲性特征及其影响因素,以裸地为对照,利用室内原状土槽冲刷试验研究了草地沟头立壁0~1 m不同土层(0~10、10~20、20~40、40~60、60~80、80~100 cm)土壤理化性质和抗冲性特征。结果表明: 草地和裸地沟头土壤水稳性团聚体含量和粘聚力随土层加深均呈减小趋势。裸地沟头土壤有机质含量、土壤抗冲系数随土层深度的增加呈减小趋势,而草地沟头土壤有机质含量、土壤抗冲系数随土层加深先增加后减小,且均在10~20 cm土层达到最大值(24.30 g·kg<sup>-1</sup>和58.86 L·g<sup>-1</sup>),草地各土层土壤抗冲系数是裸地的1.7~9.3倍。沟头土壤抗冲性与土壤有机质含量、水稳性团聚体含量、黏聚力和植物根长密度呈极显著相关,其中与土壤有机质含量(r=0.98)的关系最密切。该研究可为黄土高塬沟壑区沟头溯源侵蚀机理的研究提供基础数据,并为有效防治该区域水土流失提供科学依据。
Response of plant community characteristics of urban remnant mountains to different ways and intensity of artificial disturbance
城市遗存山体植被群落特征对不同人为干扰方式及强度的响应
Influence of varying cover-soil thickness on the restoration of degraded riparian grassland
覆土厚度对受损河滩草地群落特征的影响
Preliminary study of the protective effects of plants on earthen sites—The earthen sites in eastern Inner Mongolia as examples
植物对土遗址的保护作用初探——以内蒙古东部地区土遗址为例
Soil anti-scourabilities of four typical herbaceous plants and their responses to soil properties, root traits and slope position in Northeast China
DOI:10.3390/su142416807
URL
[本文引用: 3]

Vegetation has been proven to be an effective measure to mitigate soil erosion in most regions and climates. However, it is not clear how some herbaceous plants affect the ability of soil to resist slope flow erosion in the Mollisol region of Northeast China. In this study, four herbaceous plant plots of 50 m × 4.5 m, including Zea mays L., Sorghum bicolor × Sudanense, Avena sativa L. and Lolium multiflorum Lam., were established in a sloping land with an abandoned land as the control to detect the effect of herbaceous plants on soil anti-scourability (ANS). A hydraulic flume experiment was carried out to determine the soil ANS, and the root traits and soil properties were also measured at different slope positions. The results showed that the mean soil ANS ranged from 17.55 to 94.77 L g−1 among different herbaceous plants, of which the Lolium multiflorum Lam. showed the strongest controlling effect on soil ANS (259.87%), followed by Sorghum bicolor × Sudanense (66.87%) and Avena sativa L. (18.12%), while the soil ANS of Zea mays L. decreased by 33.37% compared with the control. Soil ANS varied with slope position, and the mean soil ANS at the upslope was 116.50–134.21% higher than that of the middle slope and downslope. Additionally, soil ANS was positively related to root mass density (RMD), root length density (RLD), root surface area density (RSAD), soil total porosity and field capacity but was negatively related to soil bulk density (p < 0.05). Furthermore, the Lolium multiflorum Lam. exhibited better root distribution (i.e., high RSAD, RLD, RMD, and low root diameter) and soil physical structure (i.e., high soil porosity structure, water-holding capacity and low bulk density) than other plant species. Thus, the Lolium multiflorum Lam. is beneficial for enhancing soil erosion resistance to overland flow, especially at the up and middle slopes, and it could be preferred to control sloped soil erosion in Northeast China.
Effects of different vegetation restoration models on soil scour resistance in dump of open-pit coal mine
不同植被恢复模式对露天煤矿排土场土壤抗冲性的影响
A review of the research on Sanxingdui culture in the past forty years
三星堆文化研究四十年
Differences of species diversity of herbaceous vegetation and soil anti-scourability in different habitats of riparian zone along Wenjiang Section of Jinma River
金马河温江段河岸带不同生境草本植物多样性和土壤抗冲性差异
Species composition and niche characteristics of secondary plant communities on regenerated landslides after earthquake
地震滑坡体自然恢复后次生植物群落物种组成及生态位特征
Effects of stand density on understory species diversity and soil anti-scourability of Cupressus funebris plantation in Yunding Mountain, Sichuan, China
林分密度对四川云顶山柏木人工林林下物种多样性和土壤抗冲性的影响
Root reinforcement to soils provided by common Ethiopian highland plants for gully erosion control
Plant community structure and species diversity differences in alpine grassland in the Qilian Mountains with different levels of degradation
祁连山高寒草地不同退化程度植物群落结构与物种多样性研究
DOI:10.11686/cyxb2018302
[本文引用: 1]

为祁连山康乐草原生产力恢复与提高提出有效措施、生物多样性保护和资源可持续利用提供理论依据,采用样方法对祁连山高寒草地不同退化程度植物群落结构和土壤特性进行调查、测定和分析,并运用5个多样性指标(Margalef丰富度指数、Dominance优势度指数、Simpson多样性指数、Evenness均匀度指数和Shannon多样性指数)研究了其物种多样性变化。结果表明:1)轻度退化草地(LDG)-中度退化草地(MDG)-重度退化草地(SDG),不同退化草地植物群落特征(密度、高度、频度、总盖度和地上生物量)整体呈现降低趋势且差异显著(P<0.05),表现为LDG>MDG>SDG;2)研究区植物共15科35属39种,其中豆科、蔷薇科、禾本科、菊科和莎草科中的植物均具备较强生态适应性,各退化程度草地植被型分别为草地早熟禾+珠芽蓼、赖草+矮生嵩草、矮生嵩草+赖草,其中禾草是群落的优势种;3)高寒草地功能群植物呈现杂类草最多,禾草类次之,毒草类占有比例最少,其中在不同退化草地杂类草、毒草类重要值分别为75.14%(SDG)>48.67%(LDG)>30.05%(MDG)、20.81%(LDG)>18.01%(SDG)>17.11%(MDG);4)不同退化草地群落物种优势度指数在重度退化草地最高为0.23,而轻度退化草地物种Margalef丰富度指数最高为2.64、Shannon多样性指数最高为2.09;5)随退化程度加重,土壤全磷、全氮、有机质和含水量呈现下降的趋势,pH呈升高的趋势,且不同退化草地土壤环境因子含量对植被生长贡献率不同。综上所述,随着康乐草地退化程度增加群落结构向单一趋势演替且环境限制因子也发生相应变化。
Effects of root characteristics of shrub community on soil anti-scourability in the Jiajin Mountains, Sichuan Province
DOI:10.13292/j.1000-4890.202011.012
[本文引用: 1]

We examined the impacts of shrub community roots on soil antiscourability in alpine gorge area in Jiajin Mountains of Sichuan Province. The Ward cluster analysis method was employed to divide communities into different types. Field sampling and undisturbed soil erosion experiment were conducted to analyze the root distribution characteristics of different community types and their effects on soil erosion resistance. The results showed that shrub communities in Jiajin Mountains could be divided into four types, with root length density and root surface area density following the order of<em>Quercus semicarpifolia</em>+<em>Salix wallichiana</em><em>Fragaria vesca</em> community (type Ⅳ) > <em>Rhododendron vernicosum</em><em>Ligularia fischeri</em> community (type Ⅰ) ><em>R. tatsienense</em>+<em>Cotoneaster subadpressus</em><em>Pteridium aquilinum</em>var. latiusculumcommunity (type Ⅱ) ><em>Q. semicarpifolia</em>+<em>C. subadpressus</em><em>P. aquilinum</em>var. <em>latiusculum</em> community (type Ⅲ); (2) Each community was dominated by roots of <1 mm diameter, while community type Ⅳ had the highest root biomass; (3) Results of the undisturbed soil erosion test showed that soil sand content in each community type decreased over time and then tended to be gentle, while the soil antiscourability coefficient was fluctuatingly increased with erosion time. The soil of type Ⅳ had stronger antiscourability; (4) Results of correlation analysis showed that roots of 0.5-1 mm diameter, total root weight density and total root volume were the main factors influencing soil anti-scourability of shrubs in Jiajin Mountains. Our results provide a basis for studies of soil erosion pattern of shrub community in the alpine gorge area.
四川夹金山灌丛群落根系特征对土壤抗冲性的影响
Root architecture of main tree species and the effects on soil reinforcement in typical black soil region
DOI:10.13287/j.1001-9332.202105.003
[本文引用: 1]

To explore root architecture and its effects on soil reinforcement of main tree species in typical black soil region, we measured root spatial distribution characteristics, root fractal characte-ristics, and geometric morphological characteristics of <i>Amygdalus triloba</i>, <i>Caragana microphylla</i>, <i>Betula platyphylla</i>, <i>Acer negundo</i>, <i>Picea koraiensis</i>, <i>Pinus sylvestris </i>var<i>. mongolica</i>, using whole root excavation method and WinRHIZO Pro LA2004 root analysis system. All the examined species are distributed widely in typical black soil region. The vertical uprooting force was determined by <i>in-situ </i>uprooting tests. The results showed that inclined roots were dominant in <i>A. triloba</i>, horizontal roots were dominant in <i>C. microphylla</i>, <i>B. platyphylla</i>, <i>A. negundo</i> and <i>P. koraiensis</i>, and the horizontal and vertical distribution of roots were commensurable in <i>P. sylvestris </i>var<i>. mongolica</i>. Except for the total root surface area of <i>B. platyphylla</i> and the total root length of <i>P. koraiensis</i>, the total root length and root surface area of shrub species were significantly greater than those of arbor species, while deciduous broad-leaved trees were significantly larger than coniferous evergreen trees. The total root volume of <i>B. platyphylla</i> was significantly larger than that of <i>C. microphylla</i>,<i> A. negundo</i>, <i>P. koraiensis </i>and <i>P. sylvestris </i>var<i>. mongolica</i>. The root fractal dimension and abundance of <i>A. triloba</i>, <i>C. microphylla</i>, <i>B. platyphylla </i>were significantly higher than those of <i>P. koraiensis</i> and <i>P. sylvestris </i>var<i>. mongolica</i>. The average maximum uprooting force of <i>A. triloba</i>, <i>C. microphylla</i>, and <i>A. negundo</i> was significantly higher than that of <i>B. platyphylla</i>, <i>P. koraiensis</i>,<i> </i>and <i>P. sylvestris </i>var<i>. mongolica</i>. Due to the role of total root length, total root surface area and the number of inclined roots, root system of <i>A. triloba</i>, <i>C. microphylla</i> and <i>A. negundo </i>showed strong soil reinforcement capacity. <i>A. triloba</i>, <i>C. microphylla</i> and <i>A. negundo</i> could be used as the option-preferred tree species when constructing soil and water conservation vegetation in typical black soil region.
典型黑土区主要树种根系构型特征及其对固土能力的影响
DOI:10.13287/j.1001-9332.202105.003
[本文引用: 1]

为量化典型黑土区主要树种根系构型特征,探究其对固土能力的影响,以该区分布较广的榆叶梅、小叶锦鸡儿、白桦、糖槭、红皮云杉、樟子松单株个体为研究对象,采用全根挖掘和WinRHIZO Pro LA2004分析系统相结合对其根系空间分布、几何形态、分形等特征进行测定,同时采用原位整株根系拉拔的方法量化根系垂直拉拔力。结果表明: 榆叶梅以倾斜根为主,小叶锦鸡儿、白桦、糖槭和红皮云杉以水平根为主,樟子松根系在水平和垂直分布上较为均衡;除白桦总根表面积和红皮云杉总根长外,灌木树种总根长、总根表面积显著大于乔木,落叶阔叶乔木总根长、总根表面积显著大于针叶常绿乔木,白桦总根体积显著大于小叶锦鸡儿、糖槭、红皮云杉和樟子松;榆叶梅、小叶锦鸡儿和白桦根系分形维数和分形丰度显著大于红皮云杉和樟子松;榆叶梅、小叶锦鸡儿和糖槭整株根系平均最大垂直拉拔力显著大于白桦、樟子松和红皮云杉。主要受根系总根长、总根表面积和倾斜根数量的影响,榆叶梅、小叶锦鸡儿和糖槭根系表现出较强的固土能力,可作为典型黑土区水土保持植被构建中优先选择的树种。
Assessment to the geo-environmental status and problem prevention of Sanxingdui Ruins
三星堆遗址环境地质现状评估及问题防治
Effects of pruning treatment on plants of Caragana microphylla community in typical steppe of Inner Mongolia
平茬对内蒙古典型草原小叶锦鸡儿群落植物的影响
DOI:10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2019.04.029
[本文引用: 2]

为了了解平茬对灌丛群落草本植物的影响,本文以内蒙古典型草原小叶锦鸡儿(Caragana microphylla Lam)群落为研究对象,设置了不平茬、一年平茬1次和一年平茬2次共3种处理,分析了平茬前后群落特征与植被化学计量特征的变化。结果表明:与未平茬相比,两种平茬处理下群落内禾本科植物密度均显著增加,平茬第二年禾本科生物量显著高于未平茬处理;平茬后两年内草地群落物种多样性指数随平茬次数增加均有增加趋势,且一年平茬2次处理时,Margalef丰富度指数显著高于未平茬处理;草本群落总生物量随平茬次数增加呈现先下降后增加的变化趋势;平茬后植被C、N含量、C/N比无显著变化,但植被N/P比显著增加。可见,平茬处理改变了小叶锦鸡儿群落的结构特征,提高了群落物种多样性及禾本科植物的密度,有助于典型草原的植被恢复。
Relationship between soil anti-scourability and soil physical properties in karst mountain areas
喀斯特高原山地土壤抗冲性与土壤物理性质的关系