鲎隶属节肢动物门肢口纲剑尾目, 是地球仅存的肢口纲物种, 其起源可追溯至4.45亿年前, 有海洋“活化石”之称(Rudkin & Young, 2009)。世界上现存4种鲎科生物, 分别为美洲鲎(Limulus polyphemus)、中华鲎(Tachypleus tridentatus)、圆尾蝎鲎(Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda)和巨鲎(Tachypleus gigas), 中国沿海地区仅有中华鲎和圆尾蝎鲎分布(Luo et al, 2020)。鲎的生活史跨越不同生境类型, 幼鲎多分布于潮间带, 成鲎则栖息于水深30 m以内沿岸海域(Shuster & Sekiguchi, 2009; Chen et al, 2015)。以中华鲎血液为核心原材料制备的鲎试剂(tachypleus amebocyte lysate, TAL)广泛应用于注射类药物(Novitsky, 2015)和疫苗的内毒素检测(Arnold, 2020; Waycott, 2020)。历史上中华鲎曾广泛分布于中国长江口以南的东海和南海近岸海域, 最北达舟山群岛, 最南分布于北部湾海域(王彝豪, 1984; 梁广耀, 1985; Sekiguchi, 1988)。20世纪80年代以来由于过度捕捞、栖息地严重破坏等原因, 中华鲎资源急剧下降, 在东南沿海许多海域几近消失(翁朝红等, 2012)。2019年IUCN宣布中华鲎为濒危(Endangered, EN)物种(Laurie et al, 2019), 2021年我国将中华鲎和圆尾蝎鲎正式列为国家二级重点保护野生动物。中华鲎种群资源枯竭将直接危及鲎试剂产业, 医药检测行业对鲎血的巨大需求与中华鲎种群“濒危”现状间的矛盾日益凸显。
识别适宜分布区域是珍稀濒危动物保护的关键环节之一。人工智能和机器学习方法逐渐成为研究物种与栖息环境适生性的重要手段(Gallagher et al, 2010), 物种分布模型作为模拟和预测物种地理分布的有效工具, 被广泛应用于预测物种适生性分布(Gelviz-Gelvez et al, 2015)。其中最大熵 (maximum entropy, MaxEnt)模型具有不依赖物种生物学参数、不需要物种缺失点, 受样本数量偏差影响小等特性, 即使在分布数据较少的情况下也能获得较好的预测精度(Merow et al, 2013; Padalia et al, 2014), 被广泛应用于珍稀濒危动植物分布评估、入侵生物的适生区预测、重要生态系统修复和全球气候变化对物种分布的影响预测等, 在生物地理学、保护生物学和生态学等相关研究中都发挥着重要作用(Mamun et al, 2018; Wei et al, 2018; Li et al, 2019; Yan et al, 2020)。
本研究通过对中国南海北部近海海域成鲎及北部湾潮间带幼鲎资源调查, 探讨了鲎资源分布现状及种群规模, 并利用MaxEnt模型对北部湾中国沿岸中华鲎幼鲎潜在栖息地进行研究, 以期为鲎栖息地保护和种群资源恢复提供数据支撑和决策依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 研究区域概况
北部湾位于中国南海西北部, 是典型的半封闭式亚热带海湾, 东临雷州半岛和海南岛, 北依广西壮族自治区, 西临越南, 与琼州海峡和南海相连。北部湾拥有多样的生态系统类型, 为许多重要、濒危的海洋生物提供了关键栖息地, 是中国乃至东南亚重要的海岸带与海洋生物多样性热点区域。
表1 北部湾幼鲎调查站位潮位信息表
Table 1
| 编号 Number | 站位 Survey station | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 平均高潮位 Mean high tide level (m) | 平均低潮位 Mean low tide level (m) | 参考潮汐站位 The closest tidal station |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 渔洲坪 Yuzhouping | 108°22′ E | 21°38′ N | 3.7 | 1.15 | 防城港 Fangchenggang |
| 2 | 螃蟹档 Pangxiedang | 108°49′ E | 21°37′ N | 3.88 | 1.37 | 龙门 Longmen |
| 3 | 中三墩 Zhongsandun | 108°52′ E | 21°37′ N | |||
| 4 | 西背岭 Xibeiling | 109°10′ E | 21°24′ N | 4.0 | 1.3 | 北海 Beihai |
| 5 | 下村 Xiacun | 109°12′ E | 21°25′ N | |||
| 6 | 竹林盐场 Zhulinyanchang | 109°16′ E | 21°25′ N | |||
| 7 | 坡尾底 Poweidi | 109°33′ E | 21°31′ N | 5.05 | 2.16 | 铁山港 Tieshangang (石头埠) (Shitoubu) |
| 8 | 沙田 Shatian | 109°39′ E | 21°30′ N | |||
| 9 | 榕根山 Ronggenshan | 109°40′ E | 21°29′ N | |||
| 10 | 乌坭 Wuni | 109°45′ E | 21°29′ N | |||
| 11 | 草潭 Caotan | 109°48′ E | 21°21′ N | 4.07 | 1.51 | 下泊 Xiabo |
| 12 | 澄迈湾 Chengmaiwan | 109°59′ E | 19°56′ N | 2.46 | 0.92 | 马村港 Macungang |
| 13 | 新盈 Xinying (I) | 109°31′ E | 19°54′ N | 3.15 | 1.07 | 新盈 Xinying |
| 14 | 新英 Xinying (II) | 109°16′ E | 19°43′ N | 3.07 | 1.05 | 洋浦 Yangpu |
潮位数据来源: 国家海洋信息中心,
Tide level data source: National Marine Data and Information Service,
1.2 鲎资源调查方法
1.2.1 近海海域成鲎资源调查
2018年和2019年南海北部近海的鲎渔获数据来源于2018年9-10月和2019年4月南海北部近海渔业资源调查, 采用“北渔60011”单船底拖网进行作业, 船体主机功率441 kW, 网具404目。拖网采样均在白天进行, 每个站的拖网时间为1 h。
鲎资源密度根据传统扫海面积法估算(王腾等, 2020), 公式如下:
式中, D为资源密度(kg/km2); Y为单位时间的渔获率(kg/h); A为单位时间的扫海面积(km2/h); E为逃逸率。
1.2.2 潮间带幼鲎调查
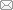
2019年和2020年, 于7-8月白天低潮时进行潮间带幼鲎调查。每个调查站点根据地形特点、潮间带宽度、与红树林的距离和与人为干扰活动距离等因素设置1-4个调查区域, 各调查区域间距大于200 m, 其中新盈设1个调查区域; 螃蟹档、中三墩、西背岭、下村、沙田、榕根山、乌坭、澄迈湾、新英设2个调查区域; 坡尾底设3个调查区域; 渔洲坪、竹林盐场、草潭设4个调查区域。各调查区域由4条垂直于海岸走向的样线组成, 样线长500 m, 宽4 m, 样线间隔125 m (图1)。由2人分别负责每条样线两侧各2 m的范围, 匀速搜索幼鲎踪迹, 现场记录每个区域内中华鲎和圆尾蝎鲎两种幼鲎的数量并逐只测量个体的前体宽度, 测量及记录后将幼鲎原处放回。
图1
图1
北部湾幼鲎调查样线示意图
Fig. 1
Schematic diagram of survey line of juvenile Tachypleus tridentatus in Beibu Gulf
1.2.3 中华鲎、圆尾蝎鲎种类区分
根据剑尾截面和表面是否光滑对中华鲎和圆尾蝎鲎的种类进行区分; 中华鲎剑尾截面为三角形, 且尾部上方有3个明显的固定棘, 而圆尾蝎鲎剑尾截面呈圆形, 且表面光滑(Chiu & Morton, 2003)。
1.3 幼鲎MaxEnt模型建立
1.3.1 物种分布数据
物种分布数据主要来源于全球生物多样性信息网络(GBIF,
1.3.2 环境变量数据
温度、盐度、距岸线距离等环境因素是影响潮间带生物生长分布的重要指标。中华鲎幼鲎主要生长于潮间带区域, 分布受到海洋和陆地环境双重影响。本研究基于此将海陆环境变量数据进行融合、标准化处理, 以期提高模型准确性。具体操作如下: 首先将已下载完成的环境变量数据导入ArcGIS软件, 利用“切片栅格”工具按照研究区域的海岸带范围进行数据裁切; 之后在海岸带范围内建立缓冲区, 利用“扩展”工具提取缓冲区内的数据向海洋或陆地方向进行数据扩展, 以实现陆地与海洋数据的融合。
本研究选取的13个环境因子主要筛选自Pati等(2021)预测印度东北海岸巨鲎产卵场采用的19种生物气候因子(附录2), 以及广东省潮间带红树林适生区预测所用到的海表温度、盐度和地形高程数据(晁碧霄等, 2020)。研究采用的生物气候因子来自世界气候数据库(www.worldclim.org); 海表温度数据来自Remote Sensing Systems (RSS)公司提供的Microwave Optimally Interpolated SST daily products产品(V5.0版)并进行统计加工; 海表盐度数据来自RSS公司提供的SMAP Salinity V3 Validated Release的Level 3 8-day running averages产品, 利用ArcGIS对获取的海表温度和盐度数据进行预处理, 将环境因子的数字图层全部在ArcGIS中统一为WGS1984坐标系, 用重采样统一环境因子的空间分辨率, 使其与分辨率最低的环境数据集相同, 并且统一裁剪范围。地形数据由美国地球物理中心(National Geophysical Data Center, NGDC)发布的ETOP01地形高程和海洋海底地形数据提取, 并通过ArcGIS Pro 2.4.3软件空间分析模块计算岸线距离等数据。为避免影响因子间的相互作用对模型结果产生影响, 将同类型环境变量数据进行相关性分析(附录3), 去除相关性较高(|r| > 0.8)的因子(Chakraborty et al, 2016; Wei et al, 2018; Jayasinghe & Kumar, 2019), 输入MaxEnt模型的环境因子见表2。
表2 主要环境变量对幼年中华鲎分布的贡献率及重要性
Table 2
| 环境变量 Environmental variables | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 重要性 Permutation importance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 平均海表温度 Mean sea surface temperature (sst) | 45.9 | 10.2 |
| 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of the wettest quarter (bio 8) | 36 | 21.3 |
| 距海岸线欧氏距离 Euclidean distance to the coastline (coastline) | 4.4 | 44.4 |
| 最暖月最高温 Max temperature of the warmest month (bio 5) | 3.1 | 3.9 |
| 降水季节性变化 Precipitation seasonality (bio 15) | 2.8 | 0.6 |
| 年平均气温 Annual mean temperature (bio 1) | 2.4 | 5.2 |
| 海底地形高程 Seabed topographic elevation (etopo 1) | 2.3 | 9.4 |
| 年平均降水量 Annual precipitation (bio 12) | 0.8 | 0.2 |
| 最干月降水量 Precipitation of the driest month (bio 14) | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| 平均海表盐度 Mean sea surface salinity (sss) | 0.5 | 2.2 |
| 气温季节性变化 Temperature seasonality (bio 4) | 0.4 | 1 |
| 等温性 Isothermality (bio 3) | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| 气温日较差 Mean diurnal range (bio 2) | 0.2 | 0.5 |
1.3.3 模型运行及评估
本研究使用MaxEnt 3.4.1软件进行预测分析。将物种分布数据的75%作为训练数据用于建立模型, 剩下25%作为测试数据用于模型检验, 模型运行时Settings中“regularization multiplier”为默认值1, 重复运行模式为“Subsample”; 重复运行10次, 并取平均结果为最终实验结果; 创建响应曲线、绘制变量重要性刀切图, 使用受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve, ROC)对模型的精度进行评价。ROC曲线(附录4)下方与坐标轴围成的面积为AUC (area under the curve)值, AUC值越高通常表明模型的效果越好, AUC值为0.5-0.6表明模型预测结果失败; 为0.6-0.7表明模型预测结果较差; 为0.7-0.8表明模型预测结果一般; 为0.8-0.9表明模型预测结果较好; 为0.9-1.0表明模型预测结果优秀。MaxEnt模型运算得到各环境变量对模型预测的贡献率和重要性, 环境变量重要性表征单个环境变量对模型结果的影响, 环境变量贡献率考虑不同环境变量间的相互影响。
1.3.4 适生等级划分
MaxEnt软件模拟输出结果值在0-1之间, 越接近1表示物种越可能存在, 利用ArcGIS重分类方法中自然间断点分级法将适宜区间(0-1)由低到高分为4个级别: 0-0.1为不适生区、0.1-0.3为低适生区、0.3-0.5为中适生区、大于0.5为高适生区。
2 结果
2.1 中国南海北部近海鲎资源状况
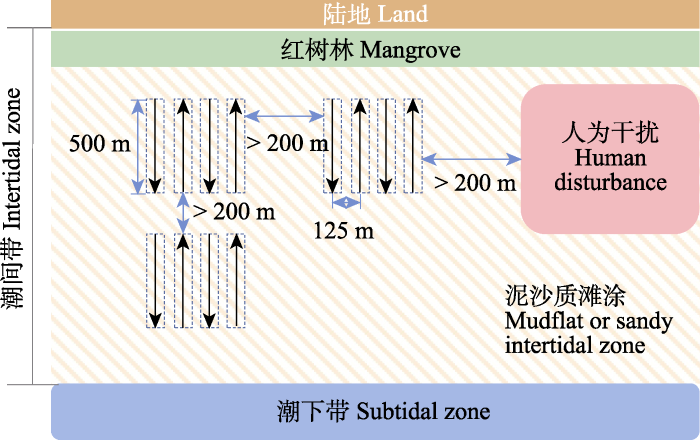
中国南海北部近海海域鲎资源拖网调查结果如图2所示。99个站点2次调查结果显示, 仅在15个站点累计发现18只成年中华鲎, 其中2018年有7个站点共发现9只中华鲎, 出现率仅为7.07% (7/99), 2019年有8个站点共发现9只中华鲎, 出现率为8.08% (8/99)。两次拖网调查均未发现圆尾蝎鲎。这一结果表明鲎当前在中国南海北部海域的分布较为稀疏, 其空间分布区域主要集中于北部湾海域。鲎的资源估算结果表明其数量在本研究区总体较少, 15个调查站点鲎资源密度为5.33-16.00 ind./km2, 资源密度最高值位于北部湾南部湾口。
图2
图2
2018年和2019年中国南海北部海域成鲎分布情况
Fig. 2
The distribution of horseshoe crabs in the offshore waters of northern South China Sea in 2018 and 2019
2.2 北部湾沿岸潮间带幼鲎资源现状
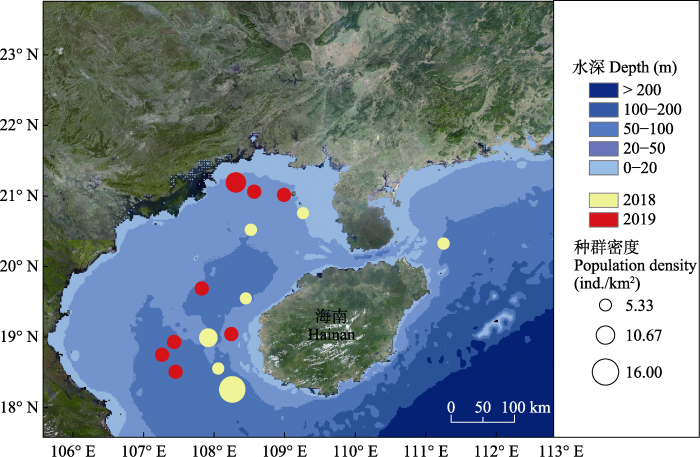
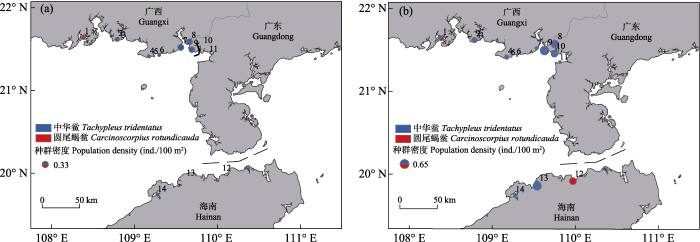
本研究潮间带实地调查结果与GBIF中北部湾中国海域中华鲎分布情况基本一致。2019年10个调查点幼鲎丰度为0.01-0.33 ind./100 m2, 其中坡尾底、沙田和榕根山幼鲎丰度相对较高(图3a); 2020年14个调查点幼鲎丰度为0.01-0.65 ind./100 m2, 其中沙田、榕根山和新盈幼鲎丰度相对较高; 竹林盐场、中三墩、下村幼鲎丰度相对较低, 均低于0.01 ind./100 m2 (图3b)。调查发现北部湾海南沿岸海域仍存在鲎育幼场, 草潭、渔洲坪、螃蟹档、西背岭、坡尾底、沙田、榕根山、乌坭是中华鲎和圆尾蝎鲎的共同栖息地, 中三墩、下村、竹林盐场、新盈、新英仅发现中华鲎, 澄迈湾仅发现圆尾蝎鲎。从物种分布来看, 北部湾沿岸潮间带中华鲎幼鲎丰度明显高于圆尾蝎鲎。
图3
图3
2019年(a)和2020年(b)北部湾潮间带幼鲎分布。1: 渔洲坪; 2: 螃蟹档; 3: 中三墩; 4: 西背岭; 5: 下村; 6: 竹林盐场; 7: 坡尾底; 8: 沙田; 9: 榕根山; 10: 乌坭; 11: 草潭; 12: 澄迈湾; 13: 新盈; 14: 新英。
Fig. 3
Juvenile horseshoe crab distribution in the intertidal zone of Beibu Gulf in 2019 (a) and 2020 (b). 1, Yuzhouping; 2, Pangxiedang; 3, Zhongsandun; 4, Xibeiling; 5, Xiacun; 6, Zhulinyanchang; 7, Poweidi; 8, Shatian; 9, Ronggenshan; 10, Wuni; 11, Caotan; 12, Chengmaiwan; 13, Xinying (I); 14, Xinying (II).
2.3 MaxEnt模型模拟结果
2.3.1 预测精度分析
经过变量筛选与模拟实验得出中华鲎幼鲎ROC曲线(附录4), 模型训练集AUC值为0.947, 表明本研究MaxEnt模型对中华鲎幼鲎适生区模拟预测结果可信度极高。
2.3.2 各影响因子的重要性
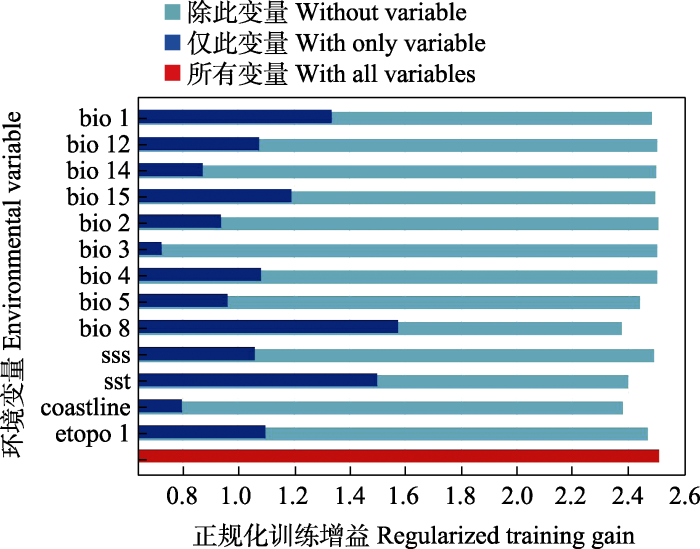
所有环境变量中, 按贡献率从高到低排序依次为平均海表温度(sst, 45.9%)、最湿季均温(bio 8, 36%)、距海岸线欧式距离(coastline, 4.4%)、最暖月最高温(bio 5, 3.1%)、降水季节性变化(bio 15, 2.8%)、年平均气温(bio 1, 2.4%)和海底地形高程(etopo 1, 2.3%) (表2)。
运用MaxEnt模型刀切算法评估各环境变量对物种分布的影响程度, 即环境变量被轮流逐一剔除, 用剩余变量参与运算并以柱状图形式表示各变量对模型的贡献值(图4), 得到最湿季均温(bio 8)、平均海表温度(sst)、年平均气温(bio 1)和降水季节性变化(bio 15) 4个环境变量对中华鲎幼鲎潜在分布预测较为重要, 表明环境变量中包含的信息对于模型结果意义较大。
图4
图4
基于刀切法的环境因子重要性分析。环境变量的含义见
Fig. 4
Importance analysis of environmental factors based on Jackknife method. The meanings of the environmental variables are shown in
2.3.3 中华鲎幼鲎适生环境因子范围
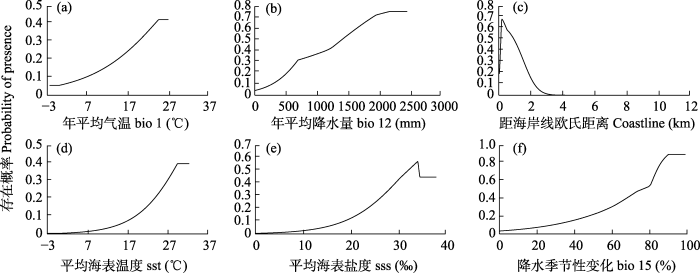
主要环境因子与中华鲎幼鲎分布概率的响应曲线如图5所示, 在一定范围内中华鲎幼鲎存在概率随年平均气温和平均海表温度升高而升高, 当年平均气温和平均海表温度分别达到25℃和30℃时中华鲎幼鲎存在概率达到最大。中华鲎幼鲎分布概率与年平均降水量和降水季节性变化分别在0-2,200 mm和0-90%范围内呈正相关。海表盐度在0-34范围内, 随着盐度上升中华鲎幼鲎存在概率上升。中华鲎幼鲎分布概率与距海岸线欧氏距离呈负相关, 离海岸线较近区域中华鲎幼鲎存在概率较大, 距海岸线越远幼鲎分布概率越低。
图5
图5
MaxEnt模型中幼年中华鲎对环境变量的响应曲线。环境变量的含义见
Fig. 5
Response curves of juvenile Tachypleus tridentatus to environmental variables in MaxEnt models. The meanings of the environmental variables are shown in
2.3.4 幼鲎潜在分布区
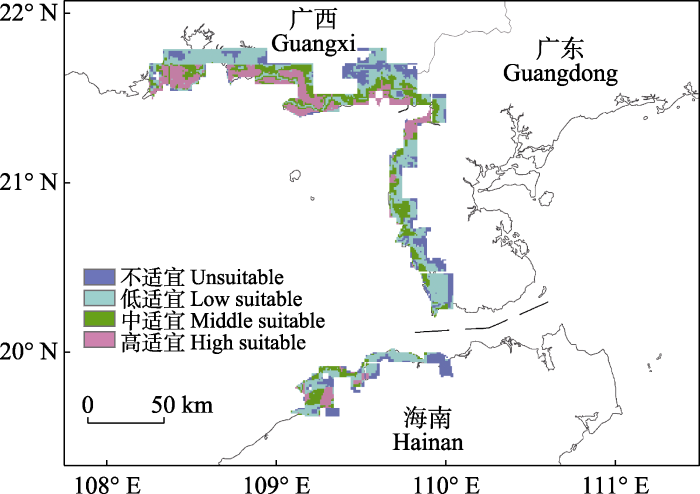
基于MaxEnt模型对北部湾潮间带中华鲎幼鲎生境适生性进行预测, 将连续概率分布在ArcGIS中进行重分类, 即高适宜区、中适宜区、低适宜区和不适宜区(图6)。结果表明高适宜区占18.39%, 中适宜区占22.48%, 低适宜区占39.30%, 不适宜区占19.84%。中华鲎幼鲎高适宜区主要分布于北部湾广西沿岸海域, 北部湾广东、海南沿岸海域各有一处高适宜区, 分别是广东省遂溪县和海南省儋州新英湾。
图6
图6
北部湾潮间带中华鲎幼鲎潜在栖息地分布图
Fig. 6
Potential suitable habitats of juvenile Tachypleus tridentatus in intertidal zone of the Beibu Gulf of China
3 讨论
3.1 北部湾中国地区鲎资源现状
20世纪80年代以来中华鲎资源急剧下降, 各地区科研人员开始对鲎资源分布展开调查。迄今为止, 中国的香港和台湾地区, 以及新加坡已完成幼鲎生境调查, 结果表明适宜幼鲎生长的育幼场数量十分有限(Cartwright-Taylor et al, 2011; Hsieh & Chen, 2015; Kwan et al, 2016; Lee & Morton, 2016)。北部湾是现今中华鲎资源最丰富的地区(Xie et al, 2020), 2009年Hu等(2015)对西背岭、金海湾和下村3个站点的调查显示, 幼鲎平均丰度为2.16-3.34 ind./100 m2; 2018年Xie等(2020)对广西沿岸海域15个鲎育幼场调查结果表明, 幼鲎丰度为0.06-7.64 ind./100 m2, 其中有11个鲎育幼场幼鲎丰度大于1 ind./100 m2, 6个鲎育幼场幼鲎丰度大于2 ind./100 m2。本研究于2019-2020年对北部湾沿岸三省潮间带幼鲎开展调查, 结果显示14个调查点幼鲎丰度为0.01-0.65 ind./100 m2。
北部湾广东海域潮间带幼鲎生境调查发现, 雷州半岛西海岸的大部分滨海湿地已极少发现幼鲎, 走访当地渔民得知近些年极少见到上岸产卵的成鲎。儋州新英、临高新盈和澄迈湾潮间带幼鲎调查结果显示, 北部湾海南北部潮间带区域目前仍存在鲎育幼场, 下一步可针对海南岛东岸、南岸等地鲎育幼场信息空白区域开展调查。近岸海域是成鲎的重要栖息地, 本次中国南海北部海域成鲎资源调查仅在北部湾及琼州海峡东侧海域发现少量成鲎。20世纪90年代以前北部湾的鲎年产量可达120-140万只(廖永岩和李晓梅, 2001), 2006年广东省南部海区拖网调查仍可发现少量中华鲎资源(翁朝红等, 2012)。Hu等(2015)、Xie等(2020)、Liao等(2019)以及本研究均是在繁殖季节对北部湾潮间带幼鲎进行调查, 均未能发现成鲎产卵现象, 表明北部湾中国近岸海域成鲎资源量已相当匮乏。随着北部湾地区经济发展, 沿海资源开发利用活动愈加频繁, 给滨海湿地重要物种和栖息地带来巨大压力, 包括围填海工程占据大面积滨海湿地, 野生动物非法贸易破坏珍稀濒危物种野生种群, 不合理的渔业作业消耗大量自然资源等。北部湾滨海湿地物种和生态面临多种多样且严重程度不一的人类活动威胁, 导致生物多样性减少、外来物种增加、天然栖息地衰退、生态服务功能减弱等状况。本研究成鲎调查结果可以确认近年中国南海北部近岸海域鲎资源处于严重衰退状态, 部分海域中华鲎种群自然分布几近消失, 存在区域性灭绝风险, 中华鲎资源科学保护已成为当务之急。
3.2 基于MaxEnt模型预测中华鲎幼鲎适生条件和适生区域
物种与环境之间的关系是物种生态需求和空间分布研究的重要内容。本研究表明对中华鲎幼鲎分布贡献率较高的几个关键因子中, 温度是影响中华鲎分布和生长的重要环境因子, 通过MaxEnt模型对北部湾中国沿岸潜在分布预测响应曲线可知, 中华鲎幼鲎偏向于选择气温和海表温度较高区域作为栖息地, 中华鲎幼鲎生境适宜性随平均气温和平均海表温度上升逐渐增加, 温度在一定程度上决定了鲎的分布区域, 这可能是气候相对较冷的长江口以北地区未见鲎分布记载的原因之一。幼鲎生长发育速度随水温升高而加快, 在水温低于25℃时低龄期幼鲎将停止生长发育(王德祥等, 2001; 洪水根, 2011)。中华鲎幼鲎对盐度的适应范围较广, 盐度在10-35时均可存活, 30-35是幼鲎发育的适宜盐度(王德祥等, 2001), 本研究显示海表盐度为34时分布概率最大。中华鲎幼鲎分布概率还与距海岸线欧氏距离呈负相关, 离海岸线较近区域中华鲎幼鲎分布概率较大, 距海岸线渐远幼鲎分布概率逐渐降低, 这与幼鲎不断生长其栖息地逐步向海洋迁移的生态习性相适应(Seino et al, 2000; Cheng et al, 2015)。降水量对MaxEnt模型预测贡献也较大, 在年平均降水量0-2,200 mm区间, 随着降水量增加幼鲎分布概率逐渐增大, 年均降水量大于2,200 mm时幼鲎分布概率较低。降水量对幼鲎分布影响的机制尚未有相关报道, 潮间带底质类型及其他生物因素(物种自我扩散能力等)可能对幼鲎分布产生影响, 有待进一步深入研究。
本研究幼鲎生境实地调查和预测分析结果与颜明艳等(2019)预测广东企水湾、流沙湾幼鲎分布结果差异较大。本研究潜在栖息地分布预测图AUC值为0.947, 远高于颜明艳等(2019)的AUC值(0.816), 可能与研究中物种分布基础数据以及环境变量选择有关。本研究通过扩大调查范围, 增加物种分布数据量, 有效提高了预测结果可靠性。颜明艳等(2019)将红树林作为重要的环境变量, 根据唐秋霞和王友绍(2021)对雷州半岛红树林群落分布格局的研究可知, 广东企水湾和流沙湾均有红树林分布, 这与颜明艳等(2019)预测的幼鲎分布结果相吻合。中华鲎倾向于在红树林区域附近高潮带沙滩产卵, 其幼鲎多在靠近红树林的泥滩区域栖息觅食(Li, 2008①(①Li HY (2008) The Conservation of Horseshoe Crabs in Hong Kong. Master dissertation, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong.); Kwan et al, 2016)。Xie等(2020)调查发现幼鲎的分布与红树林、海草床分布和沉积物的理化性质有关, 多数幼鲎种群分布于红树林附近泥沙滩和海草床区域, 特别是在叶绿素a和有机碳含量普遍较高的潮沟附近。如附录5所示, 我们比较了北部湾中国海域中华鲎幼鲎适宜分布区与红树林分布的关系, 中华鲎幼鲎适宜分布区附近均有红树林分布, 说明红树林等潮间带植被可能对幼鲎分布、生长具有重要作用。
本研究结果显示北部湾中国沿岸海域中华鲎幼鲎高适宜区面积占18.39%, 其中广西沿岸海域中华鲎幼鲎高适宜区分布较多, 预测高适宜区完全覆盖了Xie等(2020)在广西沿岸海域识别的15个鲎育幼场。广东雷州半岛西海岸当前仅有遂溪县一地为高适宜区, 北部湾海南沿岸海域幼鲎高适宜区分布相对集中, 主要分布于新英湾附近, 与野外调查结果一致, 高度吻合说明本研究实地调查区域已基本涵盖了北部湾中国海域三省沿岸的已知幼鲎种群存在点。下一步我们将对模型预测的中适宜区展开调查, 进一步完善北部湾中国海域鲎资源和幼鲎生境分布本底数据。在今后的鲎保护行动中, 对幼鲎高适宜区应进行重点保护, 中适生区加强监测和生境修复, 幼鲎人工放流地点选择时应尽可能避免低适生区特别是不适生区。
附录 Supplementary Material
附录1 本文用于建立模型的中华鲎物种分布数据
Appendix 1 Species distribution data of Tachypleus tridentatus for establishing MaxEnt model
附录2 世界气候数据库中的19个生物气候因子
Appendix 2 The 19 bioclimatic variables in World Climate Database
附录3 MaxEnt模型中19个生物气候因子间的相关性
Appendix 3 Correlation analysis of 19 bioclimatic variables in MaxEnt model
附录4 MaxEnt模型ROC曲线验证结果
Appendix 4 Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve verification results of MaxEnt model
附录5 北部湾中国海域中华鲎幼鲎栖息地红树林分布
Appendix 5 Mangrove distribution in juvenile Tachypleus tridentatus habitat in the Beibu Gulf of China
参考文献
Distribution and abundance of horseshoe crabs Tachypleus gigas and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda around the main island of Singapore
DOI:10.3354/ab00346 URL [本文引用: 1]
Predicting distribution of major forest tree species to potential impacts of climate change in the central Himalayan region
DOI:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.10.006 URL [本文引用: 1]
Potential suitable habitat of mangroves and conservation gap analysis in Guangdong Province with MaxEnt Modeling
DOI:10.13292/j.1000-4890.202011.009
[本文引用: 1]

Mangrove forest is a woody community occurring in the intertidal zone of tropical and subtropical coasts, with important ecological functions. Guangdong Province has the largest area of mangrove in China, and thus is critical for mangrove protection. Maximum entropy model (MaxEnt), a species distribution model, is extensively applied in biodiversity conservation. This study compiled a dataset of mangrove distribution and key environmental variables in Guangdong Province. With this dataset, a mangrove MaxEnt was built, which was used to predict the potential suitable zones of mangroves in Guangdong Province and to identify the key environmental variables influencing mangrove distribution. Outcomes of the modeling were further used to assess conservation gaps. The results showed that the most important environmental variables affecting mangrove distribution were temperature, sea surface temperature, and precipitation. The suitable range for annual mean temperature was 22.37-23.58 ℃, for mean sea surface temperature of the coldest quarter was 23.15-23.34 ℃, for annual precipitation was 1647.14-1809.61 mm, and for precipitation of driest month was 23.6-27.2 mm. The most suitable areas for mangrove in Guangdong were mainly concentrated in Pearl River Estuary to Daya Bay coast, and Leizhou Peninsula to Yangjiang coast. Conservation gaps of mangrove were mainly located in Yangjiang Port, Zhenhai Bay, Pearl River Estuary, and Red Bay. Our findings could provide a scientific basis for improving and advancing the spatial layout of mangrove protection and restoration in Guangdong Province.
基于MaxEnt模型的广东省红树林潜在适生区和保护空缺分析
Co-occurrence of juvenile horseshoe crabs Tachypleus tridentatus and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda in an estuarine bay, southwestern China
DOI:10.3354/ab00641 URL [本文引用: 1]
The morphological differentiation of two horseshoe crab species, Tachypleus tridentatus and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda (Xiphosura), in Hong Kong with a regional Asian comparison
DOI:10.1080/00222930210149753 URL [本文引用: 1]
Predicted impact of exotic vines on an endangered ecological community under future climate change
DOI:10.1007/s10530-010-9814-8 URL [本文引用: 1]
Ecological niche modeling under climate change to select shrubs for ecological restoration in Central Mexico
DOI:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.09.082 URL [本文引用: 1]
Modeling the climate suitability of tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) in Sri Lanka in response to current and future climate change scenarios
DOI:10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.03.025 URL [本文引用: 1]
Present population and habitat status of potentially threatened Asian horseshoe crabs Tachypleus tridentatus and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda in Hong Kong: A proposal for marine protected areas
DOI:10.1007/s10531-016-1084-z URL [本文引用: 2]
Changes in the distributions of juvenile horseshoe crabs (Arthropoda: Chelicerata) (2002-2014) related to environmental perturbations at Pak Nai and Ha Pak Nai, Deep Bay, Hong Kong SAR, China
DOI:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.04.037
PMID:27158048
[本文引用: 1]

A survey of juvenile Asian horseshoe crabs in 2002 on the mudflats along Hong Kong's north-western shoreline abutting Deep Bay identified two species, Tachypleus tridentatus and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda, and assessed their population characteristics. Since the 2002 survey, there have been significant habitat changes to this natal site for the two species. By employing the same, but expanded, sampling protocol, a further survey was, therefore, conducted twelve years later in 2014. A general population decline was recorded for T. tridentatus whereas for C. rotundicauda there was an increase and its distribution had become more widespread. The distribution patterns of the two species were also shown to have changed. The potential factors that might be responsible for recorded changes in the species' population characteristics between 2002 and 2014 are related to anthropogenic perturbations, including environmental habitat alterations notably the building of a bridge linking Hong Kong to Shenzhen in China. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Spatiotemporal evolution and impacts of climate change on bamboo distribution in China
DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109265 URL [本文引用: 1]
Preliminary investigation on horseshoe crabs resources in Beibu Gulf
北部湾鲎资源的初步调查
Present situation of horseshoe crab resources in the sea area of China and tactics of preservation
中国海域鲎资源现状及保护策略
根据近几年来的实地调查研究结果,初步分析了 的种类资源及地理分布、资源的价值、我国的资源现状、我国 资源减少的原因,指出了对我国 资源进行保护的必要,提出了保护策略。
Wisdom of crowds reveals decline of Asian horseshoe crabs in Beibu Gulf, China
DOI:10.1017/S003060531700117X
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Population decline among Asian horseshoe crabs in Asia is increasingly reported, but knowledge of their population and ecological status in China is limited. We conducted community interviews in 30 fishing villages around Beibu Gulf in Guangxi, China, to collect distribution information about the potential spawning/nursery grounds of Tachypleus tridentatus and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda, and any imminent threats to their populations. Based on the results from 400 respondents we identified 45 potential spawning/nursery grounds distributed widely along the shores of Beibu Gulf. We visited 10 of these sites and verified the presence of juvenile horseshoe crabs by field surveys. Nearly all respondents reported an overall depletion in horseshoe crab populations from these 45 sites, which they attributed mainly to unsustainable fishing practices. Respondents who reported having seen horseshoe crab mating pairs on shores were mostly older people, which may suggest a considerable reduction in horseshoe crabs coming to the shores to spawn in recent years. The mean daily harvest of adult T. tridentatus offshore, as indicated by fishers, has declined from c. 50–1,000 in the 1990s to 0–30 individuals during 2011–2016. Our Wisdom of Crowds approach, supported by confirmatory field surveys, is a cost-effective method for assessing the population status of horseshoe crabs, and the level of threat they face. Similar approaches with other species are likely to be particularly valuable in the Asia–Pacific region, where well-structured population monitoring is largely unaffordable.
Research development on horseshoe crab: A 30-year bibliometric analysis
DOI:10.3389/fmars.2020.00041 URL [本文引用: 1]
Distribution pattern prediction of an invasive alien species largemouth bass using a maximum entropy model (MaxEnt) in the Korean Peninsula
DOI:10.1016/j.japb.2018.09.007 URL [本文引用: 1]
A practical guide to MaxEnt for modeling species’ distributions: What it does, and why inputs and settings matter
DOI:10.1111/ecog.2013.36.issue-10 URL [本文引用: 1]
Modeling potential invasion range of alien invasive species, Hyptis suaveolens (L.) Poit. in India: Comparison of MaxEnt and GARP
DOI:10.1016/j.ecoinf.2014.04.002 URL [本文引用: 1]
Predicting Tachypleus gigas spawning distribution with climate change in northeast coast of India
DOI:10.12911/22998993/131244 URL [本文引用: 1]
Dispersion mechanism of hatchlings of horseshoe crab Tachypleus tridentatus at tidal flat off the Yasaka rivermouth in Moriye Bay
Characteristics and distribution pattern of mangrove community in the Leizhou Peninsula
雷州半岛红树林群落特征及其分布格局
Influence of environmental factors on development of embryo and larvae in Tachypleus tridentatues
几种因子对中国鲎胚胎和幼体发育的影响
Acoustic survey of fisheries resources and spatial distribution in the Guishan wind farm area
珠海桂山风电场水域渔业资源声学评估与空间分布
The northern distribution of Tachypleus tridentatus leach in China Seas
中国鲎在我国分布之北界
Predicting the current and future cultivation regions of Carthamus tinctorius L. using MaxEnt model under climate change in China
DOI:10.1016/j.gecco.2018.e00477 URL [本文引用: 2]
Distribution and resource of Chinese horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus) in Fujian and other coast water of China
福建及中国其他沿岸海域中国鲎资源分布现状调查
Nursery habitat for Asian horseshoe crabs along the northern Beibu Gulf, China: Implications for conservation management under baseline gaps
DOI:10.1002/aqc.v30.2 URL [本文引用: 5]
Predicting the potential distribution of an invasive species, Erigeron canadensis L., in China with a maximum entropy model
Prediction of potential distribution areas of Chinese horseshoe crab and mangrove horseshoe crab in the Beibu Gulf of Guangxi based on MaxEnt model and their population conservation strategies
基于MaxEnt模型评估北部湾潮间带中国鲎和圆尾鲎稚鲎的潜在地理分布及种群保育对策
Distribution characteristics of jack mackerel (Trachurus japonicus) habitat in the offshore waters of northern South China Sea
南海北部近海竹荚鱼栖息地分布特征
根据2014—2017年南海北部近海渔业资源调查的8个航次数据,结合遥感影像数据,包括海表温、盐度、叶绿素,对近海竹荚鱼空间分布的季节性变化进行分析。将单位捕捞努力量渔获量(catch per unit effort,CPUE)作为适宜性指数(suitability index,SI),分别采用最大值法、最小值法、算术平均法、几何平均法按季度建立栖息地适宜性指数(habitat suitability index,HSI)模型,并对各模型进行精度检验。结果表明:SI模型拟合准确,均呈单峰分布;几何平均法更适用各季HSI建模,模型平均准确度达到92%,CPUE高的渔场主要分布于HSI大于0.6的海域,其他HSI高值海域为潜在渔场。对各季环境因子进行主成分分析,发现海表温的影响最为显著。研究表明,栖息地适宜性指数模型可较好分析南海北部近海竹荚鱼资源丰度及空间分布。