瓦氏黄颡鱼(Pelteobagrus vachelli)隶属于鲿科 黄颡鱼属, 广泛分布于长江及其支流, 是长江常见的底栖定居性鱼类(丁瑞华, 1994)。过度捕捞等人为因素导致其资源衰退, 瓦氏黄颡鱼被认为是中度超额开发物种(陈大庆等, 2002)。另外, 水电工程的建设导致许多河段水位抬高, 淹没大量砾石和水草等附着物, 影响粘性卵的附着, 造成瓦氏黄颡鱼等产粘性卵鱼类的产卵场消失(姚维志, 2018)。虽然渔业资源调查显示, 瓦氏黄颡鱼目前在长江渔获物中的占比仍处于优势地位, 但是其群体呈现出低龄化和小型化的现象, 渔获物中大部分个体未达到性成熟, 3龄以上繁殖群体较少, 不利于其资源的可持续利用(杨家云, 1994; 熊飞等, 2015)。遗传多样性是物种进化和适应的基础, 维持群体遗传多样性有利于物种长期的进化和生存(Nakajima et al, 2020)。瓦氏黄颡鱼是长江重要的经济鱼类, 探明其群体遗传多样性和遗传结构, 对于评估其种质状况和制定合理的管理政策至关重要。
长江上游是水电大坝梯级开发集中、河流生境破碎化严重的区域, 已建成三峡、向家坝、溪洛渡等多座大型水电站(Cheng et al, 2015)。关于长江上游鱼类的相关研究主要集中在特有鱼类和洄游性鱼类等方面(Song et al, 2016; Liu et al, 2017), 而对于广布种及定居性鱼类的关注较少。关于瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构的研究, 涉及长江上游区域的较少, 且所用的分子标记多为线粒体DNA标记(Wang et al, 2004), 获得的遗传信息有限。单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphism, SNP)是基因组变异的主要方式之一, 其遗传稳定性好、通量高。重测序技术将新获得的序列与已知的参考基因组序列进行比对, 获取大量的SNP位点, 为群体遗传研究提供了重要手段(Kang et al, 2017)。本研究利用基因组重测序的方法获取高通量SNP标记, 分析了长江上游三峡大坝-白鹤滩大坝之间8个不同江段(太平溪、巴南、合川、岷江口、宜宾、邵女坪、桧溪、冯家坪)瓦氏黄颡鱼的遗传多样性和遗传分化水平, 探讨了长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构, 以期为长江上游鱼类遗传种质资源保护和管理提供依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 研究区域和样本采集
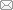
2019年8月-10月于长江上游采集瓦氏黄颡鱼样品, 采集区域为三峡大坝至白鹤滩大坝约1,300 km的江段。共设置8个采样点, 分别为太平溪(TP)、巴南(BN)、合川(HC)、岷江口(MJ)、宜宾(YB)、邵女坪(SN)、桧溪(HX)和冯家坪(FJ) (图1, 表1)。样点太平溪、巴南和宜宾位于三峡大坝(2003年截流)和向家大坝(2008年截流)间, 该河段长度约1,000 km, 生境相对完好, 存在从上游河流生境到库区生境的变化。其中, 太平溪和巴南分别位于三峡水库的库首和库尾。样点邵女坪和桧溪位于向家大坝和溪洛渡大坝(2007年截流)之间。样点冯家坪位于溪洛渡大坝和白鹤滩大坝(2015年截流)之间。样点合川位于支流嘉陵江, 与长江干流有草街水电站(2005年截流)阻隔。样点岷江口处于岷江支流的下游, 与长江干流相隔约18 km的距离, 其上游有犍为水电站(2019年截流)。
图1
图1
长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼的样点分布。S1: 太平溪(TP); S2: 巴南(BN); S3: 合川(HC); S4: 岷江口(MJ); S5: 宜宾(YB); S6: 邵女坪(SN); S7: 桧溪(HX); S8: 冯家坪(FJ)。
Fig. 1
Sampling sites of Pelteobagrus vachelli in the upper reaches of Yangtze River. S1, Taipingxi (TP); S2, Banan (BN); S3, Hechuan (HC); S4, Minjiangkou (MJ); S5, Yibin (YB); S6, Shaonüping (SN); S7, Huixi (HX); S8, Fengjiaping (FJ).
表1
瓦氏黄颡鱼8个群体的样点信息。样点缩写见
Table 1
| 群体 Population | 采样时间 Sampling time | 样本数 No. of sample | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 坡降 Channel slope (m/km) | 生境类型 Habitat type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 太平溪 TP | 2019.8 | 14 | 110 | 0.12 | 水库 Reservoir |
| 巴南 BN | 2019.8 | 25 | 160 | 0.20 | 回水区 Backwater area |
| 合川 HC | 2019.9 | 4 | 187 | 1.85 | 水库 Reservoir |
| 岷江口 MJ | 2019.10 | 25 | 257 | 2.26 | 河流 River |
| 宜宾 YB | 2019.10 | 6 | 253 | 0.70 | 河流 River |
| 邵女坪 SN | 2019.10 | 12 | 296 | 0.90 | 水库 Reservoir |
| 桧溪 HX | 2019.10 | 25 | 356 | 1.40 | 河流 River |
| 冯家坪 FJ | 2019.10 | 25 | 578 | 1.50 | 河流 River |
取瓦氏黄颡鱼的尾鳍和背部肌肉组织, 用95%乙醇固定, 带回实验室保存备用。每个样点能获取的瓦氏黄颡鱼种群数量不同, 当样点获取的样本量较大时, 随机选取25个样本进行研究, 当样点获取的样本量小于25个时, 使用全部的样本进行研究(表1)。
1.2 基因组DNA提取和重测序文库的构建
瓦氏黄颡鱼基因组DNA采用Foregene动物组织基因组试剂盒进行提取, 获取的基因组DNA用TE缓冲液溶解。用1%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测基因组DNA样品是否有降解和杂质, 用NanoDrop one超微量分光光度计(Thermo Scientific)检测基因组DNA纯度和浓度。
取约1 μg基因组DNA模板, 根据TruSeq DNA Sample Preparation Guide (Illumina, 15026486 Rev.C)的方法及流程进行重测序文库制备。具体如下: 用超声破碎的方法将DNA随机打断, 挑选350 bp的片段进行DNA片段的末端修复和3'端加A反应, 然后加上测序接头, 通过PCR反应富集目的片段, 形成测序文库。检测合格的文库在安诺优达基因科技有限公司的HiSeq X Ten测序平台上进行双端测序(PE150), 得到150 bp的raw reads。对raw reads进行过滤, 去除带接头的序列, 过滤N含量超过10%的序列, 去除质量值低于10的碱基数超过整条序列50%的reads, 得到clean reads。
1.3 序列比对及SNP变异检测
利用Bowtie2软件(Langmead et al, 2012)将得到的瓦氏黄颡鱼clean reads与近缘种黄颡鱼参考基因组(Gong et al, 2018)进行比对, 把序列定位在参考基因组上相应位置, 统计测序深度、基因组覆盖度等信息。利用GATK (McKenna et al, 2010)和Samtools (Li et al, 2009)检测SNP位点。利用Vcftools软件(Danecek et al, 2011)进行SNP位点过滤, 过滤标准为: 质量值(quality value) ≥ 30, 次等位基因频率(minor allele frequency, MAF) ≥ 5%, 哈迪-温伯格平衡检验(Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium test, HWE) ≥ 0.01, 所有个体中每个位点缺失基因型的个体不超过4个。
1.4 遗传多样性和遗传结构分析
利用Vcftools软件(Danecek et al, 2011)计算每个群体的SNP数量、核苷酸多样性指数(π)和遗传分化指数(Fst)。瓦氏黄颡鱼的群体遗传结构利用Admixture软件(Alexander et al, 2009)进行分析, K值设置为1-10, 对聚类结果进行交叉验证, 采用交叉验证错误率最低值判断最优聚类数。在RAxML v8.1.17软件中(Stamatakis, 2014)基于GTR + I + G模型的Bayesian方法构建最大似然树(maximum likelihood, ML), 设置100,000次重复。使用Eigen软件(Price et al, 2006)进行主成分分析(principal component analysis, PCA), 使用Plink软件(Purcell et al, 2007)计算IBS (identity by state, IBS)值来评估群体的遗传相似度。
1.5 环境因子对遗传结构的影响
环境因子主要考虑海拔高度、河流坡降、地理距离和隔离时间等因素。用GPS测量每个样点的海拔高度(精度1 m); 河道坡降即单位河段长度的落差, 按样点上游5 km和下游5 km的河段范围计算; 地理距离(沿着河道测量)利用ArcGIS 10.5的大比例尺流域地形图进行测量; 隔离时间从大坝截流时间算起。用R软件里的cor.test函数分析遗传多样性指数(SNP数量、核苷酸多样性指数)与河道坡降和海拔的相关性。用R软件vegan程序(Dixon, 2003)进行Mantel检验, 分析遗传分化指数与地理距离和隔离时间的关系, 遗传分化指数采用线性化的[Fst/(1-Fst)]遗传分化指数。
2 结果
2.1 高通量测序数据分析
共获得了瓦氏黄颡鱼136个样本的基因组重测序序列, 序列已上传至GenBank (Bioproject accession number为PRJNA803961, Biosample accession numbers为SAMN25692057-SAMN25692192)。各群体的测序参数统计如表2, 共得到了1,345.21 Gb的clean data, 平均测序质量值Q30为92.78%, 平均测序深度为8.95ⅹ, 平均测序比对率为50.73%, 平均基因组覆盖率为69.43%。
表2 瓦氏黄颡鱼8个群体重测序数据及群体遗传多样性参数
Table 2
| 群体 Population | 样本数 No. of sample | Clean data (Gb) | Q30 (%) | 测序深度Sequencing depth | 序列比对率 Sequence mapped (%) | 基因组覆盖度Coverage of genomic reference (%) | SNP数目 Number of SNP | 核苷酸多样性指数Nucleotide diversity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 太平溪 TP | 14 | 145.22 | 93.11 | 9.54 | 54.31 | 72.92 | 4,172,876 | 2.44 × 10‒3 |
| 巴南 BN | 25 | 236.41 | 92.82 | 8.71 | 53.43 | 71.68 | 3,543,176 | 2.81 × 10‒3 |
| 合川 HC | 4 | 35.77 | 92.81 | 8.38 | 49.94 | 66.28 | 534,504 | 8.59 × 10‒4 |
| 岷江口 MJ | 25 | 217.32 | 92.73 | 8.25 | 50.68 | 66.39 | 419,733 | 5.60 × 10‒4 |
| 宜宾 YB | 6 | 50.16 | 91.87 | 7.44 | 48.50 | 67.36 | 563,968 | 6.76 × 10‒4 |
| 邵女坪 SN | 12 | 128.29 | 92.79 | 9.37 | 49.09 | 69.64 | 457,603 | 5.75 × 10‒4 |
| 桧溪 HX | 25 | 258.76 | 92.79 | 9.20 | 49.22 | 68.87 | 597,465 | 6.60 × 10‒4 |
| 冯家坪 FJ | 25 | 273.27 | 92.78 | 9.57 | 49.06 | 69.73 | 441,092 | 5.84 × 10‒4 |
| 总体 Total | 136 | 1,345.21 | 92.78 | 8.95 | 50.73 | 69.43 | 7,341,959 | 1.19 × 10‒3 |
2.2 遗传多样性
通过与黄颡鱼参考基因组比对, 共获得了瓦氏黄颡鱼7,341,959个SNP位点, SNP数量从419,733 (岷江口)到4,172,876 (太平溪), 群体最大的SNP数量约为最小SNP数量的10倍, 显示了SNP数量较大的变化范围。在三峡大坝-白鹤滩大坝江段, 瓦氏黄颡鱼上游群体的SNP数量和核苷酸多样性指数低于下游的太平溪和巴南群体(表2)。
2.3 群体遗传结构
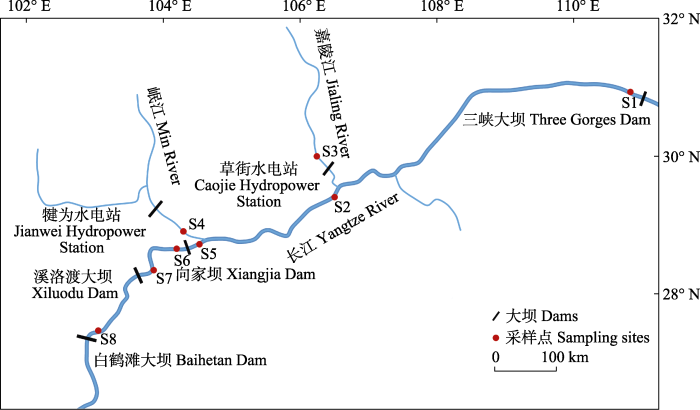
当K = 3时, 交叉验证错误率最小(图2a), 显示瓦氏黄颡鱼群体可分为3个不同遗传分支(图2b)。冯家坪和岷江口的所有个体属于group 1, 邵女坪和宜宾所有个体属于group 2, 冯家坪、岷江口、邵女坪和宜宾群体的遗传背景较为单一; 桧溪和合川的群体有2种遗传背景, 桧溪绝大多数个体属于group 2, 少量个体属于group 1; 合川群体里group 1和group 2遗传来源的个体数量大体相当; 巴南和太平溪有3种遗传背景的个体, 显示这两个地理位置的瓦氏黄颡鱼遗传来源较为丰富, 其中group 1所占的比例最大, group 3所占的比例最小(图2b)。PCA分析(图2c)和ML聚类树(图2d)也进一步验证了这种结果。
图2
图2
基于SNP标记分析8个瓦氏黄颡鱼群体的遗传结构。(a)由交叉验证错误率确定的最优分组数; (b) K = 3时, 所有个体的分组情况; (c) PCA聚类情况; (d) ML聚类树。样点缩写见
Fig. 2
Genetic structure based on SNP markers in eight populations of Pelteobagrus vaclerii. (a) The optimal number of clusters determined by cross-validated error rate valley. (b) Population structure (K = 3) of all individuals. (c) PCA plot of every individual. (d) ML phylogenetic tree. Site abbreviations are shown in
2.4 群体遗传分化
冯家坪与岷江口遗传分化指数较小(0.016), 但这两个群体与其他群体间的遗传分化指数较大(0.075-0.261)。桧溪、邵女坪和宜宾之间的遗传分化指数为负值或值较小(‒0.008至0.002), 这3个群体的遗传背景非常相似, 但桧溪和邵女坪群体与其他群体遗传分化指数较大(0.068至0.257)。合川与巴南和太平溪之间也为负值或者值较小(‒0.109至0.050),另外宜宾群体与巴南和太平溪之间的遗传分化指数也较小(‒0.020至0.050) (表3), 结合structure结构图来看, 巴南和太平溪的一部分遗传背景与合川相似, 一部分遗传背景与宜宾相似。另外, 我们比较3种遗传分支之间的遗传分化指数(structure图中的group 1、group 2、group 3), group 1与group 2间的遗传分化指数为0.260, group 2与group 3间的遗传分化指数为0.485, group 1与group 3间的遗传分化指数为0.510, 可以看出, 瓦氏黄颡鱼3种遗传分支之间存在较大的遗传分化。
表3 长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼两两群体之间的遗传分化指数
Table 3
| 群体 Population | 太平溪 TP | 巴南 BN | 合川 HC | 岷江口 MJ | 宜宾 YB | 邵女坪 SN | 桧溪 HX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巴南 BN | 0.050 | ||||||
| 合川 HC | ‒0.109 | ‒0.039 | |||||
| 岷江口 MJ | 0.112 | 0.143 | 0.075 | ||||
| 宜宾 YB | ‒0.020 | 0.043 | 0.152 | 0.233 | |||
| 邵女坪 SN | 0.068 | 0.112 | 0.192 | 0.235 | 0.000 | ||
| 桧溪 HX | 0.126 | 0.154 | 0.079 | 0.179 | ‒0.008 | 0.002 | |
| 冯家坪 FJ | 0.125 | 0.152 | 0.092 | 0.016 | 0.261 | 0.257 | 0.193 |
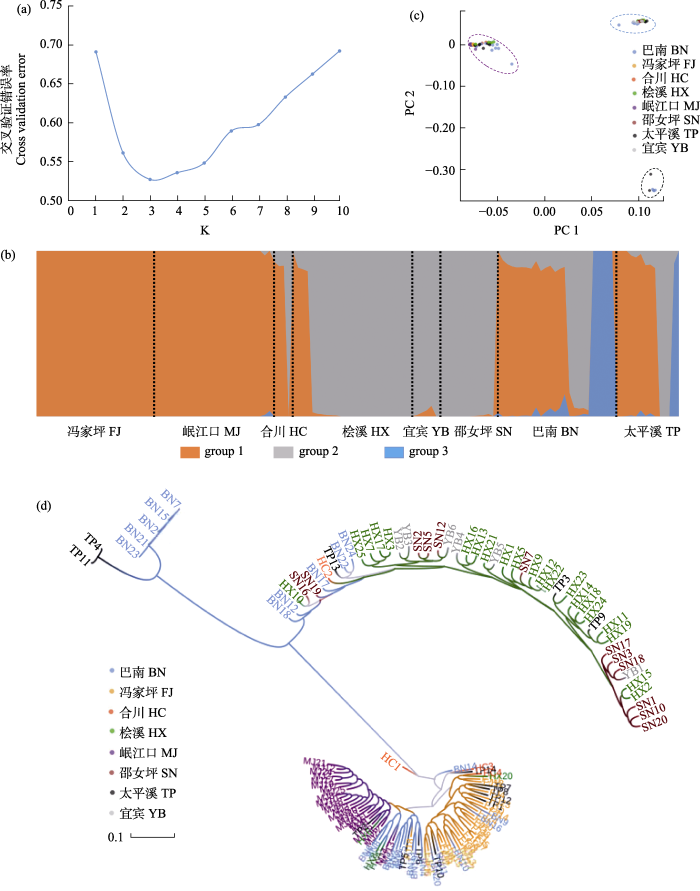
IBS结果显示, 3个遗传分支内个体间的遗传相似度值均较高, 其中group 2的遗传相似度最高, group 1其次, group 3遗传相似度最低(图3)。
图3
图3
瓦氏黄颡鱼3个遗传分支内个体间的遗传相似度IBS值
Fig. 3
Genetic similarity within three genetic groups based on identity by state (IBS)
2.5 环境因素对遗传结构的影响
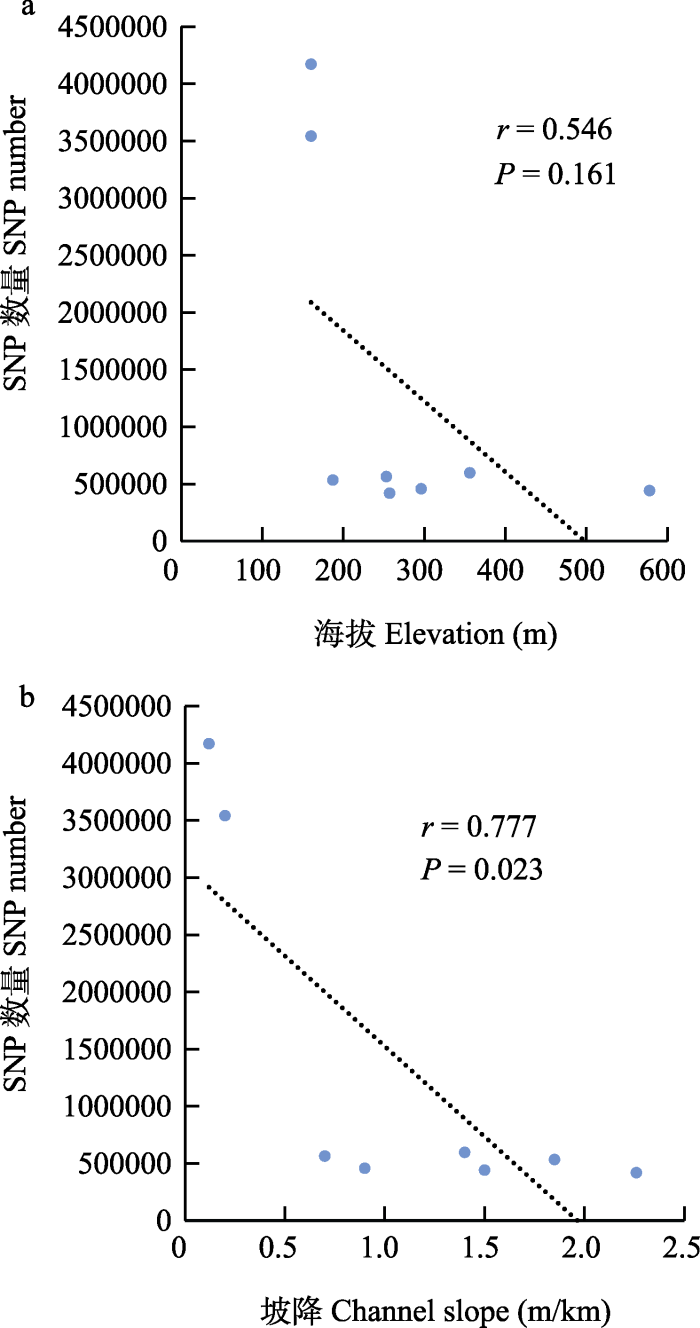
图4
图4
瓦氏黄颡鱼SNP数量与河道海拔(a)和坡降(b)的相关性分析。P < 0.05表示显著相关。
Fig. 4
Correlation analysis of the SNP numbers with elevation (a) and channel slope (b). P < 0.05 indicates significant correlation.
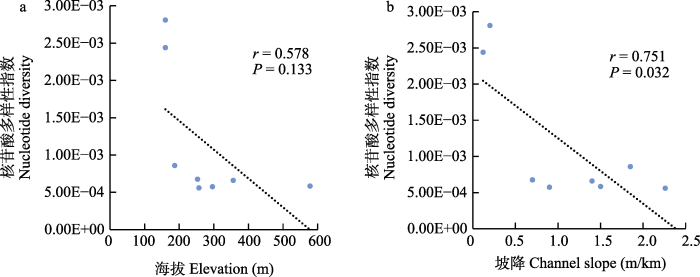
图5
图5
瓦氏黄颡鱼核苷酸多样性指数与海拔(a)和坡降(b)的相关性分析。P < 0.05表示显著相关。
Fig. 5
Correlation analysis of nucleotide diversity with elevation (a) and channel slope (b). P < 0.05 indicates significant correlation.
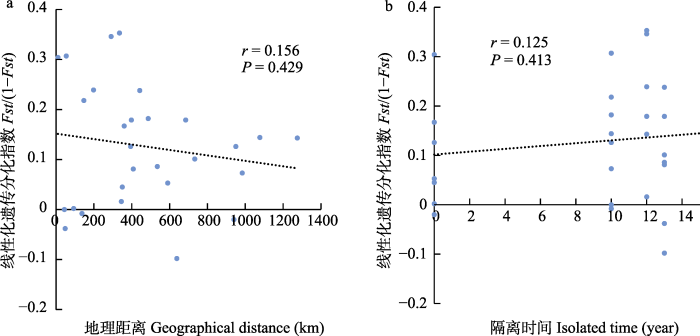
Mantel 检验显示, 遗传分化指数与地理距离和隔离时间相关性不显著(图6), 表明当前瓦氏黄颡鱼的群体遗传分化受地理距离和隔离时间的影响不明显。
图6
图6
遗传分化(a)与地理距离(b)和隔离时间的Mantel检验。Fst: 遗传分化指数。
Fig. 6
Mantel test of genetic differentiation with geographical distance and isolated time. Fst, Index of genetic differentiation.
3 讨论
3.1 瓦氏黄颡鱼遗传多样性与遗传结构
在三峡大坝-白鹤滩大坝江段, 瓦氏黄颡鱼上游群体SNP数量和核苷酸多样性指数明显小于下游的太平溪和巴南群体, 从群体结构图中也可以看出, 瓦氏黄颡鱼下游的太平溪和巴南群体有3种遗传背景, 遗传来源较丰富, 而上游的岷江口、宜宾、邵女坪和冯家坪群体仅有1种遗传背景, 遗传来源较为单一。因此, 瓦氏黄颡鱼在下游得到了较多的遗传补充, 而在上游得到的遗传补充较少。类似的下游群体遗传多样性较上游丰富的现象在长江其他鱼类中也存在, 如黑尾近红鲌(Ancherythroculter nigrocauda) (Zhai et al, 2019)和中华纹胸鮡(Glyptothorax sinensis) (张力文等, 2020)。本研究中, 瓦氏黄颡鱼上游群体具有更低的遗传多样性, 更易发生遗传漂变作用, 在鱼类遗传多样性保护中需要特别关注。
长江上游个体之间的遗传相似度较高, 这可能跟繁殖群体的减少相关, 已有的研究表明瓦氏黄颡鱼资源呈现低龄化和小型化的趋势, 3龄以上的繁殖群体占比较少(杨家云, 1994; 熊飞等, 2015)。虽然目前瓦氏黄颡鱼在渔获物中仍占较大的比例(吕浩等, 2018), 其高繁殖力能快速补偿损失的成熟个体, 扩大群体规模, 然而, 局部种群的消失或大部分成熟个体的消失, 会造成遗传多样性的丧失。较低的遗传多样性并不总是意味着种群数量的必然下降, 长江上游大坝建设后, 一些江段的水流变缓, 瓦氏黄颡鱼的某些基因型可能更适应这种缓流的环境。但是, 低遗传多样性对物种长期的生存和进化是不利的(Cook & Sullivan, 2018)。
3.2 环境因素对瓦氏黄颡鱼群体结构的影响
河流坡降通常限制鱼类的迁移、扩散, 从而影响鱼类的基因流和种群遗传结构。Kanno等(2011)研究表明, 河流坡降是影响美洲红点鲑(Salvelinus fontinalis)种群遗传结构的主要因子。本研究结果显示坡降对瓦氏黄颡鱼SNP数量和核苷酸多样性指数造成了显著影响, 水流的高度落差可能是阻碍瓦氏黄颡鱼扩散和基因交流的原因之一。
瓦氏黄颡鱼不同江段的群体遗传分化较大, 但是Mantel检验遗传分化指数与地理距离无显著相关性。宜宾与岷江口地理距离相隔较近, 但是遗传分化值达到了0.233。冯家坪与岷江口相距较远, 遗传分化值仅为0.016, 在这些群体中, 地理距离似乎并不是群体遗传分化的主要原因, 奠基者效应和生境差异则更可能造成了目前的遗传分化格局。冯家坪到太平溪江段最大距离达1,300 km左右, 海拔落差470 m左右, 其间地形复杂, 流域内环境时空变化较大, 不同局域环境的适应性差异可能产生群体遗传分化(Xu et al, 2017)。
高通量测序技术为鱼类遗传分析提供了大量的分子标记, 为群体遗传模式的研究提供了强有力的工具。本研究鉴定了瓦氏黄颡鱼大量的SNP位点, 阐明了长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传多样性和遗传结构。瓦氏黄颡鱼上游群体具有更低的遗传多样性, 更易发生遗传漂变, 在鱼类遗传多样性保护中需要特别关注。长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼存在显著的遗传结构, 可分为3种不同的遗传分支, 不同遗传分支之间分化较大, 可视为3个不同遗传单元进行种质资源管理。
参考文献
Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals
DOI:10.1101/gr.094052.109
PMID:19648217
[本文引用: 1]

Population stratification has long been recognized as a confounding factor in genetic association studies. Estimated ancestries, derived from multi-locus genotype data, can be used to perform a statistical correction for population stratification. One popular technique for estimation of ancestry is the model-based approach embodied by the widely applied program structure. Another approach, implemented in the program EIGENSTRAT, relies on Principal Component Analysis rather than model-based estimation and does not directly deliver admixture fractions. EIGENSTRAT has gained in popularity in part owing to its remarkable speed in comparison to structure. We present a new algorithm and a program, ADMIXTURE, for model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. ADMIXTURE adopts the likelihood model embedded in structure. However, ADMIXTURE runs considerably faster, solving problems in minutes that take structure hours. In many of our experiments, we have found that ADMIXTURE is almost as fast as EIGENSTRAT. The runtime improvements of ADMIXTURE rely on a fast block relaxation scheme using sequential quadratic programming for block updates, coupled with a novel quasi-Newton acceleration of convergence. Our algorithm also runs faster and with greater accuracy than the implementation of an Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm incorporated in the program FRAPPE. Our simulations show that ADMIXTURE's maximum likelihood estimates of the underlying admixture coefficients and ancestral allele frequencies are as accurate as structure's Bayesian estimates. On real-world data sets, ADMIXTURE's estimates are directly comparable to those from structure and EIGENSTRAT. Taken together, our results show that ADMIXTURE's computational speed opens up the possibility of using a much larger set of markers in model-based ancestry estimation and that its estimates are suitable for use in correcting for population stratification in association studies.
A preliminary study of the fisheries biology of main commercial fishes in the middle and upper reaches of the Yangtze River
长江中上游主要经济鱼类的渔业生物学特征
Potential effects of dam cascade on fish: Lessons from the Yangtze River
DOI:10.1007/s11160-015-9395-9 URL [本文引用: 1]
Microsatellite DNA variation among samples of bronze gudgeon, Coreius heterodon, in the mainstem of the Yangtze River, China
DOI:10.1007/s10228-012-0329-4 URL [本文引用: 1]
Associations between riffle development and aquatic biota following low head dam removal
DOI:10.1007/s10661-018-6716-1 [本文引用: 1]
The variant call format and VCFtools
DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr330
PMID:21653522
[本文引用: 2]

The variant call format (VCF) is a generic format for storing DNA polymorphism data such as SNPs, insertions, deletions and structural variants, together with rich annotations. VCF is usually stored in a compressed manner and can be indexed for fast data retrieval of variants from a range of positions on the reference genome. The format was developed for the 1000 Genomes Project, and has also been adopted by other projects such as UK10K, dbSNP and the NHLBI Exome Project. VCFtools is a software suite that implements various utilities for processing VCF files, including validation, merging, comparing and also provides a general Perl API.http://vcftools.sourceforge.net
Population structure and genetic diversity of trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) above and below natural and man-made barriers in the Russian River, California
DOI:10.1007/s10592-006-9183-0 URL [本文引用: 1]
Vegan, a package of R functions for community ecology
DOI:10.1111/jvs.2003.14.issue-6 URL [本文引用: 1]
Chromosomal-level assembly of yellow catfish genome using third-generation DNA sequencing and Hi-C analysis
Population genetics analysis of the Nujiang catfish Creteuchiloglanis macropterus through a genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphisms resource generated by RAD-seq
DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-02853-3
[本文引用: 1]

Advances in genome scanning using high-throughput sequencing technologies has led to a revolution in studies of non-model organisms. The glyptosternoid fish Creteuchiloglanis macropterus, is widely distributed in the main stem and tributaries of the Nujiang River basin. Here, we analyzed IIB restriction-site-associated DNA (2b-RAD) sequences and mitochondrial DNA sequences, to assess the genomic signature of adaptation by detecting and estimating the degree of genetic differentiation among ten Creteuchiloglanis macropterus populations from the Nujiang River. The analyses revealed significant population differentiation among the up-tributaries, main stem, mid-tributary and low-tributary. Annotation of contigs containing outlier SNPs revealed that the candidate genes showed significant enrichment in several important biological process terms between up-tributaries and low-tributary, and exhibited prominent enrichment in the term macromolecular metabolic process between all tributaries and the main stem. Population dynamics analyses indicated that the Late Pleistocene glaciations strongly influenced the demographic history of C. macropterus. Our results provide strong evidence for the utility of RAD-seq in population genetics studies, and our generated SNP resource should provide a valuable tool for population genomics studies of C. macropterus in the future.
Fine-scale population structure and riverscape genetics of brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) distributed continuously along headwater channel networks
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05210.x
PMID:21819470
[本文引用: 1]

Linear and heterogeneous habitat makes headwater stream networks an ideal ecosystem in which to test the influence of environmental factors on spatial genetic patterns of obligatory aquatic species. We investigated fine-scale population structure and influence of stream habitat on individual-level genetic differentiation in brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) by genotyping eight microsatellite loci in 740 individuals in two headwater channel networks (7.7 and 4.4 km) in Connecticut, USA. A weak but statistically significant isolation-by-distance pattern was common in both sites. In the field, many tagged individuals were recaptured in the same 50-m reaches within a single field season (summer to fall). One study site was characterized with a hierarchical population structure, where seasonal barriers (natural falls of 1.5-2.5 m in height during summer base-flow condition) greatly reduced gene flow and perceptible spatial patterns emerged because of the presence of tributaries, each with a group of genetically distinguishable individuals. Genetic differentiation increased when pairs of individuals were separated by high stream gradient (steep channel slope) or warm stream temperature in this site, although the evidence of their influence was equivocal. In a second site, evidence for genetic clusters was weak at best, but genetic differentiation between individuals was positively correlated with number of tributary confluences. We concluded that the population-level movement of brook trout was limited in the study headwater stream networks, resulting in the fine-scale population structure (genetic clusters and clines) even at distances of a few kilometres, and gene flow was mitigated by 'riverscape' variables, particularly by physical barriers, waterway distance (i.e. isolation-by-distance) and the presence of tributaries.© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Fast gapped-read alignment with bowtie 2
DOI:10.1038/nmeth.1923
PMID:22388286
[本文引用: 1]

As the rate of sequencing increases, greater throughput is demanded from read aligners. The full-text minute index is often used to make alignment very fast and memory-efficient, but the approach is ill-suited to finding longer, gapped alignments. Bowtie 2 combines the strengths of the full-text minute index with the flexibility and speed of hardware-accelerated dynamic programming algorithms to achieve a combination of high speed, sensitivity and accuracy.
The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools
No decline of genetic diversity in elongate loach (Leptobotia elongata) with a tendency to form population structure in the upper Yangtze River
DOI:10.1016/j.gecco.2020.e01072 URL [本文引用: 1]
Low population differentiation revealed in the highly threatened elongate loach (Leptobotia elongata Bleeker), a species endemic to the fragmented upper reaches of the Yangtze River
The larval resources of fishes spawning drifting eggs in the lower reaches of the Minjiang River
岷江下游干流段鱼类资源现状及其多样性分析
The genome analysis toolkit: A mapreduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data
Genetic structure and population demography of white-spotted charr in the upstream watershed of a large dam
DOI:10.3390/w12092406
URL
[本文引用: 1]

White-spotted charr (Salvelinus leucomaenis leucomaenis) is an anadromous fish that has been severely harmed by human land-use development, particularly through habitat fragmentation. However, the anthropogenic impacts on populations of this species have not been evaluated, except those on small dammed-off populations. Using multiplexed ISSR genotyping by sequencing, we investigated the genetic structure of white-spotted charr in four tributaries in the upper section of the Kanayama Dam in the Sorachi River, Hokkaido Island, Japan. There were no distinct genetic structures (FST = 0.014), probably because some active individuals migrate frequently among tributaries. By model-flexible demographic simulation, historical changes in the effective population size were inferred. The result indicates that the population size has decreased since the end of the last glacial period, with three major population decline events, including recent declines that were probably associated with recent human activities. Nevertheless, populations in the watershed upstream of the Kanayama Dam are still expected to be at low risk of immediate extinction, owing to the large watershed size and the limited number of small check dams. An effective conservation measure for sustaining the white-spotted charr population is to maintain high connectivity between tributaries, such as by providing fishways in check dams during construction.
Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies
DOI:10.1038/ng1847
PMID:16862161
[本文引用: 1]

Population stratification--allele frequency differences between cases and controls due to systematic ancestry differences-can cause spurious associations in disease studies. We describe a method that enables explicit detection and correction of population stratification on a genome-wide scale. Our method uses principal components analysis to explicitly model ancestry differences between cases and controls. The resulting correction is specific to a candidate marker's variation in frequency across ancestral populations, minimizing spurious associations while maximizing power to detect true associations. Our simple, efficient approach can easily be applied to disease studies with hundreds of thousands of markers.
PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses
DOI:10.1086/519795 URL [本文引用: 1]
Multi-locus genomic analysis reveals the genetic diversity and population structure of the rock carp (Procypris rabaudi) in the upper Yangtze River
RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies
DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033
PMID:24451623
[本文引用: 1]

Phylogenies are increasingly used in all fields of medical and biological research. Moreover, because of the next-generation sequencing revolution, datasets used for conducting phylogenetic analyses grow at an unprecedented pace. RAxML (Randomized Axelerated Maximum Likelihood) is a popular program for phylogenetic analyses of large datasets under maximum likelihood. Since the last RAxML paper in 2006, it has been continuously maintained and extended to accommodate the increasingly growing input datasets and to serve the needs of the user community.I present some of the most notable new features and extensions of RAxML, such as a substantial extension of substitution models and supported data types, the introduction of SSE3, AVX and AVX2 vector intrinsics, techniques for reducing the memory requirements of the code and a plethora of operations for conducting post-analyses on sets of trees. In addition, an up-to-date 50-page user manual covering all new RAxML options is available.
Echoes of a distant time: Effects of historical processes on contemporary genetic patterns in Galaxias platei in Patagonia
DOI:10.1111/mec.13303
PMID:26147523
[本文引用: 1]

Interpreting the genetic structure of a metapopulation as the outcome of gene flow over a variety of timescales is essential for the proper understanding of how changes in landscape affect biological connectivity. Here we contrast historical and contemporary connectivity in two metapopulations of the freshwater fish Galaxias platei in northern and southernmost Patagonia where paleolakes existed during the Holocene and Pleistocene, respectively. Contemporary gene flow was mostly high and asymmetrical in the northern system while extremely reduced in the southernmost system. Historical migration patterns were high and symmetric in the northern system and high and largely asymmetric in the southern system. Both systems showed a moderate structure with a clear pattern of isolation by distance (IBD). Effective population sizes were smaller in populations with low contemporary gene flow. An approximate Bayesian computation (ABC) approach suggests a late Holocene colonization of the lakes in the northern system and recent divergence of the populations from refugial populations from east and west of the Andes. For the southern system, the ABC approach reveals that some of the extant G. platei populations most likely derive from an ancestral population inhabiting a large Pleistocene paleolake while the rest derive from a higher-altitude lake. Our results suggest that neither historical nor contemporary processes individually fully explain the observed structure and geneflow patterns and both are necessary for a proper understanding of the factors that affect diversity and its distribution. Our study highlights the importance of a temporal perspective on connectivity to analyse the diversity of spatially complex metapopulations. © 2015 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Geographic distribution of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco and Pelteobagrus vachelli in the Yangtze River based on mitochondrial DNA markers
DOI:10.1023/B:BIGI.0000043951.30411.7a URL [本文引用: 1]
Present status of fishery resources in Yibin section of the Upper Yangtze River
长江上游宜宾江段渔业资源现状研究
Genomic evidence for local adaptation in the ovoviviparous marine fish Sebastiscus marmoratus with a background of population homogeneity
DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-01742-z
[本文引用: 1]

Advances in next-generation sequencing techniques have allowed for the generation of genome-wide sequence data, to gain insight into the dynamics influencing genetic structure and the local adaptation of marine fish. Here, using genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) technique, we identified 31,119 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) for Sebastiscus marmoratus in 59 individuals from three populations in Chinese coastal waters. Based on all SNPs, there was little evidence of genetic differentiation among populations. However, outlier tests revealed 329 SNPs putatively under divergent selection across populations. Structural and phylogenetic topology analyses based on the outliers showed clear genetic differentiation among populations. Gene Ontology (GO) annotation results revealed that most of these outliers are known or hypothesized to be involved in metabolic process. Together with previous work using mitochondrial cytochrome b sequences, the present results further suggest that the population structure is strongly influenced by locally adaptive pressure. Overall, adaptive evolution in a heterogeneous environment plays an important role in inducing genetic differentiation among local populations. This study increases understanding of the factors (including gene flow and local adaptation) promoting and constraining population genetic differentiation in marine organisms.
The reproductive biology of Pelteobagrus vachelli in the Jialing River
嘉陵江瓦氏黄颡鱼的繁殖生物学
Genetic diversity and population structure of a cyprinid fish (Ancherythroculter nigrocauda) in a highly fragmented river
DOI:10.1111/jai.2019.35.issue-3 URL [本文引用: 1]
Genetic diversity and structure of Glyptothorax sinensis in upper Yangtze River
长江上游中华纹胸鮡遗传多样性及遗传结构研究