目前, 所有生物体中已被命名和描述的有效物种约有150万种, 其中, 最成功的群体是昆虫纲, 大约有1,020,007种, 约占所有动物的66%, 是全球生物多样性的重要组成部分(Zhang et al, 2011)。鞘翅目是昆虫纲的第一大目, 几乎分布于陆地上的每一个角落(Lawrence & Britton, 1994)。鞘翅目昆虫大约出现在2.85亿年前, 随后, 辐射出原鞘亚目(Archostemata)、肉食亚目(Adephaga)、菌食亚目(Myxophaga)和多食亚目(Polyphaga) (Hunt et al, 2007)。迄今, 世界已记录鞘翅目昆虫约35万至40万种, 约占世界已描述物种的25% (Stork et al, 2015)。但由于对物种的研究不成比例, 导致在已知昆虫物种中, 平均每种昆虫的研究论文数量差异很大, 鞘翅目的许多科已被完全忽略(Stork, 2018)。
鞘翅目昆虫不仅具有丰富的物种多样性, 其形态学和生物学特性也十分丰富, 在生态保护和经济社会发展中具重要作用(Hunt et al, 2007)。药用方面, 芫菁科(Meloidae)、龙虱科(Dytiscidae)、天牛科(Cerambycidae)、金龟科(Scarabaeidae)等的部分昆虫皆具一定的药用价值(臧贵君等, 2001); 生物防治方面, 捕食性甲虫如瓢虫科(Coccinellidae)、隐翅虫科(Staphylinidae)、步甲科(Carabidae)等对控制害虫数量起到了关键作用①(① 刘少番 (2016) 环京津地区部分捕食性甲虫DNA条形码研究. 硕士学位论文, 河北大学, 保定.); 植物传粉方面, 许多鞘翅目昆虫都是重要的传粉昆虫, 如露尾甲科(Nitidulidae)、金龟科、花甲科(Dascillidae)、郭公甲科(Cleridae)等(罗峰和雷朝亮, 2003); 生态平衡方面, 粪食/腐食性甲虫如蜣螂亚科(Scarabaeinae)、葬甲科(Silphidae)等, 在加快营养物质周转、抑制有害蝇类繁殖等方面具有重要作用(李久文, 2009②(②李久文 (2009) 松嫩草地牛粪中大型节肢动物群落动态及对蝇类繁殖控制研究. 硕士学位论文, 东北师范大学, 长春.); 白明和杨星科, 2010); 此外, 鞘翅目昆虫是文化昆虫学的一个重要分支, 在美学、饮食文化、建筑学等方面都有独特的文化内涵③(③ 王与琳 (2020) 中国唐诗、宋词和元曲中的文化甲虫资源与赏析. 硕士学位论文, 河北大学, 保定.)。
鞘翅目昆虫种类多、分布广, 使名录整理工作难度增大。目前, 仅少数科学家对此进行了整理, 如Zhang等(2011)在Zootaxa发表的专刊中对世界鞘翅目物种数进行了系统整理, 共记录鞘翅目昆虫5亚目24总科207科29,624属387,100种; Bouchard等(2011)首次综合所有已知的鞘翅目各级阶元名称数据, 涉及24个总科211个科541个亚科1,663个族和740个亚族。但是, 据Erwin和Johnson (2000)估计, 有超过200万种甲虫尚未描述。因此, 有必要定期对分散于各书籍和期刊中的有关鞘翅目昆虫新分类单元的记录进行总结, 以方便相关研究者参考和引用, 加快鞘翅目分类学的发展。
1 数据获取及整理
本文系统检索了Zoological Record (
2 结果
2.1 世界鞘翅目2020年新分类单元基本情况
2020年共发表世界鞘翅目新分类单元3,228个, 具体包括1个新科5个新亚科13个新族218个新属18个新亚属2,973个新种; 提出1,319个新组合610个新异名49个降级分类单元及61个升级分类单元(表1)。
表1 2020年世界甲虫新属、新种、新组合、新异名、降级和升级情况一览表
Table 1
| 科名 Families | 新属/亚属 New genera / subgenera | 新种/亚种 New species / subspecies | 新组合 New combinations | 新异名 New synonyms | 降级 Degraded | 升级 Raised | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 伪蚁形甲科 Aderidae | 3 | 20 | 40 | 4 | |||
| 觅葬甲科 Agyrtidae | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 蚁形甲科 Anthicidae | 19 | 145 | 10 | ||||
| 长角象科 Anthribidae | 8 | ||||||
| 拟长角花蚤科 Artematopodidae | 1 | 1 | |||||
| †Asiocoleidae | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 卷象科 Attelabidae | 2 | ||||||
| †Berendtimiridae | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 长蠹科 Bostrichidae | 2 | 2 | |||||
| 百合象科 Brachyceridae | 2 | 2 | |||||
| 颈萤科 Brachypsectridae | 1 | 2 | |||||
| 三锥象科 Brentidae | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | |||
| 吉丁甲科 Buprestidae | 2 | 78 | 34 | 2 | |||
| 丸甲科 Byrrhidae | 2 | ||||||
| 小花甲科 Byturidae | 1 | ||||||
| 花萤科 Cantharidae | 1 | 64 | 7 | 34 | |||
| 步甲科 Carabidae | 24 | 281 | 29 | 21 | 13 | 7 | |
| 天牛科 Cerambycidae | 21 | 240 | 205 | 73 | 6 | 11 | |
| 叶甲科 Chrysomelidae | 25 | 167 | 159 | 56 | 2 | ||
| 木蕈甲科 Ciidae | 5 | ||||||
| 郭公甲科 Cleridae | 1 | 69 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 瓢虫科 Coccinellidae | 2 | 52 | 124 | 19 | |||
| 隐食甲科 Cryptophagidae | 4 | 5 | |||||
| 扁甲科 Cucujidae | 6 | ||||||
| 象甲科 Curculionidae | 14 | 290 | 241 | 109 | 2 | 1 | |
| 圆蕈甲科 Cyclaxyridae | 3 | ||||||
| 花甲科 Dascillidae | 1 | 5 | 2 | ||||
| 皮蠹科 Dermestidae | 2 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 4 | ||
| 瘦天牛科 Disteniidae | 8 | ||||||
| 泥甲科 Dryopidae | 3 | 5 | 1 | ||||
| 龙虱科 Dytiscidae | 1 | 51 | 11 | 9 | 2 | ||
| 叩甲科 Elateridae | 1 | 69 | 27 | 14 | |||
| 溪泥甲科 Elmidae | 32 | ||||||
| 伪瓢虫科 Endomychidae | 6 | 1 | |||||
| 大蕈甲科 Erotylidae | 5 | 13 | 13 | 13 | |||
| 扁股花甲科 Eucinetidae | 1 | ||||||
| 隐唇叩甲科 Eucnemidae | 9 | 33 | 2 | ||||
| 皮坚甲科 Cerylonidae | 2 | ||||||
| 粪金龟科 Geotrupidae | 12 | 1 | |||||
| 漠金龟科 Glaresidae | 3 | ||||||
| 豉甲科 Gyrinidae | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 蜡斑甲科 Helotidae | 1 | 2 | |||||
| 长泥甲科 Heteroceridae | 2 | 6 | |||||
| 阎甲科 Histeridae | 3 | 71 | 2 | 1 | 2 | ||
| 驼金龟科 Hybosoridae | 3 | ||||||
| 平唇水龟甲科 Hydraenidae | 10 | ||||||
| 水龟甲科 Hydrophilidae | 1 | 97 | 3 | 3 | 1 | ||
| 水缨甲科 Hydroscaphidae | 1 | ||||||
| 纤口萤科 Jurasaidae* | 2 | 3 | |||||
| 萤科 Lampyridae | 1 | 44 | 7 | 4 | 1 | ||
| 薪甲科 Latridiidae | 17 | 4 | |||||
| 球蕈甲科 Leiodidae | 2 | 7 | |||||
| 单跗甲科 Lepiceridae | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 泽甲科 Limnichidae | 3 | ||||||
| 锹甲科 Lucanidae | 11 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 红萤科 Lycidae | 4 | 27 | 83 | 1 | |||
| 筒蠹科 Lymexylidae | 3 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 距甲科 Megalopodidae | 4 | ||||||
| 长朽木甲科 Melandryidae | 2 | 3 | |||||
| 芫菁科 Meloidae | 8 | 4 | 17 | 1 | |||
| 拟花萤科 Melyridae | 8 | 15 | 10 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 复变甲科 Micromalthidae | 2 | 2 | |||||
| 小扁甲科 Monotomidae | 1 | 4 | |||||
| 花蚤科 Mordellidae | 6 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 小蕈甲科 Mycetophagidae | 2 | ||||||
| 绒皮甲科 Mycteridae | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 毛象科 Nemonychidae | 2 | 2 | |||||
| 露尾甲科 Nitidulidae | 3 | 22 | 18 | 2 | 1 | ||
| 小丸甲科 Nosodendridae | 2 | ||||||
| 小粒龙虱科 Noteridae | 7 | 2 | 1 | ||||
| 红金龟科 Ochodaeidae | 1 | 3 | 5 | 1 | |||
| 眼甲科 Ommatidae | 2 | 6 | 3 | ||||
| 黑蜣科 Passalidae | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |||
| 姬花甲科 Phalacridae | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 光萤科 Phengodidae | 2 | 4 | 1 | ||||
| 皮扁甲科 Phloeostichidae | 1 | ||||||
| 扁泥甲科 Psephenidae | 1 | ||||||
| 缨甲科 Ptiliidae | 96 | ||||||
| 蛛甲科 Ptinidae | 5 | 11 | 21 | ||||
| 大花蚤科 Ripiphoridae | 1 | ||||||
| 缢胸甲科 Salpingidae | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||
| 金龟科 Scarabaeidae | 8 | 291 | 39 | 46 | 5 | 10 | |
| 沼甲科 Scirtidae | 17 | 21 | 47 | 2 | |||
| 拟花蚤科 Scraptiidae | 11 | ||||||
| 葬甲科 Silphidae | 1 | ||||||
| 锯谷盗科 Silvanidae | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | |||
| 隐翅虫科 Staphylinidae | 24 | 399 | 50 | 52 | 16 | 12 | |
| 拟步甲科 Tenebrionidae | 8 | 151 | 16 | 29 | 2 | 3 | |
| 斑蕈甲科 Tetratomidae | 1 | 2 | |||||
| 三栉牛科 Trictenotomidae | 1 | ||||||
| 皮金龟科 Trogidae | 3 | 3 | 1 | ||||
| 谷盗科 Trogossitidae | 1 | ||||||
| 暗天牛科 Vesperidae | 1 | ||||||
| 幽甲科 Zopheridae | 1 | 9 | |||||
| 总计 Total | 237 | 2,973 | 1,319 | 610 | 49 | 61 | |
* 本科隶属于叩甲总科, 但该科昆虫没有叩头机制, 雌虫幼态持续、体型与萤或花萤相似, 因此以“萤”字命名。而拉丁科名是基于微小的口器这一特征。综合考虑, 命中文科名为纤口萤科。
* This family belongs to superfamily Elateroidea, but adults without click mechanism. Neoteny presents in females and their body shape are similar to the Lampyridae or the Cantharidae, so it was named after the word “萤”. The latin name of this family is based on the character of tiny mouthparts. Therefore, this family’s Chinese name is named as “纤口萤科”.
2.2 新发表的科/亚科和族级分类群
2020年报道了一个来自巴西大西洋雨林的新科, 即Jurasaidae, 隶属于叩甲总科(Elateroidea)。另外, 新增了5个亚科, 分别是Coomaniinae、Chespiritoinae、†Antigracilinae、†Palaeotylinae和†Kryzhanovskianinae, 分别隶属于隐翅虫科、萤科(Lampyridae)、阎甲科(Histeridae)、象甲科(Curculionidae)和步甲科。
新族共计13个, 其中Acomini、Chnaunanthini、Phobetusini、Warwickiini隶属于金龟科, 其余9个是Haraiaini (隶属于长泥甲科Heteroceridae)、Coriacephilini (象甲科)、Madeirodulini (瓢虫科)、Microzaenini (步甲科)、†Pantostictini (阎甲科)、†Palpattalini (拟花萤科Melyridae)、†Burmomaceratini (毛象科Nemonychidae)、†Burmocorynini (矛象科Belidae)、†Myanmaropini (叶甲科Chrysomelidae)。
2.3 新发表的属级分类群
2020年发表世界鞘翅目昆虫新属218个新亚属18个, 分别来自54个科。其中, 现生属161个, 亚属17个, 占到了新属(亚属)的75.42%, 来自33个科, 超过1/3的现生属级分类群隶属于步甲科(23个)、叶甲科(23个)和天牛科(20个); 绝灭属57个, 亚属1个, 占总数的24.58%, 来自37个科, 接近1/4的绝灭属级分类群隶属于隐唇叩甲科(Eucnemidae, 9个)、隐翅虫科(3个)、叶甲科(2个)。
2.4 新发表的种级分类群
2020年在141个期刊/出版社的995篇文献/著作中发表了世界鞘翅目新种2,901个, 新亚种72个, 共计2,973个, 分别来自24个总科91科。其中, 数量较多的5个科分别为: 隐翅虫科(399种)、金龟科(291种)、象甲科(290种)、步甲科(281种)和天牛科(240种), 分别占新种总数的13.42%、9.79%、9.75%、9.45%和8.07%。皮扁甲科(Phloeostichidae)、姬花甲科(Phalacridae)、大花蚤科(Ripiphoridae)、绒皮甲科(Mycteridae)和三栉牛科(Trictenotomidae)等科新种仅1种。小花甲科(Byturidae)、圆蕈甲科(Cyclaxyridae)和谷盗科(Trogossitidae)等科无新增物种。
发表的新种中, 有2,835个现生种, 占新种总数的95.36%, 来自21个总科75个科。约50%的现生新种隶属于隐翅虫科(384种)、金龟科(291种)、象甲科(286种)、步甲科(280种)、天牛科(237种), 分别占现生新种的13.54%、10.26%、10.09%、9.88%和8.36%。绝灭种有138个, 占新种总数的4.64%, 来自18个总科45个科。约一半绝灭种隶属于花萤科(Cantharidae, 21种)、隐唇叩甲科(21种)、隐翅虫科(15种)、拟步甲科(Tenebrionidae, 6种)、红萤科(Lycidae, 5种), 分别占绝灭种的15.22%、15.22%、10.87%、4.35%和3.62%。
2.5 新发表的组合和异名
2020年发表的世界鞘翅目昆虫新组合共计1,319个, 涉及象甲科(241个)、天牛科(205个)、叶甲科(159个)、蚁形甲科(Anthicidae, 145个)、瓢虫科(124个)、红萤科(83个)等在内的36个科。新异名共计610个(包括属级和种级异名), 涉及象甲科(109个)、天牛科(73个)、叶甲科(56个)、隐翅虫科(52个)、金龟科(46个)等在内的42个科, 包含3个绝灭类群。
2.6 新发表的降级和升级分类群
2020年发表的世界鞘翅目昆虫新降级条目共计49个, 其中1个由科级降为亚科级, 7个由亚科级降为族级, 11个由族级降为属级, 25个由属级降为亚属级, 5个由种级降为亚种级。涉及降级最多的3个科分别为: 隐翅虫科(16个)、步甲科(13个)和天牛科(6个)。涉及到化石类群1个, 隶属于花蚤科(Mordellidae)。
发表的新升级条目共计61个, 其中4个由族级升为亚科级, 12个由属级升级为族级, 10个由亚属级升为属级, 35个由亚种级升为种级。涉及升级最多的科分别为: 隐翅虫科(12个)、天牛科(11个)和金龟科(10个), 涉及到化石类群3个。
3 新种的地域分布
以国家为单位进行统计, 2020年发表的世界鞘翅目昆虫新物种的模式标本产地涉及中国、巴西、墨西哥等118个国家和地区。有106个国家所报道的新种皆为现生种, 如巴西、厄瓜多尔和印度尼西亚等; 有9个国家报道的新种中既有现生种, 也有绝灭种, 如中国、墨西哥和澳大利亚等; 乌克兰、德国和立陶宛三国报道的新种皆为绝灭种。埃及、利比亚等国无新种报道。
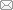
发表现生新种超过百种的国家分别为: 中国(431种)、巴西(188种)、墨西哥(163种)、厄瓜多尔(120种)、印度尼西亚(113种)、澳大利亚(109种)和越南(100种), 分别占2020年世界鞘翅目昆虫新种发表总数的14.56%、6.32%、5.58%、4.04%、3.90%、3.73%和3.36%。另外, 菲律宾、秘鲁、缅甸、泰国等在内的37个国家发表的现生新种都在10到100种之间(图1), 亚美尼亚、马拉维、法国、波多黎各和巴基斯坦等在内的其余71个国家和地区发表的现生新种数少于10种(有11个现生新种的分布地未给出)。
图1
图1
2020年记录10种及以上鞘翅目新种的国家及其新种数
Fig. 1
The countries that recorded 10 or more new species of Coleoptera in 2020 and the number of new species in each country
此外, 在缅甸、俄罗斯、波兰等12个国家中发现了绝灭新种, 其中, 发表绝灭新种最多的两个国家为缅甸(71种)和俄罗斯(35种), 其余10个国家发表的绝灭新种都在10种以下: 波兰5种, 乌克兰5种, 墨西哥3种, 多米尼加3种, 中国2种, 法国2种, 德国2种, 澳大利亚1种, 新西兰1种, 立陶宛1种。
4 来源出版物
2020年, 收录世界鞘翅目昆虫新发表种的论文/专著995篇, 涉及141个期刊或出版社(图2)。其中, 发表新种超百种的共有4个期刊: Zootaxa共发表新种论文254篇, 记录新种732个, ZooKeys 54篇264个新种, European Journal of Taxonomy 15篇182个新种, Insecta Mundi 43篇152个新种, 分别占了2020年世界鞘翅目新种数目的24.62%、8.88%、6.12%和5.11%, 这些期刊对推动新种发表做出了重要贡献。国外期刊是分类学者发表新种的主要阵地, 也有部分学者将新种论文发表在中国期刊上, 如贾凤龙等(2020)在Entomotaxonomia (《昆虫分类学报》英文版)上发表刻纹牙甲属(Thysanarthria) 1个新种; 包童(2020)在《古生物学报》上发表花蚤科1个新种, 并将短尾花蚤科(Apotomouridae)修订为短尾花蚤亚科(Apotomourinae)。
图2
图2
2020年发表世界鞘翅目新种的期刊/书名词云
Fig. 2
The term cloud of journals or monographs that published new species of Coleoptera worldwide in 2020
5 小结与展望
本文汇总了网络平台数据和专家提供的文献信息, 对隐藏其中的多样性信息进行了挖掘与分析, 由于部分新种发表期刊未收录在Zoological Record中等原因, 即使有国内外同行的支持, 本文统计数据也很可能无法做到100%完整, 但其研究结果已足以反映新分类群的基本情况。从结果不难看出, 2020年世界鞘翅目分类学取得了重大进展: 发表了包括新科、新亚科、新族、新属和新亚属等在内的3,228个新分类群, 以及2,039个阶元和名称变动; 隐翅虫科、步甲科、象甲科、天牛科等常见类群的分类学工作取得显著成果。另外, 从新种模式标本产地的分布情况不难看出, 中国、巴西、墨西哥、厄瓜多尔、印度尼西亚、澳大利亚和越南是2020年记录新种最多的7个国家, 这与各国的气候和植被类型以及对生物多样性的重视程度和保护力度的不断加强密不可分。从发表新种的期刊来看, 传统的分类学期刊Zootaxa和ZooKeys是甲虫新种发表最重要的期刊, 贡献了约1/3的新种。
虽然2020年世界鞘翅目分类工作取得了诸多成果, 但同时也暴露了许多问题: (1) Erwin和Johnson (2000)统计的1978-2000年的年平均甲虫新种发表数量为3,154种, 而2020年发表的现生甲虫新种数量仅有2,835种, 减少了319种(约占10%), 新种发现速度趋缓, 这是多方面原因共同造成的; (2)部分国家和地区2020年仅发现1种甲虫新种(如乌拉圭、文莱等), 有些国家甚至无新种记录(如埃及、利比亚等), 而有些国家甲虫新种超过百种(如中国、巴西等), 这与不同国家地区的调查力度和资源投入规模关系密切; (3)类群间研究程度的差异也十分显著, 许多类群(如隐翅虫科、步甲科等)的分类工作在不同阶元上均有进展, 而部分类群却鲜有人问津, 如水缨甲科(Hydroscaphidae)、扁泥甲科(Psephenidae)等。
综上所述, 为弄清世界鞘翅目多样性状况, 还需投入更多的人力、物力和财力, 获得更多地点的标本, 开展更多类群的分类研究; 同时, 还需不断创新传统分类学方法, 如将人工智能应用于传统分类学中, 从而实现物种更加快速准确的分类鉴定和发现新物种, 进而实现对全球生物多样性更好的了解与保护。
附录 Supplementary Material
附录1 世界鞘翅目2020年新分类单元和新名称修订清单
Appendix 1 The amendment of new taxa and new name of Coleoptera from all over the world published in 2020
附录2 世界鞘翅目分类群2020年度报告文献附录
Appendix 2 Bibliography of global Coleoptera for the year 2020
参考文献
Ecological value and conservation significances of dung beetles
蜣螂的生态价值和保护意义
A new small-bodied mordellid beetle (Coleoptera: Mordellidae) from mid-cretaceous Burmese amber and taxonomic revision
白垩纪缅甸琥珀中小型花蚤一新种(鞘翅目: 花蚤科)及对花蚤科的分类学修订
Family-group names in Coleoptera (Insecta)
DOI:10.3897/zookeys.88.807
PMID:21594053
[本文引用: 2]

We synthesize data on all known extant and fossil Coleoptera family-group names for the first time. A catalogue of 4887 family-group names (124 fossil, 4763 extant) based on 4707 distinct genera in Coleoptera is given. A total of 4492 names are available, 183 of which are permanently invalid because they are based on a preoccupied or a suppressed type genus. Names are listed in a classification framework. We recognize as valid 24 superfamilies, 211 families, 541 subfamilies, 1663 tribes and 740 subtribes. For each name, the original spelling, author, year of publication, page number, correct stem and type genus are included. The original spelling and availability of each name were checked from primary literature. A list of necessary changes due to Priority and Homonymy problems, and actions taken, is given. Current usage of names was conserved, whenever possible, to promote stability of the classification.New synonymies (family-group names followed by genus-group names): Agronomina Gistel, 1848 syn. nov. of Amarina Zimmermann, 1832 (Carabidae), Hylepnigalioini Gistel, 1856 syn. nov. of Melandryini Leach, 1815 (Melandryidae), Polycystophoridae Gistel, 1856 syn. nov. of Malachiinae Fleming, 1821 (Melyridae), Sclerasteinae Gistel, 1856 syn. nov. of Ptilininae Shuckard, 1839 (Ptinidae), Phloeonomini Ádám, 2001 syn. nov. of Omaliini MacLeay, 1825 (Staphylinidae), Sepedophilini Ádám, 2001 syn. nov. of Tachyporini MacLeay, 1825 (Staphylinidae), Phibalini Gistel, 1856 syn. nov. of Cteniopodini Solier, 1835 (Tenebrionidae); Agronoma Gistel 1848 (type species Carabus familiaris Duftschmid, 1812, designated herein) syn. nov. of Amara Bonelli, 1810 (Carabidae), Hylepnigalio Gistel, 1856 (type species Chrysomela caraboides Linnaeus, 1760, by monotypy) syn. nov. of Melandrya Fabricius, 1801 (Melandryidae), Polycystophorus Gistel, 1856 (type species Cantharis aeneus Linnaeus, 1758, designated herein) syn. nov. of Malachius Fabricius, 1775 (Melyridae), Sclerastes Gistel, 1856 (type species Ptilinus costatus Gyllenhal, 1827, designated herein) syn. nov. of Ptilinus Geoffroy, 1762 (Ptinidae), Paniscus Gistel, 1848 (type species Scarabaeus fasciatus Linnaeus, 1758, designated herein) syn. nov. of Trichius Fabricius, 1775 (Scarabaeidae), Phibalus Gistel, 1856 (type species Chrysomela pubescens Linnaeus, 1758, by monotypy) syn. nov. of Omophlus Dejean, 1834 (Tenebrionidae). The following new replacement name is proposed: Gompeliina Bouchard, 2011 nom. nov. for Olotelina Báguena Corella, 1948 (Aderidae).Reversal of Precedence (Article 23.9) is used to conserve usage of the following names (family-group names followed by genus-group names): Perigonini Horn, 1881 nom. protectum over Trechicini Bates, 1873 nom. oblitum (Carabidae), Anisodactylina Lacordaire, 1854 nom. protectum over Eurytrichina LeConte, 1848 nom. oblitum (Carabidae), Smicronychini Seidlitz, 1891 nom. protectum over Desmorini LeConte, 1876 nom. oblitum (Curculionidae), Bagoinae Thomson, 1859 nom. protectum over Lyprinae Gistel 1848 nom. oblitum (Curculionidae), Aterpina Lacordaire, 1863 nom. protectum over Heliomenina Gistel, 1848 nom. oblitum (Curculionidae), Naupactini Gistel, 1848 nom. protectum over Iphiini Schönherr, 1823 nom. oblitum (Curculionidae), Cleonini Schönherr, 1826 nom. protectum over Geomorini Schönherr, 1823 nom. oblitum (Curculionidae), Magdalidini Pascoe, 1870 nom. protectum over Scardamyctini Gistel, 1848 nom. oblitum (Curculionidae), Agrypninae/-ini Candèze, 1857 nom. protecta over Adelocerinae/-ini Gistel, 1848 nom. oblita and Pangaurinae/-ini Gistel, 1856 nom. oblita (Elateridae), Prosternini Gistel, 1856 nom. protectum over Diacanthini Gistel, 1848 nom. oblitum (Elateridae), Calopodinae Costa, 1852 nom. protectum over Sparedrinae Gistel, 1848 nom. oblitum (Oedemeridae), Adesmiini Lacordaire, 1859 nom. protectum over Macropodini Agassiz, 1846 nom. oblitum (Tenebrionidae), Bolitophagini Kirby, 1837 nom. protectum over Eledonini Billberg, 1820 nom. oblitum (Tenebrionidae), Throscidae Laporte, 1840 nom. protectum over Stereolidae Rafinesque, 1815 nom. oblitum (Throscidae) and Lophocaterini Crowson, 1964 over Lycoptini Casey, 1890 nom. oblitum (Trogossitidae); Monotoma Herbst, 1799 nom. protectum over Monotoma Panzer, 1792 nom. oblitum (Monotomidae); Pediacus Shuckard, 1839 nom. protectum over Biophloeus Dejean, 1835 nom. oblitum (Cucujidae), Pachypus Dejean, 1821 nom. protectum over Pachypus Billberg, 1820 nom. oblitum (Scarabaeidae), Sparrmannia Laporte, 1840 nom. protectum over Leocaeta Dejean, 1833 nom. oblitum and Cephalotrichia Hope, 1837 nom. oblitum (Scarabaeidae).
Recognition and revision of the Phelister blairi group (Histeridae, Histerinae, Exosternini)
DOI:10.3897/zookeys.1001.58447
PMID:33363428
[本文引用: 1]

Forty-nine new species of Neotropical Exosternini are described in this work, representing the newly recognized species group, within the large, heterogeneous taxon. Eight previously described species are also assigned to this group. Relationships within are indicated with several informal subgroups: subgroup: ( Hinton, 1935,,,,,, Marseul, 1889,,,,,,,,, Schmidt, 1893,, Reichensperger, 1939,,,,,,, ); subgroup: (,,, Kanaar, 1997,,,, Wenzel & Dybas, 1941, Schmidt, 1893, (Lewis, 1898), ); subgroup: (,,,,, ); subgroup: (,,,, ); subgroup: (, ); subgroup: (,,, ); - unplaced to subgroup: (,,, ). Lectotypes are designated for the following species: Marseul, Schmidt, Reichensperger, Schmidt, and Lewis. Preliminary phylogenetic analyses of the broader Neotropical Exosternini do not support the monophyly of the group, nor of all of these subgroups, but the majority do fall within one large clade (which is potentially paraphyletic with respect to some other Neotropical exosternine genera). More work on the phylogeny and taxonomy of this diverse fauna is needed.Michael S. Caterino, Alexey K. Tishechkin.
A revision of Cissidium Motschulsky (Coleoptera: Ptiliidae) with seventy seven new species
Nam ing species, a new paradigm for crisis management in taxonomy: Rapid journal validation of scientific names enhanced with more complete descriptions on the Internet
DOI:10.1649/0010-065X(2000)054[0269:NSANPF]2.0.CO;2 URL [本文引用: 3]
A new genus-level and two new species-level synonyms in the extinct genus Neolitochropus Lyubarsky & Perkovsky (Coleoptera: Cyclaxyridae)
DOI:10.11646/zootaxa.4894.4 URL
A comprehensive phylogeny of beetles reveals the evolutionary origins of a superradiation
DOI:10.1126/science.1146954 URL [本文引用: 2]
A new species of Thysanarthria Orchymont from China, with the first record T. bifida (Coleoptera: Hydrophilidae) in Vietnam
中国刻纹牙甲属Thysanarthria一新种及越南新记录T. bifida (鞘翅目: 牙甲科)
Biodiversity research progress
生物多样性研究进展
Beetles as pollinators
传粉甲虫的研究进展
A monograph of the Xyleborini (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Scolytinae) of the Indochinese Peninsula (except Malaysia) and China
DOI:10.3897/zookeys.983.52630 URL [本文引用: 1]
How many species of insects and other terrestrial arthropods are there on earth
DOI:10.1146/ento.2018.63.issue-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
New approaches narrow global species estimates for beetles, insects, and terrestrial arthropods
Revision of Cerabilia Laporte, 1867 (Carabidae: Abacetini) of Australia and New Caledonia
Collection and utilization of common medicinal beetles in Northeast China
东北常见药用甲虫的采集与利用
Animal biodiversity: An outline of higher-level classification and taxonomic richness
DOI:10.11646/zootaxa.3148.1 URL [本文引用: 3]