



Biodiv Sci ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (5): 606-620. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020135 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020135
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhijian Liang1,2,Jiabei Hu1,2,Sifan Hu1,2,Jingjing Zhao1,2,Kaiwen Zhou1,2,Yunbo Jiao3,Cheng Huang1,2,Xia He1,2,Anita Kar Yan Wan1,2,Lishu Li4,Fangyuan Hua5,Tien Ming Lee1,2,6,*( )
)
Received:2020-04-01
Accepted:2020-05-19
Online:2020-05-20
Published:2020-07-16
Contact:
Tien Ming Lee
Zhijian Liang, Jiabei Hu, Sifan Hu, Jingjing Zhao, Kaiwen Zhou, Yunbo Jiao, Cheng Huang, Xia He, Anita Kar Yan Wan, Lishu Li, Fangyuan Hua, Tien Ming Lee. Understanding and changing wildlife consumption behavior from a multidisciplinary perspective[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(5): 606-620.
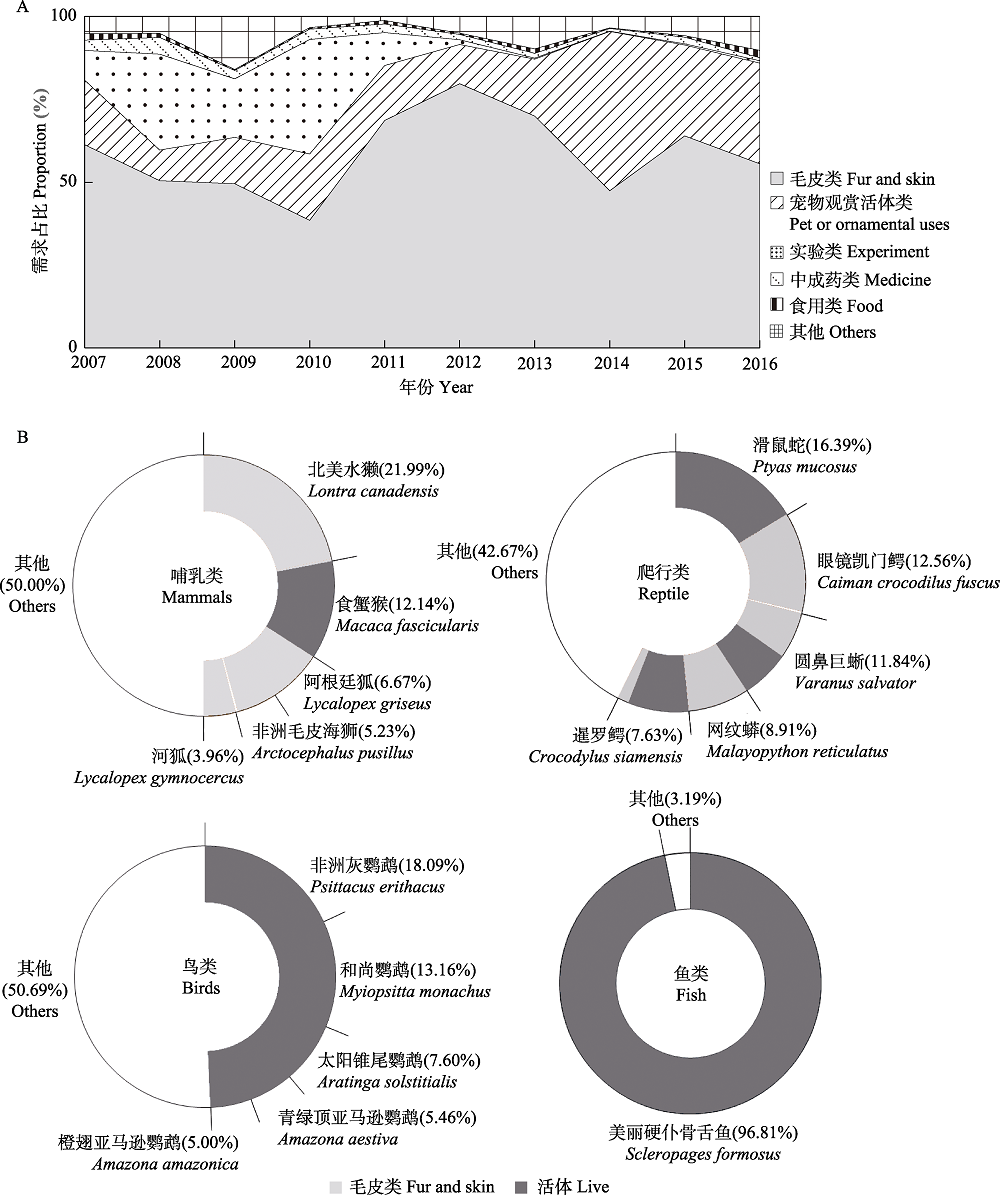
Fig. 1 Major demand types and traded species of China’s wildlife import. (A) shows the annual change in proportion of wild animals and their derivatives imported into China between 2007 and 2016. Data is categorized into five trade commodity types—animal fur, medicinal, edible (including health care products), experimental animals, pets or ornamental uses (data retrieved from the State Forestry Administration); (B) shows the proportion of major traded species by sector size and the major trade commodity types (data retrieved from CITES Trade Database, https://trade.cites.org/). Between 2007 and 2016, the volume of China’s legal amphibian import is very small, with total number of WOEs less than 3,000.
| 贸易链 Trade chains | 利益方类型 Category | 说明 Description |
|---|---|---|
| 供货方 Suppliers | 生计型 Subsistence | 满足自身基本物质需求 Non-commercial harvest for household or local use |
| 商业导向型 Specialist commercial | 利用专业工具或技术、商业目的捕猎、养殖 Harvest and breed with an explicit commercial orientation that often involves specialist skills or technologies | |
| 机会主义型 Opportunist | 如在采集蘑菇过程中偶遇猎物 eg. in the process of gathering mushrooms, come across wild animals | |
| 无意型 Bycatch | 无意的捕猎, 如野生动物掉入水池 Unintentional harvest of non-target species (eg. wild animals fall into the pool) | |
| 娱乐型 Recreational | 以愉悦为目的 Harvest for enjoyment | |
| 应对型 Reactionary | 因为不满而捕猎, 如人兽冲突 Harvest associated with discontent or protest (eg. in reaction to conflict with wildlife) | |
| 组织型 Logistician | 组织偷猎、收货、计划贸易等 Involved in ordering, aggregation, finance and plan trade. etc. | |
| 中间商 Intermediaries | 走私型 Specialized smuggler | 跨境运输 Transboundary smuggling |
| 机构合谋型 Government colluder | 利用职务之便纵容非法贸易 Involved in using an official government position | |
| 不知情第三方 Unknowing third party | 如快递公司 eg. express companies | |
| 处理方 Processor | 处理加工野生动物制品 Involved in product transformation | |
| 批发、零售 Launderer and vendor | 直接面对消费者的商家 Direct sale to consumers | |
| 体验型 Experiential | 追求感官体验或猎奇 Desire to fulfil hedonistic pleasure or satisfy curiosity | |
| 消费者 Consumers | 社会型 Social | 如通过消费展示财富、地位 eg. highlight wealth, social standing through consumption |
| 功能型 Functional | 如使用保健品、药物 eg. use nutriments and medicines | |
| 经济型 Financial | 如投资动物制品或收费展示动物 eg. buy wildlife products as investment strategy or exhibition for income | |
| 精神型 Spiritual | 如宗教放生 eg. free captive animals for religious brief |
Table 1 Typology of key actor roles in wildlife trade
| 贸易链 Trade chains | 利益方类型 Category | 说明 Description |
|---|---|---|
| 供货方 Suppliers | 生计型 Subsistence | 满足自身基本物质需求 Non-commercial harvest for household or local use |
| 商业导向型 Specialist commercial | 利用专业工具或技术、商业目的捕猎、养殖 Harvest and breed with an explicit commercial orientation that often involves specialist skills or technologies | |
| 机会主义型 Opportunist | 如在采集蘑菇过程中偶遇猎物 eg. in the process of gathering mushrooms, come across wild animals | |
| 无意型 Bycatch | 无意的捕猎, 如野生动物掉入水池 Unintentional harvest of non-target species (eg. wild animals fall into the pool) | |
| 娱乐型 Recreational | 以愉悦为目的 Harvest for enjoyment | |
| 应对型 Reactionary | 因为不满而捕猎, 如人兽冲突 Harvest associated with discontent or protest (eg. in reaction to conflict with wildlife) | |
| 组织型 Logistician | 组织偷猎、收货、计划贸易等 Involved in ordering, aggregation, finance and plan trade. etc. | |
| 中间商 Intermediaries | 走私型 Specialized smuggler | 跨境运输 Transboundary smuggling |
| 机构合谋型 Government colluder | 利用职务之便纵容非法贸易 Involved in using an official government position | |
| 不知情第三方 Unknowing third party | 如快递公司 eg. express companies | |
| 处理方 Processor | 处理加工野生动物制品 Involved in product transformation | |
| 批发、零售 Launderer and vendor | 直接面对消费者的商家 Direct sale to consumers | |
| 体验型 Experiential | 追求感官体验或猎奇 Desire to fulfil hedonistic pleasure or satisfy curiosity | |
| 消费者 Consumers | 社会型 Social | 如通过消费展示财富、地位 eg. highlight wealth, social standing through consumption |
| 功能型 Functional | 如使用保健品、药物 eg. use nutriments and medicines | |
| 经济型 Financial | 如投资动物制品或收费展示动物 eg. buy wildlife products as investment strategy or exhibition for income | |
| 精神型 Spiritual | 如宗教放生 eg. free captive animals for religious brief |
| [1] | Arena PC, Steedman C, Warwick C (2012) Amphibian and reptile pet markets in the EU: An investigation and assessment. Animal Protection Agency, Brighton, UK. http://faada.org/userfiles/ARPM2012_v122[2].pdf. (accessed on 2020-03-10) |
| [2] | Baillie JEM, Hilton-Taylor C, Stuart SN (2004) 2004 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: A global species assessment. International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources, Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK. |
| [3] |
Benítez-López A, Alkemade R, Schipper AM, Ingram DJ, Verweij PA, Eikelboom JAJ, Huijbregts MAJ (2017) The impact of hunting on tropical mammal and bird populations. Science, 356, 180-183.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] |
Biggs D, Cooney R, Roe D, Dublin HT, Allan JR, Challender DWS, Skinner D (2017) Developing a theory of change for a community-based response to illegal wildlife trade. Conservation Biology, 31, 5-12.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
Blair ME, Le MD, Sethi G, Thach HM, Nguyen VTH, Amato G, Birchette M, Sterling EJ (2017) The importance of an interdisciplinary research approach to inform wildlife trade management in Southeast Asia. BioScience, 67, 995-1003.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Brashares JS, Abrahms B, Fiorella KJ, Golden CD, Hojnowski CE, Marsh RA, McCauley DJ, Nuñez TA, Seto K, Withey L (2014) Wildlife decline and social conflict. Science, 345, 376-378.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] | Brashares JS, Golden CD, Weinbaum KZ, Barrett CB, Okello GV (2011) Economic and geographic drivers of wildlife consumption in rural Africa. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 13931-13936. |
| [8] |
Burn SM (1991) Social psychology and the stimulation of recycling behaviours: The block leader approach. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 21, 611-629.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Bush ER, Baker SE, Macdonald DW (2014) Global trade in exotic pets 2006-2012. Conservation Biology, 28, 663-676.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Butler P, Green K, Galvin D (2013) The principles of Pride: The science behind the mascots. Rare, Arlington, VA. https://www.rare.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Rare-Principles-of-Pride.pdf. (accessed on 2020-05-21) |
| [11] |
Challender DWS, Harrop SR, MacMillan DC (2015) Understanding markets to conserve trade-threatened species in CITES. Biological Conservation, 187, 249-259.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Challender DWS, Hinsley A, Milner-Gulland EJ (2019) Inadequacies in establishing CITES trade bans. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 17, 199-200.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Chaves WA, Valle DR, Monroe MC, Wilkie DS, Sieving KE, Sadowsky B (2017) Changing wild meat consumption: An experiment in the central Amazon, Brazil. Conservation Letters, 11, e12391.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Cheung GCK, Chang CY (2011) Cultural identities of Chinese business: Networks of the shark-fin business in Hong Kong. Asia Pacific Business Review, 17, 343-359.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Christakis NA, Fowler JH (2009) Connected: The Surprising Power of Our Social Networks and How They Shape Our Lives. Little, Brown and Company, New York. |
| [16] |
Cialdini RB (2003) Crafting normative messages to protect the environment. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 12, 105-109.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Cialdini RB, Kallgren CA, Reno RR (1991) A focus theory of normative conduct: A theoretical refinement and reevaluation of the role of norms in human behavior. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 24, 201-234. |
| [18] | Coalition to End Wildlife Trafficking Online (2020) Offline and in the wild: A progress report of the Coalition to End Wildlife Trafficking Online. https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5b53e9789772ae59ffa267ee/t/5e5c32496b59fb4dac1baf55/1583100496539/Offline+and+In+the+Wild+-+Coalition+2020+Progress+Report.pdf. (accessed on 2020-03-18) |
| [19] |
Curtin S (2005) Nature, wild animals and tourism: An experiential view. Journal of Ecotourism, 4, 1-15.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Daut EF, Brightsmith DJ, Peterson MJ (2015) Role of non-governmental organizations in combating illegal wildlife-pet trade in Peru. Journal for Nature Conservation, 24, 72-82.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Davis EO, Glikman JA, Crudge B, Dang V, Willemsen M, Nguyen T, O’Connor D, Bendixsen T (2019) Consumer demand and traditional medicine prescription of bear products in Vietnam. Biological Conservation, 235, 119-127.
DOI URL |
| [22] | DeWan A, Green K, Li X, Hayden D (2013) Using social marketing tools to increase fuel-efficient stove adoption for conservation of the golden snub-nosed monkey, Gansu Province, China. Conservation Evidence, 10, 32-36. |
| [23] |
Downes E (2018) “A very good livelyhood”: The native animal fur trade in Victoria. History Australia, 15, 89-112.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Drury R (2011) Hungry for success: Urban consumer demand for wild animal products in Vietnam. Conservation and Society, 9, 247-257.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Dutton AJ, Hepburn C, Macdonald DW (2011) A stated preference investigation into the Chinese demand for farmed vs. wild bear bile. PLoS ONE, 6, e21243.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Fabinyi M, Liu N (2014) Seafood banquets in Beijing: Consumer perspectives and implications for environmental sustainability. Conservation & Society, 12, 218-229. |
| [27] |
Fabinyi M, Liu N, Song Q, Li R (2016) Aquatic product consumption patterns and perceptions among the Chinese middle class. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 7, 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Fei YL, Zhou YW, Liu DW, Hou SL, Pan HC (2019) The harm and regulation of the networked illegal trade of wildlife. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 40, 1031-1034. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 费宜玲, 周用武, 刘大伟, 侯森林, 潘恒昌 (2019) 野生动物非法贸易网络化的危害和监管. 野生动物学报, 40, 1031-1034.] | |
| [29] |
Feng Y, Siu K, Wang N, Ng KM, Tsao SW, Nagamatsu T, Tong Y (2009) Bear bile: Dilemma of traditional medicinal use and animal protection. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine, 5, 2.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] |
Gao Y, Clark SG (2014) Elephant ivory trade in China: Trends and drivers. Biological Conservation, 180, 23-30.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Garnett EE, Balmford A, Sandbrook C, Pilling MA, Marteau TM (2019) Impact of increasing vegetarian availability on meal selection and sales in cafeterias. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 20923-20929. |
| [32] | General Office of the State Council (2017) Notice of the General Office of the State Council on the orderly cessation of commercial processing and sale of ivory and its products. The Bulletin of the State Council of the People’s Republic of China, 3, 97-98. (in Chinese) |
| [ 中华人民共和国国务院 (2017) 国务院办公厅关于有序停止商业性加工销售象牙及制品活动的通知. 中华人民共和国国务院公报, 3, 97-98.] | |
| [33] | GlobeScan (2019) Demand under the Ban—China Ivory Consumption Research 2019. GlobeScan Incorporated, Hong Kong. https://d2ouvy59p0dg6k.cloudfront.net/downloads/demand_under_the_ban_china_ivory_consumption_research_2019_final.pdf. (accessed on 2020-05-23) |
| [34] | GlobeScan, National Geographic Society (2015) Reducing the Demand for Ivory: An International Study. GlobeScan Incorporated, Hong Kong. https://globescan.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Reducing_Demand_For_Ivory_National_Geographic_Society_GlobeScan_Full_Report_11August2015.pdf. (accessed on 2020-05-23) |
| [35] |
Gonzalez LF, Montes GA, Puig E, Johnson S, Mengersen K, Gaston KJ (2016) unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and artificial intelligence revolutionizing wildlife monitoring and conservation. Sensors, 16, 1-18.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Harfoot M, Glaser SAM, Tittensor DP, Britten GL, McLardy C, Malsch K, Burgess ND (2018) Unveiling the patterns and trends in 40 years of global trade in CITES-listed wildlife. Biological Conservation, 223, 47-57.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Harrison RD, Sreekar R, Brodie JF, Brook S, Luskin M, O'Kelly H, Rao M, Scheffers B, Velho N (2016) Impacts of hunting on tropical forests in Southeast Asia. Conservation Biology, 30, 972-981.
DOI URL PMID |
| [38] | He GB, Li S, Liang ZY (2018) Leveraging for maximal return: Behavioral decisions that drive social development. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 50, 5-15. (in Chinese) |
| [ 何贵兵, 李纾, 梁竹苑 (2018) 以小拨大: 行为决策助推社会发展. 心理学报, 50, 5-15.] | |
| [39] |
Hou Z, Lin L, Lu L, Du F, Qian M, Liang Y, Zhang J, Yu H (2020) Public exposure to live animals, behavioural change, and support in containment measures in response to COVID-19 outbreak: A population-based cross sectional survey in China. medRxiv, doi: 10.1101/2020.02.21.20026146.
DOI URL PMID |
| [40] |
Hughes AC (2017) Understanding the drivers of Southeast Asian biodiversity loss. Ecosphere, 8, e01624.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Jenks B, Vaughan PW, Butler PJ (2010) The evolution of Rare Pride: Using evaluation to drive adaptive management in a biodiversity conservation organization. Evaluation and Program Planning, 33, 186-190.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Jiang N, Wang QW (2018) Discussion on China's wildlife enforcement cost wave under its ivory ban policy. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 39, 438-441. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姜南, 王邱文 (2018) 中国象牙禁贸政策对其野生动物执法成本的影响. 野生动物学报, 39, 438-441.] | |
| [43] | Jiao Y (2016) Greater China and transnational environmental crime: Understanding criminal networks and enforcement responses. In: Handbook of Transnational Environmental Crime (eds Elliotts L, Schaedla W), pp. 255-275. Edward Elgar Publishing Limited, Cheltenham, UK. |
| [44] |
Keene M, Pullin AS (2011) Realizing an effectiveness revolution in environmental management. Journal of Environmental Management, 92, 2130-2135.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Kiesler CA (1971) The Psychology of Commitment: Experiments Linking Behavior to Belief. Academic Press, New York. |
| [46] |
Kotler P, Zaltman G (1971) Social marketing: An approach to planned social change. Journal of Marketing, 35(3), 3-12.
URL PMID |
| [47] | Li HG, Zhang FY, Teng XJ, Hu HJ, Lv LB (2019) The status of wildlife breeding and utilization in Dehong prefecture. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 40, 87-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李宏刚, 张飞燕, 滕雪娇, 胡恒嘉, 吕龙宝 (2019) 德宏州野生动物繁育利用的现状调查分析. 野生动物学报, 40, 87-93.] | |
| [48] |
Li S, Wang DJ, Xiao ZS, Li XH, Wang TM, Feng LM, Wang Y (2014) Camera-trapping in wildlife research and conservation in China: Review and outlook. Biodiversity Science, 22, 685-695. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 李晟, 王大军, 肖治术, 李欣海, 王天明, 冯利民, 王云 (2014) 红外相机技术在我国野生动物研究与保护中的应用与前景. 生物多样性, 22, 685-695.]
DOI URL |
|
| [49] | Li YM (2001) Advances in game hunting, wildlife trade and hunting sustainability. Biodiversity Science, 9, 414-421. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李义明 (2001) 野生动物狩猎、贸易和狩猎持续性研究进展. 生物多样性, 9, 414-421.] | |
| [50] | Lin N (2017) Building a network theory of social capital. In: Social Capital: Theory and Research (eds Lin N, Cook K, Burt RS), pp. 3-29. Routledge, New York. |
| [51] | Liu Z, Jiang ZG, Yang AF (2017) Research progress on trade and consumer behavior of wild animals. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 38, 712-719. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘钊, 蒋志刚, 杨爱芳 (2017) 野生动物消费行为研究进展. 野生动物学报, 38, 712-719.] | |
| [52] | Lokhorst AM, van Dijk J, Staats H, van Dijk E, de Snoo G (2010) Using tailored information and public commitment to improve the environmental quality of farm lands: An example from the Netherlands. Human Ecology: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 38, 113-122. |
| [53] |
Margulies JD, Wong RW, Duffy R (2019) The imaginary “Asian super consumer”: A critique of demand reduction campaigns for the illegal wildlife trade. Geoforum, 107, 216-219.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Marrocoli S, Gatiso TT, Morgan D, Nielsen MR, Kühl H (2018) Environmental uncertainty and self-monitoring in the commons: A common-pool resource experiment framed around bushmeat hunting in the Republic of Congo. Ecological Economics, 149, 274-284.
DOI URL |
| [55] | McKenzie-Mohr D, Schultz PW (2014) Choosing effective behavior change tools. Social Marketing Quarterly, 20, 35-46. |
| [56] | McNamara J, Fa JE, Ntiamoa-Baidu Y (2019) Understanding drivers of urban bushmeat demand in a Ghanaian market. Biological Conservation, 239, 1-8. |
| [57] | Meneses GD, Palacio AB (2007) The response to the commitment with block-leader recycling promotion technique: A longitudinal approach. Journal of Nonprofit & Public Sector Marketing, 17, 83-102. |
| [58] |
Miteva DA, Pattanayak SK, Ferraro PJ (2012) Evaluation of biodiversity policy instruments: What works and, what doesn’t? Oxford Review of Economic Policy, 28, 69-92.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Moorhouse P, Balaskas M, D’Cruze N, Macdonald DW (2017) Information could reduce consumer demand for exotic pets. Conservation Letters, 10, 337-345.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Natusch DJD, Carter JF, Aust PW, van Tri N, Tinggi U, Mumpuni, Riyanto A, Lyons JA (2017) Serpent's source: Determining the source and geographic origin of traded python skins using isotopic and elemental markers. Biological Conservation, 209, 406-414.
DOI URL |
| [61] | Nayar A, Kanaka S (2017) A comparative study on water conservation through behavioral economics based nudging: Evidence from Indian city “a nudge in time can save nine”. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 8, 62-67. |
| [62] |
Ni Q, Wang Y, Weldon A, Xie M, Xu H, Yao Y, Zhang M, Li Y, Li Y, Zeng B, Nekaris KAI (2018) Conservation implications of primate trade in China over 18 years based on web news reports of confiscations. PeerJ, 6, e6069.
DOI URL PMID |
| [63] | Nijman V (2010) An overview of international wildlife trade from Southeast Asia. Biodiversity and Conservation, 19, 1101-1114. |
| [64] | Olmedo A, Sharif V, Milner-Gulland EJ (2018) Evaluating the design of behaviour change interventions: A case study of rhino horn in Vietnam. Conservation Letters, 11, e12365. |
| [65] |
Phelps J, Biggs D, Webb EL (2016) Tools and terms for understanding illegal wildlife trade. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 14, 479-489.
DOI URL |
| [66] | Rapid Asia (2013) Rapid Asia Flash Report: Impact Evaluation on Ivory Trade in China. IFAW PSA: “Mom, I have teeth”. Rapid Asia Company Limited, Bangkok, Thailand. https://s3.amazonaws.com/ifaw-pantheon/sites/default/files/legacy/ifaw-china-ivory-report.pdf. (accessed on 2020-5-22) |
| [67] | Reason P, Bradbury H (2008) The SAGE Handbook of Action Research: Participative Inquiry and Practice. SAGE Publications Incorporated, London. |
| [68] | Redford KH, Taber A (2000) Writing the wrongs: Developing a safe-fail culture in conservation. Conservation Biology, 14, 1567-1568. |
| [69] |
Ribeiro J, Bingre P, Strubbe D, Reino L (2020) Coronavirus: Why a permanent ban on wildlife trade might not work in China. Nature, 578, 217.
DOI URL PMID |
| [70] |
Rivalan P, Delmas V, Angulo E, Bull LS, Hall RJ, Courchamp F, Rosser AM, Leader-Williams N (2007) Can bans stimulate wildlife trade? Nature, 447, 529-530.
DOI URL PMID |
| [71] | Rogers E (2003) Diffusion of Innovations. The Free Press of Glencoe, New York. |
| [72] |
Rosen GE, Smith KF (2010) Summarizing the evidence on the international trade in illegal wildlife. EcoHealth, 7, 24-32.
DOI URL PMID |
| [73] |
Salazar G, Mills M, Veríssimo D (2019) Qualitative impact evaluation of a social marketing campaign for conservation. Conservation Biology, 33, 634-644.
DOI URL PMID |
| [74] | Schiffman LG, Wisenblit JL (2019) Consumer Behavior, 12th edn. Pearson Education. Harlow. |
| [75] | Shi YR (2017) Discussion on the publicity work of wildlife protection. Friends of Farmers Getting Rich, 7, 265. (in Chinese) |
| [ 史艳茹 (2017) 关于野生动物保护宣传工作的探讨. 农民致富之友, 7, 265.] | |
| [76] |
Solís L, Casas A (2019) Cuicatec ethnozoology: Traditional knowledge, use, and management of fauna by people of San Lorenzo Pápalo, Oaxaca, Mexico. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine, 15, 58.
URL PMID |
| [77] | St. John FAV, Mai C-H, Pei KJ-C (2015) Evaluating deterrents of illegal behaviour in conservation: Carnivore killing in rural Taiwan. Biological Conservation, 189, 86-94. |
| [78] | State Forestry Administration (2007-2016) China Forestry Statistical Yearbook. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 国家林业局(2007-2016) 中国林业统计年鉴. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [79] | Sung YH, Fong JJ (2018) Assessing consumer trends and illegal activity by monitoring the online wildlife trade. Biological Conservation, 227, 219-225. |
| [80] | ’t Sas-Rolfes M, Challender DWS, Hinsley A, Veríssimo D, Milner-Gulland EJ (2019) Illegal wildlife trade: Scale, processes, and governance. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 44, 201-228. |
| [81] | Thaler RH, Sunstein CR (2008) Nudge: Improving Decisions About Health, Wealth, and Happiness. Yale University Press, New Haven, CT. |
| [82] | The Behavioural Insights Team (2015) The Behavioural Insights Team: Update Report 2013-2015. Behavioural Insights Limited, London. Behavioural Insights Limited, London. http://www.behaviouralinsights.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/BIT_Update-Report-Final-2013-2015.pdf. (accessed on 2020-05-21) |
| [83] | Thomas-Walters L, Hinsley A, Bergin D, Doughty H, Eppel S, MacFarlane D, Meijer W, Lee TM, Phelps J, Smith RJ, Wan AKY, Veríssimo D (2020) Motivations for the use and consumption of wildlife products. Conservation Biology (in press) |
| [84] | TRAFFIC (2015) Traditional Medicine Practitioners in Viet Nam Pledge to Protect Threatened Wildlife. TRAFFIC, Cambridge, UK. https://www.traffic.org/news/traditional-medicine-practitioners-in-viet-nam-pledge-to-protect-threatened-wildlife/. (accessed on 2020-03-05) |
| [85] | Truelove HB, Carrico AR, Weber EU, Raimi KT, Vandenbergh MP (2014) Positive and negative spillover of pro-environmental behavior: An integrative review and theoretical framework. Global Environmental Change, 29, 127-138. |
| [86] | Turner JC (1991) Social Influence. Open University Press, Buckingham, UK. |
| [87] | Tyrrell P, Russell S, Western D (2017) Seasonal movements of wildlife and livestock in a heterogenous pastoral landscape: Implications for coexistence and community based conservation. Global Ecology and Conservation, 12, 59-72. |
| [88] | UNEP (The United Nations Environment Programme) (2014) Illegal trade in wildlife: The environmental, social and economic consequences for sustainable development. UNEP/ EA.1/INF/19. United Nations Environment Assembly of the United Nations Programme, First Session, 23-27 June 2014, Nairobi, Kenya. https://wedocs.unep.org/handle/20.500.11822/20396. (accessed on 2020-03-05) |
| [89] | UNODC (The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime) (2010) The Globalization of Crime: A Transnational Organized Crime Threat Assessment. United Nations Publication, New York. https://www.unodc.org/res/cld/bibliography/the-globalization-of-crime-a-transnational-organized-crime-threat-assessment_html/TOCTA_Report_2010_low_res.pdf. (accessed on 2020-03-05) |
| [90] | UNODC (The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime) (2016) World Wildlife Crime Report: Trafficking in Protected Species. United Nations Publication, New York. https://www.unodc.org/documents/data-and-analysis/wildlife/World_Wildlife_Crime_Report_2016_final.pdf. (accessed on 2020-03-05) |
| [91] |
Veríssimo D, Wan AKY (2018) Characterizing efforts to reduce consumer demand for wildlife products. Conservation Biology, 33, 623-633.
DOI URL PMID |
| [92] | Wäldchen J, Rzanny M, Seeland M, Mäder P (2018) Automated plant species identification—Trends and future directions. PLoS Computational Biology, 14(4), 1-19. |
| [93] | Wallen KE, Daut EF (2017) Exploring social influence and social marketing to reduce consumer demand for illegal wildlife. Asian Journal of Conservation Biology, 6, 3-13. |
| [94] | Wallen KE, Daut EF (2018) The challenge and opportunity of behaviour change methods and frameworks to reduce demand for illegal wildlife. Nature Conservation, 26, 55-75. |
| [95] | Wang WX, Hu YJ, Chen SZ (2017) Current situation and enlightenment of global sustainable utilization and trade of wildlife resources. World Forestry Research, 30(3), 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王文霞, 胡延杰, 陈绍志 (2017) 全球野生动物资源可持续利用与贸易现状和启示. 世界林业研究, 30(3), 1-5.] | |
| [96] | Wang WX, Yang LL, Hu YJ, Chen SZ (2019) Illegal smuggling of wild animals as recorded by China Customs Administration in recent years. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 40, 797-800. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王文霞, 杨亮亮, 胡延杰, 陈绍志 (2019) 近年我国海关野生动物走私状况分析. 野生动物学报, 40, 797-800.] | |
| [97] | Wasser RM, Jiao PB (2010) Understanding the Motivations: The First Step Toward Influencing China’s Unsustainable Wildlife Consumption. TRAFFIC East Asia, China. https://www.traffic.org/site/assets/files/6267/china-motivations-study.pdf. (accessed on 2020-03-02) |
| [98] | Webb TL, Joseph J, Yardley L, Michie S (2010) Using the internet to promote health behavior change: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of theoretical basis, use of behavior change techniques, and mode of delivery on efficacy. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 12, 1-11. |
| [99] | Willemsen M, Nguyen T (2017) Chi Briefing Baper— Providing Insights of the Impact of a Behaviour Change Campaign to Reduce the Demand for Rhino Horn in Viet Nam. TRAFFIC, Cambridge, UK. https://changewildlifeconsumers.org/toolkit/chi-initiative-world-rhino-day-briefing-paper/. (accessed on 2020-05-21) |
| [100] | Wittemyer G, Northrup JM, Blanc J, Douglas-Hamilton I, Omondi P, Burnham KP (2014) Illegal killing for ivory drives global decline in African elephants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, 13117-13121. |
| [101] | World Bank (2015) World development report 2015: Mind, society, and behavior. World Bank Group, Washington, DC. https://www.worldbank.org/en/publication/wdr2015. (accessed on 2020-03-20) |
| [102] | Wright AJ, Veríssimo D, Pilfold K, Parsons ECM, Ventre K, Cousins J, Jefferson R, Koldewey H, Llewellyn F, McKinley E (2015) Competitive outreach in the 21st century: Why we need conservation marketing. Ocean & Coastal Management, 115, 41-48. |
| [103] | Xu L (2014) Discussion on some problems of administrative law enforcement in the wild animal protection. Forest Resources Management, (4),29-33, 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 许岚 (2014) 野生动物保护行政执法若干问题的探讨——以一起无证驯养黄金蟒行政纠纷案为视角. 林业资源管理, (4),29-33, 51.] | |
| [104] | Xu L, Guan J, Lau W, Xiao Y (2016) An Overview of Pangolin Trade in China. TRAFFIC Briefing Paper. TRAFFIC, Cambridge, UK. https://www.traffic.org/site/assets/files/10569/pangolin-trade-in-china.pdf. (accessed on 2020-523) |
| [105] | Yang YJ, Shi YT, Zhang D (2019) Intergenerational effects on individual charitable donation: An innovative study on charitable donation in China. Sociological Studies, 34, 183-209, 245. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨永娇, 史宇婷, 张东 (2019) 个体慈善捐赠行为的代际效应——中国慈善捐赠本土研究的新探索. 社会学研究, 34, 183-209, 245.] | |
| [106] |
Zhang L, Hua N, Sun S (2008) Wildlife trade, consumption and conservation awareness in southwest China. Biodiversity and Conservation, 17, 1493-1516.
DOI URL PMID |
| [107] |
Zhang L, Yin F (2014) Wildlife consumption and conservation awareness in China: A long way to go. Biodiversity and Conservation, 23, 2371-2381.
DOI URL |
| [108] | Zhao XM (2004) Adhering to the Scientific Outlook on Development, promoting the strategic shift in wildlife utilization from wild to captive sources. Green China, (9), 4-8. (in Chinese) |
| [ 赵学敏 (2004) 坚持科学发展观实现野生动植物资源利用的战略转变. 绿色中国, (9), 4-8.] | |
| [109] | Zhu GS, Ding LD, Yu GL, Zhou XL (2019) Wildlife domestication and propagation industry in Zhejiang Province. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College, 25, 109-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱桂寿, 丁良冬, 俞根连, 周晓丽 (2019) 浙江省野生动物驯养繁殖业现状分析. 浙江林学院学报, 25, 109-113.] | |
| [110] | Zhu XL, Sun ZZ, Li N, Wang L, Liu KJ (2013) Exploration and thinking of grass-roots wildlife protection publicity. Henan Forestry Science and Technology. 33(1), 60-62. (in Chinese) |
| [ 朱晓雷, 孙振中, 李娜, 王璐, 刘可君 (2013) 基层野生动物保护宣传工作的探索与思考. 河南林业科技, 33(1), 60-62.] |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()