

食物网结构与功能: 理论进展与展望
收稿日期: 2020-06-15
录用日期: 2020-07-26
网络出版日期: 2020-09-13
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(31988102);国家自然科学基金(31870505);科技部重点研发计划(2017YFC0503906)
Food web structure and functioning: Theoretical advances and outlook
Received date: 2020-06-15
Accepted date: 2020-07-26
Online published: 2020-09-13
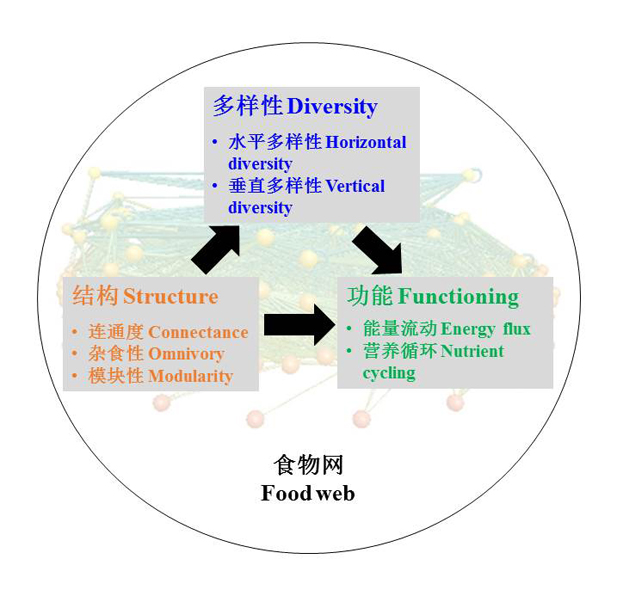
食物网刻画了物种间通过捕食而形成的复杂网络关系。阐明食物网结构与功能之间的关系, 既是生态学的基本理论问题, 也是预测全球变化背景下生态系统响应的重要依据。早期关于食物网结构与功能的研究往往是分离的, 或是基于食物链等的简单网络模型, 而近期研究基于复杂食物网模型取得了重要理论进展。本文综述了食物网研究的理论方法和近期进展, 特别介绍了复杂食物网中的结构、多样性和功能的度量指标、结构-多样性-功能之间的关系以及全球变化对食物网结构与功能的影响。本文最后对未来的一些研究方向进行了展望, 包括与功能性状和化学计量学的整合、食物网与其他网络类型的整合以及拓展食物网研究的空间和时间尺度。
王少鹏 . 食物网结构与功能: 理论进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2020 , 28(11) : 1391 -1404 . DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020240
The relationship between food web structure and functioning can have important implications for predicting the responses of ecosystems to global changes. Previous studies have mainly explored food web structure and functioning separately or in simple food web models (e.g. food chains), but recent studies made significant progress in understanding the structure and functioning of complex food webs. This paper reviews the theoretical approaches and recent advances of complex food webs. In particular, I summarize the multiple metrics for quantifying the structure, biodiversity, and functioning of complex food webs, explain the theoretical framework for modeling complex food webs, and review the recent progress in understanding the relationships between food web structure, biodiversity, and functioning, and how they respond to global changes. I end with discussion on potential future directions by integrating food web theory with functional trait, ecological stoichiometry, other types of ecological networks, metacommunity theory, and evolutionary models.

Key words: omnivory; modularity; horizontal diversity; vertical diversity; energy flux
| [1] | Allesina S, Alonso D, Pascual M (2008) A general model for food web structure. Science, 320, 658-661. |
| [2] | Barnes AD, Jochum M, Lefcheck JS, Eisenhauer N, Scherber C, O’Connor MI, de Ruiter P, Brose U (2018) Energy flux: The link between multitrophic biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 33, 186-197. |
| [3] | Bascompte J (2009) Disentangling the web of life. Science, 325, 416-419. |
| [4] | Binzer A, Guill C, Rall BC, Brose U (2016) Interactive effects of warming, eutrophication and size structure: Impacts on biodiversity and food-web structure. Global Change Biology, 22, 220-227. |
| [5] | Borer ET, Seabloom EW, Shurin JB, Anderson KE, Blanchette CA, Broitman B, Cooper SD, Halpern BS (2005) What determines the strength of a trophic cascade? Ecology, 86, 528-537. |
| [6] | Brose U, Williams RJ, Martinez ND (2006) Allometric scaling enhances stability in complex food webs. Ecology Letters, 9, 1228-1236. |
| [7] | Brose U (2008) Complex food webs prevent competitive exclusion among producer species. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 275, 2507-2514. |
| [8] | Brose U, Archambault P, Barnes AD, Bersier L-F, Boy T, Canning-Clode J, Conti E, Dias M, Digel C, Dissanayake A, Flores AVA, Fussmann K, Gauzens B, Gray C, H?ussler J, Hirt MR, Jacob U, Jochum M, Kéfi S, McLaughlin O, MacPherson MM, Latz E, Layer-Dobra K, Legagneux P, Li YH, Madeira C, Martinez ND, Mendon?a V, Mulder C, Navarrete SA, O’Gorman EJ, Ott D, Paula J, Perkins D, Piechnik D, Pokrovsky I, Raffaelli D, Rall BC, Rosenbaum B, Ryser R, Silva A, Sohlstr?m EH, Sokolova N, Thompson MSA, Thompson RM, Vermandele F, Vinagre C, Wang S, Wefer JM, Williams RJ, Wieters E, Woodward G, Iles AC (2019) Predator traits determine food-web architecture across ecosystems. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 3, 919-927. |
| [9] | Brown JH, Gillooly JF, Allen AP, Savage VM, West GB (2004) Toward a metabolic theory of ecology. Ecology, 85, 1771-1789. |
| [10] | Burian A, Nielsen JM, Winder M (2020) Food quantity-quality interactions and their impact on consumer behavior and trophic transfer. Ecological Monographs, 90, e01395. |
| [11] | Cardinale BJ, Srivastava DS, Duffy JE, Wright JP, Downing AL, Sankaran M, Jouseau C (2006) Effects of biodiversity on the functioning of trophic groups and ecosystems. Nature, 443, 989-992. |
| [12] | Cattin MF, Bersier LF, Bana?ek-Richter C, Baltensperger R, Gabriel JP (2004) Phylogenetic constraints and adaptation explain food-web structure. Nature, 427, 835-839. |
| [13] | Chen YF, Tang Z, Li H, Han XM, Li YF, Hu C (2014) Research progress on ecosystem complexity-stability relationships based on soil food web. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 2173-2186. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | [ 陈云峰, 唐政, 李慧, 韩雪梅, 李钰飞, 胡诚 (2014) 基于土壤食物网的生态系统复杂性-稳定性关系研究进展. 生态学报, 34, 2173-2186.] |
| [14] | Chesson P, Kuang JJ (2008) The interaction between predation and competition. Nature, 456, 235-238. |
| [15] | Civitello DJ, Cohen J, Fatima H, Halstead NT, Liriano J, McMahon TA, Ortega CN, Sauer EL, Sehgal T, Young S, Rohr JR (2015) Biodiversity inhibits parasites: Broad evidence for the dilution effect. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 8667-8671. |
| [16] | Clay NA, Lehrter RJ, Kaspari M (2017) Towards a geography of omnivory: Omnivores increase carnivory when sodium is limiting. Journal of Animal Ecology, 86, 1523-1531. |
| [17] | Cohen JE, Newman CM (1985) A stochastic theory of community food webs. I. Models and aggregated data. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 224, 421-448. |
| [18] | Daufresne M, Lengfellner K, Sommer U (2009) Global warming benefits the small in aquatic ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 106, 12788-12793. |
| [19] | Davis JM, Rosemond AD, Eggert SL, Cross WF, Wallace JB (2010) Long-term nutrient enrichment decouples predator and prey production. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 107, 121-126. |
| [20] | de Ruiter PC, Neutel AM, Moore JC (1994) Modelling food webs and nutrient cycling in agro-ecosystems. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 9, 378-383. |
| [21] | Denno RF, Fagan WF (2003) Might nitrogen limitation promote omnivory among carnivorous arthropods? Ecology, 91, 3114-3117. |
| [22] | Duffy JE, Cardinale BJ, France KE, McIntyre PB, Thébault E, Loreau M (2007) The functional role of biodiversity in ecosystems: Incorporating trophic complexity. Ecology Letters, 10, 522-538. |
| [23] | Dunne JA, Williams RJ, Martinez ND (2002) Network structure and biodiversity loss in food webs: Robustness increases with connectance. Ecology Letters, 5, 558-567. |
| [24] | Eisenhauer N, Schielzeth H, Barnes AD, Barry KE, Bonn A, Brose U, Bruelheide H, Buchmann N, Buscot F, Ebeling A, Ferlian O, Freschet GT, Giling DP, H?ttenschwiler S, Hillebrand H, Hines J, Isbell F, Koller-France E, K?nig-Ries B, de Kroon H, Meyer ST, Milcu A, Müller J, Nock CA, Petermann JS, Roscher C, Scherber C, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Schmid B, Schnitzer SA, Schuldt A, Tscharntke T, Türke M, van Dam NM, van der Plas F, Vogel A, Wagg C, Wardle DA, Weigelt A, Weisser WW, Wirth C, Jochum M (2019) A multitrophic perspective on biodiversity-ecosystem functioning research. Advances in Ecological Research, 61, 1-54. |
| [25] | Elser JJ, Loladze I, Peace AL, Kuang Y (2012) Lotka re-loaded: Modeling trophic interactions under stoichiometric constraints. Ecological Modelling, 245, 3-11. |
| [26] | Elton CS (1927) Animal Ecology. Sidgwick and Jackson, London. |
| [27] | Estes JA, Terborgh J, Brashares JS, Power ME, Berger J, Bond WJ, Carpenter SR, Essington TE, Holt RD, Jackson JBC, Marquis RJ, Oksanen L, Oksanen T, Paine RT, Pikitch EK, Ripple WJ, Sandin SA, Scheffer M, Schoener TW, Shurin JB, Sinclair ARE, Soulé ME, Virtanen R, Wardle DA (2011) Trophic downgrading of planet Earth. Science, 333, 301-306. |
| [28] | Fontaine C, Guimar?es PR Jr, Kéfi S, Loeuille N, Memmott J, van der Putten WH, van Veen FJF, Thébault E (2011) The ecological and evolutionary implications of merging different types of networks. Ecology Letters, 14, 1170-1181. |
| [29] | Fronhofer EA, Legrand D, Altermatt F, Ansart A, Blanchet S, Bonte D, Chaine A, Dahirel M, De Laender F, De Raedt J, di Gesu L, Jacob S, Kaltz O, Laurent E, Little CJ, Madec L, Manzi F, Masier S, Pellerin F, Pennekamp F, Schtickzelle N, Therry L, Vong A, Winandy L, Cote J (2018) Bottom-up and top-down control of dispersal across major organismal groups. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2, 1859-1863. |
| [30] | Fu SL, Zhang WX, Shao YH, Shi LL, Liu ZF (2019) Soil Ecology--Soil Food Web and Its Ecosystem Functioning. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [30] | [ 傅声雷, 张卫信, 邵元虎, 时雷雷, 刘占锋 (2019) 土壤生态学——土壤食物网及其生态功能. 科学出版社, 北京.] |
| [31] | Fussmann KE, Schwarzmüller F, Brose U, Jousset A, Rall BC (2014) Ecological stability in response to warming. Nature Climate Change, 4, 206-210. |
| [32] | Gauzens B, Legendre S, Lazzaro X, Lacroix G (2013) Food-web aggregation, methodological and functional issues. Oikos, 122, 1606-1615. |
| [33] | Gauzens B, Barnes A, Giling DR, Hines J, Jochum M, Lefcheck JS, Rosenbaum B, Wang S, Brose U (2019) Fluxweb: An R package to easily estimate energy fluxes in food webs. Methods in Ecology & Evolution, 10, 270-279. |
| [34] | Gilman SE, Urban MC, Tewksbury J, Gilchrist GW, Holt RD (2010) A framework for community interactions under climate change. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 25, 325-331. |
| [35] | Goudard A, Loreau M (2008) Nontrophic interactions, biodiversity, and ecosystem functioning: An interaction web model. The American Naturalist, 171, 91-106. |
| [36] | Gravel D, Albouy C, Thuiller W (2016) The meaning of functional trait composition of food webs for ecosystem functioning. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 371, 20150268. |
| [37] | Guiden PW, Bartel SL, Byer NW, Shipley AA, Orrock JL (2019) Predator-prey interactions in the anthropocene: Reconciling multiple aspects of novelty. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 34, 616-627. |
| [38] | Haddad NM, Crutsinger GM, Gross K, Haarstad J, Knops JMH, Tilman D (2009) Plant species loss decreases arthropod diversity and shifts trophic structure. Ecology Letters, 12, 1029-1039. |
| [39] | Hillebrand H, Cardinale BJ (2004) Consumer effects decline with prey diversity. Ecology Letters, 7, 192-201. |
| [40] | Hirt MR, Jetz W, Rall BC, Brose U (2017) A general scaling law reveals why the largest animals are not the fastest. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 1, 1116-1122. |
| [41] | Hoek TA, Axelrod K, Biancalani T, Yurtsev EA, Liu JH, Gore J (2016) Resource availability modulates the cooperative and competitive nature of a microbial cross-feeding mutualism. PLoS Biology, 14, e1002540. |
| [42] | Holland JN, DeAngelis DL (2009) Consumer-resource theory predicts dynamic transitions between outcomes of interspecific interactions. Ecology Letters, 12, 1357-1366. |
| [43] | Holling CS (1959) Some characteristics of simple types of predation and parasitism. The Canadian Entomologist, 91, 385-398. |
| [44] | Holt RD, Grover J, Tilman GD (1994) Simple rules for interspecific dominance in systems with exploitative and apparent competition. The American Naturalist, 144, 741-771. |
| [45] | Ingram T, Harmon LJ, Shurin JB (2009) Niche evolution, trophic structure, and species turnover in model food webs. The American Naturalist, 174, 56-67. |
| [46] | Ives AR, Cardinale BJ, Snyder WE (2004) A synthesis of subdisciplines: Predator-prey interactions, and biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Ecology Letters, 8, 102-116. |
| [47] | Jiang L, Pu Z (2009) Different effects of species diversity on temporal stability in single-trophic and multitrophic communities. The American Naturalist, 174, 651-659. |
| [48] | Johnson S, Domínguez-García V, Donetti L, Munoz MA (2014) Trophic coherence determines food-web stability. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, 17923-17928. |
| [49] | Kalinkat G, Schneider FD, Digel C, Guill C, Rall BC, Brose U (2013) Body masses, functional responses and predator-prey stability. Ecology Letters, 16, 1126-1134. |
| [50] | Kéfi S, Berlow EL, Wieters EA, Navarrete SA, Petchey OL, Wood SA, Boit A, Joppa LN, Lafferty KD, Williams RJ, Martinez ND, Menge BA, Blanchette CA, Iles AC, Brose U (2012) More than a meal… integrating non-feeding interactions into food webs. Ecology Letters, 15, 291-300. |
| [51] | Knight TM, McCoy MW, Chase JM, McCoy KA, Holt RD (2005) Trophic cascades across ecosystems. Nature, 437, 880-883. |
| [52] | Krause AE, Frank KA, Mason DM, Ulanowicz RE, Taylor WW (2003) Compartments revealed in food-web structure. Nature, 426, 282-285. |
| [53] | Laigle I, Aubin I, Digel C, Brose U, Boulangeat I, Gravel D (2018) Species traits as drivers of food web structure. Oikos, 127, 316-326. |
| [54] | Leibold MA, Chase JM (2018) Metacommunity Ecology. Princeton University Press, Princeton NJ. |
| [55] | Leroux SJ, Loreau M (2008) Subsidy hypothesis and strength of trophic cascades across ecosystems. Ecology Letters, 11, 1147-1156. |
| [56] | Lindeman RL (1942) The trophic-dynamic aspect of ecology. Ecology, 23, 399-417. |
| [57] | Loeuille N, Loreau M (2005) Evolutionary emergence of size-structured food webs. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 102, 5761-5766. |
| [58] | Loeuille N (2019) Eco-evolutionary dynamics in a disturbed world: Implications for the maintenance of ecological networks. F1000Research, 8, 97. |
| [59] | Loreau M (2010) From Populations to Ecosystems: Theoretical Foundations for a New Ecological Synthesis. Princeton University Press, Princeton NJ. |
| [60] | Maureaud A, Andersen KH, Zhang L, Lindegren M (2020) Trait-based food web model reveals the underlying mechanisms of biodiversity-ecosystem functioning relationships. Journal of Animal Ecology, 89, 1497-1510. |
| [61] | May RM (1973) Stability and Complexity in Model Ecosystems. Princeton University Press, Princeton NJ. |
| [62] | McCann KS, Rasmussen JB, Umbanhowar J (2005) The dynamics of spatially coupled food webs. Ecology Letters, 8, 513-523. |
| [63] | McCann KS(2012) Food Webs. Princeton University Press, Princeton NJ. |
| [64] | Moore JC, de Ruiter PC(2012) Energetic Food Webs: An Analysis of Real and Model Ecosystems. Oxford University Press, New York. |
| [65] | Mougi A, Kondoh M (2012) Diversity of interaction types and ecological community stability. Science, 337, 349-351. |
| [66] | Naeem S, Thompson LJ, Lawler SP, Lawton JH, Woodfin RM (1994) Declining biodiversity can alter the performance of ecosystems. Nature, 368, 734-737. |
| [67] | O’Connor MI, Piehler MF, Leech DM, Anton A, Bruno JF (2009) Warming and resource availability shift food web structure and metabolism. PLoS Biology, 7, e1000178. |
| [68] | O’Gorman EJ, Zhao L, Pichler DE, Adams G, Friberg N, Rall BC, Seeney A, Zhang HY, Reuman DC, Woodward G (2017) Unexpected changes in community size structure in a natural warming experiment. Nature Climate Change, 7, 659-663. |
| [69] | O’Gorman EJ, Petchey OL, Faulkner KJ, Gallo B, Gordon TA, Neto-Cerejeira J, ólafsson JS, Pichler DE, Thompson MS, Woodward G (2019) A simple model predicts how warming simplifies wild food webs. Nature Climate Change, 9, 611-616. |
| [70] | Parmesan C, Yohe G (2003) A globally coherent fingerprint of climate change impacts across natural systems. Nature, 421, 37-42. |
| [71] | Peace A (2015) Effects of light, nutrients, and food chain length on trophic efficiencies in simple stoichiometric aquatic food chain models. Ecological Modelling, 312, 125-135. |
| [72] | Persson L, Leonardsson K, de Roos AM, Gyllenberg M, Christensen B (1998) Ontogenetic scaling of foraging rates and the dynamics of a size-structured consumer-resource model. Theoretical Population Biology, 54, 270-293. |
| [73] | Petchey OL, McPhearson PT, Casey TM, Morin PJ (1999) Environmental warming alters food-web structure and ecosystem function. Nature, 402, 69-72. |
| [74] | Pimm SL (1982) Food Webs. Springer, Dordrecht. |
| [75] | Pocock MJO, Evans DM, Memmott J (2012) The robustness and restoration of a network of ecological networks. Science, 335, 973-977. |
| [76] | Poisot T, Mouquet N, Gravel D (2013) Trophic complementarity drives the biodiversity-ecosystem functioning relationship in food webs. Ecology Letters, 16, 853-861. |
| [77] | Polis GA, Strong DR (1996) Food web complexity and community dynamics. The American Naturalist, 147, 813-846. |
| [78] | Polis GA, Sears ALW, Huxel GR, Strong DR, Maron J (2000) When is a trophic cascade a trophic cascade? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 15, 473-475. |
| [79] | Post DM (2002) The long and short of food-chain length. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 17, 269-277. |
| [80] | Rall BC, Guill C, Brose U (2008) Food-web connectance and predator interference dampen the paradox of enrichment. Oikos, 117, 202-213. |
| [81] | Rall BC, Brose U, Hartvig M, Kalinkat G, Schwarzmüller F, Vucic-Pestic O, Petchey OL (2012) Universal temperature and body-mass scaling of feeding rates. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 367, 2923-2934. |
| [82] | Rip JMK, McCann KS (2011) Cross-ecosystem differences in stability and the principle of energy flux. Ecology Letters, 14, 733-740. |
| [83] | Rosenzweig ML (1971) Paradox of enrichment: Destabilization of exploitation ecosystems in ecological times. Science, 171, 385-387. |
| [84] | Schneider FD, Brose U, Rall BC, Guill C (2016) Animal diversity and ecosystem functioning in dynamic food webs. Nature Communications, 7, 12718. |
| [85] | Seibold S, Cadotte MW, MacIvor JS, Thorn S, Müller J (2018) The necessity of multitrophic approaches in community ecology. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 33, 754-764. |
| [86] | Sentis A, Hemptinne JL, Brodeur J (2014) Towards a mechanistic understanding of temperature and enrichment effects on species interaction strength, omnivory and food-web structure. Ecology Letters, 17, 785-793. |
| [87] | Song C, Ahn S, Rohr RP, Saavedra S (2020) Towards a probabilistic understanding about the context-dependency of species interactions. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 35, 384-396. |
| [88] | Sterner RW, Elser JJ (2002) Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton NJ. |
| [89] | Stouffer DB, Bascompte J (2010) Understanding food-web persistence from local to global scales. Ecology Letters, 13, 154-161. |
| [90] | Stouffer DB, Bascompte J (2011) Compartmentalization increases food-web persistence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 3648-3652. |
| [91] | Strogatz SH (2001) Exploring complex networks. Nature, 410, 268-276. |
| [92] | Strong DR (1992) Are trophic cascades all wet? Differentiation and donor-control in speciose ecosystems. Ecology, 73, 747-754. |
| [93] | Sun SC (2017) Food-web structure and ecosystem functioning. In: Current Knowledge and Future Challenges (eds Yu ZL, Ge JP, Yu GR, Zhang DY, Fang JY, Kang L, Fu BJ, Jiao NZ), pp. 254-271. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [93] | [ 孙书存 (2017) 食物网结构与生态功能. 见: 生态学的现状与发展趋势 (于振良, 葛剑平, 于贵瑞, 张大勇, 方精云, 康乐, 傅伯杰, 焦念志编), 254-271页. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] |
| [94] | Thakur MP (2020) Climate warming and trophic mismatches in terrestrial ecosystems: The green-brown imbalance hypothesis. Biology Letters, 16, 20190770. |
| [95] | Thébault E, Loreau M (2003) Food-web constraints on biodiversity-ecosystem functioning relationships. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 100, 14949-14954. |
| [96] | Thébault E, Fontaine C (2010) Stability of ecological communities and the architecture of mutualistic and trophic networks. Science, 329, 853-856. |
| [97] | Thompson RM, Hemberg M, Starzomski BM, Shurin JB (2007) Trophic levels and trophic tangles: The prevalence of omnivory in real food webs. Ecology, 88, 612-617. |
| [98] | Thompson RM, Brose U, Dunne JA, Hall RO, Hladyz S, Kitching RL, Martinez ND, Rantala H, Romanuk TN, Stouffer DB, Tylianakis JM (2012) Food webs: Reconciling the structure and function of biodiversity. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 27, 689-697. |
| [99] | Thompson PL, Gonzalez A (2017) Dispersal governs the reorganization of ecological networks under environmental change. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 1, 0162. |
| [100] | Tilman D (1982) Resource Competition and Community Structure. Princeton University Press, Princeton NJ. |
| [101] | Tilman D, Isbell F, Cowles JM (2014) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 45, 471-493. |
| [102] | Trebilco R, Baum JK, Salomon AK, Dulvy NK (2013) Ecosystem ecology: Size-based constraints on the pyramids of life. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 28, 423-431. |
| [103] | Trussell GC, Ewanchuk PJ, Matassa CM (2006) Habitat effects on the relative importance of trait- and density-mediated indirect interactions. Ecology Letters, 9, 1245-1252. |
| [104] | Turchin P (2003) Complex Population Dynamics: A Theoretical/Empirical Synthesis. Princeton University Press, Princeton NJ. |
| [105] | Tylianakis JM, Didham RK, Bascompte J, Wardle DA (2008) Global change and species interactions in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecology Letters, 11, 1351-1363. |
| [106] | Ullah H, Nagelkerken I, Goldenberg SU, Fordham DA (2018) Climate change could drive marine food web collapse through altered trophic flows and cyanobacterial proliferation. PLoS Biology, 16, e2003446. |
| [107] | Wang L, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Wang D, Isbell F, Liu J, Feng C, Liu J, Zhong Z, Zhu H, Yuan X, Chang Q, Liu C (2019) Diversifying livestock promotes multidiversity and multifunctionality in managed grasslands. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 6187-6192. |
| [108] | Wang S, Brose U (2018) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in food webs: The vertical diversity hypothesis. Ecology Letters, 21, 9-20. |
| [109] | Wang S, Brose U, Gravel D (2019) Intraguild predation enhances biodiversity and functioning in complex food webs. Ecology, 100, e02616. |
| [110] | Welti N, Striebel M, Ulseth AJ, Cross WF, DeVilbiss S, Glibert PM, Guo L, Hirst AG, Hood J, Kominoski JS, MacNeill KL, Mehring AS, Welter JR, Hillebrand H (2017) Bridging food webs, ecosystem metabolism, and biogeochemistry using ecological stoichiometry theory. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 1298. |
| [111] | Williams RJ, Martinez ND (2000) Simple rules yield complex food webs. Nature, 404, 180-183. |
| [112] | Williams RJ, Martinez ND (2004) Limits to trophic levels and omnivory in complex food webs: Theory and data. The American Naturalist, 163, 458-468. |
| [113] | Woodson CB, Schramski JR, Joye SB (2018) A unifying theory for top-heavy ecosystem structure in the ocean. Nature Communications, 9, 23. |
| [114] | Xu GH, Li XY, Shi CH (2019) The complexity-stability relationship: Progress in mathematical models. Biodiversity Science, 27, 1364-1378. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [114] | [ 徐光华, 李小玉, 施春华 (2019) 复杂性-稳定性研究: 数学模型的进展. 生物多样性, 27, 1364-1378.] |
| [115] | Yan C, Zhang Z (2014) Specific non-monotonous interactions increase persistence of ecological networks. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 281, 20132797. |
| [116] | Yodzis P (1982) The compartmentation of real and assembled ecosystems. The American Naturalist, 120, 551-570. |
| [117] | Yodzis P, Innes S (1992) Body size and consumer-resource dynamics. The American Naturalist, 139, 1151-1175. |
| [118] | Zhang L, Takahashi D, Hartvig M, Andersen KH (2017) Food-web dynamics under climate change. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 284, 20171772. |
| [119] | Zhao L, Zhang H, O’Gorman EJ, Tian W, Ma A, Moore JC, Borrett SR, Woodward G (2016) Weighting and indirect effects identify keystone species in food webs. Ecology Letters, 19, 1032-1040. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |