



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (10): 1336-1347. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021130 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021130
所属专题: 生物入侵
收稿日期:2021-04-09
接受日期:2021-07-14
出版日期:2021-10-20
发布日期:2021-10-20
通讯作者:
唐文乔,赵亚辉
作者简介:zhaoyh@ioz.ac.cn基金资助:
Xuejian Li1,2, Wenqiao Tang1,*( ), Yahui Zhao2,*(
), Yahui Zhao2,*( )
)
Received:2021-04-09
Accepted:2021-07-14
Online:2021-10-20
Published:2021-10-20
Contact:
Wenqiao Tang,Yahui Zhao
摘要:
海河流域是南水北调中线工程的受水区之一, 为评估中线工程引发海河流域鱼类入侵的风险, 本研究统计了南水北调引水区和受水区海河流域鱼类物种多样性差异, 采用水生生物入侵能力筛查系统(aquatic species invasiveness screening kit, AS-ISK)和外来鱼类入侵风险评估体系筛选引水区有入侵风险的鱼类物种, 并用MaxEnt模型预测有入侵风险的鱼类物种在海河流域的潜在适生区。结果表明, 丁鱥(Tinca tinca)、陈氏新银鱼(Neosalanx tangkahkeii)和大口鲇(Silurus meridionalis)是具有高入侵风险的鱼类, 另有3种鱼类具有中入侵风险, 均需重点监控; 而具入侵风险鱼类的适生区预测结果表明, 海河流域南部的徒骇马颊河水系、海河水系的漳卫南运河以及环渤海地区的河流是极易发生鱼类入侵的水域。因此在海河流域高入侵风险水域应开展持续性的水生生物监测, 针对具有高入侵风险的鱼类应进行早期筛查, 此外在水资源利用和分配上应加强管理, 从源头上杜绝鱼类入侵的发生, 还应尽快开展针对东线工程的鱼类资源调查和入侵风险评估工作。
李雪健, 唐文乔, 赵亚辉 (2021) 南水北调中线工程对海河流域鱼类入侵风险分析. 生物多样性, 29, 1336-1347. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021130.
Xuejian Li, Wenqiao Tang, Yahui Zhao (2021) Risk analysis of fish invasion in Haihe River Basin caused by the central route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1336-1347. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021130.
| 指标名称 Name of the third level index | 分值Score | 指标名称 Name of the third level index | 分值Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 是否存在入侵史 Invasion history: happened or not | 2 | 个体或繁殖体在运输环境的存活率 Survival rate in transportation environment of Individual or propagule | 2 |
| 对入侵地区本地种的影响 Impact on native species of intrusion area | 1 | 迁徙范围 Migration range | 0 |
| 对入侵地区生态环境的影响 Impact on the environment of intrusion area | 1 | 水域可流通性 Water circulatability | 1 |
| 对入侵地区经济贸易的影响 Impact on the economy of intrusion area | 0 | 水域受自然干扰次数 Circumstance of disturbance in water area | 1 |
| 人工养殖规模 Scale of captive breeding | 1 | 被目的性引种与传播的程度 Circumstance of introduction and dissemination | 2 |
| 人工养殖分布 Distribution of captive breeding | 1 | 评估区渔业水产业发展的程度 Circumstance of fishery of evaluation area | 1 |
| 自然生态系统中的分布 Distribution in natural ecosystems | 1 | 其他人为活动强度 Circumstance of other human activities | 1 |
| 对水温的适应情况 Adaptation to water temperature | 2 | 繁殖干扰 Reproductive interference | 0 |
| 对水化因子的适应情况 Adaptation to hydration factors | 2 | 捕食危害 Predation hazard | 1 |
| 对水文条件的适应情况 Adaptation to hydrological conditions | 1 | 竞争压力 Pressure of competition | 1 |
| 存在天然饵料资源的情况 Circumstance of natural bait: exist or not | 2 | 是否为病原体的媒介动物 Vectors of pathogens: yes or no | 0 |
| 存在有效天敌的情况 Circumstance of natural enemies: exist or not | 2 | 对自然景观的影响 Impact on landscape | 0 |
| 存在竞争压力的情况 Circumstance of competitive pressure: exist or not | 2 | 对水环境质量的影响 Impact on water environment | 0 |
| 遗传多样性高低 Circumstance of genetic diversity | 1 | 是否为人畜病原体的媒介动物 Vector animal for human and animal: yes or no | 1 |
| 生长速度 Growth rate | 2 | 个体及其分泌物对人畜的危害 Harm of individuals and their secretions | 0 |
| 初次性成熟年龄 Age of initial sexual maturation | 1 | 对经济活动的影响 Impact on the economy | 1 |
| 繁殖次数 Breeding times | 2 | 引入渠道的规范性 Normalization of the process of introduction | 0 |
| 年繁殖量 Annual reproduction | 2 | 使用程序的规范性 Normalization of procedures | 0 |
| 繁殖方式 Reproduction methods | 0 | 公众对该外来鱼入侵的防范意识 Prevention consciousness of fish invasion | 2 |
| 育幼行为 Child-rearing behavior | 0 | 现有控制技术 Existing control technology | 2 |
| 个体形态特征可分辨程度 Degree of discrimination of individual characteristic | 1 | 控制所需成本 Cost required | 1 |
| 繁殖体形态特征 Morphological characteristics of propagules | 2 | 控制造成的负面效应 Negative effects caused by control | 1 |
表1 丁鱥的三级指标分值
Table 1 The score of the third level index of Tinca tinca
| 指标名称 Name of the third level index | 分值Score | 指标名称 Name of the third level index | 分值Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 是否存在入侵史 Invasion history: happened or not | 2 | 个体或繁殖体在运输环境的存活率 Survival rate in transportation environment of Individual or propagule | 2 |
| 对入侵地区本地种的影响 Impact on native species of intrusion area | 1 | 迁徙范围 Migration range | 0 |
| 对入侵地区生态环境的影响 Impact on the environment of intrusion area | 1 | 水域可流通性 Water circulatability | 1 |
| 对入侵地区经济贸易的影响 Impact on the economy of intrusion area | 0 | 水域受自然干扰次数 Circumstance of disturbance in water area | 1 |
| 人工养殖规模 Scale of captive breeding | 1 | 被目的性引种与传播的程度 Circumstance of introduction and dissemination | 2 |
| 人工养殖分布 Distribution of captive breeding | 1 | 评估区渔业水产业发展的程度 Circumstance of fishery of evaluation area | 1 |
| 自然生态系统中的分布 Distribution in natural ecosystems | 1 | 其他人为活动强度 Circumstance of other human activities | 1 |
| 对水温的适应情况 Adaptation to water temperature | 2 | 繁殖干扰 Reproductive interference | 0 |
| 对水化因子的适应情况 Adaptation to hydration factors | 2 | 捕食危害 Predation hazard | 1 |
| 对水文条件的适应情况 Adaptation to hydrological conditions | 1 | 竞争压力 Pressure of competition | 1 |
| 存在天然饵料资源的情况 Circumstance of natural bait: exist or not | 2 | 是否为病原体的媒介动物 Vectors of pathogens: yes or no | 0 |
| 存在有效天敌的情况 Circumstance of natural enemies: exist or not | 2 | 对自然景观的影响 Impact on landscape | 0 |
| 存在竞争压力的情况 Circumstance of competitive pressure: exist or not | 2 | 对水环境质量的影响 Impact on water environment | 0 |
| 遗传多样性高低 Circumstance of genetic diversity | 1 | 是否为人畜病原体的媒介动物 Vector animal for human and animal: yes or no | 1 |
| 生长速度 Growth rate | 2 | 个体及其分泌物对人畜的危害 Harm of individuals and their secretions | 0 |
| 初次性成熟年龄 Age of initial sexual maturation | 1 | 对经济活动的影响 Impact on the economy | 1 |
| 繁殖次数 Breeding times | 2 | 引入渠道的规范性 Normalization of the process of introduction | 0 |
| 年繁殖量 Annual reproduction | 2 | 使用程序的规范性 Normalization of procedures | 0 |
| 繁殖方式 Reproduction methods | 0 | 公众对该外来鱼入侵的防范意识 Prevention consciousness of fish invasion | 2 |
| 育幼行为 Child-rearing behavior | 0 | 现有控制技术 Existing control technology | 2 |
| 个体形态特征可分辨程度 Degree of discrimination of individual characteristic | 1 | 控制所需成本 Cost required | 1 |
| 繁殖体形态特征 Morphological characteristics of propagules | 2 | 控制造成的负面效应 Negative effects caused by control | 1 |
| 物种 Species | 评估结果 Results | 风险级别 Risk level | 物种 Species | 评估结果 Results | 风险级别 Risk level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丁鱥 Tinca tinca | 1.156 | 高入侵风险 High invasion risk | 宜昌鳅鮀 Gobiobotia filifer | 0.558 | 低入侵风险 Low invasion risk |
| 陈氏新银鱼 Neosalanx tangkahkeii | 1.127 | 中华纹胸鮡 Glyptothorax sinensis | 0.543 | ||
| 大口鲇 Silurus meridionalis | 1.074 | 嘉陵颌须鮈 Gnathopogon herzensteini | 0.515 | ||
| 中华沙塘鳢 Odontobutis sinensis | 0.961 | 中入侵风险 Medium invasion risk | 细纹颌须鮈 Gnathopogon taeniellus | 0.509 | |
| 光泽黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus nitidus | 0.929 | 白缘? Liobagrus marginatus | 0.451 | ||
| 大眼鳜 Siniperca knerii | 0.926 | 拟缘? Liobagrus marginatoides | 0.432 | ||
| 切尾拟鲿 Pseudobagrus truncatus | 0.686 | 低入侵风险 Low invasion risk | 川陕哲罗鲑 Hucho bleekeri | 0.394 | |
| 吻鮈 Rhinogobio typus | 0.684 | 司氏? Liobagrus styani | 0.325 | ||
| 短须颌须鮈 Gnathopogon imberbis | 0.667 | 秦岭细鳞鲑 Brachymystax tsinlingensis | 0.212 |
表2 基于外来鱼类入侵风险评估体系的评估结果
Table 2 The results of risk assessment system for invasion of alien fishes
| 物种 Species | 评估结果 Results | 风险级别 Risk level | 物种 Species | 评估结果 Results | 风险级别 Risk level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丁鱥 Tinca tinca | 1.156 | 高入侵风险 High invasion risk | 宜昌鳅鮀 Gobiobotia filifer | 0.558 | 低入侵风险 Low invasion risk |
| 陈氏新银鱼 Neosalanx tangkahkeii | 1.127 | 中华纹胸鮡 Glyptothorax sinensis | 0.543 | ||
| 大口鲇 Silurus meridionalis | 1.074 | 嘉陵颌须鮈 Gnathopogon herzensteini | 0.515 | ||
| 中华沙塘鳢 Odontobutis sinensis | 0.961 | 中入侵风险 Medium invasion risk | 细纹颌须鮈 Gnathopogon taeniellus | 0.509 | |
| 光泽黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus nitidus | 0.929 | 白缘? Liobagrus marginatus | 0.451 | ||
| 大眼鳜 Siniperca knerii | 0.926 | 拟缘? Liobagrus marginatoides | 0.432 | ||
| 切尾拟鲿 Pseudobagrus truncatus | 0.686 | 低入侵风险 Low invasion risk | 川陕哲罗鲑 Hucho bleekeri | 0.394 | |
| 吻鮈 Rhinogobio typus | 0.684 | 司氏? Liobagrus styani | 0.325 | ||
| 短须颌须鮈 Gnathopogon imberbis | 0.667 | 秦岭细鳞鲑 Brachymystax tsinlingensis | 0.212 |
| 物种 Species | 评估结果 Results | 置信度 Confidence | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRA | Level | BRA + CCA | Level | BRA | CCA | BRA + CCA | |
| 大口鲇 Silurus meridionalis | 48 | 高 High | 60 | 高 High | 0.99 | 0.84 | 0.99 |
| 中华沙塘鳢 Odontobutis sinensis | 37 | 高 High | 43 | 高 High | 0.99 | 0.88 | 0.98 |
| 丁鱥 Tinca tinca | 33 | 高 High | 45 | 高 High | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.99 |
| 陈氏新银鱼 Neosalanx tangkahkeii | 31.5 | 高 High | 43.5 | 高 High | 0.95 | 0.83 | 0.94 |
| 光泽黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus nitidus | 28 | 中 Medium | 32 | 中 Medium | 0.99 | 0.72 | 0.88 |
| 拟缘? Liobagrus marginatoides | 1 | 低 Low | -3 | 低 Low | 0.92 | 0.71 | 0.90 |
| 司氏? Liobagrus styani | 1 | 低 Low | -7 | 低 Low | 0.93 | 0.83 | 0.92 |
| 宜昌鳅鮀 Gobiobotia filifer | 0 | 低 Low | -6 | 低 Low | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.91 |
| 细纹颌须鮈 Gnathopogon taeniellus | -0.5 | 低 Low | -0.5 | 低 Low | 0.91 | 0.75 | 0.89 |
| 秦岭细鳞鲑 Brachymystax tsinlingensis | -1 | 低 Low | -13 | 低 Low | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.95 |
| 切尾拟鲿 Pseudobagrus truncatus | -2.5 | 低 Low | -6.5 | 低 Low | 0.84 | 0.75 | 0.83 |
| 吻鮈 Rhinogobio typus | -3.5 | 低 Low | -7.5 | 低 Low | 0.90 | 0.75 | 0.89 |
| 中华纹胸鮡 Glyptothorax sinensis | -4 | 低 Low | -4 | 低 Low | 0.91 | 0.79 | 0.90 |
| 川陕哲罗鲑 Hucho bleekeri | -5 | 低 Low | -17 | 低 Low | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.97 |
| 大眼鳜 Siniperca knerii | -8 | 低 Low | -6 | 低 Low | 0.99 | 0.75 | 0.96 |
| 短须颌须鮈 Gnathopogon imberbis | -9 | 低 Low | -11 | 低 Low | 0.95 | 0.83 | 0.94 |
| 嘉陵颌须鮈 Gnathopogon herzensteini | -9 | 低 Low | -17 | 低 Low | 0.88 | 0.75 | 0.86 |
| 白缘? Liobagrus marginatus | -10 | 低 Low | -12 | 低 Low | 0.89 | 0.75 | 0.87 |
表3 基于水生生物入侵能力筛查系统(AS-ISK)的评估结果
Table 3 The results of aquatic species invasiveness screening kit V2.3 (AS-ISK)
| 物种 Species | 评估结果 Results | 置信度 Confidence | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRA | Level | BRA + CCA | Level | BRA | CCA | BRA + CCA | |
| 大口鲇 Silurus meridionalis | 48 | 高 High | 60 | 高 High | 0.99 | 0.84 | 0.99 |
| 中华沙塘鳢 Odontobutis sinensis | 37 | 高 High | 43 | 高 High | 0.99 | 0.88 | 0.98 |
| 丁鱥 Tinca tinca | 33 | 高 High | 45 | 高 High | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.99 |
| 陈氏新银鱼 Neosalanx tangkahkeii | 31.5 | 高 High | 43.5 | 高 High | 0.95 | 0.83 | 0.94 |
| 光泽黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus nitidus | 28 | 中 Medium | 32 | 中 Medium | 0.99 | 0.72 | 0.88 |
| 拟缘? Liobagrus marginatoides | 1 | 低 Low | -3 | 低 Low | 0.92 | 0.71 | 0.90 |
| 司氏? Liobagrus styani | 1 | 低 Low | -7 | 低 Low | 0.93 | 0.83 | 0.92 |
| 宜昌鳅鮀 Gobiobotia filifer | 0 | 低 Low | -6 | 低 Low | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.91 |
| 细纹颌须鮈 Gnathopogon taeniellus | -0.5 | 低 Low | -0.5 | 低 Low | 0.91 | 0.75 | 0.89 |
| 秦岭细鳞鲑 Brachymystax tsinlingensis | -1 | 低 Low | -13 | 低 Low | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.95 |
| 切尾拟鲿 Pseudobagrus truncatus | -2.5 | 低 Low | -6.5 | 低 Low | 0.84 | 0.75 | 0.83 |
| 吻鮈 Rhinogobio typus | -3.5 | 低 Low | -7.5 | 低 Low | 0.90 | 0.75 | 0.89 |
| 中华纹胸鮡 Glyptothorax sinensis | -4 | 低 Low | -4 | 低 Low | 0.91 | 0.79 | 0.90 |
| 川陕哲罗鲑 Hucho bleekeri | -5 | 低 Low | -17 | 低 Low | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.97 |
| 大眼鳜 Siniperca knerii | -8 | 低 Low | -6 | 低 Low | 0.99 | 0.75 | 0.96 |
| 短须颌须鮈 Gnathopogon imberbis | -9 | 低 Low | -11 | 低 Low | 0.95 | 0.83 | 0.94 |
| 嘉陵颌须鮈 Gnathopogon herzensteini | -9 | 低 Low | -17 | 低 Low | 0.88 | 0.75 | 0.86 |
| 白缘? Liobagrus marginatus | -10 | 低 Low | -12 | 低 Low | 0.89 | 0.75 | 0.87 |
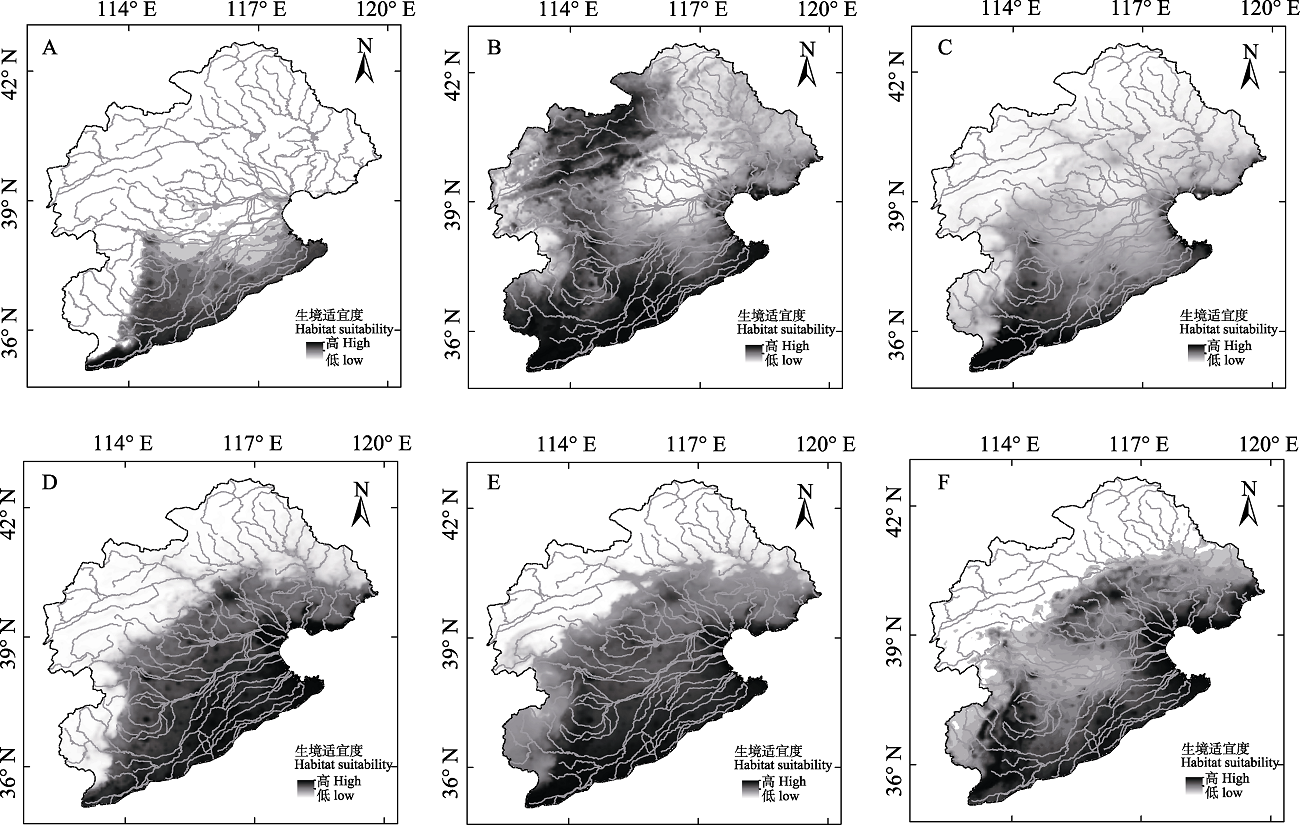
图2 具入侵风险鱼类在海河流域潜在适生区预测结果。A: 大眼鳜; B: 丁鱥; C: 光泽黄颡鱼; D: 中华沙塘鳢; E: 陈氏新银鱼; F: 大口鲇。
Fig. 2 The results of the potential habitat prediction of fish with invasion risk in Haihe River Basin. A, Siniperca knerii; B, Tinca tinca; C, Pelteobagrus nitidus; D, Odontobutis sinensis; E, Neosalanx tangkahkeii; F, Silurus meridionalis.
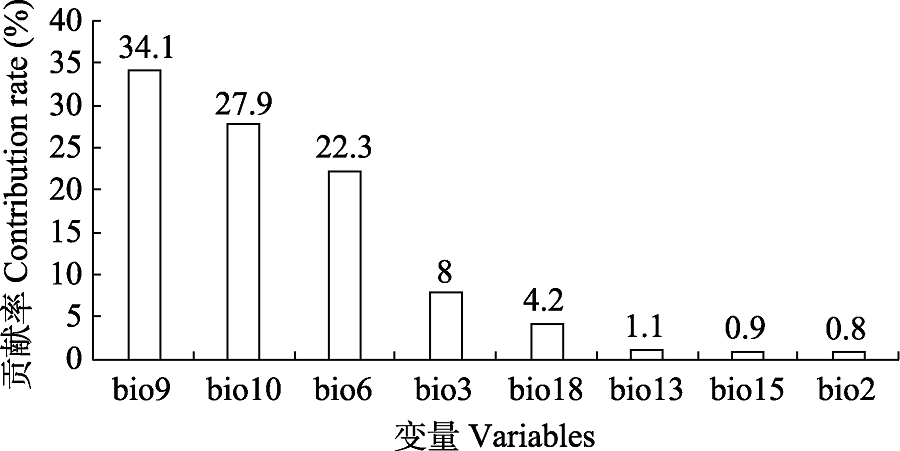
图3 大眼鳜适生区预测结果的环境变量的贡献率。bio9: 最干季平均温度; bio10: 最暖季平均温度; bio6: 最冷月最低温; bio3: 等温性; bio18: 最暖季降水量; bio13: 最湿月降水量; bio15: 降水量变异系数; bio2: 昼夜温差月均值。
Fig. 3 Contribution rate of environmental variables about the potential habitat prediction of Siniperca knerii. bio9, Mean temperature of the driest quarter; bio10, Mean temperature of the warmest quarter; bio6, Min temperature of the coldest month; bio3, Isothermality; bio18, Precipitation of the warmest quarter; bio13, Precipitation of wettest month; bio15, Precipitation seasonality; bio2, Mean diurnal range.
| [1] | An XM (2019) Open development path of Middle Route Project of South-to-North Water Diversion. Journal of Economics of Water Resources, 37(5), 48-53, 72, 79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [安晓明 (2019) 南水北调中线工程开放发展路径研究. 水利经济, 37(5), 48-53, 72, 79.] | |
| [2] | Ashworth W (1986) The Great Lake:An Environmental History. Wayne State University Press, Detroit. |
| [3] |
Austin MP (2002) Spatial prediction of species distribution: An interface between ecological theory and statistical modelling. Ecological Modelling, 157, 101-118.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Chen YR, Yang JX, Li ZY (1998) The diversity and present status of fishes in Yunnan Province. Chinese Biodiversity, 6, 272-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈银瑞, 杨君兴, 李再云 (1998) 云南鱼类多样性和面临的危机. 生物多样性, 6, 272-277.] | |
| [5] | Chen YY (1998) Fauna Sinica · Osteichthyes · Cypriniformes. II. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [陈宜瑜 (1998) 中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲤形目(中卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [6] | Cheng XY, Xu RM (2007) Current status of invasion of exotic animals in China. Bulletin of Biology, 42(9), 1-4, 64. (in Chinese) |
| [成新跃, 徐汝梅 (2007) 中国外来动物入侵概况. 生物学通报, 42(9), 1-4, 64.] | |
| [7] | Chu XL, Zheng BS, Dai DY (1999) Fauna Sinica · Osteichthyes · Siliuriformes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 褚新洛, 郑葆珊, 戴定远 (1999) 中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲇形目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] |
Copp GH, Vilizzi L, Tidbury H, Stebbing P, Tarkan AS, Miossec L, Goulletquer P (2016) Development of a generic decision-support tool for identifying potentially invasive aquatic taxa: AS-ISK. Management of Biological Invasions, 7, 343-350.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Dai YG (2017) Studies on fish fauna of Mengjiang River, Guizhou. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 52, 253-262. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [代应贵 (2017) 贵州蒙江鱼类区系组成及特征分析. 动物学杂志, 52, 253-262.] | |
| [10] | Dou XS (2019) Impact and countermeasures of East Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project on Navigation of the Grand Canal. Transportation Enterprise Management, 34(6), 97-98. (in Chinese) |
| [窦雪松 (2019) 南水北调东线工程对京杭运河航道通航的影响及对策. 交通企业管理, 34(6), 97-98.] | |
| [11] | Dou Y, Wu J, Huang C (2011) Risk assessment system and method for invasion of alien fishes. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 27, 12-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [窦寅, 吴军, 黄成 (2011) 外来鱼类入侵风险评估体系及方法. 生态与农村环境学报, 27, 12-16.] | |
| [12] | Elton CS (1958) The Ecology of Invasions by Animals and Plants. Chapman and Hall, London. |
| [13] | Feng XZ, Gou P, Su J, Fan ZM, Wang YX (2008) Nutrition compositions analysis of wild Tinca tinca L of Ereqsi River, Xinjiang. Science and Technology of Food Industry, (6), 276-279. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [冯新忠, 苟萍, 苏俊, 范镇明, 王咏星 (2008) 额尔齐斯河野生丁鱥营养成分分析. 食品工业科技, (6), 276-279.] | |
| [14] |
George SD, Baldigo BP, Rees CB, Bartron ML, Winterhalter D (2021) Eastward expansion of Round goby in New York: Assessment of detection methods and current range. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 150, 258-273.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Hao CF, Jia YW, Gong JG, Peng H (2010) Analysis on characteristics and rules of climate change of Haihe River Basin in recent 50 years. Journal of China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, 8, 39-43, 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郝春沣, 贾仰文, 龚家国, 彭辉 (2010) 海河流域近50年气候变化特征及规律分析. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 8, 39-43, 51.] | |
| [16] | Hu YC, Li Y, Luo JR, Tan XC (2006) Risk assessment system for alien aquatic animals. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Nature Science Edition), 34(10), 113-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [胡隐昌, 李勇, 罗建仁, 谭细畅 (2006) 水生动物外来物种入侵风险评估系统的建立. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 34(10), 113-115.] | |
| [17] |
Imamura A, Hayami K, Sakata MK, Minamoto T (2020) Environmental DNA revealed the fish community of Hokkaido Island, Japan, after invasion by rainbow trout. Biodiversity Data Journal, 8, e56876.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Interesova E, Vilizzi L, Copp GH (2020) Risk screening of the potential invasiveness of non-native freshwater fishes in the River Ob basin (West Siberian Plain, Russia). Regional Environmental Change, 20, 64.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Kolar CS, Lodge DM (2001) Progress in invasion biology: Predicting invaders. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 16, 199-204.
PMID |
| [20] | Kottelat M, Freyhof J (2007) Handbook of European Freshwater Fishes. Maurice Kottelat, Berlin. |
| [21] | Li MD (2011) The Fishes of Tianjin. Tianjin Science and Technology Press, Tianjin. (in Chinese) |
| [李明德 (2011) 天津鱼类志. 天津科学技术出版社, 天津.] | |
| [22] |
Li S, Chen JK, Wang XM (2016) Global distribution, entry routes, mechanisms and consequences of invasive freshwater fish. Biodiversity Science, 24, 672-685. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[郦珊, 陈家宽, 王小明 (2016) 淡水鱼类入侵种的分布、入侵途径、机制与后果. 生物多样性, 24, 672-685.]
DOI |
|
| [23] | Liu SS (2008) Asymmetric mating interactions drive widespread invasion and displacement in a whitefly. China Basic Science, 10(2), 20-21. (in Chinese) |
| 刘树生 (2008) 非对称交配互作驱动B型烟粉虱的广泛入侵及对土著烟粉虱的取代. 中国基础科学, 10(2), 20-21.] | |
| [24] |
Liu SS, Barro PJD, Xu J, Luan JB, Zang LS, Ruan YM, Wan FH (2007) Asymmetric mating interactions drive widespread invasion and displacement in a whitefly. Science, 318, 1769-1772.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Liu YS, Feng XB, Yang N (2019) Primary thought about ecological water replenishment of the Middle Route Project of South-to-North Water Diversion. Water Resources Development Research, 19(11), 5-7. (in Chinese) |
| [刘远书, 冯晓波, 杨柠 (2019) 对南水北调中线干线工程生态补水的初步思考. 水利发展研究, 19(11), 5-7.] | |
| [26] | Lou CD, Fang X, Wang D (2019) Analysis on influences of the first phase of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project on the ecological environment. Shaanxi Water Resources, (9), 83-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [楼晨笛, 方晓, 王东 (2019) 南水北调中线一期工程对生态环境的影响分析. 陕西水利, (9), 83-86.] | |
| [27] | Mooney HA, Cleland EE (2001) The evolutionary impact of invasive species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 98, 5446-5451. |
| [28] | Pan Y, Cao WX, Xu LP, Yin SR (2006) History and approach of invasion from domestic and abroad fishes. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 21, 72-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [潘勇, 曹文宣, 徐立蒲, 殷守仁 (2006) 国内外鱼类入侵的历史及途径. 大连水产学院学报, 21, 72-78.] | |
| [29] | Pan Y, Cao WX, Xu LP, Yin SR, Bai L (2007) Process, mechanism, and research method of fish invasion. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 18, 687-692. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [潘勇, 曹文宣, 徐立蒲, 殷守仁, 白璐 (2007) 鱼类入侵的过程、机制及研究方法. 应用生态学报, 18, 687-692.] | |
| [30] |
Phillips SJ, Anderson RP, Schapire RE (2006) Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecological Modelling, 190, 231-259.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Pimentel D, Lach L, Zuniga R, Morrison D (2000) Environmental and economic costs of nonindigenous species in the United States. BioScience, 50, 53-65.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Ruebush BC, Sass GG, Chick JH, Stafford JD (2012) In-situ tests of sound-bubble-strobe light barrier technologies to prevent range expansions of Asian carp. Aquatic Invasions, 7, 37-48.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Ruykys L, Ta KAT, Bui TD, Vilizzi L, Copp GH (2021) Risk screening of the potential invasiveness of non-native aquatic species in Vietnam. Biological Invasions, 23, 2047-2060.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Shen ZY, Xiao YC, Ma Y, Chen L (2016) Ecological risk assessment of exotic plant invasion. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 52, 189-195. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈珍瑶, 肖月晨, 马晔, 陈磊 (2016) 外来植物入侵生态风险评价. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 52, 189-195.] | |
| [35] |
Smartt J (2007) A possible genetic basis for species replacement: Preliminary results of interspecific hybridisation between native crucian carp Carassius carassius (L.) and introduced goldfish Carassius auratus (L.). Aquatic Invasions, 2, 59-62.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Sun WT, Liu YT (2010) Research progress of risk analysis of biological invasion. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 26(7), 233-236. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙文涛, 刘雅婷 (2010) 生物入侵风险分析的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 26(7), 233-236.] | |
| [37] | Wang D, Wu J, Dou Y, Huang C (2008) Investigation of exotic cultured fishes in Jiangsu Province and primary evaluation of their invasive risk. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 20(11), 99-102. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王迪, 吴军, 窦寅, 黄成 (2008) 江苏水产养殖鱼类外来物种调查及其生物入侵风险初探. 江西农业学报, 20(11), 99-102.] | |
| [38] | Wang D, Wu J, Dou Y, Huang C (2009) Study on fish environmental risk of allopatry introduced in China domestic. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 37, 8544-8546. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王迪, 吴军, 窦寅, 黄成 (2009) 中国境内异地引种鱼类环境风险研究. 安徽农业科学, 37, 8544-8546.] | |
| [39] | Wang H (2020) The South-to-North Water Diversion Project is getting more and more exciting. China Water Resources, (23), 10-13. (in Chinese) |
| [王慧 (2020) 南水北调大文章越来越精彩. 中国水利, (23), 10-13.] | |
| [40] | Wang L, Gan H, Zhao SX, Wang F, You JJ, Wang L (2009) Ecological and environmental impact analysis of first phase of South-to-North Water Transfer Project on water-recipient areas. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 7(6), 4-7, 53. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汪林, 甘泓, 赵世新, 王芳, 游进军, 王琳 (2009) 南水北调东、中线一期工程对受水区生态环境影响分析. 南水北调与水利科技, 7(6), 4-7, 53.] | |
| [41] | Wang SA, Wang ZM, Li GL, Cao YP, Zhang ZW, Xu XJ, Sun JH (2001) Fauna of Hebei:Fish. Hebei Science & Technology Press, Shijiazhuang. (in Chinese) |
| [王所安, 王志敏, 李国良, 曹玉萍, 张忠文, 徐学军, 孙介华 (2001) 河北动物志:鱼类. 河北科学技术出版社, 石家庄.] | |
| [42] | Wang YC, Sun YL, Zhang J, Wang ZL (2014) Climate change characteristics of Haihe River Basin in recent 51 years. Journal of Tianjin Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 34(4), 58-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王永财, 孙艳玲, 张静, 王中良 (2014) 近51年海河流域气候变化特征分析. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 34(4), 58-63.] | |
| [43] | Wang YS, Yang YY (2005) South-to-North Water Transfer Project of China. Yangtze River, 36(7), 2-5, 71. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汪易森, 杨元月 (2005) 中国南水北调工程. 人民长江, 36(7), 2-5, 71.] | |
| [44] | Wang YZ, Guo SY, Cui WY (2017) Practice and development of rivers and lakes health assessment in Haihe River Basin. Haihe Water Resources, (4), 7-11. (in Chinese) |
| [王乙震, 郭书英, 崔文彦 (2017) 海河流域河湖健康评估的实践与发展. 海河水利, (4), 7-11.] | |
| [45] |
Wei FW, Nie YG, Miao HX, Lu H, Hu YB (2014) Advancements of the researches on biodiversity loss mechanisms. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 430-437. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [魏辅文, 聂永刚, 苗海霞, 路浩, 胡义波 (2014) 生物多样性丧失机制研究进展. 科学通报, 59, 430-437.] | |
| [46] | Xiong F, Li WC, Pan JZ (2008) Present status of alien fishes and analysis of relative problems in Fuxian Lake in Yunnan Province. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 20(2), 92-94, 96. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [熊飞, 李文朝, 潘继征 (2008) 云南抚仙湖外来鱼类现状及相关问题分析. 江西农业学报, 20(2), 92-94, 96.] | |
| [47] | Xiong YH, Qi WG, Wang ZJ (2010) Operation risk study on the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project (Part I): Risk identification in the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 8(3), 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [熊雁晖, 漆文刚, 王忠静 (2010) 南水北调中线运行风险研究(一): 南水北调中线工程风险识别. 南水北调与水利科技, 8(3), 1-5.] | |
| [48] | Xiong YL, Zhao N (2020) Analysis of variation in pan evaporation and its influencing factors in Haihe River Basin. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 18(2), 22-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [熊玉琳, 赵娜 (2020) 海河流域蒸发皿蒸发量变化及其影响. 南水北调与水利科技, 18(2), 22-30.] | |
| [49] | Xu HL (2019) Construction and achievements of flood control, drought relief and disaster reduction systems in the Haihe River Basin. China Flood & Drought Management, 29(10), 61-70. (in Chinese) |
| [徐和龙 (2019) 海河流域防汛抗旱减灾体系建设与成就. 中国防汛抗旱, 29(10), 61-70.] | |
| [50] | Yang JX, Pan XF, Chen XY, Wang XA, Zhao YP, Li JY, Li ZY (2013) Overview of the artificial enhancement and release of endemic freshwater fish in China. Zoological Research, 34, 267-280. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨君兴, 潘晓赋, 陈小勇, 王晓爱, 赵亚鹏, 李建友, 李再云 (2013) 中国淡水鱼类人工增殖放流现状. 动物学研究, 34, 267-280.] | |
| [51] | Yang XL, Wang DL (2007) External invasive animals. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 19(6), 125-127, 130. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨小林, 王德良 (2007) 外来入侵动物. 江西农业学报, 19(6), 125-127, 130.] | |
| [52] | Yin MC (1995) Fish Ecology. China Agricultural Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [殷名称 (1995) 鱼类生态学. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [53] | Yin W, Wang C, Xin XK (2020) Thinkings on water quality management of main channel in Middle Route of South-to-North Water Transfer Project. Yangtze River, 51(3), 17-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [尹炜, 王超, 辛小康 (2020) 南水北调中线总干渠水质管理问题与思考. 人民长江, 51(3), 17-24.] | |
| [54] | Yu X, Wang YH, He HZ, Chen J (2020) Analysis of nutritional components in muscle of hybrid (Tinca tinca & Cyprinus carpio). China Fisheries, (8), 79-81. (in Chinese) |
| [于潇, 王延晖, 贺海战, 陈杰 (2020) 丁鱥鱼与黄河鲤杂交种肌肉营养成分分析. 中国水产, (8), 79-81.] | |
| [55] | Yuan ZJ, Shen YJ, Chu YM, Qi YQ (2009) Variations and distribution of temperature and precipitation of Haihe River Basin in recent 40 years. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 16(3), 24-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [袁再健, 沈彦俊, 褚英敏, 齐永青 (2009) 海河流域近40年来降水和气温变化趋势及其空间分布特征. 水土保持研究, 16(3), 24-26.] | |
| [56] | Yue PQ (2000) Fauna Sinica · Osteichthyes · Cypriniformes. III. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [乐佩琦 (2000) 中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲤形目(下卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [57] | Zhang CG, Shao GZ, Wu HL, Zhao YH, Xing YC, Niu CY (2020) Species Calalogue of China (Vol. 2): Animals, Vertebrates (V), Fishes (II). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张春光, 邵广昭, 伍汉霖, 赵亚辉, 邢迎春, 牛诚祎 (2020) 中国生物物种名录(第二卷): 动物, 脊椎动物(V), 鱼类(II). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [58] | Zhang CG, Zhao YH (2013) Fishes in Beijing and Adjacent Areas. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张春光, 赵亚辉 (2013) 北京及其邻近地区的鱼类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [59] | Zhang DC, Zheng JL (2019) Preliminary study on invasion of alien fish species after construction of hydropower projects. Yangtze River, 50(2), 83-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张登成, 郑娇莉 (2019) 水电工程建设前后外来鱼类入侵问题初步研究. 人民长江, 50(2), 83-89.] | |
| [60] | Zhang J (2008) Biodiversity and conservation of Salangids. Bulletin of Biology, 43(6), 4-6. (in Chinese) |
| [张洁 (2008) 银鱼科鱼类及其物种多样性保护. 生物学通报, 43(6), 4-6.] | |
| [61] | Zhang Q, Hao JF (2011) Research progress on invasion mechanism of alien invasive species. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 39(6), 94-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张巧, 郝建锋 (2011) 外来物种入侵机制的研究进展. 贵州农业科学, 39(6), 94-98.] | |
| [62] |
Zhang XA, Sui XY, Lü Z, Chen YF (2014) A prediction of the global habitat of two invasive fishes (Pseudorasbora parva and Carassius auratus) from East Asia using MaxEnt. Biodiversity Science, 22, 182-188. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[张熙骜, 隋晓云, 吕植, 陈毅峰 (2014) 基于MaxEnt的两种入侵性鱼类(麦穗鱼和鲫)的全球适生区预测. 生物多样性, 22, 182-188.]
DOI |
|
| [63] | Zhang ZG (2017) Artifical propagation technique of Tinca tinca. Ocean and Fishery, (4), 60-62. (in Chinese) |
| [张沾光 (2017) 丁鱥鱼人工繁殖技术. 海洋与渔业, (4), 60-62.] | |
| [64] | Zhao YH, Tang WQ, Zhang CG (2002) Status and protection of fish resources in the Shiwan Dashan Mountains, Guangxi, China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 37(6), 43-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵亚辉, 唐文乔, 张春光 (2002) 广西十万大山地区的鱼类资源现状和保护对策. 动物学杂志, 37(6), 43-47.] | |
| [65] | Zhao YH, Zhang CG (2001) Fish fauna and zoogeographical analysis of Shi Wan Da Shan Mountains, Guangxi, China. Biodiversity Science, 9, 336-344. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵亚辉, 张春光 (2001) 广西十万大山地区的鱼类区系及其动物地理学分析. 生物多样性, 9, 336-344.] | |
| [66] | Zheng HZ, Zhang Z, Wu HM, Lei XH (2016) Study on the daily optimized dispatching and economic operation of cascade pumping stations in water conveyance system. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 47, 1558-1565. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑和震, 张召, 吴辉明, 雷晓辉 (2016) 梯级泵站输水系统日优化调度及经济运行研究. 水利学报, 47, 1558-1565.] | |
| [67] | Zhou HT, Na XD, Zang SY, Xie RF (2016) Applications of maximum entropy (MaxEnt) model in species habitat study. Environmental Science and Management, 41(3), 149-151. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周海涛, 那晓东, 臧淑英, 解瑞峰 (2016) 最大熵(MaxEnt)模型在物种栖息地研究中的应用. 环境科学与管理, 41(3), 149-151.] |
| [1] | 郦珊, 陈家宽, 王小明. 淡水鱼类入侵种的分布、入侵途径、机制与后果[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(6): 672-685. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()