



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 24063. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024063 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024063
彭昀月1,*( )(
)( ), 罗永梅1(
), 罗永梅1( ), 靳彤2(
), 靳彤2( ), 李佳颖3, 陈玉峰4
), 李佳颖3, 陈玉峰4
收稿日期:2024-02-22
接受日期:2024-10-28
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2025-01-05
通讯作者:
* E-mail:
Yunyue Peng1,*( )(
)( ), Yongmei Luo1(
), Yongmei Luo1( ), Tong Jin2(
), Tong Jin2( ), Jiaying Li3, Yufeng Chen4
), Jiaying Li3, Yufeng Chen4
Received:2024-02-22
Accepted:2024-10-28
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-05
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要:
近些年, 我国光伏与风电装机量和发电量迅猛增长, 引发对其生态问题的关注与探讨, 而减缓生态影响的措施和工具方法也亟需更多的认识和应用。本文根据陆上集中式光伏和风电电场的生态影响研究, 综述了国内外光伏与风电电场的生态影响减缓措施, 发现早期合理规划选址可以有效、低成本地规避不利影响, 并从景观角度总结了减缓生态影响的规划方法, 包括用于风险筛查的环境和社会影响评估(environmental and social impact assessment, ESIA)和敏感性地图绘制, 用于综合空间规划的发展系统规划(Development by Design, DbD)、空间规划和敏感性地图绘制结合及可再生能源与生物资源的兼容性计算等方法, 从而依据生态影响和风险进行可再生能源选址。最后, 结合我国国情, 我们建议通过加强光伏和风电场生态影响研究、简化选址流程、强化跨部门协调优化生态友好选址(如废弃矿区再利用)、建立生态监测体系, 并完善政策支持与技术标准, 因地制宜推动创新生态友好型可再生能源发展模式, 确保生态保护措施贯穿项目全周期。
中图分类号:
彭昀月, 罗永梅, 靳彤, 李佳颖, 陈玉峰 (2025) 减缓陆上集中式光伏及风电电场生态影响的早期选址规划方法与工具. 生物多样性, 33, 24063. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024063.
Yunyue Peng, Yongmei Luo, Tong Jin, Jiaying Li, Yufeng Chen (2025) Early siting methods and tools for mitigating ecological impacts of onshore centralized photovoltaics and wind farms. Biodiversity Science, 33, 24063. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024063.
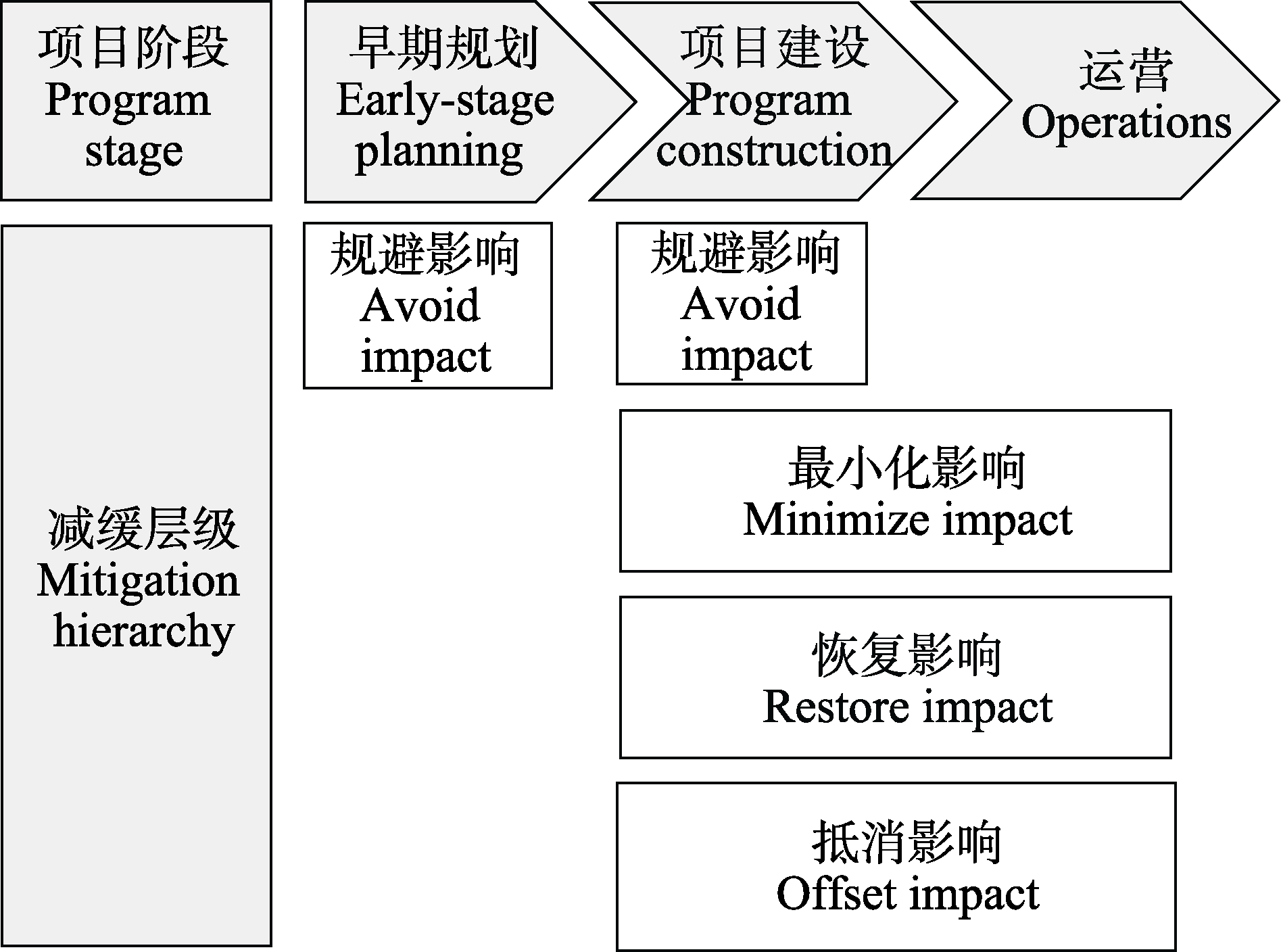
图1 集中式光伏及风电项目开发周期中的减缓措施层级。参考Bennun等(2021)绘制。
Fig. 1 The hierarchy of mitigation measures in the life cycle of centralized large-scale photovoltaics and wind farms, adapted from Bennun et al (2021).
| 工具 Tools | 描述 Description |
|---|---|
| 生物多样性综合评估工具 Integrated Biodiversity Assessment Tool (IBAT) | 提供全球生物多样性空间数据的在线平台, 包括法定保护地、IUCN红色物种名录和全球生物多样性重要区域等。 Online platform for global spatial data on biodiversity, including legally protected areas, the IUCN Red List of Species and globally important areas for biodiversity. |
| 全球生物多样性信息服务网络平台 The Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) | 提供免费获取生物多样性数据的国际网络数据平台。该平台提供各种陆生和水生物种分布数据集, 同时还能追踪物种迁移。 An international web-based data platform that provides free access to biodiversity data. The platform provides datasets on the distribution of a wide range of terrestrial and aquatic species and also tracks species migration. |
| 翱翔鸟类敏感性地图工具 The Soaring Bird Sensitivity Map Tool | 提供东非大裂谷-红海迁徙路线上翱翔鸟类等物种分布信息, 帮助新开发的光伏和风电项目进行负责任地选址决策。 Provide information on the distribution of species such as soaring birds along the East African Rift Valley-Red Sea migration route to help make responsible siting decisions for new photovoltaic and wind power projects. |
| 关键地点网络工具 The Critical Sites Network Tool | 提供非洲和欧亚大陆西部对近300种水鸟至关重要的分布地点信息。 Provides information on distribution sites in Africa and western Eurasia that are critical for nearly 300 species of waterbirds. |
| 保护星球数据库 The Protected Planet Database | 一个可以集中访问世界保护地数据库(World Database of Protected Areas, WDPA)、基于其他有效区域保护措施(OECMs)的数据库、全球保护地管理成效数据库(Global Database on Protected Area Management Effectiveness, GD-PAME)和相关信息的平台。 A platform that provides unified access to the World Database of Protected Areas (WDPA), databases based on other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs), the Global Database on Protected Area Management Effectiveness (GD-PAME) and other related information platforms. |
表1 可再生能源项目生物多样性风险评估相关工具
Table 1 Tools related to biodiversity risk assessment for renewable energy projects
| 工具 Tools | 描述 Description |
|---|---|
| 生物多样性综合评估工具 Integrated Biodiversity Assessment Tool (IBAT) | 提供全球生物多样性空间数据的在线平台, 包括法定保护地、IUCN红色物种名录和全球生物多样性重要区域等。 Online platform for global spatial data on biodiversity, including legally protected areas, the IUCN Red List of Species and globally important areas for biodiversity. |
| 全球生物多样性信息服务网络平台 The Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) | 提供免费获取生物多样性数据的国际网络数据平台。该平台提供各种陆生和水生物种分布数据集, 同时还能追踪物种迁移。 An international web-based data platform that provides free access to biodiversity data. The platform provides datasets on the distribution of a wide range of terrestrial and aquatic species and also tracks species migration. |
| 翱翔鸟类敏感性地图工具 The Soaring Bird Sensitivity Map Tool | 提供东非大裂谷-红海迁徙路线上翱翔鸟类等物种分布信息, 帮助新开发的光伏和风电项目进行负责任地选址决策。 Provide information on the distribution of species such as soaring birds along the East African Rift Valley-Red Sea migration route to help make responsible siting decisions for new photovoltaic and wind power projects. |
| 关键地点网络工具 The Critical Sites Network Tool | 提供非洲和欧亚大陆西部对近300种水鸟至关重要的分布地点信息。 Provides information on distribution sites in Africa and western Eurasia that are critical for nearly 300 species of waterbirds. |
| 保护星球数据库 The Protected Planet Database | 一个可以集中访问世界保护地数据库(World Database of Protected Areas, WDPA)、基于其他有效区域保护措施(OECMs)的数据库、全球保护地管理成效数据库(Global Database on Protected Area Management Effectiveness, GD-PAME)和相关信息的平台。 A platform that provides unified access to the World Database of Protected Areas (WDPA), databases based on other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs), the Global Database on Protected Area Management Effectiveness (GD-PAME) and other related information platforms. |
| 工具 Tools | 描述 Description |
|---|---|
| 生态系统服务工具包 Ecosystem Services Toolkit (EST) | 定性或定量评估生态系统服务的工具。 Tools for qualitative or quantitative assessment of ecosystem services. |
| 保护地效益评估工具 Protected Areas Benefits Assessment Tool (PA-BAT) | 从不同利益相关方的角度出发, 标准化地评估保护地生态系统效益。 Standardized assessment of ecological benefits of protected areas from different stakeholders’ perspectives. |
| 生态系统服务站点评估工具包 Toolkit for Ecosystem Service Site-based Assessment (TESSA) | 基于GIS的在景观尺度上模拟生态系统服务的工具包, 指导识别特定地点的重要生态环境服务、获取测量所需的数据。 A GIS-based toolkit for modeling ecosystem services at the landscape scale, guiding the identification of important ecosystem services at a given site and the acquisition of data needed for measurement. |
| 生态系统服务人工智能平台 Artificial Intelligence for Ecosystem Services (ARIES) | 为综合模拟和评估社会、经济和环境状况而设计的生态系统服务模型平台。 An ecosystem services modeling platform designed for integrated simulation and assessment of social, economic and environmental conditions. |
| 自然成本评估 Co | 用于生态系统空间分析和评估人类干预的影响的基于Web的建模工具, 可评估生态系统、保护优先级、经济价值、协同效益、压力和威胁等。 Web-based modeling tools for spatial analysis of ecosystems and assessment of the impact of human interventions, assessing ecosystems, conservation priorities, economic values, co-benefits, pressures and threats. |
| 生态系统服务评估软件 Integrate Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Tradeoffs (InVEST) | 用于在不同情景下量化模拟生态系统服务过程、评估生态系统服务及其经济价值的软件模型, 可支持生态系统管理和决策。 Software models for the quantitative simulation of ecosystem service processes and the valuation of ecosystem services and their economic value under different scenarios to support ecosystem management and decision-making. |
| 生态系统服务多尺度综合模型 Multiscale Integrated Models of Ecosystem Services (MIMES) | 旨在整合不同生态和经济模型来模拟生态系统服务过程的模型。 Models designed to integrate different ecological and economic models to simulate ecosystem service processes. |
| 生态系统服务社会价值评估模型 Social Values for Ecosystem Services (SolVES) | 基于ArcGIS的生态系统服务社会价值评估模型, 可识别和分析群体社会价值认知, 如美学和娱乐价值。 An ArcGIS-based model for assessing the social value of ecosystem services identifies and analyzes group perceptions of social value, such as aesthetic and recreational values. |
| 水世界 WaterWorld | 采用定量的生物物理指标模拟在当前条件下以及不同情景下相关的水文服务, 可了解水文生态系统服务、水资源和水相关的风险因素。 The use of quantitative biophysical indicators to model hydrological services under current conditions and relevant hydrological services under different scenarios provides insights into hydrological ecosystem services, water resources and water-related risk factors. |
| Aqueduct水风险图集 Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas | 全球水资源风险地图工具, 帮助用户了解全球水资源风险和机遇。 Global Water Risk Map tool to help users understand global water risks and opportunities. |
| 拉姆萨尔湿地信息服务 Ramsar Site Information Service | 查找全球所有国际重要湿地信息的平台。 A platform to find information on all internationally important wetlands around the world. |
| 减缓和监测实践工具 Mitigation and Monitoring Practices Tool | 通过分类和筛选减缓和监测措施来评估管理成效的工具。 Tools for assessing management effectiveness by categorizing and screening mitigation and monitoring measures. |
| 巴黎实践——探索全球清洁能源潜力 Paris to Practice—Exploring Global Clean Energy Potential | 探索在改造后的土地上开发低影响可再生能源的潜力, 实现国家自主贡献目标(NDCs)。 Explore the potential for low-impact renewable energy development on converted lands to meet Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) targets. |
| 为风能正确选址 Site Wind Right | 一种基于GIS的交互式在线地图技术, 结合风力资源、野生动物栖息地、土地利用和基础设施的数据, 提供美国中部大平原17个州的风能选址决策信息。 A GIS-based interactive online mapping technology that combines wind resource, wildlife habitat, land use, and infrastructure data to provide information for wind energy siting decisions in 17 states in the Central Great Plains of the United States. |
表2 其他减缓光伏与风电电场生态影响的早期选址规划工具
Table 2 Other tools related to early siting strategies of mitigating ecological impacts of photovoltaics and wind farms
| 工具 Tools | 描述 Description |
|---|---|
| 生态系统服务工具包 Ecosystem Services Toolkit (EST) | 定性或定量评估生态系统服务的工具。 Tools for qualitative or quantitative assessment of ecosystem services. |
| 保护地效益评估工具 Protected Areas Benefits Assessment Tool (PA-BAT) | 从不同利益相关方的角度出发, 标准化地评估保护地生态系统效益。 Standardized assessment of ecological benefits of protected areas from different stakeholders’ perspectives. |
| 生态系统服务站点评估工具包 Toolkit for Ecosystem Service Site-based Assessment (TESSA) | 基于GIS的在景观尺度上模拟生态系统服务的工具包, 指导识别特定地点的重要生态环境服务、获取测量所需的数据。 A GIS-based toolkit for modeling ecosystem services at the landscape scale, guiding the identification of important ecosystem services at a given site and the acquisition of data needed for measurement. |
| 生态系统服务人工智能平台 Artificial Intelligence for Ecosystem Services (ARIES) | 为综合模拟和评估社会、经济和环境状况而设计的生态系统服务模型平台。 An ecosystem services modeling platform designed for integrated simulation and assessment of social, economic and environmental conditions. |
| 自然成本评估 Co | 用于生态系统空间分析和评估人类干预的影响的基于Web的建模工具, 可评估生态系统、保护优先级、经济价值、协同效益、压力和威胁等。 Web-based modeling tools for spatial analysis of ecosystems and assessment of the impact of human interventions, assessing ecosystems, conservation priorities, economic values, co-benefits, pressures and threats. |
| 生态系统服务评估软件 Integrate Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Tradeoffs (InVEST) | 用于在不同情景下量化模拟生态系统服务过程、评估生态系统服务及其经济价值的软件模型, 可支持生态系统管理和决策。 Software models for the quantitative simulation of ecosystem service processes and the valuation of ecosystem services and their economic value under different scenarios to support ecosystem management and decision-making. |
| 生态系统服务多尺度综合模型 Multiscale Integrated Models of Ecosystem Services (MIMES) | 旨在整合不同生态和经济模型来模拟生态系统服务过程的模型。 Models designed to integrate different ecological and economic models to simulate ecosystem service processes. |
| 生态系统服务社会价值评估模型 Social Values for Ecosystem Services (SolVES) | 基于ArcGIS的生态系统服务社会价值评估模型, 可识别和分析群体社会价值认知, 如美学和娱乐价值。 An ArcGIS-based model for assessing the social value of ecosystem services identifies and analyzes group perceptions of social value, such as aesthetic and recreational values. |
| 水世界 WaterWorld | 采用定量的生物物理指标模拟在当前条件下以及不同情景下相关的水文服务, 可了解水文生态系统服务、水资源和水相关的风险因素。 The use of quantitative biophysical indicators to model hydrological services under current conditions and relevant hydrological services under different scenarios provides insights into hydrological ecosystem services, water resources and water-related risk factors. |
| Aqueduct水风险图集 Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas | 全球水资源风险地图工具, 帮助用户了解全球水资源风险和机遇。 Global Water Risk Map tool to help users understand global water risks and opportunities. |
| 拉姆萨尔湿地信息服务 Ramsar Site Information Service | 查找全球所有国际重要湿地信息的平台。 A platform to find information on all internationally important wetlands around the world. |
| 减缓和监测实践工具 Mitigation and Monitoring Practices Tool | 通过分类和筛选减缓和监测措施来评估管理成效的工具。 Tools for assessing management effectiveness by categorizing and screening mitigation and monitoring measures. |
| 巴黎实践——探索全球清洁能源潜力 Paris to Practice—Exploring Global Clean Energy Potential | 探索在改造后的土地上开发低影响可再生能源的潜力, 实现国家自主贡献目标(NDCs)。 Explore the potential for low-impact renewable energy development on converted lands to meet Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) targets. |
| 为风能正确选址 Site Wind Right | 一种基于GIS的交互式在线地图技术, 结合风力资源、野生动物栖息地、土地利用和基础设施的数据, 提供美国中部大平原17个州的风能选址决策信息。 A GIS-based interactive online mapping technology that combines wind resource, wildlife habitat, land use, and infrastructure data to provide information for wind energy siting decisions in 17 states in the Central Great Plains of the United States. |
| [1] |
Arlidge WNS, Bull JW, Addison PFE, Burgass MJ, Gianuca D, Gorham TM, Jacob C, Shumway N, Sinclair SP, Watson JEM, Wilcox C, Milner-Gulland EJ (2018) A global mitigation hierarchy for nature conservation. Bioscience, 68, 336-347.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Bennun L, van Bochove J, Ng C, Fletcher C, Wilson D, Phair N, Carbone G (2021) Mitigating Biodiversity Impacts Associated with Solar and Wind Energy Development: Guidelines for Project Developers. IUCN, Gland & The Biodiversity Consultancy, Cambridge. https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/2021-004-En.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-05) |
| [3] | Blaydes H, Potts SG, Whyatt JD, Armstrong A (2021) Opportunities to enhance pollinator biodiversity in solar parks. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 145, 111065. |
| [4] | Cameron D, Parker S, Cohen B, Randall J, Christian B, Moore J, Crane L, Morrison S (2012) Solar Energy Development in the Western Mojave Desert: Identifying Areas of Least Environmental Conflict for Siting and A Framework for Compensatory Mitigation of Impacts. https://www.scienceforconservation.org/assets/downloads/West-Mojave-Assessment-2012.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-05) |
| [5] | Dhar A, Naeth MA, Jennings PD, Gamal El-Din M (2020) Perspectives on environmental impacts and a land reclamation strategy for solar and wind energy systems. Science of the Total Environment, 718, 134602. |
| [6] | Drewitt AL, Langston RHW (2006) Assessing the impacts of wind farms on birds. Ibis, 148, 29-42. |
| [7] | EC (European Commission) (2020) Guidance Document on Wind Energy Developments and EU Nature Legislation. Publications Office of the European Union. https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2779/457035. (accessed on 2024-02-05) |
| [8] | Gamboa G, Munda G (2007) The problem of windfarm location: A social multi-criteria evaluation framework. Energy Policy, 35, 1564-1583. |
| [9] | Gasparatos A, Doll CNH, Esteban M, Ahmed A, Olang TA (2017) Renewable energy and biodiversity: Implications for transitioning to a green economy. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 70, 161-184. |
| [10] | Gove B, Williams LJ, Beresford AE, Roddis P, Campbell C, Teuten E, Langston RHW, Bradbury RB (2016) Reconciling biodiversity conservation and widespread deployment of renewable energy technologies in the UK. PLoS ONE, 11, e0150956. |
| [11] |
Greif S, Siemers BM (2010) Innate recognition of water bodies in echolocating bats. Nature Communications, 1, 107.
PMID |
| [12] | Hamed TA, Alshare A (2022) Environmental impact of solar and wind energy—A review. Journal of Sustainable Development of Energy, Water and Environment Systems, 10, 1-23. |
| [13] | Hernandez RR, Easter SB, Murphy-Mariscal ML, Maestre FT, Tavassoli M, Allen EB, Barrows CW, Belnap J, Ochoa-Hueso R, Ravi S, Allen MF (2014) Environmental impacts of utility-scale solar energy. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 29, 766-779. |
| [14] | Hernandez RR, Hoffacker MK, Murphy-Mariscal ML, Wu GC, Allen MF (2015) Solar energy development impacts on land cover change and protected areas. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 13579-13584. |
| [15] | Hise C, Obermeyer B, Ahlering M, Wilkinson J, Fargione J (2022) Site wind right: Identifying low-impact wind development areas in the central United States. Land, 11, 462-462. |
| [16] | Hötker H, Thomsen K-M, Jeromin H (2006) Impacts on Biodiversity of Exploitation of Renewable Energy Sources: The Example of Birds and Bats. Nature and Biodiversity Conservation Union (NABU), Bergenhusen. https://eolien-biodiversite.com/IMG/pdf/englischewindkraftstudie_1252510701.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-05) |
| [17] | Hui JX, Han X, Cui C, Luo YM (2020) Eco-friendly onshore wind power development policy recommendations. Electric Power Equipment Management, (9), 27-28, 37. (in Chinese) |
| [惠婧璇, 韩雪, 崔成, 罗永梅 (2020) 生态友好的陆上风电发展政策建议. 电力设备管理, (9), 27-28, 37.] | |
| [18] | IEA (International Energy Agency) (2024) Renewables 2023: Analysis and Forecast to 2028. https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/96d66a8b-d502-476b-ba94-54ffda84cf72/Renewables_2023.pdf. (accessed on 2024-09-12) |
| [19] | Jaber S (2013) Environmental impacts of wind energy. Journal of Clean Energy Technologies, 1, 251-254. |
| [20] | Kagan RA, Viner TC, Trail PW, Espinoza EO (2014) Avian Mortality at Solar Energy Facilities in Southern California: A Preliminary Analysis. National Fish and Wildlife Forensics Laboratory, Ashland. https://efiling.energy.ca.gov/GetDocument.aspx?tn=202538. (accessed on 2024-02-05) |
| [21] | Kati V, Kassara C, Vrontisi Z, Moustakas A (2021) The biodiversity-wind energy-land use nexus in a global biodiversity hotspot. Science of the Total Environment, 768, 144471. |
| [22] | Kiesecker JM, Evans JS, Fargione J, Doherty K, Foresman KR, Kunz TH, Naugle D, Nibbelink NP, Niemuth ND (2011) Win-win for wind and wildlife: A vision to facilitate sustainable development. PLoS ONE, 6, e17566. |
| [23] | Kim JY, Koide D, Ishihama F, Kadoya T, Nishihiro J (2021) Current site planning of medium to large solar power systems accelerates the loss of the remaining semi-natural and agricultural habitats. Science of the Total Environment, 779, 146475. |
| [24] | Li LM (2022) Artificial intelligence makes wind farms less of a “bird killer”. China Energy News, 2022-06-27. (in Chinese) |
| [李丽旻 (2022) 人工智能让风电场不再是“鸟类杀手”. 中国能源报, 2022-06-27.] | |
| [25] | Liang YJ, Liu LJ (2018) Integration of ecosystem services and landscape pattern: A review. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 7159-7167. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [梁友嘉, 刘丽珺 (2018) 生态系统服务与景观格局集成研究综述. 生态学报, 38, 7159-7167.] | |
| [26] | Liechti F, Guélat J, Komenda-Zehnder S (2013) Modelling the spatial concentrations of bird migration to assess conflicts with wind turbines. Biological Conservation, 162, 24-32. |
| [27] | Liu Y, Zhang RQ, Ma XR, Wu GL (2020) Combined ecological and economic benefits of the solar photovoltaic industry in arid sandy ecosystems. Journal of Cleaner Production, 262, 121376. |
| [28] |
Marques AT, Santos CD, Hanssen F, Muñoz AR, Onrubia A, Wikelski M, Moreira F, Palmeirim JM, Silva JP (2020) Wind turbines cause functional habitat loss for migratory soaring birds. Journal of Animal Ecology, 89, 93-103.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Montag H, Parker DG, Clarkson T (2016) The effects of solar farms on local biodiversity: A comparative study. Clarkson and Woods, Somerset & Wychwood Biodiversity, Devon. https://www.clarksonwoods.co.uk/download/Solar_Farms_Biodiversity_Study.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-05) |
| [30] | Nazir MS, Ali N, Bilal M, Iqbal HMN (2020) Potential environmental impacts of wind energy development: A global perspective. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 13, 85-90. |
| [31] | Neugarten RA, Langhammer PF, Osipova E, Bagstad KJ, Bhagabati N, Butchart SH, Dudley N, Elliott V, Gerber LR, Arrellano CG, Ivanić K-Z, Kettunen M, Mandle L, Merriman JC, Mulligan M, Peh KS, Raudsepp-Hearne C, Semmens DJ, Stolton S, Willcock S (2018) Tools for Measuring, Modelling, and Valuing Ecosystem Services. IUCN, Gland. https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/PAG-028-En.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-05) |
| [32] | Obermeyer B, Manes R, Kiesecker J, Fargione J, Sochi K (2011) Development by design: Mitigating wind development’s impacts on wildlife in Kansas. PLoS ONE, 6, e26698. |
| [33] | Parker G, Green L (2014) Biodiversity Guidance for Solar Developments. Building Research Establishment (BRE) National Solar Centre, Watford. https://files.bregroup.com/bre-co-uk-file-library-copy/filelibrary/pdf/Brochures/NSC-Biodiversity-Guidance.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-05) |
| [34] |
Peng YY, Luo YM, Xu ZN, Jin T (2024) Ecological impacts of centralized large-scale photovoltaics and wind farms: Progress and prospects. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23212. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[彭昀月, 罗永梅, 徐泽楠, 靳彤 (2024) 集中式大型光伏及风电电场生态影响研究: 进展与展望. 生物多样性, 32, 23212.]
DOI |
|
| [35] |
Rehbein JA, Watson JEM, Lane JL, Sonter LJ, Venter O, Atkinson SC, Allan JR (2020) Renewable energy development threatens many globally important biodiversity areas. Global Change Biology, 26, 3040-3051.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Sayed ET, Wilberforce T, Elsaid K, Rabaia MKH, Ali Abdelkareem M, Chae KJ, Olabi AG (2021) A critical review on environmental impacts of renewable energy systems and mitigation strategies: Wind, hydro, biomass and geothermal. Science of the Total Environment, 766, 144505. |
| [37] | Stevens L, Anderson B, Cowan C, Colton K, Johnson D (2017) The Footprint of Energy: Land Use of U.S. Electricity Production. https://docs.wind-watch.org/US-footprints-Strata-2017.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-05) |
| [38] | Stoms DM, Dashiell SL, Davis FW (2013) Siting solar energy development to minimize biological impacts. Renewable Energy, 57, 289-298. |
| [39] | Száz D, Mihályi D, Farkas A, Egri Á, Barta A, Kriska G, Robertson B, Horváth G (2016) Polarized light pollution of matte solar panels: Anti-reflective photovoltaics reduce polarized light pollution but benefit only some aquatic insects. Journal of Insect Conservation, 20, 663-675. |
| [40] | Tang BJ, Wu DH, Zhao X, Zhou T, Zhao WQ, Wei H (2017) The observed impacts of wind farms on local vegetation growth in Northern China. Remote Sensing, 9, 332. |
| [41] | Taylor R, Conway J, Gabb O, (2014) Potential Ecological Impacts of Ground-mounted Photovoltaic Solar Panels in the UK: An Introduction and Literature Review. BSG Ecology, Newport. https://www.bsg-ecology.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Solar-Panels-and-Wildlife-Review-2019.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-05) |
| [42] | The Nature Conservancy, Energy Research Institute of National Development and Reform Commission (2015) Eco-friendly Spatial Distribution of Renewable Energy Development in China (2016-2030). (in Chinese) |
| [ 大自然保护协会, 国家发展和改革委员会能源研究所 (2015) 生态友好的中国可再生能源发展空间布局(2016-2030).] https://www.tnc.org.cn/Upload/File/202205/20220530141102_4571.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-05) | |
| [43] | Wang SF, Wang SC, Smith P (2015) Ecological impacts of wind farms on birds: Questions, hypotheses, and research needs. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 44, 599-607. |
| [44] | Weis T, Doukas A, Anderson K, Howell G (2010) Landowners’ Guide to Wind Energy in Alberta. Pembina Institute: Calgary. https://www.pembina.org/reports/alberta-landowners-guide-wind.pdf. (accessed on 2024-02-05) |
| [45] | Wu JG, Gong Q, Wang Y (2023) The impacts of wind farms on ecosystems, biodiversity, and the environments. Ecological Economy, 39, 167-178. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴建国, 巩倩, 王阳 (2023) 风电场对生态系统、生物多样性及环境的影响. 生态经济, 39, 167-178.] | |
| [46] | Zhu YK, Li YD, Lou YQ, Zhou J, Sun YH (2016) Impact of wind farm on birds and mitigation strategies. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 51, 682-691. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱永可, 李阳端, 楼瑛强, 周江, 孙悦华 (2016) 风力发电对鸟类的影响以及应对措施. 动物学杂志, 51, 682-691.] |
| [1] | 彭昀月, 罗永梅, 徐泽楠, 靳彤. 集中式大型光伏及风电电场生态影响: 进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23212-. |
| [2] | 刘向, 张鹏, 刘建全. 无机肥料是青海塔拉滩光伏电站植被恢复过程中的限制性因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 22100-. |
| [3] | 张立博, 李春荣, 陈国远, 刘方正, 罗建武, 周越, 冯春婷, 王伟. 江苏盐城滨海地区风机对鸟类的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22173-. |
| [4] | 干晓静, 李博, 陈家宽, 马志军. 生物入侵对鸟类的生态影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(5): 548-557. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn