《中国生物物种名录(2023版)》报告中国现有高等植物38,844种, 比2021版增加了557种, 增量部分除了过往的漏载物种之外, 还包括部分新发表的物种和新名称变动(The Biodiversity Committee of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2023)。这些新物种和名称变动分散在各种植物学期刊和专著中, 需要及时收集整理, 并在具体类群研究专家的指导下尽快收录于中国生物物种名录之中。2000年以来, 中国平均每年发表220个维管植物新分类群、发现32个国家级新记录, 并有310个植物名称发生变化(Du et al, 2020)。2020年中国新发表高等植物312种, 国家级新记录48个; 2021年新发表高等植物289种, 国家级新记录62个; 年度植物名称新增和变动的数量占全国总植物物种数量的1.5% (杜诚等, 2021, 2022)。由于国际性的植物名称索引, 如International Plant Names Index (IPNI,
1 数据来源和处理方法
本文系统检索和整理了曾经发表植物类群或名称的228种期刊和新出版的相关书籍, 并通过中国知网(
2 2022年度中国植物新分类群及名称变动情况
2.1 植物新分类群的基本状况
仅从数据来看, 2022年中国植物新物种和种下分类群的发表数量为488个, 达到了历史极值, 占当年全球植物新分类群(2,396个)数量的20.4%。但其中有182个新分类群(175种1杂交种1亚种5变种)是中国台湾退休学者应绍舜在自行编印的电子出版物New Taxa New Names中发表的, 除2019年的第1卷外, 2020-2021年发布的卷册因使用了不规范的国际标准书号(ISBN)而属于无效发表。2022年应绍舜重新给后续卷册申请了独立的ISBN号, 进而使得2020-2022年出版的卷册重新成为有效发表的载体, 但有效发表日期全部集中在了2022年。为了避免大量数据对年度物种数据造成冲击, 造成数据失真, 同时由于该电子出版物上发表的物种没有经过同行评议, 因此本数据集仅收录其中合格发表的名称, 而不将其纳入下文中的数据分析。
306个新分类群中有155个在发表时提供了除形态学信息之外的分子系统学、染色体、微形态、基因组等方面的证据, 综合性证据的使用率超过50%, 较2021年(38.4%)有了进一步的提高。此外, 306个新分类群中有165个依据IUCN标准评估了濒危等级, 其中极危(CR) 46个、濒危(EN) 18个、易危(VU) 25个、近危(NT) 3个、无危(LC) 17个、数据缺乏(DD) 56个。新发表的类群中有89种(占比29.1%)在发表时被认为处于受威胁状态, 较2021年受威胁种占比(26.3%)进一步提高。
2.2 发表的高阶新分类群
2022年中国高等植物共发表了12个新属(与历年持平), 其中苔藓植物3个, 石松类和蕨类植物1个, 被子植物8个, 所有新属的发表均提供了详细的分子系统学证据。另外还有1个新族和1个新组被发表。由于次级分类单位往往在科属的系统订正类文献中出现, 容易被漏载, 所以未来还有增加的可能。2022年中国高等植物新发表的新属和其他高阶类群见附录2。
2.3 新分类群所属的科属统计
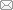
2022年发表的新种及种下分类群隶属于83科171属, 科级水平(图1)主要集中在苦苣苔科(28种1亚种)、兰科(20种3杂交种3变型)、菊科(17种)、毛茛科(11种1变种)、报春花科(10种), 属级水平主要集中在凤仙花属(Impatiens, 8种2变种)、秋海棠属(Begonia, 8种)、薹草属(Carex, 7种1变种)、卷柏属(Selaginella, 7种)、报春花属(Primula, 7种)、耳蕨属(Polystichum, 7种)、小檗属(Berberis, 7种)、报春苣苔属(Primulina, 6种)、马铃苣苔属(Oreocharis, 6种)。发表5个新分类群以上的科和3个新分类群以上的属及其包含的物种分别见附录3和附录4。
图1
图1
2022年发表5个以上中国植物新分类群的科
Fig. 1
Families of more than five new taxa described from China in 2022
2.4 新分类群和新记录种的地理分布
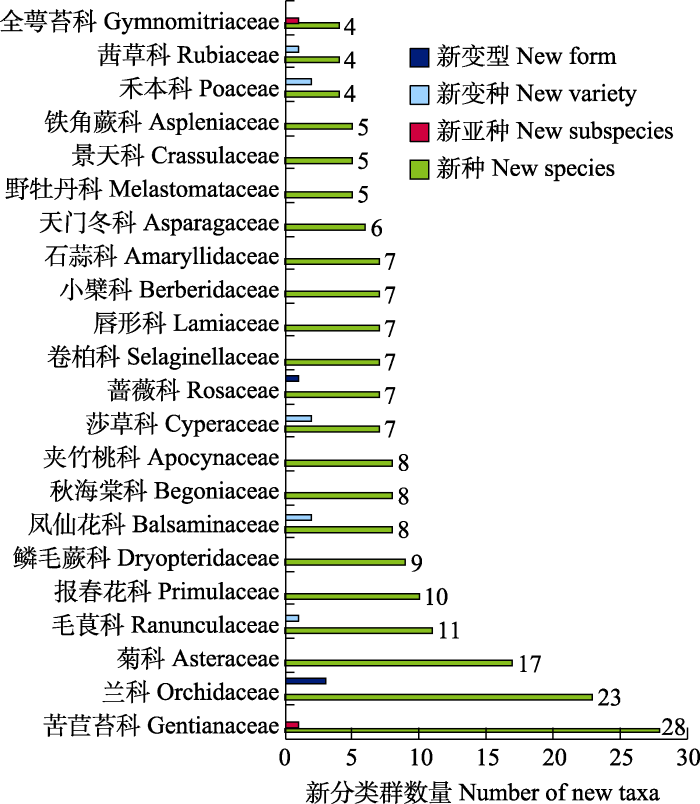
2022年发表的新种及种下分类群和国家级新记录种主要分布在云南(67种2杂交种1亚种1变种2变型11新记录)、四川(38种1亚种1变种1变型2新记录)、西藏(35种1亚种2变种19新记录)、广西(35种1新记录)、贵州(24种)等西南省区(图2)。云南省仍稳居中国植物新种和新记录种发现的第一位; 贵州省新种发现数量排序首次进入第5名, 显示了学者对贵州丰富的喀斯特地貌区域植物的关注; 北京、天津、宁夏、吉林、香港和澳门没有关于新分类群和国家级新记录种的报道。各省发表的新分类群和新记录物种见附录5。
图2
图2
2022年中国各省区发表的新分类群和国家级新记录物种数量(北京、天津、宁夏、吉林、香港、澳门等无新分类群或新记录物种)
Fig. 2
The provincial number of Chinese new taxa and national new record species published in 2022 (Beijing, Tianjin, Ningxia, Jilin, Hong Kong, and Macau without new taxa or new record are not included)
新分类群发现最多的县级单位是墨脱, 2022年共记录了18个新分类群和6个国家级新记录种, 发现新分类群较多的县级单位还有麻栗坡、仁化、康定、易门、文山、荔波、环江、错那等, 发现新记录种较多的县级单位有吉隆、聂拉木等。
2.5 中国植物名称的其他变动
2022年涉及的中国植物新组合(等级)名称有122个, 新名称有11个, 集中在大戟科(31个)、豆科(17个)、百合科(12个)、平藓科(11个)、柏科(5个)、唇形科(5个)等少数几个科, 73.6%的名称的发表是基于分子系统学证据综合研究进行的物种归属处理。这样的处理一般只带来属名的变动, 对物种数量无影响。
2022年有103个植物名称被处理为76个物种的异名, 这些异名中除去代表相同实体的名称外还有91个名称被归并。此外还有4个物种从其他物种独立出来, 这些分类学名称处理造成物种数量减少11个。
2022年高等植物净增加346个分类群, 占全国高等植物总量的0.89%。当年度新发表的研究论文和专著中的名称组合、异名归并等分类学处理导致240个高等植物名称发生了变动, 占全国高等植物总数的0.62%, 与上年数据基本持平。总体植物名称变化率为1.5%, 值得引起相关学者重视。
2.6 发表中国植物新分类群和名称的学者
2022年发表的306个中国高等植物新分类群由258个中外作者团队发表。其中215个中国作者团队发表了252个新分类群, 25个外国作者团队发表了29个新分类群, 18个中外合作团队发表了其余的25个新分类群。这些中外作者团队中有中国学者359人, 外国学者51人。2022年发表中国植物新分类群数量最多的中国学者是金孝锋(发表12个新分类群), 外国学者是Souravjyoti Borah和Julian F. Harber (各发表7个新分类群)。
2022年中国高等植物的133个新组合和新名称由51个中外作者团队发表。其中30个中国作者团队发表了50个名称, 13个外国作者团队发表了75个名称, 8个中外合作团队发表了其余的8个名称。这些中外作者团队中有中国学者64人, 外国学者35人。2022年发表中国植物新组合及新名称数量最多的中国学者是宋柱秋(发表6个名称), 外国学者是Adrianus C. Bouman (发表30个名称)。
2022年参与中国高等植物命名的学者有473人, 其中中国学者393人, 而第一次参与命名的有111人, 这些新增学者的详细资料和标准拼写见附录6。
2.7 发表中国高等植物名称的出版物
2022年发表中国植物名称相关内容的书籍有1部; 期刊有62种, 共发表相关文章403篇。306个新分类群发表在1部书籍和44种期刊之中, 其中发表新分类群最多的期刊是PhytoKeys (81个)和Phytotaxa (79个), 其他发表新分类群较多的期刊还有Taiwania、Plant Diversity、Nordic Journal of Botany、《广西植物》等, PhytoKeys发表的中国植物新分类群数量首次超过Phytotaxa。
3 中国植物名称索引介绍
在连续发布中国植物新物种及名称变动报告的基础上, 中国植物分类学文献研究团队整合了2000年以来所有涉及到中国植物的新分类群、国家级新记录、名称变动、异名处理、名称订正、排除分布、重新发现以及模式化的信息, 建立了中国植物名称索引(Chinese Plant Name Index, CPNI,
附录 Supplementary Material
附录1 2022年中国植物新分类群和新名称变化数据集
Appendix 1 Data of new taxa and name changes for Chinese plants in 2022
附录2 2022年发表的中国植物高阶新分类群
Appendix 2 New higher taxa of Chinese plants in 2022
附录3 2022年发表中国植物5个分类群以上的科及所包含的类群
Appendix 3 Families of more than five new taxa described from China in 2022 and the taxa included
附录4 2022年发表中国植物3个分类群以上的属及所包含的类群
Appendix 4 Genera of more than three new taxa described from China in 2022 and the taxa included
附录5 2022年中国有新分类群和新记录物种发表的28个省级行政区的植物分布情况
Appendix 5 Distribution of new taxa and new record taxa published by 28 provinces in China in 2022
附录6 2022年中国植物新分类群学名中新增的中国作者名录
Appendix 6 List of newly added Chinese authors in the scientific names of new taxa of Chinese plants in 2022
参考文献
Twenty years of Chinese vascular plant novelties, 2000 through 2019
DOI:10.1016/j.pld.2020.08.004
[本文引用: 3]

From 2000 to 2019, 11,895 new names or new additions to the Chinese vascular flora were proposed by 4226 individuals (4086 articles and 140 books), as documented in the Chinese Plant Names Index (CPNI). During those 20 years, 4407 new taxa of vascular plants were described from China, including 7 new families, 132 new genera, 3543 new species, 68 new subspecies, 497 new varieties and 160 new forms. Additionally, 3562 new combinations and names at new rank and 306 new replacement names were also proposed. Among these various new names were 150 invalid names and 108 illegitimate names, including some that have not been resolved. Six hundred and forty three vascular plants were reported as new to China, while 2349 names were reduced to synonyms of 1406 taxa. The data show that the Chinese flora increased in size at the rate of about 200 taxa annually during those years. Despite the increased attention given to biodiversity in recent years, the evidence indicates that a large number of species in China have yet to be discovered. Further basic investigation of the Chinese flora is needed. Additionally, in the past two decades only 8.5% of the newly published species have been based on molecular evidence, but in the past five years such data have increased significantly, reaching about 20%. Molecular data will undoubtedly become increasingly significant in the discovery of new species in the coming years. Yunnan, Guangxi, Sichuan, Xizang and Taiwan were important sources of new discoveries, with more than 3300 new taxa and records from these five provinces. By area, Taiwan and Hainan, two islands in southern China, have the highest density of newly discovered species. Regional plant surveys are still needed, especially in areas in the southwest and on the southern islands.
Annual report of new taxa and new names for Chinese plants in 2020
中国植物新分类群、新名称2020年度报告
2021 annual report on new taxa and nomenclatural changes of Chinese plants
中国植物新分类群、新名称变化2021年年度报告