中国拥有长约18,000 km的大陆海岸线, 沿海分布岛屿6,500多个, 管辖海域面积约470万km2 (张庆君和赵良波, 2018)。在地理学气候带上, 中国海域纵跨温带、暖温带、亚热带和热带; 在水文环境上, 中国近海拥有黑潮暖流、黄海冷水团以及其他独特的沿岸流、上升流、环流等; 在水文地貌上, 中国陆地沿岸形成了与海流相呼应的独特的河口、海湾、砂滩、红树林沼泽以及潮间带等多种环境。广阔的海域面积、多变的气候类型、复杂的地理条件为中国孕育了丰富的海洋生物资源, 造就了中国海洋生物多样性的总体格局。这种生物多样性格局使得中国海洋成为重要的海洋生物多样性资源宝库, 同时也提供了丰富的实地考察研究空间(陈清潮, 1997; 李纯厚和贾晓平, 2005)。我国学者曾对中国的海洋生物多样性从不同领域和研究方法上进行过多次总结和探讨(权洁霞等, 1999; 王安利等, 2000; 刘瑞玉, 2011; 邵广昭, 2011)。
近10年来, 随着国家经济的快速发展, 我国海洋生物多样性的研究和保护越发受到重视。《生物多样性》期刊先后组织了以“海洋生物普查” (CoML)计划中国区海洋生物多样性为主题的专辑(孙军, 2011)和以全球变化下的海洋多样性为主题的专辑(孙军等, 2016)。两期专辑阐明了中国海洋生物多样性研究的基本情况。此后其他的海洋类期刊也陆续出版了相关的以海洋生物多样性为主题的中英文专辑, 如: 以中国近海新物种报道为主题的Acta Oceanologica Sinica专辑(Sun, 2018); 以中国海底栖生物为主题的《海洋与湖沼》专辑(徐奎栋, 2020); 以印太交汇区海洋生物多样性中心形成演化过程为主题的《海洋与湖沼》专辑(陈楠生和王凡, 2021); 以保护大黄海生态系统为主题的Acta Oceanologica Sinica专辑(Sun et al, 2022)等。
本文着眼于近10年我国在海洋生物多样性研究上的新进展, 从遗传、物种以及生态系统3个层次依次对海洋生物多样性进行了总结, 同时应用文献计量软件VOSviewer对发表的相关研究成果进行了分析。所涉及的内容既包括有关经济发展过程中的人为扰动, 如过度捕捞、污染物排放、微塑料等造成海洋生物多样性丧失的研究, 又涵盖了全球气候变化, 如海水表层暖化和酸化直接或间接影响海洋生物群落结构改变的研究。本文最终统筹了中国海洋生物多样性保护的成就并展望了学科未来的发展方向。
1 中国近海遗传多样性研究
遗传多样性通常指群落内不同种群之间或一个种群内不同个体的遗传变异(夏铭, 1999)。自20世纪90年代以后, 分子生物学技术开始被应用到海洋生物群落结构分析中, 当时研究的焦点主要集中在具有保守序列的16S rDNA上(柳承璋等, 2002)。基因组学(genomic)和后基因组学(post-genomic)的发展使我们可以在群落水平上研究微生物的遗传多样性, 从系统进化的层面探究海洋生物多样性(孙军, 2011)。对于海洋生物来说, 遗传标记是研究海洋生物遗传和变异的基本方法和手段(王惠君等, 2018)。随着生物学的快速发展, 遗传标记的种类已经从形态学、细胞遗传学、生物化学发展到如今的分子生物学领域。近10年来中国海洋浮游生物遗传多样性正处在热点研究的快速发展阶段, 新技术的出现和研究海域的拓展使得中国海洋生物学家对海洋生物类群遗传多样性的研究获得了较为瞩目的成果。分子生物学技术的快速发展将海洋生物遗传多样性的研究带入了新的发展阶段, 一系列分子标记方法使人们更容易从DNA分子水平获取信息(崔朝霞等, 2011)。
1.1 浮游生物
分子生物学技术与浮游植物遗传多样性的紧密结合主要体现在分子生态学的研究上, 得益于遗传标记方法的快速迭代, 尤其是20世纪80年代左右出现的DNA分子标记技术, 分子方法在浮游植物生态学的研究领域硕果累累。第一代分子标记以限制性片段长度多态性(RFLP)为代表, 在当前海洋生物资源开发利用的基因工程中有着广泛的应用。李炜等(2013)利用PCR-RFLP技术, 并结合16S rRNA基因文库对亚历山大藻的藻际细菌多样性进行了研究, 结果表明这些细菌可能在赤潮的生消过程中起着重要的调控作用。第二代分子标记基于简单重复序列的多态性, 以简单重复序列分析(SSR)为代表, 其根据DNA简单序列的多态性来进一步分析浮游植物的遗传变化。第三代分子标记以单核苷酸多态性(SNP)为代表, 以高通量测序技术为基础的最新一代分子标记技术能够更大范围地帮助分析浮游植物的物种组成、系统进化方向等群落生态学的内容(李祎等, 2013)。过去我国对于真核微生物中的浮游植物多样性知之甚少, 对浮游生物的群落研究多基于传统的显微镜观察方法, 因此主要集中在某些容易观察的生物类群上, 例如桡足类、纤毛虫、甲藻、硅藻链状群体等有限的微型真核生物类群, 特别是由于缺乏合适的研究方法, 对超微型和微型浮游植物的研究并不充分, 而分子生物学技术的应用使得形态分类学上难以区分的浮游植物物种得到了有效的辨识。Chen等(2021)通过形态观察和高通量测序技术相结合的实验方法对比了胶州湾浮游植物群落多样性和物种丰富度, 发现高通量测序元编码结果远多于形态学观察的结果, 这说明部分物种在形态学观察中可能被忽视, 而高通量测序技术为浮游植物物种鉴定提供了分子描述, 从而弥补了这一缺陷。目前, 基于形态学的分类鉴定方法结合基因组学、转录组学、蛋白质组学以及整合了这几种组学方法的整合组学, 来研究海洋自然群落环境中浮游植物的物种组成、群落结构及其生态功能, 已逐渐成为浮游植物遗传多样性的研究热点之一。
相对于浮游植物, 浮游动物遗传多样性的研究则更加充分。近10年来分子生物学技术的发展使得许多在形态分类学上难以确定进化位置的浮游动物可通过系统发生学(phylogenetics)的手段来分析其系统发育关系。Gao等(2017)提取了1,700多种纤毛虫的基因组DNA, 利用核糖体小亚基RNA (SSU rRNA)对标记基因进行了测序, 最终基于基因序列数据并结合形态分类学特征的分析, 完成了对纤毛虫目2/3物种的系统发育研究。这对帮助厘清纤毛虫这一高度分化生物类群的系统发育进化关系具有重要意义, 并且在新型基因标记选择和拓扑结构优化理论上存在指导作用。李超伦等(2011)对DNA条形码在浮游动物生态学上的应用进行了比较全面的总结, 分析了DNA条形码在浮游动物分类鉴定(例如, 种群鉴定、新种和隐形种的发现)以及食物网营养关系研究方面区别于传统光学显微镜方法的优势。季莹莹等(2019)基于28S rDNA分析了南海刺长腹剑水蚤(Oithona setigera)的单倍体多样性和种群遗传结构, 发现该物种可以实现远距离扩散且容易受到南海海流影响, 并推断其种群遗传结构可能是由生殖隔离造成的。浮游动物分子标记技术运用较为成熟的主要有核糖体DNA (rDNA)、微卫星、核糖体RNA (rRNA)、线粒体细胞色素C氧化酶第一亚基(COI)等, 它们在浮游动物种类鉴定和进化的研究中发挥了重要作用。DNA条形码、高通量测序技术、宏条形码等已逐渐成为研究浮游动物群落遗传多样性以及系统发育的有力工具。
1.2 底栖生物
随着分子生物学技术的发展, DNA条形码技术的引进为底栖生物多样性研究带来了新手段, 但我国目前这方面的应用仍有局限性(杨梅等, 2018), 表现在研究成果主要围绕一些经济物种、潮间带和近海常见物种展开。董志国等(2013)发现中国沿海三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)拥有较高的遗传多样性。张志伟等(2010)研究了我国沿海不同地理类群原种文蛤(Meretrix meretrix)的遗传多样性, 结果表明各底栖种群的遗传多样性较高, 具有较大的改良潜力, 其中广西北海种群最适合作为选择育种的基础群。Li等(2020)研究了浅水萨氏真蛇尾(Ophiura sarsii)黄海种群的遗传多样性, 揭示了其系统发育。此外, 也有少数涉及深海冷泉大型底栖动物群落基因多样性的研究, 扩展了国内相关研究的空间范围(Yao et al, 2022)。在微型底栖生物方面, 龚骏等(2013)介绍了海岸带沉积物中氮循环功能微生物基于16S rRNA基因的物种多样性, 以及nifH、amoA等关键功能基因的多样性。
1.3 游泳生物
线粒体DNA多态性标记是DNA序列分析技术的重要分子标记方法之一, 线粒体DNA有严格遵循母系遗传、无遗传重组等优点, 为游泳生物遗传结构及多样性研究提供了重要载体。其中COI基因分子标记在鱼类群体与进化遗传中应用广泛, 在物种鉴定(梁日深等, 2021)、群落结构分布调查(Shan et al, 2021)、基因测序(Li et al, 2019)等方面有着重要作用, 为新物种的记录提供了科学依据(张国庆等, 2022)。RAPD技术不需要设计特殊引物, 能够更为便捷地扩增整个基因组, 广泛应用于鱼类的遗传多样性检测, 郑天伦等(2013)利用RAPD分子标记对鮸鱼(Miichthys miiuy)野生群体和养殖群体的遗传多样性进行研究, 发现鮸鱼的大部分遗传变异存在于种群内, 仅10.32%的变异来自群体间。相比较于线粒体Cytb基因序列分析, RAPD技术在研究斜带石斑鱼(Epinephelus coioides)种内遗传变异方面具有更高的灵敏性和多态性(陈兴汉等, 2014)。微卫星具有分布密度大、高度杂合、扩增稳定等特点, 多次应用于海洋生物遗传多样性的研究中。谷德贤等(2021)利用微卫星分子标记分析了渤海湾5个海域的口虾蛄(Oratosqilla oratoria)遗传多样性, 结果表明这5个群体遗传多样性水平较高。此外, 生物信息学在游泳动物遗传多样性的研究中也有所建树, 如王海山等(2022)利用生物信息学研究了鲹科鱼类的线粒体基因组, 分析了不同属间亲缘关系的远近。
1.4 大型藻类
生活环境、生活周期、遗传变异等因素会导致大型海藻的外形发生变化, 这给依据形态特征的经典分类学工作带来巨大困难。最近10年, 经典分类与分子手段结合进行大型海藻鉴定成为新趋势。例如, 姚雪等(2011)研究发现UPA (universal plastid amplicon)、COI、rbcL、18S rRNA 4个基因片段具有较高的通用性, 在我国常见大型海藻中扩增效果较好, 其中rbcL和UPA较适合作为鉴定大型红藻的分子标记(Du et al, 2015)。在绿藻的分类鉴定中, tufA、rbcL、ITS、18S rDNA的应用较多(丁兰平等, 2012), 中国首次记录的长茎葡萄蕨藻(Caulerpa lentillifera)便是通过测定tufA和rbcL基因证实其分支单系性(Gao et al, 2020)。尽管中国大型海藻多样性研究在近10年飞速发展, 但仍然存在许多问题。由于我国沿海经济的发展, 大型海藻资源受到较大破坏, 导致大型海藻的物种多样性降低(张才学等, 2020), 大型海藻分布的潮间带环境复杂, 潮差根据季节、月份变化较大, 没有固定规律, 对修复工作的开展有较大影响。同时, 分类学人才流失严重, 经典的形态鉴定法与分子手段存在一定冲突(丁兰平等, 2011)。因此, 要保护沿岸地区大型海藻的栖息环境, 应该对其生长海域的各项理化指标做好监测, 并建设人工藻礁, 丰富大型海藻物种多样性(杨晓龙等, 2018)。同时要重视分类学、吸引分类学人才, 培养知识储备丰富的高水平研究者。在分子系统发育学上, 要筛选合适的分子标记, 构建真实的物种树(丁兰平等, 2022)。
2 中国近海物种多样性研究
2.1 浮游生物
当前中国海洋浮游生物多样性正处在热点研究的快速发展阶段, 近10年来对海洋浮游生物各种类群的物种多样性研究取得了较为瞩目的成果。围绕浮游植物这一主题, 我国研究人员在渤海、黄海、东海、南海等海域(王雨等, 2011; 郭术津等, 2013, 2014; 刘海娇等, 2015)以及中国众多沿岸海湾环境中开展了研究, 并逐渐聚焦到太平洋、印度洋等世界性的大洋海域, 重点分析和研究了多种不同海域中浮游植物的物种组成和地理时空条件下的分布差异情况及其对环境因子的响应。Wang等(2022)就环境因素和水层混合对孟加拉湾浮游植物群落结构的影响进行了研究, 共鉴定出276种浮游植物, 并发现蓝藻丰度明显受到海水垂直混合的影响。陈卓等(2018)对热带西太平洋的浮游植物的物种组成、优势种以及群落多样性情况进行了初步调查。这类研究为我国对大洋生态系统物种水平多样性的理解提供了基础资料, 并为进一步探索大洋浮游植物群落组成做了重要补充。在这些基础研究的支持下, 中国海洋生物分类研究在浮游植物领域已出版了《中国海藻志》6卷15册。根据我们研究团队的不完全统计, 我国已记录的海洋浮游植物物种多达2,788种, 其中以硅藻纲和甲藻纲居多, 分别为1,879种和577种。近10年来, 一些极端环境或极特殊海洋环境中的浮游植物物种多样性研究成为热点, 如热带珊瑚礁海域、深海等海域(柯志新等 2011; 栾青杉等, 2012; 张武昌等, 2014), 这些工作填补了我国在这些偏远区域海洋浮游植物物种多样性的记录空白。过去我国研究人员受限于深海探测技术能力和研究经费的不足, 对深海的研究进步缓慢。随着我国自行研制的载人深潜器“蛟龙号”的技术突破, 使得海山生态系统的研究在近10年得到了突飞猛进的发展。2014-2019年, 中国科学院海洋研究所开展了5个航次的大规模深海海山生物调查, 调查中新增海山生物以及潜在的细菌90余种, 中国学者发表的海山新分类群包括: 海绵1新属5新种、珊瑚虫纲3新种、软体动物2新种、甲壳动物5新种、棘皮动物海参1新种(徐奎栋等, 2020)。这些工作填补了中国海洋浮游生物在地域上物种多样性的研究空白。随着统计学学科不断与海洋生物学、生态学等学科交叉融合, 利用生态动力学模型分析海洋生物物种多样性特征以及水文环境的变化趋势逐渐成为该领域的一大研究热点。Chen等(2018)使用连续特征建模方式, 通过假设无限丰富度和大小分布的方差表示浮游植物多样性, 研究了浮游植物物种多样性对生产力的影响。其结果表明在相对稳定的条件下, 较小种的分布其贡献的初级生产力可以提高, 同时也证明了物种的性状优化有益于提高生物的适应能力。在这种条件下, 生物群落的物种多样性越高其对环境变化的适应能力也就越强。Flombaum等(2013)提出了海洋微藻的谱系定量生态位模型, 从而回答了蓝藻门中的原绿球藻(Prochlorococcus)和聚球藻(Synechococcus)在当前以及未来全球性细胞丰度和分布的问题。
确定浮游生物的分布是研究海洋浮游生物物种多样性的重要任务之一, 这方便我们确定具体海域的浮游生物的研究内容以及开发利用潜力(张武昌等, 2021)。浮游动物通过内部各类群的差异性来体现自身多样性的特点, 不过某一生境中浮游动物的类群组成在短时间内往往是稳定且不易改变的, 因此, 体现浮游动物的物种多样性首先应该要体现研究海域及生境的差异性(徐兆礼, 2011)。全球气候正在发生大范围的变化, 近年来, 有研究证明极地地区海冰的覆盖范围是影响浮游生物群落组成、生物多样性和群落初级生产力的主要因素(Lin et al, 2021)。20世纪以来地球海水温度升高、海冰大量减少给极地海洋生物多样性带来了不同程度的影响。牟文秀等(2021)对南极夏季浮游动物的群落结构进行了基础资料的研究, 发现极地地区主要由桡足类、磷虾、毛颚类、被囊动物组成, 其中桡足类占据绝对优势, 并发现南极周边海流的运动过程是浮游动物群落分布模式的主要控制因素。近年来, 中国科学家对极地地区的研究热度逐渐升温, 这一选择是具有前瞻性的长远战略眼光。在世界资源逐步匮乏的现代社会, 极地地区蕴含的丰富矿产、海洋生物等资源或许将是人类走向未来的重要物质支撑, 未来极地海洋的深入研究可能成为适应全球气候变化的重要选择。
随着海洋生态学理论的不断发展进步, 研究人员越来越重视浮游动物在能量流动和物质循环方面发挥的承上启下的调控作用, 并且更加注重浮游动物的生态功能。Sikder等(2019)在中国黄海沿岸水域进行水质状况评价研究的同时, 通过分析纤毛虫营养-功能类群的评价模式在不同污染梯度范围内出现的显著变化, 发现功能型原生动物类群的生态特征可用于海洋生态系统水质状况的评价。在物种组成上, 我国研究人员对中国海域浮游动物的种类数进行了补充和修订, 目前已记录了1,911种浮游动物(孙军等, 2019)。这些工作发掘了更大尺度、更加特殊的海洋生态环境与浮游动物之间的内在联系并补充了对浮游动物各类群的了解, 从而逐渐揭示浮游动物种类组成与不同生境之间的紧密关联, 将浮游动物的物种多样性研究提升到一个更加完整的层次上。
2.2 底栖生物
近10年, 海洋底栖生物物种多样性的研究已经由单纯的记录描述转入底栖群落与多种环境因子间的耦合研究阶段。张敬怀(2014)探讨了河口近岸大型底栖动物物种多样性的空间变化规律, 结果表明物种多样性自河口向近岸及向深水有先升高后降低的趋势。Xu等(2014)研究了大型底栖动物群落物种多样性对富营养化胁迫的响应。将环境因子, 如水动力条件、盐度、深度、温度、氧含量等与底栖动物物种多样性联合起来(Dou et al, 2016; Arbi et al, 2017)。随着经济的快速发展, 环境问题越发凸显, 底栖物种多样性对水产养殖(张莹等, 2011)、围海造陆(马长安等, 2012; Yang et al, 2016)、渔业捕捞(韩庆喜等, 2011)、热污染(赵升等, 2013; Sun et al, 2022)等人为扰动的响应成为研究热点。在生态压力日益紧迫的背景下, 红树林人工种植恢复、人工鱼礁、生态保护区等生态恢复工程取得了一定效果。唐以杰等(2012)研究发现人工恢复红树林植被的过程中大型底栖动物物种多样性快速增长。孙习武等(2011)报道了海州湾大型底栖动物物种多样性在人工鱼礁投放后呈现逐年上升的趋势。
随着技术水平的进步和底栖学科的发展, 我国研究人员的研究空间已经从近岸拓展至大洋, 从陆架延伸到了深海。Wang等(2014)和Liu等(2019)先后在白令海开展工作, 发现白令海陆架大型底栖生物群落结构具有丰度高、生物量大、生产力高、异质性强的特点, 但其生态系统稳定性很容易受物种损失的影响。Liu等(2015)调查了南大洋南设得兰群岛潮间带的大型底栖动物, 发现在砾石沉积物中的群落具有最高的物种多样性。“蛟龙号”深潜器的成功入海标志着我国底栖生物多样性研究已经打开了迈向深海未知研究空间的新篇章, Yao等(2022)使用遥控深潜设备调查了冷泉的底栖物种多样性, 共鉴定出5门12科12种大型底栖动物。Dong等(2021)报道了“深海勇士”号载人潜水器在南海海马冷泉获得的底栖动物分布信息。这些研究成果丰富了有关深海物种的资料。
2.3 游泳生物
我国20世纪40年代开始对游泳动物分类进行研究, 近10年发展迅速。鱼类是游泳动物的主要组成部分, 由于其巨大的生物量以及重要的经济价值, 在海洋生态系统中发挥着关键作用。科研人员对游泳动物物种多样性的研究主要集中于群落结构和多样性分布的时空变化, 时间跨度长, 调查区域广泛而全面。吕振波等(2012)和朱剑等(2016)调查了中国沿海鱼类的群落结构与分布, 为其多样性研究与保护提供了科学依据。对虾蟹等甲壳类群落及其与环境因子关系的研究也不断更新(罗西玲等, 2015; 吴强等, 2018)。在对游泳动物时空变化进行探究的同时, 相应的研究方法也在不断进步。Zhang等(2019)将回声探测仪与中水拖网结合, 调查了南海中上层游泳动物的群落结构与生物量, 对该海域生物多样性有了更全面的认识。麻秋云等(2015)利用碳氮同位素对胶州湾游泳生物的食物网营养位置进行研究, 构建了胶州湾食物网的连续营养谱。宋伦等(2013)采用ABC曲线法(abundance biomass comparison curves)和粒径谱理论对鸭绿江口近岸海域多样性水平和稳定性状况等进行了分析, 发现游泳生物群落主要以小型个体为主, 稳定性较差。
2.4 大型藻类
不同区系大型海藻物种多样性的研究内容同样集中于群落组成和分布特征。潮间带作为海陆交界地带, 具有很高的生物多样性, 众多学者对潮间带大型海藻多样性进行了调查分析, 对明确中国沿岸大型海藻多样性以及资源保护具有重要意义(陈自强等, 2013; 张才学等, 2020)。除了现场采样调查外, 也可利用遥感等方法对大型藻类的组成分布进行调查, 如陈莹等(2020)基于GOCI卫星数据对黄海海域绿潮进行了监测。姚启学等(2016)使用ArcGIS软件进行距离分析和地形分析, 并分别结合藻类调查数据对其分布进行研究。吴祖立和章守宇(2019)指出, 在台风“海葵”的风浪作用下, 枸杞岛大型底栖海藻的优势种和生物量有所减少, 并提出投放抗风浪礁体的措施。人类活动和气候变化的影响会破坏大型海藻的多样性, 利用遥感等方法加强大面积监测海藻分布、探究海藻对环境变化的适应机制, 有助于潮间带海藻场的恢复和重建。
3 中国近海生态系统多样性研究
海洋生态系统是地球上面积最大且结构最复杂的生态系统, 也是地球生态环境的调节器和人类生命支持系统的重要组成部分。海洋生态系统按海区划分, 可以分为浅海生态系统、深海生态系统、大洋生态系统、火山口生态系统、河口生态系统、海湾生态系统、上升流生态系统等。按生物群落划分, 可以分为红树林生态系统、珊瑚礁生态系统、海草床生态系统等, 这些类型在我国均有分布。位于海岸带的红树林、珊瑚礁和海草床等典型生态系统蕴藏着丰富的生物多样性, 深海生态系统更是海洋生物多样性的宝库。近年来海洋生态系统的健康状况得到了广泛关注, 滨海湿地的开发利用、近海石油开发、高密度海水养殖等人类活动不同程度地改变了当地海洋生态系统的结构和功能, 围填海工程直接侵占了生物栖息地, 导致生境破碎, 对海洋生物多样性造成威胁(杜建国等, 2011)。
红树林生态系统生境特殊, 是世界上最富多样性、生产力最高的海洋生态系统之一, 具有重要的生态、社会和经济价值, 是研究人员研讨植物耐盐抗性、改良盐碱地的良好材料。截至2019年, 我国红树林面积为2.89万ha, 近10年来总体面积有所增加, 但仍小于20世纪50年代的约5万ha (耿国彪, 2022)。红树林生态系统是高度动态和异质的系统, 需要进行长周期、大范围的监测, 除了理化指标, 水体中的浮游植物同样是监测的重点。通过评估浮游植物群落结构长周期的时空分布和多样性水平变化, 可以监测甚至预测红树林生态系统的健康程度(刘玉和黄玉山, 1995; 王雨等, 2010; 高宇和林光辉, 2018)。海洋中微塑料对海洋生态系统的污染同样值得关注, 作为近些年才被提出的新型污染物, 其对红树林生态系统健康的影响有待进一步的系统普查, 以探究红树林生态系统对其降解能力和在富集过程中对生物和环境的影响(李一璠等, 2022)。
珊瑚礁生态系统被称为海洋中的“热带雨林”, 生物多样性极高。受全球气候变化以及人类活动的影响, 珊瑚礁生态系统受到不同程度的破坏, 珊瑚礁的修复至关重要。随着渔业技术的发展, 人类的捕捞活动造成的渔业诱导进化导致鱼类资源向小型化、繁殖力下降的趋势发展, 不利于群落稳定。大型年长鱼类在种群的季节性繁殖和维护群落稳定性上起主导作用, 对所处的生态系统有更强的适应性, 更有利于物种多样性的维持。尤其是珊瑚礁生态系统中的鱼类功能群, 年长的鱼类对维持珊瑚礁正常生长的生态作用将越发明显(于道德等, 2021)。对珊瑚礁生态系统结构和生物多样性水平的评估, 慢慢从特定物种或单个生态系统修复工程向大尺度的生态修复转变, 系统修复理论、技术体系及其应用有待进一步探索提升(龙丽娟等, 2019)。
红树林、珊瑚礁和海草床通常在地理位置上相邻, 三者相互联系又相互区分, 关系十分复杂, 受到物种迁徙、营养循环以及广泛的物理性质影响等。我国在对受损海洋生态系统的修复工作中采取了多种举措进行资源的整合, 既有共性上的整体规划, 又有针对各自结构、功能上的特点, 有的放矢地开展海洋生态系统环境修复工作。参照未被干扰的同类型生态系统, 采取生物修复、人工移植等方式, 从试点区域到全面协同修复(王丽荣等, 2018)。
深海生态系统同样面临一系列挑战, 如深海生物多样性下降、深海资源开采带来的生态破坏、陆源污染物等。深海生物多样性的丧失可能会损害深海生态系统的功能和可持续性(Danovaro et al, 2008)。虽然我国深海探测技术起步较晚, 但近10年在对深海的探索中取得了可喜的成果。目前, 我国拥有常压潜水装置、水下无人无缆水下机器人等深海探测装备, “蛟龙号”载人潜水器可以到达海底7,000 m的深度, “奋斗号”载人潜水器更是成功坐底深度10,909 m的马里亚纳海沟, “国之重器”的研发展示了我国在深海探测技术上的突飞猛进, 也为研究深海生物多样性奠定了基础。我国研究人员可以利用深海探测设备在空间及时间尺度上进一步认识深海生物多样性以及深海中广泛分布的海山、冷泉、热液等生态环境, 进而将深海生物多样性和深海环境建立起联系, 发展深海生态理论模型, 对深海生物多样性保护提供条件支持(谢伟和殷克东, 2019; 程娇等, 2021)。
近10年来, 我国陆续开展了河口、海藻床、红树林等典型生态系统恢复工作, 以及岸线整治等海洋生态保护修复工作。对多种生态系统进行全面的理化、生物等指标的调查和长时间的监测, 修复前评估, 修复时规划, 修复后监测。积极应用现代分子生物技术, 如细胞工程、分子育种等, 科学养殖, 合理开发海洋资源。使用分子手段对低丰度的可能出现的入侵物种进行监测(李晗溪等, 2019), 积极利用遥感进行大范围监测, 利用统计学和算法进行合理推论。
4 海洋生物多样性的文献计量分析
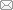
本文文献信息来自于Web of Science核心数据库和中国知网数据库, 主题词分别为“marine biodiversity”和“海洋生物多样性”, 时间范围为2011-2021年, 国家地区限定为China, 最终分别得到文献1,176篇和866篇, 总计2,042篇。统计发现近4年的增长速度有了显著提升, 2021年文献发表数量是2011年的3倍(图1)。
图1
图1
2011-2021年中国海洋生物多样性研究相关文献的年际变化
Fig. 1
Interannual variation in the literatures related to marine biodiversity studies in China from 2011 to 2021
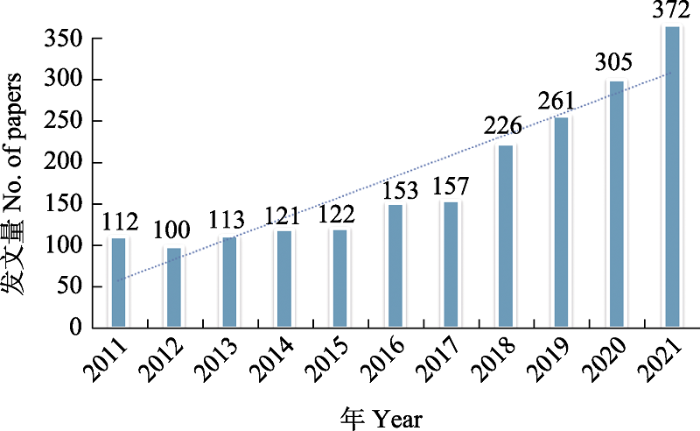
图2
图2
2011-2021年中国海洋生物多样性文献中文关键词共现图(数据来源于中国知网数据库)
Fig. 2
Keyword co-occurrence map of Chinese marine biodiversity literatures from 2011 to 2021 (data from CNKI database)
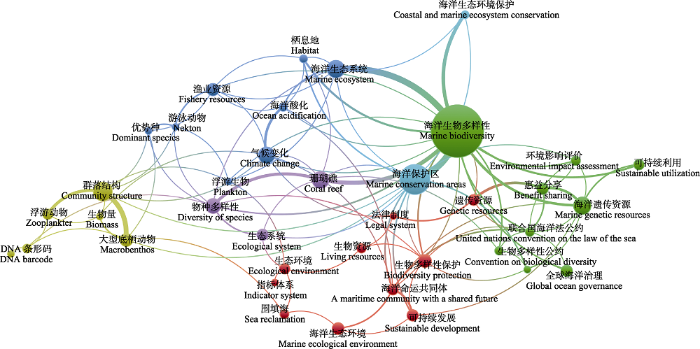
图3
图3
2011-2021年中国海洋生物多样性研究英文关键字共现图(数据来源于Web of Science数据库)
Fig. 3
Keyword co-occurrence map for marine biodiversity studies in China from 2011 to 2021 (data from Web of Science database)
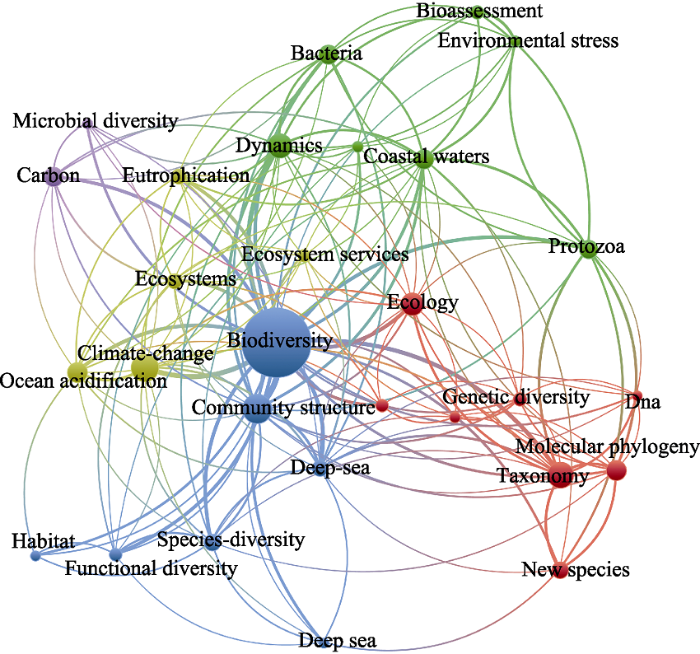
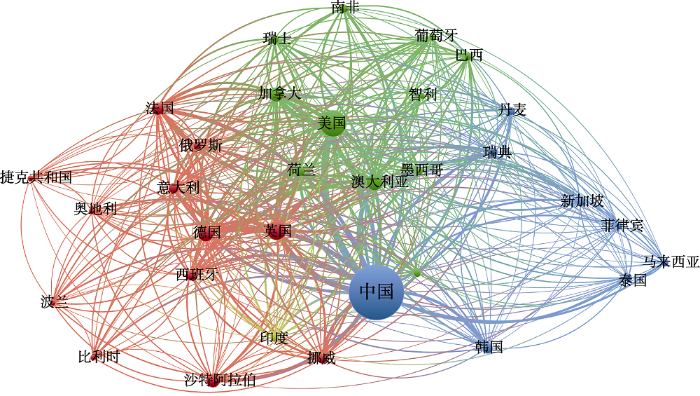
在国际交流方面, 我国学者与美、英、澳、德等国家合作密切, 在近岸海域问题上与东亚各国交流密切。我国研究人员主动参与国际重大计划, 学习先进经验技术和法律制度, 并针对我国现状建立有中国特色的规划路线。近海典型生态系统依然面临着气候变化和人为影响等多重压力, 是未来的重点研究内容(图4)。
图4
图4
2011-2021年中国海洋生物多样性研究国家合作共现图(数据来源于Web of Science数据库)
Fig. 4
International cooperation co-existence map for marine biodiversity studies in China from 2011 to 2021 (data from Web of Science database)
公众也越来越认识到海洋的重要性, 围填海项目地停止和整改, 沿海城市针对典型生态系统的修复工作趋于完善。随着研究技术的更迭, 我们走向深海, 走进微观, 在更高的纬度上探究海洋生物多样性。历史的变迁, 当下的分布, 未来的趋势, 从生物基因到整个海洋环境这一平衡/非平衡的系统中, 我们对广袤海洋的探索还将更加深入(孙军, 2011)。
5 展望
中国海是一个生物多样性较高的区域, 靠近全球的海洋生物多样性中心, 其生物多样性高居世界第三。尽管我们已在海洋生物多样性方面开展了很多工作, 但仍然有许多工作亟待开展。
我们对中国海新的物种, 特别是无脊椎动物和原生动物的描述仍然在不断积累; 在对新的生态系统进行分类和取样以及对其中物种和栖息地进行长期监测方面仍需要加大努力; 外来物种的入侵将继续改变中国近海的生物多样性, 仍需持续监测; 对中国近海生物多样性的高异质性也不尽了解, 仍需尝试整合空间数据和时间的变动趋势, 需要在大尺度、可视化宏观生态模式下进行分析研究; 中国近海是一个复杂的区域, 生态环境和人类活动影响交汇并相互作用, 它们对海洋生物多样性产生的巨大潜在影响仍需评估; 虽然我们对生物多样性的单一胁迫因子已经非常了解, 但对多重因子及其交互作用影响的了解则非常有限; 我们也有必要对保护和管理中国近海生物多样性的措施进行全面分析; 在多样性保护与管理上, 还存在研究资金投入不够、基本科研条件还相对落后、管理的教条主义和部门壁垒, 以及民众的认知和参与度不够等一系列问题。
由于中国国土几乎横跨了从世界陆地最高极的珠穆朗玛峰到海洋最深处的马里亚纳海沟, 同时也是世界人口最多和人为活动最强烈的地区, 因此中国珠穆朗玛峰-马里亚纳海沟的断面在物理环境、生态和社会经济上都有一个很显著的梯度, 在这样一个断面上的生物多样性研究可被视为一个范式, 一个陆海统筹、古今结合的理想场所。国家有必要加大在一些典型海洋生态系统水平生物多样性研究的投入, 也有必要让更多的民众参与到海洋生物多样性的保护中来。
参考文献
Benthic habitat health assessment using macrofauna communities of a sub-tropical semi-enclosed bay under excess nutrients
DOI:S0025-326X(17)30262-X
PMID:28363430
[本文引用: 1]

This research was conducted to assess the ecosystem health of Daya Bay benthic habitat, investigate the effects of anthropogenic nutrients, and evaluate the application of ecological indicators for benthic health assessment. Environmental indicators and macrobenthic communities, were investigated during summer and winter 2015. Results indicated a strong seasonality in biotope of intertidal and subtidal zones. Lower macrobenthic diversity were calculated from subtidal inner bay, reflecting the effects of anthropogenic nutrients. However, intertidal sites in that part were indicated to be in a relatively healthier ecological status. Seasonal effects of excess nutrients on benthic habitat were reflected in ecological indicators. It is concluded that the excess nutrients at spatiotemporal scales, influences on the health of benthic habitat. Eventually, it is recommended by this research that, with considering the natural/anthropogenic circumstances, the taxonomic and phylogenetic ecological indicators would be helpful tools to evaluate the benthic health of a typical sub-tropical semi-enclosed bay.Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Effect of phytoplankton size diversity on primary productivity in the North Pacific: Trait distributions under environmental variability
DOI:10.1111/ele.13167 URL [本文引用: 1]
Preface
前言
Current status and prospects of marine biodiversity in China
中国海洋生物多样性的现状和展望
Diversity and seasonal variation of marine phytoplankton in Jiaozhou Bay, China revealed by morphological observation and metabarcoding
DOI:10.1007/s00343-021-0457-7 URL [本文引用: 1]
Analysis of RAPD and mitochondrial Cytb gene sequences of three cultured stocks of Epinephelus coioides from Guangdong Province, China
广东沿海3个斜带石斑鱼养殖群体的RAPD和线粒体Cytb基因序列变异分析
Remote-sensing monitoring of green tide and its drifting trajectories in Yellow Sea based on observation data of geostationary ocean color imager, China
结合GOCI数据的黄海绿潮遥感监测及漂移轨迹研究
Netz-phytoplankton community structure of the tropical Western Pacific Ocean in summer 2016
2016年秋季热带西太平洋网采浮游植物群落结构
Community structure of benthic algae and its seasonal variation in the rocky intertidal zone of Sanya
DOI:10.5846/stxb201203010277 URL [本文引用: 1]
三亚岩相潮间带底栖海藻群落结构及其季节变化
Progress on the origin, evolution and biogeographic pattern of megafauna biodiversity in deep-sea chemosynthetic ecosystems, China
深海化能生态系统大型生物多样性分布格局及其起源演化研究进展
Genetic diversity of marine animals in China: A summary and prospectiveness, China
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.19125 URL [本文引用: 1]
中国重要海洋动物遗传多样性的研究进展
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.19125
[本文引用: 1]

海洋动物遗传多样性的研究不仅可以揭示物种的起源与进化历史, 而且为遗传资源的保存、海水养殖动物育种和遗传改良及整个海洋生态环境的修复和稳定等工作提供理论依据。本文概述了近十几年来我国重要海洋动物(主要包括鱼类、虾蟹类和贝类)遗传多样性研究所取得的成果, 具体阐述其在种质鉴定、系统进化、群体遗传结构分析和良种培育等方面的应用, 以期进一步推动海洋动物遗传多样性研究, 加快优良种质的培育, 促进海水养殖业的健康发展, 实现海洋生物资源的合理开发和可持续利用。
Exponential decline of deep-sea ecosystem functioning linked to benthic biodiversity loss
DOI:10.1016/j.cub.2007.11.056
PMID:18164201
[本文引用: 1]

Recent investigations suggest that biodiversity loss might impair the functioning and sustainability of ecosystems. Although deep-sea ecosystems are the most extensive on Earth, represent the largest reservoir of biomass, and host a large proportion of undiscovered biodiversity, the data needed to evaluate the consequences of biodiversity loss on the ocean floor are completely lacking.Here, we present a global-scale study based on 116 deep-sea sites that relates benthic biodiversity to several independent indicators of ecosystem functioning and efficiency. We show that deep-sea ecosystem functioning is exponentially related to deep-sea biodiversity and that ecosystem efficiency is also exponentially linked to functional biodiversity. These results suggest that a higher biodiversity supports higher rates of ecosystem processes and an increased efficiency with which these processes are performed. The exponential relationships presented here, being consistent across a wide range of deep-sea ecosystems, suggest that mutually positive functional interactions (ecological facilitation) can be common in the largest biome of our biosphere.Our results suggest that a biodiversity loss in deep-sea ecosystems might be associated with exponential reductions of their functions. Because the deep sea plays a key role in ecological and biogeochemical processes at a global scale, this study provides scientific evidence that the conservation of deep-sea biodiversity is a priority for a sustainable functioning of the worlds' oceans.
Advances and problems with the study of marine macroalgae of China seas, China
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07128 URL [本文引用: 1]
中国大型海藻的研究现状及其存在的问题
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07128
[本文引用: 1]

结合最新的研究结果, 本文对中国大型海藻区系划分、区系的种类组成、分布特征、研究成果、现状和存在的问题等进行了介绍、总结和分析。目前, 中国海藻区系可划分为4个小区, 即黄海西区、东海西区、南海北区和南海南区。大型海藻物种数达到1,277种, 其中蓝藻门6目21科57属161种(及变种)、红藻门15目40科169属607种(及变种)、褐藻门11目24科62属298种(及变种), 绿藻门11目21科48属211种(及变种)。简要地介绍了它们的区系分布、垂直分布、时空变化等方面的分布特征。文中还对我国大型海藻的研究现状及存在的问题进行了简短分析, 以期有益于我国大型海藻多样性研究的发展。
Classification status and prospects of the family Ceramiaceae, Rhodophyta, China
红藻门仙菜科Ceramiaceae的分类现状与展望
The application and perspective of DNA barcoding technology on the macroalgae China
DNA条形码技术在大型海藻学研究中的应用及前景
Report of epibenthic macrofauna found from Haima cold seeps and adjacent deep-sea habitats
South China Sea. Marine Life Science & Technology,
Genetic diversity and genetic differentiation of swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus) from six geographical populations of China Sea based on mitochondrial D-loop gene, China
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1231.2013.38630 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于线粒体D-loop基因的中国海三疣梭子蟹遗传多样性与遗传分化研究
Macrobenthos Diversity response to hydrological connectivity gradient
DNA barcode assessment of Ceramiales (Rhodophyta) in the intertidal zone of the northwestern Yellow Sea
DOI:10.1007/s00343-015-4088-8 URL [本文引用: 1]
Strategies for the marine biodiversity conservation based on the integrated coastal zone management, China
以海岸带综合管理为工具开展海洋生物多样性保护管理
Present and future global distributions of the marine cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus
First record of Caulerpa lentillifera J. Agardh (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta) from China
DOI:10.1080/17451000.2019.1702215 URL [本文引用: 1]
Systematic studies on ciliates (Alveolata, Ciliophora) in China: Progress and achievements based on molecular information
DOI:S0932-4739(16)30123-7
PMID:28545995
[本文引用: 1]

Due to complex morphological and convergent morphogenetic characters, the systematics of ciliates has long been ambiguous. Since 1990, the Laboratory of Protozoology, Ocean University of China, in collaboration with other research groups worldwide, has carried out a series of integrative investigations on ciliate systematics. To date, genomic DNA has been extracted from about 1700 ciliate strains, and phylogenetic analyses have been performed for two-thirds of orders. Main findings are: (1) Classifications of about 50 hypotrichous species have been resolved, although the monophylies of three hypotrichous orders remain unconfirmed; (2) Euplotia and two orders and all seven families within them are monophyletic assemblages; (3) Lynnella represents an order-level taxon, and is separated from two sister monophyletic subclasses Oligotrichia and Choreotrichia; (4) the peritrich families Zoothamniidae and Vorticellidae are separated from each other, and Zoothamnium exhibits a high genetic diversity; (5) the scuticociliate order Philasterida is monophyletic and separated from loxocephalids, and the thigmotrichids is a suborder within Pleuronematida; (6) 14 classes were recovered including one new class Protocruziea, and Mesodiniea is basal to subphyla Intramacronucleata and Postciliodesmatophora; (7) mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I heteroplasmy was reported in ciliates for the first time, and candidate barcoding genes for Frontonia species identification were identified.Copyright © 2017 Elsevier GmbH. All rights reserved.
Algal diversity and their importance in ecological processes in typical mangrove ecosystems
DOI:10.17520/biods.2018080
[本文引用: 1]

Algae are important flora in mangrove ecosystems. Algae can be divided into three ecological groups, namely phytoplankton, benthic microalgae, and macroalgae in mangrove ecosystems, which play important roles in organic carbon production and nutrient cycle. Despite the importance of algae for ecosystem function, studies of mangrove ecosystems have focused on higher plants and animals, with few studies of algae. Due to their abundance in mangrove ecosystems, studies of algae can broaden our understanding about the structure and function of mangrove ecosystems. In this review, we first briefly introduce algal groups and their ecological importance in mangrove ecosystems. Then, we emphasize species composition and geographical distribution of phytoplankton, benthic diatoms and macroalgae, and their importance in key ecological processes such as primary production, water pollution, element cycle, and carbon stock dynamics in mangrove ecosystem. The researches have showed that the species number of phytoplankton and benthic diatoms in mangroves varied from dozens to hundreds, and diatoms are dominant both in species composition and abundance, which are important primary producer, animal food, and pollution indicator. Macroalgae are mainly composed of red algae, green algae, brown algae and blue-green algae. Green algae are dominant in species richness whereas red algae are abundant in quantity. Algae contribute significantly to the carbon pool by sequestering and cycling carbon. We propose that future studies should focus on algal diversity and its role in ecological processes in mangrove ecosystems. Furthermore, we suggest that studies of algae should be part of comprehensive investigations on long-term ecosystem dynamics. The influence of continental runoff and tidal patterns on algal diversity and blue carbon dynamics in mangrove areas also deserve more attention, on account of being directly related to nutrient replenishment and dynamics. Since algal diversity in mangrove sediment is influenced by physico-chemical and biological condition of the system, it could be used as an indicator of climate change and effects of anthropogenic activity on mangrove ecosystems.
典型红树林生态系统藻类多样性及其在生态过程中的作用
DOI:10.17520/biods.2018080
[本文引用: 1]

藻类是红树林生态系统重要的生物类群, 根据生态习性可分为浮游植物、底栖微藻和大型藻类三个生态类群, 它们在红树林生态系统生物多样性、初级生产、元素循环等方面起着重要作用。但在红树林生态系统中, 关注重点多集中在红树植物和动物, 对其中的藻类重视不够, 且多数研究集中在近20年以及亚洲的红树林区。事实上, 红树林生态系统藻类非常丰富, 其多样性研究有助于深入揭示红树林生态系统的结构与功能。本文介绍了红树林生态系统藻类的组成类群及其重要性, 重点对红树林区浮游植物、底栖硅藻和大型海藻的种类组成、地理分布及其与初级生产力、水质污染、元素循环、碳库形成等生态过程中的作用的研究动态和进展等进行了总结。根据已有研究, 红树林区浮游植物和底栖硅藻的种类数一般为几十到上百种, 其中硅藻在种类和数量上都占绝对优势, 它们是重要的初级生产者、饵料生物和水质污染指示生物; 红树林区底栖大型藻类主要由红藻、绿藻、褐藻、蓝藻组成, 绿藻的种类较多, 红藻在数量上占优势; 藻类是红树林湿地碳库的重要贡献者, 在红树林湿地生态系统碳汇和碳循环中起重要作用。红树林生态系统是个高度动态和异质的系统, 今后应加强红树林藻类多样性的长周期、大尺度变化及不同生境藻类的综合研究, 关注大陆径流和潮汐对藻类多样性和蓝碳的影响, 借助沉积物藻类记录, 探明红树林区藻类的长周期变化, 反演气候变化和人类活动对红树林生态系统的影响过程和机制。
Protect and restore mangroves and maintain marine ecosystems
保护修复红树林维护海洋生态系统
Phylogenetic and functional diversity of nitrogen cycling microbes in coastal sediments
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.12027
[本文引用: 1]

The coastal zone contains diverse habitats which are usually characterized by strong environmental gradients (e.g. salinity, nutrients and pollutants). This makes the coastal zone an ideal experimental laboratory for describing microbial diversity and testing hypotheses on community structure, function and control. Coastal sediment is of significance in nutrient regeneration and transformation involving different assemblages of microbes in the nitrogen cycle. This review focuses on 16S rRNA gene-based phylogenetic diversity and the key enzyme encoding gene-based (e.g. nifH, amoA, narG, nirS, nirK, nosZ, nrfA, hzo and hzs) functional diversity of nitrogen fixing, ammonia oxidizing and anaerobic ammonia oxidation (Anammox) bacteria as well as bacteria and fungi involved in denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA). Characteristics of community composition and diversity of nitrogen cycling microbes in different habitats (e.g. estuarine, intertidal flats, seagrass or seaweed beds, mangroves, salt marsh, coral reefs, and shallow seas), and their spatiotemporal patterns under benthic pollution or bioturbation are reviewed. Future directions for a better understanding diversity of nitrogen cycling microbes are suggested, such as culture methods and technologies, and single-cell sequencing, etc.
海岸带沉积物中氮循环功能微生物多样性
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.12027
[本文引用: 1]

海岸带生境类型多样, 环境梯度明显, 是研究微生物多样性、群落结构与功能关系及调控机制的天然实验场。沉积物是海岸带环境中营养盐再生与转化发生的重要场所, 其中多种微生物类群在氮素循环过程中扮演重要角色。本文重点介绍海岸带沉积物中固氮菌、氨氧化菌、厌氧氨氧化菌、反硝化与硝酸盐铵化微生物的基于16S rRNA基因的物种多样性和基于关键酶基因nifH、amoA、narG、nirS、nirK、nosZ、nrfA、hzo、hzs等的功能多样性; 总结了在海岸带特有生境(如河口、潮间带、海草藻床、红树林、盐沼、珊瑚礁、浅海等)及污染胁迫、生物扰动等条件下各功能类群的群落组成特征及时空变化规律, 并提出今后需要重点关注新的培养技术和方法的开发, 以进一步提高微生物的可培养性, 将单细胞基因组测序与分析技术、DNA和RNA结合起来研究, 以全面了解氮循环微生物多样性、参与介导硝酸盐铵化过程的微生物多样性等方面。
Genetic diversity of wild populations of mantis shrimp Oratosqilla oratoria in Bohai Bay using microsatellite markers
利用微卫星分子标记分析渤海湾的口虾蛄遗传多样性
Phytoplankton community in the Bohai Sea and its relationship with environmental factors
渤海浮游植物群落结构及与环境因子的相关性分析
Phytoplankton communities in the Northern Yellow Sea in autumn 2011, China
2011年秋季北黄海浮游植物群落
Preliminary study of the impact of fishery trawling on epifauna community in the coastal water of Weihai Port
渔业捕捞对威海港附近海域底上大型底栖群落结构影响的初步研究
Genetic structure of Oithona setigera from South China Sea based on 28S rDNA gene
基于28S rDNA的南海刺长腹剑水蚤(Oithona setigera)种群遗传多样性研究
DOI:10.11978/2018112
[本文引用: 1]

长腹剑水蚤属是海洋中小型浮游动物中最为丰富的类群之一, 在生物地理学与海洋生态学研究中均具有重要地位。本研究基于28S rDNA分析了南海长腹剑水蚤属中较为常见的刺长腹剑水蚤Oithona setigera的单倍型多样性和种群遗传结构。结果显示, 792bp长度的核苷酸片段中, 碱基G+C的平均含量为58.2%, 高于A+T含量(41.8%)。种群平均遗传距离Φ<sub>ST</sub>为0.011。在22个种群共计186个个体中, 发现了28个单倍型, 其中单倍型H10在21个种群中均被发现, 最远距离超过1000km, 说明刺长腹剑水蚤可以实现远距离的扩散且受到南海海流影响。Mantel检验结果显示, 刺长腹剑水蚤种群遗传距离和地理距离无线性相关性(R=-0.04615, P=0.678); RDA变差分解结果显示, 空间变量全模型对种群遗传结构的解释率为53.3%, 结合种群平均遗传距离Φ<sub>ST</sub>为0.011, 我们判断目前观测到的刺长腹剑水蚤的种群遗传结构可能由历史上种群扩展带来的拓殖隔离造成。
Plankton community structure and diversity in coral reefs area of Sanya Bay, Hainan Province, China
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.06145 URL [本文引用: 1]
三亚珊瑚礁分布海区浮游生物的群落结构
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.06145
[本文引用: 1]

为了更好地了解珊瑚礁区生物群落应对环境变化的生态响应机制, 以及浮游生物群落结构与珊瑚礁发展发育的关系, 我们于2006年10月26日至11月10日对三亚珊瑚礁保护区9个有珊瑚礁分布的站点进行了浮游生物群落结构的调查。共鉴定出浮游植物种类61属130种(包括变种、变型), 其中硅藻门48属101种, 甲藻门10属25种, 蓝藻门2属3种, 金藻门1属1种。硅藻门的角毛藻属(Chaetoceros)种类最多, 根管藻属(Rhizosolenia)的种类次之。调查海区浮游植物的细胞丰度范围为348–11,320个/L, 平均为3,247个/L。在浮游植物群落中硅藻占绝对优势, 平均丰度为3,230个/L, 占总密度的99.5%。调查海区共鉴定出浮游动物76种, 其中桡足类29种, 水母类17种, 浮游幼虫10种, 毛颚类7种, 被囊类6种, 浮游腹足类4种, 十足类、多毛类和介形类各1种。调查海区浮游动物的密度范围为43–190个/m<sup>3</sup>, 平均为114个/m<sup>3</sup>。优势类群为桡足类、各类幼虫和毛颚类, 平均分别占浮游动物总密度的28.5%, 27.7%和13.6%。各站位浮游植物的多样性指数和均匀度平均分别为3.98和0.70, 浮游动物的多样性指数和均匀度平均分别为4.37和0.87。鹿回头和大东海海域的浮游植物密度大, 而生物多样性指数低。活的造礁石珊瑚种数和覆盖率高的站点的浮游生物多样性也较高。
Advances and hot topics for the marine biodiversity protection in China
中国海洋生物多样性保护研究进展与几个热点问题
DNA barcoding and its application to marine zooplankton ecology
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.10173
[本文引用: 1]

As the main components of marine biota, zooplankton play vital roles in the marine biodiversity, trophic relationships and ecosystem dynamics. However, morphological identification of zooplankton is time-consuming and even impossible for some taxa, especially for pelagic larvae. Diversity of marine zooplankton is believed to be underestimated. DNA Barcodes (short DNA sequences for species recognition and discrimination) provide powerful tools for rapid species identification and are quickly applied in marine zooplankton ecological researches. Here we give a general introduction on the concept, advantages, and limitations of DNA barcoding. We review the multiple applications of DNA barcodes (mainly focused on the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (mtCOI) gene) in the marine zooplankton ecological researches, which include rapid species identification, cryptic species reveal, trophic relationship analysis, invasive species monitoring, historical range expansion, population genetic and biogeographic analysis. We anticipate that DNA barcoding techniques will be increasingly used by marine ecologists. With the DNA barcode reference libraries completing and new high-throughput tools such as next generation sequencing developing, DNA barcoding will provides more information that, not only for species identification and discovery, but also help to improve our understanding of zooplankton biodiversity and their functions in marine ecosystems.
DNA条形码及其在海洋浮游动物生态学研究中的应用
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.10173
[本文引用: 1]

浮游动物的准确鉴定是浮游动物生态学研究的基础。传统的基于形态特征的鉴定不仅费时费力, 而且部分类群特别是浮游幼体由于形态差异细微, 鉴定存在困难, 导致物种多样性被低估。DNA条形码(DNA barcodes)技术为浮游动物物种鉴定提供了一个有力工具, 已迅速应用于海洋浮游动物生态学研究。本文介绍了DNA条形码的基本概念、优势及局限性, 总结了该技术(主要是基于线粒体细胞色素C氧化酶第一亚基(mtCOI)基因序列片段的DNA条形码)在海洋浮游动物物种快速鉴定、隐种发现、营养关系研究、生物入侵种监测、群落历史演变反演、种群遗传学以及生物地理学中的成功应用。随着DNA条形码数据库信息量覆盖率的不断提高和新一代测序技术的快速发展, DNA条形码将提供除了种类鉴定外更加丰富的信息, 从而帮助人们更好地理解海洋浮游动物的多样性及其在生态系统中的功能, 推动海洋浮游动物生态学的发展。
Environmental DNA (eDNA)-metabarcoding-based early monitoring and warning for invasive species in aquatic ecosystems
DOI:10.17520/biods.2018233
[本文引用: 2]

Biological invasion is a major threat to multiple ecosystems across the globe, causing severe damages to ecological integrity, loss of biodiversity, economic and social development and even human health. With the rapid development in aquaculture, shipping and aquarium and ornamental trades in the past several decades, China has become one of the countries most influenced by invasive species. Studies have clearly shown that the development and application of robust early monitoring and warning is one of the most effective ways to prevent and possibly control invasive species in aquatic ecosystems. Compared to terrestrial ecosystems, there remain several technical difficulties for developing early monitoring and warning in aquatic habitats. The technical challenges are mainly due to several features of aquatic biological communities such as high biodiversity and complex structure, a large number of microscopic species, extremely low population density and lack of available taxonomic keys for species identification. With the rapid development of high-throughput sequencing techniques, environmental DNA (eDNA)-metabarcoding has become the top priority method for developing the early monitoring and warning programs in aquatic ecosystems. In this review, we aim to synthesize the research progress on eDNA-metabarcoding and its application to early monitoring and warning of invasive species in aquatic ecosystems. In addition, we briefly discuss the technological advantages of eDNA-metabarcoding for the early monitoring and warning programs. Finally, we propose research perspectives for solutions to technical issues for false positive and false negative errors in the eDNA-metabarcoding process.
基于环境DNA-宏条形码技术的水生生态系统入侵生物的早期监测与预警
DOI:10.17520/biods.2018233
[本文引用: 2]

外来生物入侵是继生境破坏后造成生物多样性丧失的第二大威胁因素, 已对入侵地的生态安全、经济和社会发展及人类健康等造成严重负面影响, 成为21世纪五大全球性环境问题之一。作为水产养殖、航运和水生宠物交易大国, 我国水生生态系统的生物入侵问题尤为严重。研究表明, 系统地构建并应用早期监测预警技术是防控水生生态系统生物入侵最有效的途径。和陆生生物相比, 水生生物群落的物种繁多、群落结构复杂、生物形体微小且在入侵初期群体规模极小、隐匿于水下、可用于物种鉴定的外部形态缺乏, 使得在水生生态系统中构建并应用早期监测和预警体系在技术层面更具挑战。随着高通量测序技术的快速发展, 环境DNA-宏条形码技术成为构建水生生态系统入侵生物早期监测与预警技术的首选。本文主要综述了基于环境DNA-宏条形码技术的水生生态系统入侵生物的早期监测与预警技术方法; 解析了环境DNA-宏条形码监测系统的应用现状、技术优势; 着重探讨了影响监测结果准确性的I型和II型错误及其产生原因, 并为避免两类错误提供了可行的优化/改进方案; 最后对该方法在水生入侵生物监测中的应用前景进行了展望。
An overview of studies on marine macrobenthic biodiversity from Chinese waters: Principally from the Yellow Sea
我国海洋大型底栖生物多样性研究及展望: 以黄海为例
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.09126
[本文引用: 1]

本文综述了我国海洋大型底栖生物生态学和生物多样性研究进展, 指出在该领域已有的研究中以胶州湾、长江口、福建和浙江沿岸等海域研究较多, 其他海域还需要加强。介绍了常规大型底栖生物群落研究(包括种类组成、栖息密度(丰度)、生物量、生物多样性、次级生产力、能量级等)中的研究方法, 环境变化、环境污染、海洋工程建设等对大型底栖生物的影响等方面的主要研究成果和进展, 并重点以黄海为例, 列举了已有的主要调查项目和研究成果。我国已有的研究表明, 渤海海域底栖动物区系简单, 大型底栖生物共413种, 种数在四个海区中最少, 优势种主要是低温、广盐暖水种; 年总平均生物量为19.83 g/m<sup>2</sup>, 以软体动物占有绝对优势; 年总平均栖息密度474个/m<sup>2</sup>, 多毛类和软体动物为主要贡献类群。黄海大型底栖生物共853种, 优势种为狭盐性北温带种; 北黄海年总平均生物量为99.66 g/m<sup>2</sup>, 以棘皮动物最高; 南黄海年总平均生物量为27.69 g/m<sup>2</sup>, 多毛类贡献量最高; 北黄 海年总平均密度为2,017.40个/m<sup>2</sup>, 而南黄海只有88.67个/m<sup>2</sup>差异较大; 北黄海大型底栖生物的总平均密度和生物量远高于其他海域。南黄海年平均次级生产力为4.98 g(去灰干重)/m<sup>2</sup>, 两个高生产力区位于黄海冷水团两侧。东海共发现大型底栖生物1,300种, 主要优势种类有45种, 与黄海优势种生物之间有很大差别; 东海平均生物量的季节变化不显著, 基本趋势为春季>冬季>夏季>秋季; 东海各海域的年总平均生物量浙江海域(28.22 g/m<sup>2</sup>)>长江口海域(15.55 g/m<sup>2</sup>) >台湾海峡(8.98 g/m<sup>2</sup>); 年总平均栖息密度为164个/m<sup>2</sup>, 呈现由北向南逐渐增加的趋势。南海大型底栖生物共发现1,661种, 明显高于渤、黄、东海, 部分优势种类与东海相同, 与黄海、渤海差别较大; 年总平均生物量为20.06 g/m<sup>2</sup>, 基本趋势为春季>冬季>秋季>夏季, 软体动物和棘皮动物为主要贡献类群; 年总平均栖息密度为198个/m<sup>2</sup>, 夏季>春季>冬季>秋季, 多毛类生物为主要贡献者。指出随着人类活动和全球气候变化对海洋环境的影响越来越剧烈, 对海洋生物资源和生物多样性的保护显得尤为急迫, 而对海洋大型底栖生物长期的变化规律、变化机理、未来变化趋势预测的研究, 是探究海洋大型底栖生物生态服务功能, 提出资源有效保护和合理开发建议, 使之永续利用的基础和迫切任务。
Complete mitochondrial genome sequence and phylogenetic analysis of Myoxocephalus scorpius (Linnaeus, 1758)
Advances in research of marine microbial diversity and molecular ecology
海洋微生物多样性及其分子生态学研究进展
Research progress on distribution characteristics and environmental behavior of microplastics in mangrove forests
红树林环境中微塑料污染分布特征及生态风险研究进展
Genetic differentiation and evolutionary history of the circumpolar species Ophiura sarsii and subspecies Ophiura sarsii vadicola (Ophiurida: Ophiuridae)
DNA barcoding and molecular phylogenetic relationships of Epinephelus species from western Pacific coastal areas
西太平洋沿海石斑鱼属鱼类DNA条形码及分子系统进化研究
Decline in plankton diversity and carbon flux with reduced sea ice extent along the Western Antarctic Peninsula
DOI:10.1038/s41467-020-20314-w URL [本文引用: 1]
Application of molecular biotechniques in research on marine microbial diversity: A review
分子生物学技术在海洋微生物多样性研究中的应用
Seasonal variations of netz-phytoplankton community in East China Sea continental shelf from 2009-2011
2009-2011年东海陆架海域网采浮游植物群落的季节变化
Functional trait composition and diversity patterns of marine macrobenthos across the Arctic Bering Sea
DOI:10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.03.029
[本文引用: 1]

The use of functional trait analysis has been advocated to uncover the global mechanisms behind biodiversity responses to environmental variation, but the application of this approach to the Arctic macrobenthic community is underdeveloped relative to that used for other organism groups. Based on several summer surveys (July to September 2010, 2012, 2014 and 2016) in the Bering Sea, we used biological trait analysis (BTA) to quantify the composition and diversity of macrobenthic biological traits along an environmental gradient ranging from the shallowest portion of the continental shelf to the shelf break and deep basin. Our results show a clear shift in the macrobenthic functional composition through the application of abundance-and biomass-based measurements in six different subregions of the Bering Sea. The macrobenthic community of the south-western shelf and shelf break of the Bering Sea, an area with silty-sand sediment, was mainly composed of taxa characterized by high body flexibility, vermiform, and tube-dweller/burrower modalities or large, semi-motile, deposit feeder and flattened dorsally modalities. However, the community of the north-eastern shelf of the Bering Sea with sandy sediment was mainly characterized by organisms characterized as motile surface crawlers and carnivores/scavengers. Similar to the factors that determine the taxonomic distribution and composition of the macrobenthos, sediment composition and depth were found to be the main factors that affect the distribution of the macrobenthic functional structure in the study area. The species and functional diversity of the macrobenthos show a strong linear relationship, potentially indicating that the community exhibits relatively low functional redundancy and that the benthic ecosystem is vulnerable to species loss or regime shifts.
Progress of marine biodiversity studies in China Seas
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.13185 URL [本文引用: 1]
中国海物种多样性研究进展
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.13185
[本文引用: 1]

中国海的生物多样性研究是中国科学院青岛海洋生物研究室1950年成立后开始大规模系统进行的。经过半个多世纪的努力, 迄今已有千篇论文和约200部专著出版。主要专著《中国动物志》“无脊椎动物”已出版47卷, 其中27卷为海洋生物, 5年计划编写中17卷; 《中国动物志》“脊椎动物”鱼类11卷, 哺乳类1卷; 《中国海藻志》8卷, 待出版4卷, 编写中3卷。另外, 《海洋科学集刊》已出版的50卷中有22卷是海洋生物的专刊; 另有《西沙群岛生物考察专辑》6卷。其中有代表性的著作《中国海洋生物种类与分布》(黄宗国, 1994)集成国内外文献, 记载物种20,278种(内有化石种及异名应除去)。2008年出版的《中国海洋生物名录》(刘瑞玉主编)记录22,629现生种, 比1994年相同门类多5,118种, 仅次于澳大利亚和日本, 居世界第三位。主要进展是取得了中国海翔实可靠的物种鉴定、编目和分布数据。此外还参加了国际“物种2000”计划项目, 交出的“中国生物名录”比2008年名录显著增多。全部物种正进行“世界海洋物种登录”(WoRMS), 可供与世界不同海域和生境的种类多样性作比较研究。完成国家标准《海洋生物分类代码》(国家质量技术监督局1999发布)的修订, 纠正了种名和分类系统的错误, 增补了物种, 保证了作为国家标准的高水平, 待付印。完成全国濒危物种评估, 负责编写《中国物种红色名录》1、3、2卷海洋无脊椎动物部分; 结果发现濒危物种显著增多。1997–2000年“专属经济区大陆架环境资源调查”的结果进一步显示陆架海域生物多样性和主要资源衰退, 还提出了应采取的措施。中国参加了国际重大项目“海洋生物普查计划”, 进行了浮游动物普查, 提交了中国国家汇总报告——中国海生物多样性研究, 交PLoS ONE出版。全面加强了多样性和濒危种的保护, 全国已建立国家级海洋自然保护区33个, 特别保护区21个。论文在肯定中国海生物多样性研究进展和成绩的同时, 指出了存在的主要不足是调查采集和研究的生境主要在陆架浅海, 深海大洋特殊生境刚刚起步; 多样性调查缺少全国统一计划行动, 缺全面的多样性“背景值”资料。而监测、采集、研究不够; 评估、保护亟待加强。文终提出了几点涉及学科发展和多样性监测、评估、保护的关键性建议。
Quantitative distribution and functional groups of intertidal macrofaunal assemblages in Fildes Peninsula, King George Island, South Shetland Islands, Southern Ocean
DOI:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.09.015 URL [本文引用: 1]
Macrofaunal community structure in the Laizhou Bay in summer and the comparison with historical data
莱州湾夏季大型底栖动物群落结构特征及其与历史资料的比较
Study on the population structure and pollution ecology of algae in mangrove area in Futian, Shenzhen
红树林区污水对藻类种群结构的影响
A review on ecological restoration techniques of coral reefs
DOI:10.11978/2019066
[本文引用: 1]

Coral reefs play vital roles in the construction, protection, and adhesion of reefs, and they protect coastal and national territories as well. Coral reefs have also been considered as tropical rainforests in the marine ecosystem with their abundant biodiversity. More than 200 species of coral reefs exist in the South China Sea; however, some of them have been severely damaged due to natural climate change and human activities in recent years, which threats marine and island safety. Therefore, ecological restoration for coral reef ecosystem is necessary and urgent. In this paper, we summarized the status of coral reefs, technical progress of ecological restoration, and important issues of coral reefs. Furthermore, a novel multidimensional restoration model based on system integrity was proposed and applied in restoring coral reefs, which may provide a new way to restore marine ecosystem.
珊瑚礁生态系统修复研究进展
DOI:10.11978/2019066
[本文引用: 1]

健康的珊瑚礁生态系统具有造礁、护礁、固礁、防浪护岸、防止国土流失的功能。同时, 珊瑚礁生态系统生物多样性极高, 被称为海洋中的“热带雨林”。我国南海拥有200多个珊瑚岛、礁与沙洲, 是世界海洋珊瑚礁最丰富的区域之一。近年来, 由于全球气候变化和围填海等人类活动的影响, 珊瑚礁生态系统受到了不同程度的影响或破坏, 危及海洋生态与岛礁安全, 珊瑚礁生态系统的修复至关重要。本文对珊瑚礁生态系统的现状、修复方法及存在的问题进行了总结, 并在此基础上创新性地提出了基于系统的珊瑚礁多维生态系统修复模式并付诸实践, 以期提供更有效的珊瑚礁生态系统修复新方法。
Fish community diversity during spring and autumn in the Yellow Sea off the coast of Shandong
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.08239 URL [本文引用: 1]
黄海山东海域春、秋季鱼类群落多样性
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.08239
[本文引用: 1]

根据2006年春季(5月)和秋季(10月)黄海山东海域疏目变水层双拖网调查数据, 作者对该海域鱼类群落多样性、空间分布及长度谱特征进行了研究。调查共捕获鱼类61种, 其中鲈形目种类最多(27种), 其次为鲱形目(8种)和鲉形目(7种); 按摄食类型可分为浮游动物食性、浮游动物/底栖动物食性、底栖动物食性、底栖动物/游泳动物食性、游泳动物食性、杂食性、碎屑食性7个类群, 其中浮游动物食性占渔获物重量组成的82.5%。春、秋季鱼类群落均主要由小型种类占优势, 春季优势种有3种, 为玉筋鱼(Ammodytes personatus)、鳀(Engraulis japonicus)和方氏锦鳚(Pholis fangi), 秋季优势种有5种, 分别是鳀、青鳞小沙丁鱼(Sardinella zunasi)、玉筋鱼、小黄鱼(Larimichthys polyactis)和赤鼻棱鳀(Thryssa kammalensis)。丰富度指数(D)、Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H')、均匀度指数(J')的空间异质性明显, 表现出近岸海域(尤其是青岛–乳山南部近岸海域)较高, 深水区较低的态势, 但多样性指数的季节间差异不显著。资源量与Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H')、均匀度指数(J')、功能团多样性指数(FD)均呈负相关关系, 与种类丰富度指数(D)则无相关关系。春、秋季鱼类群落长度谱曲线斜率均小于–0.2, 而截距均大于10, 与该海域1985年及2000年的研究结果相比, 长度谱斜率显著降低、截距显著增加, 这与小型个体种类占优势密切相关。与历史资料相比, 黄海山东海域鱼类群落多样性下降, 小型个体比例上升, 资源呈衰退趋势。
Phytoplankton community in adjoining water of the Antarctic Peninsula during austral summer 2010
2010年夏南极半岛邻近海域的浮游植物群落
Species composition and diversity of crab assemblage in Haizhou Bay
DOI:10.17520/biods.2014205
[本文引用: 1]

The species composition and diversity of crab assemblage in Haizhou Bay was assessed using bottom-trawl survey data collected in March, May, July, September, and December, 2011. Crab species composition and the spatio-temporal variations in species diversity of communities were examined using ecological diversity indices. In total, 34 crab species belonging to 18 families and 27 genera were caught during the surveys. There were 16 warm water species, 15 warm temperate species and 3 cold temperate species. Margalef’s species richness index (D) was highest in March and lowest in December while the Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H′) and Pielou evenness index (J′) were highest in July and lowest in December. Diversity, richness, and evenness also varied spatially over time. In March, May and July the highest values occurred in the northern area of the survey site and lowest in the southern part. In September, values were lowest in the central survey site and high in the northern and southern areas. In December, values were low in northern survey site and high in southern areas. The number of individuals per haul per hour varied spatially and temporally by month with higher numbers in March, May and December. Correlation analysis showed that crab community species diversity was significantly affected by water temperature, salinity, depth and the season in Haizhou Bay. The spatio-temporal variations in species composition and diversity of crab assemblage in Haizhou Bay are primarily related to the seasonal changes in environmental factors such as bottom water temperature and the spatial distribution of main dominant species.
海州湾蟹类群落种类组成及其多样性
DOI:10.17520/biods.2014205
[本文引用: 1]

本研究根据2011年3月、5月、7月、9月和12月在海州湾海域进行的渔业资源底拖网调查数据, 采用Margalef种类丰富度指数(D)、Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H′)和Pielou均匀度指数(J′)等分析了该海域蟹类群落种类组成及其多样性的时空变化。结果表明, 本次调查共捕获蟹类34种, 隶属于18科27属, 其中玉蟹科种数最多, 有3属4种。从适温属性来看, 主要以暖水种(16种)和暖温种(15种)为主, 冷温种3种。蟹类群落各多样性指数的月际间变化较大, 其中物种丰富度指数(D)3月最高, 12月最低; 多样性指数(H′)和均匀度指数(J′)均在7月最高, 12月最低。多样性指数的空间分布呈现一定的月变化: 在3月、5月、7月均表现为北高南低; 9月为中部低, 南、北部海域较高; 12月均呈南高北低的趋势。蟹类单位网次渔获尾数空间分布格局呈现明显的月变化; 平均单位网次渔获尾数呈现一定的月变化, 总体上表现为3月、5月、12月高于7月和9月。Pearson相关分析结果表明, 在5月, 多样性指数(H′)和均匀度指数(J′)与底层水温呈显著负相关, 与底层盐度呈极显著正相关, 多样性指数还与水深呈显著正相关; 12月均匀度指数与底层水温和水深均呈极显著负相关, 与底层盐度呈显著负相关; 在3月、7月和9月, 各多样性指数与底层水温、底层盐度及水深均无显著相关性。海州湾蟹类种类组成及多样性的时空变化主要与海州湾地处温带海域、水温等海洋环境因子的季节变化以及优势种的数量分布有关。
The influence of a reclamation project on the macrobenthos of an East Nanhui tidal flat
围垦对南汇东滩湿地大型底栖动物的影响
Construction of a continuous trophic spectrum for the food web in Jiaozhou Bay using stable isotope analyses
应用稳定同位素技术构建胶州湾食物网的连续营养谱
The zooplankton community in Cosmonaut Sea: Community structure and environmental factors
南极夏季宇航员海浮游动物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系
The application of taxonomic diversity in macrobenthic ecology: Taking Yellow Sea for example
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.155
[本文引用: 1]

Using all available taxonomic data, we updated the master list of macrobenthos for the Yellow Sea, analyzed its taxonomic diversities and 95% probability funnels. There have been 1,360 species, belonging to 17 phyla, 35 classes, 91 orders, 368 families and 842 genera of macrobenthos recorded in the Yellow Sea. The value of average taxonomic distinctness for the region was 93.7, and the variation in taxonomic distinctness was 213.6. To explore the efficacy of these two diversity measures for environmental assessment, we superimposed estimates of these two values for some moderately polluted sites in Jiaozhou Bay on the 95% probability funnels, and all of the stations fell significantly below the 95% probability funnel of average taxonomic distinctness. This result shows the good application foregound of taxonomic diversity in marine pollution monitoring.
分类多样性在大型底栖动物生态学方面的应用: 以黄海底栖动物为例
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.155
[本文引用: 1]

根据文献资料, 系统整理了黄海大型底栖动物物种名录, 并得到了其平均分类差异指数和分类差异变异指数的理论平均值及95%置信区间漏斗图。结果表明, 黄海共有大型底栖动物1,360种, 分属于17门35纲91目368科842属。其平均分类差异指数的理论平均值为93.7, 分类差异变异指数为213.6。将已知受到中度扰动的胶州湾部分站位真实值叠加到平均分类差异指数的95%置信区间漏斗图中, 发现全部站位均显著低于95%置信区间, 显示了平均分类差异指数在海洋污染监测方面的良好应用前景。
Studies on the genetic diversity of marine organisms: A review
海洋生物遗传多样性研究现状
DNA barcoding of fish in Mischief Reef—Fish diversity of a reef-fish community from Nansha Islands
DOI:10.3389/fmars.2020.618954 URL [本文引用: 1]
Ten years accomplishment of Census of Marine Life
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08182 URL [本文引用: 1]
十年有成的“海洋生物普查计划”
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08182 [本文引用: 1]
Spatial variations in trophic-functional patterns of periphytic ciliates and indications to water quality in coastal waters of the Yellow Sea
The stress response of biological communities in China’s Yalu River Estuary and neighboring waters
DOI:10.5846/stxb201201310131 URL [本文引用: 1]
鸭绿江口及邻近海域生物群落的胁迫响应
Marine biodiversity: Why so high?
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.03227 [本文引用: 3]
海洋生物多样性: 为什么存在高的多样性?
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.03227 [本文引用: 3]
Protection of marine species diversity in China
Progress on marine biological studies in China over the past 70 years
中国海洋生物研究70年
Dynamics of ecosystems and anthropogenic drivers in the Yellow Sea large marine ecosystem
Marine biodiversity under global climate change
DOI:10.17520/biods.2016195 [本文引用: 2]
全球气候变化下的海洋生物多样性
DOI:10.17520/biods.2016195 [本文引用: 2]
The application of diversity indices in marine phytoplankton studies
多样性指数在海洋浮游植物研究中的应用
Preliminary study on macrobenthos in the second phase artificial reef construction area of Haizhou Gulf
海州湾人工鱼礁二期工程海域大型底栖生物初步研究
Microhabitat thermal environment controls community structure of macrobenthos on coastal infrastructures
DOI:10.1016/j.ecss.2022.108060 URL [本文引用: 1]
Climate change and marine ecosystems: Impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability
气候变化与海洋生态系统及服务: 影响、适应和脆弱性——IPCC AR6 WGII报告之解读性
Succession of macrofauna communities in wetlands of Sonneratia apetala artificial mangroves during different ecological restoration stages
DOI:10.5846/stxb201104210525 URL [本文引用: 1]
不同生态恢复阶段无瓣海桑人工林湿地中大型底栖动物群落的演替
Study on marine organism diversity in China
中国海洋生物多样性的研究
Methodological options for molecular marker technology in marine biology research
分子标记技术在海洋生物研究中的方法选择
Evolution analysis of members in family Carassiidae based on mitochondrial genome
基于线粒体基因组的鲹科鱼类进化分析
Community structure and spatial distribution of macrobenthos in the shelf area of the Bering Sea
Progress in marine ecosystem restoration
海洋生态系统修复研究进展
Distribution and environmental impact factors of picophytoplankton in the Eastern Indian Ocean
Spatial and temporal variation of phytoplankton and impacting factors in Jiulongjiang Estuary of Xiamen, China
九龙江河口浮游植物的时空变动及主要影响因素
Phytoplankton diversity and assessment of trophic state in Futian mangroves in Shenzhen
深圳红树林水体浮游植物多样性与营养状态评价
Research on the diversity of marine ecosystems
海洋生态系统多样性研究
Inter-annual variation in the community structure of crustaceans in the Bohai Sea during summer
渤海夏季甲壳类群落结构的年际变化
Effect of typhoon on the distribution of macroalgae in the seaweed beds of Gouqi Island, Zhejiang Province
台风对浙江枸杞岛大型底栖海藻分布的影响分析
DOI:10.13304/j.nykjdb.2018.0695
[本文引用: 1]

为深入认识台风对浙江岛礁大型底栖海藻分布的影响,为枸杞岛海藻场的恢复与重建工作提供基础资料,利用2012年11号强台风“海葵”的气象资料、嵊山气象站数据以及台风来临前(2012年5月)和台风过后(2012年8月)枸杞岛的大型底栖海藻、底质调查和暴波强度试验数据,运用线性回归分析“海葵”作用下枸杞岛最小气压和最大风速的变化情况,通过相对重要性指数确定枸杞岛海藻优势种并结合枸杞岛底质特征和暴波强度变化分析了优势种生物量分布变化对“海葵”的响应。结果表明,受“海葵”影响,枸杞岛附近海域的最小气压992.9 hPa,最大风速20 m/s,风力达9级水平,风向东东南—东南东向。在台风产生的风浪作用下,枸杞岛南面站点暴波强度大于北面站点。台风前后海藻的种类组成变化不显著。研究期间枸杞岛海藻优势种为瓦氏马尾藻(Sargassum vachellianum)、叉珊藻(Jania decussato-dichotoma)和网地藻(Dictyota dichotoma),主要种为铜藻(Sargassum horneri)、鸭毛藻(Symphyocladia latiuscula)和珊瑚藻(Corallina officinalis)。优势种和主要种海藻的生物量分布随暴波强度指数的增大而减小。结合台风对枸杞岛海藻场大型底栖海藻分布和生物量变化的影响结果,提出枸杞岛海藻场养护工作中应选择受台风影响较小的海域进行,并投放抗风浪能力强的礁体设施。
Research progress of genetic diversity
遗传多样性研究进展
Development trend of deep-sea ecosystem and marine protected areas
深海海洋生态系统与海洋生态保护区发展趋势
Biodiversity and biogeography of marine microbenthos: Progress and prospect
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.15121 URL [本文引用: 1]
海洋微型底栖生物的多样性与地理分布
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.15121
[本文引用: 1]

海洋微型底栖生物是指生活于海洋沉积物中及表面的所有单细胞原核和真核微型生物, 包括原核微生物、真核微藻及原生动物等光合自养和异养的类群。与水体相比, 海洋底栖生境孕育了形态和功能多样性更高的微型生物, 在陆架浅海单位体积沉积物中其丰度较之水体中同类生物高一至几个数量级, 而深海则孕育着特殊进化环境下新奇多样且数量庞大的微型底栖生物, 是维持海洋生物多样性、海洋生态系统结构和功能不可或缺的部分。迄今对于微型生物是全球性还是限定性分布一直存在争议, 对其解答受到分类研究欠缺及采样不足的制约。分子生物学从正反两方面提供了理论依据, 但无法得出一个普遍接受的观点。海洋微型底栖生物的多样性研究侧重于物种多样性及群落结构与分子多样性, 较为显著的进展体现在原核微生物的分子多样性及底栖真核微藻的物种多样性研究, 对于海洋底栖原生动物的多样性研究则相较滞后。本文综述了国内外对海洋微型底栖生物各主要类群 的分类学和多样性研究进展, 探讨了各类群在全球的潜在物种多样性, 并就我国未来加强海洋微型底栖生物多样性构成、分布与变动及驱动变化的因子以及底栖微食物网的研究提出了建议。
Preface
Marine taxonomy in the China Seas and Western Pacific Ocean: Progress and prospects
中国海及西太平洋生物分类研究进展及展望
Structure and taxonomic composition of free-living nematode and macrofaunal assemblages in a eutrophic subtropical harbour, Hong Kong
DOI:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.01.023
PMID:24467853
[本文引用: 1]

The spatial and seasonal taxonomic composition patterns of macrofauna and nematodes in a eutrophic subtropical harbour, previously suffered from sewage pollution, were studied in relation to a number of sediment parameters. In the polluted, inner-harbour area, levels of organic contents and heavy metals were high, whereas species number, abundance and diversity of nematodes and macrofauna were the lowest in comparison to the cleaner, outer-harbour area. Different taxonomic composition patterns of nematodes and macrofaunal assemblages were found between inner-harbour and outer-harbour area, which was highly correlated with sediment nutrient levels. Different responses of macrofaunal and nematode communities to sewage pollution suggested that macrofauna might be more tolerant than nematodes to eutrophic conditions due to their ability to modify the sediment. The present findings indicated the usefulness of studying both nematode and macrofaunal communities, in order to reveal different aspects of the benthic ecosystems in response to organic enrichment. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
The past and the future of zooplankton diversity studies in China seas
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.11120 URL [本文引用: 1]
中国近海浮游动物多样性研究的过去和未来
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.11120
[本文引用: 1]

中国是世界上南北纬度跨度最大的国家之一。复杂的气候、水文和地形因素形成了我国海洋环境的多样性, 也造就了浮游动物多样性的格局。我国浮游动物多样性的研究经历了分类、分布为主、环境变化对浮游动物的影响和浮游动物环境适应研究等阶段。在我国, 地形、季风和水团是形成海洋环境格局的三大驱动力, 因此不同环境对浮游动物的影响是较为活跃的研究方面。无论在我国还是在世界上, 浮游动物对环境适应的研究是薄弱环节, 研究方法的缺乏是重要的原因。近年来, 已经解决了利用现场调查获得的多学科观测数据和资料(field data)结合统计方法求得种类最适温度、最适温度区间等生态学参数的技术难点。yield-density函数模型, 麦夸特(Marquardt)法曲线拟合, 中值定理, 龙贝格(Romberg)积分法计算等数学方法得到应用。这些研究方法应用在生态类群划分是一项创新, 对于浮游动物多样性成因分析有重大意义, 未来浮游动物多样性应从不同生境、不同时空尺度、不同分类单元、不同粒径谱、不同生态类群和不同测度方法等多个方向展开, 而这些领域的应用研究是浮游动物多样性最具前景的方向。
Advances in DNA barcoding of macrozoobenthos in coastal waters of China
中国近海大型底栖动物DNA条形码的研究进展
Effect of activities associated with coastal reclamation on the macrobenthos community in coastal wetlands of the Yellow River Delta, China: A literature review and systematic assessment
Spatial-temporal variations of benthic macroalgae and their responses to variations in the environment in the artificial reef zones of Laoshan Bay
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1118.2018.17268 URL [本文引用: 1]
崂山湾人工礁区大型底栖海藻时空格局及对环境变化的响应
Community characteristics and genetic diversity of macrobenthos in Haima cold seep
DOI:10.3389/fmars.2022.920327 URL [本文引用: 2]
Study on the macroalgae based on the ArcGIS in Nanji Islands Marine Nature
基于ArcGIS的南麂列岛潮间带大型底栖藻类研究
Development and application of DNA barcoding technology for macroalgae
大型海洋藻类DNA条形码技术的开发与应用
An ecosystem perspective on fisheries conservation based on the importance of the big old fish
大型年长鱼类对海洋生态系统生物资源养护的作用
Seasonal succession of macroalgae community in Naozhou Island
DOI:10.11978/2019026
[本文引用: 2]

Seasonal investigation of intertidal zones of Naozhou Island was conducted from April 2011 to January 2012. The results show that there were 64 species of macroalgae in this Sargasso field, including 15 species of Phaeophyta, 28 species of Rhodophyta, 20 species of Chlorophyta and one species of Cyanophyta, accounting for 23.44%, 43.75%, 31.25% and 1.56% of the total species, respectively. Among the 64 species, 43 species were thriving in spring, 24 species were emerging in summer, 29 species were active in autumn and 31 in winter. Only nine species were thriving throughout the whole year, including six species of Rhodophyta, two species of Chlorophyta and one species Phaeophyta, while there were 14 species living through three seasons. There were about 12-26 common species that can be found between two seasons and the species turnover rate was from 0.42 to 0.78, associated with higher turnover rates in spring and summer and lower rates in autumn and winter. Moreover, there were 13 dominant species but only Pterocladiella capillacea was the all-year dominant species, while Sargassum hemiphyllum and Corallina pilulifera were the dominant species over three seasons. Average biomass vary greatly with season, with the order of spring (848.14 g·m-2)> winter (378.57 g·m-2)> autumn (297.99 g·m-2)> summer (294.15 g·m-2). There is clearly vertical variation in the species distribution as the species number increases significantly from high tidal zone to low tidal zone, while the biomass show similar changing trend, indicating both species and biomass increase with water depth in the tidal zone. The Shannon-Weinner index was from 0.03 to 2.33, with an annual average of 1.10, while the Pielou's index was from 0.01 to 0.70, with an annual average of 036; the Margalef index varied from 0.15 to 1.65, with an annual average of 0.72; and the Simpson’s dominance index varied from 0.01 to 0.78, with an annual average of 0.39. The total water content of seaweeds changes ranged from 51.42% to 97.52%, with an average moisture of 85.21%. The total organic carbon content of seaweeds varied from 4.34% to 42.06%, with an average of 27.99%, indicating a strong carbon storage capacity. We find a clear negative correlation between the biomass of large seaweeds and dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN), with a coefficient of 0.49 (P<0.05). The lower DIN of seawater during spring and winter is coincided with microalgae thriving seasons.
硇洲岛大型海藻群落的季节演替
DOI:10.11978/2019026
[本文引用: 2]

2011年4月至2012年1月对硇洲岛潮间带大型海藻进行了周年的季节调查, 结果表明, 调查海域大型海藻共有64种。其中褐藻门15种, 占总种类数的23.44%; 红藻门28种, 占总种类数的43.75%; 绿藻门20种, 占总种类数的31.25%; 蓝藻门1种, 占总种类数的1.56%。其种类数春季最多, 共43种; 夏季24种; 秋季29种; 冬季31种。有9个物种为4个季节共有种, 有14个物种为3个季节共有种。各季节间共有种类数为12~26种, 季节间种类更替率为0.42~0.78, 春夏季种类更替率最高, 秋冬季种类更替率最低。优势种共有13种, 仅拟鸡毛菜Pterocladiella capillacea为全年优势种, 而半叶马尾藻Sargassum hemiphyllum和小珊瑚藻Corallina pilulifera为3个季节共有优势种。调查海域大型海藻生物量季节变化明显, 平均生物量春季最高, 冬季次之, 夏季最低。不同物种其垂直分带明显, 从高潮区往低潮区种类数不断增多; 生物量也是从高潮区往低潮区逐渐增大。物种多样性指数变化范围为0.03~2.33, 年均值为1.10; 均匀度变化范围为0.01~0.70, 年均值为0.36; 种类丰富度指数变化范围为0.15~1.65, 年均值为0.72; 辛普森优势度指数变化范围为0.01~0.78, 年均值为0.39。各大型海藻含水率变化范围在51.92%~97.52%, 平均值为85.21%; 总有机碳含量变化范围在4.34%~42.06%, 平均为27.99%。相关性分析发现, 调查海域大型海藻生物量与无机氮(DIN)呈显著负相关, 相关系数为0.49(P<0.05), 与其他环境因子的相关性不明显。在大型海藻生长旺盛的冬春季, 海水中的无机氮(DIN)含量最低, 与其他自然海域冬季营养盐积累规律显著不同。
The morphological and molecular phylogenetic studies of a new record Gymnothorax species in the coastal waters of China: Gymnothorax mucifer
我国近海裸胸鳝属鱼类新记录种——黏裸胸鳝(Gymnothorax mucifer)形态与分子系统学研究
Species composition and biomass density of mesopelagic nekton of the South China Sea continental slope
The variation of biodiversity of macrobenthic fauna with salinity and water depth near the Pearl Estuary of the northern South China Sea
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13141
[本文引用: 1]

To study the relationship between macrobenthic fauna and environmental factors, we investigated four transects from coast to deep-sea waters near the Pearl Estuary in the northern South China Sea from July -August 2006 (Summer, wet season), April-May 2007 (Spring, normal water season), and October-December 2007 (Autumn, dry season). A total of 273 species, 256 species and 148 species were identified in spring, summer and autumn, respectively. Macrobenthic fauna belonging to the Annelida phylum had the greatest species richest, followed by Arthropoda, Mollusca, and Echinodermata. The species richness, abundance and biomass of macrobenthic fauna increased from estuary sites to coastal sites, and decreased from coastal sites to deep-sea sites. The Shannon-Wiener index of macrobenthic fauna was higher in coastal sites than those in estuary and deep-sea sites. The species evenness of macrobenthic fauna was the highest in deep-sea sites, followed by coast and estuary sites. The k-dominance curves of macrobenthic fauna were higher in estuary and deep-sea sites than that in coastal sites. These results show that the macrobenthic biodiversity was the highest in coastal sites. Species richness, abundance, and biomass of macrobenthic fauna are negatively correlated with water depth in spring and autumn, but only biomass of macrobenthic fauna is negatively correlated with water depth in summer. The species richness, abundance, Shannon-Wiener index, and species evenness of macrobenthic fauna are positively correlated with salinity in the bottom of the water column in summer, but are not correlated in spring and autumn.
珠江口及邻近海域大型底栖动物多样性随盐度、水深的变化趋势
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13141
[本文引用: 1]

利用2006年7-8月(夏季)、2007年4-5月(春季)和2007年10-12月(秋季)珠江丰水期、平水期和枯水期3个航次在南中国海北部珠江口附近海域4条由河口、近岸到深水区调查断面的数据, 研究大型底栖动物多样性由河口-近岸-深水的变化趋势及与环境因子的关系。春季、夏季和秋季分别获得大型底栖动物273、256和148种, 各季节均以环节动物种类最多, 节肢动物次之。大型底栖动物种类数、丰度、生物量和Shannon-Wiener多样性指数均由河口向近岸海域升高, 再由近岸向外海深水区降低。Pielou均匀度深水区最高, 其次为近岸。河口和深水区大型底栖动物k-优势度曲线位于近岸浅水域曲线之上, 表明生物多样性由河口向近岸升高, 而由近岸向深水则降低。大型底栖动物与环境因子Pearson相关性分析表明, 春、秋季大型底栖动物种类数、丰度和生物量与水深呈显著的负相关, 秋季种类多样性指数和均匀度也与水深呈显著的负相关性, 而夏季仅生物量与水深呈显著的负相关; 春、秋季大型底栖动物种类数、生物量、丰度、多样性指数和种类均匀度与盐度的相关性不显著, 但是夏季大型底栖动物种类数、丰度、多样性指数和种类均匀度与盐度呈显著正相关。单位面积(0.2 m<sup>2</sup>)内, 珠江口及邻近海域大型底栖动物在近岸浅水区较深水区和河口生物多样性高, 且生物量丰富。
Progress and prospect in marine benthology in China
中国海洋底栖生物学发展回顾与展望
Overview of China’s ocean satellite development
我国海洋卫星发展综述
Phytoplankton in the deep sea, a review
深层海洋浮游植物研究综述
Biogeography of epipelagic marine plankton
上层海洋浮游生物地理分布
Ecological characteristics of macrobenthic communities and their relation to water environmental factors in four bays of southern Shandong Peninsula
山东半岛南部海湾底栖动物群落生态特征及其与水环境的关系
SRAP analysis on germplasm of wild Meretrix meretrix off Chinese coasts
我国沿海不同地理原种文蛤(Meretrix meretrix)的SRAP分析
Effects of thermal water discharged from Huangdao power plant on structure of macrozoobenthos
黄岛电厂温排水对大型底栖生物群落的影响
Genetic diversity status and conservation strategies of Miichthys miiuy
鮸鱼的遗传多样性现状及保护策略
Status of fishery resources near Daishan Island in Zhejiang Province, China
浙江岱山岛附近海域春秋季渔业资源调查研究