Investigation of species diversity of myxomycetes in Dabie Mountains
- College of Life Sciences, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210023
Received date: 2023-07-04
Accepted date: 2023-11-29
Online published: 2023-11-29
Abstract
Aims Myxomycetes (or Myxogastrea) are one of the elementary taxa of the biodiversity components in terrestrial ecosystems. Myxomycetes play important ecological roles in forests. Dabie Mountains are one of the most important mountains with biodiversity significance in Central China and even in China. However, the previous survey of the species diversity of myxomycetes is limited to the site of Tiantangzhai National Forest Park. Myxomycetes in other areas of the Dabie Mountains are unknown. In this study, we are striving to fully obtain and understand the basic information of myxomycete species diversity to reveal species compositions and distribution characteristics of myxomycetes in the Dabie Mountains.
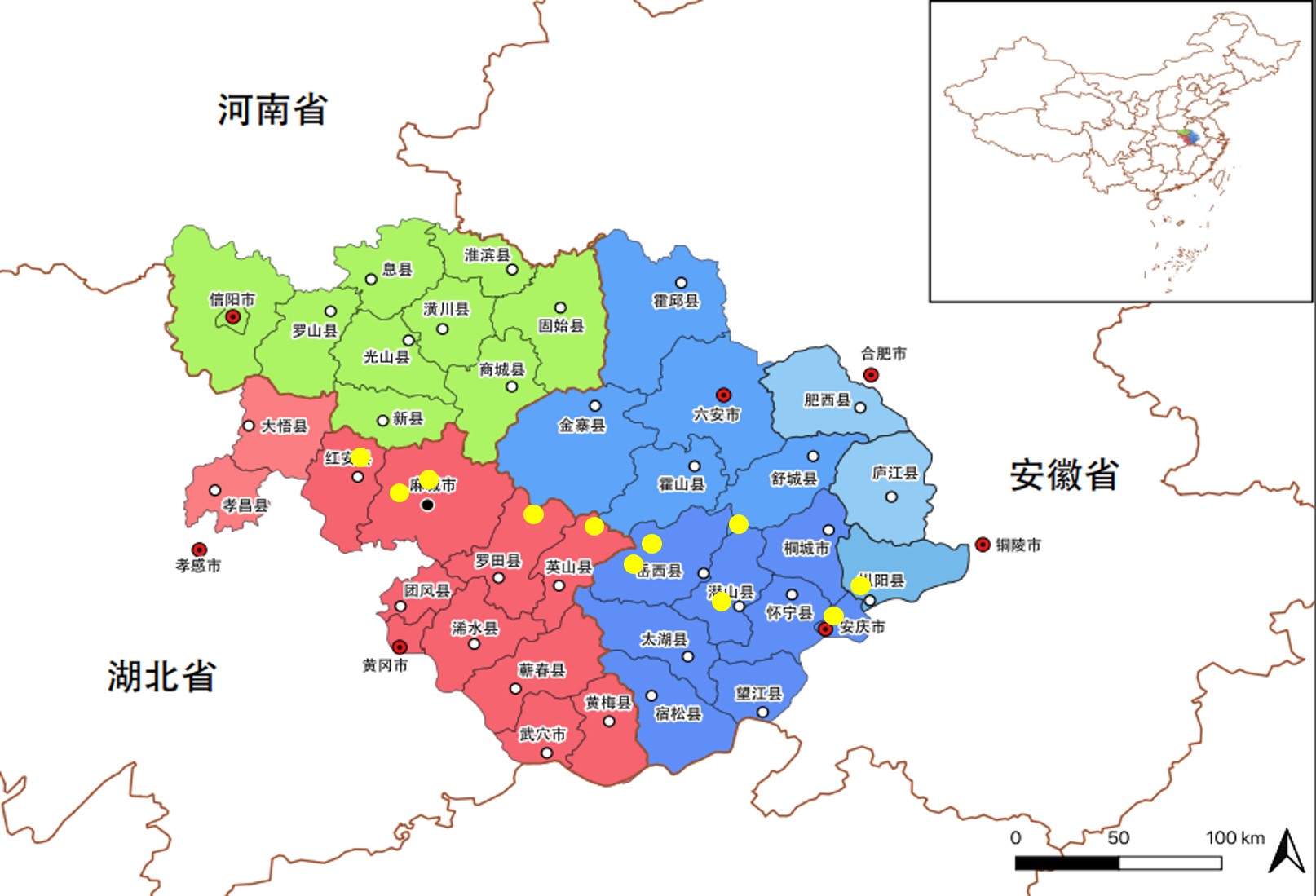
Method An investigation into myxomycete species was conducted in 21 nature reserves or national forest parks in the Dabie Mountains during August 2020 and September 2022. The habitats of species were surveyed and recorded. Specimens were collected directly in the field and harvested in moist chamber culture. Species were identified based on morphological taxonomy.
Results A total of 984 specimens were obtained by field collection and substrate wet chamber culture and all myxomycete specimens were identified as 93 species belonging to 32 genera, 13 families, and 6 orders. Presently in China, Craterium muscorum and Diderma fragile were only recorded in the Dabie Mountains. Totally, 48 species including Ophiotheca pedata, Stemonitis herbatica and Trichia varia for the Dabie Mountains were firstly recorded. Based on the principle dividing relative abundance (RA) of myxomycete species, 11 species were abundant (RA > 3%), 8 species were common (RA = 1.5%-3.0%), 30 species were occasional (RA = 0.5%-1.5%) and 44 species were rare (RA < 0.5%). Species richness of myxomycetes varied among different habitats, types of substrates and forest types in the Dabie Mountains. The species richness at Dongzhai Nature Reserve, Henan Province was higher than those at other 20 protective areas, in which 41 species were found, the species/genus ratio was 1.95, and 3 species were specific. The richness of myxomycete species on rotten wood was higher than those on living bark, living grass and litters, on which 77 species were found, the species/genus ratio was 2.75, and 42 species were specific. The richness of myxomycete species in conifer-broadleaf mixed forest was higher than those in the coniferous forest and broad-leaved forest, in which 81 species were found, the species/genus ratio was 2.89, and 28 species were specific.
Conclusion The species composition and richness of myxomycetes are different among 21 protective areas of the Dabie Mountains, thus forming different species distribution patterns. The species diversity of myxomycetes in rotten wood and conifer-broadleaf mixed forests is higher than those on other growth substrate and single forest type. It provides important information on myxomycete diversity for a comprehensive understanding of the biodiversity in the Dabie Mountains.
Cite this article
Di Lin , Shuanglin Chen , Que Du , Wenlong Song , Gu Rao , Shuzhen Yan . Investigation of species diversity of myxomycetes in Dabie Mountains[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2024 , 32(2) : 23242 . DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023242
References
| [1] | Archaux F (2009) Could we obtain better estimates of plot species richness from multiple-observer plant censuses? Journal of Vegetation Science, 20, 603-611. |
| [2] | Balaoro-Banzuela RC, Ocenar-Bautista CE, Buebos-Esteve DE, Claudio-Paragas CY, Limbo-Dizon JE, Dagamac NHA (2023) Rapid diversity assessment of litter myxomycete assemblages in the upland and coastal terrains of San Fernando City, La Union, Philippines. Biodiversitas, 24, 2877-2886. |
| [3] | Cabutaje EM, Pecundo MH, dela Cruz TEE (2021) Diversity of myxomycetes in typhoon-prone areas: A case study in beach and inland forests of Aurora and Quezon Province, Philippines. Sydowia, 73, 113-132. |
| [4] | Chao A, Chazdon RL, Colwell RK, Shen TJ (2005) A new statistical approach for assessing similarity of species composition with incidence and abundance data. Ecology Letters, 8, 148-159. |
| [5] | Dahl MB, Brejnrod AD, Russel J, S?rensen SJ, Schnittler M (2019) Different degrees of niche differentiation for bacteria, fungi, and myxomycetes within an elevational transect in the German Alps. Microbial Ecology, 78, 764-780. |
| [6] | Dai Q, Yan SZ, Yao HQ, Chen SL (2013) Myxomycete diversity in hilly forests of East China. Biodiversity Science, 21, 507-513. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戴群, 闫淑珍, 姚慧琴, 陈双林 (2013) 华东丘陵林地黏菌的物种多样性. 生物多样性, 21, 507-513.] | |
| [7] | Deng SQ (1963) Fungi of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [邓叔群 (1963) 中国的真菌. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] | Gao Y, Chen SL (2021) Research progress on distribution and ecology of Myxogastrea. Mycosystema, 40, 2537-2549. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高扬, 陈双林 (2021) 黏菌分布格局与生态学研究进展. 菌物学报, 40, 2537-2549.] | |
| [9] | Gao Y, Song HY, Zhou F, Chen SL, He G, Yan JQ, Sun QB, Long HZ, Zhai ZJ, Hu DM, Hu HJ (2022) Community of soil-inhabiting myxomycetes shares similar assembly mechanisms with fungi, and is affected by bacterial community in subtropical forests of China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 175, 108854. |
| [10] | Gao Y, Yan SZ, Wang GW, He G, Chen SL (2018) Notes on myxomycetes from Baotianman National Nature Reserve of Henan Province. Journal of Fungal Research, 16, 170-181. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高扬, 闫淑珍, 王高伟, 何刚, 陈双林 (2018) 河南宝天曼自然保护区黏菌初报. 菌物研究, 16, 170-181.] | |
| [11] | Keller HW, Everhart SE, Kilgore CM (2022) The myxomycetes:Introduction, basic biology, life cycles, genetics, and reproduction. In: Myxomycetes: Biology, Systematics, Biogeography and Ecology, 2nd edn. (eds Stephenson SL, Rojas C), pp. 1-45. Academic Press, London. |
| [12] | Lado C (2005-2023) An on-line Nomenclatural Information System of Eumycetozoa. http://www.nomen.eumycetozoa.Com. (accessed on 2023-04-25) |
| [13] | Lado C, Eliasson U (2022) Taxonomy and systematics:Current knowledge and approaches on the taxonomic treatment of myxomycetes. In: Myxomycetes: Biology, Systematics, Biogeography and Ecology, 2nd edn. (eds Stephenson SL, Rojas C), pp. 269-324. Academic Press, London. |
| [14] | Li HZ (1989) Myxomycetes from China. IV. Taxonomic study on the myxomycetes of Shennongjia. In: Fungi and Lichens of Shennongjia (ed. Mycological and Lichenological Expedition to Shennongjia, Academia Sinica), pp. 1-78. World Publishing Corporation, Beijing. (in Chinese). |
| [李惠中 (1989) 中国黏菌IV:神农架地区黏菌的分类研究. 见: 《神农架地区真菌与地衣》 (中国科学院神农架真菌地衣考察队主编), 1-78页. 世界图书出版社, 北京.] | |
| [15] | Li M, Gao Y, Zhang X, Wang R, Chen SL, Yan SZ (2021) Specific composition and ecological characteristics of myxomycetes in Xingshan County, Hubei Province. Mycosystema, 40, 357-371. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李敏, 高扬, 张鲜, 王睿, 陈双林, 闫淑珍 (2021) 湖北省兴山县黏菌的物种组成与生态特征. 菌物学报, 40, 357-371.] | |
| [16] | Li M, Tao X, Li B, Du Q, Zhu XQ, Huang DM, Yan SZ, Chen SL (2021a) Spatiotemporal distribution and dynamic changes of myxomycetes in subtropical forests of China. Fungal Ecology, 53, 101078. |
| [17] | Li M, Wang GW, Gao Y, Dou MZ, Wang ZQ, Yan SZ, Chen SL (2021b) Distribution and diversity of myxomycetes in Tiantangzhai National Forest Park, China. PeerJ, 9, e12059. |
| [18] | Li Y, Li HZ, Wang Q, Chen SL (2008a) Flora Fungorum Sinicorum·Myxomycetes (I): Ceratiomyxales, Echino- steliales, Liceales, Trichiales. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李玉, 李惠中, 王琦, 陈双林 (2008a) 中国真菌志·黏菌卷(I): 鹅绒菌目, 刺轴菌目, 无丝菌目和团毛菌目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [19] | Li Y, Li HZ, Wang Q, Chen SL (2008b) Flora Fungorum Sinicorum·Myxomycetes (II): Physarales, Stemonitales. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李玉, 李惠中, 王琦, 陈双林 (2008b) 中国真菌志·黏菌卷II: 绒泡菌目, 发网菌目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [20] | Liu CH, Chang JH, Yang FH (2007) Myxomycetous genera Perichaena and Trichia in Taiwan. Botanical Studies, 48, 91-96. |
| [21] | Liu QS, Yan SZ, Chen SL (2015) Species diversity of myxomycetes associated with different terrestrial ecosystems, substrata (microhabitats) and environmental factors. Mycological Progress, 14, 17-39. |
| [22] | Ma KP (2015) Biodiversity monitoring in China: From CForBio to Sino BON. Biodiversity Science, 23, 1-2. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (2015) 中国生物多样性监测网络建设: 从CForBio到Sino BON. 生物多样性, 23, 1-2.] | |
| [23] | Ma KP, Liu CR, Liu YM (1995) Measurement of biotic community diversity: II. β diversity. Chinese Biodiversity, 3, 38-43. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平, 刘灿然, 刘玉明 (1995) 生物群落多样性的测度方法. Ⅱ. β多样性的测度方法. 生物多样性, 3, 38-43.] | |
| [24] | Macabago SAB, Stephenson SL, dela Cruz TEE (2016) Diversity and distribution of myxomycetes in coastal and mountain forests of Lubang Island, Occidental Mindoro, Philippines. Mycosphere, 7, 18-29. |
| [25] | Mueller GM, Schmit JP, Leacock PR, Buyck B, Cifuentes J, Desjardin DE, Halling RE, Hjortstam K, Iturriaga T, Larsson KH, Lodge DJ, May TW, Minter D, Rajchenberg M, Redhead SA, Ryvarden L, Trappe JM, Watling R, Wu QX (2007) Global diversity and distribution of macrofungi. Biodiversity and Conservation, 16, 37-48. |
| [26] | Ndiritu GG, Spiegel FW, Stephenson SL (2009) Distribution and ecology of the assemblages of myxomycetes associated with major vegetation types in Big Bend National Park, USA. Fungal Ecology, 2, 168-183. |
| [27] | Novozhilov YK, Rollins A, Schnittler M (2022) Ecology and distribution of myxomycetes. In: Myxomycetes: Biology, Systematics, Biogeography and Ecology, 2nd edn. (eds Stephenson SL, Rojas C), pp. 325-376. Academic Press, London. |
| [28] | Novozhilov YK, Schnittler M (2008) Myxomycete diversity and ecology in arid regions of the Great Lake Basin of western Mongolia. Fungal Diversity, 30, 97-119. |
| [29] | Rojas C, Stephenson SL (2012) Rapid assessment of the distribution of myxomycetes in a southwestern Amazon forest. Fungal Ecology, 5, 726-733. |
| [30] | Ruggiero MA, Gordon DP, Orrell TM, Bailly N, Bourgoin T, Brusca RC, Cavalier-Smith T, Guiry MD, Kirk PM (2015) A higher level classification of all living organisms. PLoS ONE, 10, e0130114. |
| [31] | Schnittler M, Stephenson SL (2000) Myxomycete biodiversity in four different forest types in Costa Rica. Mycologia, 92, 626-637. |
| [32] | Shen XS (1995) An analysis of flora on the vegetation of the Dabie Mountains. Journal of Anhui University (Natural Science Edition), 19(4), 89-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈显生 (1995) 大别山区植物区系的分析. 安徽大学学报(自然科学版), 19(4), 89-94.] | |
| [33] | Snell KL, Keller HW (2003) Vertical distribution and assemblages of corticolous myxomycetes on five tree species in the Great Smoky Mountains National Park. Mycologia, 95, 565-576. |
| [34] | Song WL, Lin D, Li M, Du Q, Chen SL (2022) Four new records of myxomycetes from China. Phytotaxa, 567, 181-188. |
| [35] | Stephenson SL (1989) Distribution and ecology of myxomycetes in temperate forests. II. Patterns of occurrence on bark surface of living trees, leaf litter, and dung. Mycologia, 81, 608-621. |
| [36] | Stephenson SL, Kalyanasundaram I, Lakhanpal TN (1993) A comparative biogeographical study of myxomycetes in the mid-appalachians of eastern north America and two regions of India. Journal of Biogeography, 20, 645-657. |
| [37] | Stephenson SL, Marbaniang TM, Gupta P, Rojas C (2020) Assemblages of corticolous myxomycetes associated with species of Pinus (Pinaceae) in four different regions of the world. Nova Hedwigia, 111, 199-217. |
| [38] | Tang Y, Zhang Z, Wang R, Zhang YH, Liu SS (2017) Preliminary study on seed plants flora of Dabie Mountain in Anhui Province. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 37, 1438-1446. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [唐瑶, 张震, 王瑞, 张云华, 刘伸伸 (2017) 安徽大别山区种子植物区系的初步研究. 西北植物学报, 37, 1438-1446.] | |
| [39] | Wang GW, Yan SZ, Gao Y, He G, Chen SL (2017a) Notes on myxomycetes from Tiantangzhai of Anhui Province. Journal of Fungal Research, 15, 121-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王高伟, 闫淑珍, 高扬, 何刚, 陈双林 (2017a) 安徽天堂寨黏菌初报. 菌物研究, 15, 121-128.] | |
| [40] | Wang GW, Yan SZ, Xu MQ, Dai Q, Yao HQ, Liu QS, Chen SL (2017b) The myxomycete species in Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Anhui of Eastern China. Mycosystema, 36, 454-465. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王高伟, 闫淑珍, 徐美琴, 戴群, 姚慧琴, 刘歧莎, 陈双林 (2017b) 华东苏、浙、皖三省的黏菌物种. 菌物学报, 36, 454-465.] | |
| [41] | Wu Q, Chen X, Cao Q, Chen YT, Yue W (2022) Variation characteristics of agricultural climatic resources in area of Dabie Mountains in China from 1961 to 2020. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 51(2), 75-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [伍琼, 陈曦, 曹强, 陈砚涛, 岳伟 (2022) 1961-2020年大别山区农业气候资源变化特征分析. 河南农业科学, 51(2), 75-85.] | |
| [42] | Yao YJ, Li Y, Liu P (2023) China checklist of fungi. In: Catalogue of Life China. Biodiversity Committee of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [姚一建, 李玉, 刘朴 (2023) 中国真菌名录. 见: 中国生物物种名录. 中国科学院生物多样性委员会, 北京.] http://www.sp2000.org.cn/. (accessed on 2023-05-01) | |
| [43] | Zhang B, Li Y (2014) Dictydiaethalium dictyosporangium sp. nov. from China. Mycotaxon, 129, 455-458. |
| [44] | Zhang B, Li Y (2016) A new species and two new records of Stemonitidaceae from China. Phytotaxa, 267, 151-156. |
| [45] | Zhao HN, Xu XQ, Dai D, Wang SY, Zhang B, Li Y (2022) Review on moist chamber cultures of myxomycetes. Journal of Fungal Research, 20, 51-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵慧楠, 徐晓琪, 戴丹, 王赛禹, 张波, 李玉 (2022) 真黏菌湿室培养研究进展. 菌物研究, 20, 51-64.] | |
| [46] | Zhu CX, Peng HS (2021) Analysis of new plant taxa and their medicinal value during the last 40 years of Dabie Mountains. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 36, 6627-6630. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱晨星, 彭华胜 (2021) 大别山区近40年植物新分类群及其药用价值分析. 中华中医药杂志, 36, 6627-6630.] |