全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析
- 中国疾病预防控制中心传染病预防控制所媒介生物控制室, 传染病溯源预警与智能决策全国重点实验室, 北京 102206
收稿日期: 2023-05-25
录用日期: 2023-07-31
网络出版日期: 2023-08-14
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(31970005);国家科技重大专项(2017ZX10303404)
Analysis for the prevalence of global bat-borne Bartonella
- Department of Vector Biology and Control, National Institute for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention, National Key Laboratory of Intelligent Tracking and Forecasting for Infectious Diseases, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing 102206
Received date: 2023-05-25
Accepted date: 2023-07-31
Online published: 2023-08-14
摘要
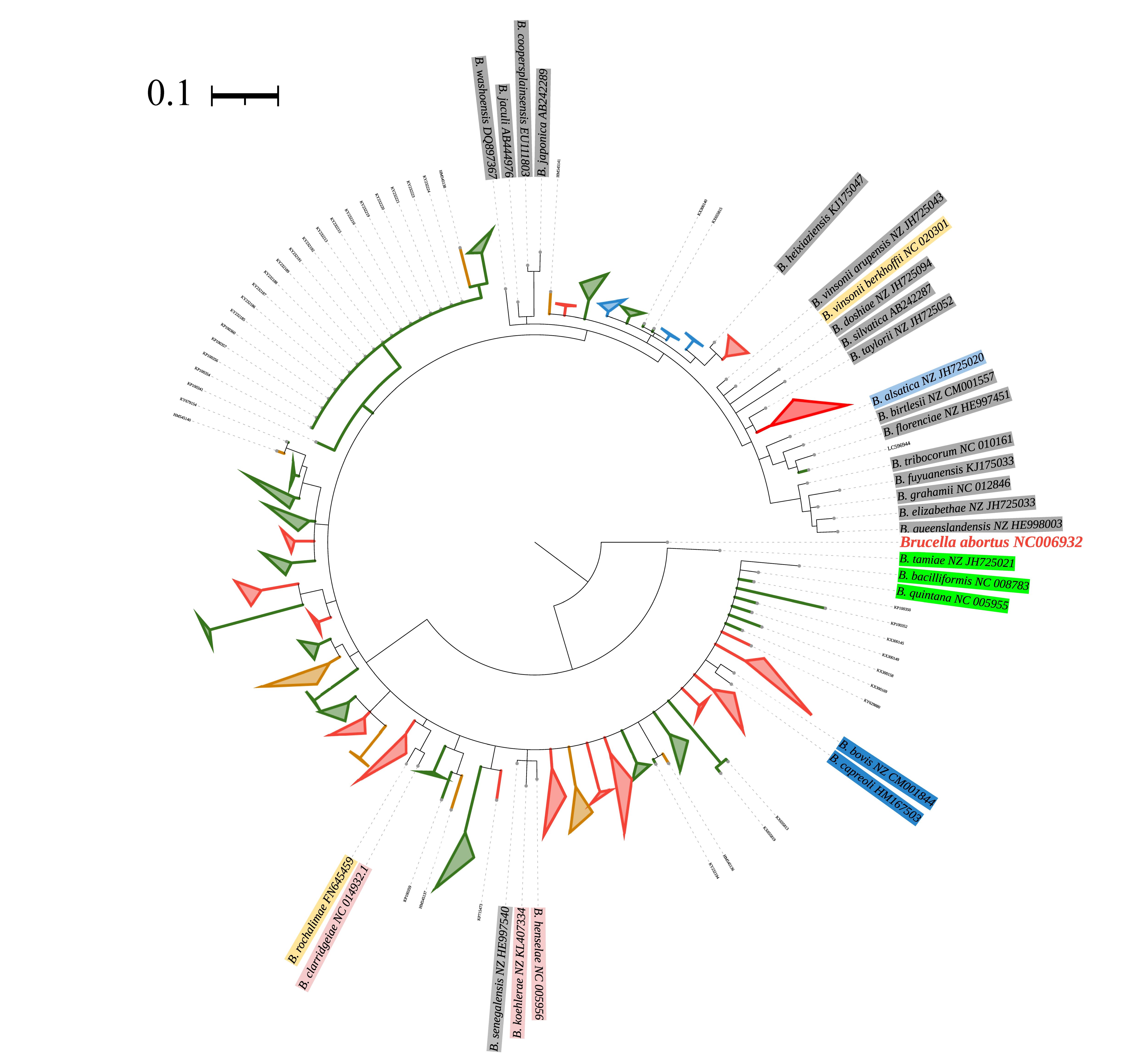
巴尔通体是一群全球广泛分布的细菌, 部分种类能引起多种人兽共患病, 宿主包括食肉类、反刍类、啮齿类、灵长类以及海洋中鲸类等哺乳动物。近年来, 世界各地陆续报道蝙蝠能够携带巴尔通体。为了解全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行情况, 本文系统检索汇总了自2005年以来世界各地对蝙蝠巴尔通体的研究, 较为详细地描述了巴尔通体在蝙蝠这一大类群中的感染状况、宿主分布及遗传进化关系等信息。分析发现, 在31个国家和地区的106种蝙蝠体内检测到巴尔通体, 表明蝙蝠是巴尔通体重要的动物宿主。通过对蝙蝠巴尔通体柠檬酸合酶基因(citrate synthase gene, gltA)序列构建系统发育树, 发现绝大多数蝙蝠巴尔通体与其他宿主来源的巴尔通体亲缘关系较远, 构成蝙蝠巴尔通体独立的类群, 初步揭示这一类巴尔通体具有宿主特异性特征, 提示巴尔通体可能与宿主蝙蝠存在协同进化关系。
本文引用格式
李庆多 , 栗冬梅 . 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023 , 31(9) : 23166 . DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023166
Abstract
Background & Aim Bartonellae is a worldwide group of bacteria that causes a variety of zoonoses. Their hosts include carnivores, ruminants, rodents, and even mammals such as marine whales. Recently, it has been discovered that Bartonellae can infect bats, one of the important host animals for Bartonellae, worldwide. This review summarizes studies of bat-borne Bartonella worldwide since 2005 to illustrate the prevalence of Bartonellae in bats.
Context & Conclusions Bartonellae has been detected in 106 bat species in 31 countries and regions around the world, indicating that bats are major animal hosts. The feeding habit of bats does not affect whether they can carry Bartonellae, which has been found in bats with multiple feeding habits. The phylogenetic tree based on gltA sequences of bat-borne Bartonella displayed that most bat-borne Bartonella sequences are distant from other host-derived Bartonella and constituted a bat-origin Bartonella group. Bat-borne Bartonella, which has spread with bats worldwide, is host-specific to a certain extent. It is hinted that there is coevolution between Bartonellae and bat hosts.

Key words: Bartonella; bat; bacteria; genetic diversity; phylogenetic analysis; coevolution
参考文献
| [1] | André MR, Gutiérrez R, Ikeda P, Amaral RB, Sousa KCM, Nachum-Biala Y, Lima L, Teixeira MMG, Machado RZ, Harrus S (2019) Genetic diversity of Bartonella spp. in vampire bats from Brazil. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 66, 2329-2341. |
| [2] | Anh PH, Van Cuong N, Son NT, Tue NT, Kosoy M, Woolhouse MEJ, Baker S, Bryant JE, Thwaites G, Carrique-Mas JJ, Rabaa MA (2015) Diversity of Bartonella spp. in bats, southern Vietnam. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 21, 1266-1267. |
| [3] | Bai Y (2011) Bartonella spp. in bats, Guatemala. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 17, 1269-1272. |
| [4] | Bai Y, Gómez J, Kosoy MY, Recuenco S, Osikowicz LM, Rupprecht C, Gilbert AT (2012) Prevalence and diversity of Bartonella spp. in bats in Peru. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 87, 518-523. |
| [5] | Bai Y, Osinubi MOV, Osikowicz L, McKee C, Vora NM, Rizzo MR, Recuenco S, Davis L, Niezgoda M, Ehimiyein AM, Kia GSN, Oyemakinde A, Adeniyi OS, Gbadegesin YH, Saliman OA, Ogunniyi A, Ogunkoya AB, Kosoy MY (2018) Human exposure to novel Bartonella species from contact with fruit bats. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 24, 2317-2323. |
| [6] | Bai Y, Urushadze L, Osikowicz L, McKee C, Kuzmin I, Kandaurov A, Babuadze G, Natradze I, Imnadze P, Kosoy M (2017) Molecular survey of bacterial zoonotic agents in bats from the country of Georgia (Caucasus). PLoS ONE, 12, e171175. |
| [7] | Becker DJ, Bergner LM, Bentz AB, Orton RJ, Altizer S, Streicker DG (2018) Genetic diversity, infection prevalence, and possible transmission routes of Bartonella spp. in vampire bats. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 12, e0006786. |
| [8] | Breitschwerdt EB (2017) Bartonellosis, One Health and all creatures great and small. Veterinary Dermatology, 28, 96-e21. |
| [9] | Brook CE, Bai Y, Dobson AP, Osikowicz LM, Ranaivoson HC, Zhu QY, Kosoy MY, Dittmar K (2015) Bartonella spp. in fruit bats and blood-feeding ectoparasites in Madagascar. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 9, e0003532. |
| [10] | Chomel BB, Obregón-Morales C, Olave-Leyva JI, Aréchiga-Ceballos N, Stuckey MJ, Moreno-Sandoval H, Aguilar-Setién A, Salas-Rojas M, Galvez-Romero G (2017) Bartonella infection in hematophagous, insectivorous, and phytophagous bat populations of central Mexico and the Yucatan Peninsula. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 97, 413-422. |
| [11] | Cicuttin GL, De Salvo MN, La Rosa I, Dohmen FEG (2017) Neorickettsia risticii, Rickettsia sp. and Bartonella sp. in Tadarida brasiliensis bats from Buenos Aires, Argentina. Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 52, 1-5. |
| [12] | Concannon R, Wynn-Owen K, Simpson VR, Birtles RJ (2005) Molecular characterization of haemoparasites infecting bats (Microchiroptera) in Cornwall, UK. Parasitology, 131, 489-496. |
| [13] | Davoust B, Marié JL, Dahmani M, Berenger JM, Bompar JM, Blanchet D, Cheuret M, Raoult D, Mediannikov O (2016) Evidence of Bartonella spp. in blood and ticks (Ornithodoros hasei) of bats, in French Guiana. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 16, 516-519. |
| [14] | Dietrich M, Tjale MA, Weyer J, Kearney T, Seamark ECJ, Nel LH, Monadjem A, Markotter W (2016) Diversity of Bartonella and Rickettsia spp. in bats and their blood-feeding ectoparasites from South Africa and Swaziland. PLoS ONE, 11, e0152077. |
| [15] | Ferreira MS, Guterres A, Rozental T, Novaes RLM, Vilar EM, Oliveira RC, Fernandes J, Forneas D, Junior AA, Brand?o ML, Cordeiro JLP, Del Valle Alvarez MR, Althoff SL, Moratelli R, Cordeiro-Estrela P, Silva RCD, Lemos ERS (2018) Coxiella and Bartonella spp. in bats (Chiroptera) captured in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest biome. BMC Veterinary Research, 14, 279. |
| [16] | Gon?alves-Oliveira J, Rozental T, Guterres A, Teixeira BR, Elise Andrade-Silva B, da Costa-Neto SF, Furtado MC, Moratelli R, D’Andrea PS, Lemos ERS (2020) Investigation of Bartonella spp. in Brazilian mammals with emphasis on rodents and bats from the Atlantic Forest. International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife, 13, 80-89. |
| [17] | Han HJ, Li ZM, Li X, Liu JX, Peng QM, Wang R, Gu XL, Jiang Y, Zhou CM, Li D, Xiao X, Yu XJ (2022) Bats and their ectoparasites (Nycteribiidae and Spinturnicidae) carry diverse novel Bartonella genotypes, China. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 69, e845-e858. |
| [18] | Han HJ, Wen HL, Zhao L, Liu JW, Luo LM, Zhou CM, Qin XR, Zhu YL, Zheng XX, Yu XJ (2017) Novel Bartonella species in insectivorous bats, northern China. PLoS ONE, 12, e0167915. |
| [19] | Hou SL, Koh FX, Nuryana I, Sitam FT, Tay ST (2018) Molecular detection of Bartonella spp. in Malaysian small flying foxes (Pteropus hypomelanus). Tropical Biomedicine, 35, 293-299. |
| [20] | Ikeda P, Marinho Torres J, Perles L, Louren?o EC, Herrera HM, de Oliveira CE, Zacarias Machado R, André MR (2020) Intra- and inter-host assessment of Bartonella diversity with focus on non-hematophagous bats and associated ectoparasites from Brazil. Microorganisms, 8, 1822. |
| [21] | Ikeda P, Seki MC, Carrasco AOT, Rudiak LV, Miranda JMD, Gon?alves SMM, Hoppe EGL, Albuquerque ACA, Teixeira MMG, Passos CE, Werther K, Machado RZ, André MR (2017) Evidence and molecular characterization of Bartonella spp. and hemoplasmas in neotropical bats in Brazil. Epidemiology and Infection, 145, 2038-2052. |
| [22] | Judson SD, Frank HK, Hadly EA (2015) Bartonellae are prevalent and diverse in Costa Rican bats and bat flies. Zoonoses and Public Health, 62, 609-617. |
| [23] | Kaiser PO, Riess T, O’Rourke F, Linke D, Kempf VAJ (2011) Bartonella spp.: Throwing light on uncommon human infections. International Journal of Medical Microbiology, 301, 7-15. |
| [24] | Kamani J, Baneth G, Mitchell M, Mumcuoglu KY, Gutiérrez R, Harrus S (2014) Bartonella species in bats (Chiroptera) and bat flies (Nycteribiidae) from Nigeria, West Africa. Vector Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 14, 625-632. |
| [25] | Kosoy M, Bai Y, Lynch T, Kuzmin IV, Niezgoda M, Franka R, Agwanda B, Breiman RF, Rupprecht CE (2010) Bartonella spp. in bats, Kenya. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 16, 1875-1881. |
| [26] | Li DM, Yang WH, Li QD, Han X, Song XP, Pan H, Feng Y (2021) High prevalence and genetic variation of Bartonella species inhabiting the bats in southwestern Yunnan. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1245-1255. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | [栗冬梅, 杨卫红, 李庆多, 韩茜, 宋秀平, 潘虹, 冯云 (2021) 巴尔通体在滇西南蝙蝠中高度流行并具有丰富的遗传变异特征. 生物多样性, 29, 1245-1255.] |
| [27] | Lilley TM, Veikkolainen V, Pulliainen AT (2015) Molecular detection of Candidatus Bartonella hemsundetiensis in bats. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 15, 706-708. |
| [28] | Lilley TM, Wilson CA, Bernard RF, Willcox EV, Vesterinen EJ, Webber QM, Kurpiers L, Prokkola JM, Ejotre I, Kurta A, Field KA, Reeder DM, Pulliainen AT (2017) Molecular detection of Candidatus Bartonella mayotimonensis in north American bats. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 17, 243-246. |
| [29] | Lin J, Hsu Y, Chomel BB, Lin L, Pei J, Wu S, Chang C (2012) Identification of novel Bartonella spp. in bats and evidence of Asian gray shrew as a new potential reservoir of Bartonella. Veterinary Microbiology, 156, 119-126. |
| [30] | McKee CD, Kosoy MY, Bai Y, Osikowicz LM, Franka R, Gilbert AT, Boonmar S, Rupprecht CE, Peruski LF (2017) Diversity and phylogenetic relationships among Bartonella strains from Thai bats. PLoS ONE, 12, e0181696. |
| [31] | Mitchell MM, Vicente-Santos A, Rodríguez-Herrera B, Corrales-Aguilar E, Gillespie TR (2022) Genetic diversity of Bartonella spp. in cave-dwelling bats and bat flies, Costa Rica, 2018. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 28, 488-491. |
| [32] | Mühldorfer K (2013) Bats and bacterial pathogens: A review. Zoonoses and Public Health, 60, 93-103. |
| [33] | Müller A, Sepúlveda P, Di Cataldo S, Cevidanes A, Lisón F, Millán J (2020) Molecular investigation of zoonotic intracellular bacteria in Chilean bats. Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 73, 101541. |
| [34] | Nabeshima K, Sato S, Brinkerhoff RJ, Amano M, Kabeya H, Itou T, Maruyama S (2023) Prevalence and genetic diversity of Bartonella spp. in northern bats (Eptesicus nilssonii) and their blood-sucking ectoparasites in Hokkaido, Japan. Microbial Ecology, 85, 298-306. |
| [35] | Nabeshima K, Sato S, Kabeya H, Kato C, Suzuki K, Maruyama S (2020) Isolation and genetic properties of Bartonella in eastern bent-wing bats (Miniopterus fuliginosus) in Japan. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 83, 104354. |
| [36] | Noguchi H, Battistini TS (1926) Etiology of Oroya fever: I. Cultivation of Bartonella bacilliformis. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 43, 851-864. |
| [37] | Olival KJ, Dittmar K, Bai Y, Rostal MK, Lei BR, Daszak P, Kosoy M (2015) Bartonella spp. in a Puerto Rican bat community. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 51, 274-278. |
| [38] | Oren A, Garrity GM (2021) Valid publication of the names of forty-two phyla of prokaryotes. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 71, 005056. |
| [39] | Parte AC, Sardà Carbasse J, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Reimer LC, G?ker M (2020) List of Prokaryotic names with standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) moves to the DSMZ. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 70, 5607-5612. |
| [40] | Poofery J, Narapakdeesakul D, Riana E, Arnuphapprasert A, Nugraheni YR, Ngamprasertwong T, Wangthongchaicharoen M, Soisook P, Bhodhibundit P, Kaewthamasorn M (2022) Molecular identification and genetic diversity of Bartonella spp. in 24 bat species from Thailand. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 69, e717-e733. |
| [41] | Qiu YJ, Kajihara M, Nakao R, Mulenga E, Harima H, Hang’ombe BM, Eto Y, Changula K, Mwizabi D, Sawa H, Higashi H, Mweene A, Takada A, Simuunza M, Sugimoto C (2020) Isolation of Candidatus Bartonella rousetti and other bat-associated Bartonellae from bats and their flies in Zambia. Pathogens, 9, 469. |
| [42] | Reeves WK, Beck J, Orlova MV, Daly JL, Pippin K, Revan F, Loftis AD (2016) Ecology of bats, their ectoparasites, and associated pathogens on Saint Kitts Island. Journal of Medical Entomology, 53, 1218-1225. |
| [43] | Stuckey MJ, Boulouis HJ, Cliquet F, Picard-Meyer E, Servat A, Aréchiga-Ceballos N, Echevarría JE, Chomel BB (2017) Potentially zoonotic Bartonella in bats from France and Spain. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 23, 539-541. |
| [44] | Szentiványi T, Markotter W, Dietrich M, Clément L, An?ay L, Brun L, Genzoni E, Kearney T, Seamark E, Estók P, Christe P, Glaizot O (2020) Host conservation through their parasites: Molecular surveillance of vector-borne microorganisms in bats using ectoparasitic bat flies. Parasite, 27, 72. |
| [45] | Szubert-Kruszyńska A, Stańczak J, Cieniuch S, Podsiad?y E, Postawa T, Michalik J (2019) Bartonella and Rickettsia infections in Haematophagous Spinturnix myoti mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) and their bat host, Myotis myotis (Yangochiroptera: Vespertilionidae), from Poland. Microbial Ecology, 77, 759-768. |
| [46] | Urushadze L, Bai Y, Osikowicz L, McKee C, Sidamonidze K, Putkaradze D, Imnadze P, Kandaurov A, Kuzmin I, Kosoy M (2017) Prevalence, diversity, and host associations of Bartonella strains in bats from Georgia (Caucasus). PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 11, e0005428. |
| [47] | Veikkolainen V, Vesterinen EJ, Lilley TM, Pulliainen AT (2014) Bats as reservoir hosts of human bacterial pathogen, Bartonella mayotimonensis. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 20, 960-967. |
| [48] | Wray AK, Olival KJ, Morán D, Lopez MR, Alvarez D, Navarrete-Macias I, Liang E, Simmons NB, Lipkin WI, Daszak P, Anthony SJ (2016) Viral diversity, prey preference, and Bartonella prevalence in Desmodus rotundus in Guatemala. Ecohealth, 13, 761-774. |