北京地区油松与大叶黄杨叶际表生真菌多样性及群落组成
Diversity and community composition of epiphytic fungi in the phyllosphere of Pinus tabuliformis and Euonymus japonicus in Beijing, northern China
北京地区油松与大叶黄杨叶际表生真菌多样性及群落组成 |
| 崔玉进, 李婉莹, 周青青, 赵恒, 吴芳, 员瑗 |
|
Diversity and community composition of epiphytic fungi in the phyllosphere of Pinus tabuliformis and Euonymus japonicus in Beijing, northern China |
| Yujin Cui, Wanying Li, Qingqing Zhou, Heng Zhao, Fang Wu, Yuan Yuan |
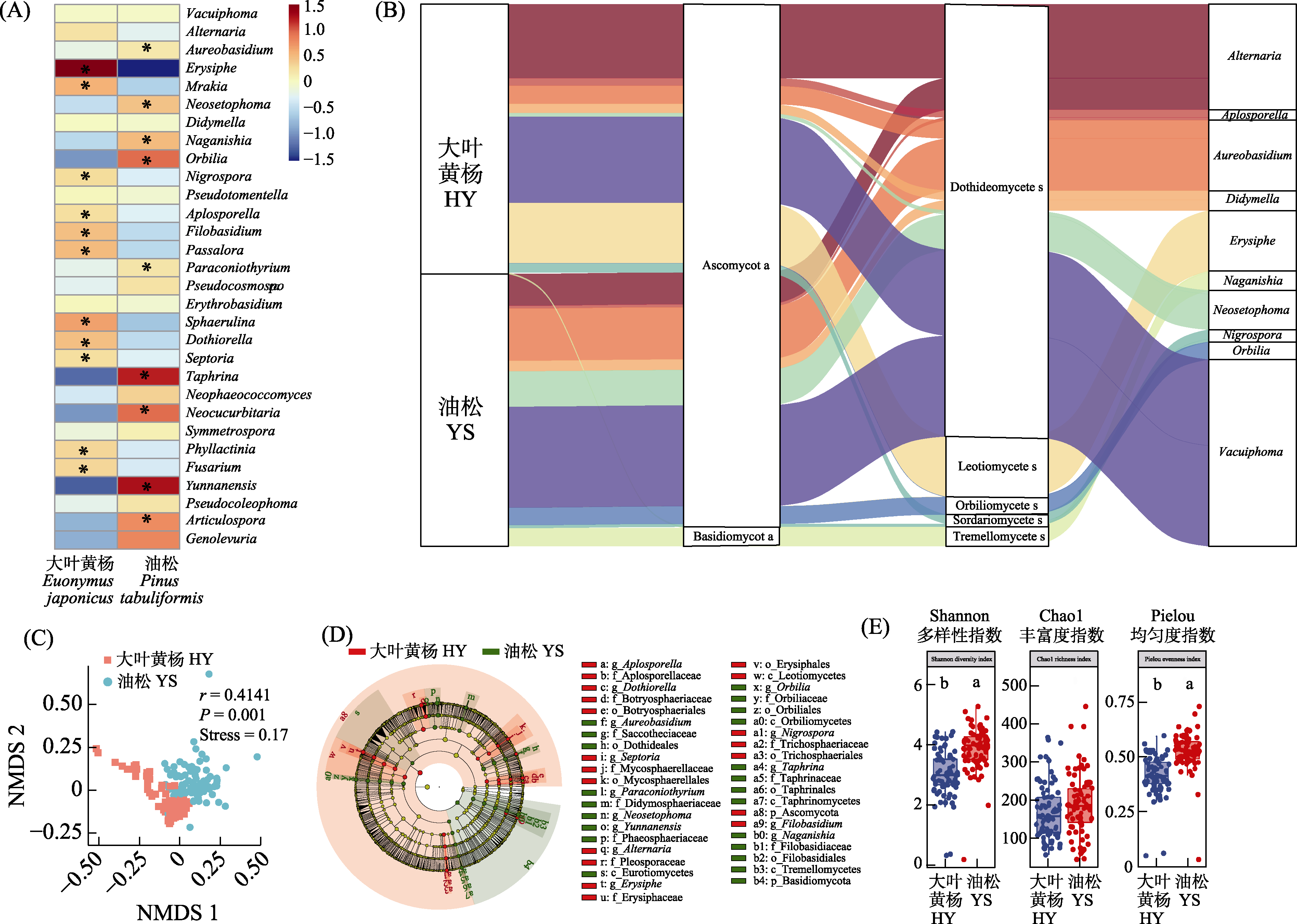
| 图5 油松与大叶黄杨的叶际表生真菌的多样性与群落组成。A: 油松与大叶黄杨相对丰度前30的属间热图(数据经过lg处理); B: 油松与大叶黄杨的群落组成桑基图; C: 油松与大叶黄杨的NMDS分析图; D: 油松与大叶黄杨的线性判别分析; E: 油松与大叶黄杨的α多样性箱线图。热图中的“*”与箱线图中的不同小写字母表示组间差异显著(Kruskal-Wallis, P < 0.05)。 |
| Fig. 5 The diversity and community structure of epiphytic fungi in the phyllosphere of Pinus tabuliformis and Euonymus japonicus at different seasons; A, Heat map of top 30 genera in relative abundance ranking of fungi (data processed by log10); B, Sankey diagram of two trees; C, Non-metric multidimensional scaling analysis of two trees; D, Linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe) of two trees; E, The alpha diversity index of two trees. YS, P. tabuliformis, HY, E. japonicus. The “*” in heat map and different letters in the box plot indicates that there was significant difference between groups (Kruskal-Wallis, P < 0.05). |

|