粤港澳大湾区城市化进程对区域内鸟类分布及栖息地连通性的影响
The impact of urbanization on regional bird distribution and habitat connectivity in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area
粤港澳大湾区城市化进程对区域内鸟类分布及栖息地连通性的影响 |
| 张琼悦, 邓卓迪, 胡学斌, 丁志锋, 肖荣波, 修晨, 吴政浩, 汪光, 韩东晖, 张语克, 梁健超, 胡慧建 |
|
The impact of urbanization on regional bird distribution and habitat connectivity in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area |
| Qiongyue Zhang, Zhuodi Deng, Xuebin Hu, Zhifeng Ding, Rongbo Xiao, Chen Xiu, Zhenghao Wu, Guang Wang, Donghui Han, Yuke Zhang, Jianchao Liang, Huijian Hu |
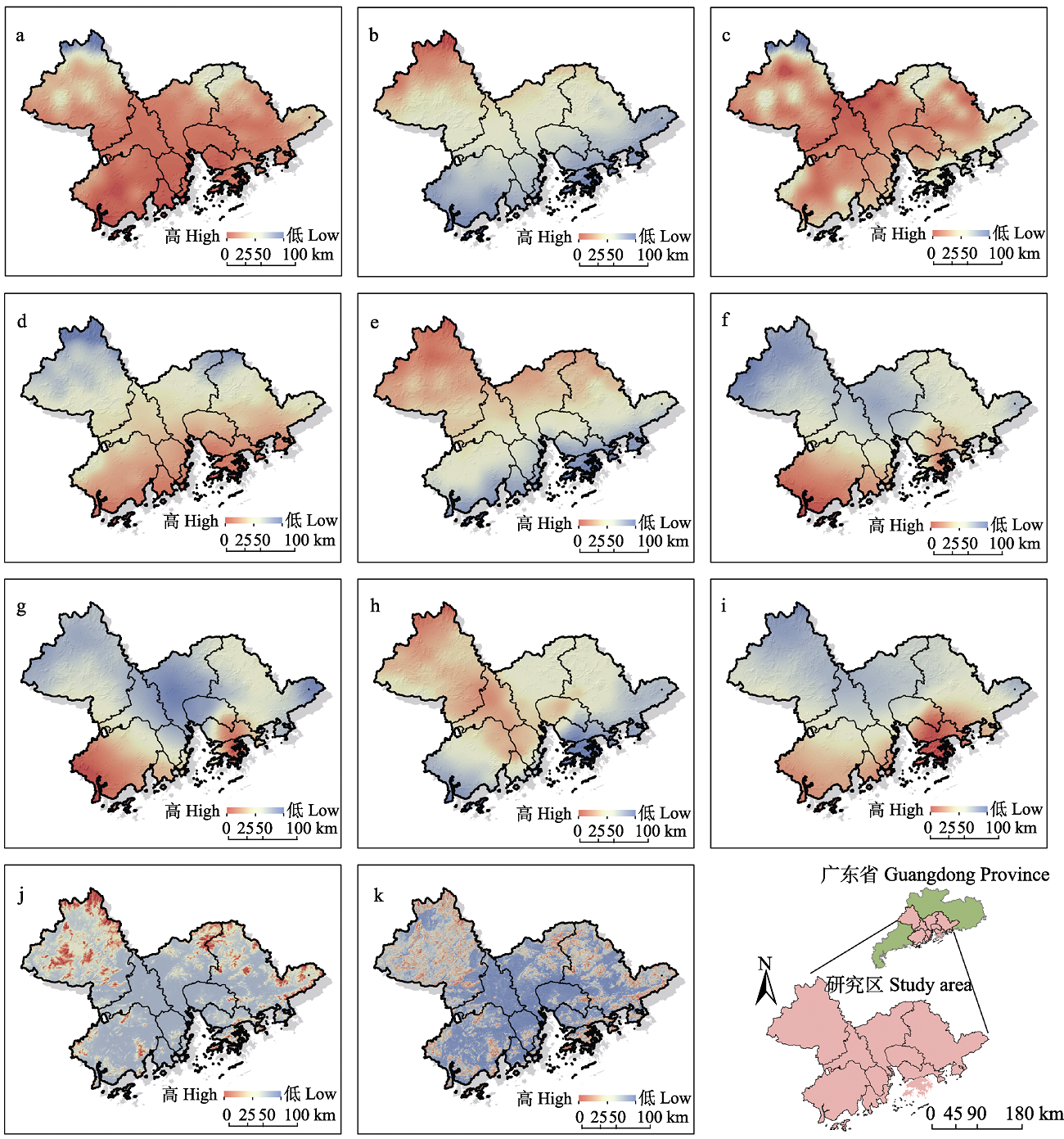
| 图1 粤港澳大湾区2015年非城市化环境因子(气候)。a: 年平均气温; b: 气温季节变化; c: 最暖月最高气温; d: 最冷月最低气温; e: 气温年变化; f: 年均降水量; g: 最湿月降水量; h: 最干月降水量; i: 降水量季节变化; j: 海拔; k: 坡度。 |
| Fig. 1 Climate factors in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area during 2015. a, Annual mean temperature, AMT; b, Temperature seasonality, TS; c, Maximum temperature of the warmest month, MTWM; d, Minimum temperature of the coldest month, MTCM; e, Temperature annual range, TAR; f, Annual precipitation, AP; g, Precipitation of the wettest month, PWM; h, Precipitation of the driest month, PDM; i, Precipitation seasonality, PS; j, Elevation, ELEV; k, Slope, SLP. |

|