岛屿面积与气候共同影响舟山群岛种子植物丰富度格局
Island area and climate jointly impact seed plant richness patterns across the Zhoushan Archipelago
岛屿面积与气候共同影响舟山群岛种子植物丰富度格局 |
| 商晓凡, 张健, 高浩杰, 库伟鹏, 毕玉科, 李修鹏, 阎恩荣 |
|
Island area and climate jointly impact seed plant richness patterns across the Zhoushan Archipelago |
| Xiaofan Shang, Jian Zhang, Haojie Gao, Weipeng Ku, Yuke Bi, Xiupeng Li, Enrong Yan |
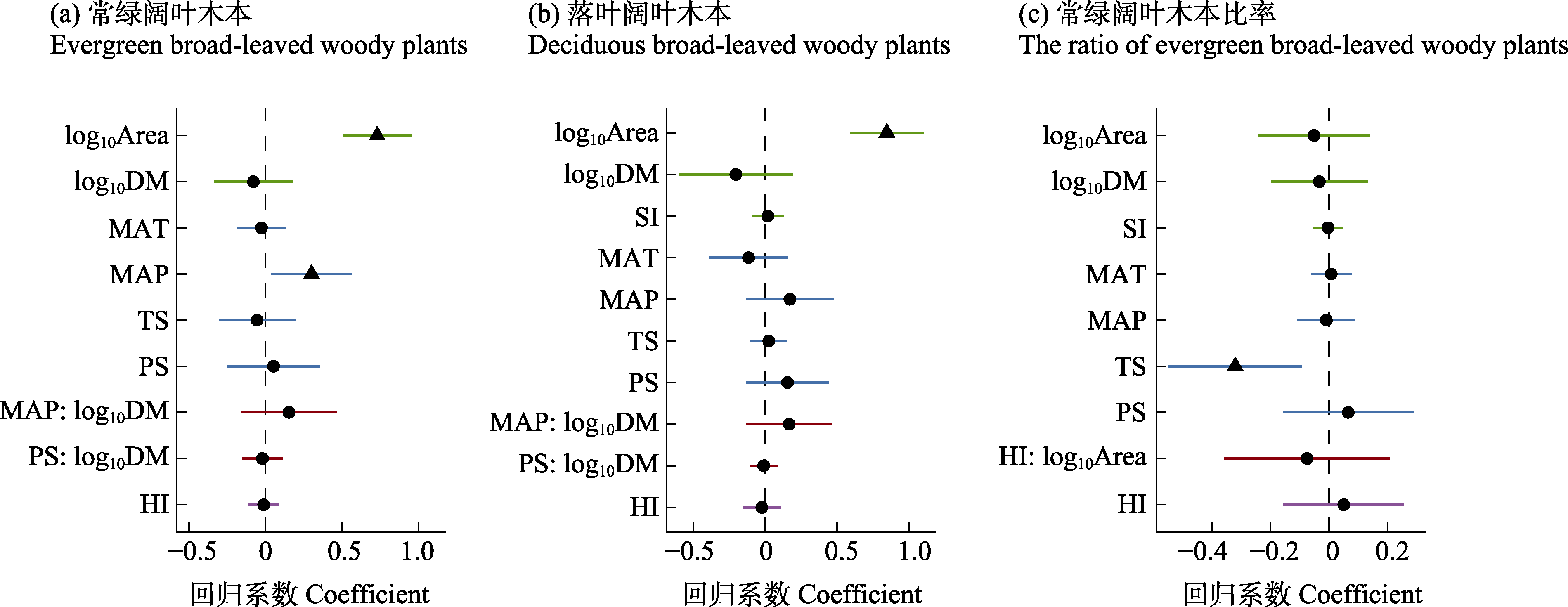
| 图5 岛屿属性、气候与人类影响对木本植物丰富度的影响。(a)常绿阔叶木本; (b)落叶阔叶木本; (c)常绿阔叶木本占总阔叶木本植物的比率。直线代 |
| Fig. 5 Effects of island physical characteristics, climate and human influence on woody plant richness. (a) Evergreen broad-leaved woody plants; (b) Deciduous broad-leaved woody plants; and (c) The ratio of evergreen broad-leaved woody plant richness to all broad-leaved woody plant richness. The straight line represents the 95% confidence interval. The left side of the vertical dashed line indicates negative correlations, while the right for positive correlations. The triangles indicate statistically significant estimates of standardized coefficients, and the dot points show the non-significant ones. Island characteristics, climate, human influence and their interactions are represented in green, blue, purple and red, respectively. Variable abbreviations are the same in |

|