鸟类迁徙对图们江下游湿地声景时间格局的影响
Effects of bird migration on the temporal patterns of the wetland soundscape in the downstream region of the Tumen River Basin of China
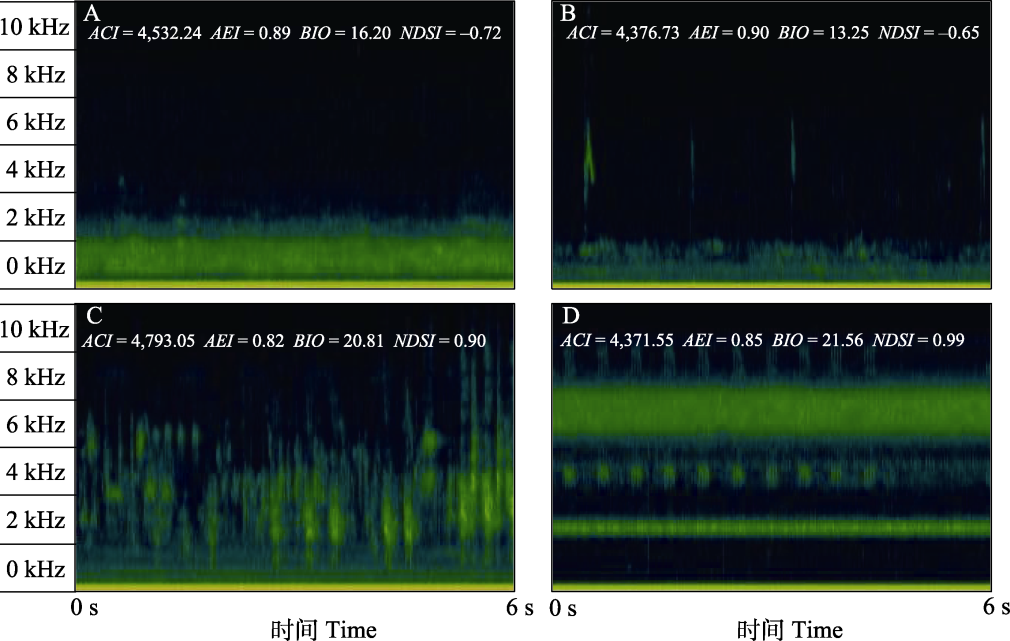
A代表只有雁类声信号的声景; B代表雁类和其他鸟类声信号都存在的声景; C代表无雁类声信号, 主要为2-11 kHz频段鸟类声信号的声景; D代表多种昆虫持续性声信号主导的声景。时频图在Kaleidoscope Pro软件(Wildlife Acoustics)中绘制, 使用短时傅里叶变换和Hann窗。
(A) A soundscape with only wild geese vocal signals; (B) A soundscape with both wild geese and other bird vocal signals; (C) A soundscape devoid of wild geese vocal signals and dominated by bird vocal signals in the 2-11 kHz; (D) A soundscape dominated by multiple insect persistent vocal signals. Spectrograms were drawn with Kaleidoscope Pro software (Wildlife Acoustics), using short-time Fourier transform and Hann window type.